Abstract
The continuous investigation of water resources is essential to assess pollution risks. This study investigated a groundwater assessment in the coastal belt of Tamil Nadu’s Kovilpatti Taluk, Thoothukudi district. Twenty-one groundwater samples were collected during the pre-monsoon and post-monsoon seasons, analyzing water quality parameters, namely pH, EC, Cl−, SO42−, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3−, TH, Na2+, and K+. The Water Quality Index (WQI) was computed and it is observed that 5% of pre-monsoon and 9% of post-monsoon samples were unsuitable for drinking. SAR, MHR, RSC, %Na and Kelley’s index were used to determine irrigation suitability. Pre-monsoon shows 29% (MHR) and 71% (RSC) unsuitable, and post-monsoon shows 59% (MHR) and 9% (RSC) unsuitable. Coastal activity, urbanization, and industrialization in Kovilpatti resulted in the degradation of groundwater quality. Solving this coastal issue requires sustainable wastewater treatment and strict industrial discharge guidelines. Spatial distribution plots, Box plots, Gibbs plots, Piper plots, Wilcox plots and Correlation Matrices had similar results to the computed WQI and its physical–chemical parameters. According to the human health risk assessment, the Mooppanpatti, Illuppaiurani, and Vijayapuri regions show high health risks due to the nitrate and fluoride concentration in the groundwater. Kadambu, Melparaipatti, Therkuilandhaikulam, and Vadakku Vandanam have low levels, posing a minimal health risk.
1. Introduction
Freshwater resources have decreased recently due to urbanization and insufficient rainfall [1,2]. Groundwater is a significant source of water since the depletion of surface water and subsurface water resources have become increasingly important in many areas of India in recent years [3]. The dangers of using groundwater includes contamination and pollution. Drinking contaminated groundwater can have serious health consequences, including blue baby disorder from nitrate and fluorosis from fluoride [4]. To protect against pollution, the water resources must be constantly monitored. Understanding water management and the sustainable utilization of water resources requires monitoring groundwater quality [5]. Pollution typically refers to introducing harmful or hazardous substances into the environment on a larger scale, due to human activities. Contamination, on the other hand, is a broader term that refers to introducing undesirable elements or impurities on a smaller scale, often localized. Groundwater quality in Kovilpatti, a coastal town, has declined significantly, mainly due to coastal activities [6,7]. The local people and the environment have expressed alarm over the deterioration of the groundwater. The uncontrolled release of non-purified household and industrial effluents into nearby natural waters, notably the coastal areas, is one of the primary causes of poor groundwater quality [8]. Groundwater pollution is due to the discharge of hazardous chemicals and pollutants into the environment by industrial activities around Kovilpatti. Inappropriate waste management procedures and the careless application of chemical pesticides and fertilizers in agriculture have also worsened matters [9]. These substances may leak into the groundwater, lowering its quality and irrigation suitability and making it unfit for human consumption. Additionally, excessive groundwater withdrawal for agriculture and other uses has caused the aquifers to become contaminated with saltwater [10]. As a result, the groundwater is starting to taste salty, making it unusable for many purposes and seriously harming agricultural production [11,12]. A comprehensive strategy, including strict legislation, the monitoring of industrial discharges, better waste management systems, and the promotion of sustainable agriculture practices, is required to address the problem. To protect the groundwater resources in Kovilpatti and provide a sustainable and healthy environment for its citizens, cooperation between the government, industries, and neighborhood groups is crucial [13,14].
The recharge area beneath determines the quality of the groundwater. The seasonal and regional variations in groundwater quality are controlled by these geochemical processes [15,16,17]. The primary cause of groundwater fluoride pollution is the weathering and leaching of rocks. On the other hand, agricultural practices such the use of pesticides are the main cause of nitrate contamination in groundwater [18]. One instrument for evaluating the quality of groundwater and surface water is the Water Quality Index (WQI). Numerous studies have used a range of indicators, such as sodium percentage (%Na+), sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), residual sodium carbonate (RSC), and magnesium hazard ratio (MHR), to determine whether water is suitable for irrigation [19,20,21]. When evaluating data on water quality, GIS is a crucial tool for comprehending the geographical distribution of contaminants and changes in water quality over time [22]. Innovations in involving local communities, decision-makers, and stakeholders in the groundwater management process help in ensuring sustainable resource use and minimizing conflicts [23,24,25,26,27,28].
The research scope encompasses the cotton and matchstick production sectors. Contamination sources in this study area are typically divided into organic and inorganic categories. The chemical waste emanating from industrial discharge, particularly substances such as red phosphorous and nitrogen, poses significant health risks to the local population, manifesting as fluorosis, cancer, and respiratory complications, among others. Residents in close proximity to these industries frequently suffer from symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain due to groundwater pollution, which primarily results from the release of red phosphorus by matchstick manufacturers and other pollution sources.
Moreover, the infiltration of chemical contaminants into groundwater from rainwater percolating through rock layers adds another layer of health concerns. As a result, the need for effective groundwater treatment in Kovilpatti before it is considered safe for drinking becomes paramount [29]. It is worth noting that this study marks the first comprehensive exploration of these severe issues within the study area and southern Tamil Nadu. The objective of this investigation is to assess the suitability of groundwater in Kovilpatti taluk, Thoothukudi district, for both drinking and industrial purposes. The primary goals of the study include: 1. Conducting an initial assessment and interpretation of the groundwater quality in Kovilpatti Taluk. 2. Determining the suitability of the groundwater for drinking and irrigation. 3. Employing spatial maps to identify areas at risk of contamination. The study involves an analysis of water quality in comparison to WHO and BIS standards. Additionally, it assesses the suitability for irrigation using parameters such as RSC, SAR, Na%, KR, PI, MHR, and PS. The study also seeks to identify the water type and composition through the use of Chandha plots, Piper timber plots, and Gibbs plots. Ultimately, the primary goal is to identify sources of pollution.
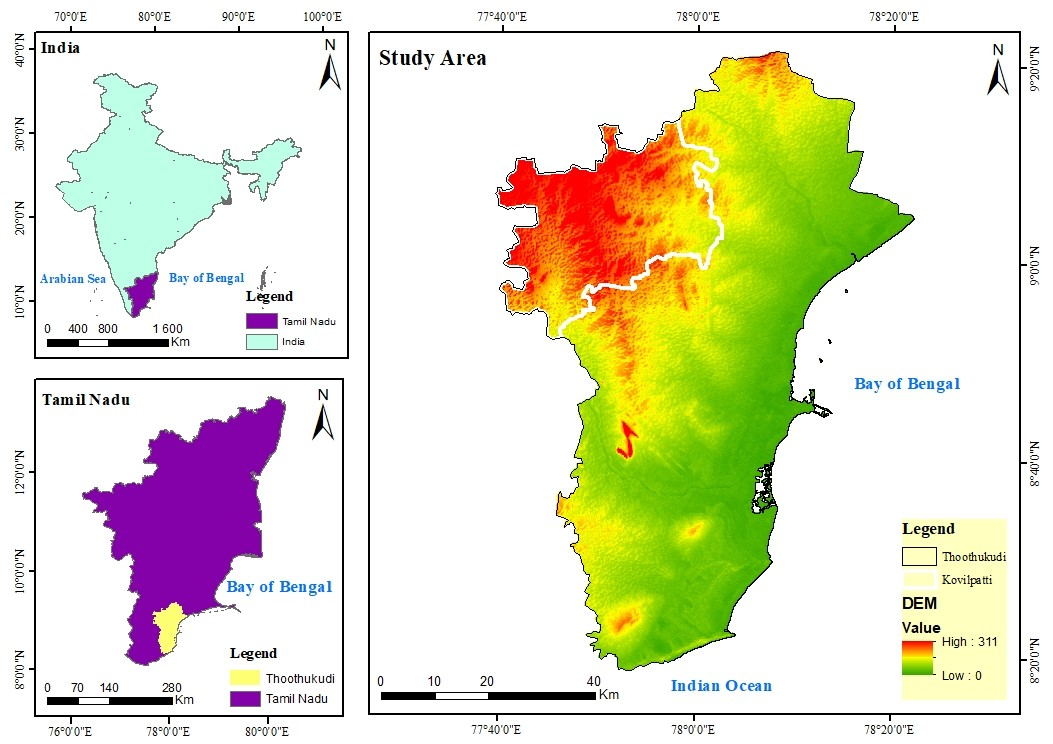
2. Study Area
The Tuticorin district is situated in Tamil Nadu’s southernmost region. Eight talukas make up the district’s administrative division. Kovilpatti, the headquarter of the talukas, was chosen amongst the eight talukas for the study and the sample was collected from different locations in the Kovilpatti region. The taluk’s population density is about 390 people per square kilometer, and the total area was about 823.37 Sq.km. Kovilpatti Taluk has a tropical climate with 761 mm of annual precipitation. In this study area, the average annual temperature is 28.8 °C. There are no larger bodies of water in the Tuticorin district, and the Tamirabarani river provides water for all essential uses, including irrigation.
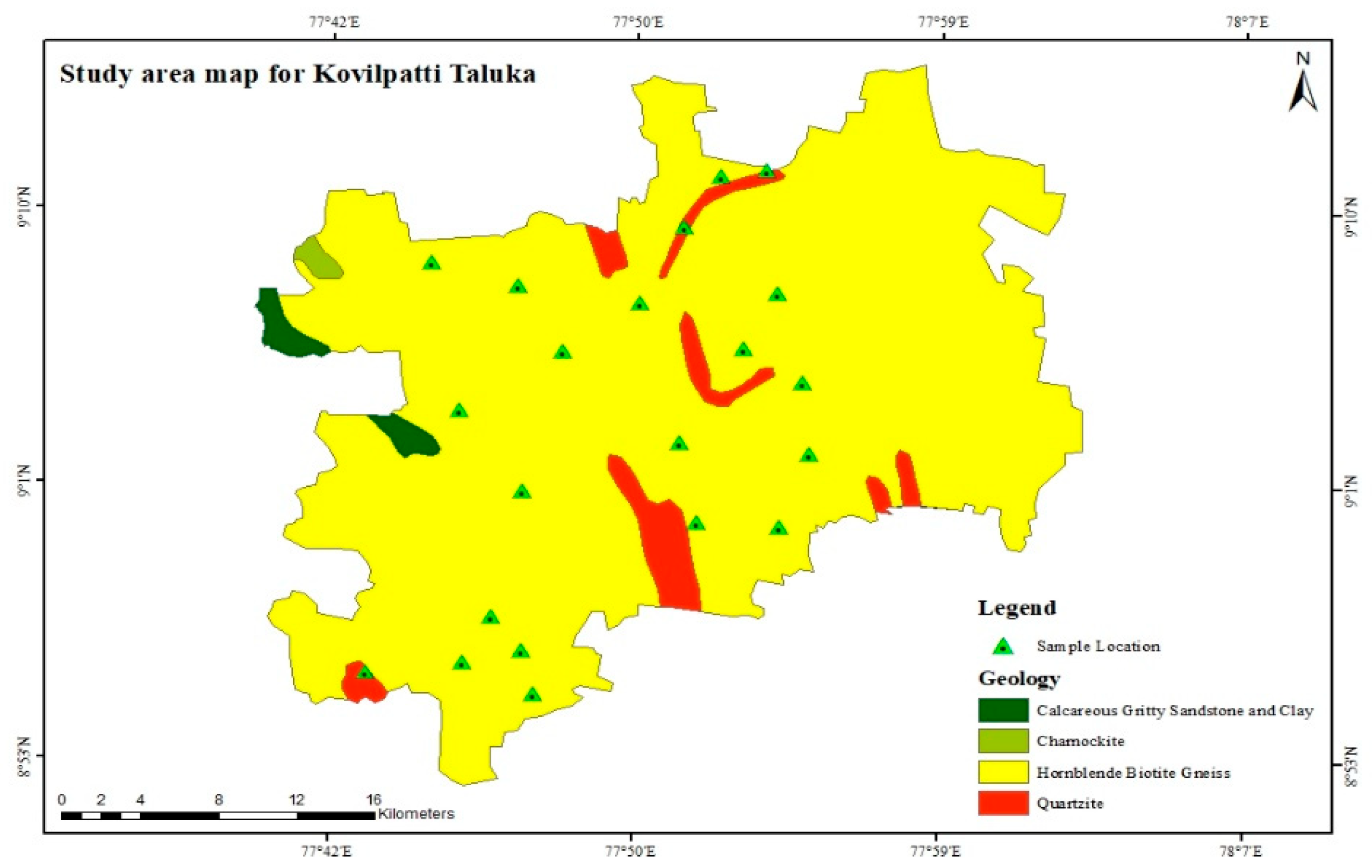
Water is supplied from public wells and private boreholes to meet the needs of people, industries, and irrigation activity. Based on the local recharge mode, the groundwater drawn up through each borehole will have unique properties. According to their concentration values, physical and chemical characteristics are typically used to categorize groundwater. Direct groundwater consumption is no longer advised. Because of the untreated introduction of contaminants from industries to the ground, water contains cations and anions in varying concentrations above the recommended limits. Most of the research region is covered by hornblende biotite gneiss geology features. Calcareous gritty sandstone and clay, charnockite, and quartzite are some of the features covered.
