Abstract
Some invasive alien species (IAS) may constitute an important threat to global biodiversity due to major ecological impacts. In 2014, the European Union (EU) introduced a regulation (EU) No 1143/201 on the prevention and management of the introduction and spread of IAS. EU member states are required to carry out an analysis of the introduction and spread of potential IAS in their territories. In the case of aquatic alien species, shipping is considered as the main pathway for their introduction. In this study, a horizon-scanning tool was applied for identifying potential aquatic IAS introduced by shipping into the EU Baltic Sea Region (BSR) countries. This tool has mostly been applied on a country level, but it is more reasonable to study the invasive potentiality at a regional scale, especially for aquatic species that generally disperse over long distances. Individual Baltic countries may also benefit from the results of this study. The result of the horizon-scanning method that we applied produced a list of 27 potential aquatic invaders for the EU BSR countries introduced by international marine and inland shipping. In order, Asia (34% of the species), North America (27% of the species), and Indo-Pacific (23% of the species) were the most frequently listed geographical origins of concern. Marine habitat was the most frequent of the potential IAS, accounting for 41% of the species. Fish (26% of the species), Mollusks (18% of the species), and Crustacea (15% of the species) were the most frequent taxonomic groups. The list of potential IAS was prioritized from highest to lowest probability of invasion (establishment, spread, and impact). Eight species reached the highest probability of invasion. One of the potential IAS, Mytilus galloprovincialis, is native to the Mediterranean Region. These results provide valuable information that policy makers can use to develop more efficient prevention strategies for IAS introduced by shipping into the Baltic Sea.
1. Introduction
Ships are global dispersers of aquatic organisms [1,2]. These organisms commonly attach to the ship’s hulls and/or are transported in ballast water and then released when the water is exchanged [3,4]. Both international marine and inland shipping [2,5,6] are identified as important pathways of non-indigenous aquatic species introduction. The documentation of pathways is essential to detect future invasive alien species (IAS) in a certain region using a horizon-scanning tool [7].
IAS, spreading outside their natural distribution ranges, are important threats for biodiversity, economies, and human health [5,8]. In fact, they are considered as one of the leading causes of global biodiversity loss [9]. Besides, IAS generate economic costs [10,11]. Some of these costs include, e.g., fish-based and recreational activities, the modification of local infrastructure connected with the marine environment [10]. Most of these costs result from management actions: eradication and control [12,13,14]. Moreover, once established, IAS can rapidly expand their ranges across national borders [15]. Therefore, the prevention of the initial introduction and spread should be prioritized as the most cost-efficient measure to combat potential impacts of IAS [16,17]. An effective identification of IAS at early stages of invasion allows countries to act fast when species preventative measures fail [18,19]. For both prevention and rapid action, the identification of IAS is essential as they are likely to spread into new territories [20].
In 2014, the European Union (EU) introduced a regulation (EU) No 1143/2014 on the prevention and management of the introduction and spread of IAS. This regulation provides opportunities for methodological improvements and the applications of new tools to identify potential IAS. Moreover, EU member states are required to carry out a comprehensive analysis and prioritization of the potential IAS in their territories [17]. Fighting the known and established IAS is essential to recover native ecosystems, but the prevention of future invasions has also been identified by the EU as one of the most important steps in the control and management of IAS. Horizon scanning is a predictive tool that has been used by researchers and stakeholders to identify potential IAS, which may be useful to initiate further management actions [7]. This tool was not previously used to the prevention and early identification of IAS in the Baltic Sea. This tool has mostly been applied on a country level, but it is more reasonable to study the invasive potentiality at a regional scale, especially for aquatic species that generally disperse over long distances.
