Phosphorus Recovery and Simultaneous Heavy Metal Removal from ISSA in a Two-Compartment Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
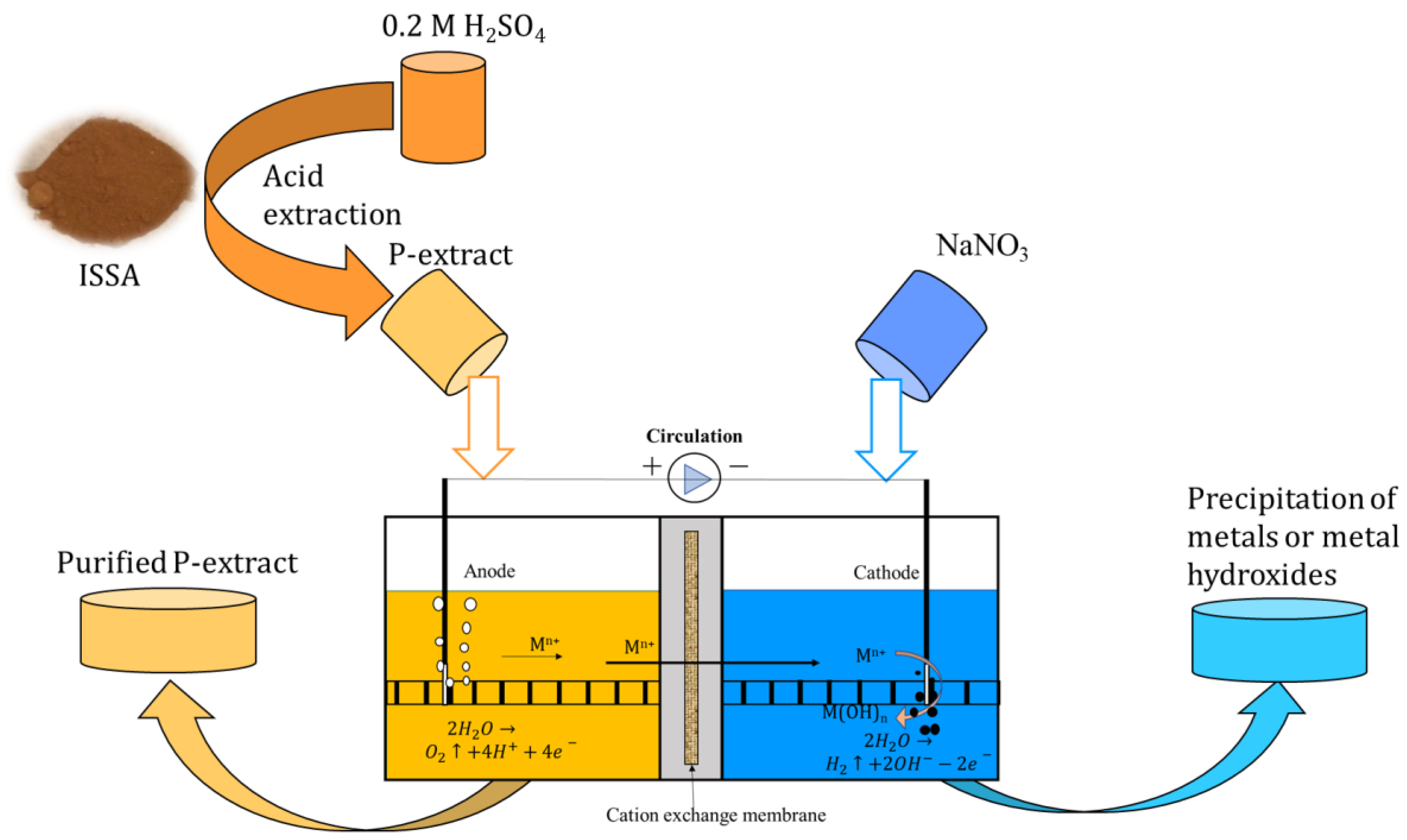
2. Experimental Process
2.1. P Extract from ISSA
2.2. EDR Experiments
- The reduction efficiency was calculated from the decrease in heavy metals/metals in the anolyte and verified from the increase in heavy metals/metals in the catholyte. The acceptable mass balances were set in the range of 90–110%.
- The total volume decrease in electrodes was considered when the EDR duration was higher than 96 h.
- An analysis of variance was run for each element and sample, and each of these currents was carried out twice for trend line rectification. The overall results were shown in one trend line.
