Multi-Algorithm Hybrid Optimization of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Networks for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Prediction Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sources of Data
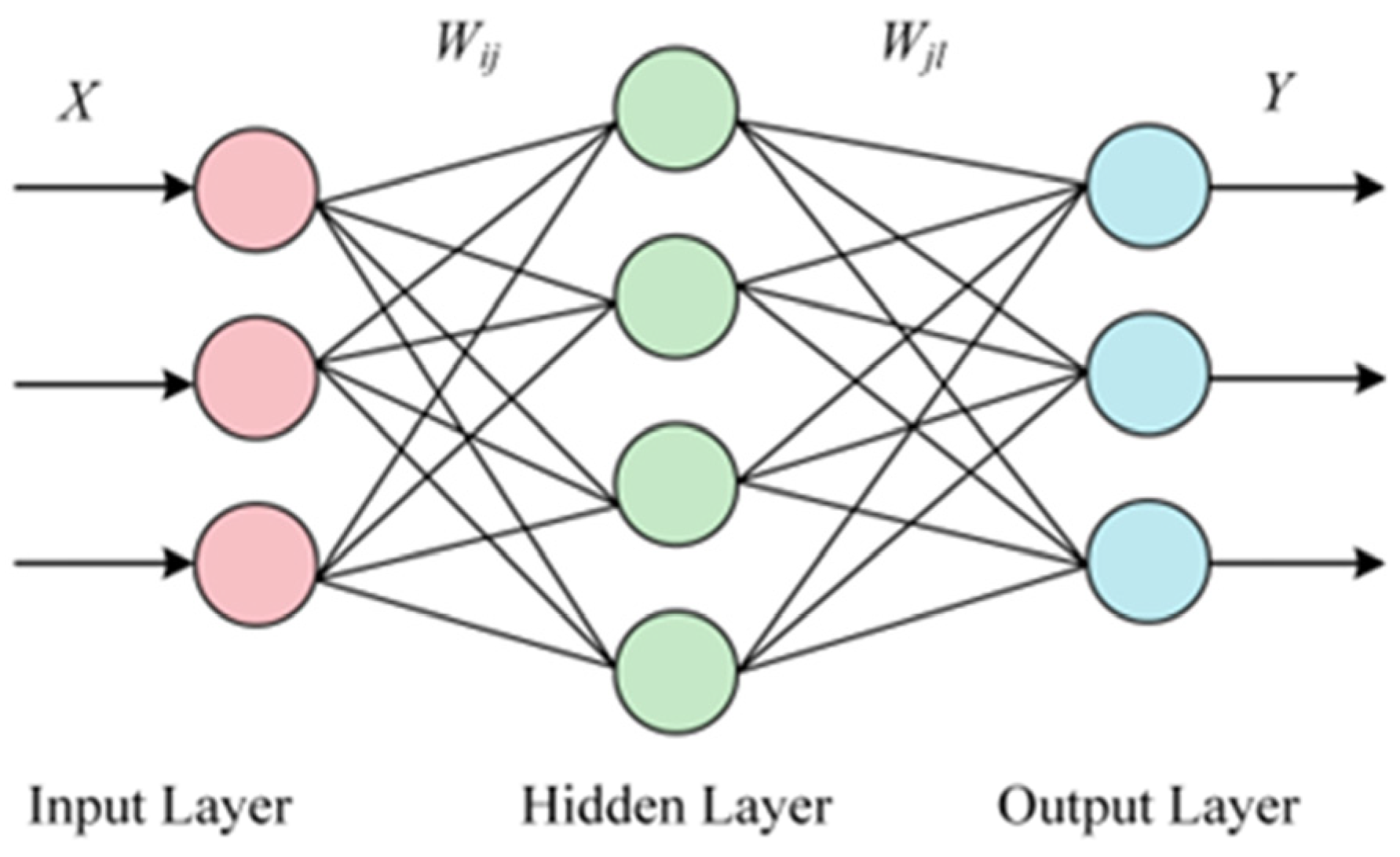
2.2. BP Neural Network
2.3. BP Neural Networks’ Genetic Algorithm Optimization
2.4. Particle Swarm Optimization for BP Neural Networks
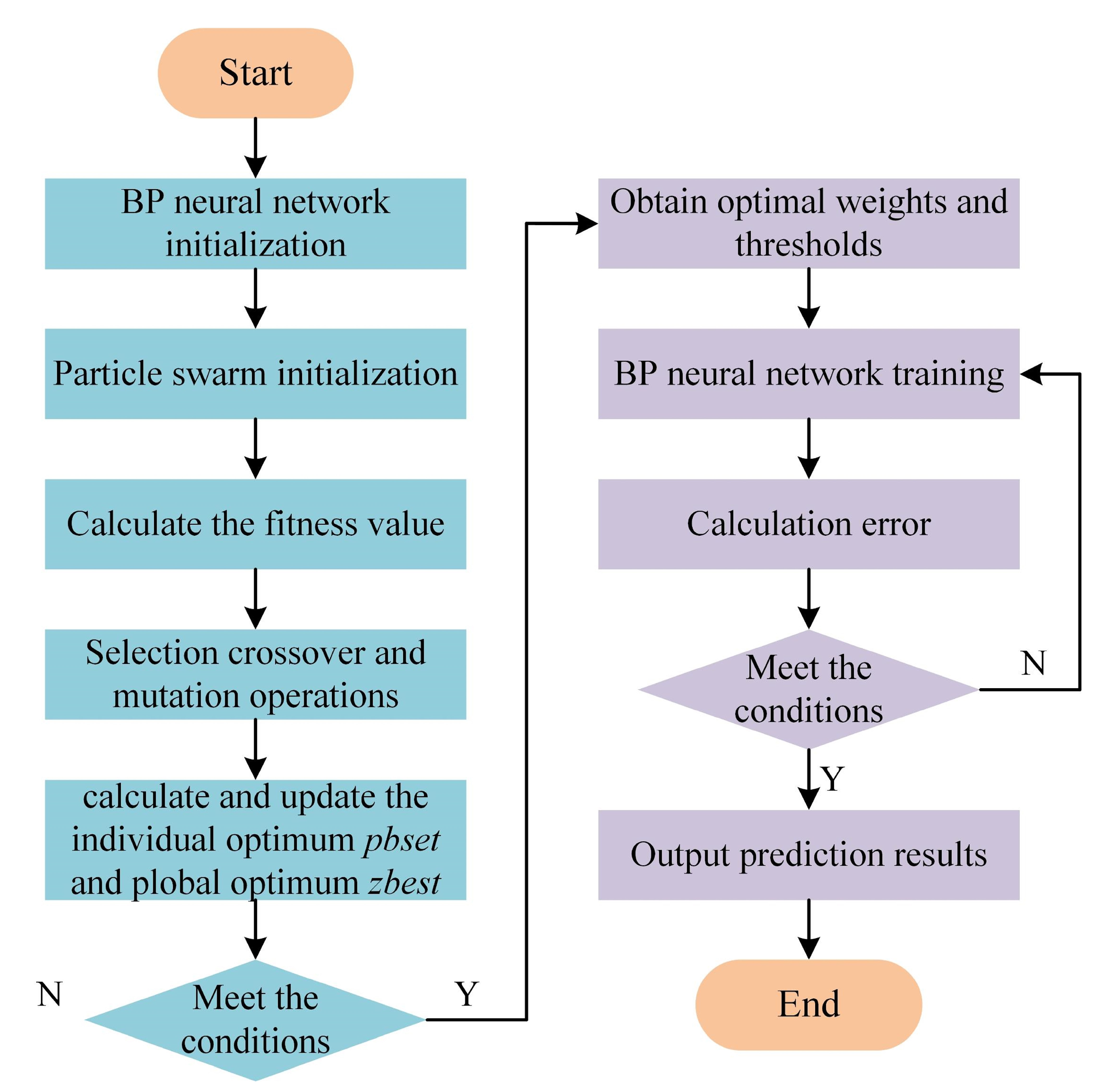
2.5. Hybrid Optimization of BP Neural Network
2.6. Criteria for Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Correlation Analysis between ET0 and Meteorological Factors
3.2. Simulation Analysis of ET0 Prediction Model
3.3. Analysis of Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Temperature (Tmax, Tave, Tmin), hours of sunlight (N), relative humidity (RH), wind speed (U), and average air pressure (AP) all had an effect on reference crop evapotranspiration (ET0). And when the input factors include temperature (Tmax, Tave, Tmin), daylight hours (N), and relative humidity (RH), the model performance is better than other input combinations, indicating that this input combination is optimum for building the model.
