Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah
Abstract
:1. Introduction
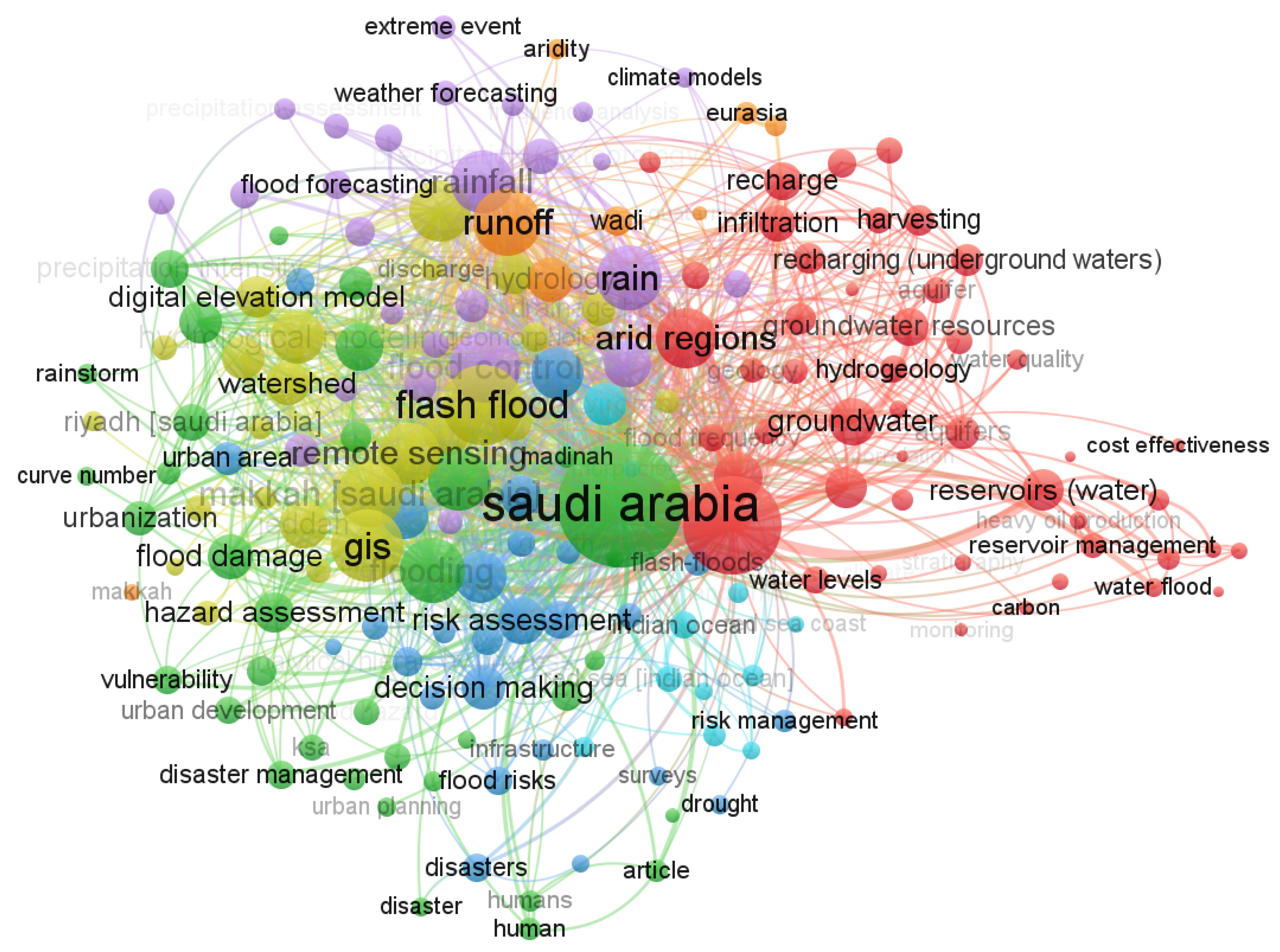
2. Bibliometric Analysis
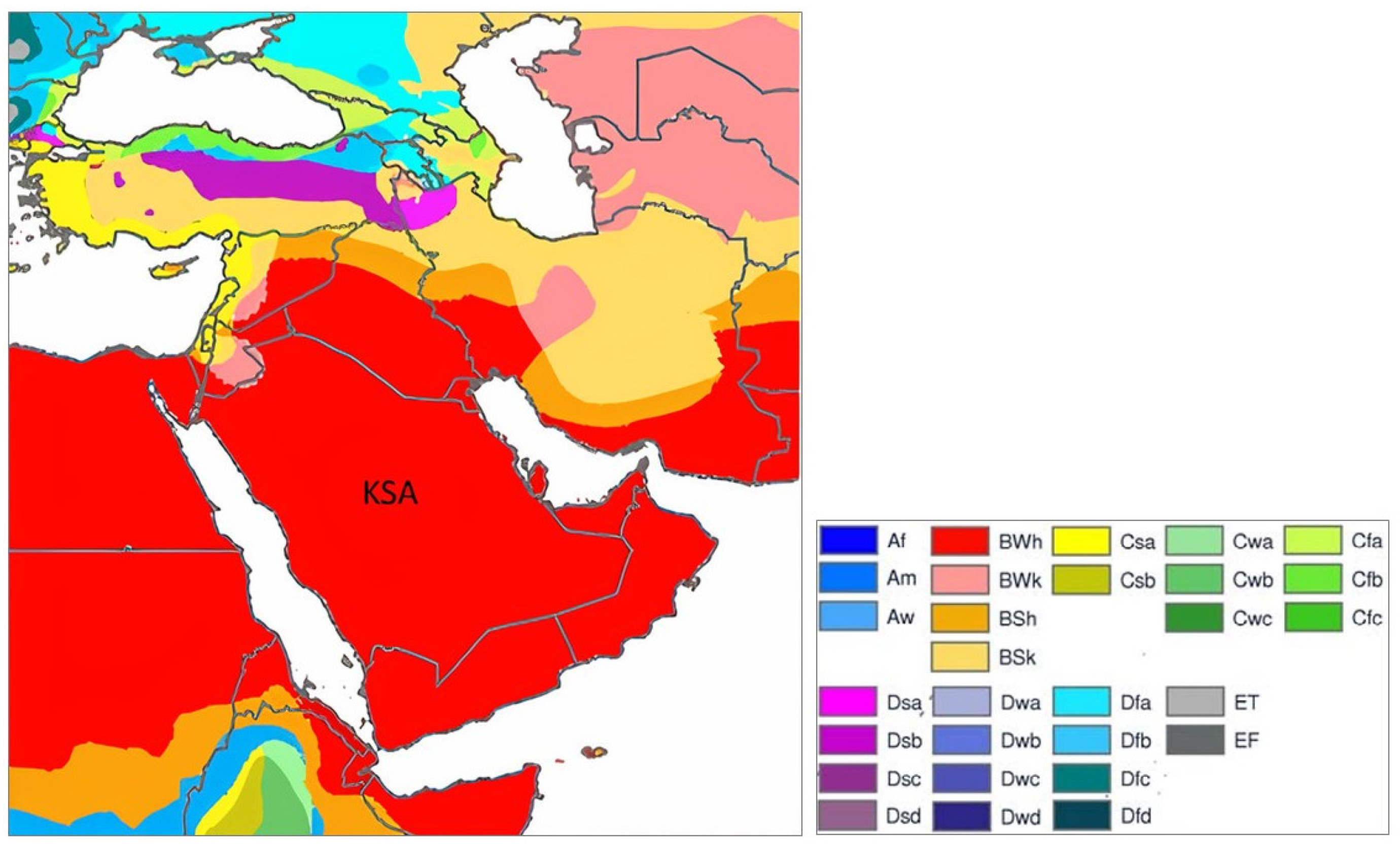
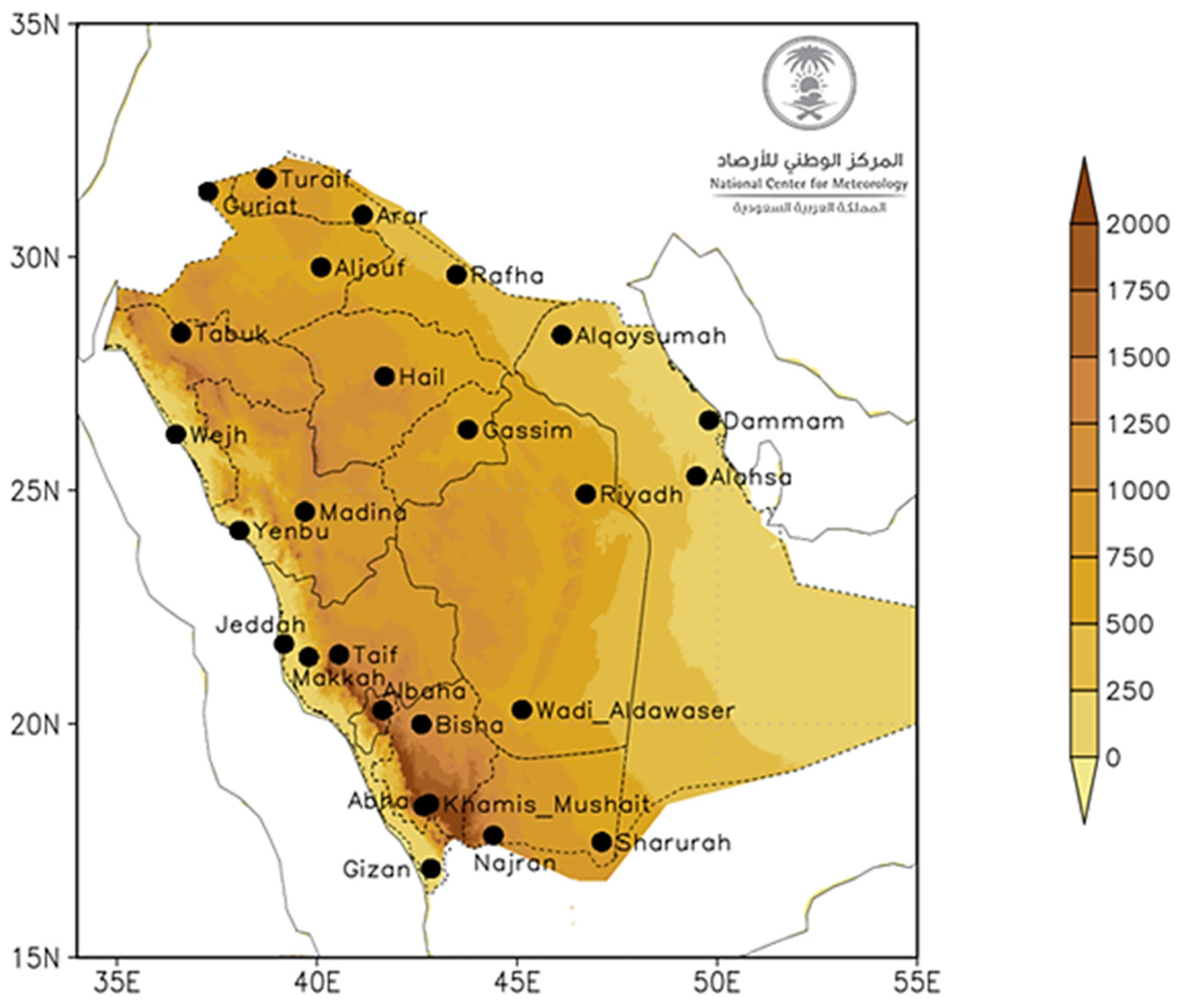
3. Climatic Classification of the Kingdom
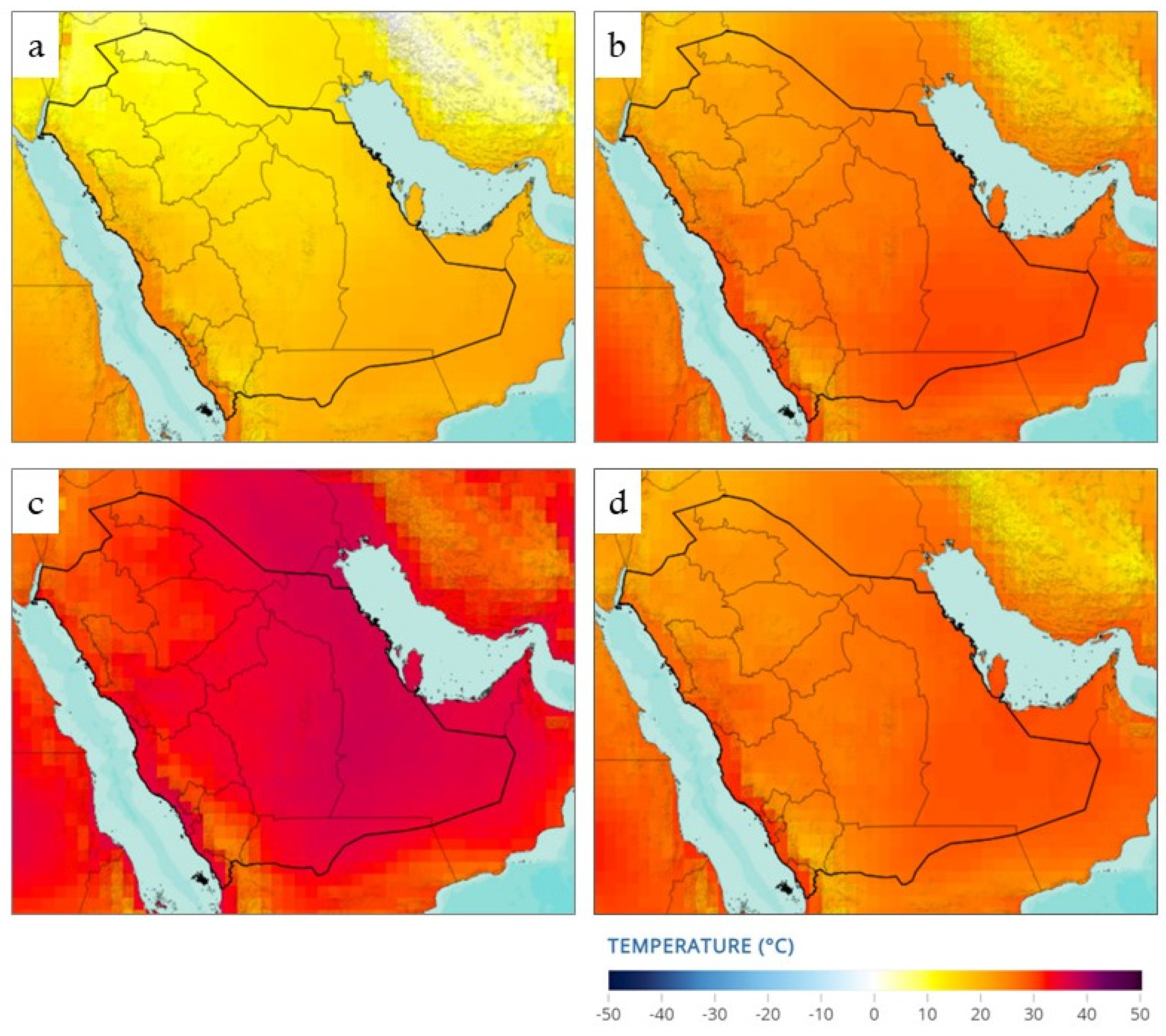
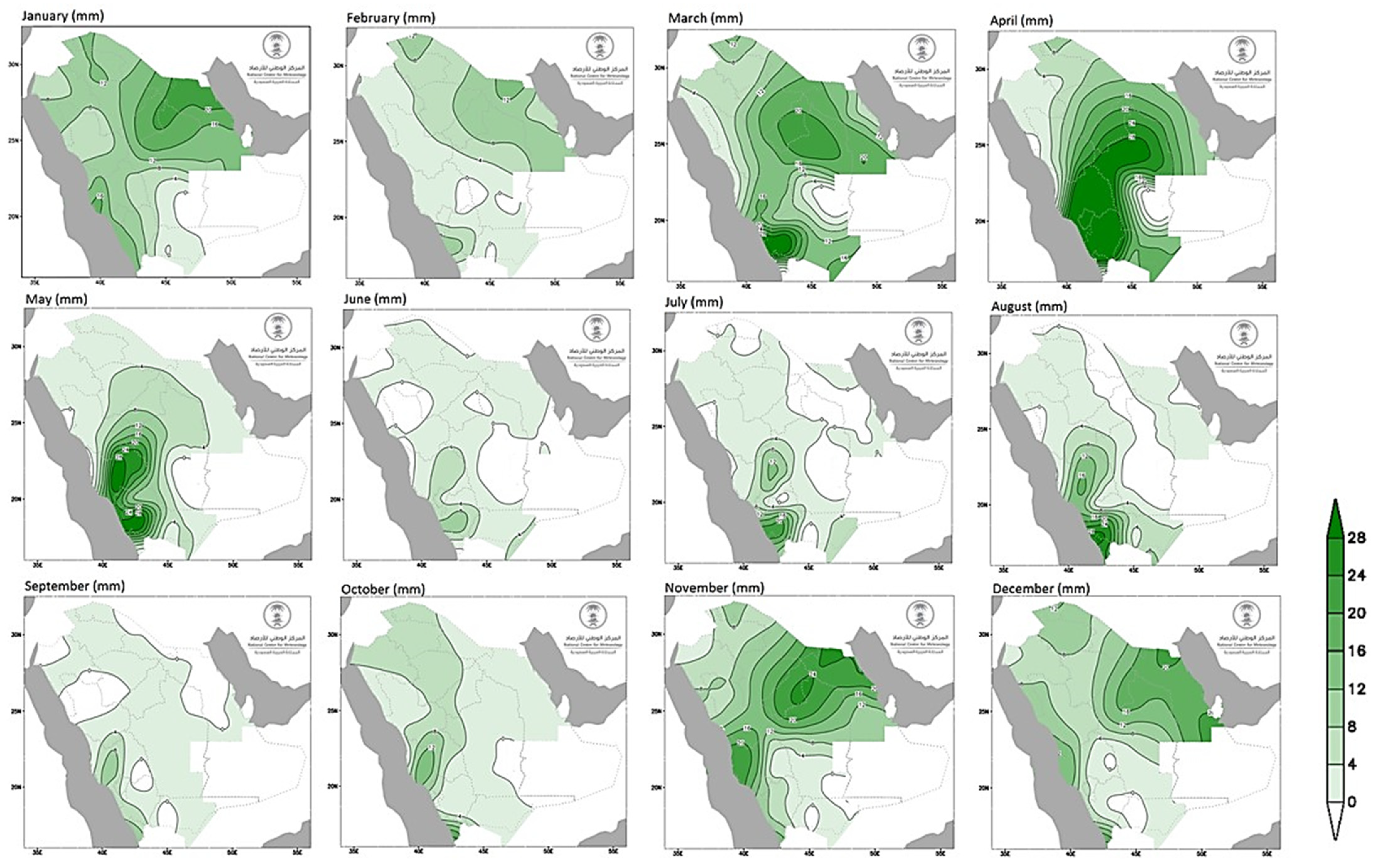
4. Climate Change’s Effects on Flooding in Saudi Arabia
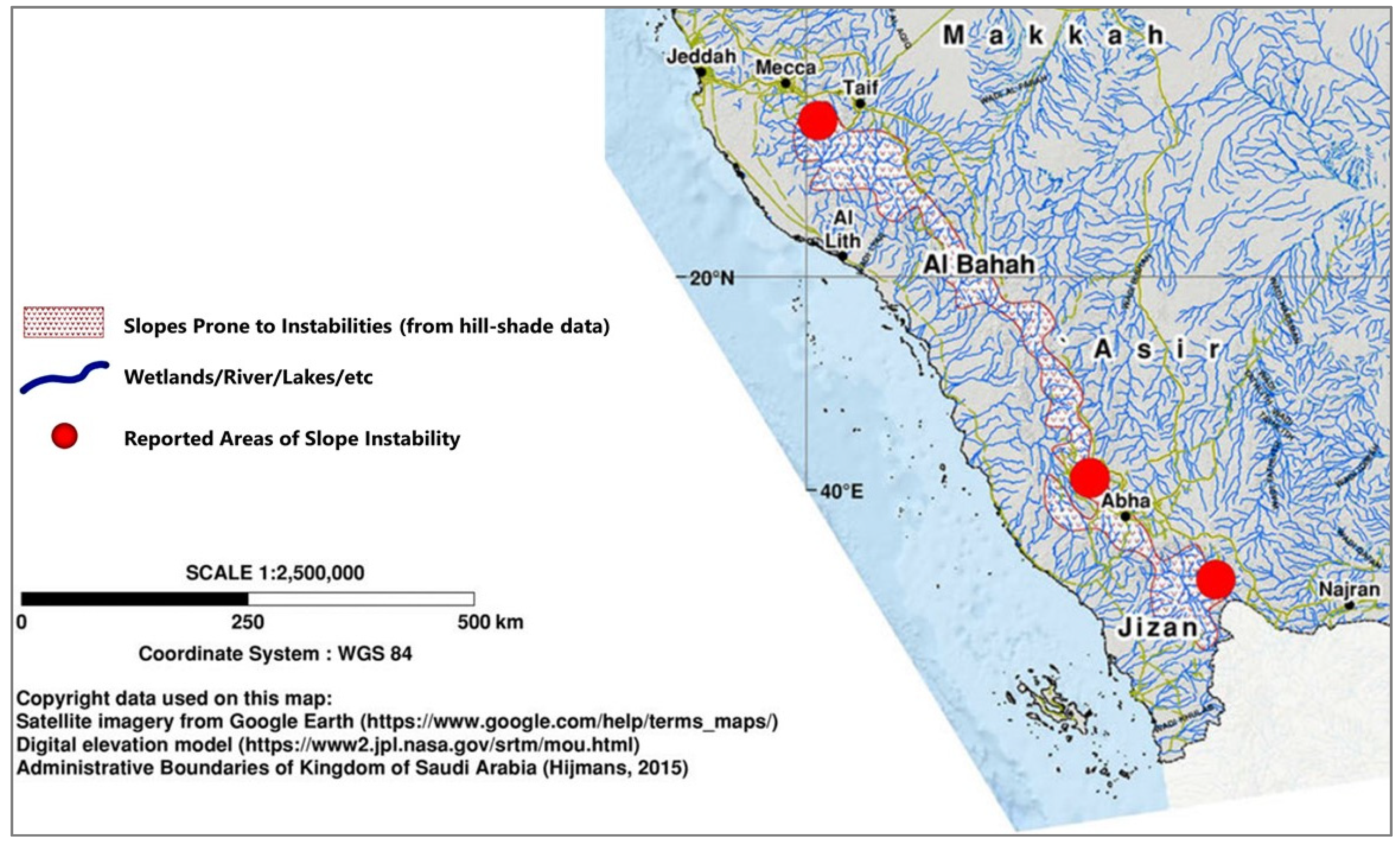
5. Topography Associated with Slope Instability and Flash Flooding in the Kingdom
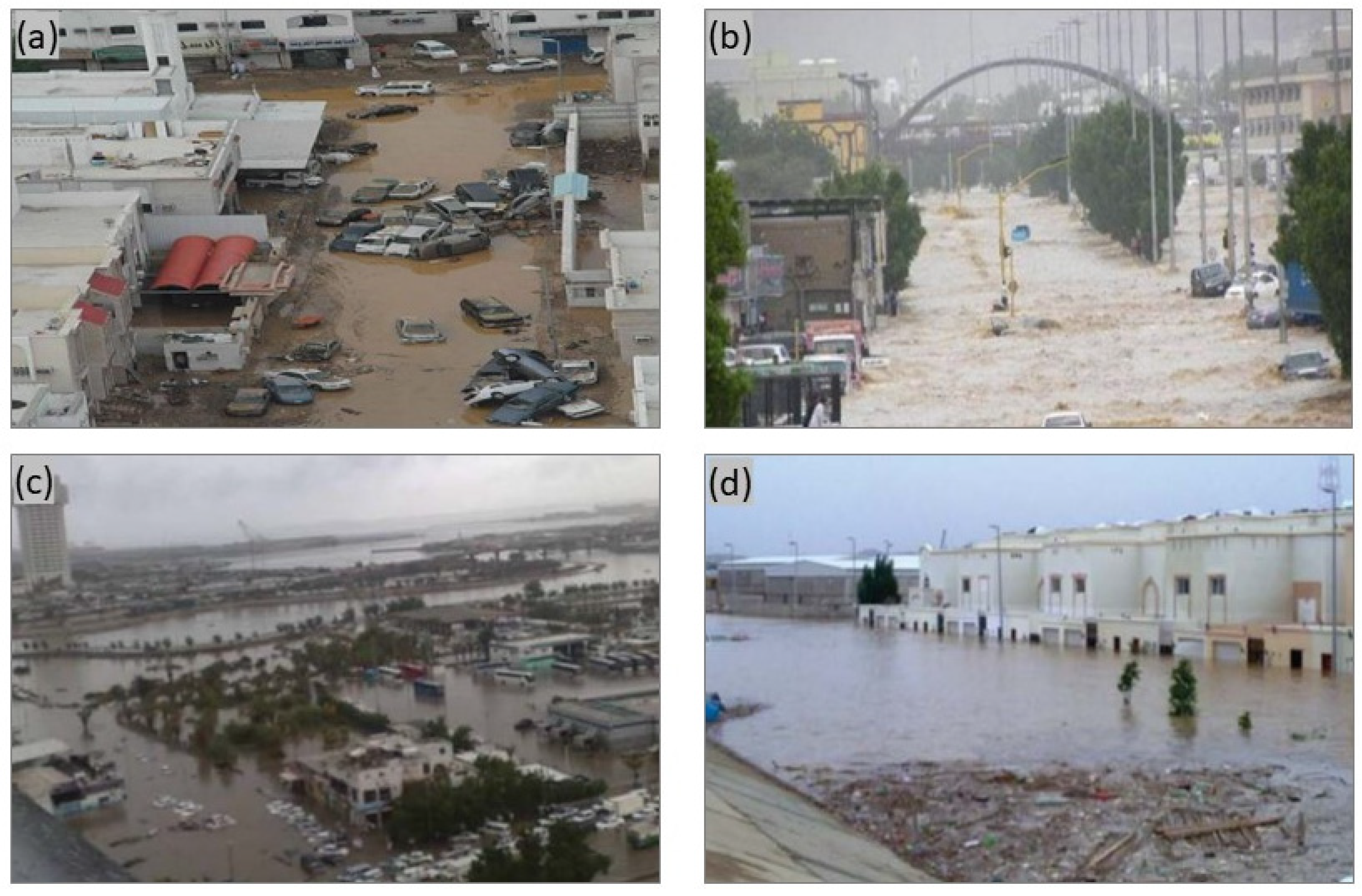
6. Major Flash Flood Events in Jeddah City
7. Geomorphology, Geology and Urbanization in nearby Jeddah City
8. Rainfall Characteristics of Jeddah City
9. Urban Expansion of Jeddah City
10. Current Drainage Systems and their Features—Jeddah City
11. Flood Controls in Jeddah
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Youssef, A.M.; Maerz, N.H. Overview of some geological hazards in the Saudi Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 3115–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, B. Morphometric Parameters and Geospatial Analysis for Flash Flood Susceptibility Assessment: A Case Study of Jeddah City along the Red Sea Coast, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebaie, I.H.; Kawara, A.Q.; Alnahit, A.O. Mapping and Assessment of Flood Risk in the Wadi Al-Lith Basin, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.H.; Saegh, A.M. Flash Flood Risk Assessment Due to a Possible Dam Break in Urban Arid Environment, the New Um Al-Khair Dam Case Study, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank Group. Climate Change Knowledge Portal (CCKP). 2023. Available online: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/country/saudi-arabia (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Almaliki, A.H.; Zerouali, B.; Santos, C.A.G.; Almaliki, A.A.; da Silva, R.M.; Ghoneim, S.S.; Ali, E. Assessing coastal vulnerability and land use to sea level rise in Jeddah province, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dano, U.L. Flash flood impact assessment in Jeddah city: An analytic hierarchy process approach. Hydrology 2020, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dano, U.L.; Abubakar, I.R.; AlShihri, F.S.; Ahmed, S.M.; Alrawaf, T.I.; Alshammari, M.S. A multi-criteria assessment of climate change impacts on urban sustainability in Dammam Metropolitan Area, Saudi Arabia. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. World Development Report 2010: Development and Climate Change. 2019. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/4387 (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Ghanim, A.A.J.; Shaf, A.; Ali, T.; Zafar, M.; Al-Areeq, A.M.; Alyami, S.H.; Irfan, M.; Rahman, S. An Improved Flood Susceptibility Assessment in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, Using Advanced Machine Learning Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; McCabe, M.F.; Stenchikov, G.; Evans, J.P.; Kucera, P.A. Simulation of Flash-Flood-Producing Storm Events in Saudi Arabia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting Model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subyani, A. Flood Hazards Analysis of Jeddah City, Western Saudi Arabia. J. King Abdulaziz Univ. Sci. 2012, 23, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquharson, F.; Meigh, J.; Sutcliffe, J. Regional flood frequency analysis in arid and semi-arid areas. J. Hydrol. 1992, 138, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flerchinger, G.; Cooley, K. A ten-year water balance of a mountainous semi-arid watershed. J. Hydrol. 2000, 237, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subyani, A.M. Hydrologic behavior and flood probability for selected arid basins in Makkah area, western Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2011, 4, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.R.; Fowler, H.J. Characterising flash flood response to intense rainfall and impacts using historical information and gauged data in Britain. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 11, S121–S133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, K.A.; Al Mosallam, M.S.; Aldaajani, T.Z.; Al-Namazi, A.A. Landforms characterization of Saudi Arabia: Towards a geomorphological map. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.E.L.; Zachariah, M.; Saeed, F.; Siddiqi, A.; Kamil, S.; Mushtaq, H.; Arulalan, T.; AchutaRao, K.; Chaithra, S.T.; Barnes, C.; et al. Climate change increased extreme monsoon rainfall, flooding highly vulnerable communities in Pakistan. Environ. Res. Clim. 2023, 2, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Areeq, A.M.; Sharif, H.O.; Abba, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Al-Suwaiyan, M.; Benaafi, M.; Yassin, M.A.; Aljundi, I.H. Digital elevation model for flood hazards analysis in complex terrain: Case study from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 