2.3. Migration of Metal(loid)s and P in Electrolytes
2.4. Characterization of the Precipitates in the Cathode
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electromigration of Heavy Metals/Metals
3.2. Optimal Duration of the EDR Process for Heavy Metal/Metal Removal
3.3. Voltammetry and pH Variation
3.4. Precipitates in Catholyte
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirkelund, G.M.; Magro, C.; Guedes, P.; Jensen, P.E.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytic removal of heavy metals and chloride from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and air pollution control residue in suspension—Test of a new two compartment experimental cell. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donatello, S.; Cheeseman, C.R. Recycling and recovery routes for incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA): A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2328–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzet, S.; Peplinski, B.; Bodkhe, S.Y.; Cornel, P. Recovery of phosphorus and aluminium from sewage sludge ash by a new wet chemical elution process (SESAL-Phos-recovery process). Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franz, M. Phosphate fertilizer from sewage sludge ash (SSA). Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzel, H.; Krüger, O.; Hermann, L.; Adam, C. Sewage sludge ash—A promising secondary phosphorus source for fertilizer production. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Peplinski, B.; Michaelis, M.; Kley, G.; Simon, F.G. Thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge ashes for phosphorus recovery. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzet, S.; Peplinski, B.; Cornel, P. On wet chemical phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash by acidic or alkaline leaching and an optimized combination of both. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, J.S.; Guo, M.Z.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Donatello, S.; Poon, C.S. Phosphorus recovery and leaching of trace elements from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA). Chemosphere 2018, 193, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Lejon, T. Comparison of 2-compartment, 3-compartment and stack designs for electrodialytic removal of heavy metals from harbour sediments. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Phosphorous recovery from sewage sludge ash suspended in water in a two-compartment electrodialytic cell. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebbers, B.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E. Comparison of two different electrodialytic cells for separation of phosphorus and heavy metals from sewage sludge ash. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournie, T.; Rashwan, T.L.; Switzer, C.; Gerhard, J.I. Phosphorus recovery and reuse potential from smouldered sewage sludge ash. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, L.; Caneghem, J.V. Recovery of phosphorus from sewage sludge ash: Influence of chemical addition prior to incineration on ash mineralogy and related phosphorus and heavy metal extraction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Nakamura, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Omori, D.; Haruta, S. Development of a novel phosphorus recovery system using incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) and phosphorus-selective adsorbent. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.-S.; Xue, Q.; Poon, C.S. Alkaline modification of the acid residue of incinerated sewage sludge ash after phosphorus recovery for heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions. Waste Manag. 2021, 123, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, P.; Couto, N.; Ottosen, L.M.; Ribeiro, A.B. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash through an electrodialytic process. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viader, R.P.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Electrodialytic extraction of phosphorus from ash of low-temperature gasification of sewage sludge. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Lejon, T.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M. Applying multivariate analysis as decision tool for evaluating sediment-specific remediation strategies. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkelund, G.M.; Ottosen, L.M.; Villumsen, A. Investigations of Cu, Pb and Zn partitioning by sequential extraction in harbour sediments after electrodialytic remediation. Chemosphere 2010, 79, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, R.; Gzara, L.; Lajimi, R.H.; Hafiane, A. Treatment of textile wastewater by a hybrid ultrafiltration/electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 132, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Aji, B.; Yavuz, Y.; Koparal, A.S. Electrocoagulation of heavy metals containing model wastewater using monopolar iron electrodes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 86, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Bejan, D.; Bunce, N.J. Removal of arsenic from synthetic acid mine drainage by electrochemical pH adjustment and coprecipitation with iron hydroxide. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4500–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadyrbaeva, T.Z. Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions using a novel hybrid liquid membrane—Electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 99, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.R.; Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Effect of pulse current on acidification and removal of Cu, Cd, and As during suspended electrodialytic soil remediation. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 107, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Lejon, T. An optimised method for electrodialytic removal of heavy metals from harbour sediments. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 173, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Kirkelund, G.M. Electrodialytic remediation of fly ash from co-combustion of wood and straw. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 181, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilhan, F.; Kabuk, H.A.; Kurt, U.; Avsar, Y.; Sari, H.; Gonullu, M.T. Evaluation of treatment and recovery of leachate by bipolar membrane electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 75, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, L.