The Synergy of Water Resource Agglomeration and Innovative Conservation Technologies on Provincial and Regional Water Usage Efficiency in China: A Super SBM-DEA Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Empirical Methods
Super SBM Data Envelopment
3.2. Econometric Strategy
3.2.1. Evaluating Cross-Dependence and Unit Root
3.2.2. Implementing Westerlund’s (2005) Approach
3.2.3. Driscoll and Kraay
4. Results
4.1. Spatial Graphing Assessment
4.2. Empirical Findings and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Central Region | Beijing | Western Region |
| Anhui | Fujian | Chongqing |
| Heilongjiang | Guangdong | Gansu |
| Henan | Hainan | Guangxi |
| Hubei | Hebei | Guizhou |
| Hunan | Jiangsu | Inner Mongolia |
| Jiangxi | Shandong | Ningxia |
| Jilin | Shanghai | Qinghai |
| Shanxi | Tianjin | Shaanxi |
| Yunnan | Zhejiang | Sichuan |
| Eastern Region | Liaoning |
| Variables | Units | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage Efficiency | Inputs: Labor, capital stock, Water use. Bad output: sewage. Desired output: GDP | National Bureau of Statistics of China Ministry of Environmental Protection of China China Agricultural Machinery Industry Yearbook |
| GDP | Gross domestic output per capita | |
| Water Resources | Total Water Resources (100 million m3) | |
| Recycling | Recycling of Wastewater (10,000 tons) | |
| Irrigation Sprinkling | Sprinkler Irrigation (1000 hectares) | |
| Water Reservoir | Number of reservoirs | |
| Population | Total population | |
| Industry | Secondary industry | |
| Education | Graduates Secondary Schools |
References
- Obaideen, K.; Shehata, N.; Sayed, E.T.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Olabi, A.G. The role of wastewater treatment in achieving sustainable development goals (SDGs) and sustainability guideline. Energy Nexus 2022, 7, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Behrens, P.; Tukker, A.; Scherer, L. Water use of electricity technologies: A global meta-analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Gong, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J. Study on the coupling coordination relationship between water-use efficiency and economic development. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, W.J.; Loucks, D.P. Water management: Current and future challenges and research directions. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Hu, B. Spatiotemporal dynamics of water supply–demand patterns under large-scale paddy expansion: Implications for regional sustainable water resource management. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 285, 108388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Miller, T.R.; Ishii, N.; Kawasaki, A. Global spatio-temporal change assessment in interregional water stress footprint in China by a high resolution MRIO model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, C.; Xiong, X. Innovation and environmental total factor productivity in China: The moderating roles of economic policy uncertainty and marketization process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9558–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Paranychianakis, N.V.; Angelakis, A.N. Water supply and water scarcity. Water 2020, 12, 2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Harden, C.P.; Liu, Y. Comparison of water resources management between China and the United States. