Study on Numerical Modeling for Pollutants Movement Based on the Wave Parabolic Mild Slope Equation in Curvilinear Coordinates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Numerical Model of Wave Propagation
2.2. Numerical Model of Nearshore Currents
2.3. Numerical Model of Nearshore Pollutant Transport under Co-Action of Waves and Currents
3. Results and Discussion
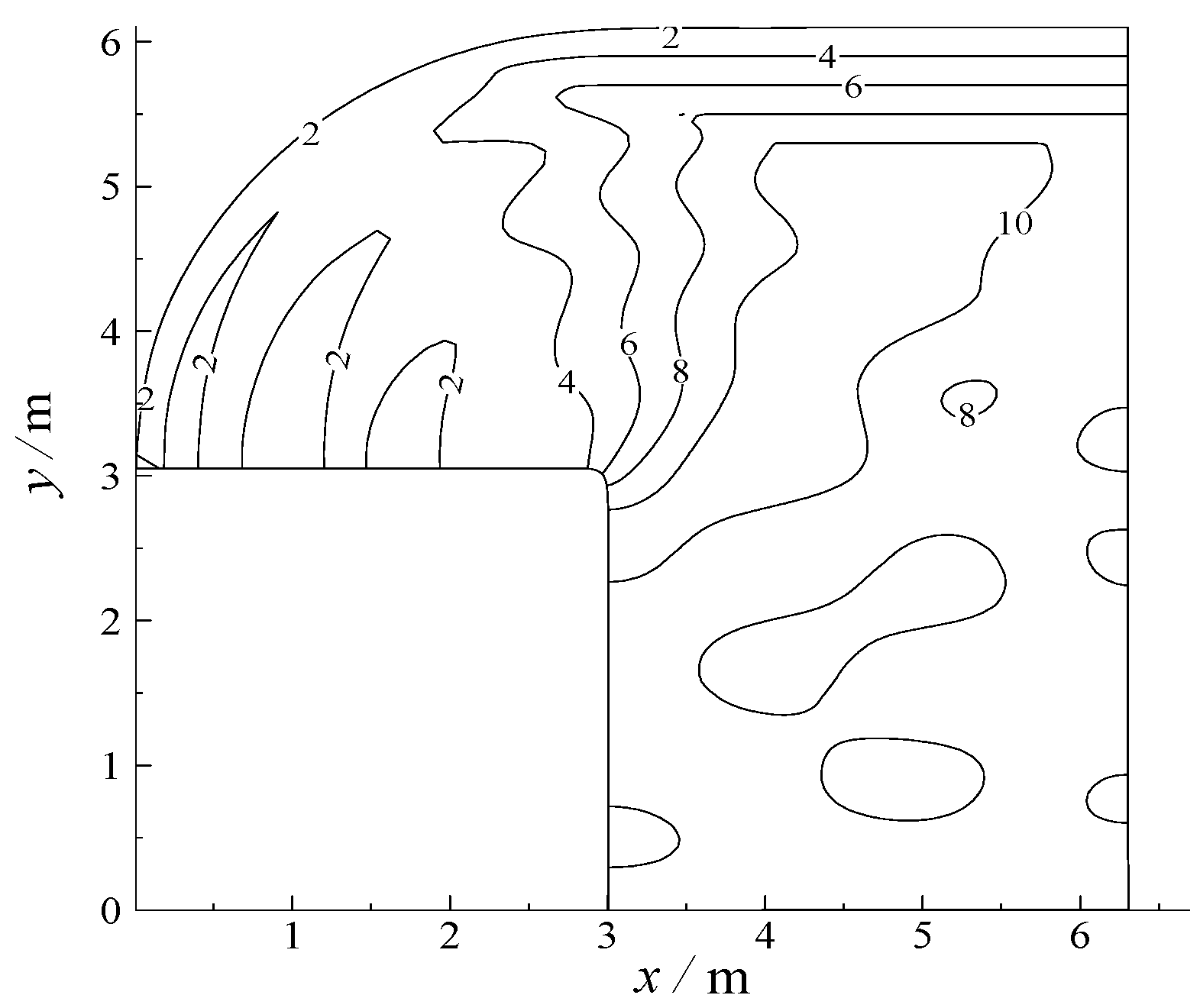
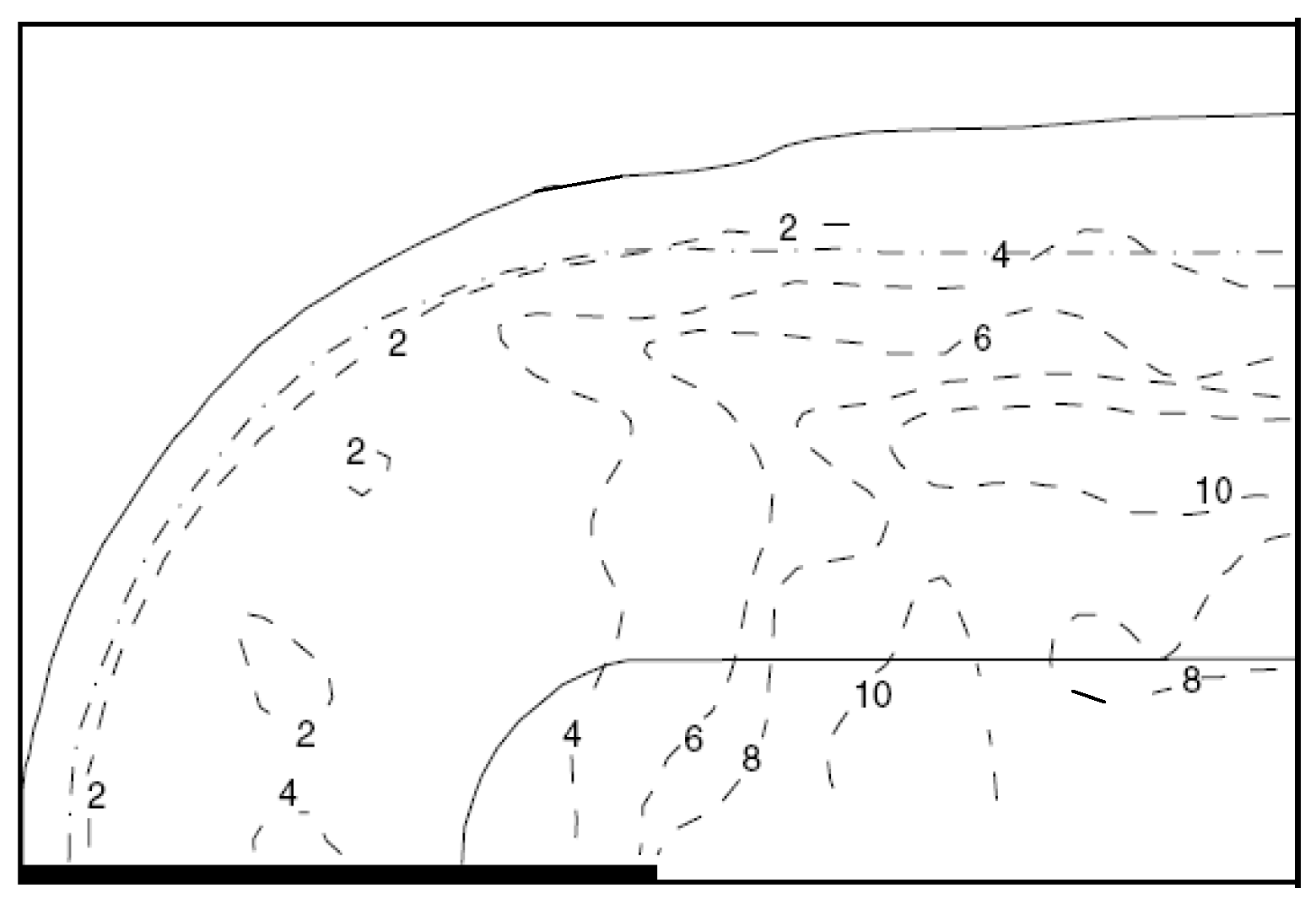
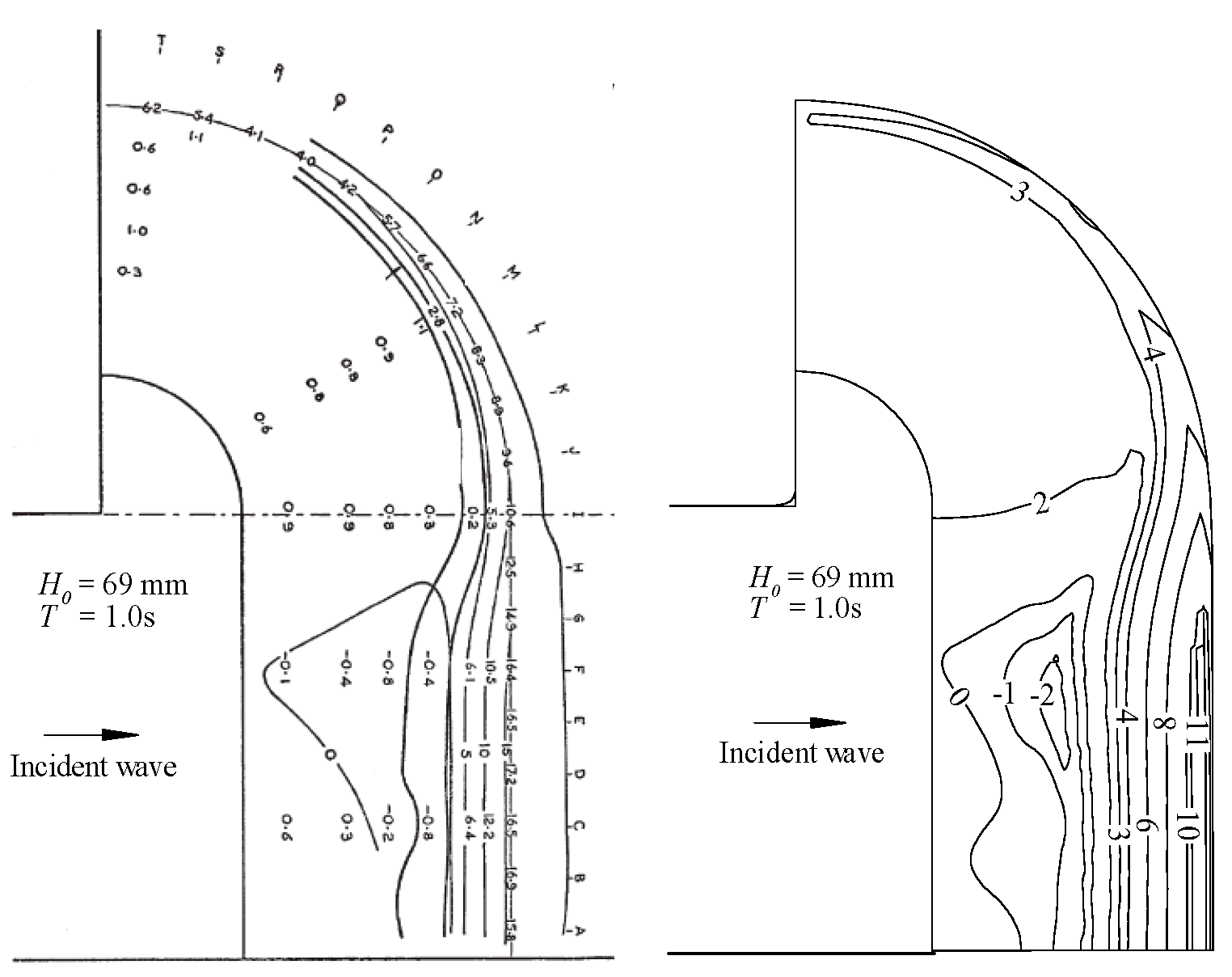
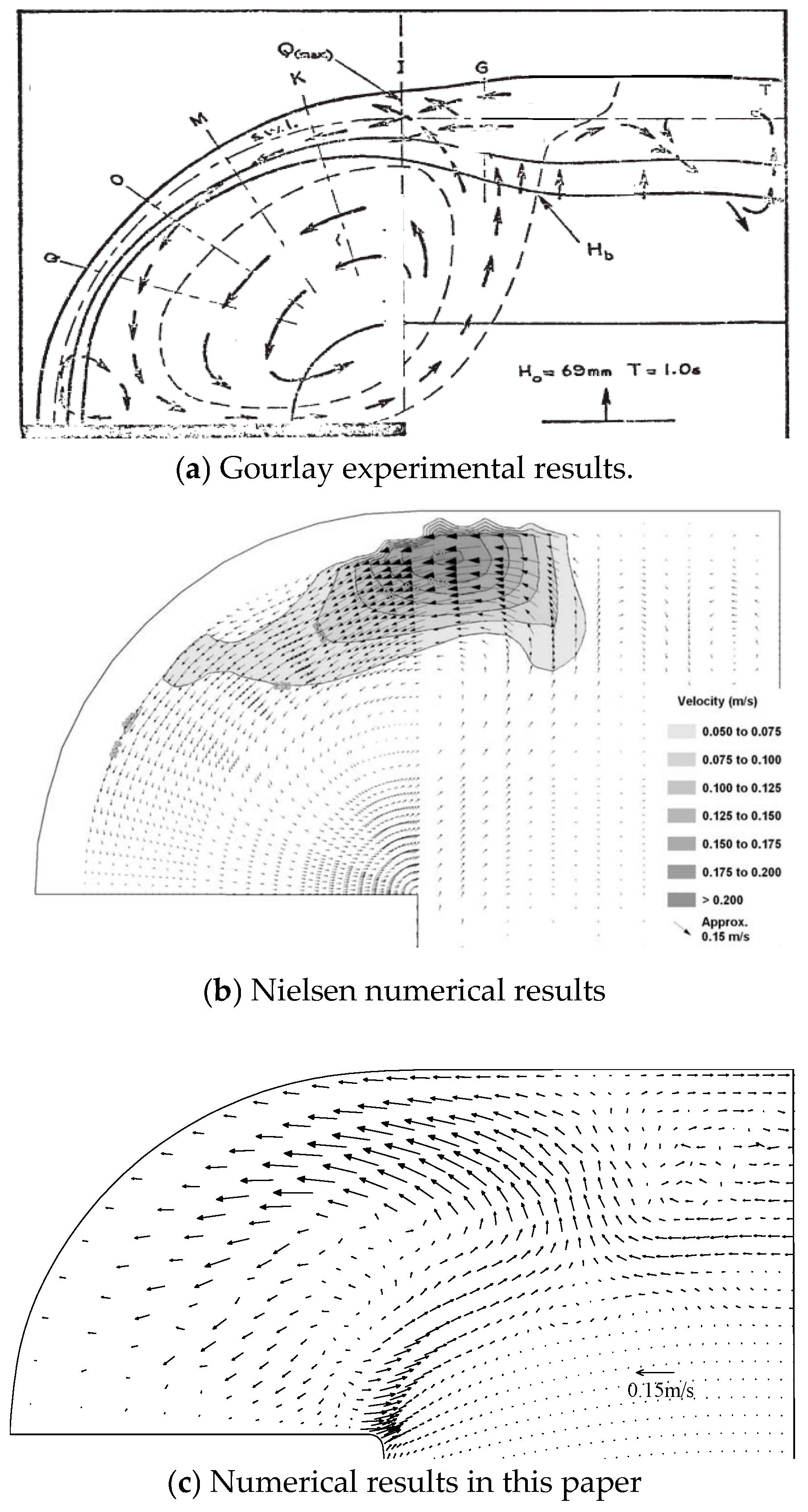
3.1. Validation of Physical Experiments on Nearshore Currents and Pollutant Transport
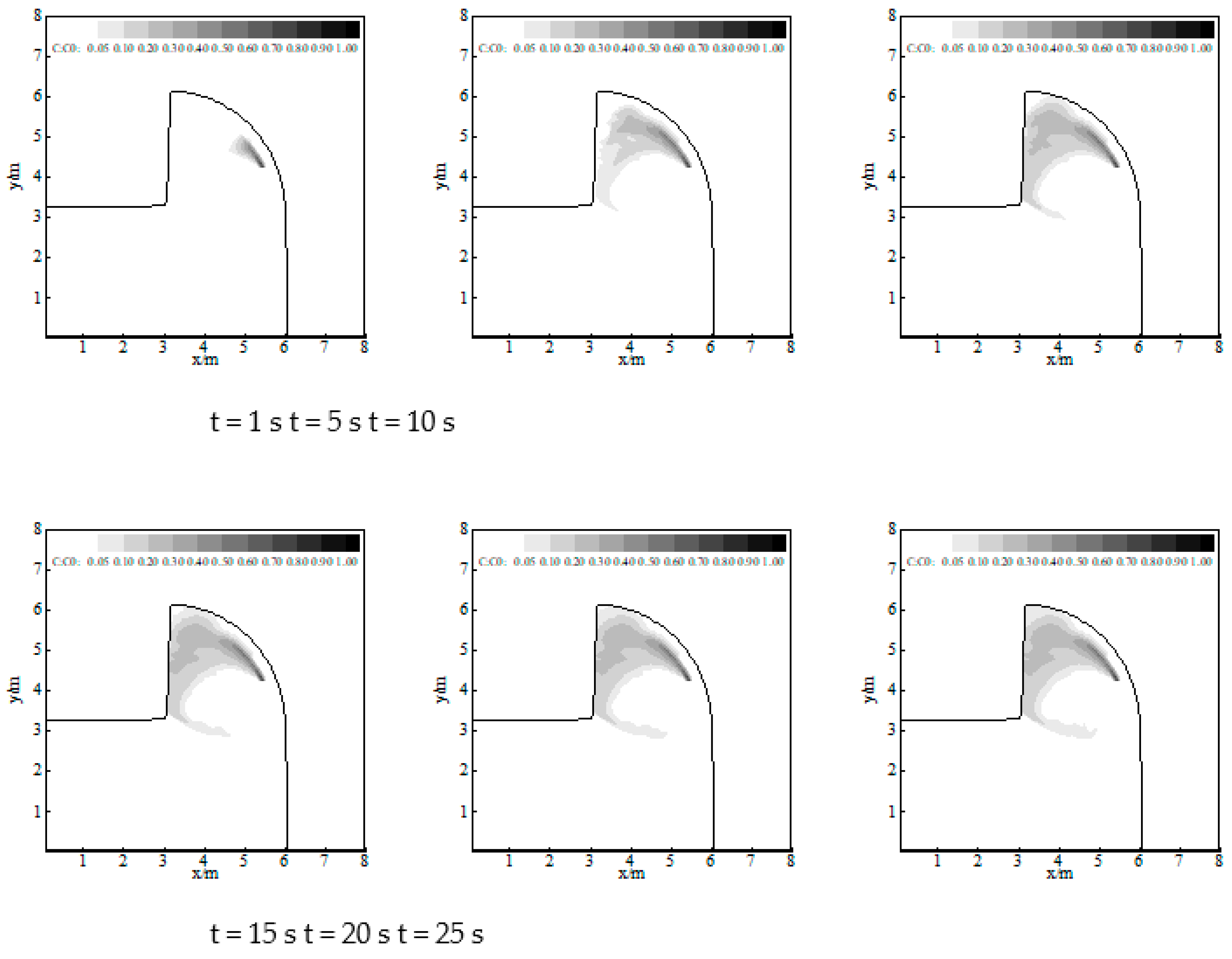
3.2. Numerical Simulation of Pollutant Transport in Gourlay Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, D.H. Science and technology problems in coastal and offshore engineering. J. Dalian Univ. Technol. 2000, 40, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.D.; Gui, Q.Q.; Zou, Z.L.; He, L.L.; Chen, W.; Jiang, M.T. Experimental study and numerical simulation of mean longshore current for mild slope. Wave Motion. 