Study of Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis in Songhua River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
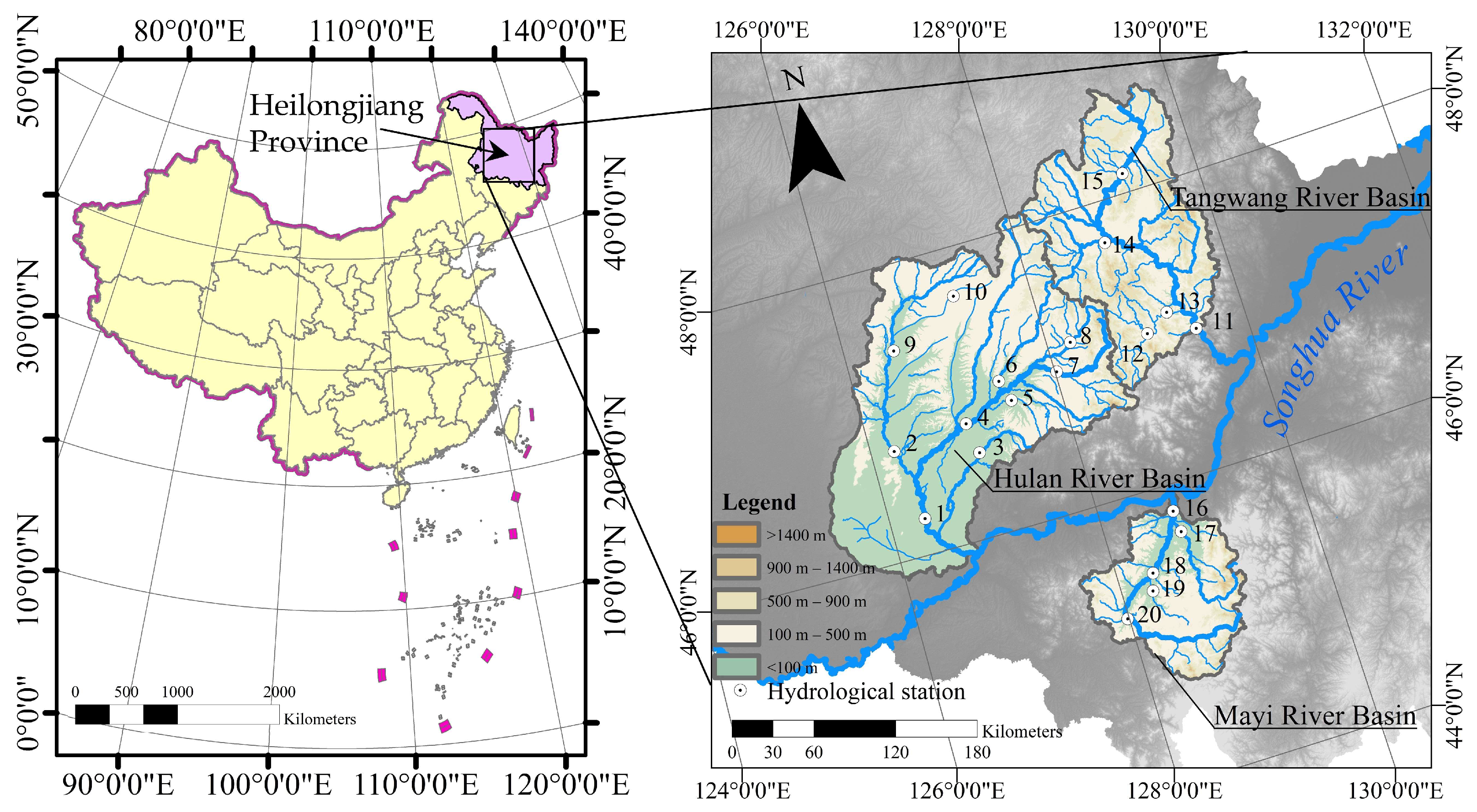
2. Study Areas and Data
2.1. Study Areas
2.2. Data
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mann–Kendall Mutation Test
3.2. Pettitt Test
3.3. Generalized Additive Models for Location, Scale, and Shape Framework
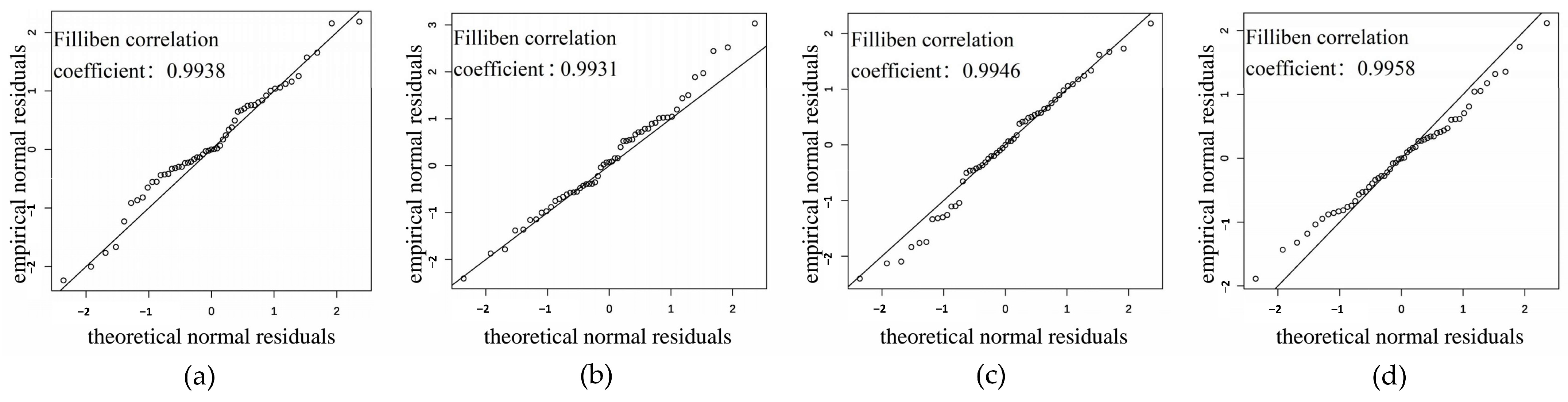
3.4. Model Evaluation and Residual Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Mutation Test for Flood Extremum Sequences
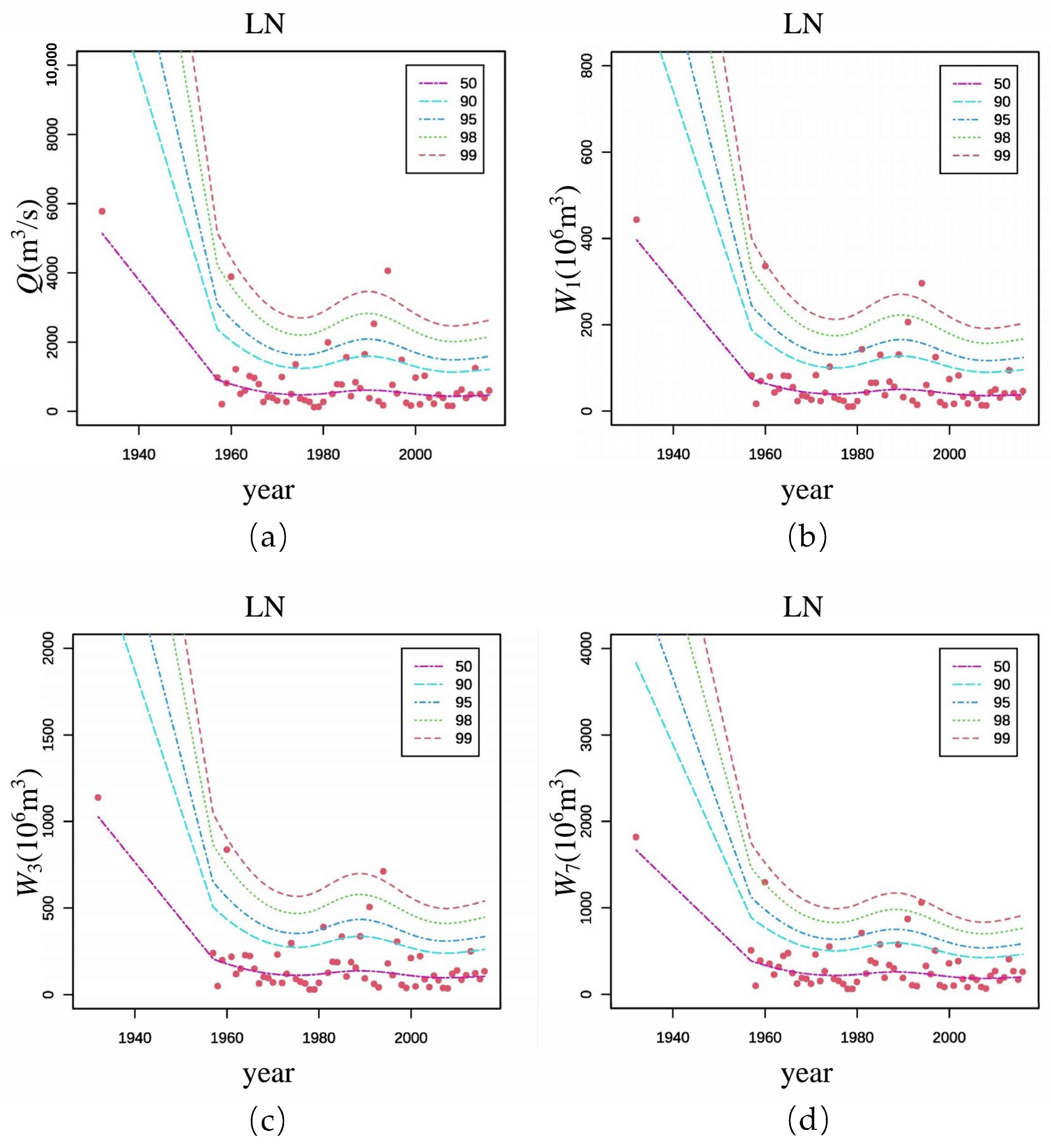
4.2. FFA by Time-Covariate GAMLSS and Spatial Distribution of Optimal Theoretical Distribution
4.3. FFA by Precipitation-Covariate GAMLSS and Spatial Distribution of Optimal Theoretical Distribution
4.4. FFA under Stationarity Assumption
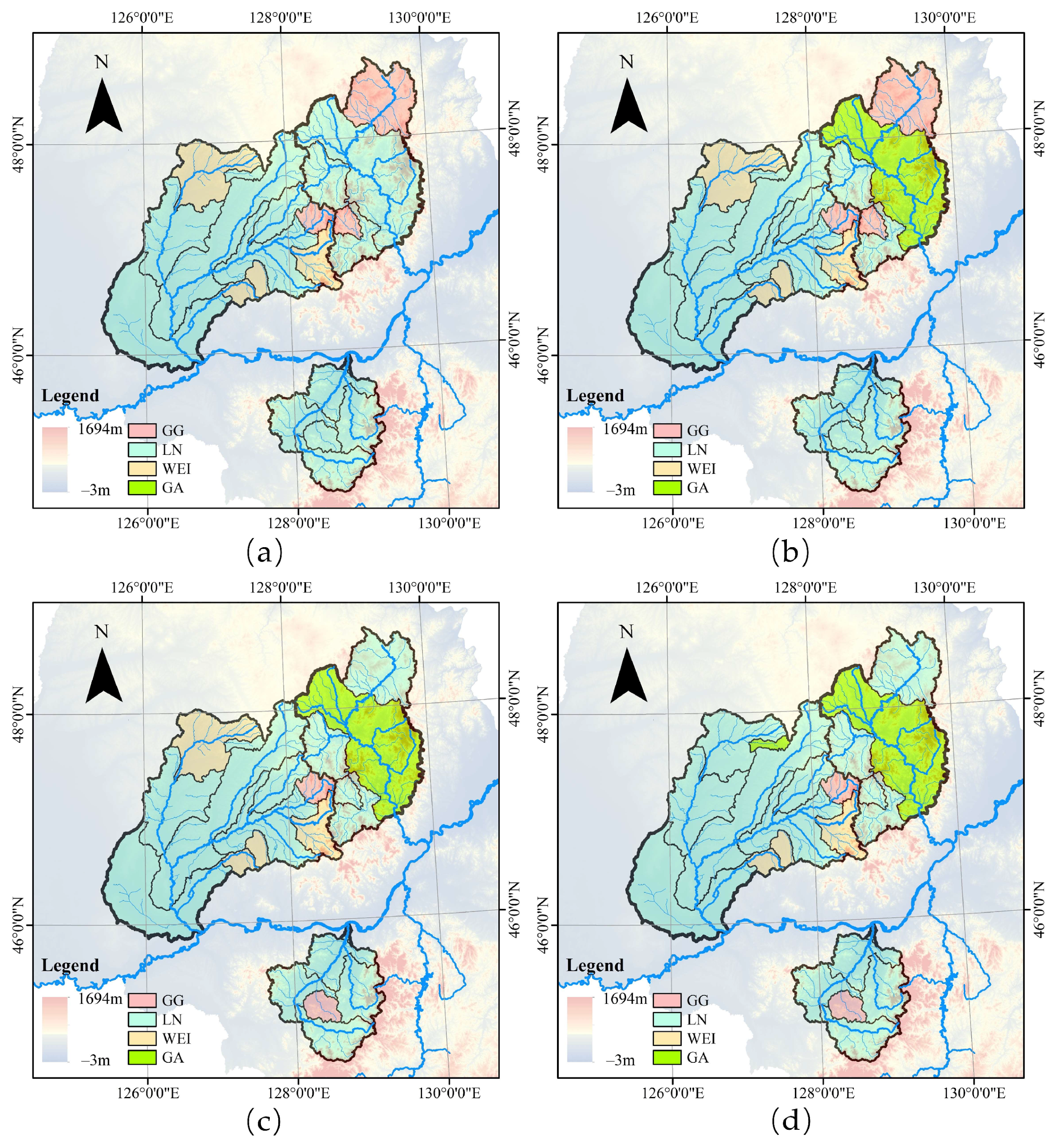
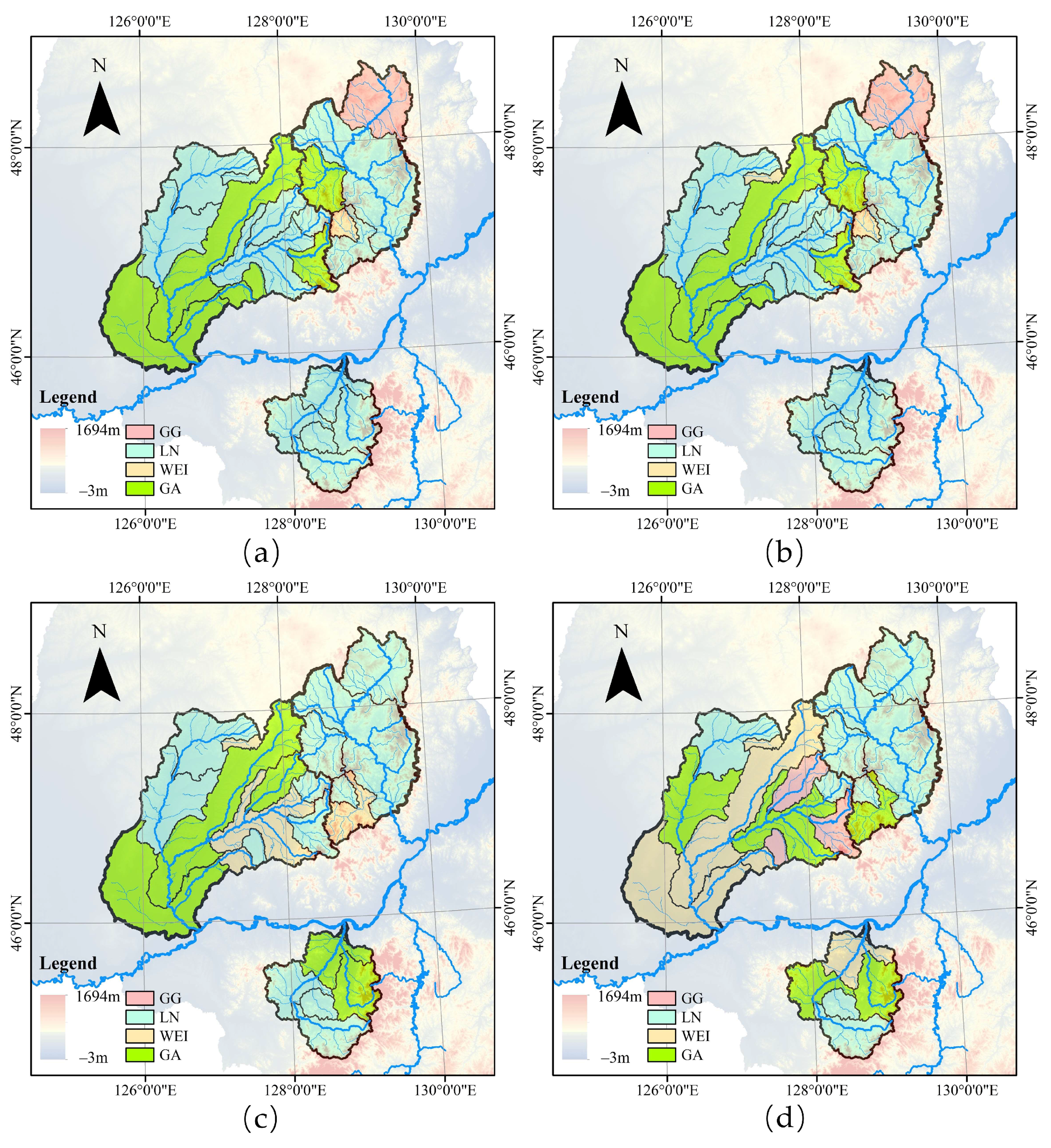
4.5. An Attempt to Apply NS-FFA in the Work of River Management Scope Demarcation
5. Conclusions and Discussion
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Optimal Distribution of Flood Extreme Value Considering Time Covariates at Stations in Hulan River Basin
| Characteristic | Station | Fitted Distribution | Location Parameter β | Scale Parameter σ | AIC | SBC |
| Q | Beiguan | GG | 33.199 − 0.014 × t | −0.383 | 761.0 | 769.5 |
| Chenjiadian | LN | −1.199 + 0.002 × cs(t) | −0.435 | 444.4 | 455.5 | |
| Lanxi | LN | 32.901 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −88.292 + 0.044 × cs(t,2) | 1052.7 | 1070.5 | |
| Lianhe | WEI | 49.277 − 0.022 × cs(t,1) | 168.934 − 0.085 × cs(t,1) | 525.5 | 536.1 | |
| Nihe | WEI | 49.610 − 0.023 × cs(t,2) | −7.317 + 0.004 × cs(t,2) | 610.8 | 627.8 | |
| Ougenhe | LN | 52.896 − 0.024 × cs(t,2) | −93.045 + 0.047 × cs(t,2) | 613.2 | 628.3 | |
| Qinjia | LN | 43.224 − 0.019 × pb(t,2) | −22.244 + 0.011 × pb(t,2) | 990.1 | 1004.9 | |
| Qinggang | LN | 30.922 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −94.675 + 0.047 × cs(t,2) | 580.7 | 595.4 | |
| Qing’anzhen | WEI | 63.869 − 0.030 × cs(t,1) | 45.780 − 0.023 × cs(t,1) | 472.1 | 483.2 | |
| Tieli | WEI | 25.759 − 0.010 × cs(t,2) | 58.709 − 0.029 × cs(t,2) | 876.7 | 894.5 | |
| W1 | Beiguan | GG | 29.009−0.014 × t | −0.459 | 428.4 | 436.9 |
| Chenjiadian | LN | −3.504 + 0.002 × cs(t) | −0.587 | 187.7 | 198.8 | |
| Lanxi | LN | 30.416 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −88.636 + 0.045 × cs(t,2) | 717.8 | 735.6 | |
| Lianhe | WEI | 47.539 − 0.023 × cs(t,1) | 164.278 − 0.082 × cs(t,1) | 310.5 | 321.1 | |
| Nihe | WEI | 46.855 − 0.023 × cs(t,2) | −7.646 + 0.004 × cs(t,2) | 288.0 | 305.1 | |
| Ougenhe | LN | 48.903 − 0.023 × cs(t,2) | −93.097 + 0.047 × cs(t,2) | 366.1 | 381.2 | |
| Qinjia | LN | 41.257 − 0.019 × pb(t) | −22.466 + 0.011 × pb(t) | 661.8 | 676.5 | |
| Qinggang | LN | 28.487 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −94.912 + 0.048 × cs(t,2) | 352.9 | 367.6 | |
| Qing’anzhen | WEI | 58.358 − 0.029 × cs(t,1) | 53.450 − 0.027 × cs(t,1) | 227.3 | 238.4 | |
| Tieli | WEI | 20.827 − 0.009 × cs(t,2) | 59.334 − 0.030 × cs(t,2) | 519.8 | 537.5 | |
| W3 | Beiguan | GG | −0.662 | 518.3 | 526.8 | |
| Chenjiadian | LN | 1.570 + 0.0002 × cs(t) | −0.643 | 268.4 | 279.5 | |
| Lanxi | LN | 30.966 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −88.954 + 0.045 × cs(t,2) | 860.3 | 878.1 | |
| Lianhe | WEI | 49.792 − 0.023 × cs(t,1) | 161.483 − 0.081 × cs(t,1) | 398.8 | 409.3 | |