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Dallimer, M.; Stringer, L.C.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, T. Does economic agglomeration lead to efficient rural to urban land conversion? An examination of China’s metropolitan area development strategy. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, C.; Gu, C.; Chen, L.; Li, S. A proposal for the theoretical analysis of the interactive coupled effects between urbanization and the eco-environment in mega-urban agglomerations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1431–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrić, I.; Vrsalović, A.; Perković, T.; Čuvić, M.A.; Šolić, P. IoT approach towards smart water usage. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Chen, J.M. Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality. Innovation 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Innovation and government intervention: A comparison of Singapore and Hong Kong. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, A.; Rozelle, S.; Lohmar, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Water saving technology and saving water in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Farmers’ adoption of water-saving irrigation technology alleviates water scarcity in metropolis suburbs: A case study of Beijing, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlenbrook, S.; Yu, W.; Schmitter, P.; Smith, D.M. Optimizing the water we eat—Rethinking policy to enhance productive and sustainable use of water in agri-food systems across scales. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.; Messer, K.D.; Wu, S. Applying behavioral insights to improve water security. Choices 2017, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, B.K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C.; Chakraborty, S.; Gautam, A. Water security in a changing environment: Concept, challenges and solutions. Water 2021, 13, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg, A.; Pardo, R.; Frontini, A.; Daryoush, T. Reaching for Blue Gold—How the EU Can Rise to the Water Challenge while Reaping the Rewards; EPC Issue Paper No. 80; 2015; Available online: http://aei.pitt.edu/69692/1/pub_6142_reaching_for_blue_gold.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Azad, M.A.; Ancev, T.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Efficient water use for sustainable irrigation industry. