Effect of Salinity on Performance and Microbial Community during Granulation Process in a Sequencing Batch Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor Start-Up and Operation
2.2. Inoculated Sludge and Synthetic Wastewater
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect on Granulation Process
3.2. Effect on EPS Secretion
3.3. Effect on Performance of Reactor
3.4. Effect on Microbial Community Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefebvre, O.; Moletta, R. Treatment of organic pollution in industrial saline wastewater: A literature review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3671–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Carvajal, L.C.; Sanz-Martin, J.L.; Barragan-Huerta, B.E. Biodegradation of organic pollutants in saline wastewater by halophilic microorganisms: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 9578–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, D. Experimental Study on Shortcut Nitrification of Sewage from Flushing Toilet with Seawater. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 4–5 July 2009; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Ihm, S.K. Heterogeneous catalytic wet air oxidation of refractory organic pollutants in industrial wastewaters: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Pendashteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.R.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, H.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Zeng, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, C. Effect of salinity on removal performance and activated sludge characteristics in sequencing batch reactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, A. Specific nutrient removal rates in saline wastewater treatment using sequencing batch reactor. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, H.D.; Park, J.H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhao, F. Effect of different salinity adaptation on the performance and microbial community in a sequencing batch reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.M.; Khiadani, M.H.; Fatehizadeh, A.; Taheri, E. Validation of linear and non-linear kinetic modeling of saline wastewater treatment by sequencing batch reactor with adapted and non-adapted consortiums. Desalination 2014, 344, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Ye, L.