Over time, changes in the locality’s water quality standards over a region contribute to the emergence of new diseases. These kinds of activities are also made easier by the geological conditions of the soil there. In this taluk, there were almost 82 villages. To learn about the features of the groundwater, we framed a grid measuring 6 × 6 sq. Km and fixed 21 stations as our sampling points. Even though there are many small, medium, and giant tanks in this area, they are essentially dry for around 6 to 7 months of the year, and starting in March, farmers mostly rely on accessible groundwater resources. On a gross basis, just 15% of the area seeded is watered under tanks. Murappanad and Srivaikundam have various canal networks along the Tamiraparani river. The groundwater beneath the irrigation tanks and along riverbanks has recently been tapped by farmers using big-diameter dugwells and dug-cum bore wells. The location map for the chosen research region, Kovilpatti Taluk, is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Study area location map of Kovilpatti Taluk.
The geographical characteristics and climate of the area have an impact on its hydrological formation. The Thamirabarani river, which runs through the area and has its source in the Western Ghats, is the taluk’s primary water source. The hydrology of Kovilpatti is also influenced by the numerous tiny rivers, streams, and irrigation tanks there. The region has a tropical climate, with rainfall primarily coming from the southwest and northeast monsoons. Groundwater is essential for maintaining agriculture and providing the needs of the people, but overuse has raised issues with groundwater quality and depletion.
In Kovilpatti Taluk, sulfate (SO42−) sources can originate from both natural and anthropogenic (human-induced) processes. Naturally, sulfate can be present in groundwater and surface water due to the weathering of sulfur minerals, volcanic emissions, and atmospheric deposition. Additionally, organic matter decay in soils can release sulfates. Anthropogenic sources may include industrial activities, especially those related to mining and metal processing, as well as agricultural practices involving sulfur-containing fertilizers and wastewater discharge. Monitoring and managing sulfate sources are essential to ensure water quality and prevent environmental contamination in Kovilpatti Taluk.
3. Materials and Methods
Pre-monsoon (July to December 2018) and post-monsoon (January to June 2018) groundwater samples were taken from 21 stations using hand pumps whose depths ranged between 150 and 100 feet below the ground level (bgl). Figure 2 shows the sampling location of the study area of Kovilpatti Taluk.

Figure 2.
Location map of the samples in the study area of Kovilpatti Taluk.
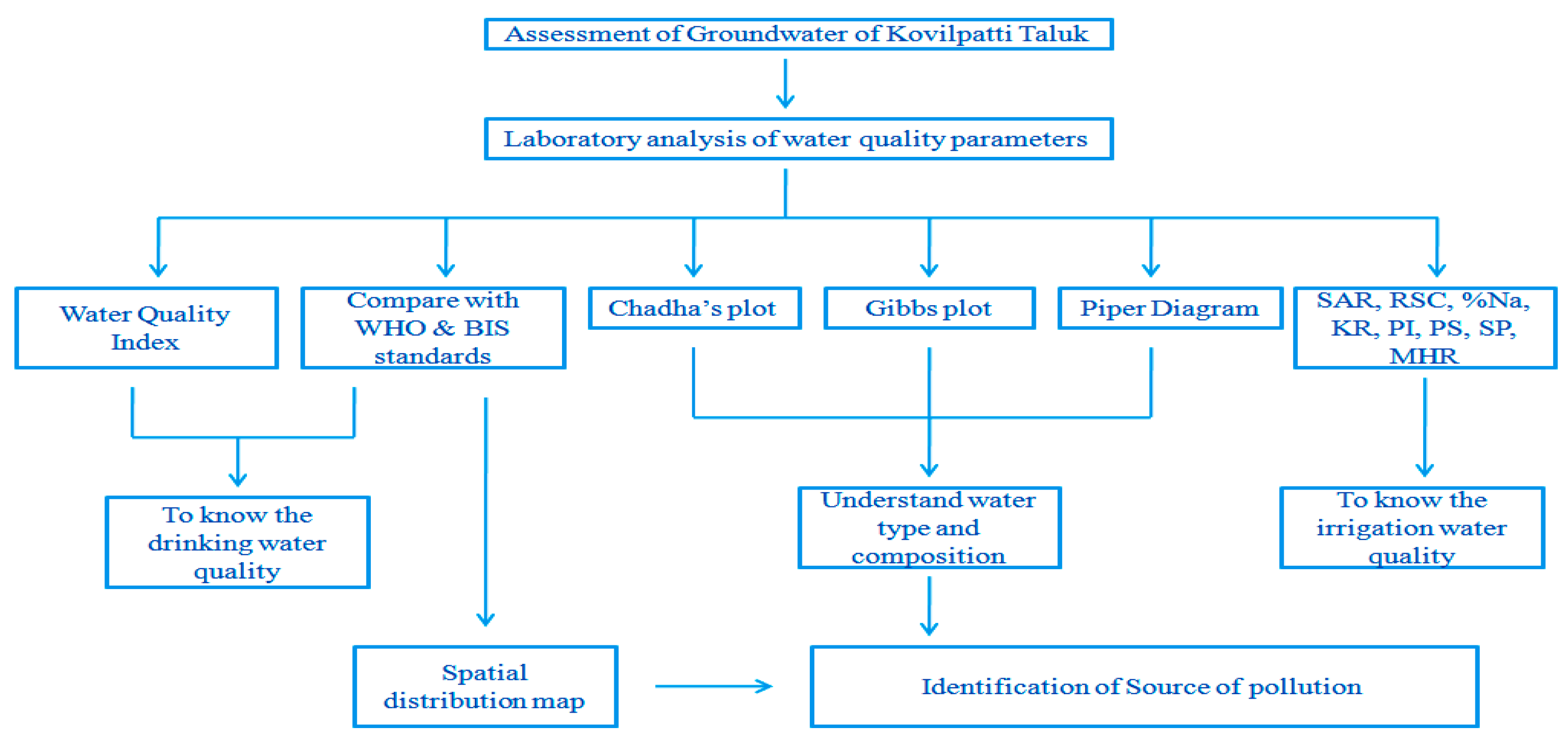
High-density polyethene (HDPE) bottles measuring 1 L were used to collect the samples. Specific parameters such as pH, TDS, and EC were measured using standard portable digital meters (EC/ORP meter, pH meter, TDS meter) in the station. Following the recommended protocol by APHA, the samples were analyzed to determine the concentration of chloride (Cl−), alkalinity (CO3−, HCO3−), and total hardness (Ca2+, Mg2+). Sulphate was determined using a spectrophotometer and barium chloride as an additive. Sodium was examined using a flame photometer. Figure 3 displays the flowchart for this investigation.
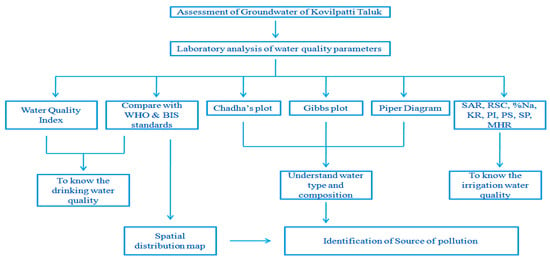
Figure 3.
The entire methodology flow chart for this research region for Kovilpatti Taluk.
3.1. Water Quality Index
The WQI is a numerical expression for characterizing water quality that is cumulatively calculated and based on measuring several water quality parameters. The WQI measures the overall effect of numerous water quality metrics and considers whether surface and groundwater suit their intended uses. The Water Quality Index is a measure used to classify surface and groundwater pollution levels. Based on WQI scores of 50, 50–100, 100–200, 200–300, and >300, water samples are categorized as too good, good, bad, extremely bad, and no use for drinking, respectively [30,31]. The WQI is calculated using the procedures below:
Step 1: Calculation of relative weight by using Equation (1).
where Wi is the relative weight of each parameter, wi is the parameter’s weight in terms of wi, and n is the parameters in their whole.
Step 2: Calculation of the Qi value by using Equation (2).
where Qi stands for quality rating, Si is the WHO water quality standard, and Ci is the concentration of each parameter (mg/L).
Step 3: Equation (3) was then used to derive the Water Quality Index.
3.2. Irrigation Water Quality
The chemical composition, or the mineral composition of irrigation water, is the primary determinant of its quality. Certain physical and biological traits, such as turbidity and the presence of algae, bacteria, or viruses, can also affect the appropriateness of water which could be used for irrigation. Relative to Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, the concentration of the bicarbonate (HCO3−) and carbonate (CO32−) anions is in residual sodium carbonates (RSC). Excessive amounts of chemicals render plants poisonous or disturb their ionic equilibrium. The metrics of irrigation water quality were assessed using the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR), residual sodium carbonate (RSC) [7], sodium percentage [32], Kelly’s ratio [12], and magnesium hazard ratio (MHR) [33]. Each value was expressed as mg/L.
3.3. Spatial Analysis
Kriging interpolation can be used to display groundwater quality data spatially. The predicted values come from the weighted averages of the neighboring sample locations. This spatial interpolation worked when the sample points were dense enough to capture the regional variance [34,35]. For making kriging software such as Excel (version 2016) and ArcGIS, the data list could be prepared in an Excel format before using the ArcGIS software 10.8 version, using the ARC GIS toolbar, to run the data and process the interpolation.
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA)
An HHRA is studied to determine the effects of water quality characteristics on health, and it is looked at in both adults and children. Pollutants can enter the human body by ingestion, contact with the skin, or inhalation. The current investigation examined the cutaneous and ingested modes of transformation. The average daily exposure dose for ingestion and cutaneous absorption by water was calculated using Equations (9)–(13).
ADDing and ADDder are the daily exposure doses to water (in mg/kg/day) by ingesting and dermal activity; Cw is the actual concentration of the water samples in mg/L; ED is the exposure duration in years; IR is the ingestion rate (L/day); EF is the exposure frequency (day/year); BW stands for body weight on average (kg); AT denotes the typical time (days). (Table 1 reveals the standard values for the calculation of HI). The average skin surface area in square centimeters that is exposed to water is SA; Kp is the water’s coefficient for dermal activity and is 0.001 for Na2+, F−, NO3−, and Cl; ET stands for exposure time (day/hour); the water quality parameters’ reference dosage, or RfD, is measured in mg/kg/day (F− is 0.06 and NO3− is 1.6); the Hazard Index is also known as HI; and the Hazard Quotient is also known as HQ ingestion and dermal.