| Nihe | WEI | 44.319 − 0.021 × cs(t,2) | −7.795 + 0.004 × cs(t,2) | 394.0 | 411.0 | |
| Ougenhe | LN | 46.176 − 0.021 × cs(t,2) | −94.088 + 0.047 × cs(t,2) | 455.9 | 471.0 | |
| Qinjia | LN | 42.423 − 0.019 × pb(t) | −23.773 + 0.012 × pb(t) | 796.4 | 811.0 | |
| Qinggang | LN | 29.497 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −95.310 + 0.048 × cs(t,2) | 449.5 | 464.1 | |
| Qing’anzhen | WEI | 56.775 − 0.027 × cs(t,1) | 55.404 − 0.028 × cs(t,1) | 310.6 | 321.7 | |
| Tieli | WEI | 20.538 − 0.008 × cs(t,2) | 58.328 − 0.029 × cs(t,2) | 636.7 | 654.5 | |
| W7 | Beiguan | GG | 14.859 − 0.0003 × bfp(t,2) | −0.803 | 572.8 | 581.2 |
| Chenjiadian | GA | −0.082 + 0.001 × cs(t) | −0.666 | 317.8 | 328.9 | |
| Lanxi | LN | 31.515 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −90.416 + 0.045 × cs(t,2) | 958.9 | 976.6 | |
| Lianhe | LN | 56.087 − 0.026 × cs(t,1) | −124.62 + 0.062 × cs(t,1) | 458.0 | 468.5 | |
| Nihe | WEI | 41.249 − 0.019 × cs(t,2) | −4.250 + 0.002 × cs(t,2) | 449.9 | 466.9 | |
| Ougenhe | LN | 42.091 − 0.019 × cs(t,2) | −94.626 + 0.047 × cs(t,2) | 510.7 | 525.8 | |
| Qinjia | LN | 43.256 − 0.019 × pb(t) | −25.114 + 0.013 × pb(t) | 883.3 | 897.7 | |
| Qinggang | LN | 30.062 − 0.013 × cs(t,2) | −95.860 + 0.048 × cs(t,2) | 516.1 | 530.8 | |
| Qing’anzhen | WEI | 54.494 − 0.026 × cs(t,1) | 59.978 − 0.030 × cs(t,1) | 353.7 | 364.8 | |
| Tieli | WEI | 19.522 − 0.008 × cs(t,2) | 58.085 − 0.029 × cs(t,2) | 702.7 | 720.5 |
Appendix A.2. Optimal Distribution of Flood Extreme Value Considering Time Covariates at Stations in Tangwang River Basin
| Characteristic | Station | Fitted Distribution | Location Parameter β | Scale Parameter σ | AIC | SBC |
| Q | Chenming | LN | 27.311 − 0.010 × pb(t) | −0.445 | 1083.7 | 1092.9 |
| Dailing | GG | 24.092 − 0.010 × cs(t) | −0.565 | 668.2 | 682.6 | |
| Nancha | LN | 5.661 | −12.681 + 0.006 × cs(t) | 818.6 | 831.3 | |
| Wuying | GG | 17.659 − 0.006 × t | −0.783 | 779.8 | 788.2 | |
| Yichun | LN | 30.590 − 0.012 × pb(t) | −2.680 + 0.001 × pb(t) | 847.7 | 859.0 | |
| W1 | Chenming | GA | 26.682 − 0.011 × pb(t) | −0.518 | 751.0 | 760.1 |
| Dailing | GG | 14.653 − 0.006 × cs(t) | −0.551 | 341.1 | 355.6 | |
| Nancha | LN | 9.929 − 0.004 × cs(t) | −0.455 | 489.9 | 502.6 | |
| Wuying | GG | 14.925 − 0.006 × pb(t) | −0.805 | 475.7 | 484.1 | |
| Yichun | LN | 21.341 − 0.009 × pb(t) | −3.957 + 0.002 × pb(t) | 514.7 | 525.7 | |
| W3 | Chenming | GA | 26.819 − 0.011 × pb(t) | −0.539 | 879.4 | 888.5 |
| Dailing | LN | 11.687 − 0.004 × cs(t) | −0.543 | 432.3 | 444.7 | |
| Nancha | LN | 8.864 − 0.003 × cs(t) | −0.499 | 592.7 | 605.3 | |
| Wuying | LN | 16.036 − 0.006 × pb(t) | 14.707 − 0.008 × pb(t) | 592.0 | 602.7 | |
| Yichun | LN | 3.952 | −5.410 + 0.002 × cs(t,1) | 606.6 | 615.0 | |
| W7 | Chenming | GA | 26.156 − 0.010 × pb(t) | −0.565 | 960.7 | 969.8 |
| Dailing | LN | 11.020 − 0.004 × cs(t) | −0.576 | 493.8 | 506.1 | |
| Nancha | LN | 9.494 − 0.003 × cs(t) | −0.530 | 661.4 | 674.0 | |
| Wuying | LN | 4.778 | 11.547 − 0.006 × pb(t) | 662.9 | 669.8 | |
| Yichun | LN | 4.479 | −7.616 + 0.004vcs(t,1) | 663.6 | 672.1 |
Appendix A.3. Theoretical Optimal Time-Covariate Distribution Quantile Curves in Hulan, Tangwang, and Mayi River Basins
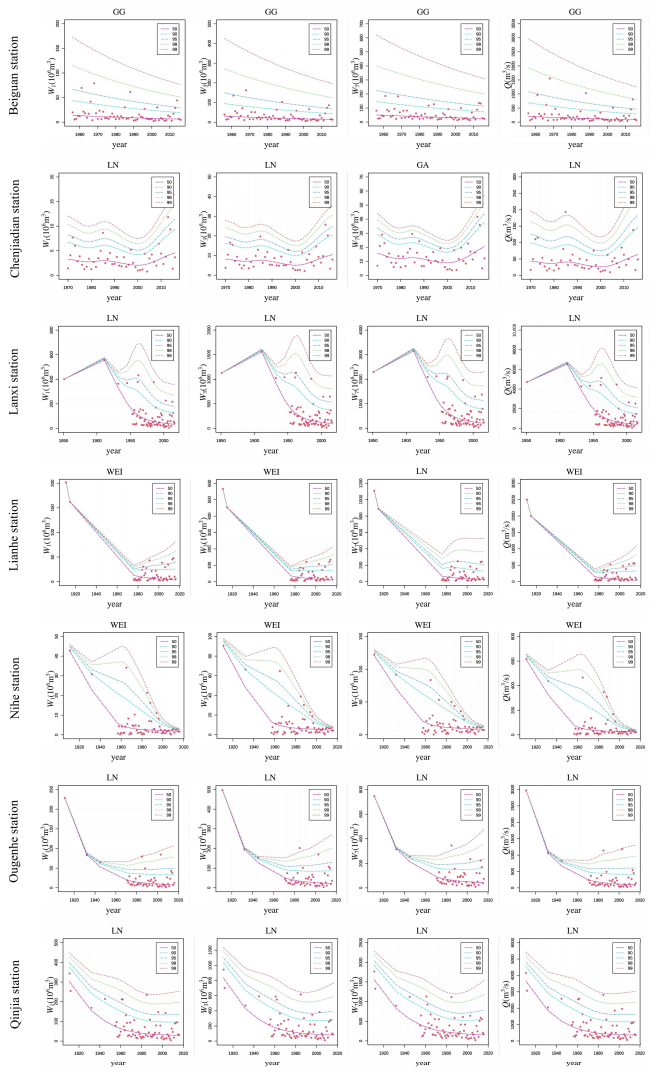
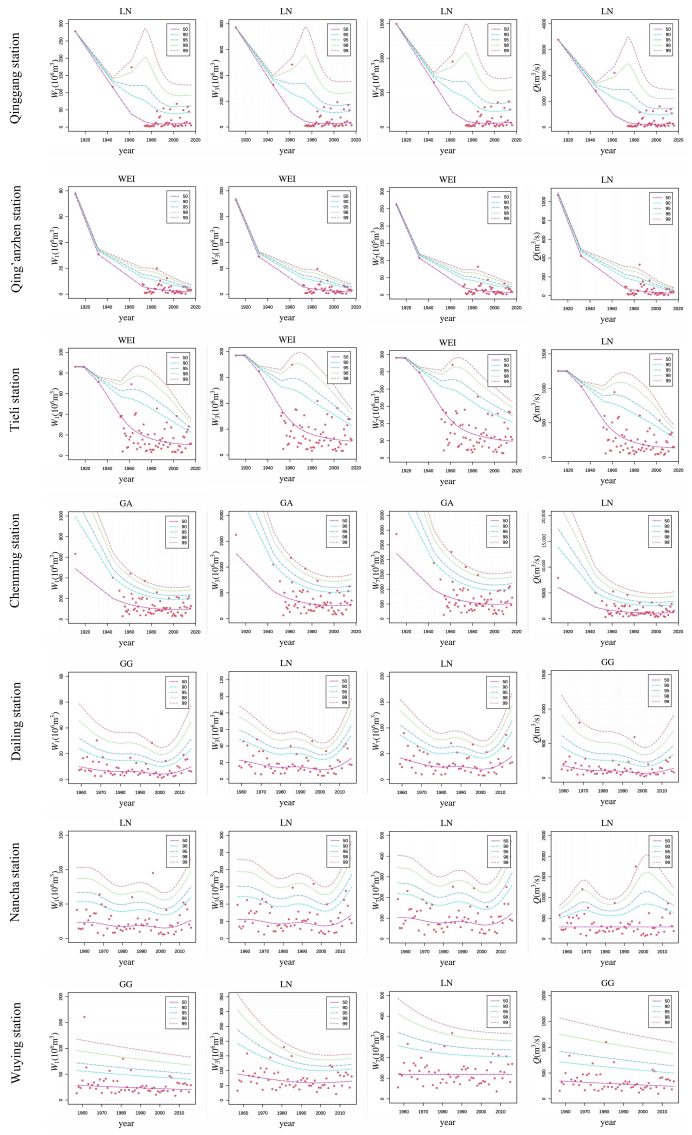
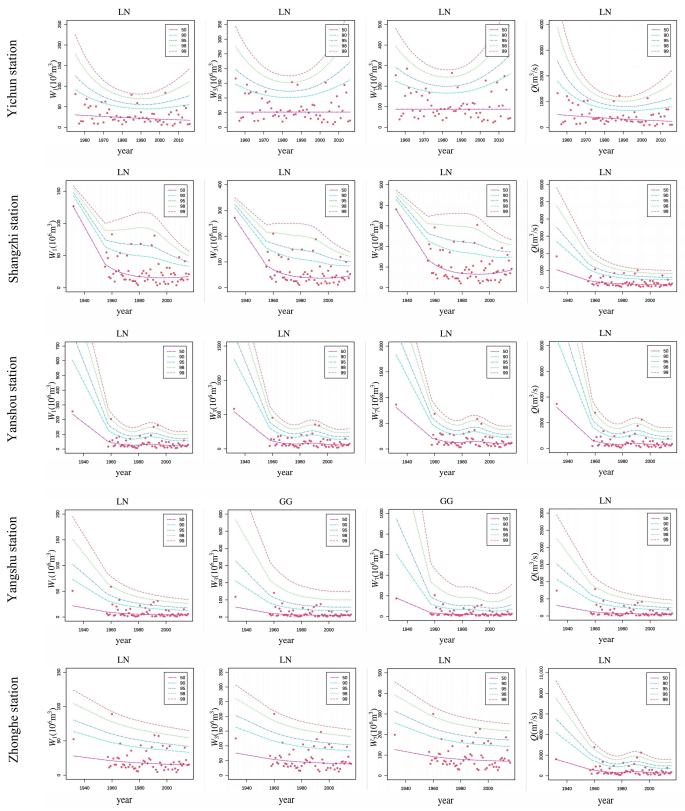
Appendix A.4. Optimal Probability Distribution Results of Flood Extremum in Hulan River Basin under Stationary Condition
