River-Blocking Risk Analysis of the Bageduzhai Landslide Based on Static–Dynamic Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Landslide Investigation
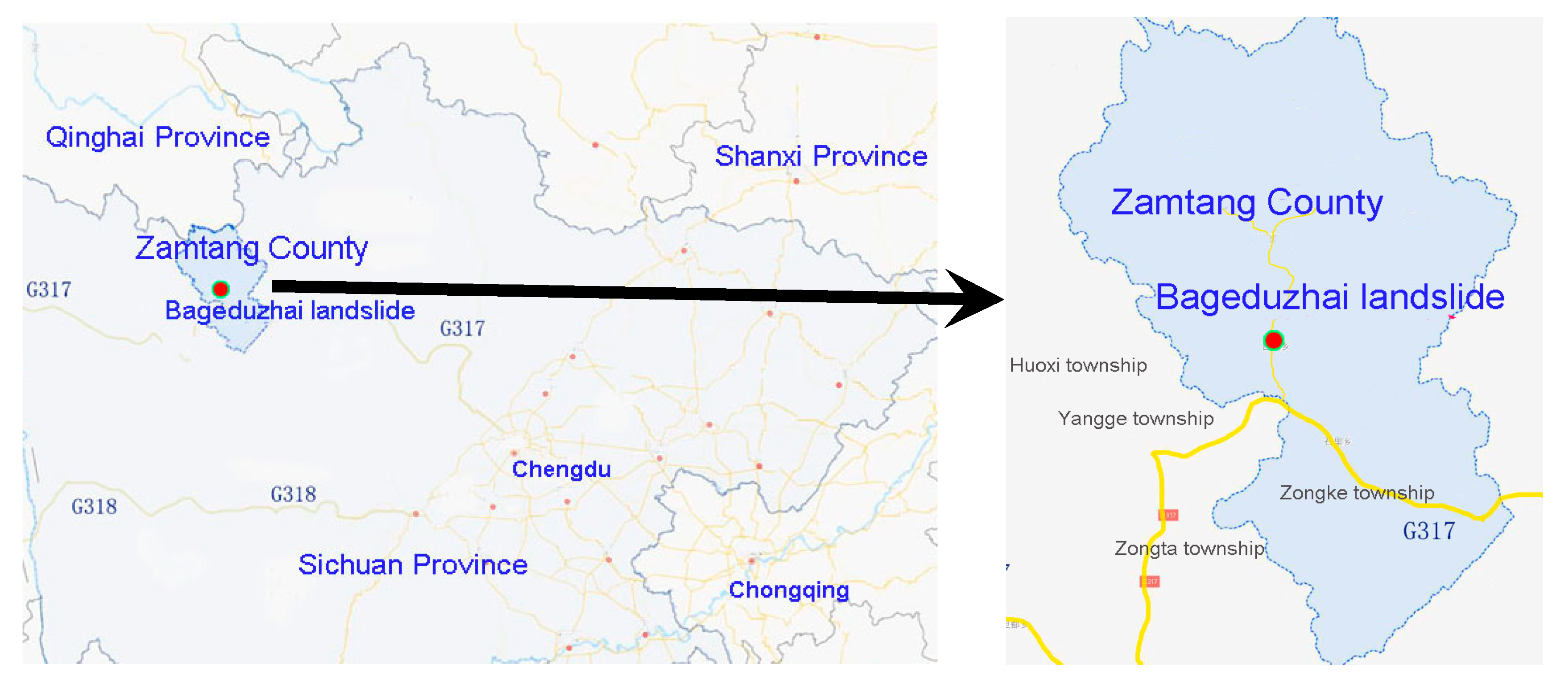
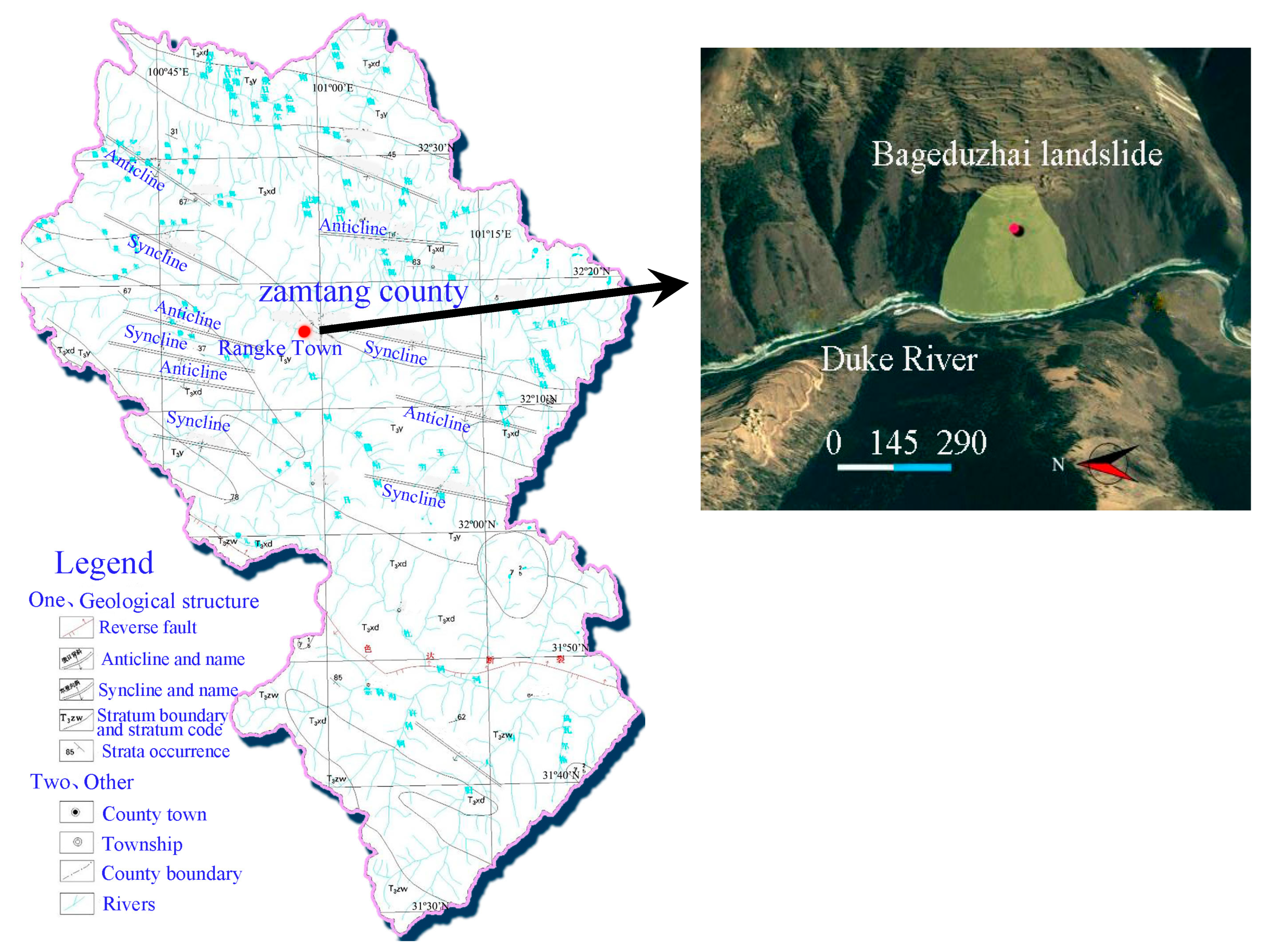
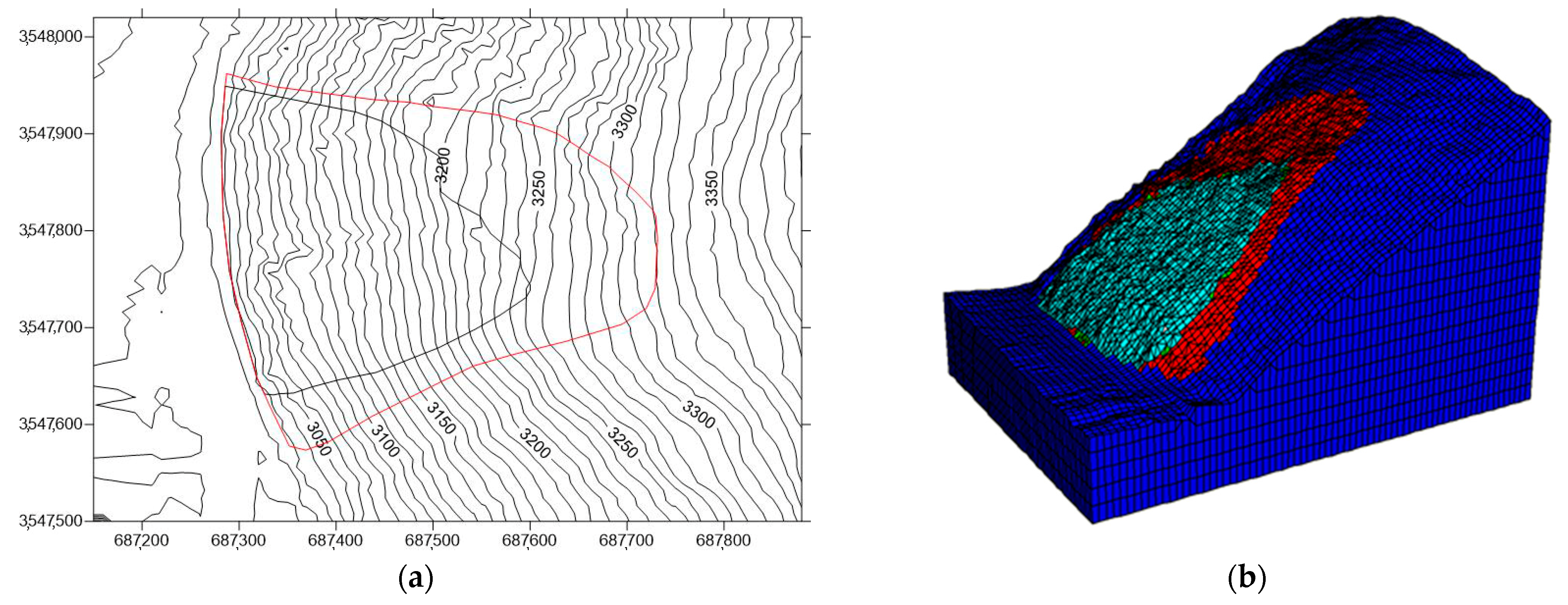
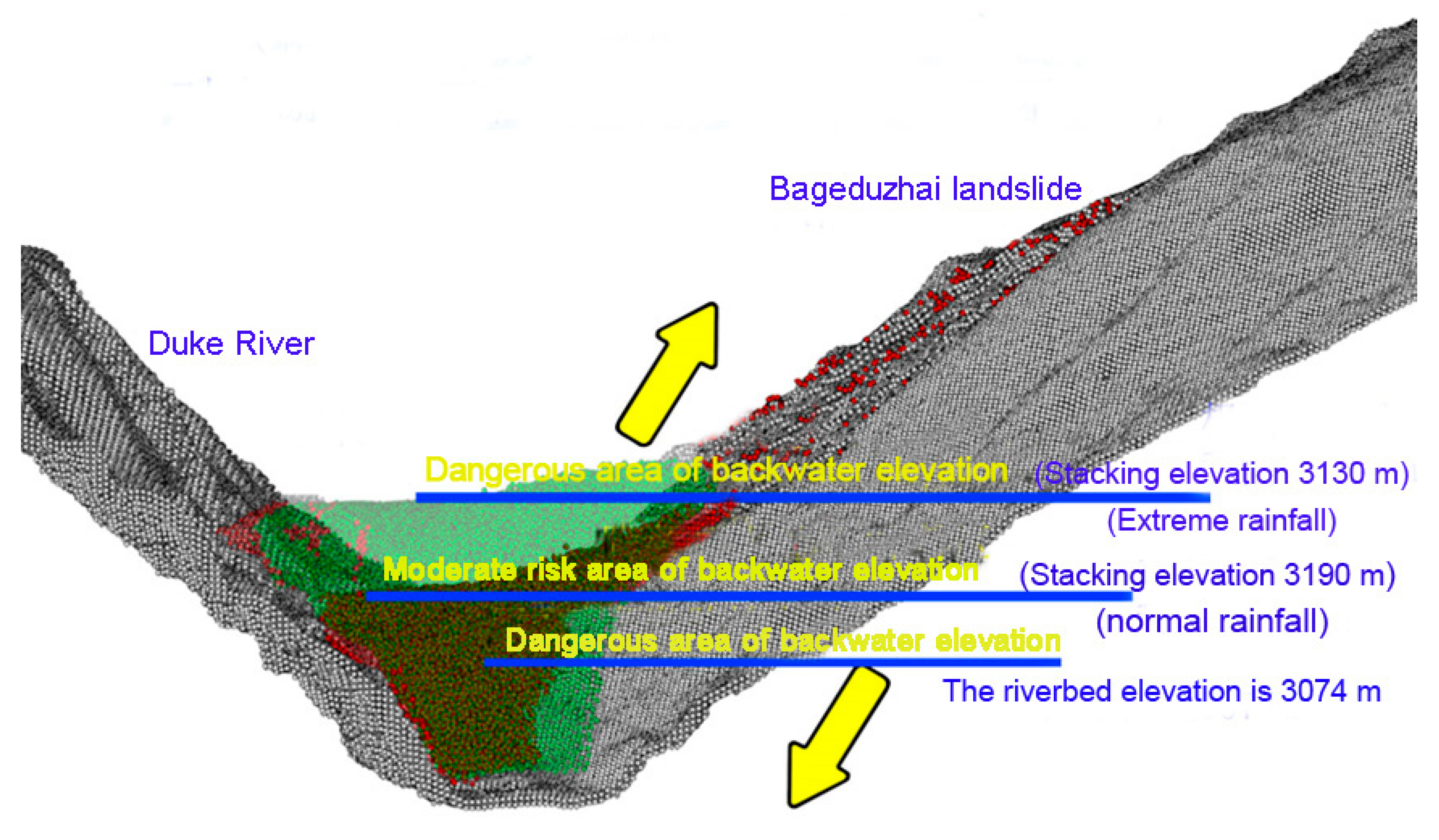
2.1. Research Area Overview
2.2. Landslide Characteristics
2.2.1. Overall Characteristics of Landslides
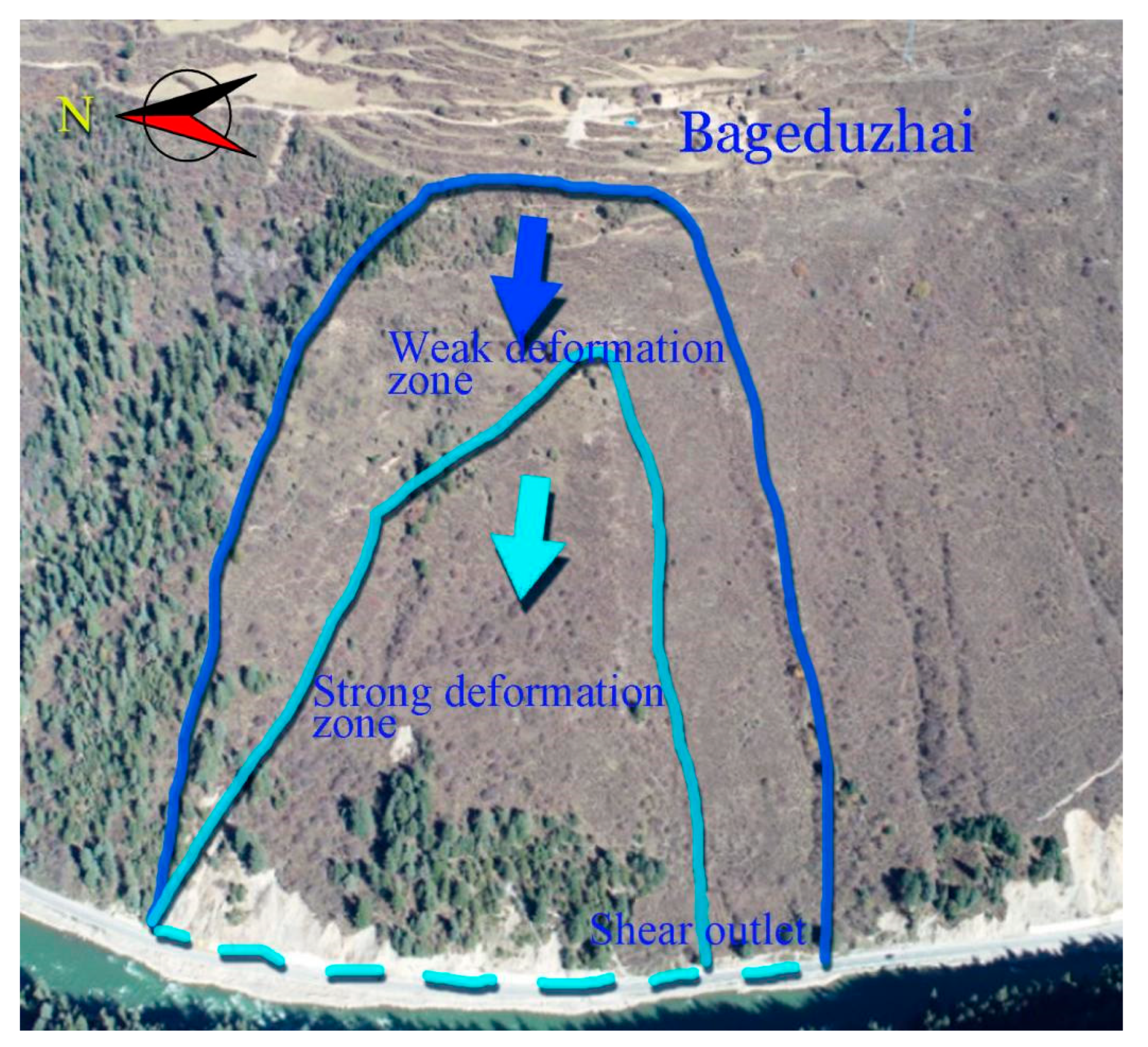
2.2.2. Landslide Deformation and Failure Characteristics
2.2.3. Instability Mechanism of the Bageduzhai Landslide
3. Calculation Conditions and Parameter Calibration
3.1. Calculation Conditions
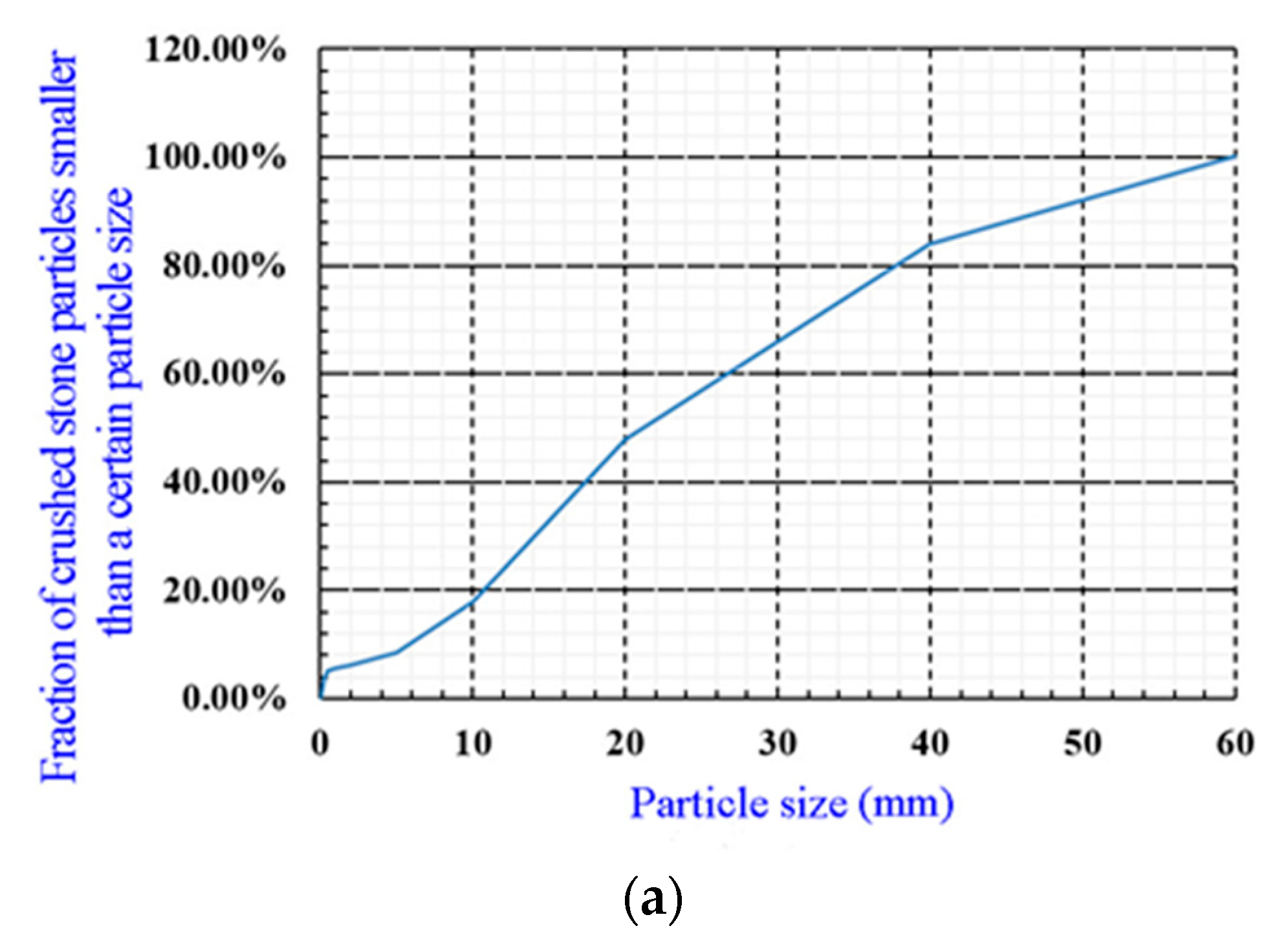
3.2. Calculation Parameters
4. Landslide Deformation and Stability Analysis under Different Conditions
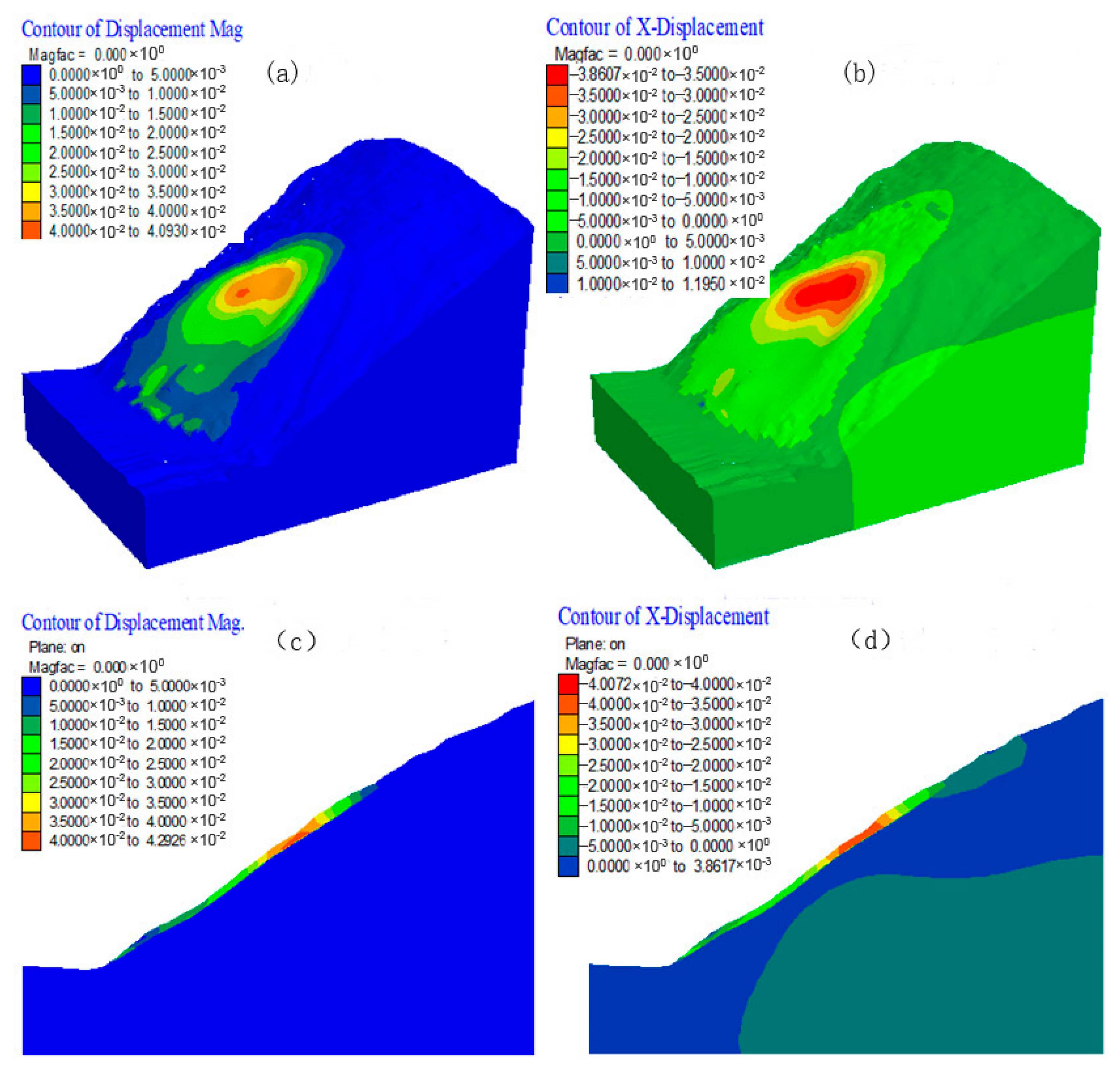
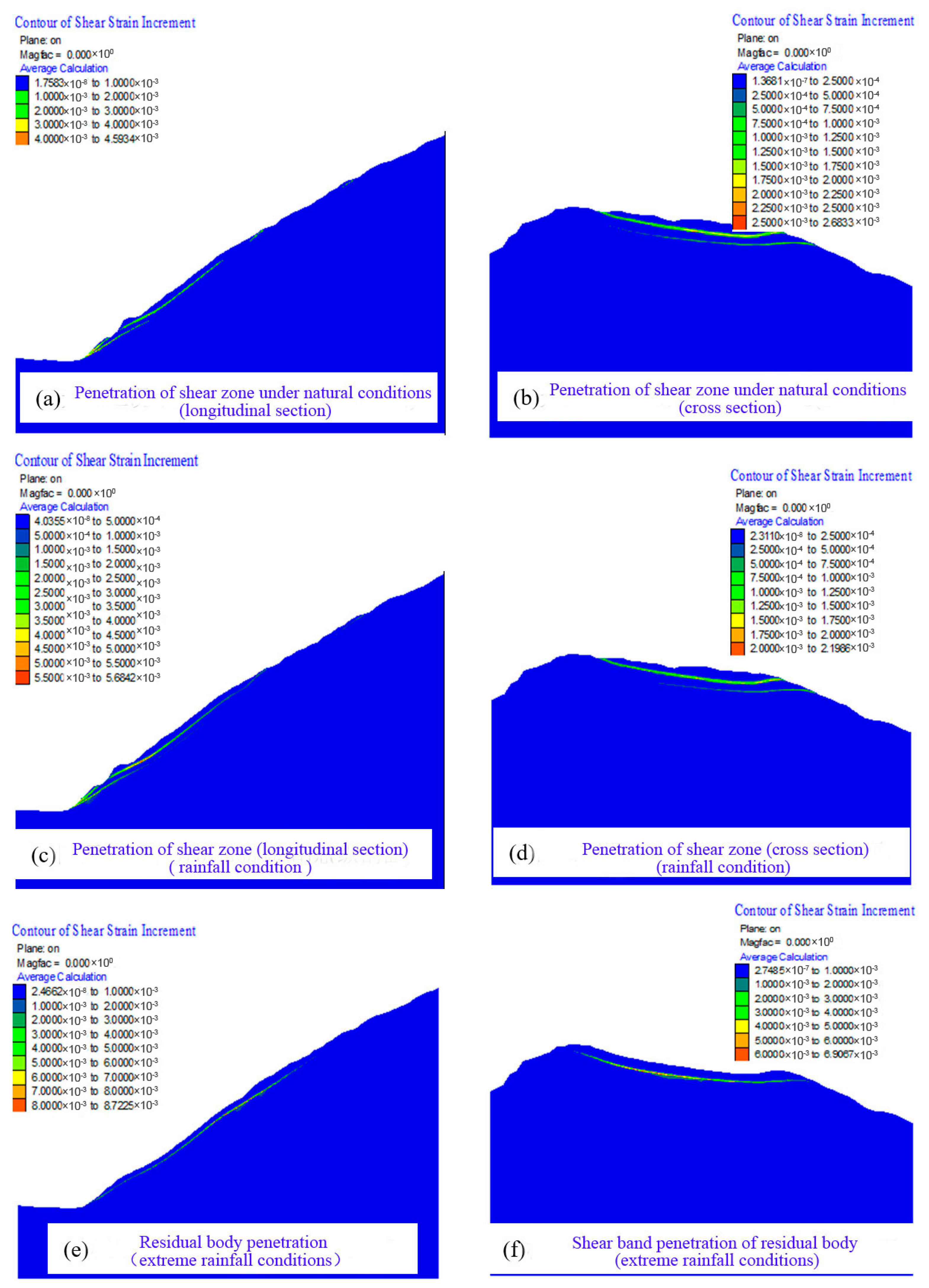
4.1. Deformation Characteristics of Landslides under Ordinary Rainfall Conditions
4.2. Deformation Characteristics of Landslides under Extremely High-Intensity Rainfall Conditions
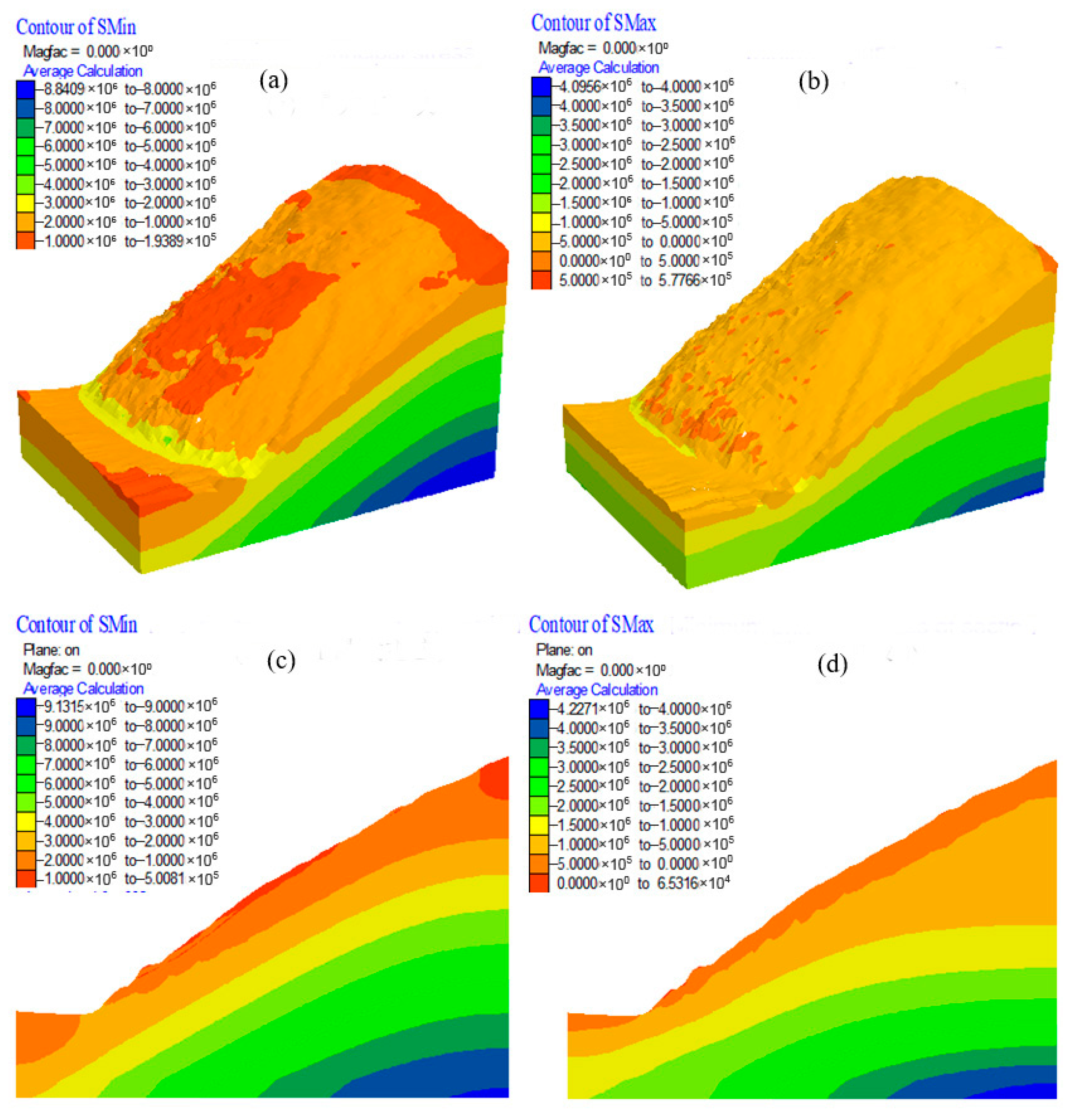
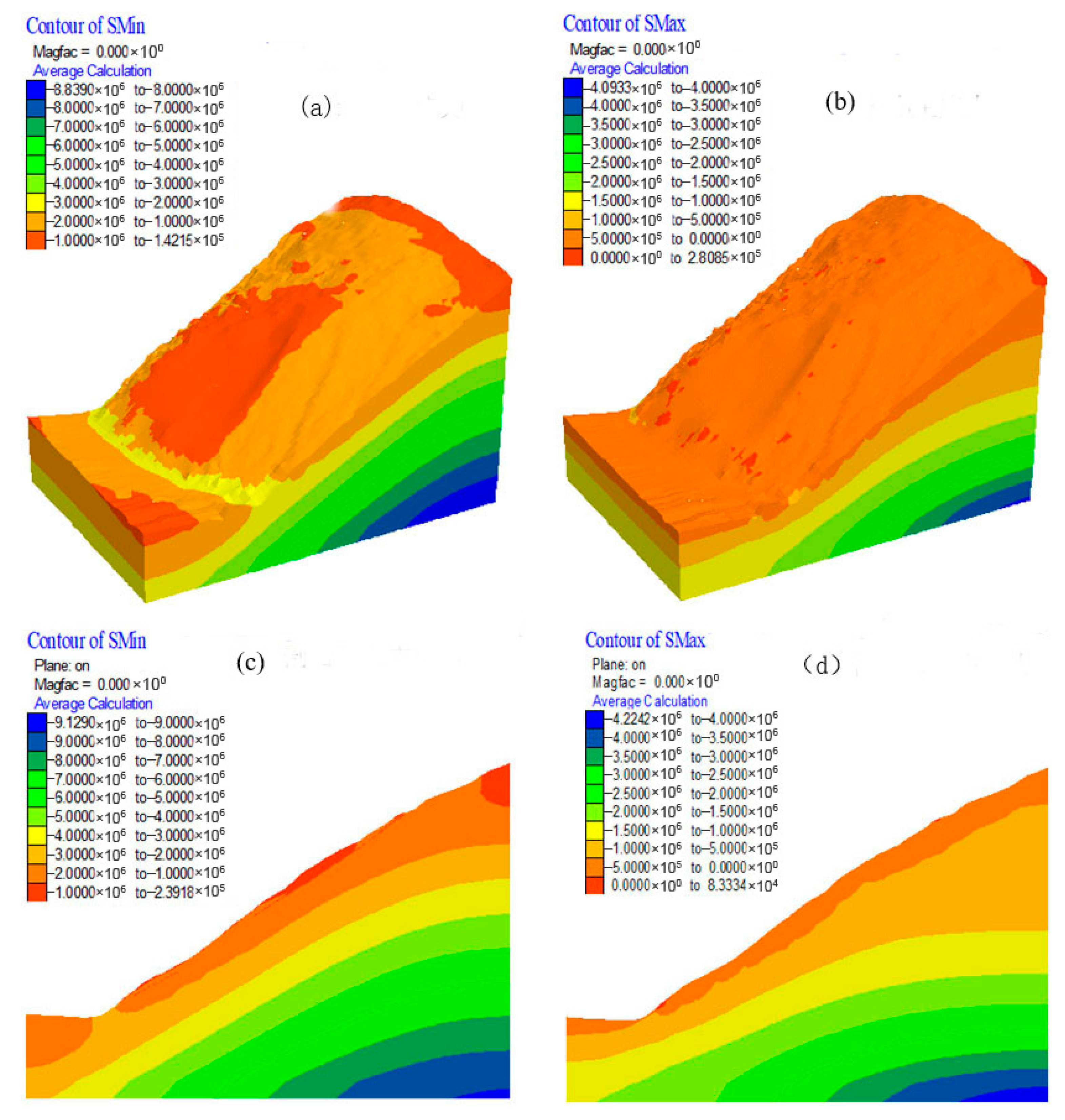
4.3. Landslide Stability Analysis
5. Landslide Dynamics Analysis under Different Conditions
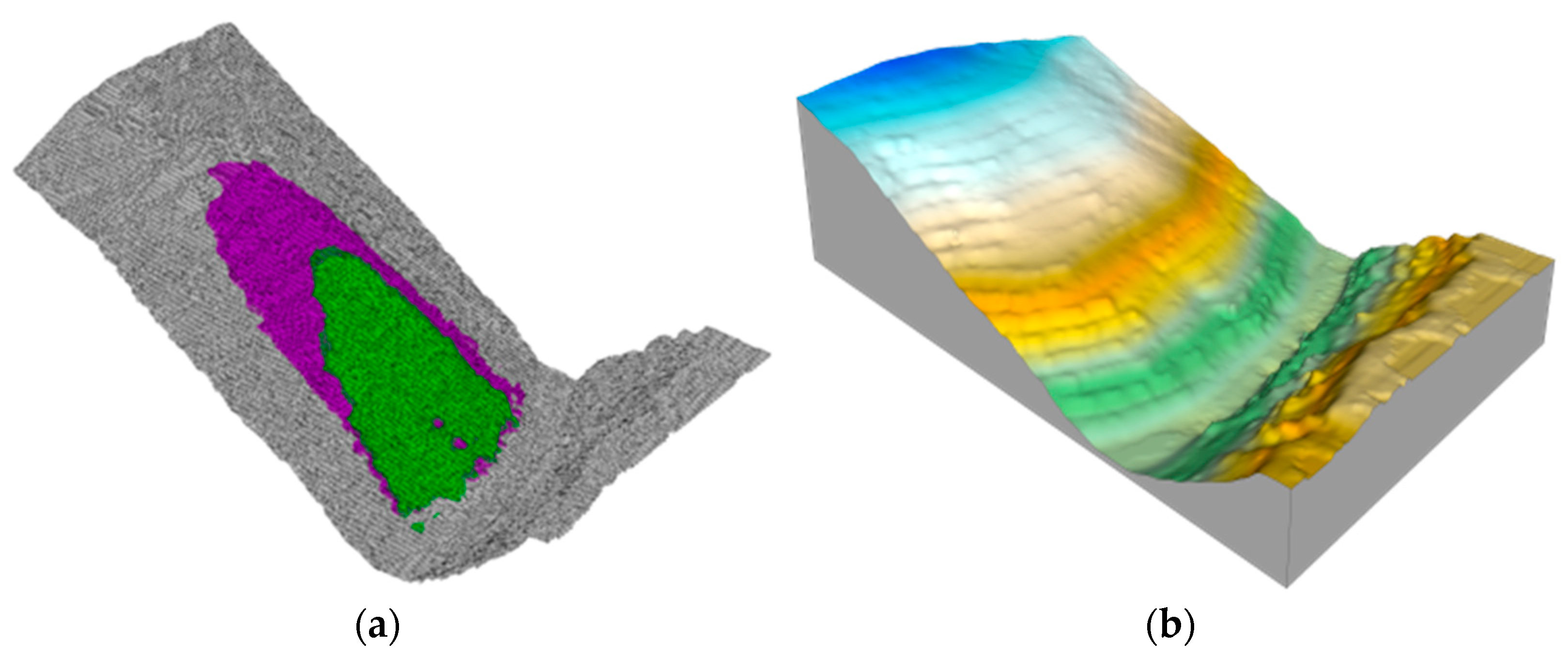
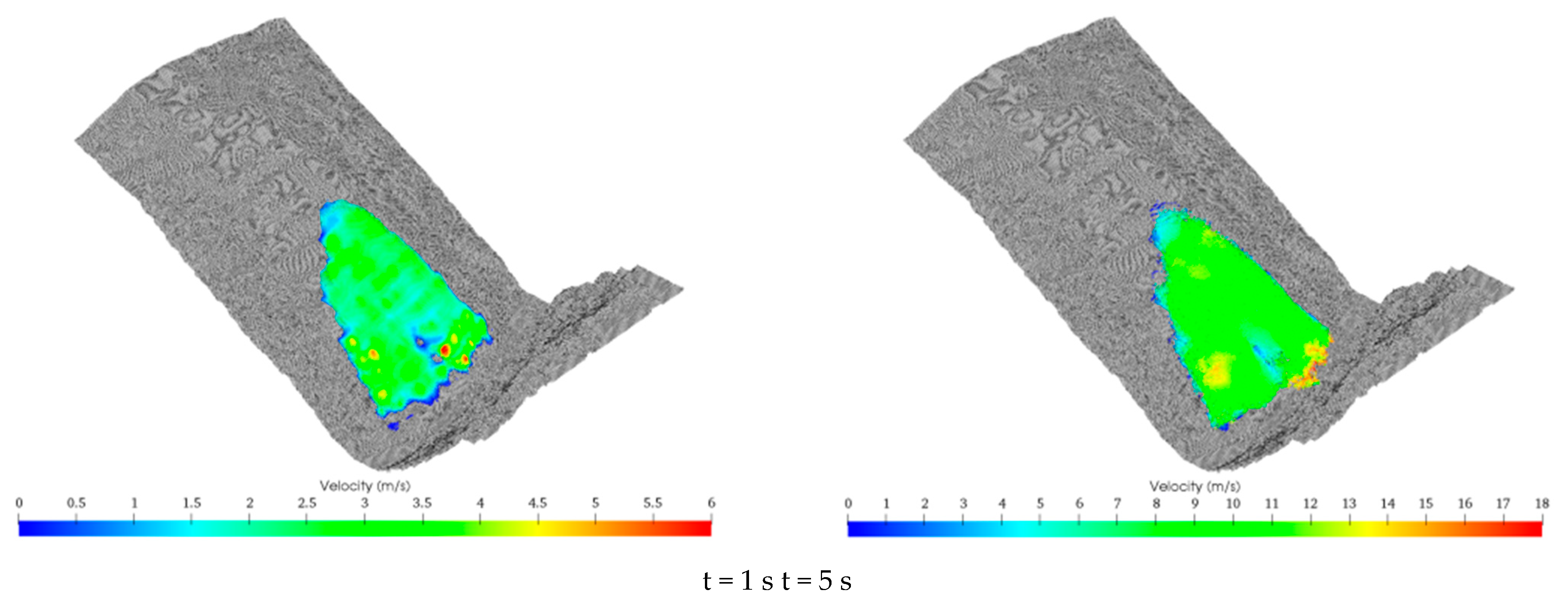
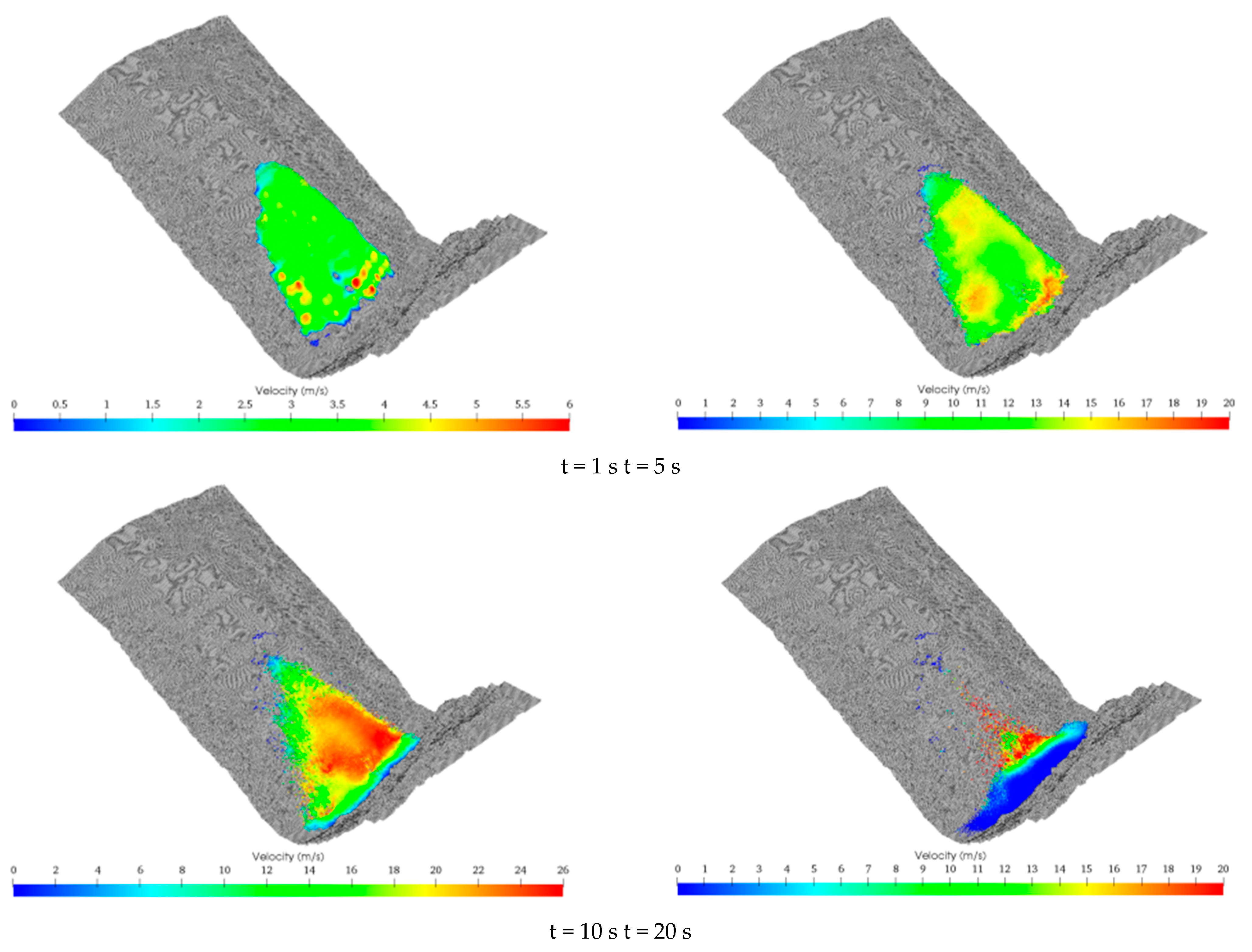
