The Pilot Study of a Dual-Media Filter Consisting of Mortar and Modified Zeolite for Removing Heavy Metals from Expressway Stormwater Runoff
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Media
2.2. Selection of Adsorbent
2.2.1. Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity of Filter Media
2.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.3. Field Tests
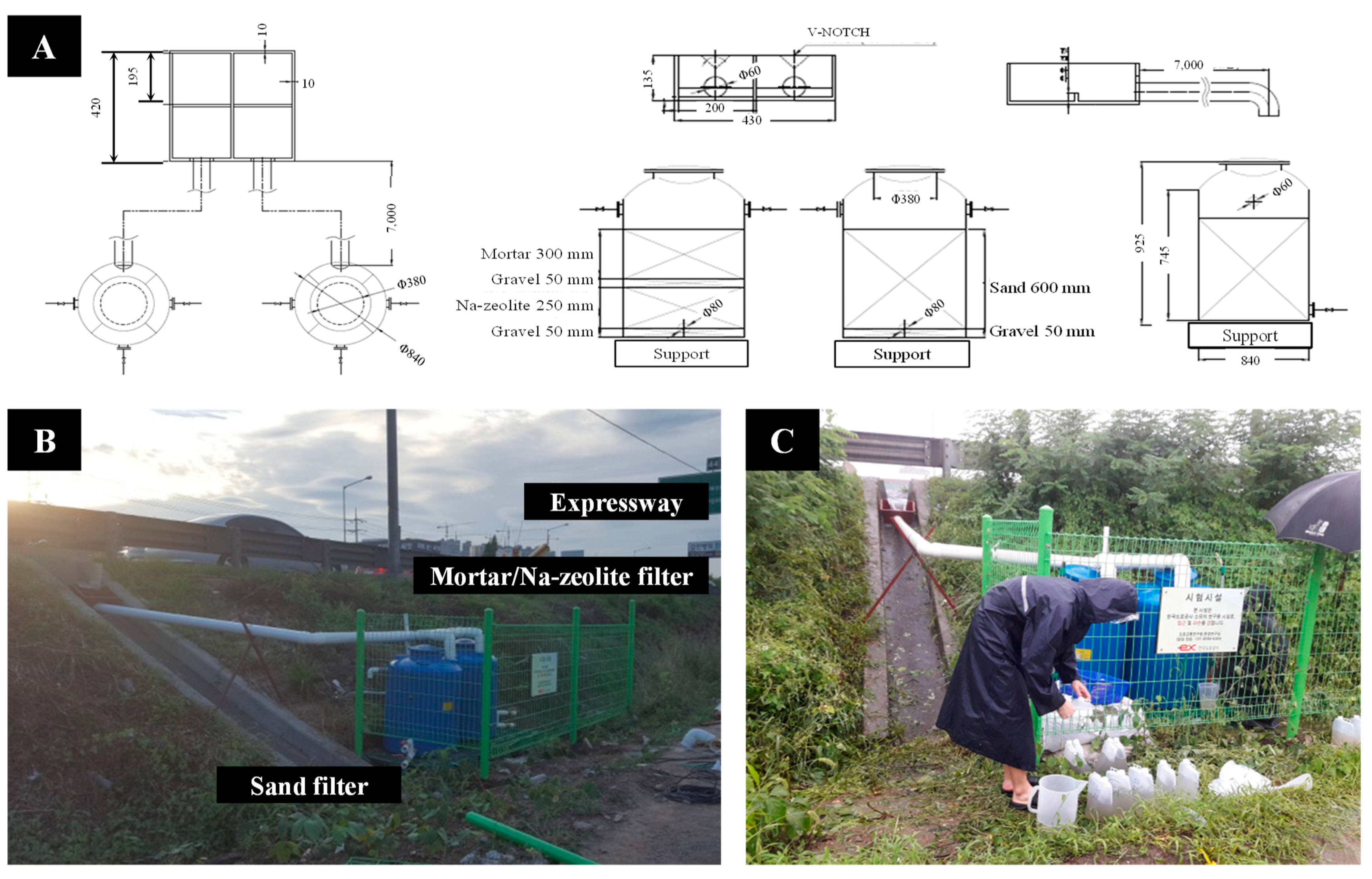
2.3.1. Pilot Scale Plant
2.3.2. Monitoring
2.3.3. In Situ Evaluation of Hydraulic Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cu Adsorption on Adsorbents
3.1.1. Equilibrium Adsorption
3.1.2. Adsorption Kinetics
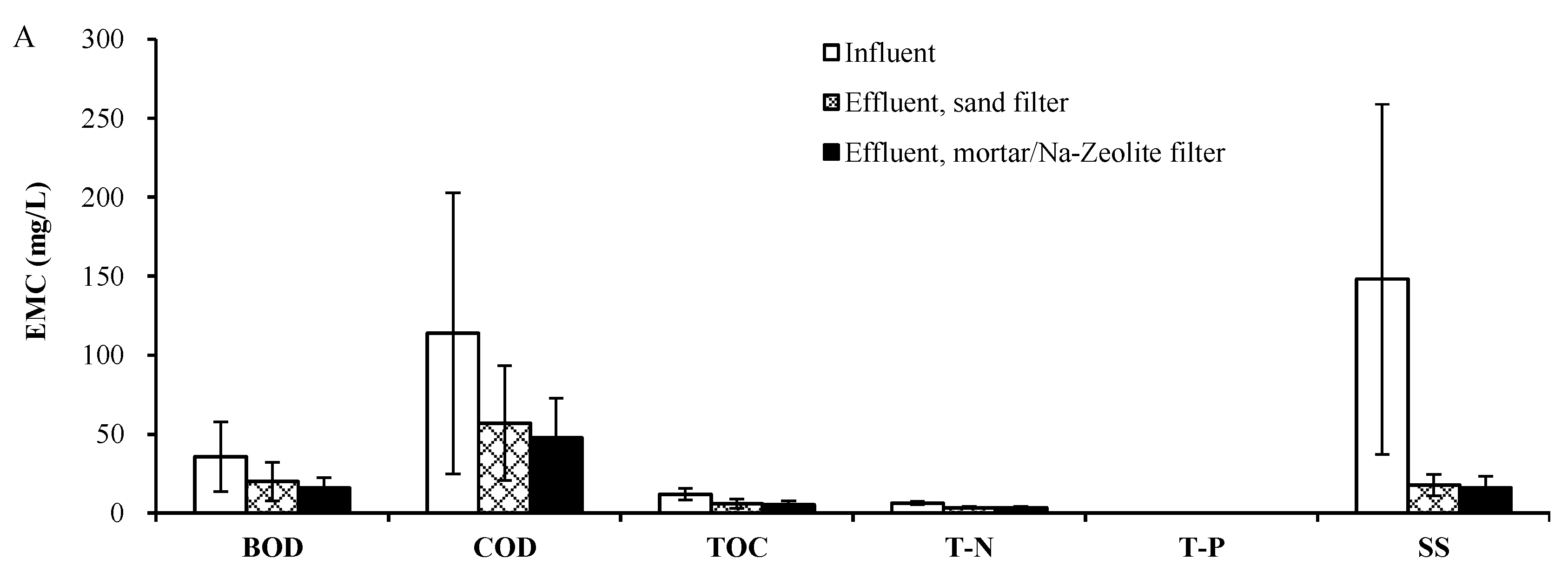
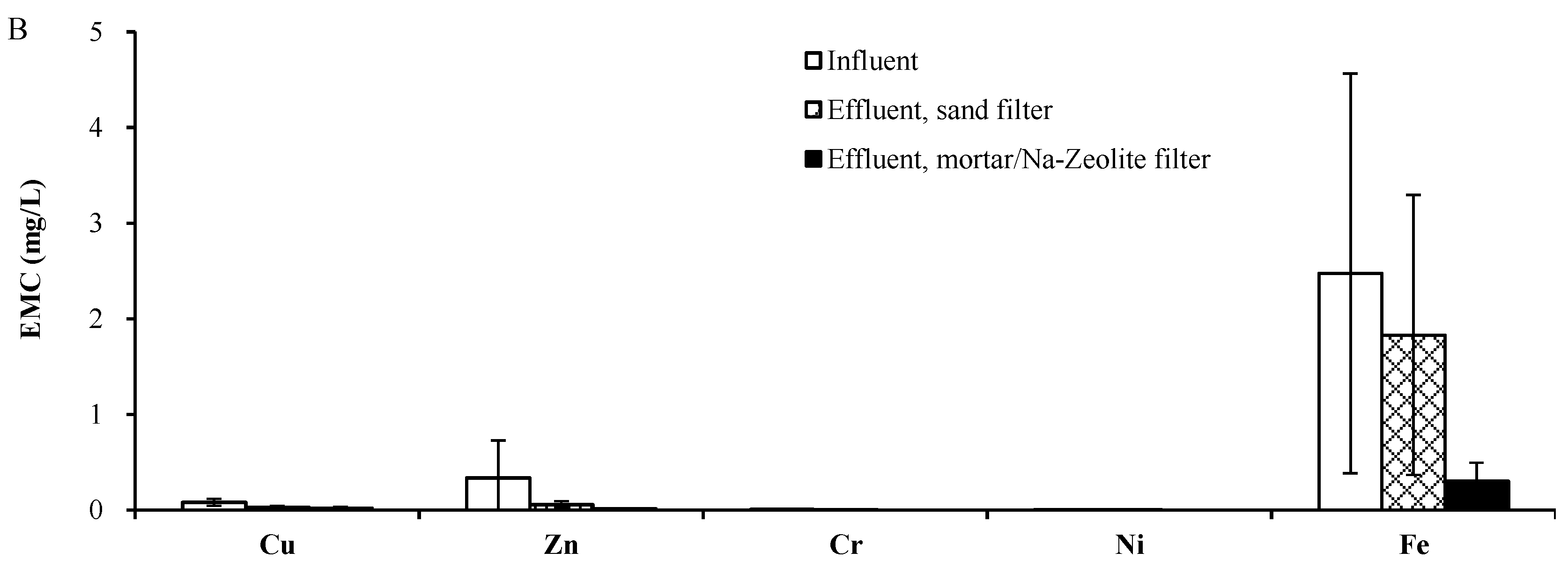
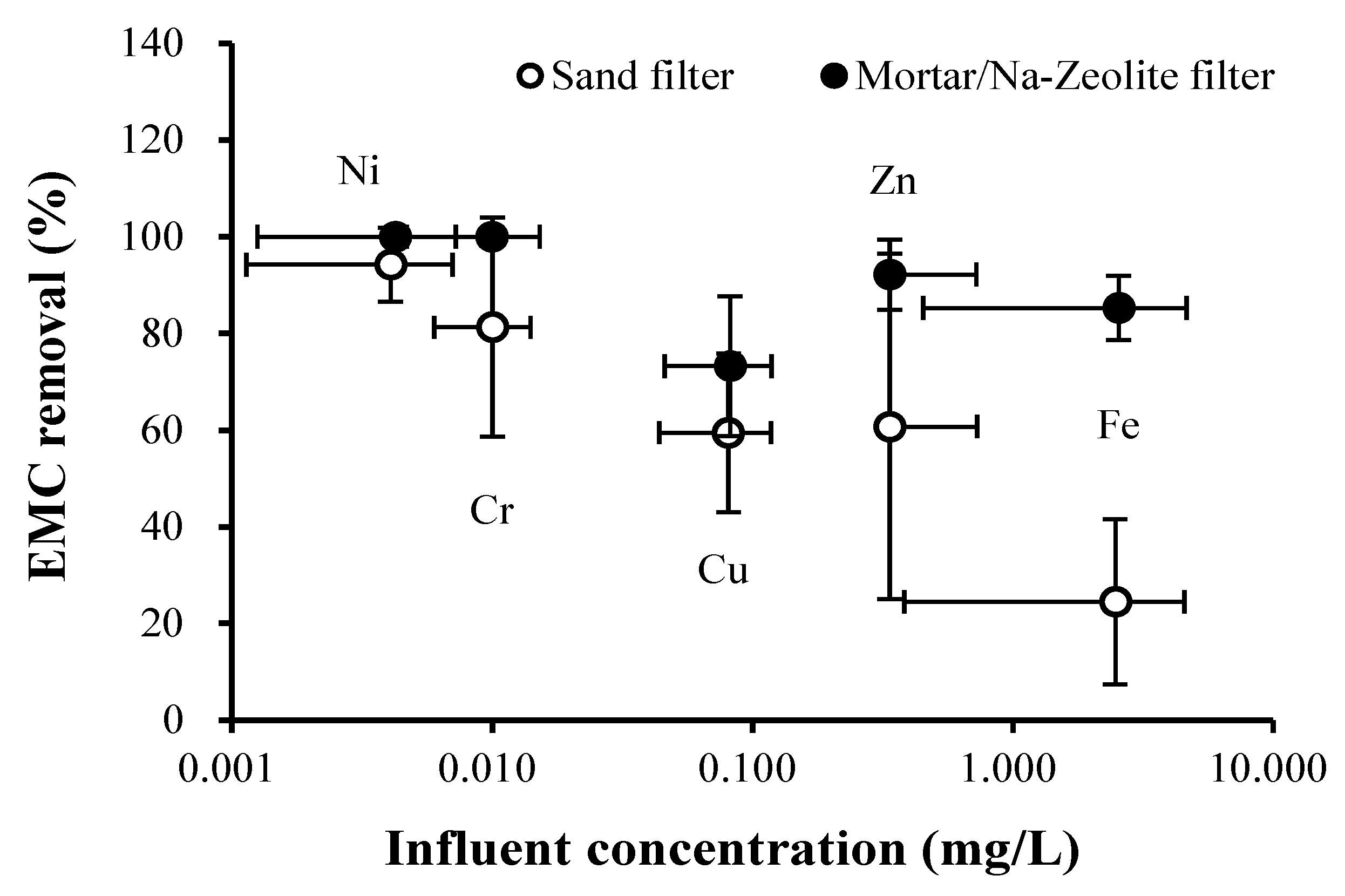
3.2. Field Test
3.2.1. Rainfall Monitoring
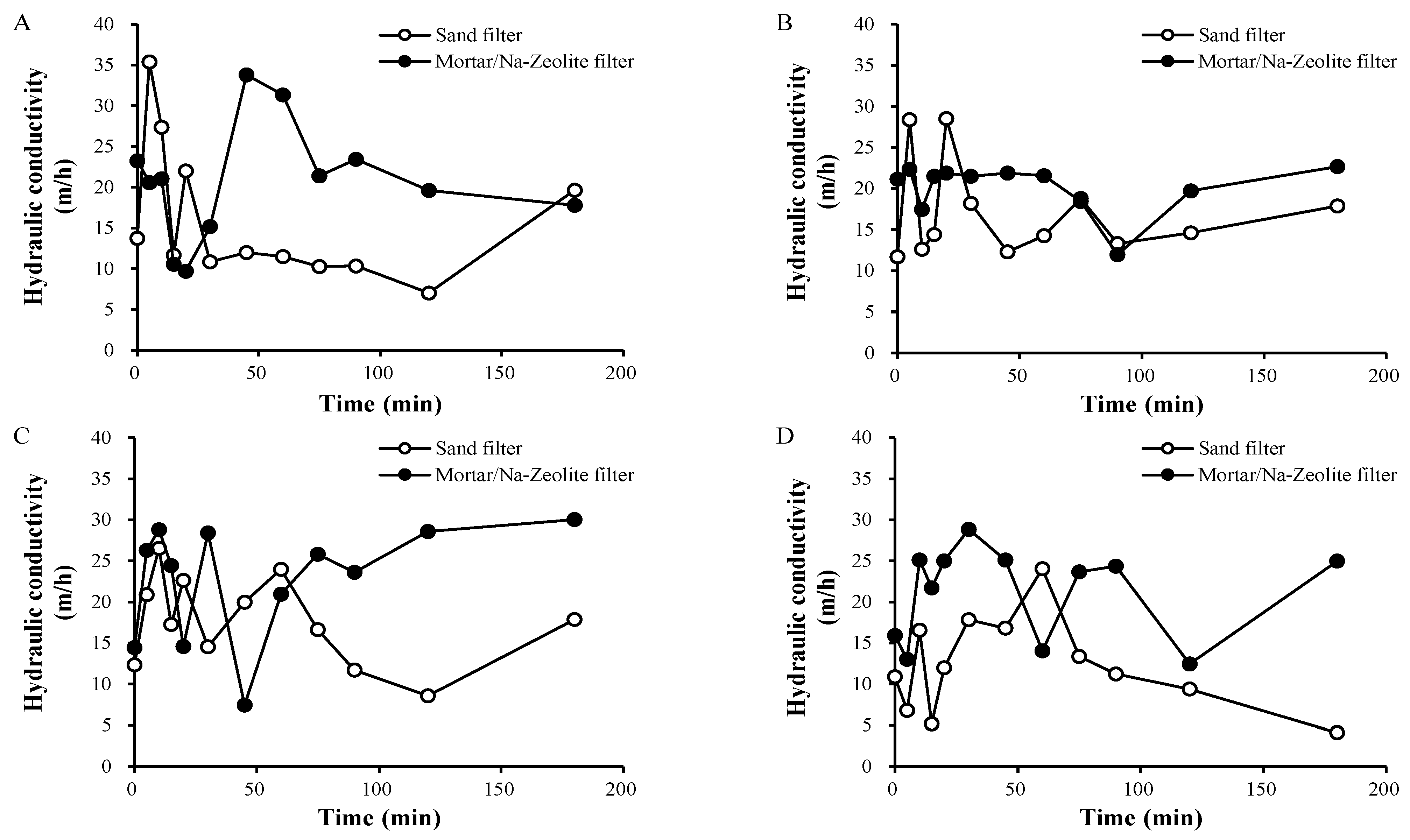
3.2.2. In Situ Hydraulic Conductivity Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baum, P.; Kuch, B.; Dittmer, U. Adsorption of Metals to Particles in Urban Stormwater Runoff—Does Size Really Matter? Water 2021, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosby, C.J.; Fullen, M.A.; Booth, C.A.; Searle, D.E. A dynamic approach to urban road deposited sediment pollution monitoring (Marylebone Road, London, UK). J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 105, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Hilbig, H.; Badenberg, S.C.; Fassnacht, J.; Drewes, J.E.; Helmreich, N. Heavy metal removal mechanisms of sorptive filter materials for road runoff treatment and remobilization under de-icing salt applications. Water Res. 2016, 102, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.-C.; Weng, C.-H. Effects of Rainfall Patterns on Highway Runoff Pollution and Its Control. Water Environ. J. 2015, 29, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyawardana, P.