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, R.; Song, J. Agricultural water use efficiency and rebound effect: A study for China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejas Moncaleano, D.C.; Pande, S.; Rietveld, L. Water use efficiency: A review of contextual and behavioral factors. Front. Water 2021, 3, 685650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.C. Industrial water-use technical efficiency and potential reduction of CO2 emissions: Evidence from industry-level data. Carbon Manag. 2019, 10, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, A.; Romano, G.; Campedelli, B. Economies of scale, scope, and density in the Italian water sector: A two-stage data envelopment analysis approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4559–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamkhani, A.; Moridi, A. Optimal development of agricultural sectors in the basin based on economic efficiency and social equality. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamkhani, A.; Shourian, M.; Moridi, A. Optimal design and operation of a hydropower reservoir plant using a WEAP-Based simulation–optimization approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1637–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Fang, L.; Mu, L. Evaluating the impacts of water resources technology progress on development and economic growth over the Northwest, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Jiang, M.; Jiang, P.; Shen, X. Dual effects of technology change: How does water technological progress affect China’s water consumption? Iscience 2022, 25, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Yue, A.; Guan, H.; Mu, L.; Ding, Y. How Effective Is Water Technology as a Water Scarcity Remedy for the Economy in China? Water 2022, 14, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Maziotis, A. Drivers of productivity change in water companies: An empirical approach for England and Wales. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 972–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, S.C.; Yeh, F.Y. Total-factor water efficiency of regions in China. Resour. Policy 2006, 31, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Li, A.; Wu, J. The total factor productivity index of freshwater aquaculture in China: Based on regional heterogeneity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 15664–15680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Wang, P. Research on China’s aquaculture efficiency evaluation and influencing factors with undesirable outputs. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2015, 14, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Senante, M.; Maziotis, A.; Sala-Garrido, R. Assessment of the total factor productivity change in the English and Welsh water industry: A färe-primont productivity index approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 2389–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Wei, F.; Lin, X.; Li, Z. Optimal energy management of a renewable microgrid integrating water supply systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 125, 106445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. The Safety of Drinking Water in China: Current Status and Future Prospects. China CDC Wkly. 2020, 2, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.M.; Kujawa-Roeleveld, K.; Tran, D.T.; Rijnaarts, H.H. Data envelopment analysis as a tool to assess the water demand minimization potential in industrial zones in the Vietnamese Delta. Water Resour. Ind. 2022, 28, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Camacho-Poyato, E.; López-Luque, R. Application of data envelopment analysis to studies of irrigation efficiency in Andalusia. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2004, 130, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Ren, Q.; Nolan, R.H.; Wu, P.; Yu, Q. Assessing China’s agricultural water use efficiency in a green-blue water perspective: A study based on data envelopment analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, F.; Jing, L.; Chen, W. Evaluation of Water Resources Utilization Efficiency Based on DEA and AHP under Climate Change. Water 2023, 15, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach, GRIPS Research Report Series. 2003. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/51221252.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Pesaran, M.H. General Diagnostic Tests for Cross Section Dependence in Panels; (IZA Discussion Paper No. 1240); Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA): Bonn, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmeen, R.; Zhaohui, C.; Shah, W.U.H.; Kamal, M.A.; Khan, A. Exploring the role of biomass energy consumption, ecological footprint through FDI and technological innovation in B&R economies: A simultaneous equation approach. Energy 2022, 244, 122703. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, S.I.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, Z.U.; Khan, A. Exploring the impact of innovation, renewable energy consumption, and income on CO2 emissions: New evidence from the BRICS economies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 13866–13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaran, M.H. A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J. Appl. Econom. 2007, 22, 265–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S. Statistical analysis of cointegration vectors. J. Econ. Dyn. Control. 1988, 12, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroni, P. Purchasing power parity tests in cointegrated panels. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2001, 83, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C. Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J. Econom. 1999, 90, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Dolado, J.; Mestre, R. Error-correction mechanism tests for cointegration in a single-equation framework. J. Time Ser. Anal. 1998, 19, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, J. New simple tests for panel cointegration. Econom. Rev. 2005, 24, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, J.C.; Kraay, A.C. Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1998, 80, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, M.A.; Khan, S.U.D.; Ulucak, Z.