Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Organisms
2.2. Microcosm Setups
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
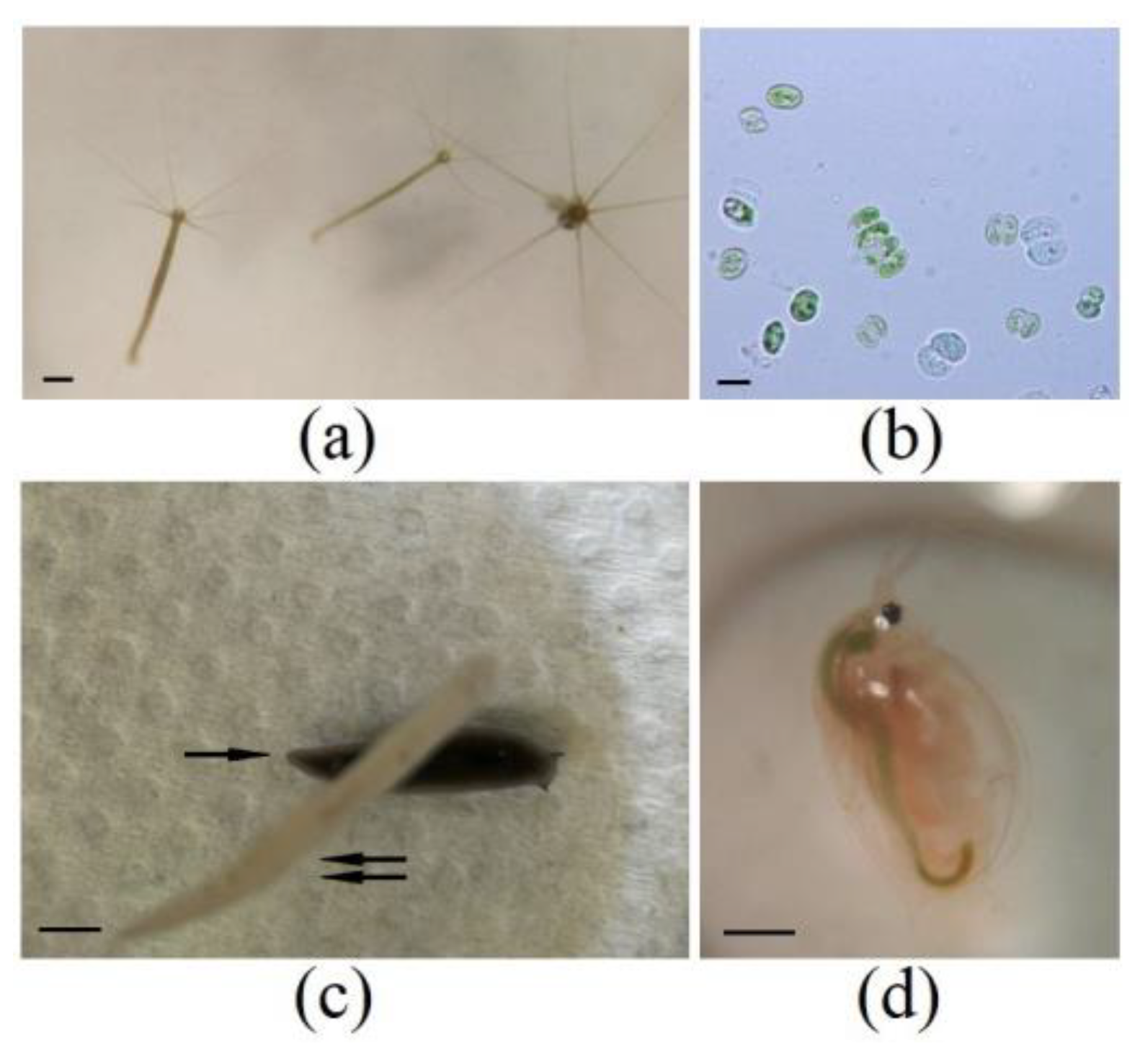
3. Results
3.1. Hunting Net Formation
3.2. A Microscopic Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HV (1) | Hydra viridissima (Pallas, 1766), 1 individual. |
| HV (5) | H. viridissima (Pallas, 1766), 5 individuals. |
| PF (1) | Polycelis felina (Dalyell, 1814), 1 individual. |
| PF (5) | P. felina (Dalyell, 1814), 5 individuals. |
| DG (1) | Dugesia gonocephala (Duges, 1830), 1 individual. |
| DG (5) | D. gonocephala (Duges, 1830), 5 individuals. |
| DM | Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820). |
| CZ | Isolated endosymbiotic microalga Desmodesmus subspicatus (Chlorophyceae) (Chodat) Hegewald et Schmidt. |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy. |
| HPF | High-Pressure Freezing. |
| FS | Freeze Substitution. |
References
- Forbes, S.A. The Lake as a Microcosm. Bull. Sci. Assoc. (Peoria IL) 1887, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, T.G.; Solan, M.; Travis, M.J.M.; Sait, S.M. Microcosm experiments can inform global ecological problems. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balčiunas, D.; Lawler, S.P. Effects of basal resources, predation, and alternative prey in microcosm food chains. Ecology 1995, 76, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoak, M.; Lawler, S.P. Persistence of an extinction-prone predator-prey interaction through metapopulation dynamics. Ecology 1996, 77, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, S.P.; Morin, P.J. Food web architecture and population dynamics in laboratory microcosms of protists. Am. Nat. 1993, 141, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, S.; Feißel, M. Effects of enrichment on three-level food chains with omnivory. Am. Nat. 2000, 155, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D. Resource competition between planktonic algae: An experimental and theoretical approach. Ecology 1977, 58, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsall, M.B.; Hassell, M.P. Apparent competition structures ecological assemblages. Nature 1997, 388, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, P.J. Productivity, intra-guild predation, and population dynamics in experimental food webs. Ecology 1999, 80, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchey, O.L. Prey diversity, prey composition, and predator population dynamics in experimental microcosms. J. Anim. Ecol. 2000, 69, 874–882. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/2647408 (accessed on 30 August 2023.). [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.J.; Salazar, M.; Remirez, J.; Moldes, O.; Wallace, R.L. Predation by invertebrate predators on the colonial rotifer Sinantherina socialis. Invert. Biol. 2006, 125, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyers, R.J. The Microcosm Approach to Ecosystem Biology. Am. Biol. Teach. 1964, 26, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidican, R.; Sandor, A.V. Microcosm experiments as a tool in soil ecology studies. Bull. UASVM Agric. 2015, 72, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.M.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Davidson, T.A.; Liu, Z.; Mazzeo, N.; Trochine, C.; Özkan, K.; Jensen, H.S.; Trolle, D.; et al. Biomanipulation as a restoration tool to combat eutrophication: Recent advances and future challenges. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2012, 47, 411–488. [Google Scholar]