Previous horizon-scanning methods to identify potential IAS have relied on intensive expert consultation and, while often presenting an overview of the potential introduction pathways for individual species, many do not include systematic analyses aimed at prioritizing introduction pathways [21,22]. Invasiveness in locations with similar ecological and climatic conditions is considered one of the most relevant criteria in predicting the invasive behavior of a species [21]. However, a previous study using horizon scanning in northern European countries did not include a formal climate match [22]. Only the European-scale horizon scan carried out by Roy et al. (2015) [23] considered the influence of European climate zones on the potential future establishment of IAS in different European regions. To the best of our knowledge, horizon-scanning was never used to intentionally identify the potential aquatic IAS introduced by shipping into different European Union countries surrounding the Baltic Sea. In this study, an approach to horizon scanning was developed and applied for identifying potential IAS, specifically those aquatic (marine, freshwater, and brackish) species introduced into the Baltic Sea Region (BSR) by shipping. The result will be a list of potential aquatic IAS (plants and animals) identified for the BSR. For each species, the probability of establishment, spread, and impact will also be assessed in order to prioritize the list of IAS. The inventory may facilitate policy decisions relating to the prevention, early detection, and eradication of potential IAS.
2. Horizon-Scanning Approach
A horizon-scanning tool [24,25,26] was applied for the identification of potential IAS introduced into the Baltic Sea (Figure 1) from the EU countries bordering the Baltic Sea: Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark. The method consists of six steps (Figure 2), following this criteria: (1) species non-native to the Baltic Sea, whose distribution range have climatic conditions matching those present in the Baltic Sea, (2) species likely introduced by shipping, (3) only considering aquatic species, (4) the taxonomic groups of the species will be plants (including Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, and Spermatophyta) and animals (vertebrates and invertebrates), (5) the species cannot be previously reported in the Baltic Sea, and (6) species will be categorized by origin and environment. The environment of potential IAS in the Baltic Sea (freshwater, brackish, and marine) was determined based on the World Register of Marine Species [27]. The salinity categories used were: brackish (0.5–30 ppt), marine (greater than 30 ppt), and freshwater (less than 0.5 ppt), based on [28]. The information regarding the origin was obtained from international databases and information portals, e.g., the Information system on aquatic non-indigenous and cryptogenic species [29] and Invasive Species Compendium (CABI) [26].
Figure 1.
The Baltic Sea with bordering EU countries: Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Germany, and Denmark (source: On The World Map—Free printable maps, accessed on 13 November 2022).

Figure 2.
Processes involved in the horizon-scanning method considered at each step of the study.
- Step 1. List of species in regions climatically matched those in the Baltic Sea Region
Only the species from regions climatically matched with the EU Baltic Sea countries (Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, and Sweden) (EU Strategy for the Baltic Sea Region) [30] were included in this horizon-scanning approach.
- Step 2. Shipping as possible introduction pathways of potential IAS to the Baltic Sea
Shipping is a possible pathway for species introduction classified according to the United Nations Environment Programme as the moving of live organisms attached to transporting vessels and associated equipment and media [31,32]. In this study, we considered only species introduced by shipping. The introduction of organisms is also possible in ships’ ballast water and on the outer hull of ships [3,4], so such introduction pathways are also considered within the shipping pathway group and were included in the horizon-scanning approach (Table 1). Note that the species we considered could also be introduced by different pathways.

Table 1.
Possible introduction pathways among shipping of potential IAS to the Baltic Sea.
- Step 3. Selecting possible aquatic habitats of potential IAS to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea represents a highly variable environment [33,34], consists of freshwater, brackish, and marine species, and potentially introduced species from different habitats (freshwater, brackish, and marine) may be possible invasive alien species [35,36]. The Baltic Sea creates a multitude of different habitats from oligohaline to polyhaline conditions, with a distinct gradient from fresh- to saltwater, including river deltas, estuaries, and saline conditions in the Danish Straits (Ref. [37]; Table 2). The information on habitat type was obtained using a horizon-scanning tool [26].

Table 2.
Possible habitats of potential IAS to the Baltic Sea.
- Step 4. Selecting the taxonomic groups of potential IAS in the Baltic Sea
The aim of the study is to assess different species that may potentially be introduced into the Baltic Sea by shipping. The taxonomic groups considered were: invertebrates, vertebrates, and plants (Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, and Spermatophyta).