2020, 99, 102651. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.M.; Tang, J.; Zheng, Y.H.; Qiu, D.H. Numerical simulation of wave current field in coastal zone based on parabolic mild slope equation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 37, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S.; Stewart, R.W. Radiation stress and mass transport in gravity waves, with application to ‘surf beats’. J. Fluid Mech. 1962, 13, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shen, Y.M.; Cui, L.; Zheng, Y.H. Numerical simulation of random wave-induced currents. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2008, 40, 455–463. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.J.; Ren, B.; Dong, P.; Zhu, G.C. Numerical analysis of wave-induced current within the inhomogeneous coral reef using a refined SPH model. Coast. Eng. 2020, 156, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.H.; Shen, Y.M.; Wu, X.G.; You, Y.G. Determination of wave energy dissipation factor and numerical simulation of wave height in the surf zone. Ocean Eng. 2004, 31, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.H.; Hajime, M. Numerical modeling of multi-directional random wave transformation in wave-current coexisting water areas. Adv. Water Sci. 2008, 19, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Shen, Y.M.; Qiu, D.H. Numerical study of pollutant movement in waves and wave-induced longshore currents in surf zone. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2008, 27, 122–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.E.; Hsiao, S.C.; Hsu, J.T. Parametric analyses of wave-Induce nearshore current system. J. Coast. Res. 2017, 33, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.T. Parabolic wave computations in non-orthogonal coordinate systems. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1988, 114, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, J.T.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Kaku, H. Parabolic approximations for water waves in conformal coordinate systems. Coast. Eng. 1994, 23, 185–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.Y.; Dalrymple, R.A.; Kirby, J.T.; Chen, Q.; Kennedy, A. A