| Characteristic | Station | Fitting Results ofP-Ⅲ Distribution | Fitting Results of Stationary GAMLSS | |||||
| Cv | Cs | AIC | SBC | Fitted Distribution | AIC | SBC | ||
| Q | Beiguan | 1.293 | 2.627 | 772.66 | 766.33 | GG | 766.1 | 772.4 |
| Chenjiadian | 0.947 | 1.969 | 445.12 | 450.67 | LN | 445.3 | 449.0 | |
| Lanxi | 1.041 | 2.111 | 1097.71 | 1104.36 | LN | 1091.2 | 1095.6 | |
| Lianhe | 1.411 | 2.842 | 537.30 | 542.58 | GG | 543.1 | 548.4 | |
| Nihe | 1.570 | 3.099 | 621.46 | 627.84 | LN | 623.0 | 627.2 | |
| Ougenhe | 1.734 | 3.476 | 636.53 | 642.20 | GG | 641.3 | 647.0 | |
| Qinjia | 0.981 | 1.999 | 1012.50 | 1019.07 | LN | 1007.2 | 1011.6 | |
| Qinggang | 1.623 | 3.253 | 590.84 | 596.33 | GG | 597.1 | 602.6 | |
| Qing’anzhen | 1.680 | 3.347 | 489.65 | 495.20 | GG | 490.5 | 496.1 | |
| Tieli | 1.006 | 2.081 | 889.24 | 895.90 | LN | 893.6 | 898.0 | |
| W1 | Beiguan | 1.100 | 2.119 | 439.87 | 433.54 | LN | 435.8 | 440.1 |
| Chenjiadian | 1.162 | 1.682 | 189.76 | 195.31 | LN | 189.0 | 192.7 | |
| Lanxi | 0.998 | 2.006 | 764.43 | 771.09 | LN | 756.3 | 760.8 | |
| Lianhe | 1.853 | 3.533 | 328.04 | 333.33 | GG | 329.5 | 334.8 | |
| Nihe | 1.469 | 2.502 | 298.42 | 304.80 | LN | 302.6 | 306.8 | |
| Ougenhe | 1.834 | 3.512 | 400.66 | 406.34 | GG | 394.6 | 400.3 | |
| Qinjia | 1.000 | 2.005 | 684.32 | 690.89 | LN | 679.0 | 683.4 | |
| Qinggang | 1.568 | 3.054 | 363.42 | 368.90 | GG | 369.4 | 374.8 | |
| Qing’anzhen | 2.020 | 3.543 | 252.19 | 257.74 | GG | 246.7 | 250.4 | |
| Tieli | 1.046 | 2.051 | 532.83 | 539.49 | LN | 536.6 | 541.1 | |
| W3 | Beiguan | 1.017 | 2.071 | 530.96 | 524.63 | LN | 528.0 | 532.2 |
| Chenjiadian | 0.863 | 1.655 | 269.37 | 274.92 | LN | 269.5 | 273.2 | |
| Lanxi | 0.995 | 2.013 | 905.35 | 912.01 | LN | 898.7 | 903.1 | |
| Lianhe | 1.743 | 3.448 | 416.76 | 422.04 | GG | 419.4 | 424.7 | |
| Nihe | 1.364 | 2.536 | 401.64 | 408.02 | LN | 410.3 | 414.5 | |
| Ougenhe | 1.704 | 3.363 | 493.62 | 499.29 | LN | 485.1 | 488.9 | |
| Qinjia | 0.952 | 1.925 | 820.32 | 826.89 | LN | 814.5 | 818.8 | |
| Qinggang | 1.502 | 2.988 | 460.21 | 465.70 | GG | 466.1 | 471.6 | |
| Qing’anzhen | 1.641 | 3.156 | 327.82 | 333.37 | LN | 328.5 | 332.2 | |
| Tieli | 1.032 | 2.107 | 643.24 | 649.90 | LN | 653.4 | 657.8 | |
| W7 | Beiguan | 0.946 | 2.003 | 576.47 | 582.80 | GG | 579.7 | 586.0 |
| Chenjiadian | 0.891 | 1.799 | 317.78 | 323.33 | LN | 318.9 | 322.6 | |
| Lanxi | 0.993 | 2.016 | 1003.49 | 1010.15 | LN | 997.9 | 1002.3 | |
| Lianhe | 1.526 | 3.052 | 471.83 | 477.11 | GG | 478.6 | 483.9 | |
| Nihe | 1.251 | 2.383 | 470.19 | 476.57 | LN | 467.7 | 472.0 | |
| Ougenhe | 1.571 | 3.139 | 541.53 | 547.20 | LN | 539.0 | 542.8 | |
| Qinjia | 0.909 | 1.843 | 907.10 | 913.67 | LN | 902.2 | 906.6 | |
| Qinggang | 1.950 | 3.886 | 530.84 | 536.33 | GG | 533.8 | 539.3 | |
| Qing’anzhen | 2.077 | 3.971 | 373.88 | 379.43 | LN | 369.6 | 373.3 | |
| Tieli | 0.969 | 2.005 | 717.55 | 724.21 | LN | 720.9 | 725.3 | |
Appendix A.5. Optimal Probability Distribution Results of Flood Extremum in Tangwang River Basin under Stationary Condition
| Characteristic | Station | Fitting Results ofP-Ⅲ Distribution | Fitting Results of Stationary GAMLSS | |||||
| Cv | Cs | AIC | SBC | Fitted Distribution | AIC | SBC | ||
| Q | Chenming | 0.968 | 2.055 | 1085.47 | 1092.04 | LN | 1091.0 | 1095.4 |
| Dailing | 1.363 | 2.775 | 683.76 | 689.94 | LN | 672.6 | 676.8 | |
| Nancha | 1.100 | 2.310 | 813.27 | 819.60 | LN | 818.3 | 822.5 | |
| Wuying | 1.850 | 3.832 | 827.67 | 833.95 | GG | 780.7 | 787.0 | |