- Step 5. Alien species were then screened using the criteria in [24]: only aquatic alien species that have not been recorded in the Baltic Sea or Baltic inland waters but are potentially able to reproduce in the target waters.
These data were obtained from the following databases: Invasive Species Compendium (CABI) [26], European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN) [38], Global Information System on Fishes (Fishbase) [39], and Global Invasive Species Database (GISD) [40].
- Step 6. Inventory of the origin and environments of the species on the list of potential IAS for the target sea. The potential IAS are categorized according to the origin and environment.
The information on the origin was obtained from international databases and information portals, e.g., the information system on the aquatic and cryptogenic non-indigenous species (AquaNIS) [29] and Invasive Species Compendium (CABI) [26].
The information on the environment of potential IAS to the Baltic Sea was obtained from the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) [41].
Prioritization of the List of Potential IAS
The list of potential IAS was prioritized based on the probability of establishment, spread, and impact of each species. Following a similar procedure used in previous studies [7,23], for each invasion stage (establishment, spread, and impact), we assigned a probability value from 1 to 5. For the introduction stage, we assumed that the probability of introduction was high for all the species in the list. Then, for each species, we multiplied the three probability values. The result was a probability of invasion for each species, being the maximum score 125 and the minimum 1. Finally, we ordered the species from higher to lower probability of invasion. The available information from the species was essential to assign the probability values. We used a semi-quantitative approach, which is useful to provide us with an idea of the species with the most invasive potential. The criteria to provide the probability scores was similar as that used in previous studies [7,23]. For instance, the species with high genetic variability and those reported to grow fast and/or tolerate a high range of environmental conditions (also habitat generalists) were considered to have a high probability of establishment. Additionally, the species known to have elevated competitive abilities were considered as those with high probabilities of establishment. The species with high reproduction capacities, able to, naturally and/or artificially (facilitated by humans), expand their distributional ranges in different areas, were contemplated as those with high probabilities to spread. The species able to adapt and evolve in the introduced range were also considered as those with high spread probabilities. Finally, we provide a high probability of impact to the species for which their negative effects to biodiversity, ecosystems, and ecosystem services are reported in the literature. If the species is considered a harmful species in other parts of the world in terms of its ecological and socioeconomic effects, then the probability of impact for that species will also be high [7,23]. The information from the species was obtained from the literature and the databases: the Global Invasive Species Database (GISD) [40] and Invasive Species Compendium (CABI) [26]. One specific criterion that we followed was: for each invasion stage of each species, we assigned the lowest probability (1) both when it is known that the probability is low and when no information is available. The method for species prioritization may not be the most precise and different researchers may assign different scores, but this surely helps managers to easily identify the most dangerous IAS and the most threatened native communities, habitats, and ecosystems and focus the efforts on them.
3. Results
The horizon-scanning tool was applied to create the list of potential IAS introduced by shipping into the Baltic Sea. The resulting list (consisting of 27 species) (Table 3) comprised potential IAS that are recommended for prevention and early eradication measures in the Baltic Sea. There are different taxonomic groups among the potential IAS: fishes, mollusks, crustaceans, tunicata, bryozoan, and plants (Chlorophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta, and Spermatophyta) (Figure 3). The most common taxon of the list was fish, following by mollusk and crustacean (Figure 3). Regarding donor regions, Asia and North America were the most frequently listed geographical origins (native ranges) of concern (Figure 4). The marine habitat region was the most frequent, accounting for 41% of the species (Figure 5).

Table 3.
List of potential IAS in the Baltic Sea introduced by shipping.
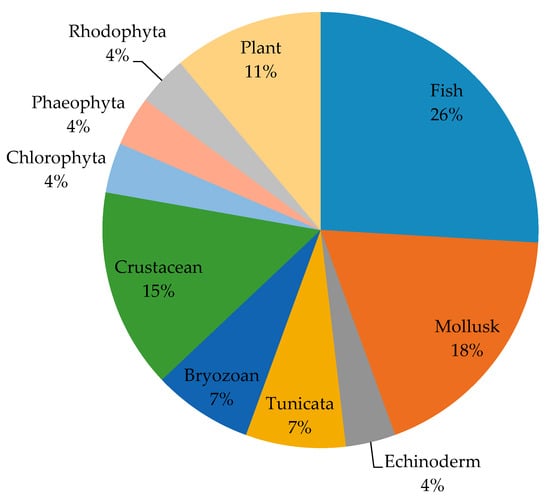
Figure 3.