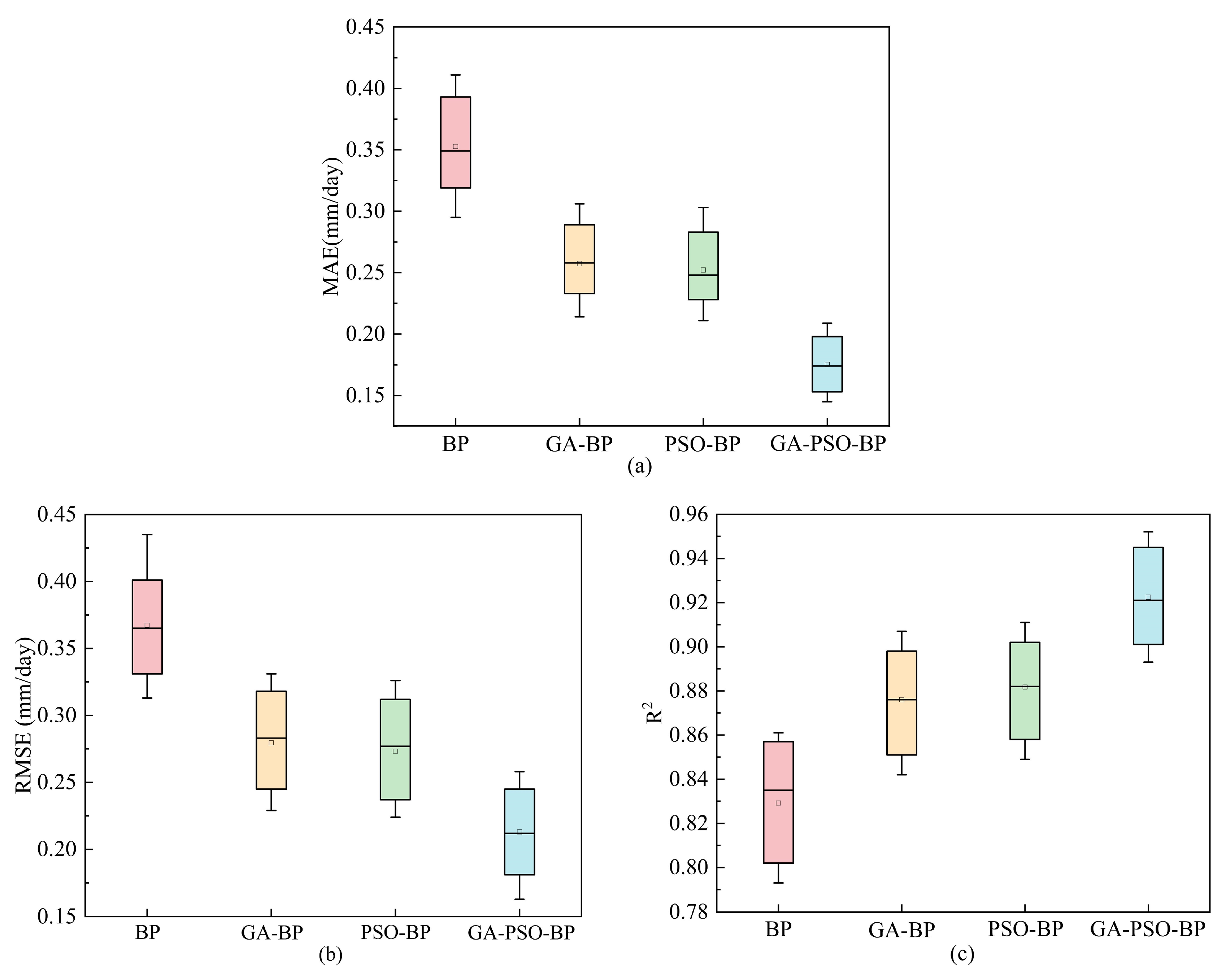
- When the four ET0 prediction models are compared under the combination of X7 input factors, the GA-PSO-BP prediction model outperforms the other three prediction models, with optimal MAE, RMSE, and R2 values of 0.145 mm/day, 0.163 mm/day, and 0.952, respectively.