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Kirkelund, G.M. Electrodialytic Separation of Phosphorus and Heavy Metals from Two Types of Sewage Sludge Ash. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 1910–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, J.-S.; Donatello, S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Wang, Q.; Poon, C.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Recovery of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash by combined two-step extraction and selective precipitation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, W.; Tao, S.; Yuan, S.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Phosphorus recovery from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) and reutilization of residues for sludge pretreated by different conditioners. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.Z.; Xu, X.J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, N.N.; Guo, N.; Yu, H.W. Development of novel assisting agents for the electrokinetic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated kaolin. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 218, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.B.; Ji, Z.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Yuan, J.S. Development of recovering lithium from brines by selective-electrodialysis: Effect of coexisting cations on the migration of lithium. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, eaab0530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassanali, A.; Giberti, F.; Cuny, J.; Kuhne, T.D.; Parrinello, M. Proton transfer through the water gossamer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13723–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, K.B.; Lejon, T.; Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M. The influence of sediment properties and experimental variables on the efficiency of electrodialytic removal of metals from sediment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5312–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, L.; Li, J.-S.; Donatello, S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Poon, C.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Use of Mg/Ca modified biochars to take up phosphorus from acid-extract of incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) for fertilizer application. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.E.; Ottosen, L.M.; Ferreira, C.; Villumsen, A. Kinetics of electrodialytic extraction of Pb and soil cations from a slurry of contaminated soil fines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 138, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, S.M.; Daud, W.R.W.; Kim, B.H.; Somalu, M.R.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Muchtar, A.; Jahim, J.M.; Lim, S.S.; Chang, I.S. Comparison of performance and ionic concentration gradient of two-chamber microbial fuel cell using ceramic membrane (CM) and cation exchange membrane (CEM) as separators. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.R.; Ottosen, L.M.; Mortensen, J. Electrodialytic soil remediation enhanced by low frequency pulse current—Overall chronopotentiometric measurement. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Seno, M. Concentration Polarization and Water Dissociation in Ion-Exchange Membrane Electrodialysis—Mechanism of Water Dissociation. J. Chem. Soc. -Faraday Trans. I 1986, 82, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.X.; Wang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Xu, T.W. Water electro-transport with hydrated cations in electrodialysis. Desalination 2015, 365, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, G. Cation selective glass electrodes and their mode of operation. Biophys. J. 1962, 2, 259–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| P Extract | pH | Concentration of Major Metal(loid)s (mg/L) | Concentration of Minor Metal(loid)s (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid extract of the ISSA | 1.5 | Ca (2068), P (1792), Al (1309), Mg (6), Fe (4.6), Zn (0.7), Cu (0.3), Mn (0.16). | As (10.6), Ni (10.8), Pb (10.2). |
| Metal(loid)s | Aqueous Species | Concentration (mmol/L) | Log K |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | Ca2+ | 33.71 | −2.01 |
| CaSO4 | 16.48 | −1.75 | |
| CaH2PO4+ | 1.16 | −3.07 | |
| Al | AlSO4+ | 29.46 | −1.67 |
| Al(SO4)2− | 12.47 | −2.04 | |
| Al3+ | 6.57 | −3.39 | |
| Mg | Mg2+ | 0.25 | −4.15 |
| Fe | FeH2PO42+ | 0.04 | −4.93 |
| FeSO4+ | 0.03 | −4.66 | |
| Fe(SO4)2− | 3 × 10−3 | −5.65 | |
| Fe3+ | 2.6 × 10−3 | −6.8 | |
| Zn | Zn2+ | 3 × 10−3 | −5.53 |
| Cu | Cu2+ | 5 × 10−3 | −5.88 |
| Mn | Mn2+ | 3 × 10−3 | −6.08 |
| Pb | Pb2+ | 4.8 × 10−5 | −7.87 |
| PbH2PO4+ | 2.3 × 10−6 | −6.78 | |
| As | H3AsO3 | 1.4 × 10−4 | −6.81 |
| ED Duration (h) | Energy Consumption (KW.h) | Element Removal Efficiency (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | Cu | Fe | Mg | Mn | Zn | Al | P | ||
| 96 | 0.05 | 73.43 | 71.62 | 40.67 | 71.26 | 66.72 | 66.32 | 39.16 | 0 |
| 168 | 0.11 | 88.61 | 82.55 | 33.02 | 83.29 | 78.26 | 79.05 | 48.13 | 3.62 |
| Electrolyte | pH | Concentration of Major Metal(loid)s (mg/L) | Concentration of Minor Metal(loid)s (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anolyte | 0.087 | Ca (822.22), P (1701), Al (718.30), Mg (2.65), Fe (4.26), Zn (0.36), Cu (0.13), Mn (0.09). | As (5.16), Ni (10.8), Pb (5.12). |
| Catholyte | 14.31 | Ca (322.22), P (309), Al (418.30), Mg (0.65), Fe (0.16), Zn (0.06). | As (1.87), Ni (3.28), Pb (1.98). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, Y.; Xu, L.; Ren, Z. Phosphorus Recovery and Simultaneous Heavy Metal Removal from ISSA in a Two-Compartment Cell. Water 2023, 15, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020226
Fang L, Zhang Z, Mei Y, Xu L, Ren Z. Phosphorus Recovery and Simultaneous Heavy Metal Removal from ISSA in a Two-Compartment Cell. Water. 2023; 15(2):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020226
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Le, Zuotai Zhang, Ying Mei, Linji Xu, and Ze Ren. 2023. "Phosphorus Recovery and Simultaneous Heavy Metal Removal from ISSA in a Two-Compartment Cell" Water 15, no. 2: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020226