Table 1.
Standard values for the calculation of HI.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Quality of Water for Drinking
The WHO created international guidelines and customized them for regional use, including drinking water quality criteria. For the pre-monsoon (July to September 2018) and post-monsoon (January to March 2018) seasons, the groundwater quality metrics are statistically summarized in Table 2. Table 3 displays the percentage of samples that are above the allowable limit. The current analysis indicates that the study region’s groundwater has an acidic pH (6.4–8.3) in the post-monsoon samples but is slightly alkaline (7.5–8.7) in the pre-monsoon samples. From the pre-monsoon group, one sample (Therku Ilandhaikulam) had a pH value of 8.7, beyond the upper acceptable pH limit (8.5). In contrast, from the post-monsoon group, one sample (Uttuppatti) had a pH value of 6.4, above the lower permissible pH limit (6.5). Pre-monsoon TDS values range from 103 to 2020 mg/L in the analyzed water samples, whereas post-monsoon TDS levels range from 70 to 2240 mg/L. The standards stipulate that TDS may not exceed 1000 ppm [2]. Oxidation-reduction potential, with the abbreviation ORP, refers to evaluating a lakes or river’s capacity to remove pollutants or decompose wastes as animal and plant remains. The amount of oxygen in the water is high when the ORP value is high.

Table 2.
Kovilpatti Taluk’s physiological chemical parameters’ minimum, maximum, and average values.

Table 3.
Percentage of samples that go over the allowed limit.
The TDS permitted limit was exceeded by 24% of the samples collected before the monsoon and 19% of the samples collected after it. The pre-monsoon and post-monsoon measurements of Attikulam’s TDS levels were higher, at 2020 and 2240 ppm, respectively. The ranges for calcium concentrations (PRM and POM) are 27 to 139 mg/L and 32 to 155 mg/L, respectively. Following the calcium ion in both sessions, the concentrations of the magnesium cation range from 5 to 98 mg/L (pre-monsoon) and 7 to 129 mg/L (post-monsoon). Ca2+ cannot be more than 75 mg/L, and Mg2+ cannot be more than 30 mg/L.
In both seasons, the levels of Ca2+ and Mg2+ are higher than these allowed thresholds. Na, which dominates in the examined samples and is found in amounts ranging from 5 to 95 mg/L (pre-monsoon) and 3 to 98 mg/L (post-monsoon), comes after Ca2+ and Mg2+. The principal cations in the groundwater from the study area are in the following order: Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Na+ > K+. The calcium and magnesium ions have reached levels beyond the permitted limit due to the leaching of limestone, dolomites, gypsum, and anhydrite, while the calcium ions may have come from the cation exchange process.
The attentiveness of Cl−, SO42−, and HCO3− varies from 30 to 1684 mg/L, 20 to 547 mg/L, and 85 to 1484 mg/L, respectively, during the pre-monsoon. Cl−, SO42−, and HCO3− concentrations during the post-monsoon vary from 6 to 1853 mg/L, 15 to 584 mg/L, and 24 to 720 mg/L, respectively. Chloride and sulfate concentrations exceed the permitted limit of 200 mg/L in both seasons. HCO3 − > SO42− > Cl− is the preferred order for anion concentration during the pre-monsoon, and Cl− > HCO3− > SO42− is the preferred order post-monsoon. The subsurface leaching of rocks may cause a higher chloride concentration during the pre-monsoon. The physiological chemical parameters of Kovilpatti Taluk show minimum, maximum, and average values in Table 3.
4.2. Water Quality Index
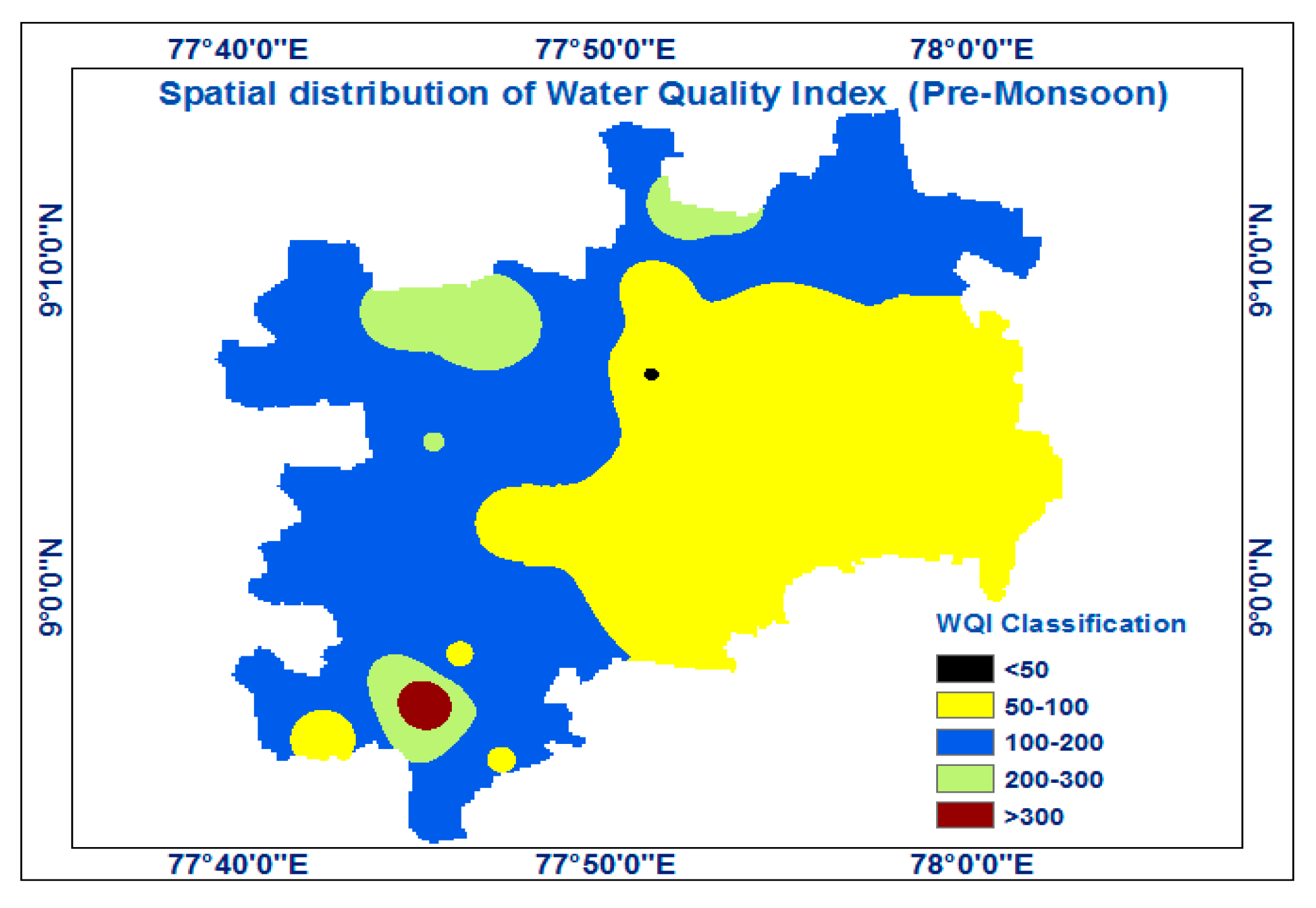
The pre-monsoon WQI values range from 37 to 212, while the post-monsoon WQI values range from 21 to 224. The WQI rating places 10% of the pre-monsoon groundwater samples in the excellent category and 52% in the good water category for drinking. Just 5% of the groundwater samples were deemed hazardous for ingestion, as opposed to 23% of the samples having terrible water quality and 10% having poor water quality. The post-monsoon seasons saw a drop in water quality from outstanding to sound, from good to awful to extremely poor. The percentages for too good, terrible, extremely bad, and no use for drinking water quality are 10%, 29%, 23%, 29%, and 9%, respectively.
4.2.1. Groundwater Suitability Assessment for Irrigation
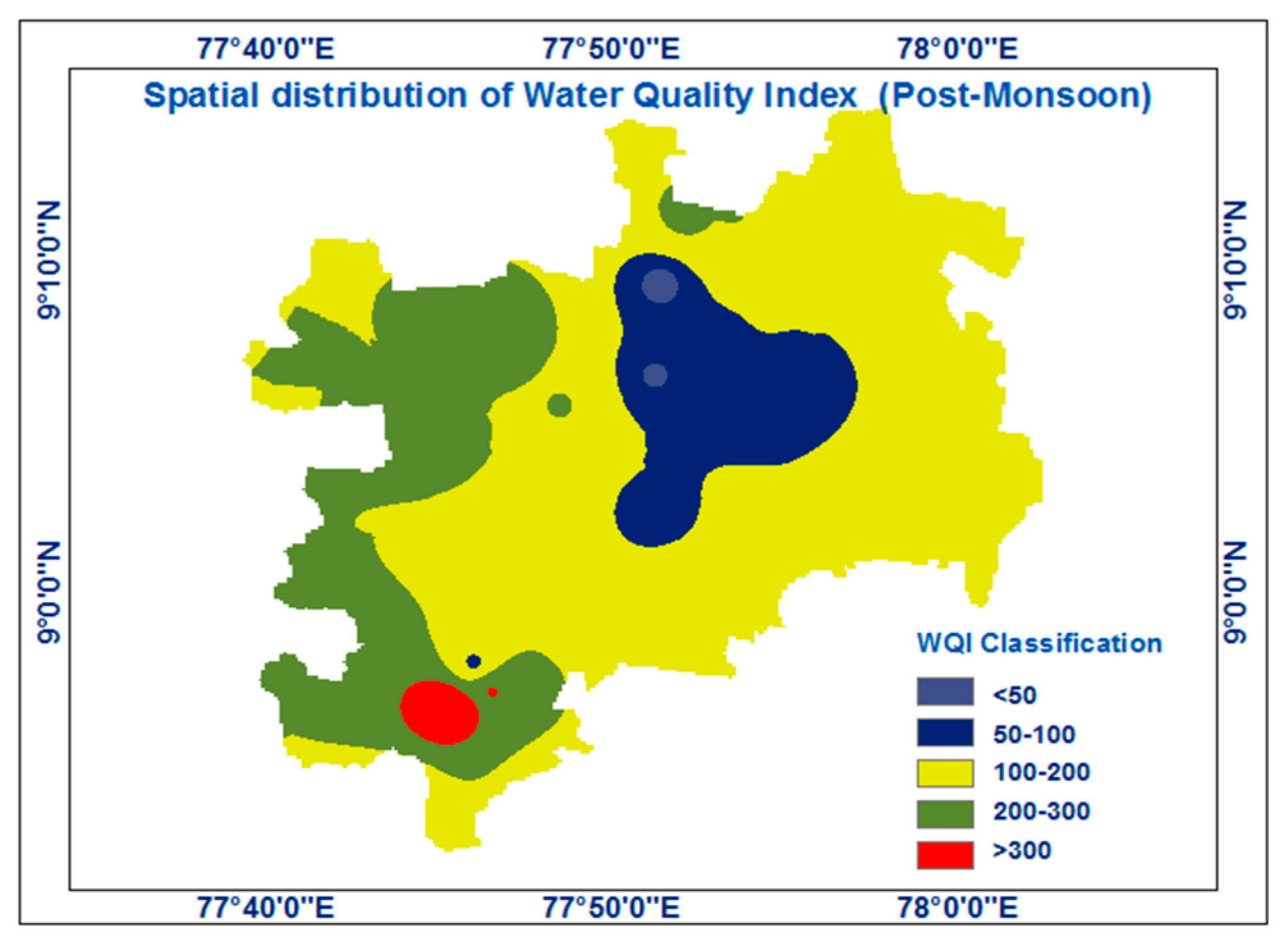
The suitability of the water for agriculture was assessed using the SAR, Na percentage, RSC, and MHR. The categorization of irrigation water quality is shown in Table 4 and Table 5. Because of rain in the post-monsoon season, most irrigation suitability measurements had higher values during the pre-monsoon seasons. Figure 4 and Figure 5 exhibits the spatial distribution of the water quality index for the pre- and post-monsoon seasons.