- Analyzing seven sets of meteorological factors input combinations reveals that the hybrid algorithm (GA-PSO) provides the best performance boost to the BP neural network, and the prediction impact of the GA-PSO-BP model is optimal under each input combination. As a result, when meteorological circumstances are constrained, the use of the GA-PSO-BP model to estimate ET0 for water resource allocation has a significant reference value.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neissi, L.; Albaji, M.; Nasab, S.B. Site Selection of Different Irrigation Systems Using an Analytical Hierarchy Process Integrated with GIS in a Semi-Arid Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 4955–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsal, J.; Girona, J.; Casadesus, J.; Lopez, G.; Stöckle, C.O. Crop coefficient (Kc) for apple: Comparison between measurements by a weighing lysimeter and prediction by CropSyst. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.; Al-Ansari, N.; El-Ssawy, W.; Graf, R.; Aghelpour, P.; He, H.M.; Hafez, S.M.; Abuarab, M. Prediction of Irrigation Water Requirements for Green Beans-Based Machine Learning Algorithm Models in Arid Region. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 1557–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.L.; Zhao, Y.K.; Song, J.F. Analysis of the regional differences in agricultural water poverty in China: Based on a new agricultural water poverty index. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.Y.; Li, Y.; Horton, R.; Feng, H. Similarity and difference of potential evapotranspiration and reference crop evapotranspiration—A review. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.L.; Wu, L.F.; Zhang, F.C.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Zheng, J. Climate change effects on reference crop evapotranspiration across different climatic zones of China during 1956–2015. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, A.; Chávez, J. Crop Evapotranspiration (ET) Estimation Models: A Review and Discussion of the Applicability and Limitations of ET Methods. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G.; Smith, M.; Raes, D. Crop evapotranspiration estimation with FAO56: Past and future. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; French, A.N. Crop Evapotranspiration. Agronomy 2019, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.C.; Braga, R.P. Estimation of Reference Evapotranspiration during the Irrigation Season Using Nine Temperature-Based Methods in a Hot-Summer Mediterranean Climate. Agriculture 2021, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Raghuwanshi, N.S.; Singh, R. Artificial neural networks approach in evapotranspiration modeling: A review. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Gong, D.Z.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of random forests and generalized regression neural networks for daily reference evapotranspiration modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Gong, Y.C.; Wang, Z.J. Accessible remote sensing data based reference evapotranspiration estimation modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellido-Jimenez, J.A.; Estevez, J.; Garcia-Marin, A.P. New machine learning approaches to improve reference evapotranspiration estimates using intra-daily temperature-based variables in a semi-arid region of Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, J.; Nazemi, A.H.; Sadraddini, A.A.; Landeras, G.; Kisi, O.; Fard, A.F.; Marti, P. Comparison of heuristic and empirical approaches for estimating reference evapotranspiration from limited inputs in Iran. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 108, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jia, Y.; Cui, N.B.; Zhao, L.; Li, C.; Gong, D.Z. Calibration of Hargreaves model for reference evapotranspiration estimation in Sichuan basin of southwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 181, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.Y. Prediction of infiltration behaviors and evaluation of irrigation efficiency in clay loam soil under Moistube (R) irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 248, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Song, J.J.; Xu, M.B.; Wang, X.L.; Yin, Z.; Liu, T.Q.; Luo, N. Prediction of the corrosion depth of oil well cement corroded by carbon dioxide using GA-BP neural network. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 394, 132127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.X.; Liu, Y.K.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhou, Z.W.; Liu, H.R. Modeling and Optimizing of NH4+ Removal from Stormwater by Coal-Based Granular Activated Carbon Using RSM and ANN Coupled with GA. Water 2021, 13, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.L.; Zhang, L.X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.W.; Meng, Z.H.; Zheng, Y. Research and Design of Hybrid Optimized Backpropagation (BP) Neural Network PID Algorithm for Integrated Water and Fertilizer Precision Fertilization Control System for Field Crops. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, Y.; Kumar, S.; Upadhyay, R. Integration of GA and neuro-fuzzy approaches for the predictive analysis of gas-assisted EDM responses. Appl. Sci. 2019, 2, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Fang, G.H.; Xie, X.M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.Z. A Multi-Dimensional Equilibrium Allocation Model of Water Resources Based on a Groundwater Multiple Loop Iteration Technique. Water 2017, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.Z. Forecast of agricultural water resources demand based on particle swarm algorithm. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2022, 72, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.Y.; Xu, D.; Meng, Y. Dynamic Evolution Analysis of Desertification Images Based on BP Neural Network. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 5645535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.Z.; Xu, Z.B.; Yu, Y.C.; Xu, H.X.; Gao, K.L. Application of a Hybrid Optimized BP Network Model to Estimate Water Quality Parameters of Beihai Lake in Beijing. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahandideh-Tehrani, M.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Loaiciga, H.A. Application of particle swarm optimization to water management: An introduction and overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, P.; Hu, S.-J. Optimal Alternative for Quantifying Reference Evapotranspiration in Northern Xinjiang. Water 2022, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadria, R.; Benabdelouhab, T.; Lionboui, H.; Salhi, A. Comparative assessment of different reference evapotranspiration models towards a fit calibration for arid and semi-arid areas. J. Arid Environ. 2021, 184, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, L. Hybrid Genetic Algorithm−Based BP Neural Network Models Optimize Estimation Performance of Reference Crop Evapotranspiration in China. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H. Neural networks and genetic algorithm approach for nonlinear evaporation and evapotranspiration modeling. J. Hydrol. 2008, 351, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-C.; Zeng, X.-M.; Li, G.; Lu, B.; Xiao, M.-Z.; Wang, B.-Z. Summer Precipitation Forecast Using an Optimized Artificial Neural Network with a Genetic Algorithm for Yangtze-Huaihe River Basin, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Month | Tmax (°C) | Tave (°C) | Tmin (°C) | U (m/s) | N (h) | RH (%) | AP (hap) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jan | −2.0 | −12.8 | −23.5 | 0.9 | 290.0 | 82 | 974 |
| Feb | 4.3 | −12.6 | −25.2 | 0.8 | 294 | 78 | 977 |
| Mar | 16 | 4.2 | −13.1 | 1.3 | 370.3 | 74 | 968 |
| Apr | 30.2 | 15.5 | −1.5 | 1.5 | 430.6 | 35 | 966 |
| May | 34.6 | 23.5 | 10.8 | 2.0 | 457.0 | 40 | 959 |
| Jun | 39.9 | 26.3 | 12.3 | 1.6 | 462.0 | 43 | 956 |
| Jul | 37.1 | 25.9 | 13.1 | 1.6 | 467.4 | 46 | 955 |
| Aug | 35.6 | 23.4 | 7.1 | 1.4 | 432.5 | 51 | 959 |
| Sep | 39.5 | 19.7 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 375.2 | 47 | 962 |
| Oct | 22.8 | 8.7 | −2.7 | 1.0 | 341.2 | 62 | 971 |
| Nov | 13.0 | −0.7 | −27.7 | 1.0 | 290.5 | 80 | 973 |
| Dec | −5.0 | −16.0 | −26.0 | 0.7 | 278.5 | 81 | 983 |
| Input | MAE (mm/day) | RMSE (mm/day) | R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | T | BP | 0.411 | 0.435 | 0.793 |
| GA-BP | 0.306 | 0.331 | 0.842 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.303 | 0.326 | 0.849 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.209 | 0.258 | 0.893 | ||
| X2 | T, U | BP | 0.393 | 0.401 | 0.802 |
| GA-BP | 0.289 | 0.318 | 0.851 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.283 | 0.312 | 0.858 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.198 | 0.245 | 0.901 | ||
| X3 | T, RH | BP | 0.361 | 0.374 | 0.813 |
| GA-BP | 0.261 | 0.295 | 0.869 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.255 | 0.286 | 0.877 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.183 | 0.231 | 0.912 | ||
| X4 | T, N | BP | 0.349 | 0.365 | 0.835 |
| GA-BP | 0.258 | 0.283 | 0.876 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.248 | 0.277 | 0.882 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.174 | 0.212 | 0.921 | ||
| X5 | T, RH, U | BP | 0.341 | 0.352 | 0.843 |
| GA-BP | 0.241 | 0.256 | 0.889 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.237 | 0.251 | 0.893 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.165 | 0.201 | 0.933 | ||
| X6 | T, N, U | BP | 0.319 | 0.331 | 0.857 |
| GA-BP | 0.233 | 0.245 | 0.898 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.228 | 0.237 | 0.902 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.153 | 0.181 | 0.945 | ||
| X7 | T, N, RH | BP | 0.295 | 0.313 | 0.871 |
| GA-BP | 0.214 | 0.229 | 0.907 | ||
| PSO-BP | 0.211 | 0.224 | 0.911 | ||
| GA-PSO-BP | 0.145 | 0.163 | 0.952 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Dong, W.; Zhu, F.; Wang, H. Multi-Algorithm Hybrid Optimization of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Networks for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Prediction Models. Water 2023, 15, 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213718
Zheng Y, Zhang L, Hu X, Zhao J, Dong W, Zhu F, Wang H. Multi-Algorithm Hybrid Optimization of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Networks for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Prediction Models. Water. 2023; 15(21):3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213718
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yu, Lixin Zhang, Xue Hu, Jiawei Zhao, Wancheng Dong, Fenglei Zhu, and Hao Wang. 2023. "Multi-Algorithm Hybrid Optimization of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Networks for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Prediction Models" Water 15, no. 21: 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213718
APA StyleZheng, Y., Zhang, L., Hu, X., Zhao, J., Dong, W., Zhu, F., & Wang, H. (2023). Multi-Algorithm Hybrid Optimization of Back Propagation (BP) Neural Networks for Reference Crop Evapotranspiration Prediction Models. Water, 15(21), 3718. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213718