| Yichun | 0.823 | 1.717 | 852.71 | 859.04 | LN | 852.5 | 856.8 | |
| W1 | Chenming | 0.972 | 2.052 | 752.32 | 758.89 | LN | 758.8 | 763.2 |
| Dailing | 0.890 | 1.649 | 345.14 | 351.32 | LN | 343.4 | 347.5 | |
| Nancha | 0.841 | 1.719 | 488.68 | 495.01 | LN | 488.8 | 493.0 | |
| Wuying | 1.849 | 3.592 | 521.34 | 527.63 | GG | 476.6 | 482.9 | |
| Yichun | 0.824 | 1.677 | 515.70 | 522.03 | LN | 516.2 | 520.4 | |
| W3 | Chenming | 0.832 | 1.775 | 887.82 | 894.39 | LN | 887.1 | 891.4 |
| Dailing | 0.825 | 1.681 | 434.87 | 441.05 | LN | 435.9 | 440.0 | |
| Nancha | 0.791 | 1.680 | 590.60 | 596.93 | LN | 592.5 | 596.7 | |
| Wuying | 1.822 | 3.708 | 646.57 | 652.85 | GG | 593.6 | 599.9 | |
| Yichun | 0.758 | 1.596 | 608.17 | 614.51 | LN | 608.4 | 612.6 | |
| W7 | Chenming | 0.810 | 1.742 | 968.66 | 975.23 | LN | 967.8 | 972.2 |
| Dailing | 0.852 | 1.794 | 495.69 | 501.87 | LN | 498.1 | 502.2 | |
| Nancha | 0.551 | 1.010 | 663.39 | 669.72 | GA | 659.8 | 664.0 | |
| Wuying | 1.590 | 3.317 | 711.85 | 718.13 | LN | 662.8 | 667.0 | |
| Yichun | 1.230 | 0.702 | 677.03 | 683.36 | LN | 665.2 | 669.4 | |
References
- Wei, Y.; Wang, X. (Eds.) Engineering Hydrology, 1st ed.; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2005; Chapter 4; pp. 59–73. ISBN 978-7-5084-2973-1. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Panel On Climate Change (Ipcc). Climate Change 2022—Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Working Group II Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; ISBN 978-1-00-932584-4. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.; Llorens, P.; Nord, G.; Calder, I.R.; Gallart, F. Modelling the Hydrological Response of a Mediterranean Medium-Sized Headwater Basin Subject to Land Cover Change: The Cardener River Basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, H. The Research of long-term forecasting of non-stationary hydrologic time series based on the improved BP neural network. In Water Conservancy Information Technology Forum; Hohai University: Nanjing, China, 2020; pp. 92–99. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity Is Dead: Whither Water Management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J. Advances in hydrological frequency analysis of non-stationary time series. Adv. Water Sci. 2011, 22, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Zeng, H.; Li, X. Non-Stationary Flood-Frequency Analysis Based on Mixed Distribution. J. Tianjin Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2013, 46, 298–303. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Dong, X.; Liao, K.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, L. Characteristics of Seasonal Changes in Extreme Temperature and Their Relativity with ENSO in the Yellow River Basin from 1960 to 2017. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, F. Research on the Evolution Characteristics of Future Climate Change in West Liao River Basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Xiong, L. Trend Analysis for the Annual Discharge Series of the Yangtze River at the Yichang Hydrological Station Based on GAMLSS. Acta Geophys. Sin. 2012, 67, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Xiao, M.; Xu, C.-Y. Stationarity of Annual Flood Peaks during 1951–2010 in the Pearl River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 3263–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Xiao, W.; Yan, D.; Wang, H. Progresses on statistical modeling of non-stationary extreme sequences and its application in climate and hydrological change. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2017, 48, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, A. Study on Generalized Pareto distribution and its Application on Frequency Analysis of Hydrology. Master’s Dissertation, Hohai University, Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Song, S. Application of generalized Pareto distribution in POT flood series frequency analysis. J. Northwest AF Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 38, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Tan, S.; Feng, P. Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis Using Univariate and Bivariate Time-Varying Models Based on GAMLSS. Water 2018, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, P.; Cipolla, G.; Treppiedi, D.; Noto, L.V. The Use of GAMLSS Framework for a Non-Stationary Frequency Analysis of Annual Runoff Data over a Mediterranean Area. Water 2022, 14, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, H.; Singh, V.P.; Ding, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y. Nonstationary Analysis of Hydrological Drought Index in a Coupled Human-Water System: Application of the GAMLSS with Meteorological and Anthropogenic Covariates in the Wuding River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Z.; Liu, X. GIS-based Risk Assessment on Rain and Flood Disasters of Songhua River. J. Catastrophology 2009, 24, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Reflections on flood management and disaster reduction in the Songhua River basin in the new period. China Flood Drought Manag. 2022, 32, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhao, Y. Analysis of Variation Trend and Mutation Characteristics of Natural Runoff in the Upstream of the Hulanhe River Basin. Water Resour. Power 2020, 38, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Impact of Groundwater Irrigation on Ammonia Nitrogen Migration Process in Hulan River Basin. Master’s Dissertation, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G. Study on the Intra-annual Runoff Distribution Characteristics in Hulan River Basin. Water Resour. Power 2018, 36, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, W.; Gao, Q.; Bai, Y.; Chen, W. Two-level zoning of aquatic ecological function for management of small and medium-sized size rivers—Case study of Mayihe River basin in Harbin Region. J. China Inst. Water Resour. Hydropower Res. 2014, 12, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y. Analysis of the evolution of precipitation runoff in the Tangwang River Basin. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2019, 47, 33–35+80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H.; Pearson, C.P.; Rosbjerg, D. Comparison of Annual Maximum Series and Partial Duration Series Methods for Modeling Extreme Hydrologic Events: 2. Regional Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 1997, 33, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Rahman, A. Comparison of Annual Maximum and Peaks-over-Threshold Methods with Automated Threshold Selection in Flood Frequency Analysis: A Case Study for Australia. Nat. Hazards 2022, 111, 1219–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Study on the Inconsistency of Flood Extreme Value Sequence and Frequency Distribution Considering Covariates. Master’s Dissertation, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, F. Modern Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Techniques of Climate, 2nd ed.; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2007; ISBN 978-7-5029-4299-1. [Google Scholar]