Table 4.
Irrigation water quality parameters in Kovilpatti Taluk.

Table 5.
Classification of Kovilpatti Taluk’s irrigation water quality parameters.

Figure 4.
The geographic distribution of the Water Quality Index (pre-monsoon).
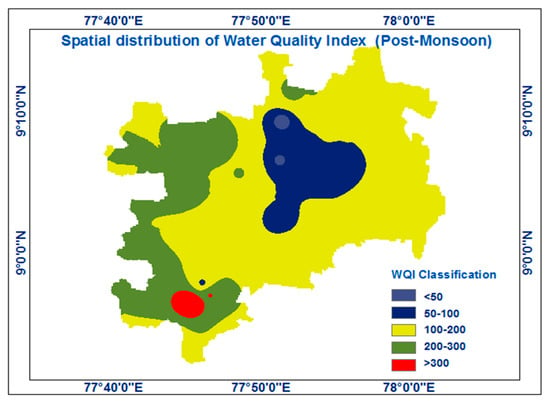
Figure 5.
The geographic distribution of the Water Quality Index (post-monsoon).
4.2.2. Sodium Absorption Ratio
Groundwater with high levels of salt causes alkaline soil. Sodium and salinity dangers are significant factors to consider when evaluating the groundwater utilized for irrigation. The SAR ratio is expressed in the Equation (4). The soil structure deteriorates when water with a high SAR is used continuously. One can use the sodium adsorption ratio in water to determine the cation-exchange processes in soil. According to the Sodium Adsorption Ratio (SAR), groundwater could be described as very friendly (10), excellent (10–18), confused (18–26), and not suitable (>26) [26,27,28,36]. The SAR in samples from Kovilpatti Taluk ranges from 0.1 to 1.6 mg/L and from 0.1 to 1.5 mg/L, with average values of 0.6 and 0.5 mg/L in the pre- and post-monsoon seasons, respectively. The Sodium Absorption Ratio results for all samples in Kovilpatti Taluk are good.
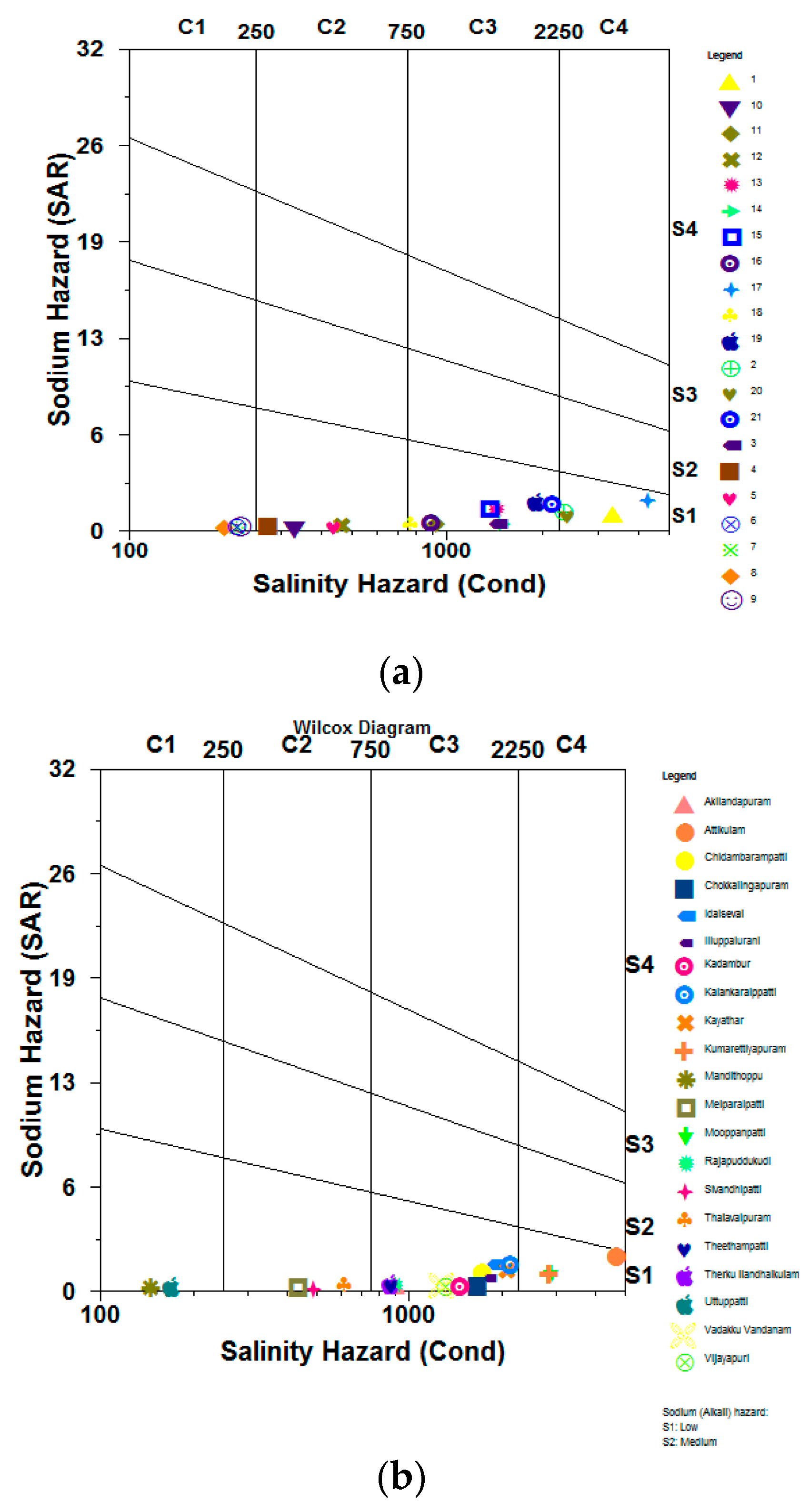
The salinity hazard parameter (EC), with a range of 198 to 4303 μS/cm and an average value of 1290 μS/cm, is used in the Wilcox diagram. According to the Wilcox diagram, 67% of the groundwater samples collected during the monsoon are labelled as C3S1 water, which denotes dangerous water with a high salinity and low sodium content. Almost 14% of the groundwater samples in the research region were given the C2S1 classification, which denotes medium salinity and low sodium risks. Without any further salinity concern, this water may be used for irrigation. Pre-monsoon groundwater samples classified as C3S1 had a 47% risk of excessive salinity and low sodium. In the research region, almost 19% of the groundwater samples were classified as C2S1, which means the water is acceptable for irrigation and has a medium salinity and low sodium danger.
4.2.3. Sodium Percent (Na%)
Extra sodium in the groundwater alters the properties of the soil and decreases its permeability. Based on the percentage of sodium, groundwater was categorized as highly suitable (20%), suitable (20–40%), permissible (40–60%), not suitable (60–80%), and entirely not suited (>80%) [37,38,39]. With an average value of 16 and 12 in the pre- and post-monsoon seasons, the Na% in the study area ranges from 3 to 39 and 2 to 32. According to the Indian Standards [2], irrigation water should have an extreme Na+ content of 60%. A %Na level above 60 may lead to Na+ accumulations, which will deteriorate the soil’s physical qualities. The groundwater samples collected from Kovilpatti Taluk have sodium concentrations that fall into the excellent and good ranges.
4.2.4. Bicarbonate Hazard
Water with a high bicarbonate concentration can combine calcium and magnesium to form salts. RSC assigns the following categories to groundwater: fair (1.25), not fair (1.25–2.5), and extreme not fair (>2.5) [40,41,42,43]. In Kovilpatti Taluk, of the analyzed samples, 29% have an adequate pre-monsoon irrigation water quality, 71% have an unsuitable pre-monsoon irrigation water quality, and 86% have a suitable post-monsoon irrigation water quality. In total, 5% of the irrigation water is questionable, and 9% is inappropriate for irrigation. The reason for the differences in alkalinity between the pre- and post-monsoon seasons is the diluting of groundwater caused by rainfall [44,45,46].
4.2.5. Magnesium Hazard Ratio
Mg2+ concentrations over Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations are referred to as MHR. Normal circumstances will create an equilibrium between the Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations in natural water [47,48]. The typical MAR values are 32 mg/L for the pre-monsoon season and 45 mg/L for the post-monsoon season. The MAR values are between 10 and 66 mg/L and 17 and 69 mg/L. In the pre- and post-monsoon seasons, Table 3 demonstrates that 81% and 41% of the samples surpass the allowed limit (50 mg/L). Additionally, the research area employed the Kelly index [2]. KI (1) (Table 4) indicates that all groundwater samples in the research area are suitable for irrigation.
4.3. Primary Elements Governing Groundwater Chemistry
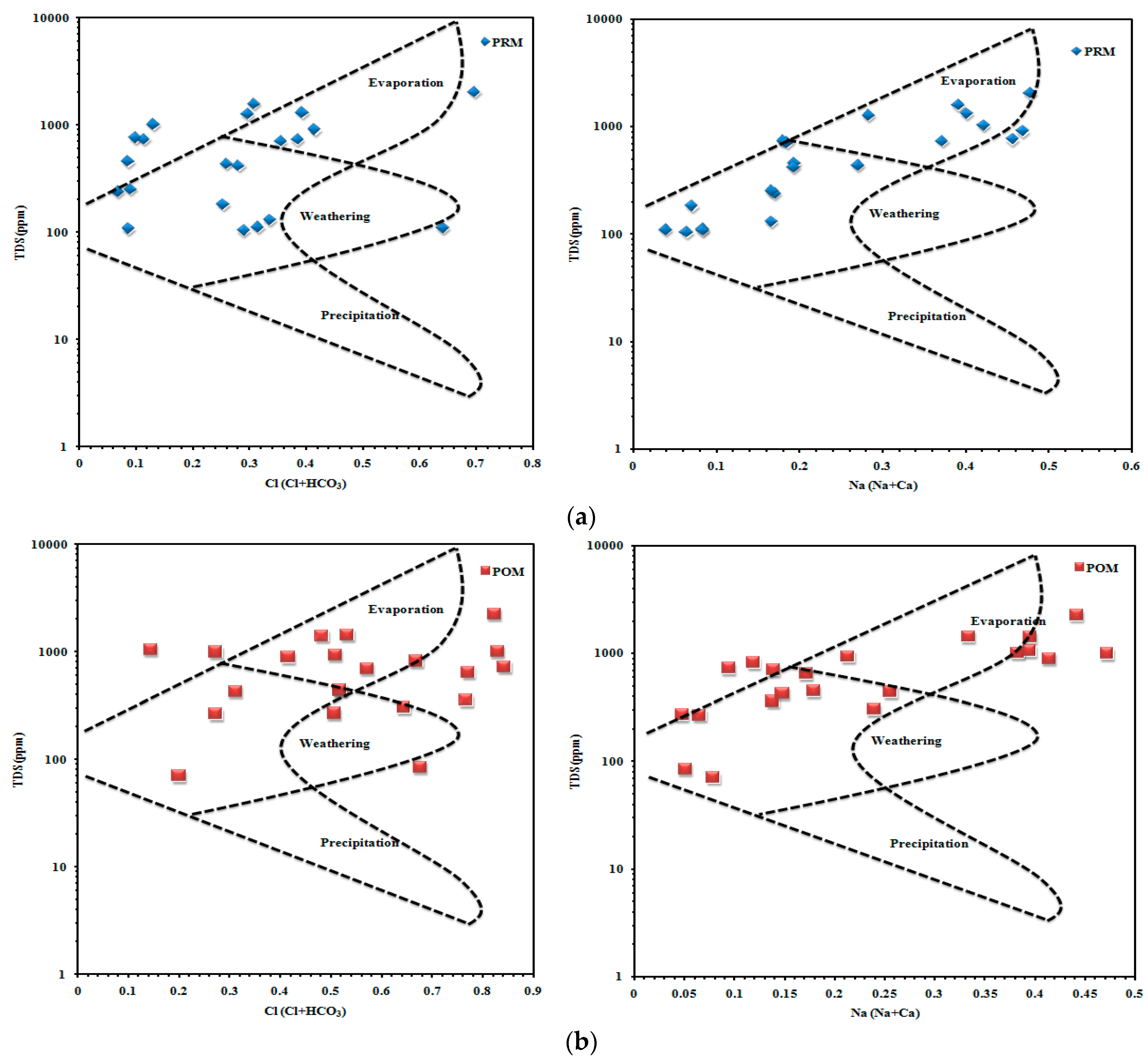
4.3.1. Gibbs Plot
The association between the lithological characteristics of the aquifer and its water composition was discovered using the Gibbs plot. Figure 6a,b shows the Gibbs plot, highlighting regions where precipitation, evaporation, and rock–water contact are the dominant processes [49]. The prominent samples are identified in the dominant fields of evaporation and the rock–water interaction in both seasons of the Gibbs plots. Because groundwater percolation predominates with rock infiltration for Cl (Cl+HCO3) and Na (Na+Ca), weathering and evaporation conditions are present before and after the monsoon. Post-monsoon seasons are less weathered regarding Cl (Cl+HCO3) and Na (Na+Ca) than pre- and post-monsoon seasons.
