Unraveling the Complexities of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Environments: Insights from Laizhou Bay’s Eastern Coast, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
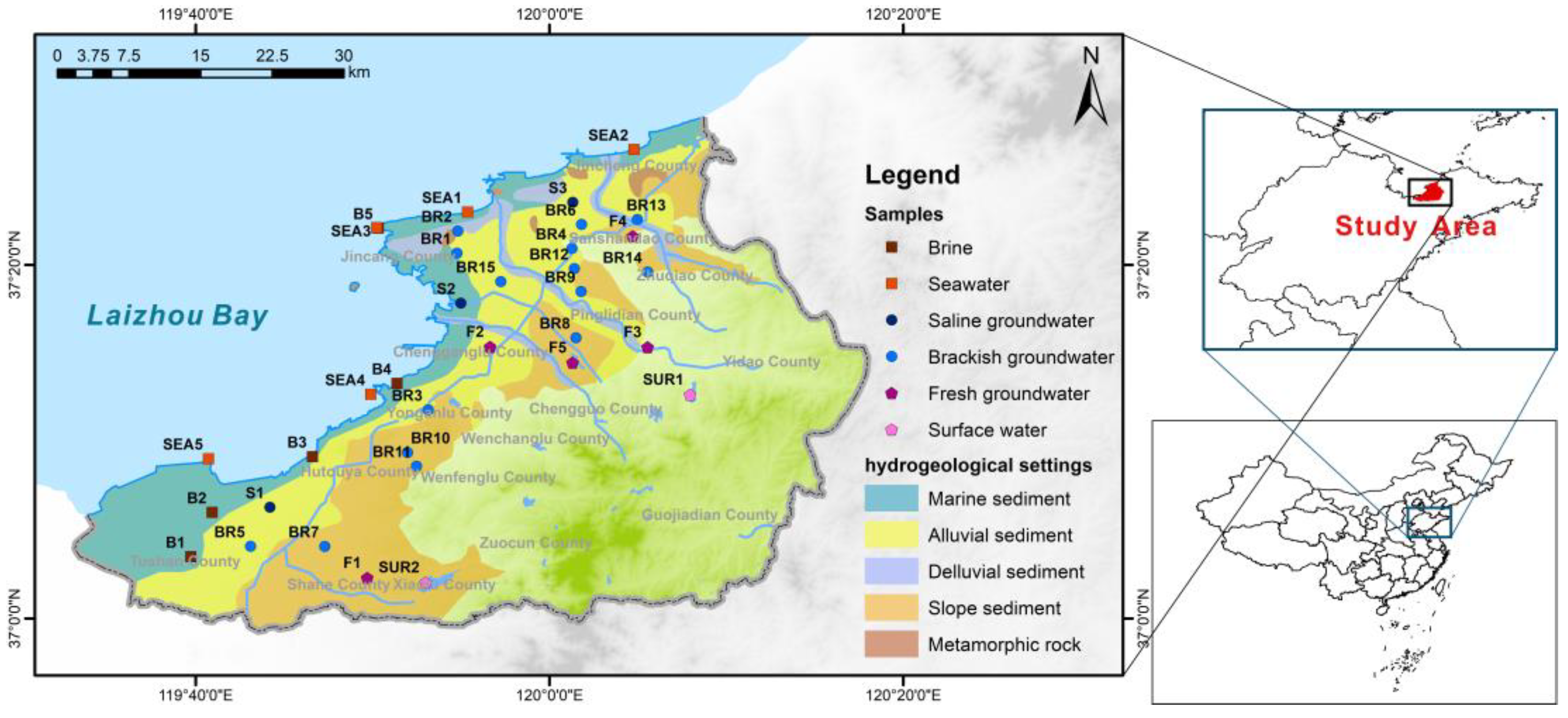
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Samples and Hydrochemistry Analyses
2.3. Stable Isotope Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Hydrochemistry Compositions
3.2. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Compositions
3.3. Chlorine Isotope Compositions
4. Discussion
4.1. Genesis of Brine: Seawater Evaporation, Halogen Precipitation, and Water–Rock Interaction
4.2. Genesis of Saline Groundwater: Evaporation of Seawater and Mixing Processes
4.3. Genesis of Brackish Groundwater: Atmospheric Precipitation and Human Activities
4.4. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Z.K.; Ma, C.M.; Zhou, A.G.; Qi, H.H.; Liu, C.F.; Cai, H.S.; Zhu, H.C. Using hydrochemical and stable isotopic (δ2H, δ18O, δ11B, and δ37Cl) data to understand groundwater evolution in an unconsolidated aquifer system in the southern coastal area of Laizhou Bay, China. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolcubal, I.; Gunduz, O.C.A.; Kurtulus, N. Origin of salinization and pollution sources and geochemical processes in urban coastal aquifer (Kocaeli, NW Turkey). Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, O. New approach in estimation of seawater intrusion footprint (SWIF) for irrigated crops using coastal groundwater. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.H.; Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Lin, Y.C.; Luo, Y.M. Influence of coastal groundwater salinization on the distribution and risks of heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basack, S.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Maity, P. A coastal groundwater management model with Indian case study. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2014, 167, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M.; Reichard, E.G. Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrol. J. 2010, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Kohfahl, C.; Song, X.F.; Xiao, G.Q.; Yang, J.L. Geochemical and isotopic evidence for palaeo-seawater intrusion into the south coast aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, 863–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, V.; Zuppi, G.M. Influence of precipitation and deep saline groundwater on the hydrological systems of Mediterranean coastal plains: A general overview. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, R.; Mendez, G.O.; Futa, K.; Danskin, W.R. A Geochemical Approach to Determine Sources and Movement of Saline Groundwater in a Coastal Aquifer. Groundwater 2014, 52, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landes, A.A.L.; Aquilina, L.; Davy, P.; Vergnaud-Ayraud, V.; Le Carlier, C. Timescales of regional circulation of saline fluids in continental crystalline rock aquifers (Armorican Massif, western France). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, L.; Ma, C.; Yuan, Y. Analysis of the Seawater Intrusion Process Based on Multiple Monitoring Methods: Study in the Southern Coastal Plain of Laizhou Bay, China. Water 2023, 15, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppmann, W.; Negrel, P.; Casanova, J.; Klinge, H.; Schelkes, K.; Guerrot, C. Halite dissolution derived brines in the vicinity of a Permian salt dome (N German Basin). Evidence from boron, strontium, oxygen, and hydrogen isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 4087–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaza, A.; Mapoma, H.W.T.; Abiye, T.A.; Clarke, S.; Kanyerere, T. Investigating Seawater Intrusion in Republic of South Africa’s Heuningnes, Cape Agulhas Using Hydrogeochemistry and Seawater Fraction Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J. Analysis on Change Characteristics of Soluble Silica in Shallow Groundwater of Coastal Area Caused by Seawater Intrusion. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 83, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.; Casanova, J.; Gaaloul, N.; Guerrot, C. Combining boron isotopes and carbamazepine to trace sewage in salinized groundwater: A case study in Cap Bon, Tunisia. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 34, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Xiong, G.Y.; Chen, G.Q.; Fu, T.F.; Yu, H.J.; Wu, J.C.; Liu, W.Q.; Su, Q.; Wang, Y.C.; Liu, S.F.; et al. Characteristics of coastal aquifer contamination by seawater intrusion and anthropogenic activities in the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 217, 104830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.R.; Taniguchi, M.; Kooi, H.; Gurdak, J.J.; Allen, D.M.; Hiscock, K.M.; Treidel, H.; Aureli, A. Beneath the surface of global change: Impacts of climate change on groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2011, 405, 532–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B. Global climate change and its impacts on water resources planning and management: Assessment and challenges. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2011, 25, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cary, L.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Bertrand, G.; Kloppmann, W.; Aquilina, L.; Martins, V.; Hirata, R.; Montenegro, S.; Pauwels, H.; Chatton, E.; et al. Origins and processes of groundwater salinization in the urban coastal aquifers of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil): A multi-isotope approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 530, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithara, S.; Pramada, S.K.; Thampi, S.G. Impact of projected climate change on seawater intrusion on a regional coastal aquifer. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.C.; Meng, F.H.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, D. The development and control of the seawater intrusion in the eastern coastal of Laizhou Bay, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 54, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, X.L.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Meng, X.M.; Alhassan, A. Salinity evolution of aquitard porewater associated with transgression and regression in the coastal plain of Eastern China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, E.F.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, L.J. Environmental evolution in the salt-water intrusion area south of Laizhou Bay since late Pleistocene. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, F.T.; Miao, J.J.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.J. Using time series analysis to assess tidal effect on coastal groundwater level in Southern Laizhou Bay, China. J. Groundw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.H.; Diao, M.N.; Wang, D.; Gao, M. Hydrochemical characteristics and salinization processes of groundwater in the shallow aquifer of Eastern Laizhou Bay, China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Qin, G.; Yu, H. Response of a Coastal Groundwater System to Natural and Anthropogenic Factors: Case Study on East Coast of Laizhou Bay, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wei, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, S.; Ning, F.; Jia, C.; Ji, Y.; Dong, F.; et al. Discussion on the Fluorosis in Seawater-Intrusion Areas Along Coastal Zones in Laizhou Bay and Other Parts of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Song, X.F.; Currell, M.J.; Yang, J.L.; Xiao, G.Q. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafouq, D.; El Mandour, A.; Elgettafi, M.; Himi, M.; Chouikri, I.; Casas, A. Hydrochemical and isotopic characterization of groundwater in the Ghis-Nekor plain (northern Morocco). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 139, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaifi, H.; Kahal, A.; Albassam, A.; Ibrahim, E.; Abdelrahman, K.; Zaidi, F.; Alhumidan, S. Integrated geophysical and hydrochemical investigations for seawater intrusion: A case study in southwestern Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, S.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Saravanan, K.; Prakash, R. Tracing groundwater salinization using geochemical and isotopic signature in Southeastern coastal Tamilnadu, India. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeldin, H.A. Delineation of Salinization and Recharge Sources Affecting Groundwater Quality Using Chemical and Isotopic Indices in the Northwest Coast, Egypt. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Forcada, E. Dynamic of Sea Water Interface using Hydrochemical Facies Evolution Diagram. Groundwater 2010, 48, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Forcada, E. Space/time development of seawater intrusion: A study case in Vinaroz coastal plain (Eastern Spain) using HFE-Diagram, and spatial distribution of hydrochemical facies. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, V.; Nakhaei, M.; Lak, R.; Kholghi, M. Assessment of seasonal groundwater quality and potential saltwater intrusion: A study case in Urmia coastal aquifer (NW Iran) using the groundwater quality index (GQI) and hydrochemical facies evolution diagram (HFE-D). Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najib, S.; Fadili, A.; Mehdi, K.; Riss, J.; Makan, A. Contribution of hydrochemical and geoelectrical approaches to investigate salinization process and seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifers of Chaouia, Morocco. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2017, 198, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, R.; Nosrati, A.; Jafari, H.; Eggenkamp, H.G.M.; Mozafari, M. Overexploitation hazards and salinization risks in crucial declining aquifers, chemo-isotopic approaches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.F.; Li, X.Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.D.; Liang, H. Groundwater-flow-system characterization with hydrogeochemistry: A case in the lakes discharge area of the Ordos Plateau, China. Hydrol. J. 2019, 27, 669–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.H.; Gao, M.S.; Hou, G.H. Evolutionary process of saline-water intrusion in Holocene and Late Pleistocene groundwater in southern Laizhou Bay. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandary, H.; Sabarathinam, C.; Al-Khalid, A. Occurrence of hypersaline groundwater along the coastal aquifers of Kuwait. Desalination 2018, 436, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.M.; Currell, M.J. Delineating multiple salinization processes in a coastal plain aquifer, northern China: Hydrochemical and isotopic evidence. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3473–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahir, M.; Ouhamdouch, S.; Carreira, P.M. Geochemical and isotopic approach to decrypt the groundwater salinization origin of coastal aquifers from semi-arid areas (Essaouira basin, Western Morocco). Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvat, D.; Michelot, J.L.; Aranyossy, J.F. Origin and residence time of salinity in the Aspo groundwater system. Appl. Geochem. 1999, 14, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Ma, T.; Chen, L.Z.; Shan, H.M.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Y.; Liu, C.F.; Cai, H.S. Genesis of salinized groundwater in Quaternary aquifer system of coastal plain, Laizhou Bay, China: Geochemical evidences, especially from bromine stable isotope. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 59, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghibi, A.; Zouhri, L.; Tarhouni, J. Groundwater modelling and marine intrusion in the semi-arid systems (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1822–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, I.; Hamzaoui-Azaza, F.; Bouhlila, R. Application of multivariate statistical analysis and hydrochemical and isotopic investigations for evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agriculture purposes: Case of Oum Ali-Thelepte aquifer, central Tunisia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, J.J.; Zhong, J.L.; Wen, H.G.; Dong, R. Assessing major factors affecting shallow groundwater geochemical evolution in a highly urbanized coastal area of Shenzhen City, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.F.A.; Yusoff, I.; Ng, T.F.; Maity, J.P.; Alias, Y.; May, R.; Alborsh, H. A study on the impact of anthropogenic and geogenic factors on groundwater salinization and seawater intrusion in Gaza coastal aquifer, C Palestine: An integrated multi-techniques approach. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 156, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Thao, N.T.; Batsaikhan, B.; Yun, S.T. Hydrochemical assessment of freshening saline groundwater using multiple end-members mixing modeling: A study of Red River delta aquifer, Vietnam. J. Hydrol. 2017, 549, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhamid, H.; Abdelaty, I.; Sherif, M. Evaluation of potential impact of Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2321–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christelis, V.; Mantoglou, A. Pumping Optimization of Coastal Aquifers Using Seawater Intrusion Models of Variable-Fidelity and Evolutionary Algorithms. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, R.; Engesgaard, P.; Sonnenborg, T.O. Origin and Dynamics of Saltwater Intrusion in a Regional Aquifer: Combining 3-D Saltwater Modeling With Geophysical and Geochemical Data. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 1792–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldor, A.; Shalev, E.; Katz, O.; Aharonov, E. Dynamics of saltwater intrusion and submarine groundwater discharge in confined coastal aquifers: A case study in northern Israel. Hydrol. J. 2019, 27, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Michael, H.A. Mechanisms, configuration typology, and vulnerability of pumping-induced seawater intrusion in heterogeneous aquifers. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 128, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Bohlke, J.K.; De Bievre, P.; Ding, T.; Holden, N.E.; Hopple, J.A.; Krouse, H.R.; Lamberty, A.; Peiser, H.S.; Revesz, K.; et al. Isotope-abundance variations of selected elements—(IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 1987–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R.; Wassenaar, L.I.; Araguas-Araguas, L.; Aggarwal, P.K. A unified Craig-Gordon isotope model of stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope fractionation during fresh or saltwater evaporation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 235, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.A.; Shawky, H.; Samy, A.; Khalil, M.M.H.; El Malky, M. Geochemical and Isotopic Evidence of Groundwater Salinization Processes in El Dabaa Area, Northwestern Coast, Egypt. Geosciences 2018, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, P.M.; Lobo de Pina, A.; da Mota Gomes, A.; Marques, J.M.; Monteiro Santos, F. Radiocarbon Dating and Stable Isotopes Content in the Assessment of Groundwater Recharge at Santiago Island, Republic of Cape Verde. Water 2022, 14, 2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.H.; Wei, Y.P.; Bao, T.; Xi, H.Y.; Li, Z.X. Identifying the origin of groundwater for water resources sustainable management in an arid oasis, China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Rao, V. Hydrogeochemical, seawater intrusion and oxygen isotope studies on a coastal region in the Puri District of Odisha, India. Catena 2019, 172, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, G.; Stigter, T.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Mussa, F.; Juizo, D. Understanding groundwater salinization mechanisms to secure freshwater resources in the water-scarce city of Maputo, Mozambique. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Q.H.; Luo, Y.X.; Yan, L.; Peng, K.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, Y.X. Groundwater salinization in a subtropical region, Beihai, southern China: Insights from hydrochemistry and multiple isotopes (H, O, S, Sr). Appl. Geochem. 2022, 141, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.D.; Sreekanth, P.D.; Reddy, D.V. Influence of hydrological and hydrogeological factors on inland groundwater salinity in a hard rock aquifer, south India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 130, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine, B.I.; Stefansson, A.; Halldorsson, S.A.; Barnes, J.D. Impact of fluid-rock interaction on water uptake of the Icelandic crust: Implications for the hydration of the oceanic crust and the subducted water flux. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 2020, 538, 116210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Guo, Q.H.; Shi, H.J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Shang, J.B.; Zhang, M.Z. Chlorine geochemistry of various geothermal waters in China: Implications for geothermal system geneses. J. Hydrol. 2023, 616, 128783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Jiang, S.Y.; Yang, T. Br/Cl, I/Cl and chlorine isotopic compositions of pore water in shallow sediments: Implications for the fluid sources in the Dongsha area, northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sinica 2017, 36, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Nadri, A.; Raeisi, E.; Kazemi, G.A.; Eggenkamp, H.G.M.; Montaseri, A. Origin of brine in the Kangan gasfield: Isotopic and hydrogeochemical approaches. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1055–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.D.; Paulick, H.; Sharp, Z.D.; Bach, W.; Beaudoin, G. Stable isotope (delta O-18, delta D, delta Cl-37) evidence for multiple fluid histories in mid-Atlantic abyssal peridotites (ODP Leg 209). Lithos 2009, 110, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrinier, P.; Destrigneville, C.; Giunta, T.; Bonifacie, M.; Bardoux, G.; Andre, J.; Lucazeau, F. Strong impact of ion filtration on the isotopic composition of chlorine in young clay-rich oceanic sediment pore fluids. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2019, 245, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, G.M.; Barnes, J.D.; John, T.; Hoffmann, J.E.; Chatterjee, R.; Stockli, D.F. Global halogen flux of subducting oceanic crust. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2022, 594, 117750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musashi, M.; Oi, T.; Kreulen, R. Chlorine isotopic compositions of deep saline fluids in Ibusuki coastal geothermal region, Japan: Using B-Cl isotopes to interpret fluid sources. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madorsky, S.L.; Straus, S. Concentration of isotopes of chlorine by the countercurrent electromigration method. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1947, 38, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, R.; Long, A.; Bentley, H.; Davis, S. Natural Chlorine Isotope Variations. Nature 1984, 309, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X. Cl/Br ratios and chlorine isotope evidences for groundwater salinization and its impact on groundwater arsenic, fluoride and iodine enrichment in the Datong basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, C.W. Applied Hydrogeology; Waveland Press Inc.: Long Grove, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, J.D.; Govindaraju, R.S.; Anderson, M.; Arabi, M.; Francés, F.; Suarez, W.; Lavado-Casimiro, W.S.; Green, T.R. Introduction to Hydrology. In Modern Water Resources Engineering; Wang, L.K., Yang, C.T., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 1–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gan, Y.; Yu, T.; Liu, C.; Zhou, A. Online Simultaneous Determination of δD and δ18O in Micro-liter Water Samples by Thermal Conversion/Elemental Analysis-Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry. Rock Miner. Anal. 2010, 29, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.D.; Zhou, A.G.; Gan, Y.Q.; Liu, C.F.; Yu, T.T.; Li, X.Q. An online method to determine chlorine stable isotope composition by continuous flow isotope ratio mass spectrometry (CF-IRMS) coupled with a Gasbench II. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Miao, Q.; Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Hou, X.; Song, Z. The Hydro-chemical Feature and Prospect on Utilisation of Shallow Groundwater in Hengshui. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Energy and Environment Technology (ICEET 2009), Guilin, China, 16–18 October 2009; p. 859. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 17, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcala, F.J.; Custodio, E. Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer to identify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal. J. Hydrol. 2008, 359, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Gnanasundar, D. Application of Cl/Br ratio to demarcate the fresh-saline water interface in coastal aquifers of northern Tamilnadu, Southern India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Chandrasekar, N.; Srinivas, Y.; Selvam, S.; Kaliraj, S.; Magesh, N.S.; Venkatramanan, S. Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the groundwater salinity in the coastal aquifers of Southern Tamil Nadu, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.; Koh, D.-C.; Jung, H.; Lee, J. The Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater Subjected to Seawater Intrusion in the Archipelago, Korea. Water 2020, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.Z.; Niyazi, B.A.M. Impact of evaporation on groundwater salinity in the arid coastal aquifer, Western Saudi Arabia. Catena 2021, 196, 104864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Miao, J.J.; Hu, B.X.; Liu, H.W.; Zhang, H.X.; Ma, Z. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in intruded coastal brine aquifers (Laizhou Bay, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21073–21090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, O.; Giunta, T.; Onstott, T.C.; Kieft, T.L.; Harris, R.L.; Nisson, D.M.; Lollar, B.S. The role of low-temperature O-18 exchange in the isotopic evolution of deep subsurface fluids. Chem. Geol. 2021, 561, 120027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Deuterium Excess of Tap Water across China and Their Significance for Water Source; Northwest Normal University: Lanzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wei, H.Z.; Williams-Jones, A.; Ma, J.; Lu, J.J.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Dong, G. Chlorine isotope fractionation during serpentinization and hydrothermal mineralization: A density functional theory study. Chem. Geol. 2021, 581, 120406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C. Distribution characteristics of subsurface brine resources on the southern coast of laizhou bay since late pleistocene. Hydrol. Eng. Geol. 2014, 41, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Dai, F.C. Isotope and hydrochemical study of seawater intrusion in Laizhou Bay, Shandong Province. Sci. China Ser. E-Tech. Sci. 2001, 44, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y. The Formation and Evolution of Underground Brine in the Coastal Plain of Laizhou Bay; Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences: Beijing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.H.; Ma, C.M.; He, Z.K.; Hu, X.J.; Gao, L. Lithium and its isotopes as tracers of groundwater salinization: A study in the southern coastal plain of Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussaoui, I.; Rosa, E.; Cloutier, V.; Neculita, C.M.; Dassi, L. Chemical and isotopic evaluation of groundwater salinization processes in the Djebeniana coastal aquifer, Tunisia. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 149, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Yang, Y.S.; Yuan, R.; Cai, Z.; Pan, S. Study of shallow groundwater quality evolution under saline intrusion with environmental isotopes and geochemistry. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; U. S. Geological Sruvey: Reston, VA, USA, 1985.
- Appelo, C.A.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaissa, M.; Gharibi, E.; Ghalit, M.; Taupin, J.D.; El Khattabi, J. Identifying the origin of groundwater salinization in the Bokoya massif (central Rif, northern Morocco) using hydrogeochemical and isotopic tools. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.V.; Coutinho, R.; Pacheco, D.; Cymbron, R.; Antunes, P.; Freire, P.; Mendes, S. Groundwater salinization in the Azores archipelago (Portugal). Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.J. A SURVEY OF CHARGE-BALANCE ERRORS ON PUBLISHED ANALYSES OF POTABLE GROUND AND SURFACE WATERS. Groundwater 1994, 32, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.C. Assessment of major ions in groundwater supplied to Monterrey metropolitan area, Mexico: Quality assurance, technical analysis, and addenda. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, M.; Hui, H.K.; Li, Y.L. Study on seawater intrusion in Laizhou bay coastal zone based on groundwater model. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2019, 14, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.; Ma, C.; Zhou, A. Unraveling the Complexities of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Environments: Insights from Laizhou Bay’s Eastern Coast, China. Water 2023, 15, 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203629
Huang P, Ma C, Zhou A. Unraveling the Complexities of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Environments: Insights from Laizhou Bay’s Eastern Coast, China. Water. 2023; 15(20):3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203629
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Peng, Chuanming Ma, and Aiguo Zhou. 2023. "Unraveling the Complexities of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Environments: Insights from Laizhou Bay’s Eastern Coast, China" Water 15, no. 20: 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203629
APA StyleHuang, P., Ma, C., & Zhou, A. (2023). Unraveling the Complexities of Groundwater Salinization in Coastal Environments: Insights from Laizhou Bay’s Eastern Coast, China. Water, 15(20), 3629. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203629