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunasekara, C.; Karunarathna, A.; Law, D.; Pramanik, B.K. Removal of Cu, Pb and Zn from Stormwater Using an Industrially Manufactured Sawdust and Paddy Husk Derived Biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Singh, A.; Suverkropp, C.; Borroum, S. Impact of Annual Average Daily Traffic on Highway Runoff Pollutant Concentrations. J. Environ. Eng. 2003, 129, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Fruchtman, B.D.; Gulliver, J.S.; Montanaro, C.; Ranieri, E.; Wuertz, S. Review of highway runoff characteristics: Comparative analysis and universal implications. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6609–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) and Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). Eisenhower Interstate Highway System Website. Available online: http://www.Fhwa.Dot.Gov/Interstate/Homepage.Cfm (accessed on 20 June 2017).
- Lee, J.; Lee, M. Stormwater runoff treatment filtration system and backwashing system. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 79, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Office of Prime Minister; Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries; Korea Ministry of Knowledge Economy; Korea Ministry of Environment; Korea Ministry of Infrastructure and Transport; Korea Nation Fire Agency; Korea Rural Development Administration; Korea Forest Service. The Third Comprehensive Non-Point Sources Management Plan (2021−2025); Korea Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2020. (In Korean)
- Sharma, R.; Vymazal, J.; Malaviya, P. Application of Floating Treatment Wetlands for Stormwater Runoff: A Critical Review of the Recent Developments with Emphasis on Heavy Metals and Nutrient Removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, J.P.; Gautier, A.; Barraud, S.; Chocat, B. The purification performance of infiltration basins fitted with pretreatment facilities: A case study. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hossain, M.A.; Furumai, H.; Nakajima, F.; Aryal, R.K. Heavy metals speciation in soakaways sediment and evaluation of metal retention properties of surrounding soil. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, M.; Katz, L.; Taylor, S. Removal of Dissolved Heavy Metals in Highway Runoff. In Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board; No. 2436; Transportation Research Board of the National Academies: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, C.; Katz, L.; Barrett, M. Removal of Dissolved Copper and Zinc from Highway Runoff via Adsorption. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2016, 2, 04015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Xie, T.; Dastgheibi, S. Removal of heavy metals from urban stormwater runoff using different filter materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, L.; Huang, T. Adsorption characteristics of construction waste for heavy metals from urban stormwater runoff. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 23, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wan, S. Enhanced Removal of Heavy Metals from Water by Hydrous Ferric Oxide-Modified Biochar. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 28702–28711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, B.; Tao, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Ding, X.; Chu, H. Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2021, 155, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiyuan, J.; Qin, Y.; Huang, Q. Modified Biochar for Arsenic Immobilization in Soil: A Critical Review. Rev. Environ. Contam. 2023, 261, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shen, X.J.; Domene, X. Comparison of biochars derived from different types of feedstock and their potential for heavy metal removal in multiple-metal solutions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitis, M.; Kaplan, S.S.; Karakaya, E.; Yigit, N.O.; Civelekoglu, G. Adsorption of natural organic matter from waters by iron coated pumice. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, S.; Ma, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, B. Stabilization of Pb, Cd, and Zn in soil by modified-zeolite: Mechanisms and evaluation of effectiveness. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günay, A.; Arslankaya, E.; Tosun, İ. Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution by Natural and Pretreated Clinoptilolite: Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.R.; Rubio, J. New Basis for Adsorption of Ionic Pollutants onto Modified Zeolites. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, H.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A. An efficient modified zeolite for simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 230, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, J.; Liao, X.; Tang, Q. The Utilization of Modified Zeolite for the Removal of Cs Ions in an Aqueous Solution: Adsorption Capacity, Isotherms, Kinetics and Microscopic Studies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichalin, O.O.; Papynov, E.K.; Nepomnyushchaya, V.A.; Ivanets, A.I.; Belov, A.A.; Dran’kov, A.N.; Yarusova, S.B.; Buravlev, I.Y.; Tarabanova, A.E.; Fedorets, A.N.; et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and spark plasma sintering of NaY zeolite as solid-state matrices for cesium-137 immobilization. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 3004–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasenko, A.E.; Shichalin, O.O.; Yarusova, S.B.; Ivanets, A.I.; Belov, A.A.; Dran’kov, A.N.; Azon, S.A.; Fedorets, A.N.; Buravlev, I.Y.; Mayorov, V.Y.; et al. A novel approach for rice straw agricultural waste utilization: Synthesis of solid aluminosilicate matrices for cesium immobilization. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2022, 54, 3250–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y. Low-cost adsorbents for urban stormwater pollution control. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Croft, K.; Pamuru, S.T.; Yuan, C.; Davis, A.P.; Kjellerup, B.V. Considerations for evaluating innovative stormwater treatment media for removal of dissolved contami-nants of concern with focus on biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.; Ren, Y.; Yang, L. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by granular hydrated Portland cement. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 3350–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praneeth, S.; Zameer, A.; Zhang, N.; Dubey, B.K.; Sarmah, A.K. Biochar admixture cement mortar fines for adsorptive removal of heavy metals in single and multimetal solution: Insights into the sorption mechanisms and environmental significance. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 155992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardel, A.; Peyneau, P.-E.; Béchet, B.; Lakel, A.; Rodriguez, F. Performance of two contrasting pilot swale designs for treating zinc, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and glyphosate from stormwater runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, K.; Qin, Y.; Wang, K.; An, Y.; Ye, J.; Wu, Z. Enhanced nutrient removal from stormwater runoff by a compact on-site treatment system. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Cheng, S.; Liang, W.; He, F.; Wu, Z. Performance of a pilot-scale constructed wetland for stormwater runoff and domestic sewage treatment on the banks of a polluted urban river. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Cirelli, G.L.; Ventura, D.; Barbagallo, S.; Licciardello, F. Hydraulic performance of horizontal constructed wetlands for stormwater treatment: A pilot-scale study in the Mediterranean. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 169, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixidó, M.; Charbonnet, J.A.; LeFevre, G.H.; Luthy, R.G.; Sedlak, D.L. Use of pilot-scale geomedia-amended biofiltration system for removal of polar trace organic and inorganic contaminants from stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, D.; Ferrante, M.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Milani, M.; Sacco, A.; Licciardello, F.; Cirelli, G.L. Metal removal processes in a pilot hybrid constructed wetland for the treatment of semi-synthetic stormwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, F.Y.; Neo, T.H.; Guo, H.; Goh, S.Z.; Ong, S.L.; Hu, J.; Lee, B.C.Y.; Ong, G.S.; Liou, C.X. Pilot and Field Studies of Modular Bioretention Tree System with Talipariti tiliaceum and Engineered Soil Filter Media in the Tropics. Water 