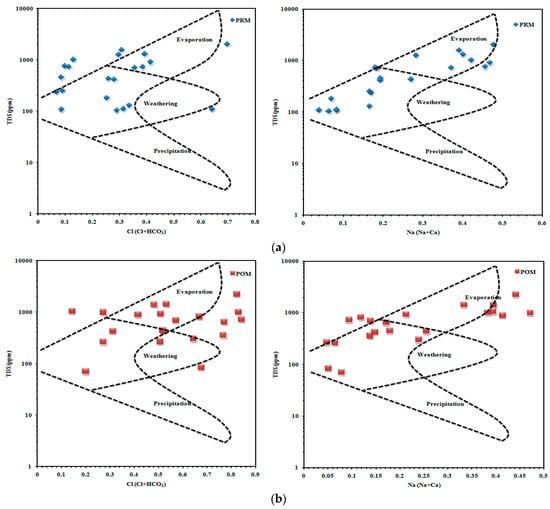
Figure 6.
(a) Gibbs plot for samples from the pre-monsoon. (b) Gibbs plot for samples from the post-monsoon.
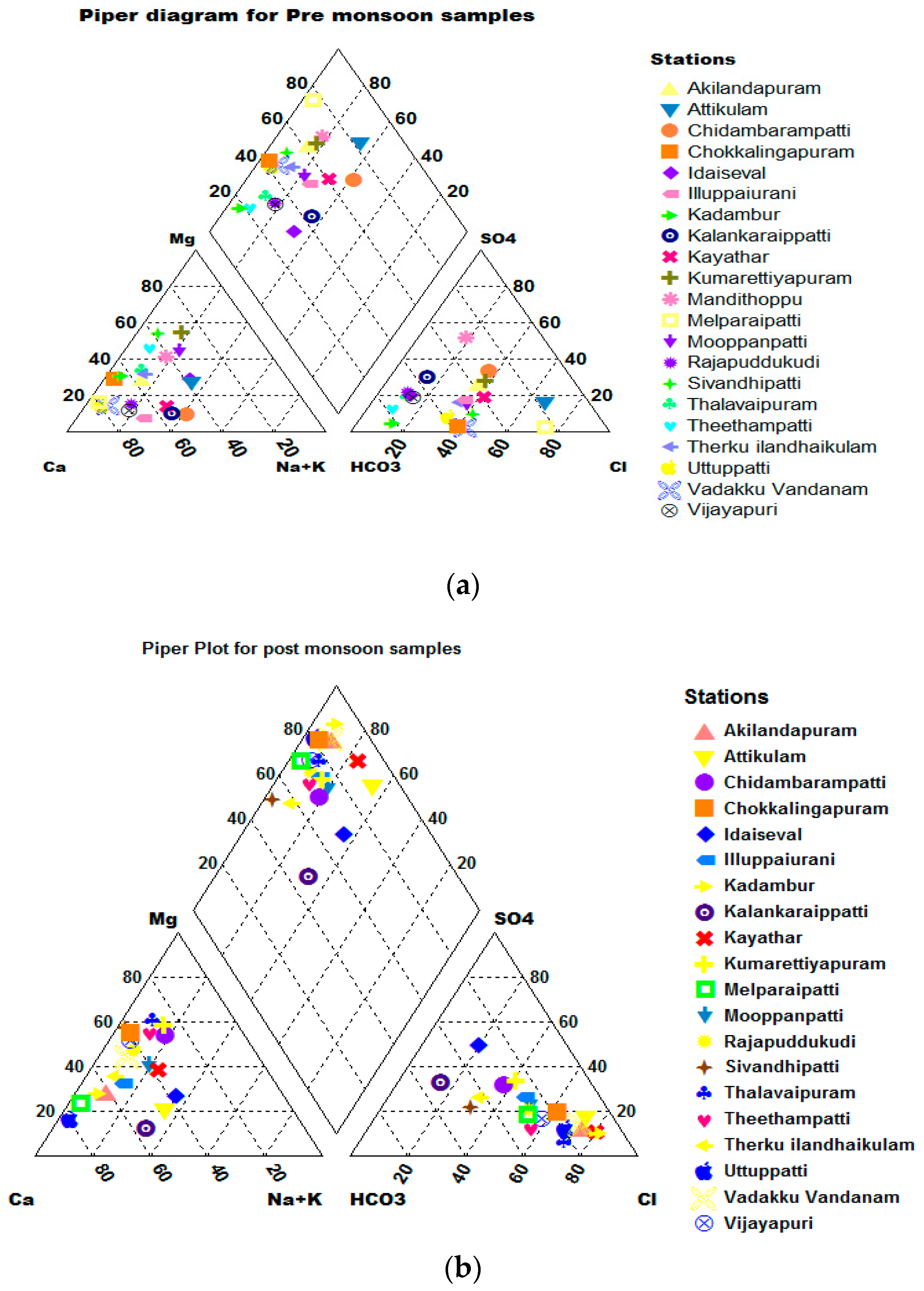
4.3.2. Piper Plot
Based on the predominate cations and anions, the piper [22] classification is used to express similarities and differences in the chemistry of various water samples. According to a Piper trilinear diagram (Figure 7a,b) during the pre-monsoon period, 29% of the water samples take on a Ca-Cl type, 38% of the samples have a mixed Mg-HCO3 and Ca-Cl type, and the remaining 33% of the samples have a Mg-HCO3 type of water dominance. In total, 90% of the samples taken during the post-monsoon have the water type Ca-Cl, while the remaining samples have a mixed water type. It implies that, in both sessions, alkaline earth minerals outnumbered alkalis [50,51,52].
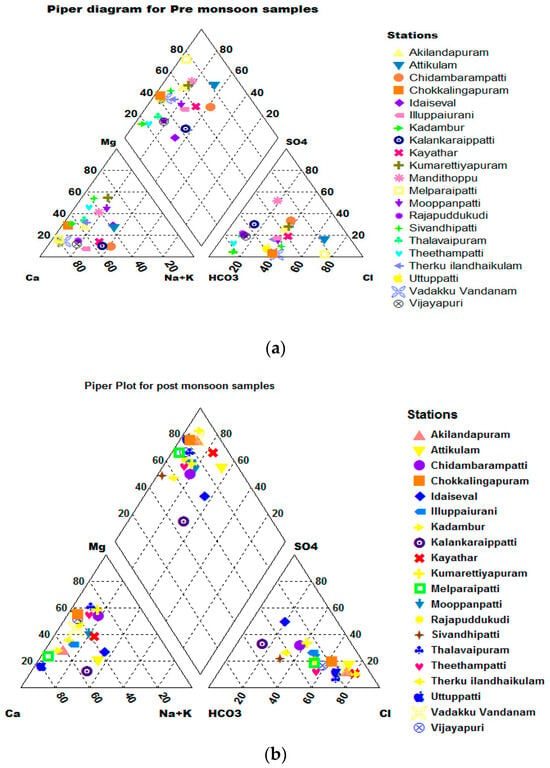
Figure 7.
(a) Piper diagram for pre-monsoon samples. (b) Piper diagram for post-monsoon samples.
4.3.3. Wilcox Plot
The groundwater’s ratio of Na to EC computed for both seasons was shown on the Wilcox diagram (Figure 8a,b). An improper sample was taken in both the pre- and post-monsoon seasons, as seen in this graph [53,54]. A few small patches are the only areas where the salinity and sodium have not increased significantly enough to make the groundwater region unsuitable for irrigation. Most samples are S1 and were collected in C1, C21, C3, and C4.
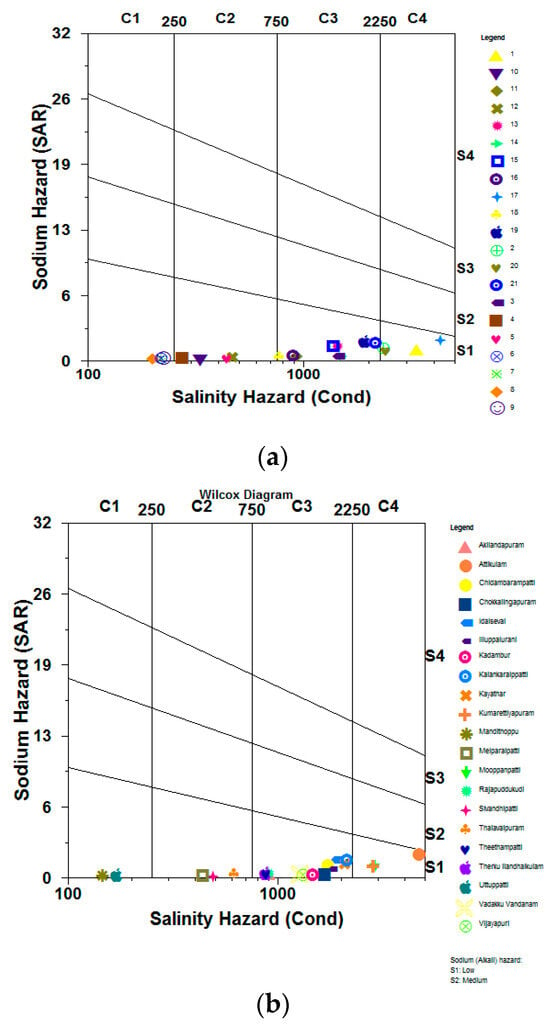
Figure 8.
(a) Wilcox plot for pre-monsoon. (b) Wilcox plot for pre-monsoon.