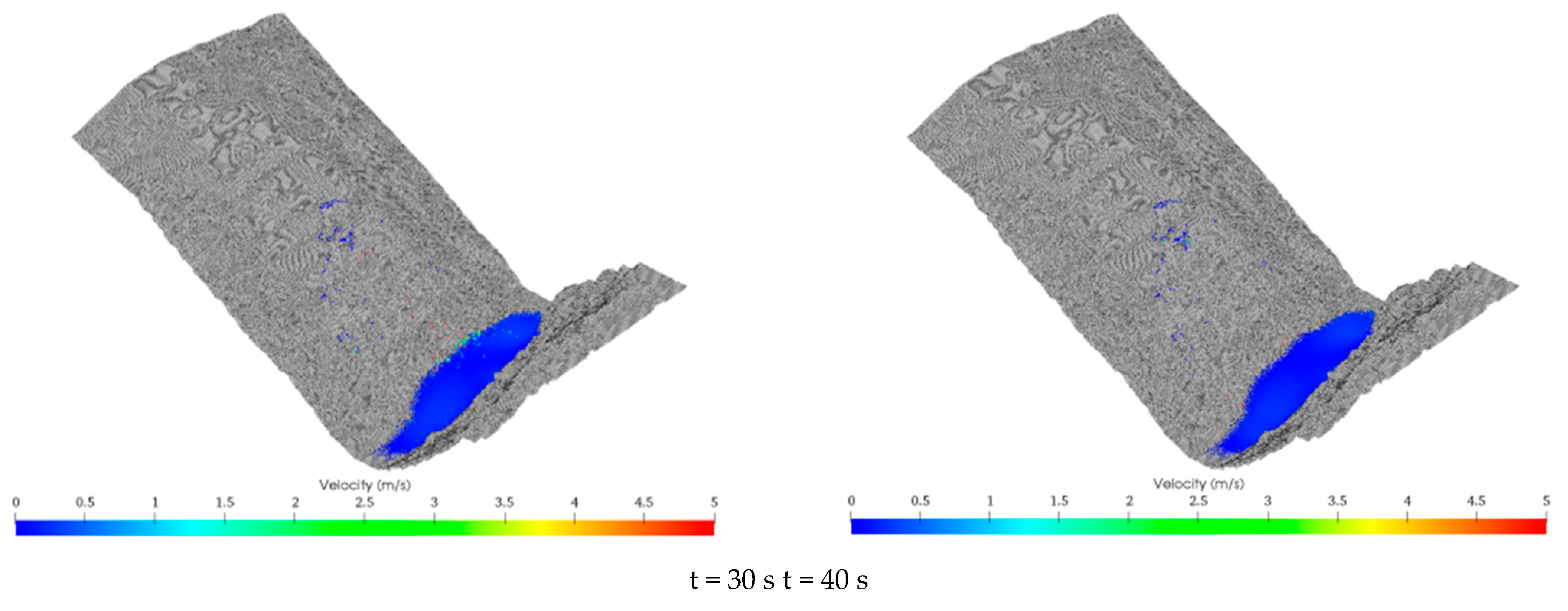
5.1. Ordinary Rainfall Conditions
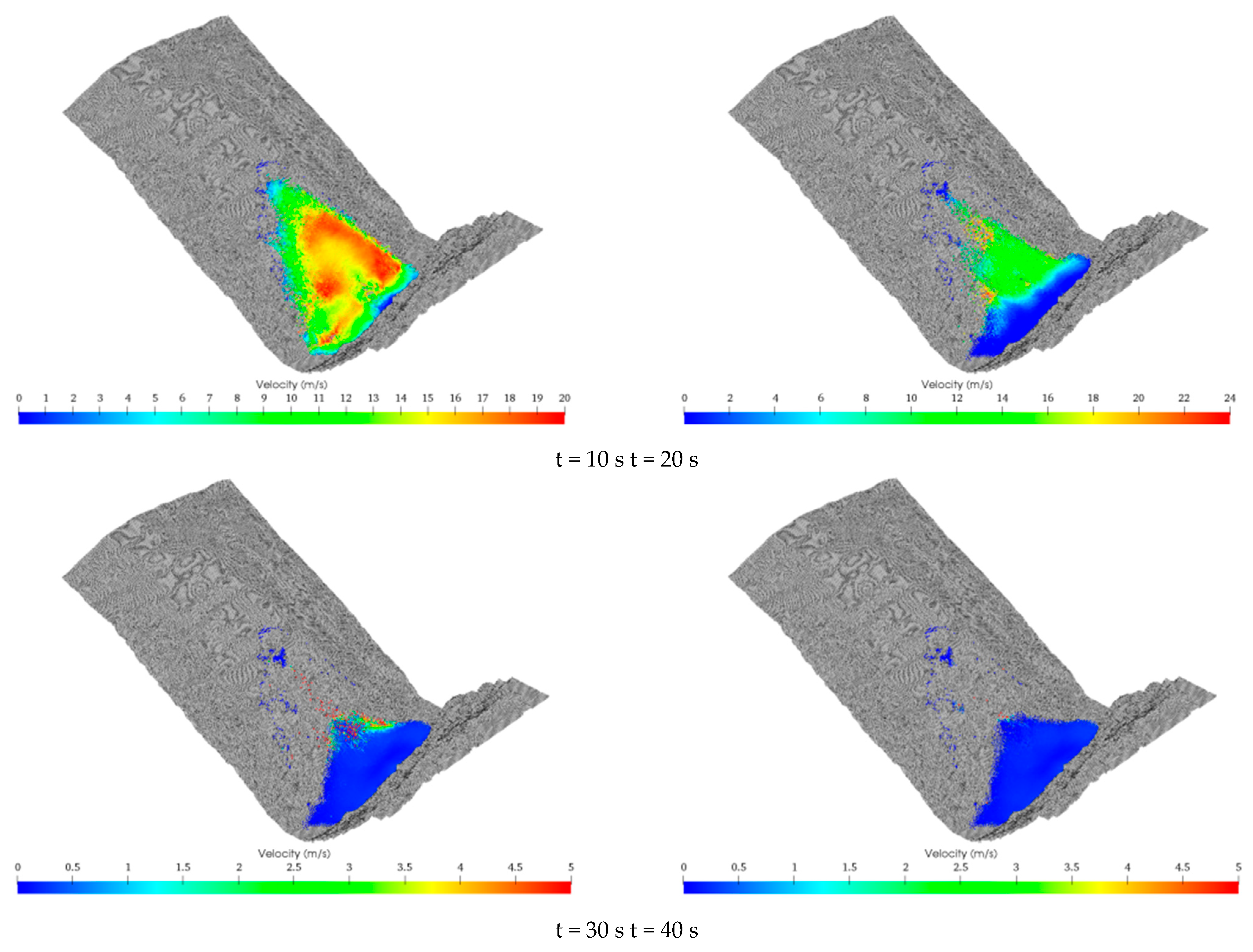
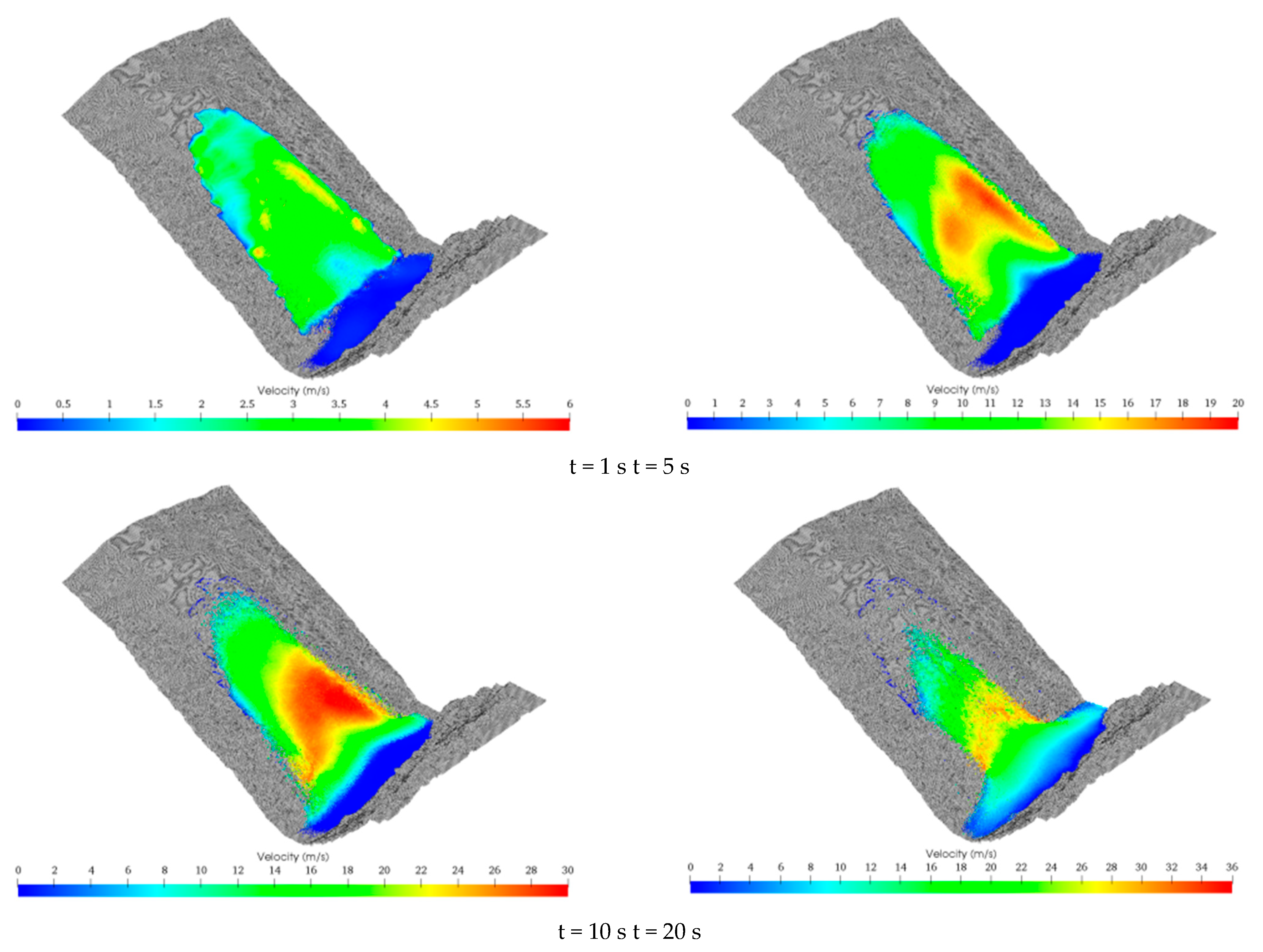
5.2. High-Intensity Rainfall Conditions
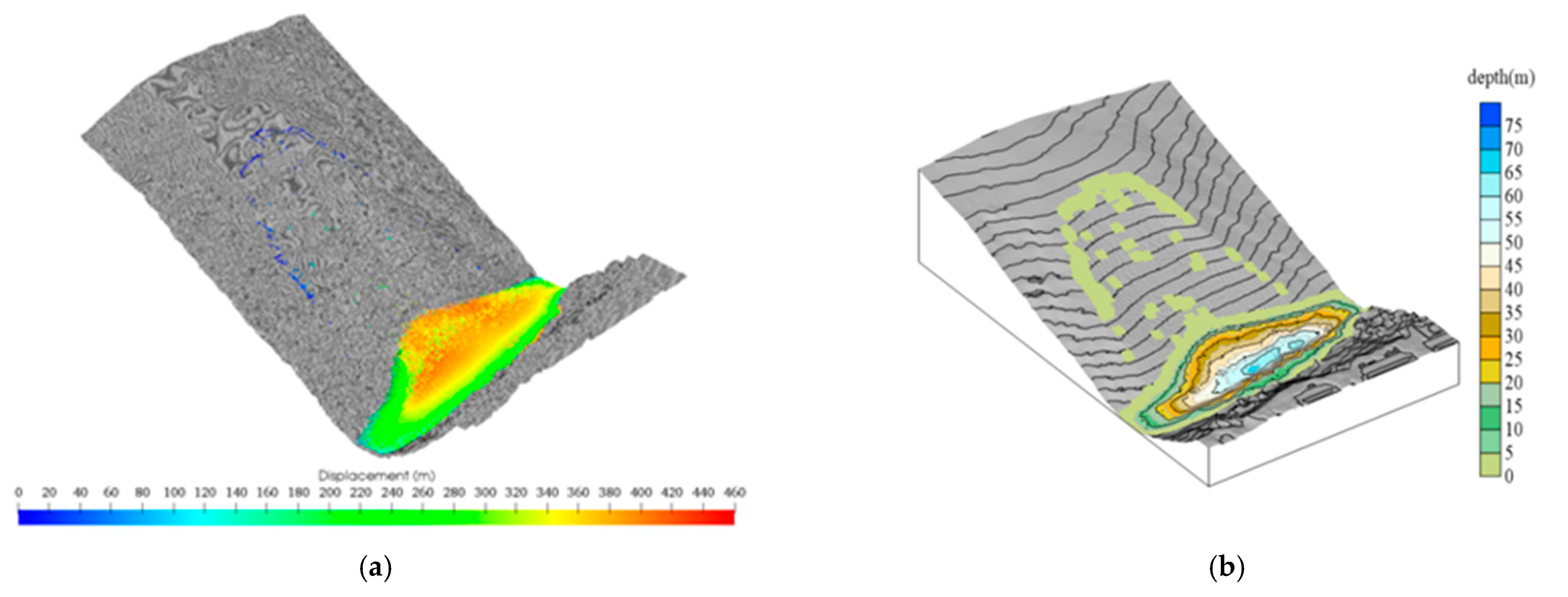
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.Q.; Cui, P.; You, Y.; Cheng, Z.L.; Khan, A.; Ye, C.Y.; Zhang, S. Dam-break risk analysis of the Attabad landslide dam in Pakistan and emergency countermeasures. Landslides 2017, 14, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifianti, Y.; Pamela Iqbal, P.; Sumaryono, H.; Omang, A.; Lestiana, H. Susceptibility Assessment of Earthquake-induced Landslides: The 2018 Palu, Sulawesi Mw 7.5 Earthquake, Indonesia. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2023, 38, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincic, M.; Gazibara, S.B.; Krkac, M.; Arbanas, S.M. Landslide susceptibility assessment of the City or Karlovac using the bivariate statistical analysis. Rud. Geol. Naft. Zb. 2022, 37, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Deep learning methods for time-dependent reliability analysis of reservoir slopes in spatially variable soils. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Shui, W.; Liu, Y.; Deng, R. Analysis of Slope Stability with Different Vegetation Types under the Influence of Rainfall. Forests 2023, 14, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, C.; Tang, L.; Gu, X.; Wang, L. Efficient time-variant reliability analysis of Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area using XGBoost and LightGBM algorithms. Gondwana Res. 2023, 123, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.E.; Schuster, R.L. The formation and failure of natural dams. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1988, 100, 1054–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Dai, F.; Long, W.; Xu, C.; Sun, J.; Cui, Z. Chronology of relict lake deposits around the Suwalong paleolandslide in the upper Jinsha River, SE Tibetan Plateau: Implications to Holocene tectonic perturbations. Geomorphology 2014, 217, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Some numerical approaches for landslide river blocking: Introduction, simulation, and discussion. Landslides 2021, 18, 3907–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhai, S.; Chen, J.; Xu, P.; Sun, X.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X. The evolution of the Samaoding paleolandslide river blocking event at the upstream reaches of the Jinsha River, Tibetan Plateau. Geomorphology 2020, 351, 106970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermini, L.; Gasagli, N. Prediction of the behaviour of landslide dams using a geomorphological dimensionless index. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Sasso, S.F.; Sole, A.; Pascale, S.; Sdao, F.; Bateman Pinzon, A.; Medina, V. Assessment methodology for the prediction of landslide dam hazard. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, C.T.; Segoni, S.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F. Geomorphic indexing of landslide dams evolution. Eng. Geol. 2016, 208, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, D.V.; Lane, P.A. Slope stability analysis by finite elements. Geotechnique 1999, 49, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, E.M.; Roth, W.H.; Drescher, A. Slope stability analysis by strength reduction. Geotechnique 1999, 49, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.H.; Goodman, R.E. 2 dimensional discontinuous deformation analysis. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 1985, 9, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.-H.; Liu, S.-G.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Fan, F.-S. Analysis of landslide-generated impulsive waves using a coupled DDA-SPH method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2016, 64, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Zheng, L.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S. Detection of contacts between three-dimensional polyhedral blocks for discontinuous deformation analysis. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2015, 78, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; Chen, C.-H. Application of DDA to simulate characteristics of the Tsaoling landslide. Comput. Geotech. 2011, 38, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingold, R.A.; Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: Theory and application to non-spherical stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 181, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucy, L.B. A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis close binary star formation. Astron. J. 1977, 82, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Fukagawa, R.; Sako, K.; Ohno, S. Lagrangian meshfree particles method (SPH) for large deformation and failure flows of geomaterial using elastic-plastic soil constitutive model. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2008, 32, 1537–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Fukagawa, R.; Sako, K.; Wells, J.C. Slope stability analysis and discontinuous slope failure simulation by elasto-plastic smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). Geotechnique 2011, 61, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Choi, C.; Ng, C.W.W. Evaluation of Critical Slip Surface in Limit Equilibrium Analysis of Slope Stability by Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Int. J. Geomech. 2019, 19, 04019032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W. Modified two-phase dilatancy SPH model for saturated sand column collapse simulations. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Jiang, Y. Study of the Dilatancy/Contraction Mechanism of Landslide Fluidization Behavior Using an Initially Saturated Granular Column Collapse Simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Lei, X.; Bi, Y.; Liu, W.; Ouyang, C. Dynamic process simulation of construction solid waste (CSW) landfill landslide based on SPH considering dilatancy effects. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; He, S.; Liu, W. Dynamic simulation of rockslide-debris flow based on an elastic-plastic framework using the SPH method. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Dai, F.; Xu, N.-W. Coupled DEM-CFD investigation on the formation of landslide dams in narrow rivers. Landslides 2017, 14, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H. Dynamic simulation of landslide dam behavior considering kinematic characteristics using a coupled DDA-SPH method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2017, 80, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; He, S.-M.; OuYang, C.