- Landkildehus, F.; Søndergaard, M.; Beklioglu, M.; Adrian, R.; Angeler, D.G.; Hejzlar, J.; Papastergiadou, E.; Zingel, P.; Çakiroğlu, A.I.; Scharfenberger, U.; et al. Climate change effects on shallow lakes: Design and preliminary results of a cross-European climate gradient mesocosm experiment. Est. J. Ecol. 2014, 63, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Symbiotic Interactions; Oxford University Press Inc.: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Jelenčić, B.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic alga as the stronger evolutionary partner in green hydra symbiosis. J. Endocyt. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačević, G.; Franjević, D.; Jelenčić, B.; Kalafatić, M. Isolation and Cultivation Endosymbiotic Algae from Green Hydra and Phylogenetic Analysis of 18S rDNA Sequences. Folia Biol. 2010, 58, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, G.; Radić, S.; Jelenčić, B.; Kalafatić, M.; Poslović, H.; Pevalek-Kozlina, B. Morphological features and isoenzyme characterization of endosymbiotic algae from green hydra. Plant. Syst. Evol. 2010, 284, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivšić, M.; Kovačević, G. Evaluation of algae farming using the Chlorella bioassay. Croat. J. Fish. 2018, 7, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kević, N.; Radić Brkanac, S.; Vincek, N.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Faraguna, F.; Kovačević, G.; Kalafatić, M.; Franjević, D. Endosymbiotic green algae in European Hydra strains show quantitative difference on morphological and isoenzyme level. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habdija, I.; Primc Habdija, B.; Radanović, I.; Špoljar, M.; Matoničkin Kepčija, R.; Vujčić Karlo, S.; Miliša, M.; Ostojić, A.; Sertić Perić, M. Protista-Protozoa i Metazoa-Invertebrata. Strukture i funkcije; Alfa d.d.: Zagreb, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pestana, J.L.T.; Baird, D.J.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Predator threat assessment in Daphnia magna: The role of kairomones versus conspecific alarm cues. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2013, 64, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoks, R.; Govaert, L.; Pauwels, K.; Jansen, B.; De Meester, L. Resurrecting complexity: The interplay of plasticity and rapid evolution in the multiple trait response to strong changes in predation pressure in the water flea Daphnia magna. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekvall, M.T.; Sha, Y.; Palmér, T.; Bianco, G.; Bäckman, J.; Åström, K.; Hansson, L.A. Behavioural responses to co-occurring threats of predation and ultraviolet radiation in Daphnia. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Introduction to Daphnia Biology. In Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia [Internet]; Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2005; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK2039/ (accessed on 30 August 2023.).
