Profiling of Antibiotic Residues in Surface Water of River Yamuna Stretch Passing through Delhi, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Global Literature Survey of Antibiotics from Surface Waters
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Sampling Location
3.3. Chemicals, Standards, and Reagents
3.4. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) Conditions
Mass Spectrophotometer
3.5. Sample Collection and Handling
3.6. Extraction of Antibiotics
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Samples
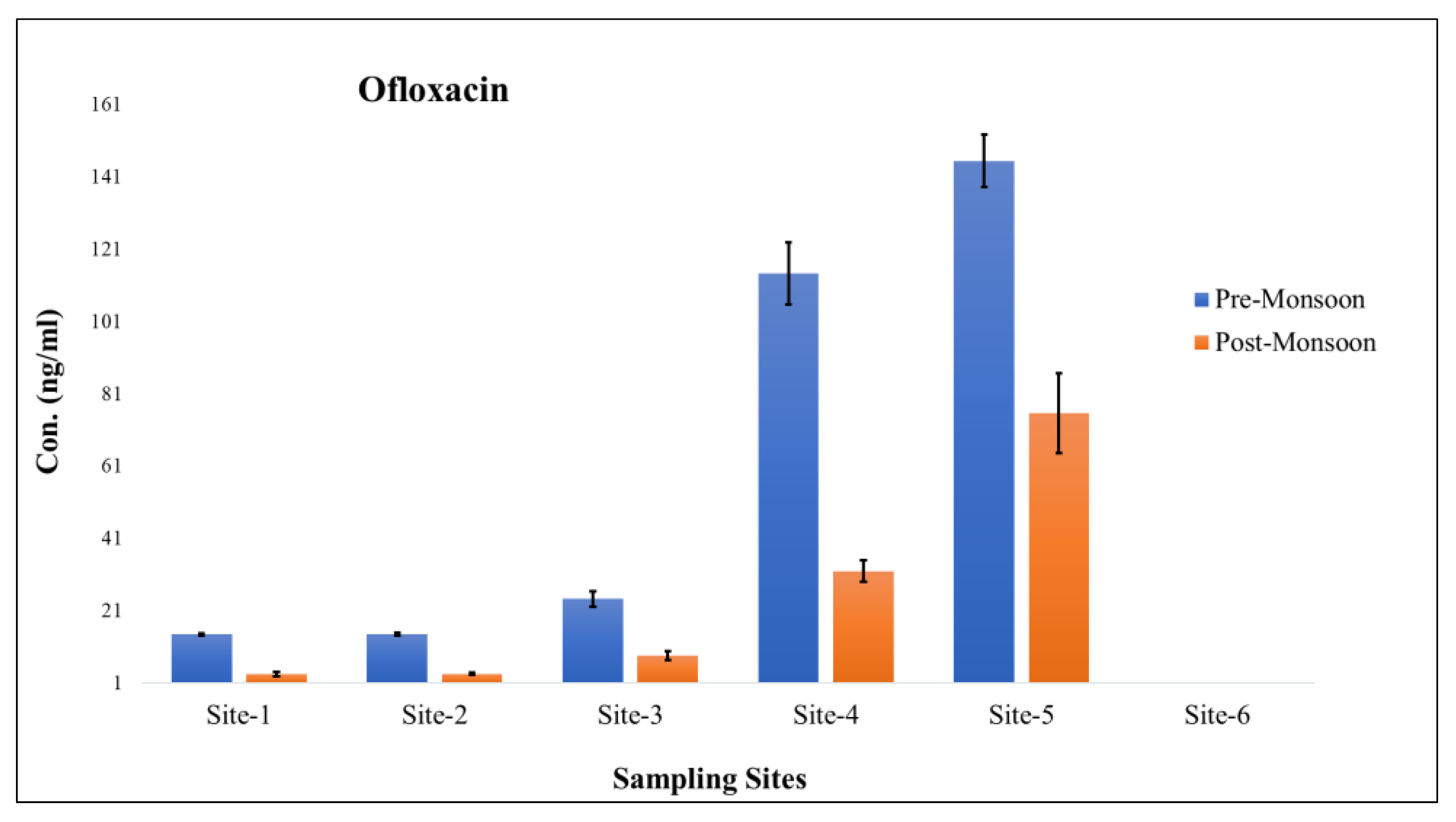
4.2. Occurrence and Concentration of Antibiotics at Different Sampling Locations
4.3. Potential Risk of Developing Antibiotic Resistance
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zafar, R.; Bashir, S.; Nabi, D.; Arshad, M. Occurrence, and quantification of prevalent antibiotics in wastewater samples from Rawalpindi and Islamabad, Pakistan. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 764, 142596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-F.; Lin, C.-F.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Hong, P.-K.A. Sorption, and biodegradation of sulfonamide antibiotics by activated sludge: Experimental assessment using batch data obtained under aerobic conditions. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3389–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, J.V.; Guerrero, C. Antibiotic residue determination in environmental waters by LC-MS. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 466–485, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerer, K. Antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review—Part I. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Hoang, L.; Nghiem, L.D.; Nguyen, N.M.H.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Trinh, Q.T.; Mai, N.H.; Chen, H.; Nguyen, D.D.; et al. Science of the Total Environment Occurrence and risk assessment of multiple classes of antibiotics in urban canals and lakes in Hanoi, Vietnam. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, K. Antibiotics: From prehistory to the present day. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Shao, H.; Huo, Z.; Xie, N.; Gu, J.; Xu, G. Typical antibiotics in the receiving rivers of direct-discharge sources of sewage across Shanghai: Occurrence and source analysis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 21579–21587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollution, C.; Board, C. Water quality status of Yamuna River (1999–2005). Assess Dev. River. 2006. Available online: http://www.yamunariverproject.org/assets/cpcb_2006-water-quality-status.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Husain, A.; Abdul, H.; Khan, N.A.; Dhingra, A.; Ahmed, S.; Naushad, M. Science of the Total Environment Effect of seasonal variation on the occurrences of high-risk pharmaceutical in drain-laden surface water: A risk analysis of Yamuna River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148484. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, R.; Sharma, P.; Kansal, A. Water quality modelling of the river Yamuna (India) using. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 83, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M.; Zafar, R. Antibiotics, AMRs, and ARGs: Fate in the environment. In Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in the Environment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 138–154. [Google Scholar]
- Basin, V.; Kimosop, S.J.; Getenga, Z.M.; Orata, F. Residue levels and discharge loads of antibiotics in wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs), hospital lagoons, and rivers. Environ. Monit. Assess 2016, 188, 532, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Manaia, C.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C.; Michael, I.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes spread into the environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhang, T. Mass flows and removal of antibiotics in two municipal wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.G.J. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, J.; Lou, Q.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y. Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the surface water of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymańska, U.; Wiergowski, M.; Sołtyszewski, I.; Kuzemko, J.; Wiergowska, G.; Woźniak, M.K. Presence of antibiotics in the aquatic environment in Europe and their analytical monitoring: Recent trends and perspectives. Microchem. J. 2019, 147, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Mittal, A.K. Risk assessment of antibiotic residues in different water matrices in India: Key issues and challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7723–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Mittal, A.K. Occurrences and fate of selected human antibiotics in influents and effluents of sewage treatment plant and effluent-receiving river Yamuna in Delhi (India). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Mehmood, S.; Rasheed, T.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Antibiotics traces in the aquatic environment: Persistence and adverse environmental impact. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 13, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical Fate and Partitioning Behavior of Antibiotics in the Aquatic Environment—A Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, H.W.; Minh, T.B.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.W.; So, M.K.; Martin, M.; Lam, P.K.S.; Richardson, B.J. Distribution, fate and risk assessment of antibiotics in sewage treatment plants in Hong Kong, South China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carballo, E.; González-Barreiro, C.; Scharf, S.; Gans, O. Environmental monitoring study of selected veterinary antibiotics in animal manure and soils in Austria. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 148, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, M.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Science of the Total Environment Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleye, A.C.; Adegoke, A.A.; Ramluckan, K.; Fick, J.; Bux, F.; Stenström, T.A. Science of the Total Environment Concentration and reduction of antibiotic residues in selected wastewater treatment plants and receiving waterbodies in Durban, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, R.B.; Eaton, A.D.; Clesceri, L.S. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater; Rice, E.W., Ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R. An introduction to water quality analysis. ESSENCE Int. J. Env. Rehab. Conserv. 2019, 9, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutiyar, P.K.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, A. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety Fate of pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) from River Yamuna, India: An ecotoxicological risk assessment approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurunthachalam, S.K. Pharmaceutical Substances in India are a Point of Great Concern? J. Waste Water Treat. Anal. 2012, 3. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, K.A.; Joshi, G.S. Evaluation of water quality index for River Sabarmati, Gujarat, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.; Suthar, S. Occurrence, seasonal variations, and ecological risk of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in River Ganges at two holy cities of India. Chemosphere 2020, 268, 129331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Khandegar, V. Dataset on assessment of River Yamuna, Delhi, India using indexing approach. Data Br. 2019, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Santiago-Martín, A.; Meffe, R.; Teijón, G.; Hernández, V.M.; López-Heras, I.; Alonso, C.A.; Romasanta, M.A.; de Bustamante, I. Pharmaceuticals and trace metals in the surface water used for crop irrigation: Risk to health or natural attenuation? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, D.L.; Keshari, A.K. Sensitivity analysis of water quality for Delhi stretch of the River Yamuna, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1487–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homem, V.; Alves, A.; Santos, L. Development and validation of a fast procedure to analyze amoxicillin in river waters by direct-injection LC-MS/MS. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 91, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Di Paolo, C.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; Seiler, T.-B.; Hollert, H. Optimization of screening-level risk assessment and priority selection of emerging pollutants–the case of pharmaceuticals in European surface waters. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, S.; Behera, M. Evaluating the effect of the antibiotic ampicillin on performance of a low-cost microbial fuel cell. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact Waste 2020, 24, 4020011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.R.; Al-haideri, H.H.; Hassan, F.M. Detection of Antibiotics in Drinking Water Treatment Plants in Baghdad City, Iraq. Adv. Public Health 2019, 2019, 7851354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Q.