119, 103330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewea, H.A.; Elfeki, A.M.; Al-Amri, N.S. Development of intensity–duration–frequency curves for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of East Anglia. Climatic Research Unit; University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Meteorology—Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. 2023. Available online: https://ncm.gov.sa/ar/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Bahrawi, J.; Alqarawy, A.; Chabaani, A.; Elfeki, A.; Elhag, M. Spatiotemporal analysis of the annual rainfall in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: Predictions to 2030 with different confidence levels. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2021, 146, 1479–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Sefry, S.A.; Pradhan, B.; Abu Alfadail, E. Analysis on causes of flash flood in Jeddah city (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) of 2009 and 2011 using multi-sensor remote sensing data and GIS. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1018–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.A. The extent of desertification on Saudi Arabia. Environ. Geol. 2004, 46, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, B.K.; Griffiths, S.; Kim, J.; Bazilian, M. Climate change and industrial F-gases: A critical and systematic review of developments, sociotechnical systems and policy options for reducing synthetic greenhouse gas emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, F.; Nadeau, K. Climate Change, Fossil-Fuel Pollution, and Children’s Health. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bolaños, T.G.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.A.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.; et al. The human imperative of stabilizing global climate change at 1.5 °C. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendžić, S.; Zovko, M.; Živković, I.P.; Lešić, V.; Lemić, D. The Impact of Climate Change on Agricultural Insect Pests. Insects 2021, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordhaus, W. Climate Change: The Ultimate Challenge for Economics. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 109, 1991–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeder, D.J. Greenhouse gas sources and mitigation strategies from a geosciences perspective. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2021, 5, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.T.D.; Nik, V.M.; Chen, D.; Scartezzini, J.