- Abe, T.; Saito, H.; Niikura, Y.; Shigeoka, T.; Nakano, Y. Embryonic development assay with Daphnia magna: Application to toxicology of aniline derivates. Chemosphere 2001, 45, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, B.E.; De Meester, L.; Pfrender, M.E.; Lampert, W.; Hairston, N.G. Linking genes to communities and ecosystems: Daphnia as an ecogenomic model. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R. Studies on Chlorella vulgaris IV. Am. J. Bot. 1941, 28, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatić, J.; Vidaković-Cifrek, Ž.; Regula, I. Trophic Level, Bioproduction and Toxicity of the Water of Lake Sakadaš (Nature Park Kopački Rit, Croatia). Limnol. Rep. 2000, 33, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, E.S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electronopaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell. Biol. 1963, 17, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reipert, S.; Goldammer, H.; Richardson, C.; Goldberg, M.W.; Hawkins, T.J.; Hollergschwandtner, E.; Kaufmann, W.A.; Antreich, S.; Stierhof, Y.D. Agitation Modules: Flexible Means to Accelerate Automated Freeze Substitution. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 903–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, H.; Hollergschwandtner, E.; Elisabeth, N.H.; Frade, P.R.; Reipert, S. Automatized freeze substitution of algae accelerated by a novel agitation module. Protist 2016, 167, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, J.; Giepmans, B.N.G. Neodymium as an alternative contrast for uranium in electron microscopy. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdi, N.; Kreuzinger-Janik, B.; Traunspurger, W. Effects of flatworm predators on sediment communities and ecosystem functions: A microcosm approach. Hydrobiologia 2016, 776, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrinec, D.; Kovačević, G.; Tramontana, P.; Peharec-Štefanić, P.; Špoljar, M. Visualisation of hunting nets formed by algae: A perfect hunting mechanism? In Proceedings of the 19th International Microscopy Congress, Sydney, Australia, 9–14 September 2018.
- Hevrøy, T.H.; Golz, A.L.; Hansen, E.L.; Xie, L.; Bradshaw, C. Radiation effects and ecological processes in a freshwater microcosm. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 203, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, G.; Petrinec, D.; Tramontana, P.; Špoljar, M. Hydra vs. turbellarians: Who is the strongest constituent in a given micro-(eco)system?—preliminary observations. In Proceedings of the 3rd Symposium of Freshwater Biology, Zagreb, Croatia, 15 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ptatscheck, C.; Brüchner-Hüttemann, H.; Kreuzinger-Janik, B.; Weber, S.; Traunspurger, W. Are meiofauna a standard meal for macroinvertebrates and juvenile fish? Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 2755–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsetaki, S.E.; Fisher, R.M.; West, S.A. Predation and the formation of multicellular groups in algae. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2016, 17, 651–669. [Google Scholar]
- Wiltshire, K.; Boersma, M.; Meyer, B. Grazer-induced changes in the desmid Staurastrum. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; van Donk, E. Morphological changes in Scenedesmus induced by infochemicals released in situ from zooplankton grazers. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.M.; Bell, T.; West, S.A. Multicellular group formation in response to predators in the alga Chlorella vulgaris. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M. Grazing resistance in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilden, B.; Majdi, N.; Kuhlicke, U.; Neu, T.R.; Traunspurger, W. Flatworm mucus as the base of a food web. BMC Ecology 2019, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donk, E.; Ianora, A.; Vos, M. Induced defences in marine and freshwater phytoplankton: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, T.; Poulsen, L.K.; Moldrup, M.; Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, P.J. Marine microalgae attack and feed on metazoans. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwallis, C.K.; Svensson-Coelho, M.; Lindh, M.; Li, Q.; Stábile, F.; Hansson, L.A.; Rengefors, K. Single-cell adaptations shape evolutionary transitions to multicellularity in green algae. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Temperature Conditions | Light Conditions | Nutritional Status of Turbellarians and Hydras | Result—Recorded Hours (after Setting up the Experiments) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.5 °C | 25 °C | Photoperiod of 8 h day/16 h night | dark | hungry | fed | 1 | 24 |