- Verstraeten, G.; Poesen, J.; Demarée, G.; Salles, C. Long-term (105 years) variability in rain erosivity as derived from 10-min rainfall depth data for Ukkel (Brussels, Belgium): Implications for assessing soil erosion rates. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D22109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasinopoulos, M.D.; Rigby, R.A.; Heller, G.Z.; Voudouris, V.; Bastiani, F.D. Flexible Regression and Smoothing: Using GAMLSS in R, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-315-26987-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. A Semi-Parametric Additive Model for Variance Heterogeneity. Stat. Comput. 1996, 6, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Parzen, E., Tanabe, K., Kitagawa, G., Eds.; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 215–222. ISBN 978-1-4612-7248-9. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buuren, S.; Fredriks, M. Worm Plot: A Simple Diagnostic Device for Modelling Growth Reference Curves. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 1259–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filliben, J.J. The Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient Test for Normality. Technometrics 1975, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Li, Y. Summary of dangerous reservoirs reinforcement in the 13th five-year plan in Heilongjiang province. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 154–155+175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X. Non-stationary Statistical Model and Its Applications in Hydro-meteorological Frequency Analysis. Master’s Dissertation, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- de Medeiros, E.S.; de Lima, R.R.; de Olinda, R.A.; Dantas, L.G.; Santos, C.A.C. Dos Space–Time Kriging of Precipitation: Modeling the Large-Scale Variation with Model GAMLSS. Water 2019, 11, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Station | Years of Dataset | Year(s) of Historical Flood Event(s) | Station | Years of Dataset | Year(s) of Historical Flood Event(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beiguan | 1956~2016 | / | Chenming | 1954~2016 | 1911, 1945, 1951 |
| Chenjiadian | 1970~2016 | / | Dailing | 1959~2016 | / |
| Lanxi | 1953~2016 | 1851, 1911, 1932, 1945 | Nancha | 1956~2016 | / |
| Lianhe | 1976~2016 | 1911, 1915 | Wuying | 1957~2016 | / |
| Nihe | 1957~2016 | 1911, 1932 | Yichun | 1957~2016 | 1955 |
| Ougenhe | 1971~2016 | 1911, 1932, 1945 | Lianhua | 1957~2016 | 1932 |
| Qinjia | 1955~2016 | 1911, 1912, 1932, 1945 | Shangzhi | 1955~2016 | 1932 |
| Qinggang | 1974~2016 | 1911, 1945, 1962 | Yanshou | 1958~2016 | 1932 |
| Qing’anzhen | 1972~2016 | 1911, 1932 | Yangshu | 1957~2016 | 1932 |
| Tieli | 1952~2016 | 1911, 1919, 1932 | Zhonghe | 1957~2016 | 1932 |
| Name | Probability Density Functions (pdf) | Parameter Link Functions |
|---|---|---|
| GA | ||
| LN | ||
| WEI | ||
| GG | ||
| GU |
| Flood Characteristics | Hydrological Stations in Hulan River Basin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lanxi | Qinggang | Nihe | Qinjia | Qing’an Zhen | Ougenhe | Tieli | Beiguan | Lianhe | Chenjiadian | |
| Q | 1967/1974 | 1981/1983 | 1998/1998 | 1969/1974 | 1998/1999 | 1988/1999 | 1969/1960 | 1981/1989 | 1982/1983 | 1973/2004 |