Ş.; Ahmad, A. Analyzing the relationship between poverty, income inequality, and CO2 emission in Sub-Saharan African countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makanda, K.; Nzama, S.; Kanyerere, T. Assessing the role of water resources protection practice for sustainable water resources management: A review. Water 2022, 14, 3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouseli, D.; Kayaga, S.M.; Kalawsky, R. Evaluating the effectiveness of residential water efficiency initiatives in England: Influencing factors and policy implications. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 2219–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmecke, M.; Fries, E.; Schulte, C. Regulating water reuse for agricultural irrigation: Risks related to organic micro-contaminants. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Kenway, S.; Mukheibir, P. How scale and technology influence the energy intensity of water recycling systems-An analytical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1457–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Buurman, J.; Van Ginkel, K.C. Urban water security: A review. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, E.; Page, D.; Vanderzalm, J.; Kaksonen, A.; Gonzalez, D. Water recycling via aquifers for sustainable urban water quality management: Current status, challenges and opportunities. Water 2018, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N. Water reuse from a circular economy perspective and potential risks from an unregulated approach. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, X.; Li, Q.; Khan, S.; Khalaf, O.I. Urban water resource management for sustainable environment planning using artificial intelligence techniques. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 86, 106515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecina, S.; Isidoro, D.; Playán, E.; Aragüés, R. Irrigation modernization and water conservation in Spain: The case of Riegos del Alto Aragón. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Abadía, R.; Camacho, E.; Rocamora, C.; Moreno, M.A. Efficient water and energy use in irrigation modernization: Lessons from Spanish case studies. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 162, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Song, J.H.; Her, Y.; Provolo, G.; Beom, J.; Jeung, M.; Yoon, K.S. Assessing the potential of agricultural reservoirs as the source of environmental flow. Water 2021, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardashov, D.; Duryagin, V.; Islamov, S. Technology for improving the efficiency of fractured reservoir development using gel-forming compositions. Energies 2021, 14, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

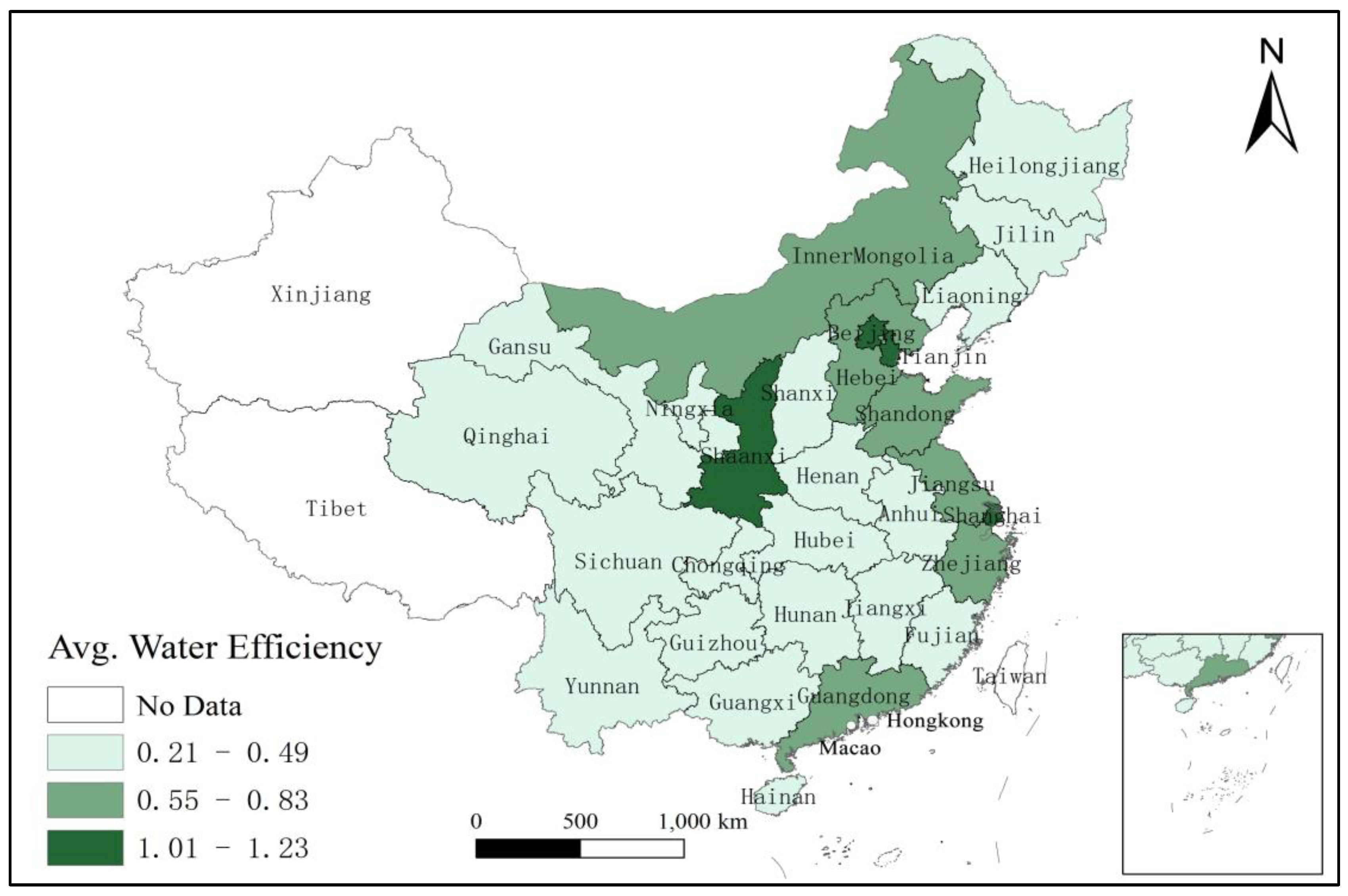
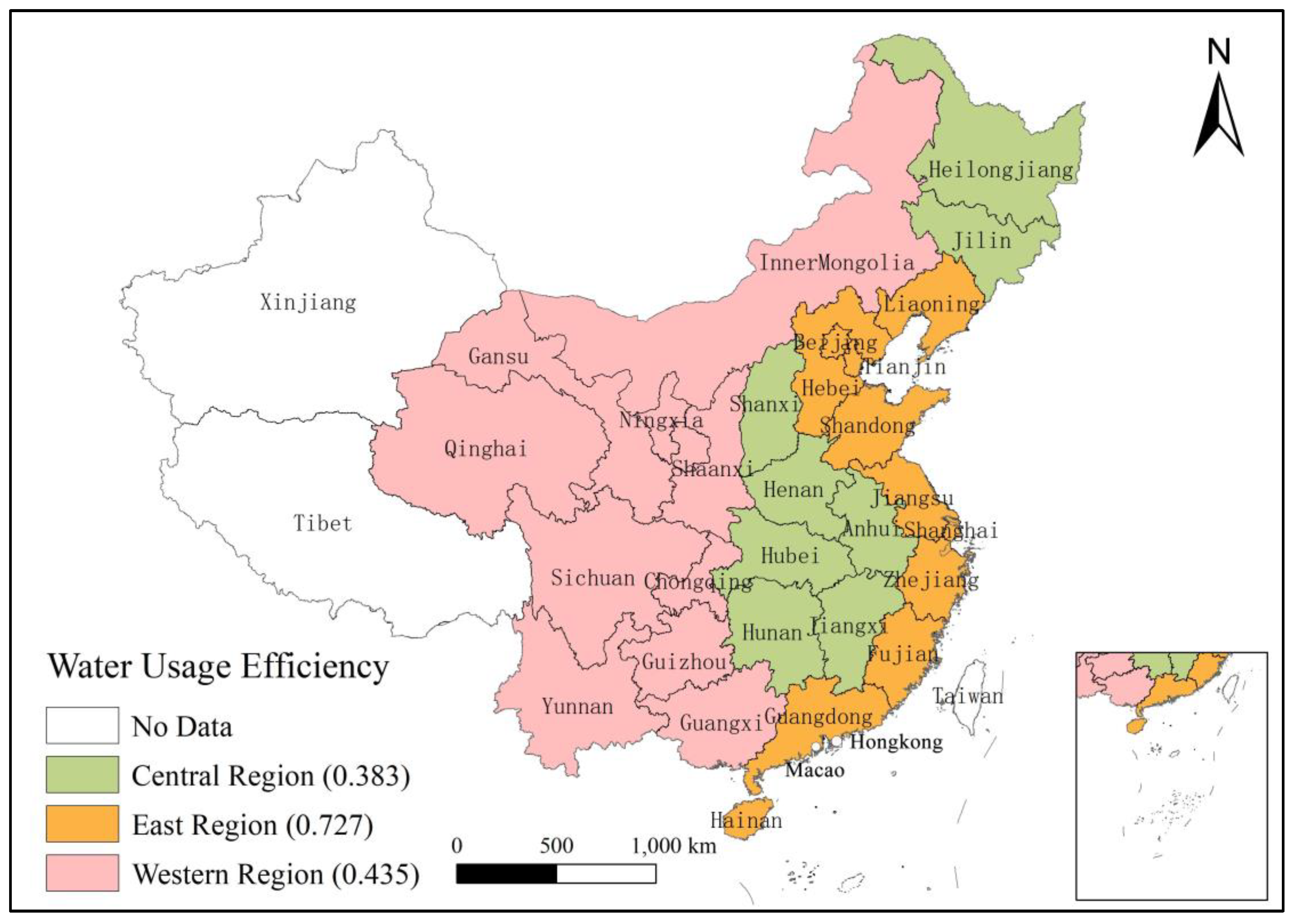
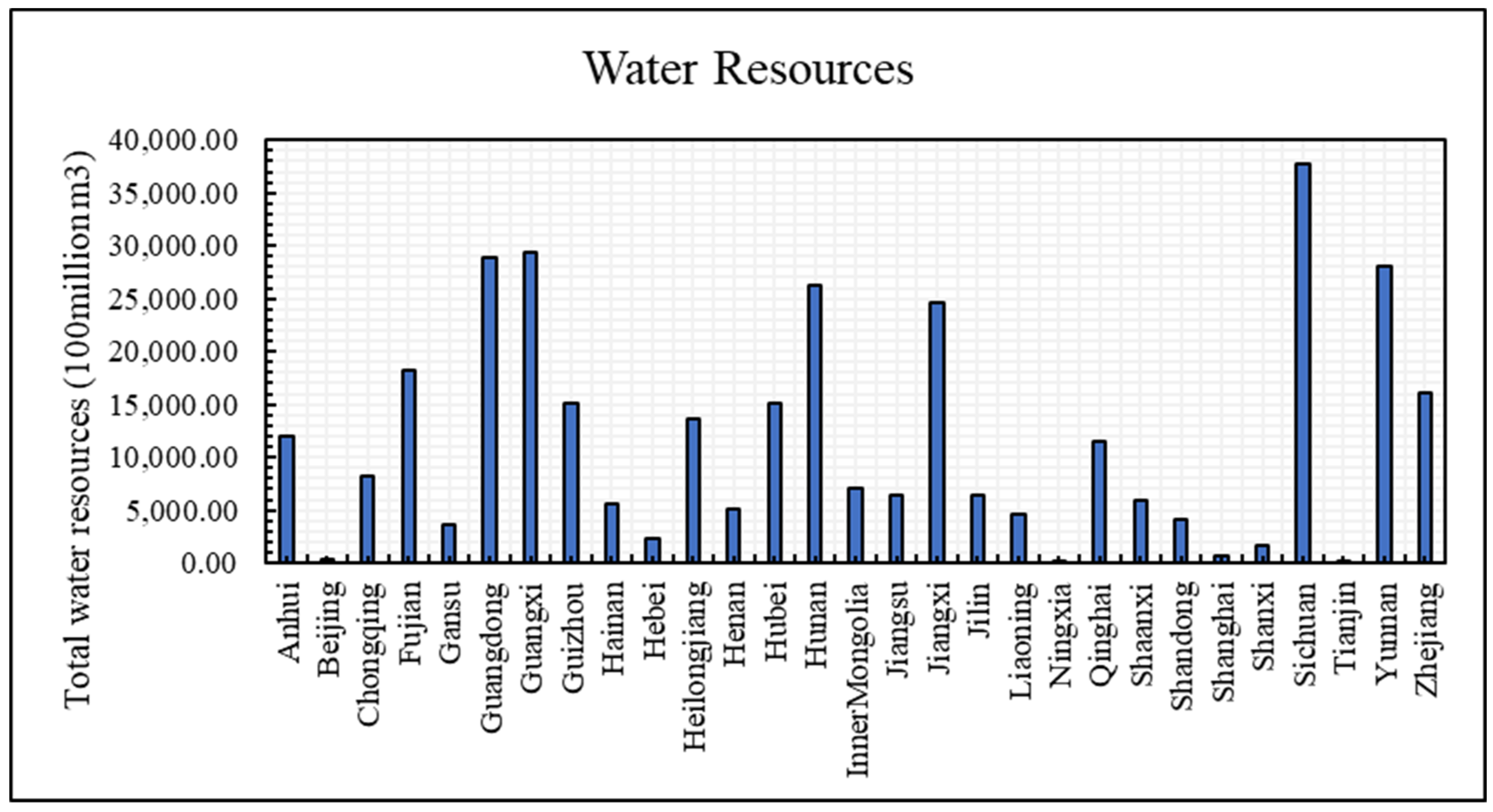

| Variable(s) | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min. | Max. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WUEF | 0.5321333 | 0.2987302 | 0.1028 | 1.8176 |