2021, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashoori, N.; Teixido, M.; Spahr, S.; LeFevre, G.H.; Sedlak, D.L.; Luthy, R.G. Evaluation of pilot-scale biochar-amended woodchip bioreactors to remove nitrate, metals, and trace organic contaminants from urban stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2019, 154, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kus, B.; Kandasamy, J.; Vigneswaran, S.; Shon, H.; Moody, G. Two stage filtration for stormwater treatment: A pilot scale study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 45, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, M.; Renman, A.; Berndtsson, L.; Renman, R. Evaluation of a sand filter material for road runoff treatment—Pilot-scale field trial focused on copper and zinc removal. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 1652–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, S.R.; Rubio, J. On the removal of Mn2+ ions by adsorption onto natural and activated Chilean zeolites. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apeagyei, E.; Bank, M.S.; Spengler, J.D. Distribution of heavy metals in road dust along an urban–rural gradient in Massachusetts. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaraman, S.; Anbuselvan, N.M.; Venkatachalam, P.; Shanmugam, S.R.; Selvasembian, R. Waste tire particles as efficient materials towards hexavalent chromium removal: Characterisation, adsorption behaviour, equilibrium, and kinetic modelling. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Ministry of Environment. Installation and Operation Manual of Non-Point Pollution Reduction Facility; Korea Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2020. (In Korean)
- Perera, T.; McGree, J.; Egodawatta, P.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Catchment based estimation of pollutant event mean concentration (EMC) and implications for first flush assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Ministry of Environment. Water Pollution Process Test Standards (Ministry of Environment Notice No. 2017-4 January 11, 2017); Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2017.