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.X. Microbial community structure and function in aerobic granular sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3967–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kreuk, M.K.; Heijnen, J.J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Simultaneous COD, nitrogen, and phosphate removal by aerobic granular sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 90, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, L.; Liang, H.; Wu, W.M. Aerobic granular sludge: Characterization, mechanism of granulation and application to wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2011, 31, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsino, S.F.; Campo, R.; Di Bella, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Cultivation of granular sludge with hypersaline oily wastewater. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gong, B.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. Bacterial community structure in simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and organic matter removal process treating saline mustard tuber wastewater as revealed by 16s rRNA sequencing. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.R.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Xie, Q.L.; Bai, S.Y. A review on aerobic granular sludge for heavy metal wastewater treatment. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 535, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsino, S.F.; Capodici, M.; Morici, C.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Simultaneous nitritation-denitritation for the treatment of high-strength nitrogen in hypersaline wastewater by aerobic granular sludge. Water Res. 2016, 88, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-S. Treatment of saline wastewater containing a high concentration of salt using marine bacteria and aerobic granule sludge. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, M.; Bassin, J.P.; de Kreuk, M.K.; Kleerebezem, R.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Evaluating the main and side effects of high salinity on aerobic granular sludge. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Gao, S.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Yu, J. Elevated salinity deteriorated enhanced biological phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor performing simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 121782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, T.; Lin, B.; Tang, Y. Effects of salinity on the performance, microbial community, and functional proteins in an aerobic granular sludge system. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassin, J.P.; Kleerebezem, R.; Muyzer, G.; Rosado, A.S.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.; Dezotti, M. Effect of different salt adaptation strategies on the microbial diversity, activity, and settling of nitrifying sludge in sequencing batch reactors. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 1281–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association (APHA): Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frølund, B.; Palmgren, R.; Keiding, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Extraction of extracellular polymers from activated sludge using a cation exchange resin. Water Res. 1996, 30, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Ma, F.; Guo, H.; Su, D. Enhanced aerobic sludge granulation in a sequencing batch reactor (SBR) by applying mycelial pellets. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Zhuge, Y.; Liu, Y.D. Enhancement of the removal and settling performance for aerobic granular sludge under hypersaline stress. Chemosphere 2018, 212, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, C.P.; Zeng, G.M. Influence of salinity on microorganisms in activated sludge processes: A review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Song, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor with mixed carbon sources: Reactor performance, extracellular polymeric substances and microbial successions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Gao, M.C.; Wei, J.F.; Ma, K.D.; Pei, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.S.; Yu, S.P. Long-term effects of salinity on extracellular polymeric substances, microbial activity and microbial community from biofilm and suspended sludge in an anoxic-aerobic sequencing batch biofilm reactor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, W.; Wei, D.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, W.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. System performance and microbial community succession in a partial nitrification biofilm reactor in response to salinity stress. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 270, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fang, F.; Guo, J.; Yan, P. Effect of EPS and its forms of aerobic granular sludge on sludge aggregation performance during granulation process based on xdlvo theory. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; She, Z.; Jin, C.; Yang, S.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, M. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances from sludge and biofilm in a simultaneous nitrification and denitrification system under high salinity stress. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1375–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Liang, H.; He, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, G. Characterization of dissolved extracellular organic matter (dEOM) and bound extracellular organic matter (bEOM) of microcystis aeruginosa and their impacts on uf membrane fouling. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2881–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Ahn, D. The effects of high salinity on nitrogen removal and the formation characteristics of aerobic granular sludge. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, S.; Hasan, M.; Aroua, M.K. Improvement of autohydrogenotrophic nitrite reduction rate through optimization of ph and sodium bicarbonate dose in batch experiments. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 107, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, Z.; Duan, W.; Chen, F. Enhancing effects of sludge biochar on aerobic granular sludge for wastewater treatment. Processes 2022, 10, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wang, Q.; She, Z.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Jin, C. Nitrogen removal pathway and dynamics of microbial community with the increase of salinity in simultaneous nitrification and denitrification process. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, T.; Han, B. Effect of glucose on nitrogen removal and microbial community in anammox-denitrification system. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Mai, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Effects of salinity build-up on the performance and microbial community of partial-denitrification granular sludge with high nitrite accumulation. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, P.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Li, S. Effects of salinity on the simultaneous anammox and denitrification process: Performance, sludge morphology and shifts in microbial communities. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2021, 8, 202099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Han, X.; Jin, Y.; Yu, J. Do increased organic loading rates accelerate aerobic granulation in hypersaline environment? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.F.; Liang, K.; Guo, F.