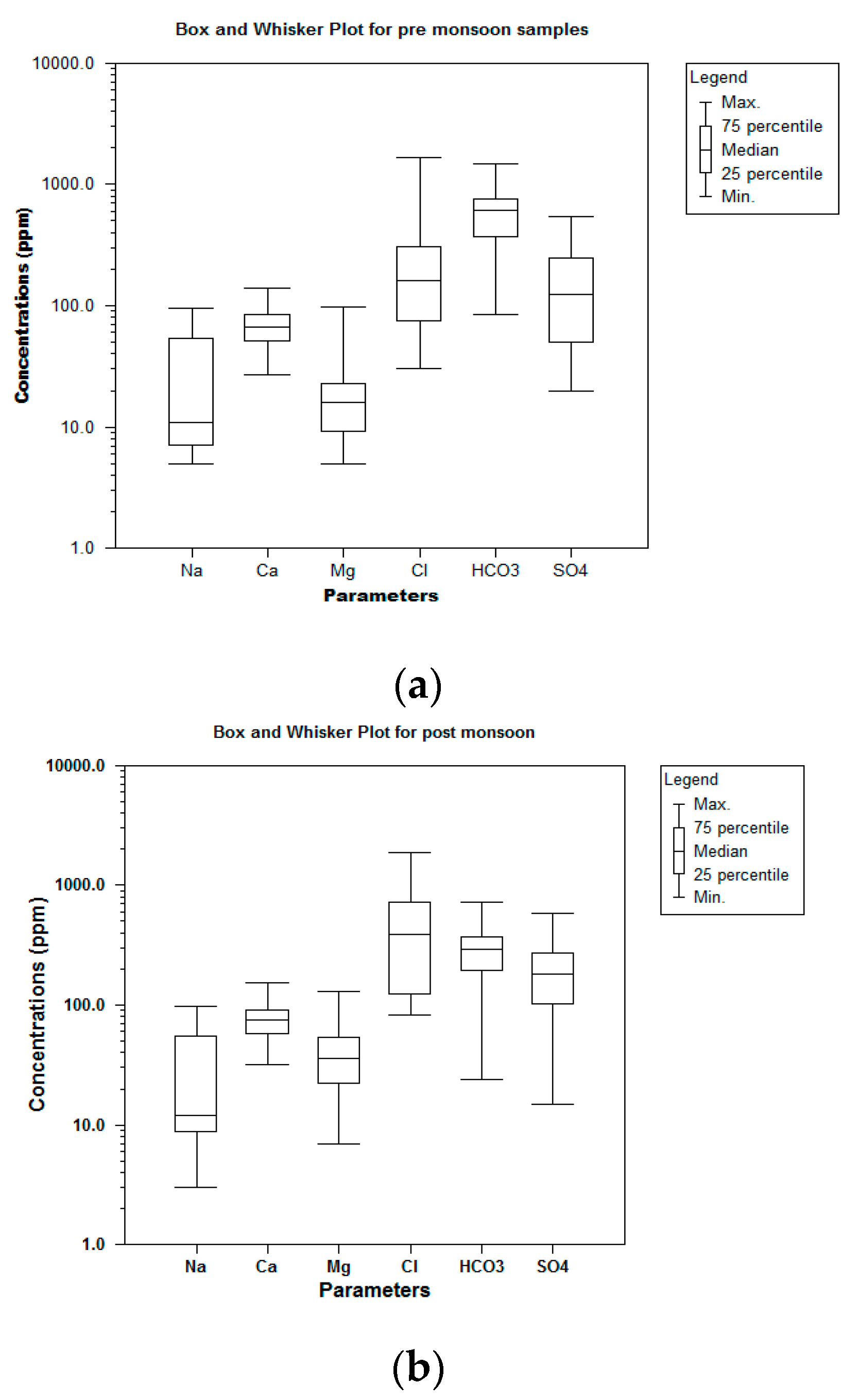
4.3.4. Box and Whisker Plot
Box and whisker plots visually represent how a data set might vary. During the pre-monsoon seasons, parameters such as Na show upper quartile maximum values, while others including Mg, Cl, HCO32−, and SO42− show lower quartile maximum values. The remaining parameter Ca remains the same, in both the lower and the upper quartiles. During the post-monsoon seasons, parameters such as Na show upper quartile maximum values, while others including Mg, Cl, HCO32−, and SO42− show lower quartile maximum values. The remaining parameter Ca remains the same in both the lower and upper quartiles. Due to changes in post-monsoon precipitation occurrences, the pre-monsoon seasons have higher values than post-monsoon seasons. Figure 9a,b shows the variation plot for pre-monsoon and post-monsoon seasons in the selected research region of the Kovilpatti Taluk region [55,56,57,58,59].
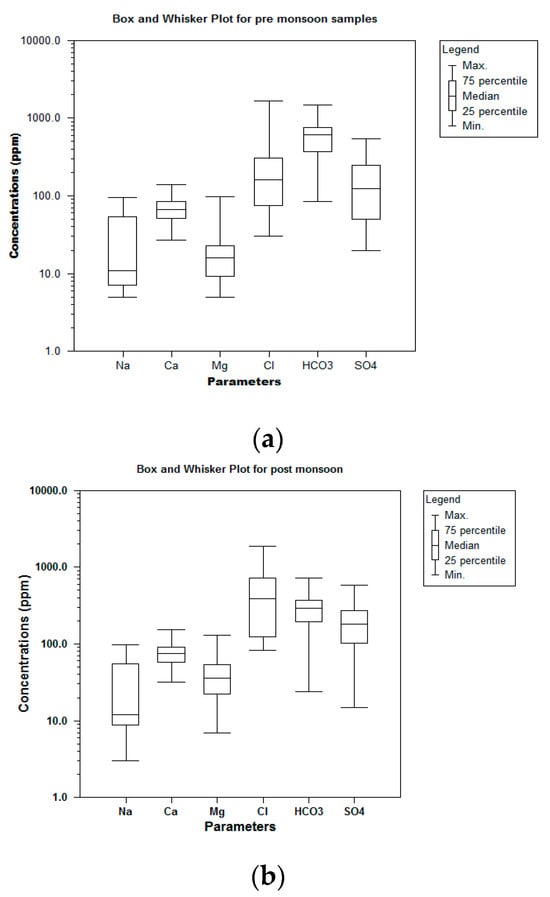
Figure 9.
(a) Box plot for pre-monsoon. (b) Box plot for post-monsoon.
4.3.5. Correlation Matrix
The correlation coefficient (r) has a value between +1 and −1. The correlation between the water quality metrics is well-linked when the r value is between 0.8 and 1, moderate between 0.5 and 0.8, and weak between 0.5 and 0. The strong positive correlation between TDS and EC (0.995), Na+ (0.901), and SO42− (0.957), and EC with SO42− (0.956) and Na+ (0.893), as well as Na+ with K+ (0.820), and SO42− were present during the pre-monsoon (0.890). TDS with Cl− (0.678) and Mg2+ (0.518), and EC with Cl− (0.701), Mg2+ (0.5), and K+ (0.784), Ca2+ with Cl− (0.548) and Na+ (0.519), and SO42− with K+ all have a moderately positive correlation (0.660). The parameters listed in Table 6a show some weak correlations with one another.

Table 6.
(a) Correlation between water quality parameters in pre-monsoon samples. (b) Correlation between water quality parameters in post-monsoon samples.
There is a significant positive correlation between TDS and EC (0.998), Na+ (0.893), and SO42− (0.977), and EC with SO42 (0.973) and Na+ (0.890), as well as Na+ with K+ (0.818) and SO42− during the post-monsoon (0.886). The TDS with Cl− (0.614), Alkalinity (0.546), and Ca2+ (0.564), and EC with Cl− (0.635), Alkalinity (0.536), Ca2+ (0.559), and K+ (0.773), and Cl− with K+ (0.653) and SO42 (0.530), and Ca2+ with Na+ (0.537), SO42− (0.582), as well as K+ with SO42, have a moderate correlation (0.715). Table 6b shows some weak correlations that exist as well. There was a correlation of 0.995 between EC and TDS, a correlation of 0.675 and 0.701 for Cl− along with TDS and EC, a 0.548 correlation between Ca2+ and Cl−, a 0.519 and 0.500 correlation between Mg2+ along with TDS and EC, 0.901, 0.893, and 0.519 correlates with Na+ along with TDS, EC, and Ca2+, 0.784 and 0.820 correlates K+ along with EC and Na+, and 0.957, 0.956, 0.890, and 0.668 correlates SO42− along with TDS, EC, Na+, and K+; these have occurred in the pre-monsoon samples collection. There was a correlation of 0.998 between EC and TDS, a 0.614 and 0.635 correlation for Cl− along with TDS and EC, a 0.546 and 0.536 correlation with alkalinity along with TDS and EC, 0.564 and 0.559 correlation between Ca2+ with TDS and EC, 0.893, 0.890, and 0.537 correlates with Na+ along with TDS, EC, and Ca2+, 0.771, 0.773, 0.653, and 0.818 correlates K+ along with TDS, EC, Cl− and Na+, and 0.977, 0.973, 0.530, and 0.582 correlates SO42− along with TDS, EC, Cl−, Na+, Ca2+, and K+; these are occurred in the post-monsoon samples collection.
4.4. Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA)
Fluoride and nitrate exposure were evaluated with Average Daily Exposure Dose (ADDing) and Dermal Exposure Dose (ADDder) for each location. Table 7 summarizes the Hazardous Human Health Risk Assessment (HHRA) for adults, with ADDing ranging from 0.84 to 2.3 mg/kg/day for fluoride and 0.1 to 0.66 mg/kg/day for nitrate, averaging 1.518 mg/kg/day. ADDder for nitrate and fluoride ranged from 0.0001 to 0.0004 mg/kg/day and averaged 0.0002 mg/kg/day. Table 8 outlines the HHRA for children, with ADDing for nitrate and fluoride ranging from 0.130 to 0.690 mg/kg/day and 4.800 to 6.260 mg/kg/day (average: 5.48 mg/kg/day). ADDder for fluoride and nitrate ranged from 0.026 to 0.051 mg/kg/day and 0.0003 to 0.001 mg/kg/day (average: 0.0004 mg/kg/day). Health Impact (HI) values exceeding 1 suggest severity. For adults, fluoride’s HI ranged from 0.68 to 1.98 (average: 1.338), while children ranged from 2.276 to 3.556 (average: 2.93). The nitrate HI for adults ranged from 0.12 to 0.82 (average: 0.450), and for children, 0.480 to 1.180 (average: 0.81). Children had higher HI values due to body weight differences [60,61,62,63,64,65,66].

Table 7.
Different parameters of human health risk assessment for Adults.

Table 8.
Different parameters of human health risk assessment for Children.