-L.; Hong, T. Quantifying the impacts of climate change and extreme climate events on energy systems. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, A.; Nik, V.M.; Carlucci, S.; Geving, S. Impacts of future weather data typology on building energy performance—Investigating long-term patterns of climate change and extreme weather conditions. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 696–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N.; Athar, H.; Jones, P.D.; Rahman, M.A. Recent climate change in the Arabian Peninsula: Annual rainfall and temperature analysis of Saudi Arabia for 1978–2009. Int. J. Clim. 2012, 32, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Fathi, H.; Zijl, W.; Alshehri, F.; Almadani, S.; Zaidi, F.K.; Aldawsri, M.; Gabr, M.E. Potential Effects of Climate Change on Agricultural Water Resources in Riyadh Region, Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, Q.Y.; Chowdhury, S. Trends of Climate Change in Saudi Arabia: Implications on Water Resources. Climate 2018, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, T.; Boardman, J.; Foster, I.; Howden, N. More rain, less soil: Long-term changes in rainfall intensity with climate change. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, J.; Armas, C.; Padilla, F.; Pugnaire, F. Climatic change and rainfall patterns: Effects on semi-arid plant communities of the Iberian Southeast. J. Arid. Environ. 2011, 75, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zawad, F.M.; Aksakal, A. Impacts of Climate Change on Water Resources in Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments (2008) and the 1st Arab Water Forum, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 16–19 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkarim, A.; Gaber, A.F.D.; Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B. Flood Hazard Assessment of the Urban Area of Tabuk City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia by Integrating Spatial-Based Hydrologic and Hydrodynamic Modeling. Sensors 2019, 19, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeh, T.; Alakhras, A.I.; Habib, M.; Alduaij, O.; Mohammad, A.H.; Alslaty, F. A Recommended Urban Plan According to Flash Flood Risk Potential Map: The Case Study of Mecca Province—Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2022, 17, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, R.; Di Matteo, N.; Gulerce, U.; Babu, V.L.S.; Rafiq, A. Geohazards of Saudi Arabia. J. Maps 2019, 15, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Alqadhi, S.; Talukdar, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Roy, S.K.; Ahmed, M. Modelling and mapping of landslide susceptibility regulating potential ecosystem service loss: An experimental research in Saudi Arabia. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 10170–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; Sultan, M.; Sefry, S.; ElKadiri, R.; Ahmed, M.; Chase, R.; Milewski, A.; Abu Abdullah, M.; Emil, M.; Chounaird, K. An assessment of landslide susceptibility in the Faifa area, Saudi Arabia, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Al-Kathery, M.; Pradhan, B. Landslide susceptibility mapping at Al-Hasher area, Jizan (Saudi Arabia) using GIS-based frequency ratio and index of entropy models. Geosci. J. 2015, 19, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Alazba, A.A. Towards a sustainable capital city: An approach for flood management and artificial recharge in naturally water-scarce regions, Central Region of Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bassam, A.M.; Zaidi, F.K.; Hussein, M.T. Natural hazards in Saudi Arabia. In Extreme Natural Hazards, Disaster Risks and Societal Implications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, W.; Amin, A. Geotechnical Hazards Associated with Desert Environment. Nat. Hazards 1997, 16, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammar, A.; Abosuliman, S.S.; Rahaman, K.R. Social Capital and Disaster Resilience Nexus: A Study of Flash Flood Recovery in Jeddah City. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, Q.U.; Alluqmani, A.E. Application of soil based low impact development system for Flash Flood management of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2021. In Press, Corrected Proof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, R.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Almazroui, M. Near-real-time spatiotemporal analysis of convection and extreme rainfall leading to a flash flood using MSG-SEVIRI and TRMM data: A case study of a flash flood in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia on the November 25, 2009. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, 12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwash, M.; Zakir, F. Tectonic analysis of the Jeddah Taif area on the basis of LANDSAT satellite data. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 1992, 15, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Sefry, S.A. Flash flood susceptibility assessment in Jeddah city (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) using bivariate and multivariate statistical models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.A.; Al-Rehaili, M.H. Geologic Map of Makkah Quadrangle, Sheet 21D. In Geoscience Map GM-107C; 1:250,000 Scale; DGMR: Makkah, Saudi Arabia, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Al Saud, M.M. The Existing Flood Controls in Jeddah. In Flood Control Management for the City and Surroundings of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, L. Heavy daily-rainfall characteristics over the Gauteng Province. Water SA 2009, 35, 49188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R. Flood as a Disaster in the Middle East Region. 2013. Volume 1. pp. 121–127. Available online: www.ijser.in (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Yesubabu, V.; Srinivas, C.V.; Langodan, S.; Hoteit, I. Predicting extreme rainfall events over Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: Impact of data assimilation with conventional and satellite observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 142, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekeli, A.E. Exploring Jeddah Floods by Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission Analysis. Water 2017, 9, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, F. Floods in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia: Unusual Phenomenon and Huge Losses. What Prognoses. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Paris, France, 12–14 September 2016; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.B.; Ameur, F. An Assessment of Jeddah’s Hydraulic Protection and Management Systems of Flood. OALib 2018, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashat, A.; Basset, H.A. Analysis of Rainfall over Saudi Arabia. JKAU Met. Env. Arid. Land Agric. Sci. 2011, 22, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almulhim, A.I.; Cobbinah, P.B.; Almufarrij, I.; Dillon, H.; Dawes, P.; Moore, D.R.; Yeung, W.; Charalambous, A.-P.; Thodi, C.; Munro, K.J. Urbanization-environment conundrum: An invitation to sustainable development in Saudi Arabian cities. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2023, 30, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, I.; Helmi, M.; Qurnfulah, E.; Naji, A.; Ibrahim, H.S. Assessment of urban growth of Jeddah: Towards a liveable urban management. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2021, 16, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeli, K.N. The realities of integrating physical planning and local management into urban development: A case study of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Habitat Int. 2008, 32, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrotrends. Jiddah, Saudi Arabia Metro Area Population 1950–2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.macrotrends.net/cities/22421/jiddah/population (accessed on 20 August 2023).
- Qari, M.H.T. Geomorphology of Jeddah Governate, with Emphasis on Drainage Systems. Earth Sci. J. King Abdul Aziz Univ. 2009, 20, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledraa, T.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.M. Planning and Management Issues and Challenges of Flash Flooding Disasters in Saudi Arabia: The Case of Riyadh City. J. Archit. Plan. 2020, 32, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wathinani, A.M.; Barten, D.G.; Borowska-Stefańska, M.; Gołda, P.; AlDulijan, N.A.; Alhallaf, M.A.; Samarkandi, L.O.; Almuhaidly, A.S.; Goniewicz, M.; Samarkandi, W.O.; et al. Driving Sustainable Disaster Risk Reduction: A Rapid Review of the Policies and Strategies in Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijji, M.; Amin, S.; Iqbal, R.; Harrop, W. A Critical Evaluation of the Rational Need for an IT Management System for Flash Flood Events in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the 2013 Sixth International Conference on Developments in E-Systems Engineering, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 16–18 December 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrazzak, M.; Elfeki, A.; Kamis, A.; Kassab, M.; Alamri, N.; Chaabani, A.; Noor, K. Flash flood risk assessment in urban arid environment: Case study of Taibah and Islamic universities’ campuses, Medina, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 780–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saud, M.M. Required Controls for Floods and Torrents in Jeddah Region. In Flood Control Management for the City and Surroundings of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; Springer Natural Hazards: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hames, A.; Al-Wagdany, A. Reconstruction of flood characteristics in urbanized arid regions: Case study of the flood of 25 November 2009 