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, G.X. Denitrification performance and microbial community under salinity and mit stresses for reverse osmosis concentrate treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhao, X.; Kang, J. Impact of carbon to nitrogen ratio on the performance of aerobic granular reactor and microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Chen, Q.; Bin, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, W.; Fu, F.; Li, P. Insight into the microbial community and its succession of a coupling anaerobic-aerobic biofilm on semi-suspended bio-carriers. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, A. Stable limited filamentous bulking through keeping the competition between floc-formers and filaments in balance. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, S.; Chen, L.; Lyu, W.; Zhang, W.; Song, J.; Hu, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, H.; et al. A comprehensive comparison between non-bulking and bulking aerobic granular sludge in microbial communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 294, 122151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, A.M.S.; Amorim, C.L.; Costa, J.; Mesquita, D.P.; Ferreira, E.C.; Castro, P.M.L. Long-term stability of a non-adapted aerobic granular sludge process treating fish canning wastewater associated to EPS producers in the core microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, H. Hydrodynamic shear force shaped the microbial community and function in the aerobic granular sequencing batch reactors for low carbon to nitrogen (C/N) municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ming, J.; Yoza, B.A.; Liang, J.; Li, Q.X.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Deng, J.; Wang, Q. Characterization of aerobic granular sludge used for the treatment of petroleum wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Han, F.; Chen, H.; Yao, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhou, W. The effect of salinity on ammonium-assimilating biosystems in hypersaline wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Gao, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.-H. Enhanced aerobic granulation at low temperature by stepwise increasing of salinity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.J.; Deng, Y.L.; Guo, X.S.; Timmons, M.B.; Lu, H.F.; Han, Z.Y.; Ye, Z.Y.; Shi, M.M.; Zhu, S.M. Simultaneous ammonia and nitrate removal in an airlift reactor using poly(butylene succinate) as carbon source and biofilm carrier. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Jin, C.; Liu, R.