| Hydra + Microalgae Microcosm | Turbellarians + Microalgae Microcosm | Turbellarians + Microalgae + D. magna Microcosm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydra viridissima + Desmodesmus subspicatus | Polycelis felina + D. subspicatus | Dugesia gonocephala + D. subspicatus | P. felina + D. subspicatus+ Daphnia magna | |||
| controls | ||||||
| H. viridissima | D. subspicatus | P. felina | D. magna | D. subspicatus + D. magna | ||
| Formation/Arrangement of Microalgae | 1 h | 24 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.5 °C | 25 °C | 13.5 °C | 25 °C | |
| Homogeneous | - | + | - | - |
| Aggregations | - | - | - | - |
| Homogeneous with aggregations | + | - | - | - |
| Net formation | - | - | + | + |
| Experimental Condition | Experimental Organisms | Net Formation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 24 h | ||
| Fed predators (13.5 °C) | HV (1) + CZ | - | - |
| HV (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Hungry predators (13.5 °C) | HV (1) + CZ | - | + |
| HV (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Fed predators (25 °C) | HV (1) + CZ | - | - |
| HV (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Hungry predators (25 °C) | HV (1) + CZ | - | - |
| HV (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Fed predators (13.5 °C) | PF (1) + CZ | - | + |
| PF (5) + CZ | + | + | |
| Hungry predators (13.5 °C) | PF (1) + CZ | + | + |
| PF (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Fed predators (25 °C) | PF (1) + CZ | + | + * |
| PF (5) + CZ | + | + * | |
| Hungry predators (25 °C) | PF (1) + CZ | - | - |
| PF (5) + CZ | - | + | |
| Fed predators (13.5 °C) | DG (1) + CZ | - | + |
| DG (5) + CZ | - | + * | |
| Hungry predators (13.5 °C) | DG (1) + CZ | + | + |
| DG (5) + CZ | - | - | |
| Fed predators (25 °C) | DG (1) + CZ | - | + * |
| DG (5) + CZ | - | + * | |
| Hungry predators (25 °C) | DG (1) + CZ | - | - |
| DG (5) + CZ | + | - | |
| Fed predators (13.5 °C) | PF (1) + CZ + DM (10) | - | - |
| PF (5) + CZ + DM (10) | + | - | |
| Hungry predators (13.5 °C) | PF (1) + CZ + DM (10) | + | + |
| PF (5) + CZ + DM (10) | + | + | |
| Fed predators (25 °C) | PF (1) + CZ + DM (10) | + | + |
| PF (5) + CZ + DM (10) | - | - | |
| Hungry predators (25 °C) | PF (1) + CZ + DM (10) | + | - |
| PF (5) + CZ + DM (10) | + | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovačević, G.; Petrinec, D.; Tramontana Ljubičić, P.; Reipert, S.; Sirovina, D.; Špoljar, M.; Peharec Štefanić, P.; Želježić, D. Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence. Water 2023, 15, 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193448
Kovačević G, Petrinec D, Tramontana Ljubičić P, Reipert S, Sirovina D, Špoljar M, Peharec Štefanić P, Želježić D. Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence. Water. 2023; 15(19):3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193448
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovačević, Goran, Daniela Petrinec, Petra Tramontana Ljubičić, Siegfried Reipert, Damir Sirovina, Maria Špoljar, Petra Peharec Štefanić, and Davor Želježić. 2023. "Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence" Water 15, no. 19: 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193448
APA StyleKovačević, G., Petrinec, D., Tramontana Ljubičić, P., Reipert, S., Sirovina, D., Špoljar, M., Peharec Štefanić, P., & Želježić, D. (2023). Formation of Microalgal Hunting Nets in Freshwater Microcosm Food Web: Microscopic Evidence. Water, 15(19), 3448. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193448