- Ujevic, I.; Odzak, A.; Baric, A. Trace metal accumulation in different grain size fractions of the sediments from a semi-enclosed bay heavily contaminated by urban and industrial wastewaters. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3055–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larroque, F.; Franceschi, M. Impact of chemical clogging on de-watering well productivity: Numerical assessment. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Coustumer, S.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Barraud, S.; Lewis, J.F. Hydraulic performance of biofilter systems for stormwater management: Influences of design and operation. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Klein, M.; Zhang, T.C. Feasibility of developing a passive sampler for sampling heavy metals in BMPs for stormwater runoff management. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandaker, S.; Toyohara, Y.; Saha, G.C.; Awual, M.R.; Kuba, T. Development of synthetic zeolites from bio-slag for cesium adsorption: Kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2020, 33, 101055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, M.; Urban, T.; Chibowski, S. Investigation of adsorption mechanism of phosphate(V) ions on the nanostructured Na-A zeolite surface modified with ionic polyacrylamide with regard to their removal from aqueous solution. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 4475–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.E.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T. Highway runoff and potential for removal of heavy metals in an infiltration pond in Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 235, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drapper, D.; Hornbuckle, A. Removal of Nutrients, Sediment, and Heavy Metals by a Stormwater Treatment Train; a Medium-Density Residential Case Study in Southeast Queensland. Water 2018, 10, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman, E. Stormwater BMP treatment performance variability for sediment and heavy metals. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 84, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, K.; Gharabaghi, B.; McBean, E.; Rudra, R.; MacMillan, G. Compost Biofilters for Highway Stormwater Runoff Treatment. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2010, 45, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, L.W.; Ring, P.; Casey, B.; Higgins, N.M.P.; Johnston, P.M. Long term heavy metal removal by a constructed wetland treating rainfall runoff from a motorway. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na Nagara, V.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R. Phosphorus and Heavy Metals Removal from Stormwater Runoff Using Granulated Industrial Waste for Retrofitting Catch Basins. Molecules 2022, 27, 7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Sand | GFH | Biochar | Zeolite | Na- Zeolite | Orchid Stone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qmax,L (mg/g) | 1.29 | 3.54 | 8.44 | 14.85 | 17.75 | 1.14 |
| KL (L/mg) | 0.017 | 2.727 | 0.061 | 1.034 | 0.002 | 0.067 | |
| r2 | 0.978 | 0.942 | 0.961 | 0.985 | 0.997 | 0.917 | |
| Freundlich | 1/n | 0.332 | 0.166 | 0.199 | 0.199 | 0.175 | 0.185 |
| KF (mg/g·(mg/L)n) | 0.157 | 1.872 | 2.576 | 6.285 | 8.023 | 0.378 | |
| r2 | 0.958 | 0.963 | 0.997 | 0.931 | 0.957 | 0.981 | |
| Parameters | Sand | GFH | Biochar | Zeolite | Na- Zeolite | Orchid Stone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo first order | k1 (min−1) | 0.193 | 0.025 | 0.069 | 0.187 | 0.067 | 0.022 |
| qe (mg/g) | 1.179 | 5.785 | 6.576 | 14.092 | 16.530 | 1.114 | |
| r2 | 0.957 | 0.972 | 0.944 | 0.985 | 0.972 | 0.976 | |
| Pseudo second order | k2 (g/mg∙min) | 3.617 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.015 |
| qe (mg/g) | 1.260 | 6.234 | 7.346 | 14.894 | 18.510 | 1.412 | |
| r2 | 0.986 | 0.996 | 0.985 | 0.998 | 0.996 | 0.970 | |
| Rainfall Events | BOD | COD | TOC | T-N | T-P | SS | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Fe | Total Metals * | Conductivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28.8 | 73.9 | 15.1 | 5.7 | 0.45 | 235.1 | 0.041 | 0.129 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 2.361 | 2.544 | 854 |