-J. Dynamic process simulation with a Savage-Hutter type model for the intrusion of landslide into river. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; He, S. A two-layer model for simulating landslide dam over mobile river beds. Landslides 2016, 13, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Su, L.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, C.; Yang, T.; Lei, Z.; Li, Z. Dynamic process of a high-level landslide blocking river event in a deep valley area based on FDEM-SPH coupling approach. Eng. Geol. 2023, 319, e2020WR028802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Fourtakas, G.; Rogers, B.D.; Lombardi, D. Two-phase fully-coupled smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) model for unsaturated soils and its application to rainfall-induced slope collapse. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 151, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Rock | Bulk Modulus K (GPa) | Shear Modulus G (GPa) |
|---|---|---|
| Bed rock | 2.00 | 1.600 |
| Secondary slip zone | 0.07 | 0.062 |
| Main sliding belt | 0.07 | 0.062 |
| Landslide mass | 0.08 | 0.075 |
| Rock | Density (kg/m3) | Cohesion (MPa) | Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bed rock | 2500 | 1.2 | 35 |
| Secondary slip zone | 2200 | 0.1 | 22 |
| Main sliding belt | 2250 | 0.15 | 25 |
| Landslide mass | 2300 | 0.18 | 28 |
| Compressive Parameters of State Equation of Landslide Mass | B (GPa) | 4.00 × 107 |
| Internal friction coefficient under normal rainfall conditions | 0.404 (22°) | |
| Internal friction coefficient under high-intensity rainfall condition | 0.363 (20°) | |
| Viscosity coefficient | η (Pa·s) | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Guo, C.; Liang, H.; Sun, X.; Ma, L.; Zhu, X. River-Blocking Risk Analysis of the Bageduzhai Landslide Based on Static–Dynamic Simulation. Water 2023, 15, 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213739
Li D, Guo C, Liang H, Sun X, Ma L, Zhu X. River-Blocking Risk Analysis of the Bageduzhai Landslide Based on Static–Dynamic Simulation. Water. 2023; 15(21):3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213739
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dexin, Chengchao Guo, Heng Liang, Xinpo Sun, Liqun Ma, and Xueliang Zhu. 2023. "River-Blocking Risk Analysis of the Bageduzhai Landslide Based on Static–Dynamic Simulation" Water 15, no. 21: 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213739
APA StyleLi, D., Guo, C., Liang, H., Sun, X., Ma, L., & Zhu, X. (2023). River-Blocking Risk Analysis of the Bageduzhai Landslide Based on Static–Dynamic Simulation. Water, 15(21), 3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213739