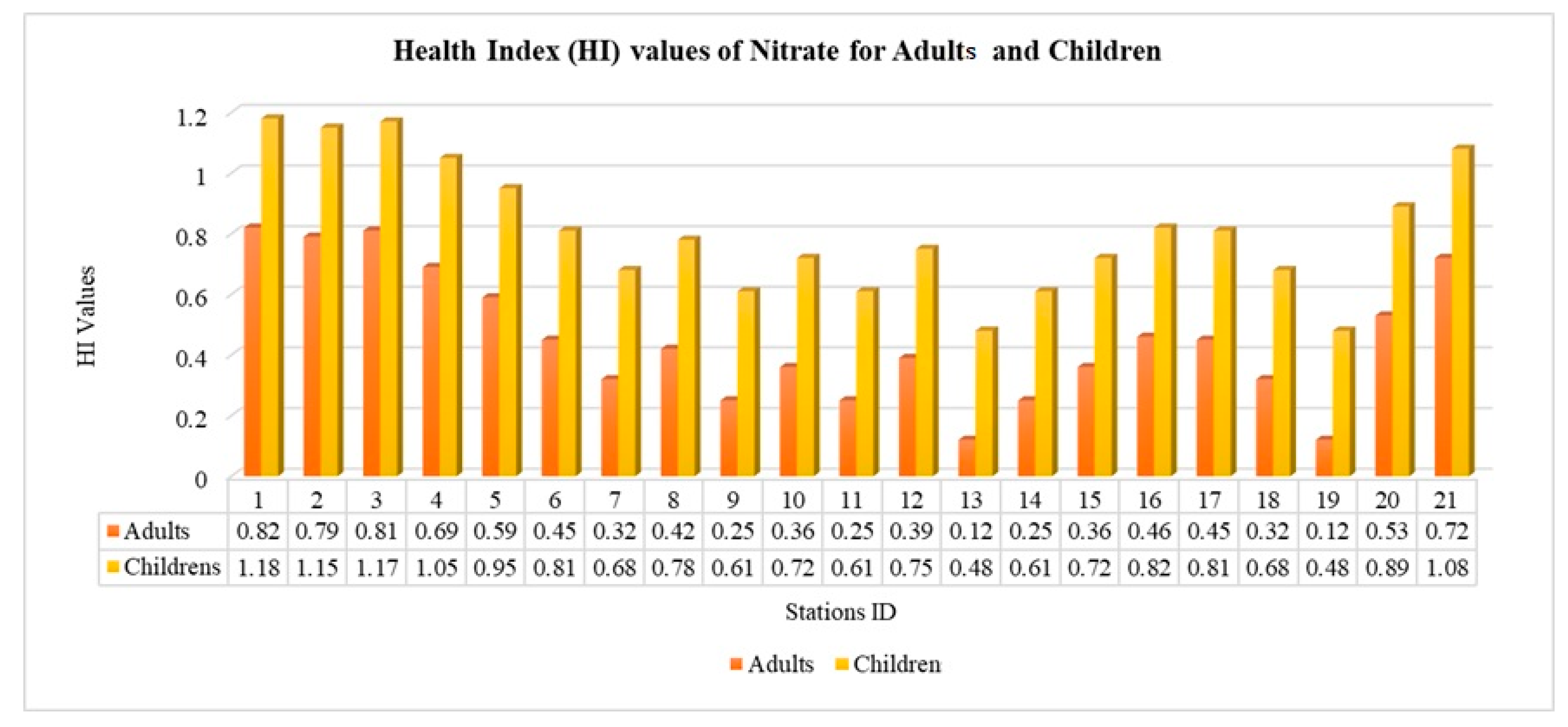
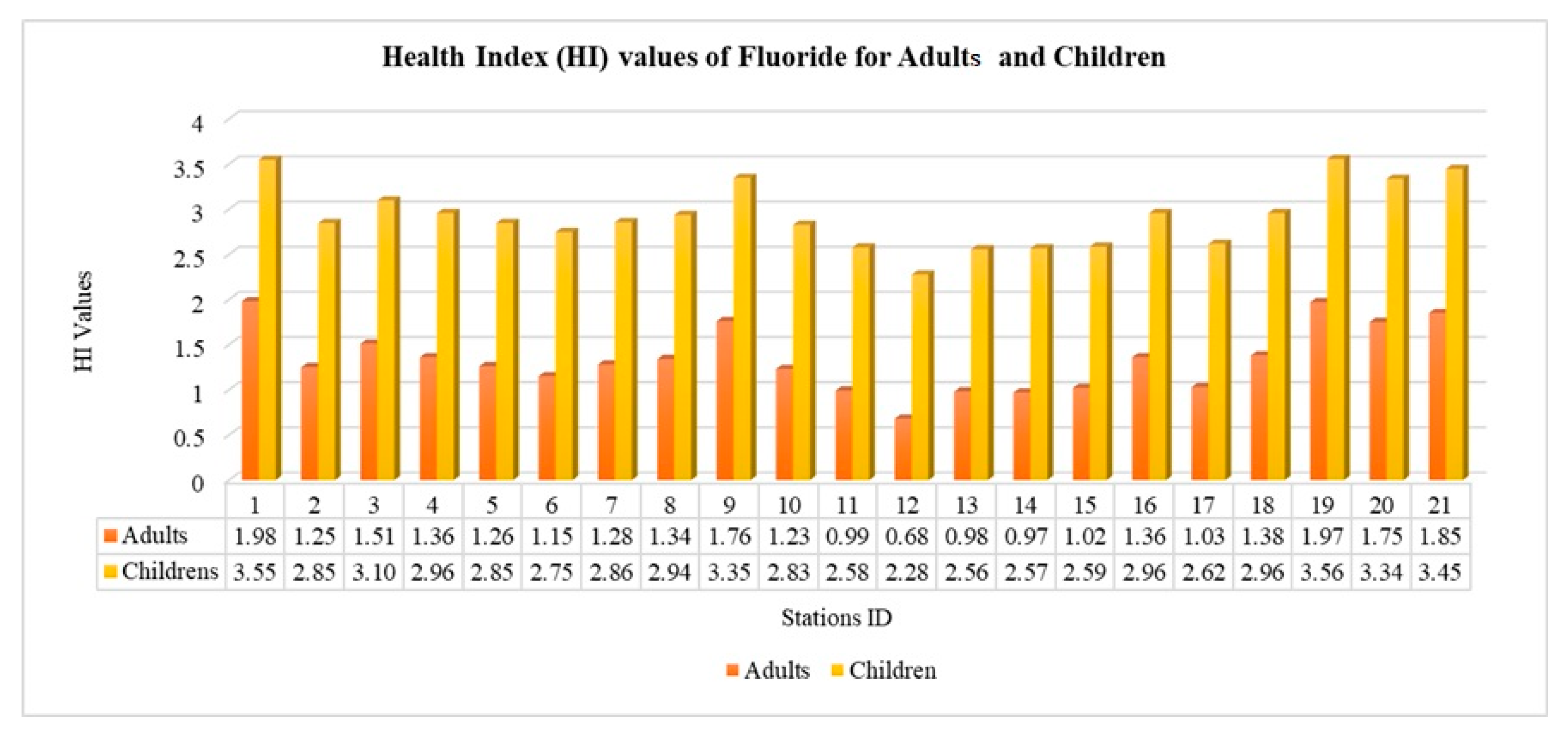
Fluoride’s HI values for adults were under 1, indicating no adverse effects. For nitrate, high HI values (exceeding 1) correlated with the highest groundwater nitrate concentrations, caused by fertilizers, organic manure, untreated sewage, and soil bacteria. Nitrate and fluoride impacted children more (70%) than adults (30%). High nitrate levels risk diseases including stomach cancer, methemoglobinemia, goitre, metabolic issues, birth abnormalities, hypertension, and cattle poisoning. Figure 10 and Figure 11 depict fluoride and nitrate HI values [67,68,69,70,71].

Figure 10.
Health Index (HI) values of nitrate for Adults and Children.

Figure 11.
Health Index (HI) values of fluoride for Adults and Children.
According to the outcome of the spatial distribution of the WQI, Kovilpatti Taluk has better quality from July to December (pre-monsoon) due to the rainfall pattern in the post-monsoon season. The Kovilpatti Taluk region has been a contaminant during the post-monsoon seasons. In these regions, sound samples are higher during pre-monsoon seasons for irrigation, which can be determined by analyzing the RSC, MHR, SAR, Na%, and Kelly ratios. In pre-monsoon, Mooppanpatti, Illuppaiurani, and Vijayapuri had high nitrate and fluoride. The human health risk assessment results from the analysis of fluoride and nitrate show that the majority show the highest values faced by children than adults. So, there is a need for more proper regulation for the respective zones. Rainfall reduced some risks. Kadambu, Melparaipatti, Therkuilandhaikulam, and Vadakku Vandanam had low risks. Mooppanpatti, Illuppaiurani, and Vijayapuri remained high post-monsoon, while other zones lowered risks. These regions need proper management plans and remedial measures to reduce the risk. Effective groundwater contaminant management plans involve regular monitoring, identifying contamination sources, implementing containment measures and considering remediation options. They also require regulatory compliance, public awareness and sustainable practices to protect and restore groundwater quality while safeguarding public health and the environment.
5. Conclusions
- As per the Water Quality Index (WQI), 5% of pre-monsoon and 9% of post-monsoon samples are unsuitable for human consumption.
- All Kovilpatti Taluk water samples meet irrigation quality indicators such as the sodium absorption ratio and sodium percent.
- Nonetheless, the Magnesium Hazard Ratio and Residual Sodium Carbonate values indicate that 29% of pre-monsoon samples and 59% of post-monsoon samples are unsuitable for irrigation, while 71% of pre-monsoon and 9% of post-monsoon samples meet the required criteria.
- The observed variation can be attributed to the interaction of alkaline earth elements with both rocks and water, which surpasses the influence of alkali elements, as demonstrated by the data from the Piper and Gibbs plots. Additionally, the correlation matrix reveals a positive correlation between TDS and EC with chloride, sodium, and sulfate.
- The Gibbs plots reveal a comparison between the pre- and post-monsoon seasons, indicating increased evaporation and decreased weathering, particularly in the case of Cl+HCO3 and Na+Ca, during the post-monsoon period. The majority of the samples, such as C1, C21, C3, and C4, fall within the S1 category.
- Box and whisker plots show more pre-monsoon values due to post-monsoon alterations from rainfall.
- Kovilpatti Taluk is moderate primarily for drinking and irrigation, with the pre-monsoon showing moderate to poor conditions due to industrialization.
- The post-monsoon improves due to precipitation. Due to high nitrate and fluoride pre-monsoon, Mooppanpatti, Illuppaiurani, and Vijayapuri pose serious health risks.
- Kadambu, Melparaipatti, Therkuilandhaikulam, and Vadakku Vandanam have low risks. With the post-monsoon, there are higher risks in Mooppanpatti and Illuppaiurani.
Author Contributions
V.S., V.L.R. and U.M.M.—Worked for Article Writing and Software Validation; S.K. and G.R.—helped for grammer and plagiarism checks; S.S., P.V. and L.N.—supported for plots preparation and field data collections; H.A.—supported for funding and reviewing the methodology; M.A.-M. and H.G.A.—contributed for language check and reviewing the results and discussions part. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The researchers would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research, Qassim University for funding the publication of this project.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this publishing article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Modibo Sidibé, A.; Lin, X.; Koné, S. Assessing Groundwater Mineralization Process, Quality, and Isotopic Recharge Origin in the Sahel Region in Africa. Water 2019, 11, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA,, 2012; p. 1360.
- BIS Indian Standard Drinking Water Specification; Bureau of Indian Standard: New Delhi, India, 2000.