| 2 | 17.8 | 54.2 | 10.2 | 5.4 | 0.31 | 44.1 | 0.065 | 0.119 | 0.015 | 0.004 | 0.800 | 1.032 | 679 |
| 3 | 28.3 | 81.1 | 7.9 | 7.0 | 0.43 | 61.0 | 0.091 | 0.174 | 0.006 | 0.000 | 1.278 | 1.548 | 1288 |
| 4 | 67.8 | 246.0 | 15.1 | 7.5 | 0.31 | 252.1 | 0.127 | 0.921 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 5.450 | 6.521 | 649 |
| Rainfall Events | BOD | COD | TOC | T-N | T-P | SS | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Fe | Total Metals * | Conductivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Effluent | 18.9 | 47.5 | 10.0 | 4.1 | 0.12 | 27.3 | 0.019 | 0.105 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.665 | 1.789 | 277 |
| Removal | 34.4 | 35.7 | 33.6 | 29.1 | 73.5 | 88.4 | 54.1 | 18.7 | 100.0 | 93.1 | 29.5 | 29.7 | 67.6 | |
| 2 | Effluent | 10.8 | 30.9 | 4.2 | 3.7 | 0.31 | 15.3 | 0.024 | 0.066 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.480 | 0.571 | 324 |
| Removal | 39.6 | 42.9 | 59.0 | 32.4 | 0.00 | 65.3 | 62.4 | 44.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 39.9 | 44.6 | 52.4 | |
| 3 | Effluent | 12.8 | 39.4 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 0.30 | 11.6 | 0.053 | 0.027 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 1.276 | 1.359 | 270 |
| Removal | 54.9 | 51.4 | 56.4 | 61.8 | 30.7 | 81.0 | 41.2 | 84.4 | 54.4 | 100.0 | 0.1 | 12.2 | 79.1 | |
| 4 | Effluent | 37.6 | 110.5 | 6.4 | 3.9 | 0.23 | 17.3 | 0.025 | 0.038 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 3.893 | 3.963 | 303 |
| Removal | 44.6 | 55.1 | 57.7 | 48.0 | 24.7 | 93.2 | 80.3 | 95.8 | 70.8 | 83.9 | 28.6 | 39.2 | 53.4 | |
| Rainfall Events | BOD | COD | TOC | T-N | T-P | SS | Cu | Zn | Cr | Ni | Fe | Total Metals * | Conductivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Effluent | 17.2 | 38.0 | 8.9 | 4.2 | 0.11 | 26.7 | 0.015 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.565 | 0.600 | 112 |
| Removal | 39.7 | 50.0 | 40.4 | 24.1 | 74.8 | 88.5 | 63.5 | 84.9 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 78.7 | 78.8 | 86.5 | |
| 2 | Effluent | 9.3 | 29.6 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 0.20 | 14.1 | 0.013 | 0.015 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.113 | 0.141 | 81 |
| Removal | 47.2 | 45.2 | 68.5 | 44.5 | 37.6 | 66.9 | 80.4 | 87.2 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 85.5 | 86.1 | 87.7 | |
| 3 | Effluent | 12.2 | 38.6 | 3.6 | 2.5 | 0.11 | 12.7 | 0.037 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.227 | 0.270 | 122 |
| Removal | 58.4 | 53.6 | 53.2 | 64.5 | 74.6 | 79.2 | 59.1 | 97.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 82.7 | 83.0 | 90.3 | |
| 4 | Effluent | 24.6 | 84.7 | 5.5 | 3.9 | 0.10 | 11.6 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.305 | 0.320 | 119 |
| Removal | 64.2 | 65.7 | 63.6 | 49.0 | 66.9 | 95.4 | 90.1 | 99.7 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 94.4 | 95.1 | 80.9 | |
| Sand Filter | Mortar/Na-Zeolite Filter | |
|---|---|---|
| Average | 15.6 | 21.2 |
| Median | 14.3 | 21.6 |
| Standard Deviation | 6.6 | 5.8 |
| Minimum | 4.1 | 7.4 |
| Maximum | 35.4 | 33.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-G.; Ko, S.-O. The Pilot Study of a Dual-Media Filter Consisting of Mortar and Modified Zeolite for Removing Heavy Metals from Expressway Stormwater Runoff. Water 2023, 15, 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203560
Kim D-G, Ko S-O. The Pilot Study of a Dual-Media Filter Consisting of Mortar and Modified Zeolite for Removing Heavy Metals from Expressway Stormwater Runoff. Water. 2023; 15(20):3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203560
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do-Gun, and Seok-Oh Ko. 2023. "The Pilot Study of a Dual-Media Filter Consisting of Mortar and Modified Zeolite for Removing Heavy Metals from Expressway Stormwater Runoff" Water 15, no. 20: 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203560
APA StyleKim, D.-G., & Ko, S.-O. (2023). The Pilot Study of a Dual-Media Filter Consisting of Mortar and Modified Zeolite for Removing Heavy Metals from Expressway Stormwater Runoff. Water, 15(20), 3560. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203560