| GDP | 50,207.69 | 54,882.67 | 5750 | 467,156 |
| WRS | 778.8157 | 720.1821 | 8.1 | 3237.3 |
| WR | 8545.81 | 13,590.28 | −3260 | 76,727 |
| SPR | 121.2325 | 246.4809 | 1.3 | 1661.17 |
| WTRS | 264.6713 | 234.1417 | 1.61 | 1263.89 |
| pop | 4.62 × 107 | 2.84 × 107 | 5,103,464 | 1.15 × 108 |
| Sind | 9392.617 | 8475.533 | 308.62 | 44,270.51 |
| EU | 267,235.2 | 171,134 | 29,313 | 749,826 |
| Variable(s) | CD-Test | p-Value | Average Joint T | Mean ρ | Mean abs(ρ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WUEF | 46.077 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| GDP | 53.538 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| WRS | 51.83 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.94 | 0.94 |
| WR | 24.294 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| SPR | 54.345 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| WTRS | 50.029 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.91 | 0.91 |
| pop | 55.116 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Sind | 53.596 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.97 | 0.97 |
| EU | 52.526 | 0.000 | 29.00 | 0.95 | 0.95 |
| Variable(s) | CIPS (2007) | |
|---|---|---|
| Level | Firs-Diff | |
| WUEF | −4.949 *** | −6.097 *** |
| GDP | 0.3904 | −6.190 *** |
| WRS | −4.838 *** | −6.158 *** |
| WR | 0.8087 | −6.190 *** |
| SPR | 0.0104 | −5.663 *** |
| WTRS | 0.7583 | −5.5772 *** |
| pop | 1.4159 | −3.8266 *** |
| Sind | 0.5389 | −4.439 *** |
| EU | −1.6853 | −4.990 *** |
| Westerlund | Statistic(s) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Resources Model | |||
| some panels are cointegrated | Variance ratio | −1.9495 | 0.0256 |
| All panels are cointegrated | −1.5521 | 0.0603 | |
| Water Technology Model | |||
| some panels are cointegrated | −1.5278 | 0.0633 | |
| All panels are cointegrated | Variance ratio | −1.5957 | 0.0553 |
| (MD1) | (MD2) | (MD3) | (MD4) | (MD5) | (MD6) | (MD7) | (MD8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Resources Effects | Water-Saving-Technology Effects | Water Resources-Technology Effects | ||||||
| Variable(s) | Dependent WUEF (Water Usage Efficiency) | |||||||
| WRS | −0.0781 *** | −0.0464 *** | −0.0524 *** | −0.00788 | ||||
| (0.00418) | (0.00711) | (0.0103) | (0.00986) | |||||
| GDP | −0.00509 | −0.0510 *** | −0.0294 * | −0.710 *** | −0.758 *** | |||
| (0.0166) | (0.00511) | (0.0142) | (0.0669) | (0.0958) | ||||
| GDP2 | 0.0313 *** | 0.0334 *** | ||||||
| (0.00293) | (0.00435) | |||||||
| WR | 0.0203 * | 0.0415 *** | 0.0107 | 0.00938 | 0.00721 | 0.00571 | ||
| (0.0106) | (0.00736) | (0.0102) | (0.0100) | (0.0123) | (0.00695) | |||
| SPR | 0.0347 ** | 0.0175 ** | 0.0154 ** | 0.0168 *** | 0.00924 | |||
| (0.0126) | (0.00641) | (0.00714) | (0.00202) | (0.00909) | ||||
| pop | −0.0739 * | −0.188 *** | −0.202 *** | −0.167 ** | ||||
| (0.0397) | (0.0568) | (0.0561) | (0.0713) | |||||
| Sind | 0.314 *** | 0.340 *** | 0.353 *** | 0.295 *** | ||||
| (0.0134) | (0.00993) | (0.00927) | (0.0206) | |||||
| EU | 0.201 *** | 0.165 *** | 0.159 *** | −0.0592 | ||||