fully nonlinear Boussinesq model in generalized curvilinear coordinates. Coast. Eng. 2001, 42, 337–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Ma, X.Z.; Zang, J.; Dong, G.H.; Ma, X.J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhou, L. Numerical investigation of harbor oscillations induced by focused transient wave groups. Coast. Eng. 2020, 158, 103670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.L.; Ma, X.Z.; Dong, G.H.; Chen, H.Z.; Liu, Q.; Zang, J. Investigation on the effects of Bragg reflection on harbor oscillations. Coast. Eng. 2021, 170, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Tao, J.H. Numerical simulation of pollutant transport acted by wave for a shallow water sea bay. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2006, 51, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Cui, L. Numerical study of pollutant transport in breaking random waves on mild slope zone. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, M.R. Wave Generated Currents; University of Queensland: Queensland, Australia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, J.T. Higher-order approximations in the parabolic equation method for water waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1986, 91, 933–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dally, W.R.; Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. Wave height verification across beaches of arbitrary profile. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 11917–11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasmeijer, B.T.; Ruessink, B.G. Modeling of waves and currents in the nearshore parametric vs. probabilistic approach. Coast. Eng. 2003, 49, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.S.; Ding, P.X.; Zhao, H.J. Numerical simulation model of wave propagation in curvilinear coordinates. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2003, 25, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.J.; Zuo, L.Q.; Shao, X.J.; Wang, H.C.; Li, H.L. A 2D mathematical model for sediment transport by waves and tidal currents. China Ocean Eng. 2005, 19, 571–586. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. Longshore currents generated by obliquely incident sea waves, 1 and 2. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 6778–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Q. A hybrid turbulence model for numerical solution of longshore current and rip current. J. Hohai Univ. 1988, 16, 76–85. [Google Scholar]
- Katopodi, I.; Ribberink, J.S. Quasi-3D modeling of suspended sediment transport by currents and waves. Coast. Eng. 1992, 18, 83–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van-Rijin, L.C. Sedimentation of dredged channels by currents and waves. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1986, 112, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, R.A. Water quality simulation study of a natural harbor. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1986, 112, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, J.W. Computational Hydraulics; Pitman Publishing Limited: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.L.; Chang, M.; Qiu, D.H.; Wang, F.L.; Dong, G.H. Experimental study of longshore currents. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. A. 2002, 17, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, C.; Apelt, C. The application of wave induced forces to a two-dimensional finite element long wave hydrodynamic model. Ocean Eng. 2003, 30, 1233–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
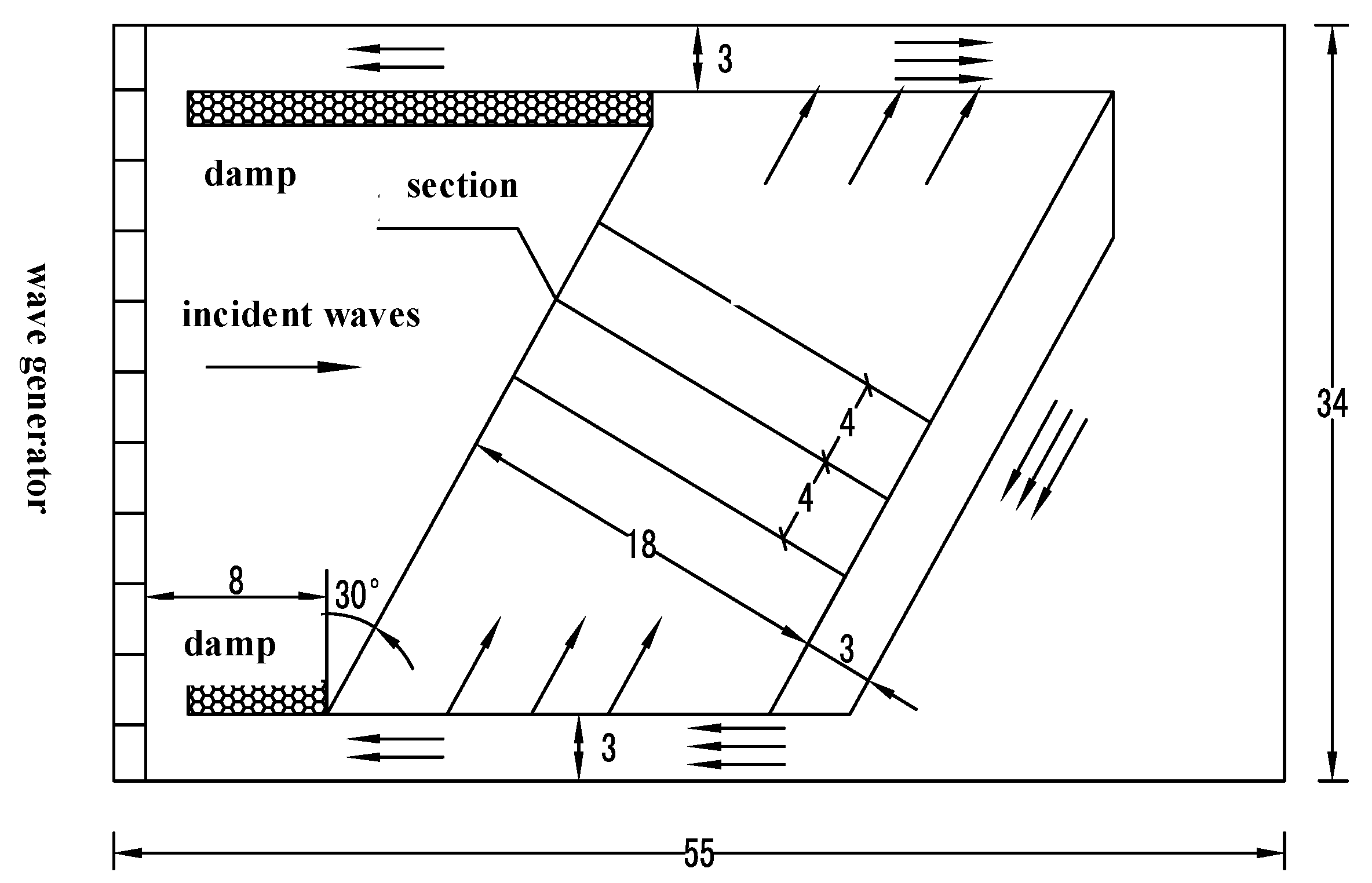
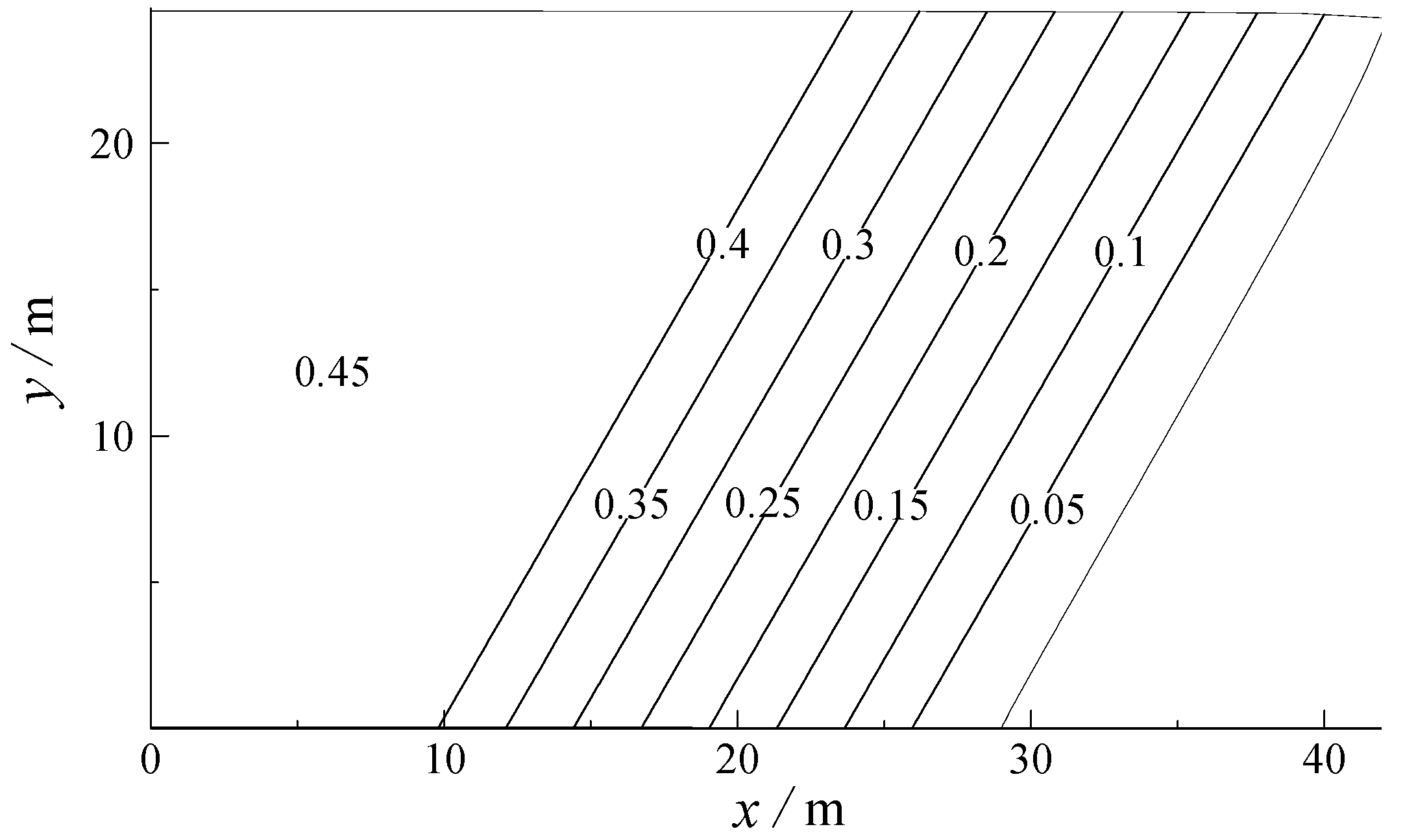
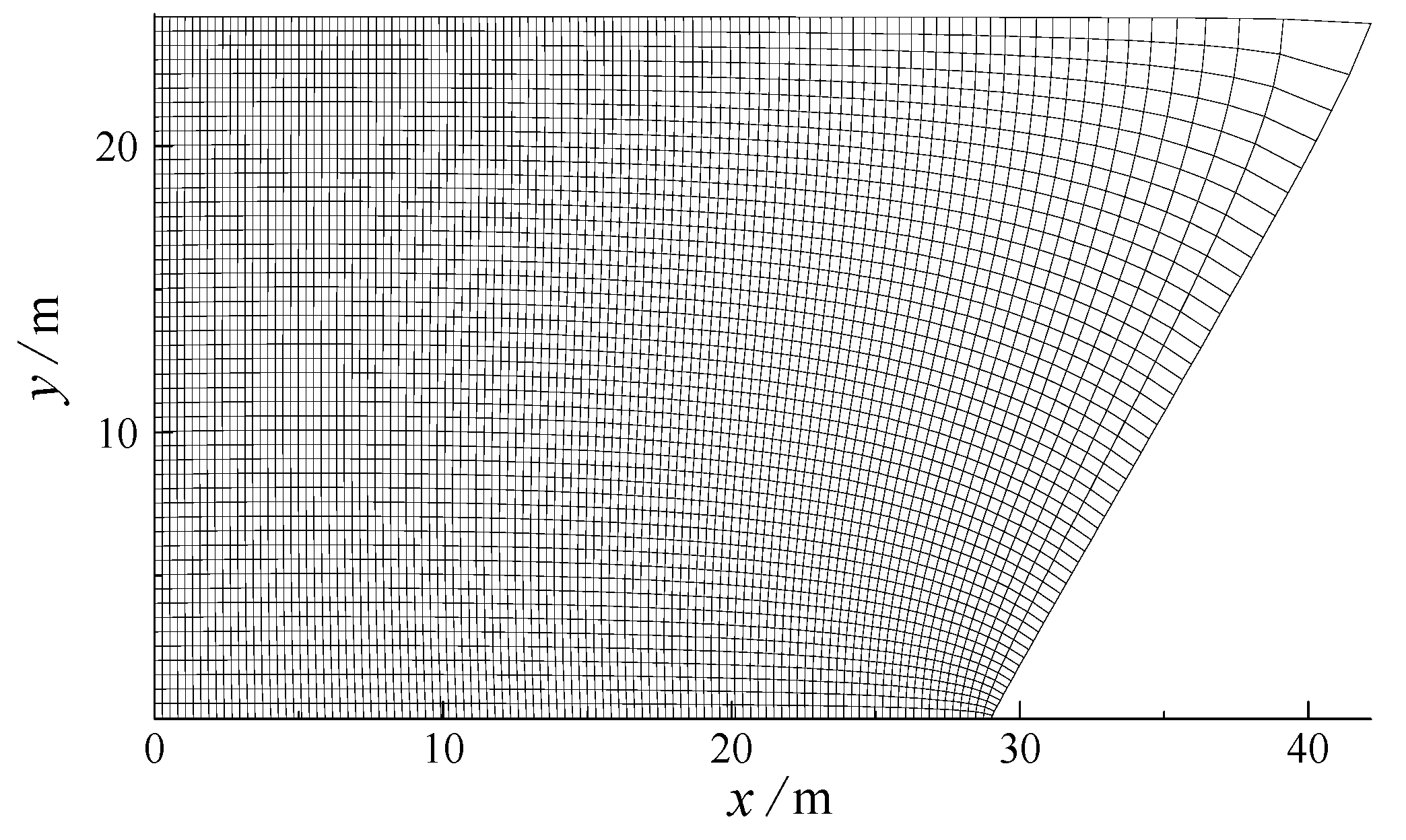


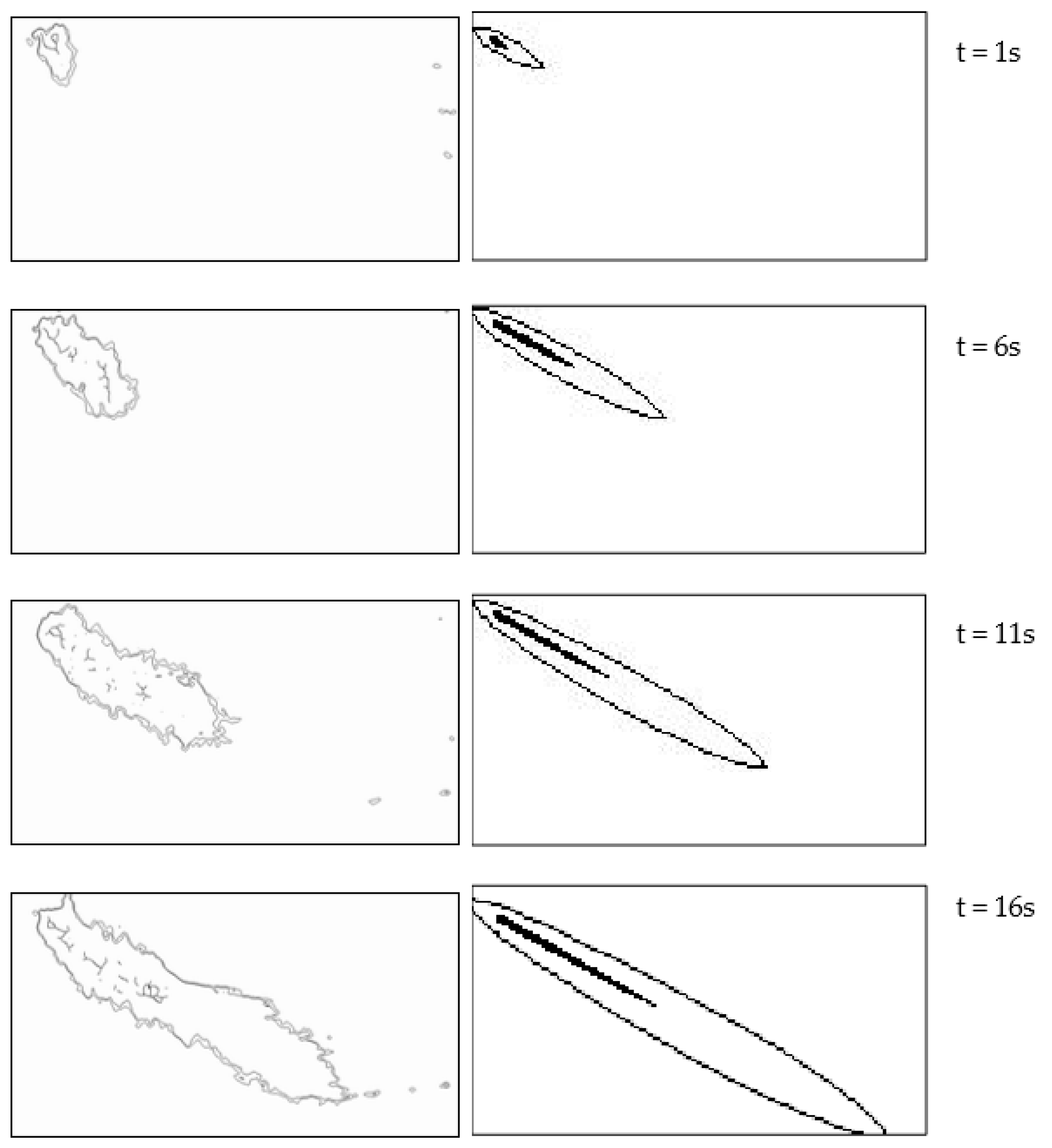
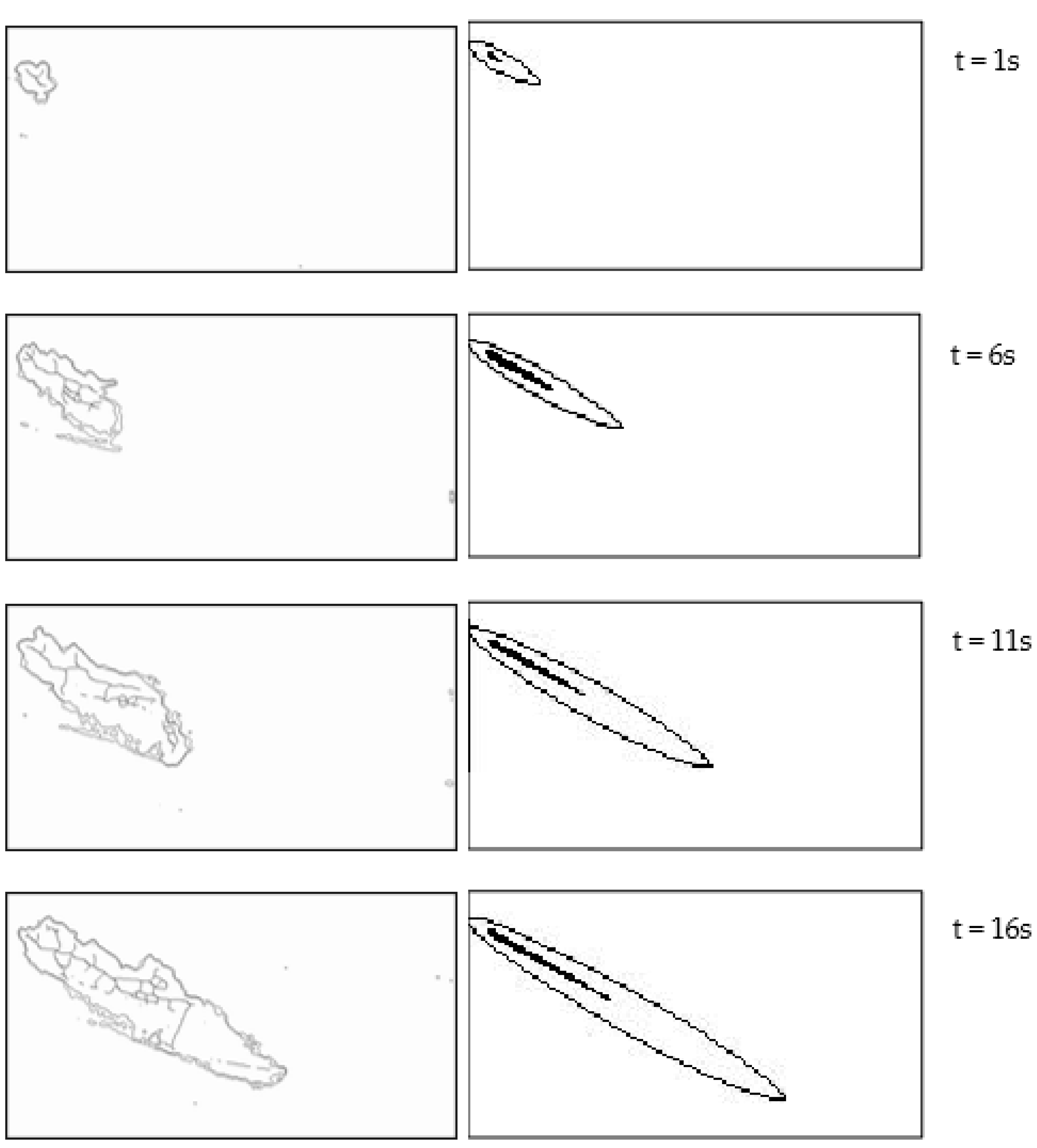
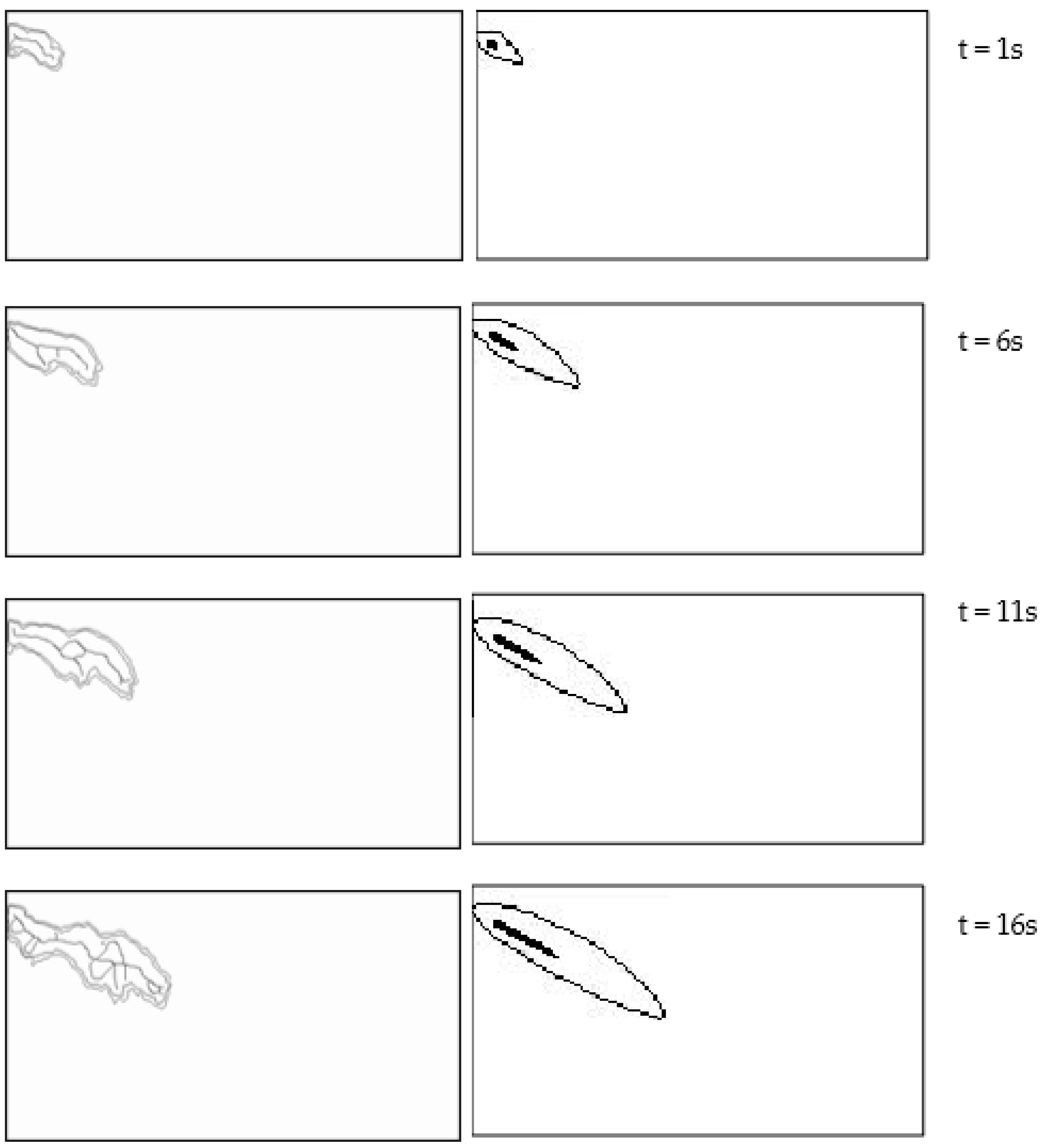
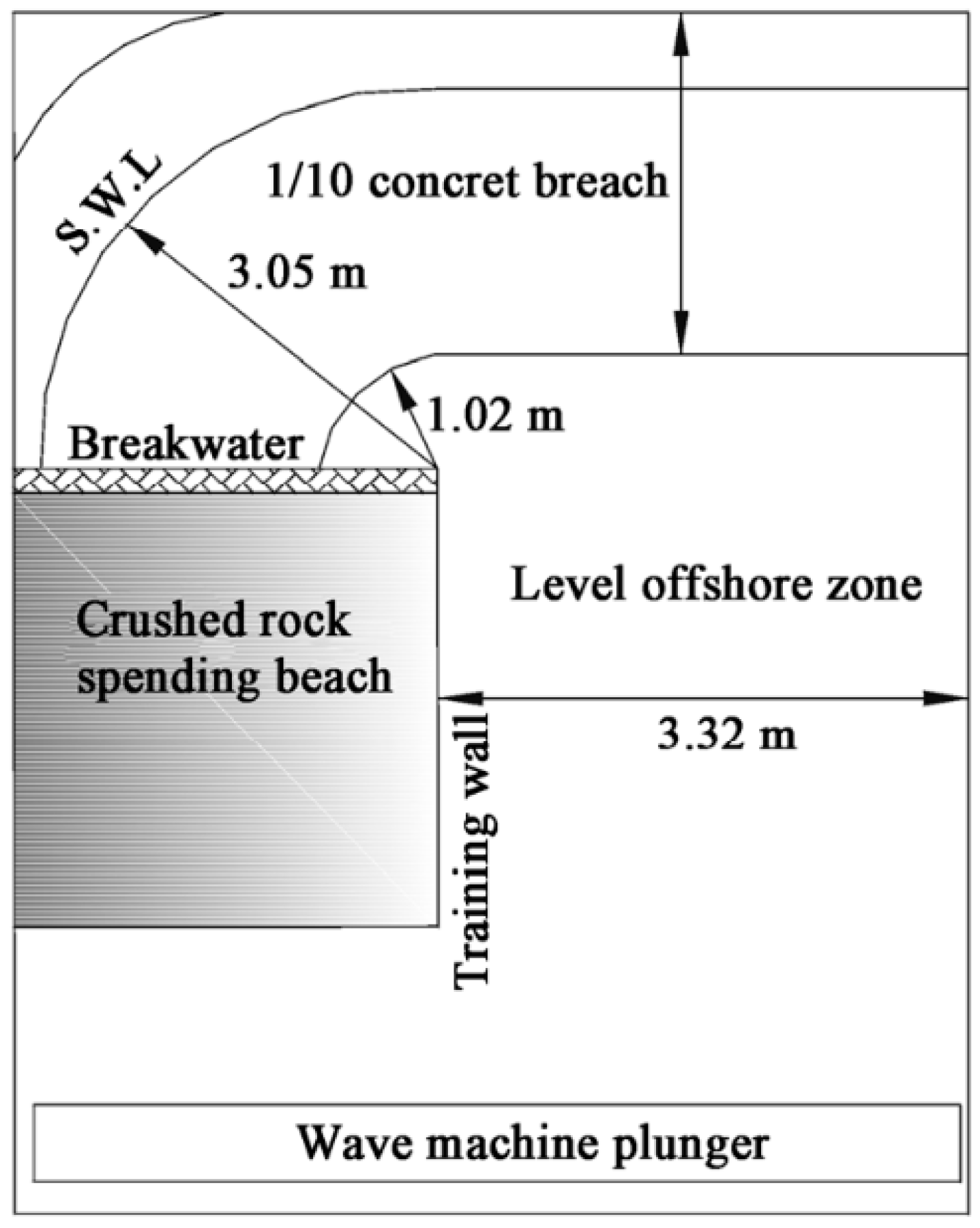

| Case | Plan Slope | h/m | θ/(°) | H0/m | T/s | γ | Cf | λ | L/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:40 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.09 | 1.0 | 0.65 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 3.0 |
| 2 | 1:40 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.05 | 2.0 | 0.65 | 0.023 | 0.007 | 3.0 |
| 3 | 1:100 | 0.18 | 0 | 0.05 | 2.0 | 0.60 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 4.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Jiang, H.; Qu, L.; Dai, Z.; Wu, L. Study on Numerical Modeling for Pollutants Movement Based on the Wave Parabolic Mild Slope Equation in Curvilinear Coordinates. Water 2023, 15, 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183251
Cui L, Jiang H, Qu L, Dai Z, Wu L. Study on Numerical Modeling for Pollutants Movement Based on the Wave Parabolic Mild Slope Equation in Curvilinear Coordinates. Water. 2023; 15(18):3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183251
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Lei, Hengzhi Jiang, Limei Qu, Zheng Dai, and Liguo Wu. 2023. "Study on Numerical Modeling for Pollutants Movement Based on the Wave Parabolic Mild Slope Equation in Curvilinear Coordinates" Water 15, no. 18: 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183251
APA StyleCui, L., Jiang, H., Qu, L., Dai, Z., & Wu, L. (2023). Study on Numerical Modeling for Pollutants Movement Based on the Wave Parabolic Mild Slope Equation in Curvilinear Coordinates. Water, 15(18), 3251. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183251