| W1 | 1967/1967 | 1981/1983 | 1997/1998 | 1969/1974 | 1998/1999 | 1988/1999 | 1969/1974 | 1981/1990 | 1982/1983 | 1973/2004 |
| W3 | 1967/1967 | 1979/1983 | 1998/1998 | 1969/1974 | 1998/1999 | 1988/1999 | 1966/1974 | 1981/1990 | 1982/1983 | 1973/2004 |
| W7 | 1967/1974 | 1981/1983 | 1998/1998 | 1969/1974 | 1999/1999 | 1988/1999 | 1969/1974 | 1979/1990 | 1980/1983 | 1973/2008 |
| Flood Characteristics | Hydrological Stations in Tangwang River Basin | Hydrological Stations in Mayi River Basin | ||||||||
| Chenming | Dailing | Nancha | Yichun | Wuying | Lianhua | Zhonghe | Yanshou | Yangshu | Shangzhi | |
| Q | 1974/1975 | 1971/1974 | 1973/1974 | 1988/1991 | 1966/1975 | 1995/1998 | 1968/1998 | 1966/1998 | 1971/1992 | 1967/1975 |
| W1 | 1974/1975 | 1968/1974 | 1974/1974 | 1990/1991 | 1972/1975 | 1995/1998 | 1969/1967 | 1966/1998 | 1971/1992 | 1967/1975 |
| W3 | 1974/1975 | 1964/1975 | 1974/1974 | 1990/1992 | 1972/1975 | 1994/1998 | 1968/1967 | 1966/1998 | 1971/1992 | 1966/1975 |
| W7 | 1974/1975 | 1964/1975 | 1974/1974 | 1991/1992 | 1966/1975 | 1995/1998 | 1967/1998 | 1966/1998 | 1971/1992 | 1960/1967 |
| Flood Characteristic | Station | Optimal Distribution | Location Parameter β | Scale Parameter σ | AIC | SBC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | Lianhua | LN | 29.955 − 0.012 × cs(t) | −0.298 | 921.7 | 934.4 |
| Shangzhi | LN | 34.507 − 0.015 × pb(t) | −0.301 | 835.5 | 844.2 | |
| Yanshou | LN | 33.975 − 0.014 × cs(t) | −0.277 | 860.2 | 872.8 | |
| Yangshu | LN | 38.396 − 0.017 × pb(t) | −0.029 | 697.9 | 705.6 | |
| zhonghe | LN | 29.962 − 0.012 × cs(t) | −0.283 | 872.8 | 885.5 | |
| W1 | Lianhua | LN | 27.507 − 0.012 × cs(t) | −0.328 | 613.0 | 625.7 |
| Shangzhi | LN | 33.475 − 0.015 × cs(t,2) | −12.730 + 0.006 × cs(t,2) | 517.7 | 534.9 | |
| Yanshou | LN | 31.388 − 0.014 × cs(t) | −0.317 | 552.3 | 564.9 | |
| Yangshu | LN | 34.550 − 0.017 × pb(t) | −0.061 | 381.8 | 389.6 | |
| zhonghe | LN | 16.055 − 0.007 × pb(t) | −0.449 | 474.4 | 481.3 | |
| W3 | Lianhua | LN | 28.917 − 0.012 × cs(t) | −0.361 | 733.0 | 745.6 |
| Shangzhi | LN | 28.229 − 0.012 × pb(t) | −0.392 | 621.7 | 630.8 | |
| Yanshou | LN | 31.122 − 0.013 × cs(t) | −0.378 | 660.2 | 672.7 | |
| Yangshu | GG | 31.284 − 0.015 × cs(t,1) | −0.216 | 490.7 | 501.3 | |
| zhonghe | LN | 16.899 − 0.007 × pb(t) | −0.506 | 581.6 | 588.8 | |
| W7 | Lianhua | LN | 29.649 − 0.012 × cs(t) | −0.433 | 802.0 | 814.7 |
| Shangzhi | LN | 24.923 − 0.010 × cs(t,2) | −9.153 + 0.004 × cs(t,2) | 677.7 | 694.9 | |
| Yanshou | LN | 30.507 − 0.013 × cs(t) | −0.453 | 718.2 | 730.7 | |
| Yangshu | GG | 32.119 − 0.015 × cs(t) | −0.391 | 541.4 | 556.2 | |
| zhonghe | LN | 15.503 − 0.006 × pb(t) | −0.598 | 640.6 | 647.9 |
| Flood Characteristic | Station | Fitting Results of P-Ⅲ Distribution | Fitting Results of Stationary GAMLSS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cv | Cs | AIC | SBC | Best Fit Distribution | AIC | SBC | ||
| Q | Lianhua | 1.163 | 2.379 | 926.96 | 933.29 | GG | 927.5 | 933.9 |
| Shangzhi | 1.071 | 2.201 | 836.69 | 843.12 | LN | 843.3 | 847.6 | |
| Yanshou | 1.111 | 2.276 | 862.79 | 869.07 | GG | 866.5 | 872.8 | |
| Yangshu | 1.252 | 2.519 | 692.33 | 698.66 | LN | 702.5 | 706.7 | |
| Zhonghe | 0.992 | 2.055 | 874.12 | 880.46 | LN | 875.7 | 879.9 | |
| W1 | Lianhua | 1.229 | 2.484 | 610.81 | 617.14 | GG | 619.4 | 625.7 |
| Shangzhi | 1.001 | 2.001 | 524.67 | 531.10 | LN | 525.7 | 530.0 | |
| Yanshou | 1.116 | 2.246 | 554.25 | 560.53 | LN | 559.5 | 563.7 | |