| (0.0337) | (0.0485) | (0.0481) | (0.0550) | |||||
| WTRS | 0.0297 * | 0.0108 ** | 0.0381 *** | 0.0345 *** | 0.0779 *** | |||
| (0.0151) | (0.00426) | (0.00279) | (0.00303) | (0.00687) | ||||
| Constant | 0.999 *** | 78.16 *** | 34.67 *** | 29.85 *** | 83.60 *** | 83.57 *** | 77.50 *** | 71.12 *** |
| (0.0471) | (3.988) | (4.072) | (4.303) | (5.200) | (6.102) | (6.119) | (6.825) | |
| Time Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 435 | 435 | 435 | 435 | 435 | 435 | 435 | 435 |
| Number of groups | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| (MD1) | (MD2) | (MD3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable(s) | Dependent WUEF (Water Usage Efficiency) | ||
| WRS | −0.0832 ** | −0.116 ** | 0.0682 |
| (0.0303) | (0.0558) | (0.120) | |
| GDP | −2.098 *** | −1.884 ** | −0.788 * |
| (0.715) | (0.734) | (0.399) | |
| GDP2 | 0.0922 *** | 0.0814 ** | 0.0348 * |
| (0.0324) | (0.0333) | (0.0174) | |
| WR | 0.264 *** | ||
| (0.0647) | |||
| SPR | 0.0311 *** | ||
| (0.00513) | |||
| pop | −0.00739 | −0.307 *** | −0.161 |
| (0.144) | (0.0463) | (0.145) | |
| Sind | 0.270 *** | 0.237 *** | 0.298 *** |
| (0.0626) | (0.0462) | (0.0433) | |
| EU | 0.281 ** | 0.0968 *** | 0.0305 *** |
| (0.127) | (0.0333) | (0.00548) | |
| WTRS | 0.300 *** | ||
| (0.0438) | |||
| WRS×WR | 0.0923 ** | ||
| (0.0358) | |||
| WRS × SPR | 0.0853 * | ||
| (0.0440) | |||
| WRS × WTRS | 0.0307 *** | ||
| (0.00538) | |||
| Constant | 12.68 *** | 26.65 ** | 48.20 *** |
| (3.981) | (10.19) | (3.023) | |
| Time Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Province Effect | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Observations | 435 | 435 | 435 |
| Number of groups | 29 | 29 | 29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasmeen, R.; Hao, G.; Ye, Y.; Shah, W.U.H.; Tang, C. The Synergy of Water Resource Agglomeration and Innovative Conservation Technologies on Provincial and Regional Water Usage Efficiency in China: A Super SBM-DEA Approach. Water 2023, 15, 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193524
Yasmeen R, Hao G, Ye Y, Shah WUH, Tang C. The Synergy of Water Resource Agglomeration and Innovative Conservation Technologies on Provincial and Regional Water Usage Efficiency in China: A Super SBM-DEA Approach. Water. 2023; 15(19):3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193524
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasmeen, Rizwana, Gang Hao, Yusen Ye, Wasi Ul Hassan Shah, and Caihong Tang. 2023. "The Synergy of Water Resource Agglomeration and Innovative Conservation Technologies on Provincial and Regional Water Usage Efficiency in China: A Super SBM-DEA Approach" Water 15, no. 19: 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193524
APA StyleYasmeen, R., Hao, G., Ye, Y., Shah, W. U. H., & Tang, C. (2023). The Synergy of Water Resource Agglomeration and Innovative Conservation Technologies on Provincial and Regional Water Usage Efficiency in China: A Super SBM-DEA Approach. Water, 15(19), 3524. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15193524