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Hu, C.; Qu, J. Microbial community structures and functions of hypersaline heterotrophic denitrifying process: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.T.; Ventosa, A.; Mellado, E. Catabolic versatility of aromatic compound-degrading halophilic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 54, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


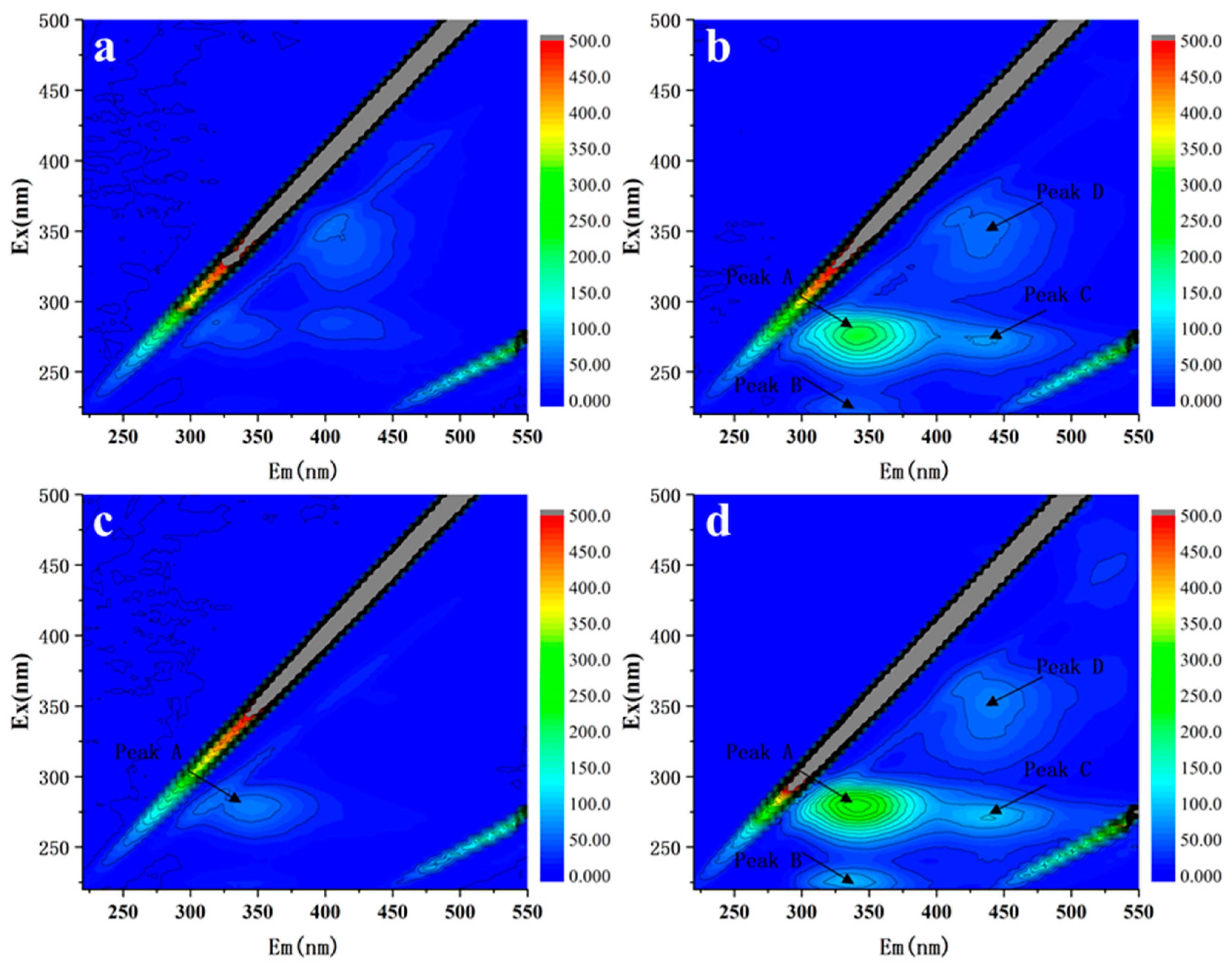
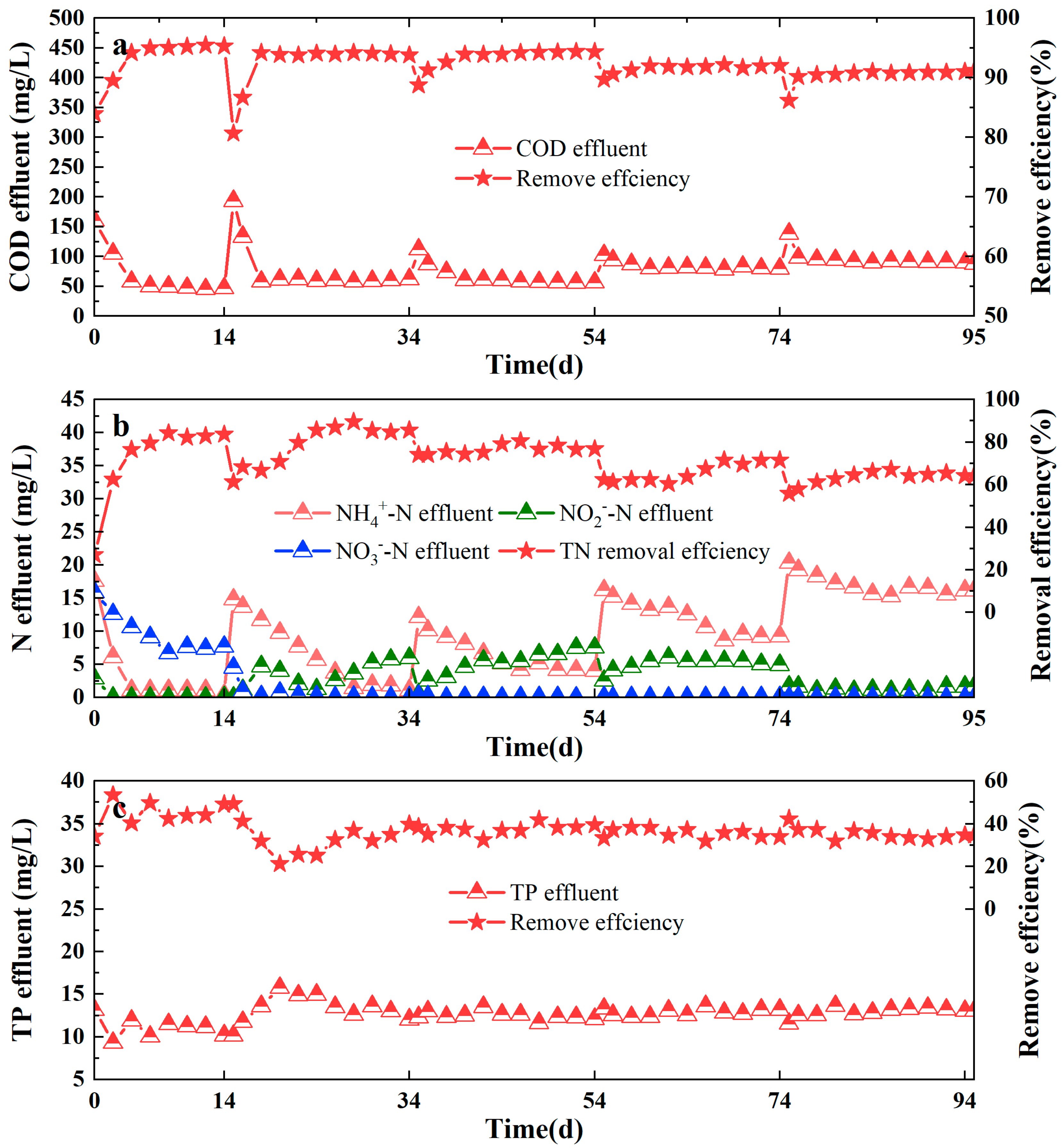
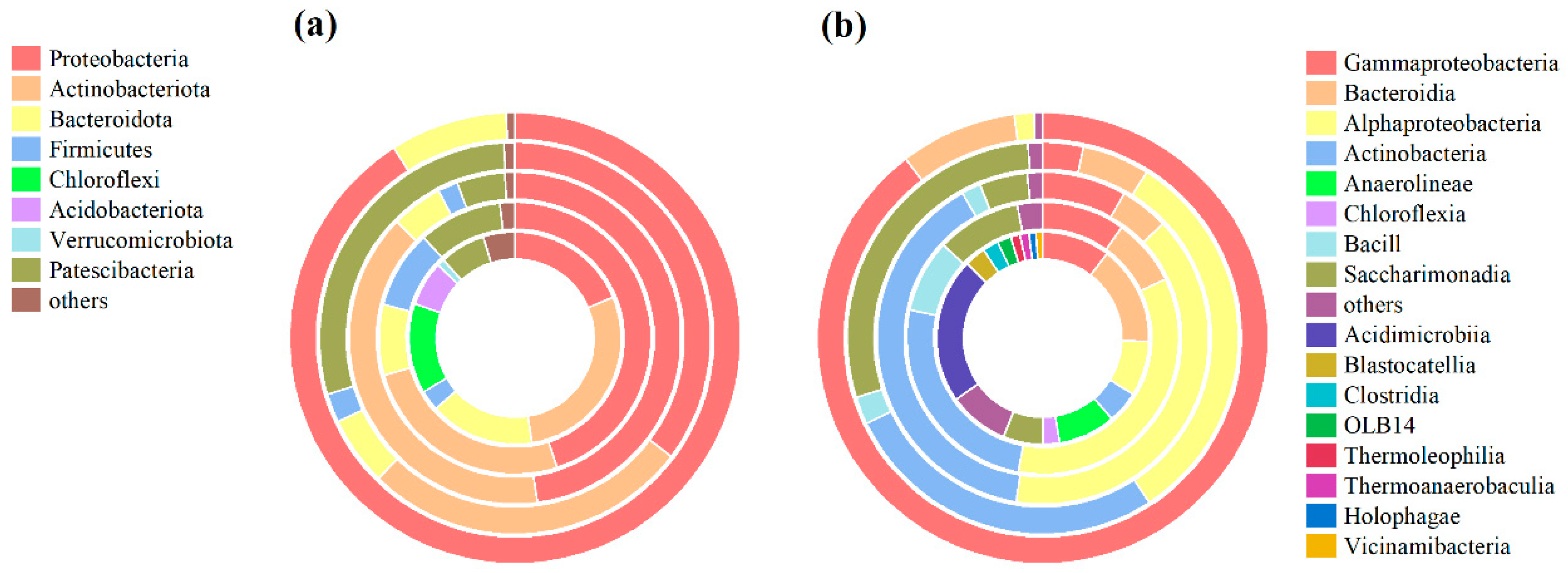
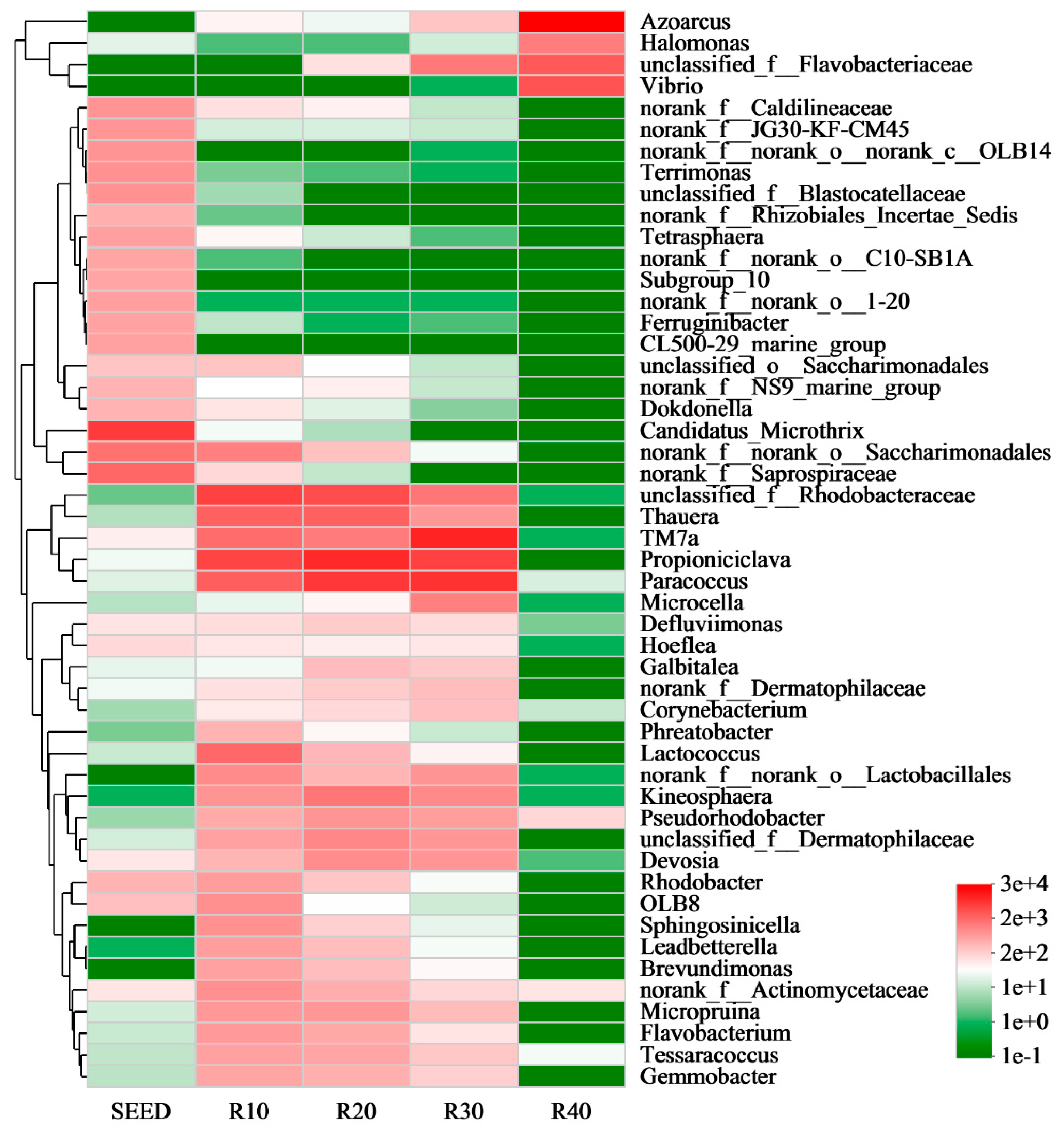
| Time (d) | Salinity (g/L) | MLVSS (g/L) | SVI5 (mL/g) | Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | — | 0.91 ± 0.17 | 257.66 ± 6.21 | 89.08 ± 0.84 |
| 14 | 0 | 1.37 ± 0.21 | 102.99 ± 5.36 | 333.71 ± 21.8 |
| 34 | 10 | 3.52 ± 0.13 | 58.47 ± 3.32 | 396.07 ± 6.14 |
| 54 | 20 | 3.43 ± 0.18 | 46.34 ± 2.36 | 443.39 ± 17.96 |
| 74 | 30 | 3.15 ± 0.17 | 50.68 ± 3.55 | 406.47 ± 10.43 |
| 95 | 40 | 2.72 ± 0.22 | 52.28 ± 3.24 | 373.09 ± 3.22 |
| Sample | Shannon | Simpson | Ace | Chao1 | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEED | 5.37 | 0.034 | 1810.31 | 1787.33 | 0.990 |
| R10 | 3.95 | 0.045 | 635.89 | 654.42 | 0.996 |
| R20 | 3.48 | 0.069 | 631.29 | 486.19 | 0.997 |
| R30 | 3.20 | 0.079 | 434.91 | 409.11 | 0.998 |
| R40 | 1.00 | 0.588 | 91.91 | 87.50 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; He, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of Salinity on Performance and Microbial Community during Granulation Process in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water 2023, 15, 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15223961
Wang M, He J, Dong X, Zhang J. Effect of Salinity on Performance and Microbial Community during Granulation Process in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water. 2023; 15(22):3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15223961
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengfei, Junguo He, Xiangke Dong, and Jie Zhang. 2023. "Effect of Salinity on Performance and Microbial Community during Granulation Process in a Sequencing Batch Reactor" Water 15, no. 22: 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15223961
APA StyleWang, M., He, J., Dong, X., & Zhang, J. (2023). Effect of Salinity on Performance and Microbial Community during Granulation Process in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water, 15(22), 3961. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15223961