-W.; Li, S.-L.; Yin, Z.-Q.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ye, W.-C. Quality evaluation of semen oroxyli through simultaneous quantification of 13 components by high performance liquid chromatography. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 8, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Q.; Cao, X.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, G. Occurrence, sources and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the groundwater: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2015, 1, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Lai, W.W.-P.; Tung, H.-H.; Lin, A.Y.-C. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals, hormones, and perfluorinated compounds in groundwater in Taiwan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carranzo, I.V. Standard Methods for examination of water and wastewater. In Anales De Hidrología Médica; Universidad Complutense de Madrid: Madrid, Spain, 2012; p. 185. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Rai, P.; Singh, A.K.; Verma, P.; Gupta, S. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals in urban wastewater of north Indian cities and risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6663–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goi, G.R.; Mittal, A.K. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) Residues in Water Environment of India: A Neglected but Sensitive Issue. Environ. Health Perspect 2012, 120, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Petrović, M.; Škrbić, B.; Živančev, J.; Ferrando-Climent, L.; Barcelo, D. Determination of 81 pharmaceutical drugs by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry with hybrid triple quadrupole–linear ion trap in different types of water in Serbia. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidha. Occurrence of high levels of fluoroquinolones in aquatic environment due to effluent discharges from bulk drug manufacturers. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact Waste 2017, 21, 5016003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, N.H.; Adak, A. Determination of antimicrobial concentration and associated risk in water sources in West Bengal state of India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtam, F.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B.; Eurin, J.; Dinh, Q.T.; Clément, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Seine River in various hydrological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Le, N.; Hoang, A.Q.; Hoang, T.T.; Nguyen, T.A.; Duong, T.T.; Pham, T.M.; Nguyen, T.D.; Hoang, V.C.; Phung, T.X.; Le, H.T.; et al. Antibiotic and antiparasitic residues in surface water of urban rivers in the Red River Delta (Hanoi, Vietnam): Concentrations, profiles, source estimation, and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Research. 2020, 28, 10622–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccato, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Bagnati, R.; Melis, M.; Fanelli, R. Source, occurrence and fate of antibiotics in the Italian aquatic environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ci, M.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, W.; Gao, X.; Xie, K.; Wang, W. Antibiotics in the surface water and sediment from the tributaries of the Xiaoqing River, China: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 247, 28003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Gu, X.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Q.; Mao, Z. Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in surface water impacted by crab culturing: A case study of Lake Guchenghu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 22619–22628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Dong, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yin, T.; He, W.; An, T.; Tang, Y.; Hou, X.; Chong, S.; Chen, D.; et al. Groundwater antibiotics and microplastics in a drinking-water source area, northern China: Occurrence, spatial distribution, risk assessment, and correlation. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, Y. Residues and risks of veterinary antibiotics in protected vegetable soils following application of different manures. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M.J.; Thomas, K.V. Determination of selected human pharmaceutical compounds in effluent and surface water samples by high-performance liquid chromatography—Electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2003, 1015, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Wong, C.K.C.; Chu, L.M. Distribution of antibiotics in wastewater-irrigated soils and their accumulation in vegetable crops in the Pearl River Delta, Southern China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 11062–11069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Vambol, V. Smart ways of hospital wastewater management, regulatory standards and conventional treatment techniques A short review. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 2019. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, M.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.; Barceló, D. Environmental risk assessment of pharmaceutical residues in wastewater effluents, surface waters and sediments. Talanta 2006, 69, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, A.; Cicero, M.R.; Prestinaci, F.; Bottoni, P.; Carere, M. Bioaccumulation and biomagnification potential of pharmaceuticals with a focus to the aquatic environment. J. Environ. Manage. 2014, 133, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.; Ciorba, P.; Döhla, M.; Exner, M.; Felder, C.; Lenz-Plet, F.; Sib, E.; Skutlarek, D.; Schmithausen, R.; Faerber, H. The investigation of antibiotic residues, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic-resistant organisms in a drinking water reservoir system in Germany. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sampling I.D | Sampling Area | Site-Description | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site-1 | Wazirabad barrage | Initial sampling point | 28.7116 | 77.235 |
| Site-2 | ISBT | 9.2 km from wazirabad barrage | 28.67417 | 77.23235 |
| Site-3 | ITO | 14.9 km from wazirabad barrage | 28.6308 | 77.2506 |
| Site-4 | Sarai Kali Khan | 18.6 km from wazirabad barrage | 28.5915 | 77.27115 |
| Site-5 | Okhla barrage | 21.5 km from wazirabad barrage | 28.54538 | 77.31149 |
| Site-6 | Jamia Millia Islamia | Reference sampling point | 28.5623 | 77.2804 |
| Antibiotics | Calibration Curve | R2 | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ofloxacin | y = 269.05x + 1172.69 | 0.992 | 362.3 | 318.3 | 1.5 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL |
| Amoxicillin | y = 221.43x + 227.59 | 0.999 | 366.2 | 114 | 1.5 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL |
| Erythromycin | y = 644.30x + 673.29 | 0.997 | 734.5 | 158.1 | 1.5 ng/mL | 5 ng/mL |
| Sampling Seasons | Sampling Locations | pH | TSS | BOD | COD | Phosphates | Nitrates | Alkalinity |
| Pre-monsoon | Site-1 | 7.03 | 36.62 | 23.68 | 98.24 | 0.91 | 3.61 | 178 |
| Site-2 | 7.24 | 35.25 | 32.24 | 82.69 | 2.02 | 5.32 | 347 | |
| Site-3 | 7.19 | 26.56 | 38.19 | 74.36 | 2.14 | 4.85 | 354 | |
| Site-4 | 7.38 | 28.31 | 39.81 | 82.58 | 3.63 | 6.72 | 358 | |
| Site-5 | 7.29 | 38.94 | 45.75 | 112.36 | 4.57 | 7.26 | 398 | |
| Average | 7.226 | 33.136 | 35.934 | 90.046 | 2.654 | 5.552 | 327 | |
| Std.Dev | 0.130 | 5.404 | 8.371 | 15.174 | 1.443 | 1.466 | 85.633 | |
| Ref-Site (6) | 7.01 | 21.41 | 19.32 | 20.23 | 0.12 | 0.23 | 25.45 | |
| Post-monsoon | Site-1 | 6.95 | 32.34 | 22.32 | 102.3 | 0.98 | 5.18 | 176 |
| Site-2 | 7.11 | 36.04 | 24.75 | 98.42 | 3.01 | 5.22 | 329 | |
| Site-3 | 7.34 | 31.43 | 34.81 | 107.2 | 3.05 | 6.08 | 367 | |
| Site-4 | 7.28 | 33.41 | 41.68 | 102.4 | 2.76 | 6.45 | 356 | |
| Site-5 | 7.13 | 47.45 | 43.32 | 105.8 | 3.07 | 7.12 | 387 | |
| Average | 7.162 | 36.134 | 33.376 | 103.224 | 2.574 | 6.01 | 323 | |
| Std.Dev | 0.154 | 6.557 | 9.573 | 3.430 | 0.900 | 0.828 | 84.803 | |
| Ref-Site (6) | 6.23 | 19.2 | 17.26 | 19.31 | 0.14 | 0.19 | 23.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akhter, S.; Bhat, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Siddiqi, W.A.; Ahmad, S.; Shrimal, H. Profiling of Antibiotic Residues in Surface Water of River Yamuna Stretch Passing through Delhi, India. Water 2023, 15, 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030527
Akhter S, Bhat MA, Ahmed S, Siddiqi WA, Ahmad S, Shrimal H. Profiling of Antibiotic Residues in Surface Water of River Yamuna Stretch Passing through Delhi, India. Water. 2023; 15(3):527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030527
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkhter, Suriyah, Mohd Aadil Bhat, Sirajuddin Ahmed, Weqar Ahmad Siddiqi, Sayeed Ahmad, and Hitesh Shrimal. 2023. "Profiling of Antibiotic Residues in Surface Water of River Yamuna Stretch Passing through Delhi, India" Water 15, no. 3: 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030527
APA StyleAkhter, S., Bhat, M. A., Ahmed, S., Siddiqi, W. A., Ahmad, S., & Shrimal, H. (2023). Profiling of Antibiotic Residues in Surface Water of River Yamuna Stretch Passing through Delhi, India. Water, 15(3), 527. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030527








