Assessing the Applicability of Mainstream Global Isoscapes for Predicting δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess in Precipitation across China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Processing
2.2. The Mainstream Precipitation Isoscape Models
2.2.1. OIPC3.2 Model
2.2.2. RCWIP1 Model
2.2.3. RCWIP2 Model
2.3. Evaluation Metric
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Variations in Precipitation δ2H, δ18O and D-Excess
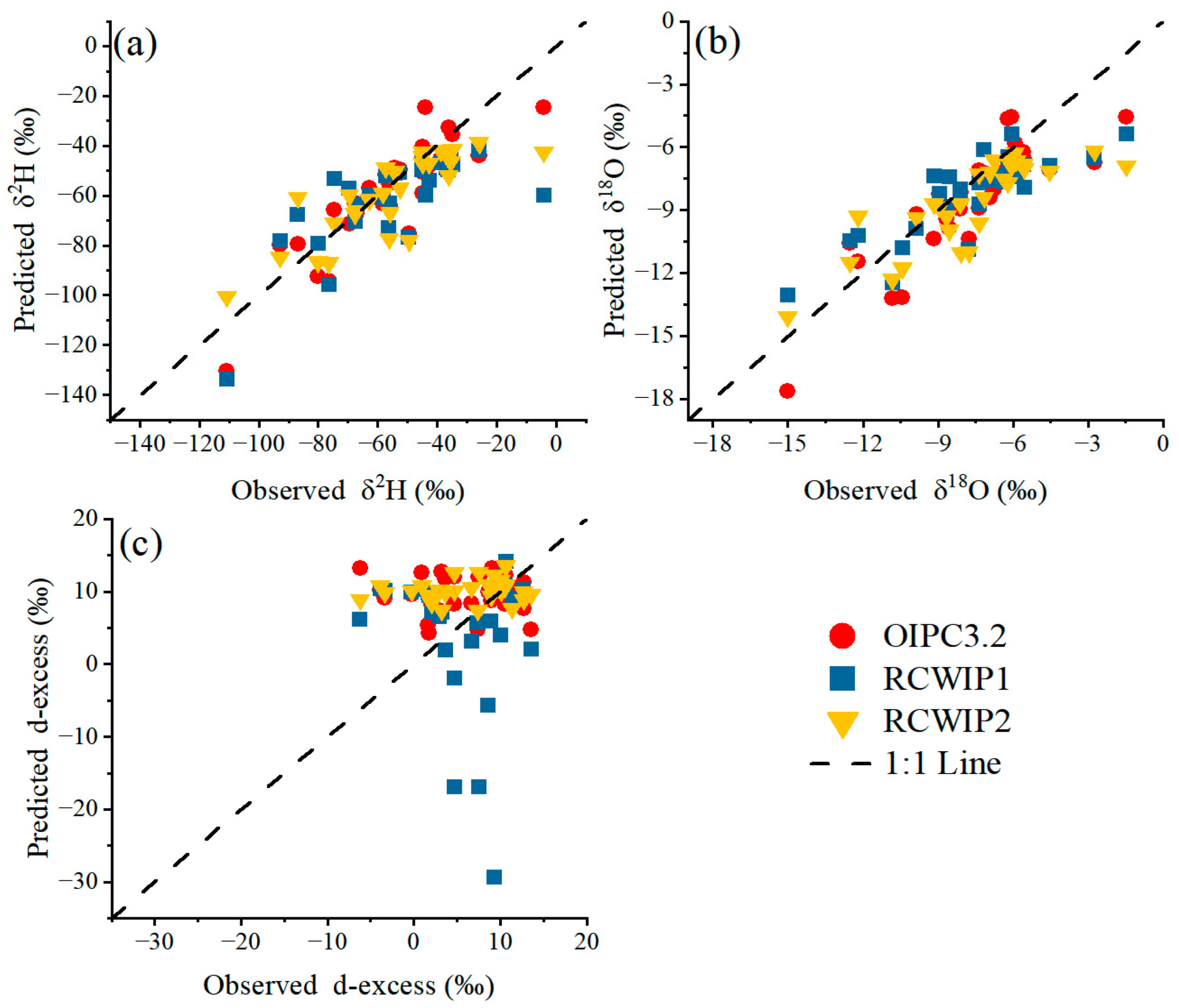
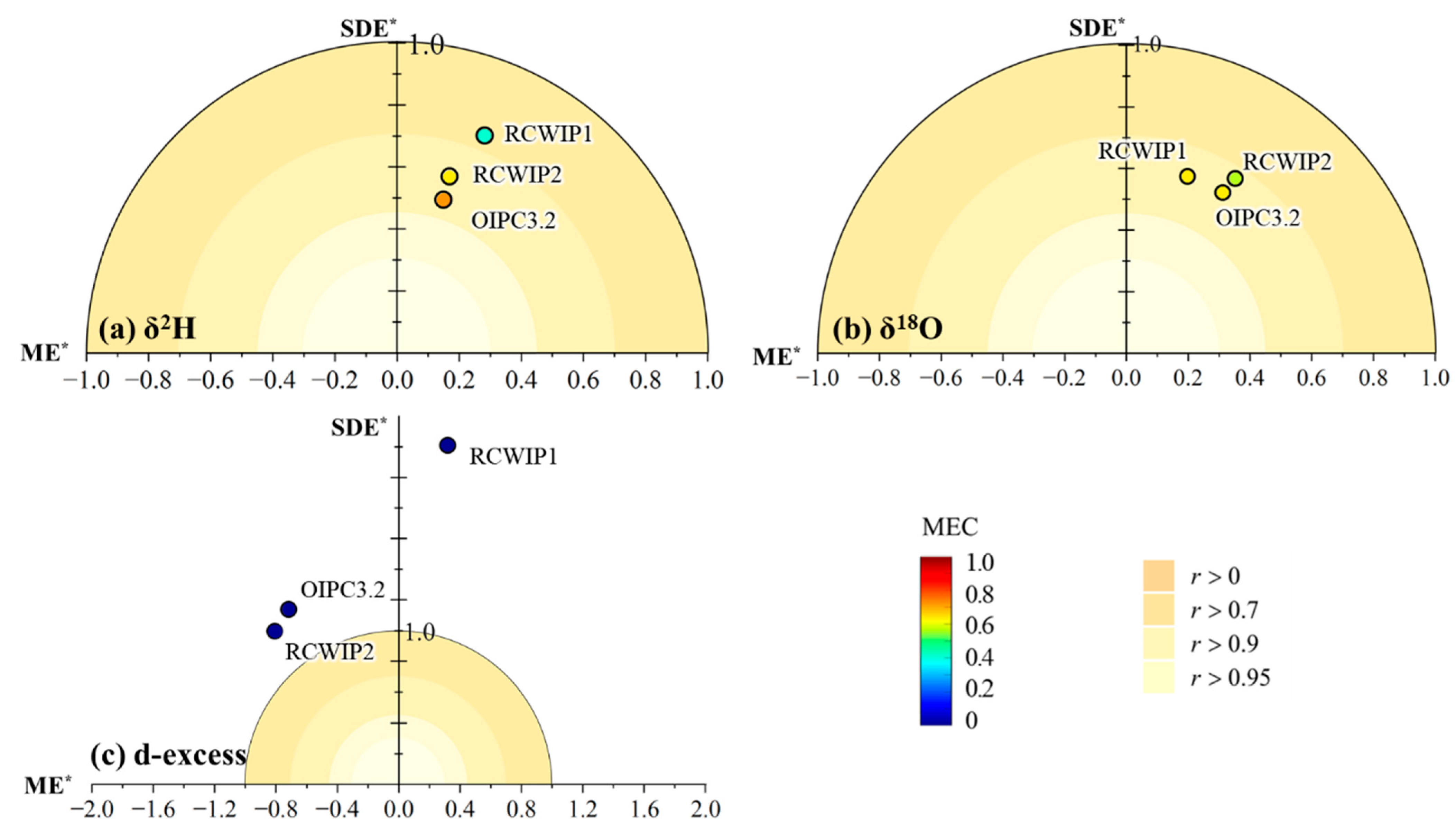
3.2. Performance Evaluation of Isoscape Models
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Three Isoscape Models
4. Discussion
4.1. Why Is the Performance of Isoscape Models Better for δ2H (δ18O) than for d-excess?
4.2. What Are the Differences between the Three Models?
4.3. The Direction for Isoscape Model Improvements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marx, C.; Tetzlaff, D.; Hinkelmann, R.; Soulsby, C. Seasonal Variations in Soil-Plant Interactions in Contrasting Urban Green Spaces: Insights from Water Stable Isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 127998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wen, M.; Li, P.; Liang, J.; Wei, H.; Li, M. An Improved Craig-Gordon Isotopic Model: Accounting for Transpiration Effects on the Isotopic Composition of Residual Water during Evapotranspiration. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boosalik, Z.; Jafari, H.; Clark, I.D.; Bagheri, R. Chemo-Isotopic Tracing of the Groundwater Salinity in Arid Regions: An Example of Shahrood Aquifer (Iran). J. Geochem. Explor. 2022, 239, 107029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brkić, Ž.; Briški, M.; Marković, T. Use of Hydrochemistry and Isotopes for Improving the Knowledge of Groundwater Flow in a Semiconfined Aquifer System of the Eastern Slavonia (Croatia). CATENA 2016, 142, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Stumpp, C.; Weiler, M.; Aeschbach, W.; Allen, S.T.; Benettin, P.; Dubbert, M.; Hartmann, A.; Hrachowitz, M.; Kirchner, J.W.; et al. The Demographics of Water: A Review of Water Ages in the Critical Zone. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 57, 800–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, H.; Si, B.; Li, M. Chloride Tracer of the Loess Unsaturated Zone under Sub-Humid Region: A Potential Proxy Recording High-Resolution Hydroclimate. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IAEA/WMO. Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. In The GNIP Database; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, J.M. Isotopic (Δ18O) Characteristics of Weekly Precipitation Collected across the USA: An Initial Analysis with Application to Water Source Studies. Hydrol. Process 2000, 14, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.M. ENSO Effects on Δ18O, Δ2H and d-Excess Values in Precipitation across the U.S. Using a High-Density, Long-Term Network (USNIP). Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2012, 26, 1893–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.T.; Kirchner, J.W.; Goldsmith, G.R. Predicting Spatial Patterns in Precipitation Isotope (Δ2H and Δ18O) Seasonality Using Sinusoidal Isoscapes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4859–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, X.; Yuan, G.; Sun, X.; Yang, L. Stable Isotopic Compositions of Precipitation in China. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 22567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wilkinson, B. Spatial Distribution of Delta O-18 in Meteoric Precipitation. Geology 2002, 30, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdélyi, D.; Hatvani, I.G.; Jeon, H.; Jones, M.; Tyler, J.; Kern, Z. Predicting Spatial Distribution of Stable Isotopes in Precipitation by Classical Geostatistical- and Machine Learning Methods. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 129129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Revenaugh, J. Interpolating the Isotopic Composition of Modern Meteoric Precipitation. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykoudis, S.P.; Argiriou, A.A. Gridded Data Set of the Stable Isotopic Composition of Precipitation over the Eastern and Central Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzer, S.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Araguás-Araguás, L.J.; Aggarwal, P.K. Global Isoscapes for Δ18O and Δ2H in Precipitation: Improved Prediction Using Regionalized Climatic Regression Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4713–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivielso, S.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Vázquez-Suñé, E.; Custodio, E.; Criollo, R. Spatial Distribution of Meteorological Factors Controlling Stable Isotopes in Precipitation in Northern Chile. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, G.J.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Hobson, K.A. Global Application of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes to Wildlife Forensics. Oecologia 2005, 143, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzer-Wassmuth, S.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Welker, J.M.; Araguás-Araguás, L.J. Improved High-Resolution Global and Regionalized Isoscapes of Δ18O, Δ2H and d-Excess in Precipitation. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Huang, T.; Man, W.; Hu, H.; Long, Y.; Li, Z.; Pang, Z. Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation: A Modified D-Excess-Based Model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, K.; Kralik, M.; Papesch, W.; Rank, D.; Scheifinger, H.; Stichler, W. Deuterium Excess in Precipitation of Alpine Regions—Moisture Recycling. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2008, 44, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishan, G.; Prasad, G.; Anjali; Kumar, C.P.; Patidar, N.; Yadav, B.K.; Kansal, M.L.; Singh, S.; Sharma, L.M.; Bradley, A.; et al. Identifying the Seasonal Variability in Source of Groundwater Salinization Using Deuterium Excess- a Case Study from Mewat, Haryana, India. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 31, 100724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landais, A.; Risi, C.; Bony, S.; Vimeux, F.; Descroix, L.; Falourd, S.; Bouygues, A. Combined Measurements of 17Oexcess and D-Excess in African Monsoon Precipitation: Implications for Evaluating Convective Parameterizations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 298, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gasse, F.; Sonzogni, C. Seasonal Evolution of the Isotopic Composition of Atmospheric Water Vapour above a Tropical Lake: Deuterium Excess and Implication for Water Recycling. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4661–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Risi, C.; Pu, T.; Lacour, J.-L.; Kong, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Xia, D. Variability of Isotope Composition of Precipitation in the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau from the Synoptic to Seasonal Time Scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2019JD031751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Qiu, X.; Du, M. Environmental Controls on Stable Isotopes of Precipitation in Lanzhou, China: An Enhanced Network at City Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Bowen, G.J.; Liu, X.; Du, M.; Chen, F.; Qiu, X.; Wang, L.; Che, Y.; Zhao, G. Water Source Signatures in the Spatial and Seasonal Isotope Variation of Chinese Tap Waters. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 9131–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araguás-Araguás, L.; Froehlich, K.; Rozanski, K. Stable Isotope Composition of Precipitation over Southeast Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 28721–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadoux, A.M.J.C.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; Brus, D.J. An Integrated Approach for the Evaluation of Quantitative Soil Maps through Taylor and Solar Diagrams. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollins, S.E.; Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J.; Cendon, D.I.; Meredith, K.T. Rainfall Isotope Variations over the Australian Continent—Implications for Hydrology and Isoscape Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 630–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansgaard, W. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus 1964, 16, 436–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedaso, Z.; Wu, S.Y. Daily Precipitation Isotope Variation in Midwestern United States: Implication for Hydroclimate and Moisture Source. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Bedaso, Z. Quantifying the Effect of Moisture Source and Transport on the Precipitation Isotopic Variations in Northwest Ethiopian Highland. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Gao, J.; Ahmed, N.; Karim, M.M.; Bhuiyan, A.Q.; Ahsan, A.; Ahmed, S. Controls on Spatiotemporal Variations of Stable Isotopes in Precipitation across Bangladesh. Atmos. Res. 2021, 247, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S. A Review of Precipitation Isotope Studies in China: Basic Pattern and Hydrological Process. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, S.; Baneschi, I.; Doveri, M.; Giannecchini, R.; Selmo, E.; Zanchetta, G. Meteorological and Geographical Control on Stable Isotopic Signature of Precipitation in a Western Mediterranean Area (Tuscany, Italy): Disentangling a Complex Signal. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P. Comparison of Remote Sensing Evapotranspiration Models: Consistency, Merits, and Pitfalls. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Song, Y. Applicability on the OIPC and RCWIP stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope data in precipitation across the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2020, 42, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Welker, J.M.; Winnick, M.J. The Seasonality of Deuterium Excess in Non-Polar Precipitation. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2021GB007245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlivat, L.; Jouzel, J. Global Climatic Interpretation of the Deuterium-Oxygen 18 Relationship for Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1979, 84, 5029–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, S.; Bailey, A.; Conroy, J.L.; Atwood, A.; Stevenson, S.; Nusbaumer, J.; Noone, D. Water Isotopes, Climate Variability, and the Hydrological Cycle: Recent Advances and New Frontiers. Environ. Res. Clim. 2023, 2, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamalikis, V.; Argiriou, A.A.; Dotsika, E. Isotopic Modeling of the Sub-Cloud Evaporation Effect in Precipitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 1059–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.; Hollins, S.E.; Meredith, K.T.; Hughes, C.E. Precipitation Stable Isotope Variability and Subcloud Evaporation Processes in a Semi-Arid Region. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Duan, L.; Xia, Y. An Hourly-Scale Assessment of Sub-Cloud Evaporation Effect on Precipitation Isotopes in a Rainshadow Oasis of Northwest China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 274, 106202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hughes, C.E.; Crawford, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, F.; Du, M.; Qiu, X.; Zhou, S. Meteoric Water Lines in Arid Central Asia Using Event-Based and Monthly Data. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, J. Variability of Precipitation in the Atacama Desert: Its Causes and Hydrological Impact. Int. J. Clim. 2006, 26, 2181–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Peng, D.Z.; Cluckie, I.D. Statistical Analysis of Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall to Hydrological Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worako, A.W.; Haile, A.T.; Rientjes, T.; Woldesenbet, T.A. Error Propagation of Climate Model Rainfall to Streamflow Simulation in the Gidabo Sub-Basin, Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes Basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tian, L.; Chai, X.; Yao, T. A Model-Based Determination of Spatial Variation of Precipitation Δ18O over China. Chem. Geol. 2008, 249, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Models | Resolution | Established Methods | Variables | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OIPC3.2 | 5′ × 5′ | BW Model | Latitude; altitude | [18] |
| RCWIP1 | 10′ × 10′ | Regionalized Cluster | Geographical and climatic parameters | [16] |
| RCWIP2 | 30″ × 30″ | Regionalized Cluster | Geographical and climatic parameters | [19] |
| Models | Objects | R2 | ME | SDE | RMSE | MEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OIPC3.2 | δ2H | 0.78 | 3.21 | 10.63 | 11.11 | 0.73 |
| δ18O | 0.75 | 0.87 | 1.45 | 1.69 | 0.63 | |
| D-excess | 0.00 | −3.74 | 5.94 | 7.02 | −0.81 | |
| RCWIP1 | δ2H | 0.53 | 6.07 | 15.09 | 16.27 | 0.43 |
| δ18O | 0.69 | 0.55 | 1.60 | 1.69 | 0.63 | |
| D-excess | 0.01 | 1.66 | 11.53 | 11.65 | −3.99 | |
| RCWIP2 | δ2H | 0.68 | 3.64 | 12.25 | 12.78 | 0.65 |
| δ18O | 0.69 | 0.98 | 1.58 | 1.86 | 0.55 | |
| D-excess | 0.02 | −4.22 | 5.20 | 6.69 | −0.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wen, M.; Lu, Y. Assessing the Applicability of Mainstream Global Isoscapes for Predicting δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess in Precipitation across China. Water 2023, 15, 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183181
Wei H, Wang J, Li M, Wen M, Lu Y. Assessing the Applicability of Mainstream Global Isoscapes for Predicting δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess in Precipitation across China. Water. 2023; 15(18):3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183181
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Haoyan, Jianlong Wang, Min Li, Mingyi Wen, and Yanwei Lu. 2023. "Assessing the Applicability of Mainstream Global Isoscapes for Predicting δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess in Precipitation across China" Water 15, no. 18: 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183181
APA StyleWei, H., Wang, J., Li, M., Wen, M., & Lu, Y. (2023). Assessing the Applicability of Mainstream Global Isoscapes for Predicting δ18O, δ2H, and d-excess in Precipitation across China. Water, 15(18), 3181. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183181