- Knobeloch, L.; Salna, B.; Hogan, A.; Postle, J.; Anderson, H. Blue Babies and Nitrate-Contaminated Well Water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishanthiny, S.C.; Thushyanthy, M.; Barathithasan, T.; Saravanan, S. Irrigation Water Quality Based on Hydro Chemical Analysis, Jaffna, Sri Lanka. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2010, 7, 100–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, S.; Kumar, G.S.; Prasanna, M.V.; Peter, A.J.; Ramanthan, A.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. A study on the hydrogeology and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater from different depths in a coastal aquifer: Annamalai Nagar, Tamilnadu, India. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, F.M. Significant carbonates in irrigation waters. Soil Sci. 1950, 69, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Kumar, S.; Bharani, R.; Magesh, N.S.; Godson, P.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality appraisal of part of south Chennai coastal aquifers, Tamil Nadu, India using WQI and fuzzy logic method. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 4, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramanan, S.; Chung, S.Y.; Ramkumar, T.; Gnanachandrasamy, G.; Vasudevan, S.; Lee, S.Y. Application of GIS and hydrogeochemistry of groundwater pollution status of Nagapattinam district of Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 4429–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Singh, R.K.; Damodaran, T.; Mishra, V.K.; Sharma, D.K.; Rai, D. Fluoride in Groundwater: Toxicological Exposure and Remedies. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2013, 16, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, K.; Heumesser, C.; Schmid, E. Groundwater nitrate contamination: Factors and indicators environ manage. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, W.P. Use of Saline Irrigation Water. Soil Sci. 1963, 95, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, M.L.; Ragunath, S.; Hemalatha, J.; Vivek, S.; Mohanraj, M.; Sampathkumar, V.; Ansari, A.M.S.; Parthiban, V.; Manoj, S. Simulation of groundwater quality for Noyyal river basin of Coimbatore city, Tamilnadu using MODFLOW. J. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, P.D.; Logesh, N.; Lakshumanan, C.; Sánchez-Zavala, J.L. Decadal-scale spatiotemporal changes in land use/land cover of El Potosi Basin at semi-arid northeast Mexico and evolution of peat fire between 1980-2020 CE. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2021, 110, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, L.; Usha, T.; Gowrappan, M.; Kasthuri, B.P.; Moorthy, P.; Chokkalingam, L. Flood Susceptibility Analysis in Chennai Corporation Using Frequency Ratio Model. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedzo, M.G.; Tsozué, D.; Mimba, M.E.; Teddy, F.; Nembungwe, R.M.; Linida, S. Importance of Rocks and Their Weathering Products on Groundwater Quality in Central-East Cameroon. Hydrology 2017, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brella, D.; Belkhiri, L.; Tiri, A.; Salhi, H.; Lakouas, F.E.; Nouibet, R.; Amrane, A.; Merdoud, R.; Mouni, L. Identification of the Groundwater Quality and Potential Noncarcinogenic Health Risk Assessment of Nitrate in the Groundwater of El Milia Plain, Kebir Rhumel Basin, Algeria. Hydrology 2023, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroud, M.; Trolard, F.; Kefi, M.; Jebari, S.; Bourrié, G. Water Quality Indices: Challenges and Application Limits in the Literature. Water 2019, 11, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M. Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater and Its Suitability for Drinking and Agricultural Use in Nahavand, Western Iran. Nat. Resour. Res. 2011, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.N.; Reddy, A.G.S.; Reddy, R.M.; Varma, K.S. Preliminary Investigations of Ground Water Quality in Hyderabad City, Andhra Pradesh, India. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2009, 7, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2015, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1953, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Mammeri, A.; Tiri, A.; Belkhiri, L.; Salhi, H.; Brella, D.; Lakouas, E.; Tahraoui, H.; Amrane, A.; Mouni, L. Assessment of Surface Water Quality Using Water Quality Index and Discriminant Analysis Method. Water 2023, 15, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L. Geochemical modeling of groundwater in the El Eulma area, Algeria. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.D.; Selvam, S.; Gopinath, S.; Logesh, N.; Sánchez-Zavala, J.L.; Lakshumanan, C. Geochemical evolution and seasonality of groundwater recharge at water-scarce southeast margin of the Chihuahuan Desert in Mexico. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdour, A.; Abdo, H.G.; Almohamad, H.; Alodah, A.; Al Dughairi, A.A.; Ghoneim, S.S.M.; Ali, E. Prediction of Groundwater Quality Index Using Classification Techniques in Arid Environments. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.O.; Abdo, H.G.; Ayejoto, D.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Danladi, E.; Saqr, A.M.; Almohamad, H.; Fahad, A. Evaluation of Groundwater contamination and the Health Risk Due to Landfills using integrated geophysical methods and Physiochemical Water Analysis. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alao, J.O.; Fahad, A.; Abdo, H.G.; Ayejoto, D.A.; Almohamad, H.; Ahmad, M.S.; Nur, M.S.; Danjuma, T.T.; Yusuf, M.A.; Francis, O.T.; et al. Effects of dumpsite leachate plumes on surface and groundwater and the possible public health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Impact of dam construction on precipitation: A regional perspective. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2022, 74, 877–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Yin, Z.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Remote sensing and geostatistics in urban water-resource monitoring: A review. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2023, 74, 747–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, L.; Keim, B.D.; Konsoer, K.; Yin, Z.; Liu, M.; Zheng, W. Spatial and wavelet analysis of precipitation and river discharge during operation of the Three Gorges Dam, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; p. 969. [Google Scholar]
- Raghunath, H.M. Groundwater, 2nd ed.; Wiley Eastern Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 1963; pp. 344–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararaj, P.; Madurai Chidambaram, S.K.; Sivakumar, V.; Natarajan, L. Groundwater quality assessment and its suitability for drinking and agricultural purpose, Dindigul taluk, Tamilnadu, India. J. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 6591–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnaiah, C.R.; Sadashivaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Assessment of Water Quality Index for the Groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E -J. Chem. 2009, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline and Alkali Soils; Agric. Handbook, 60; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Adelagun, R.O.A.; Etim, E.E.; Godwin, O.E. Application of Water Quality Index for the Assessment of Water from Different Sources in Nigeria. Promis. Tech. Wastewater Treat. Water Qual. Assess. 2021, 267, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenlerkthawin, W.; Bidorn, K.; Panneerselvam, B.; Sriariyawat, A.; Otarawanna, S.; Bidorn, B. Monitoring of nature-based solution for stabilizing eroded muddy coastline of the Chao Phraya Delta, Thailand. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023; Volume 1226, p. 012013. [Google Scholar]
- Paneerselvam, B.; Ravichandran, N.; Li, P.; Thomas, M.; Charoenlerkthawin, W.; Bidorn, B. Machine learning approach to evaluate the groundwater quality and human health risk for sustainable drinking and irrigation purposes in South India. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, S.; Dar, F.A.; Magesh, N.S.; Singaraja, C.; Venkatramanan, S.; Chung, S.Y. 2016 Application of remote sensing and GIS for delineating groundwater recharge potential zones of Kovilpatti Municipality, Tamil Nadu using IF technique. Earth Sci. Inform. 2016, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.D.; Sreekanth, P.D.; Ahmed, S.; Reddy, D.V. Evaluation of groundwater quality for irrigation in a semi-arid region of South India. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuharajan, M.B.; Aparna, S.B.; Vivek, S. Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment Phenomenon using DRASTIC & Modified DRASTIC Modeling validated with Nitrate Concentration. Glob. NEST J. 2023, 25, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, S.; Abijith, D.; Reddy, N.M.; Parthasarathy, K.S.S.; Janardhanam, N.; Sathiyamurthi, S.; Sivakumar, V. Flood susceptibility mapping using machine learning boosting algorithms techniques in Idukki district of Kerala India. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, V.; Sashik Kumar, M.C.; Natarajan, L.; Roy, P.D.; Chokkalingam, L. Vulnerability Assessment of Groundwater in Industrialized Tiruppur Area of South India using GIS-based DRASTIC model. J. Geol. Soc. India 2022, 98, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, S.; Kumar, M.C. Hydro-Geochemical and Quality Assessment of Groundwater for Irrigation Purpose in Tirupur Taluk, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2021, 22, 1836–1850. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, V.; Chidambaram, S.M.; Velusamy, S.; Rathinavel, R.; Shanmugasundaram, D.K.; Sundararaj, P.; Shanmugamoorthy, M.; Thangavel, R.; Balu, K. An integrated approach for an impact assessment of the tank water and groundwater quality in Coimbatore region of South India: Implication from anthropogenic activities. J. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Recommendations, 3rd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000; Volume 1, p. 515. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; ISBN 9789241548151. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Qiu, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, B.; Sun, K.; Cao, M. Surface multi-hazard effect of underground coal mining. Landslides 2023, 20, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Qiu, H.; Ye, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y. Distribution and Recurrence of Warming-induced Retrogressive Thaw Slumps on the Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2023, 128, e2022JF007047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, K.; Hardison, A.K.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Gao, D.; Gong, J.; Gardner, W.S. Membrane inlet mass spectrometry method (REOX/MIMS) to measure 15N-nitrate in isotope-enrichment experiments. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Quan, Q.; Yang, S.; Dong, Y. A social-ecological coupling model for evaluating the human-water relationship in basins within the Budyko framework. J. Hydrol. 2023, 619, 129361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhu, J.; Fu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Hu, Y. An augmented representation method of debris flow scenes to improve public perception. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 1521–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-K.; Wang, H.-C.; Fang, P.-H.; Liang, B.; Zheng, K.; Sun, Q.; Li, X.-Q.; Zeng, R.; Wang, A.-J. Life cycle assessment of integrated bioelectrochemical-constructed wetland system: Environmental sustainability and economic feasibility evaluation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, H.; Hu, K.; Yin, G.; Wei, Z. IA-Net: An Inception–Attention-Module-Based Network for Classifying Underwater Images from Others. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 47, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Ravichandran, N.; Kaliyappan, S.P.; Karuppannan, S.; Bidorn, B. Quality and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater for Drinking and Irrigation Purpose in Semi-Arid Region of India Using Entropy Water Quality and Statistical Techniques. Water 2023, 15, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Muniraj, K.; Pande, C.; Ravichandran, N.; Thomas, M.; Karuppannan, S. Geochemical evaluation and human health risk assessment of nitrate-contaminated groundwater in an industrial area of South India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 86202–86219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Zhong, X.; Yao, T.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y. Quantifying the major drivers for the expanding lakes in the interior Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Zhu, G.; Bhat, M.A.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Sang, L.; Lin, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, N. Water use strategy of nitraria tangutorum shrubs in ecological water delivery area of the lower inland river: Based on stable isotope data. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lu, D.; Sheng, H.; Xia, J.; Kan, P.; Yao, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Zhu, D.Z.; Liu, H. Constructed wetlands as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and pathogens: Evidence from metagenomic analysis in Chinese rural areas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Ravichandran, N.; Dumka, U.C.; Thomas, M.; Charoenlerkthawin, W.; Bidorn, B. A novel approach for the prediction and analysis of daily concentrations of particulate matter using machine learning. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 166178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Karunanidhi, D.; Kalaivanan, K.; Subramani, T.; Shanthi, D.; Balamurugan, P. Integrated hydrogeophysical and GIS based demarcation of groundwater potential and vulnerability zones in a hard rock and sedimentary terrain of Southern India. Chemosphere 2023, 316, 137305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Muniraj, K.; Duraisamy, K.; Pande, C.; Karuppannan, S.; Thomas, M. An integrated approach to explore the suitability of nitrate-contaminated groundwater for drinking purposes in a semiarid region of India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S.; Kolanuvada, S.R.; Sampath, V.; Roy, P.D.; Moorthy, P.; Natarajan, L.; Chokkalingam, L. Assessment of groundwater vulnerability using water quality index and solute transport model in Poiney sub-basin of south India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.; Panneerselvam, B.; Kaliappan, S.P. Effect of high nitrate contamination of groundwater on human health and water quality index in semi-arid region, South India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shunmugapriya, K.; Panneerselvam, B.; Muniraj, K.; Ravichandran, N.; Prasath, P.; Thomas, M.; Duraisamy, K. Integration of multi criteria decision analysis and GIS for evaluating the site suitability for aquaculture in southern coastal region, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yang, Z. Analysis for 3-D morphology structural changes for underwater topographical in Culebrita Island. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 2458–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, G.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C.; Zhao, D.; Lin, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; et al. Adaptive model for the water depth bias correction of bathymetric LiDAR point cloud data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 118, 103253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, W. Haze Grading Using the Convolutional Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Shi, P.; Jia, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Stable water isotope monitoring network of different water bodies in Shiyang River basin, a typical arid river in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 3773–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, X.; Lai, C.; Chen, L.; Shao, D.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J. Prediction modelling framework comparative analysis of dissolved oxygen concentration variations using support vector regression coupled with multiple feature engineering and optimization methods: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).