| Yangshu | 1.220 | 2.223 | 379.26 | 385.60 | GG | 386.0 | 392.3 | |
| Zhonghe | 0.861 | 1.757 | 475.73 | 482.07 | LN | 474.7 | 478.9 | |
| W3 | Lianhua | 1.279 | 2.617 | 721.90 | 728.24 | GG | 740.3 | 746.7 |
| Shangzhi | 0.991 | 2.045 | 627.19 | 633.62 | LN | 629.5 | 633.8 | |
| Yanshou | 1.088 | 2.238 | 660.12 | 666.40 | LN | 667.3 | 671.5 | |
| Yangshu | 1.177 | 2.300 | 483.25 | 489.58 | GG | 494.4 | 500.8 | |
| Zhonghe | 0.826 | 1.766 | 582.06 | 588.39 | LN | 582.2 | 586.4 | |
| W7 | Lianhua | 1.195 | 2.481 | 790.90 | 797.23 | LN | 809.9 | 814.1 |
| Shangzhi | 0.888 | 1.883 | 683.23 | 689.66 | LN | 684.7 | 689.0 | |
| Yanshou | 0.976 | 2.045 | 723.05 | 729.34 | LN | 725.5 | 729.7 | |
| Yangshu | 1.058 | 2.121 | 544.10 | 550.43 | GG | 545.6 | 552.0 | |
| Zhonghe | 0.836 | 1.847 | 638.67 | 645.00 | LN | 640.9 | 645.1 | |
| Flood Characteristic | Typical Basin | p = 10% Flood’s Extreme Value | Measured Sequence Extremum | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stationarity Assumption | Nonstationarity Assumption | |||||
| P-Ⅲ | GAMLSS-Stationary | GAMLSS-Time | GAMLSS-Precipitation | |||
| Q (m3/s) | Hulan | 2668.21 (+32.75%) | 2376.811 (+18.25%) | 1882.199 (−6.36%) * | 2641.498 (+31.42%) | 2010 (11.4%) |
| Tangwang | 3694.11 (+27.38%) | 3143.928 (+8.41%) * | 2595.534 (−10.50%) | 4211.814 (+45.23%) | 2900 (10.4%) | |
| Mayi | 2038.91 (+23.57%) | 1715.71 (+3.98%) | 1644.117 (−0.36%) * | 3165.404 (+91.84%) | 1650 (9.28%) | |
| W1 (106 m3) | Hulan | 222.98 (+31.00%) | 202.676 (+19.08%) | 160.3656 (−5.78%) * | 209.260 (+22.94%) | 170.208 (11.4%) |
| Tangwang | 301.4 (+37.88%) | 254.205 (+16.29%) | 195.572 (−10.53%) * | 332.363 (+52.05%) | 218.592 (10.4%) | |
| Mayi | 178.74 (+36.10%) | 136.591 (+4.01%) | 131.482 (+0.12%) * | 247.202 (+88.23%) | 131.328 (9.28%) | |
| W3 (106 m3) | Hulan | 630.26 (+27.08%) | 576.242 (+16.19%) | 453.966 (−8.46%) * | 445.035 (−10.26%) | 495.936 (11.4%) |
| Tangwang | 749.19 (+19.60%) | 673.833 (+7.57%)* | 527.561 (−15.78%) | 679.182 (+8.43%) | 626.4 (10.4%) | |
| Mayi | 486.91 (+44.50%) | 365.005 (+8.32%) | 348.004 (+3.28%) * | 369.042 (+9.52%) | 336.96 (9.28%) | |
| W7 (106 m3) | Hulan | 1299.3 (+24.28%) | 1191.927 (+14.01%) | 936.618 (−10.41%) | 950.234 (−9.11%) * | 1045.44 (11.4%) |
| Tangwang | 1389.76 (+26.65%) | 1249.309 (+13.85%) | 991.495 (−9.65%) * | 1258.202 (+14.66%) | 1097.366 (10.4%) | |
| Mayi | 845.45 (+46.71%) | 643.986 (+11.75%) | 597.305 (+3.65%) * | 637.124 (+10.56%) | 576.288 (9.28%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Xing, Z.; Liu, H.; Song, J.; Hou, Q.; Xu, Y. Study of Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis in Songhua River Basin. Water 2023, 15, 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193443
Wang Y, Liu M, Xing Z, Liu H, Song J, Hou Q, Xu Y. Study of Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis in Songhua River Basin. Water. 2023; 15(19):3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193443
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinan, Mingyang Liu, Zhenxiang Xing, Haoqi Liu, Jian Song, Quanying Hou, and Yuan Xu. 2023. "Study of Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis in Songhua River Basin" Water 15, no. 19: 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193443
APA StyleWang, Y., Liu, M., Xing, Z., Liu, H., Song, J., Hou, Q., & Xu, Y. (2023). Study of Nonstationary Flood Frequency Analysis in Songhua River Basin. Water, 15(19), 3443. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193443