in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammar, A. Assessing Resilient Post-Disaster Recovery of A Flash-FloodProne Area: A Study of the City of Jeddah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Ph.D. Thesis, Wilfrid Laurier University, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Alrehaili, N.R. An Investigation into Emergency Planning Requirements and Challenges of Disaster Management in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Disaster Manag. 2021, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaharani, K.H.; Al-Shayaa, M.; Baig, M.B. Water conservation in the kingdom of Saudi Arabia for better environment: Implications for extension and education. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 17, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Hersh, R. Flood Planning and Climate Forecasts at the Local Level. 2002. Available online: www.rff.org (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Alrehaili, N.R. A systematic review of the emergency planning for flash floods response in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Aust. J. Emerg. Manag. 2021, 36, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfeki, A.M.; Ewea, H.A.; Al-Amri, N.S. Development of storm hyetographs for flood forecasting in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain Shah, S.M.; Yassin, M.A.; Abba, S.I.; Lawal, D.U.; Hussein Al-Qadami, E.H.; Teo, F.Y.; Mustaffa, Z.; Aljundi, I.H. Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah. Water 2023, 15, 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203641
Hussain Shah SM, Yassin MA, Abba SI, Lawal DU, Hussein Al-Qadami EH, Teo FY, Mustaffa Z, Aljundi IH. Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah. Water. 2023; 15(20):3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203641
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain Shah, Syed Muzzamil, Mohamed A. Yassin, Sani I. Abba, Dahiru U. Lawal, Ebrahim Hamid Hussein Al-Qadami, Fang Yenn Teo, Zahiraniza Mustaffa, and Isam H. Aljundi. 2023. "Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah" Water 15, no. 20: 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203641
APA StyleHussain Shah, S. M., Yassin, M. A., Abba, S. I., Lawal, D. U., Hussein Al-Qadami, E. H., Teo, F. Y., Mustaffa, Z., & Aljundi, I. H. (2023). Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah. Water, 15(20), 3641. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203641