Taxonomic groups of the potential IAS in the Baltic Sea.
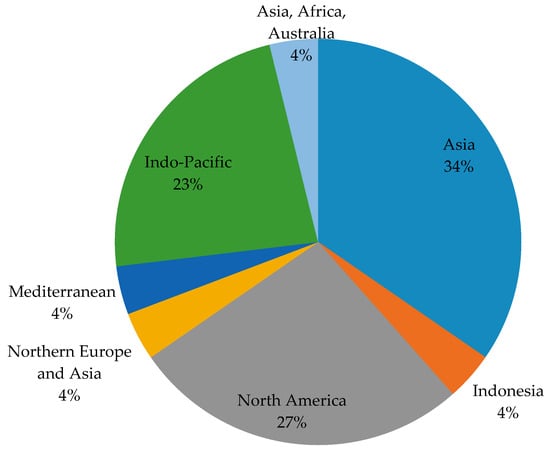
Figure 4.
Geographical origin of the potential IAS in the Baltic Sea.
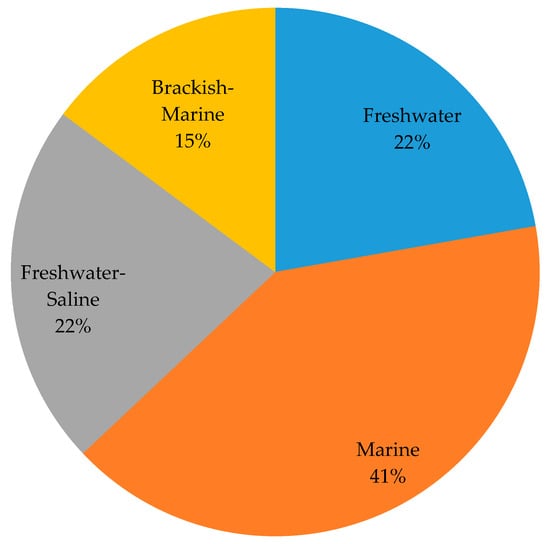
Figure 5.
Environments of the potential IAS in the Baltic Sea (information of the environment of each species was based on WoRMS [28]). Saline means brackish or marine habitats.
After the prioritization of species, we obtained four clear groups of species that shared the same probabilities of invasion (establishment, spread, and impact). The group sharing the highest probability of invasion contain eight species from different taxonomic groups: Plants (three species), Echinoderm (one species), Tunicata (one species), Crustacean (one species), Rhodophyta (one species), and Mollusk (one species). In general, fish species resulted to be less problematic, with low probabilities of invasion as compared to the other species (Table 4).

Table 4.
Prioritized list of species. The potential invasive species for the Baltic Sea are listed from highest to lowest probability of invasion. For each species, the scores (1–125) were obtained by multiplying the probabilities of establishment, spread, and impact. Probabilities are assigned based on previous information found in the literature and Global Invasive Species Database (GISD) [40] and Invasive Species Compendium (CABI) [26]. Different colors group species sharing the same scores.
4. Discussion
Shipping is considered as the most important pathway of the introduction of aquatic alien species into the Baltic Sea [42] and is in the ranking of the most serious vectors of unintentional species introduced to this sea. The introduction via ballast water, sediment, and ship bilge water is probable and needs a specific regulation and management at the regional scale to improve prevention measures [43]. Besides, existing legislation should be better implemented, e.g., the Ballast Water Management Convention BWM (IMO) [1,32]. In fact, the International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships’ Ballast Water and Sediments entered into force globally on 8 September 2017. According to IMO (2004) [43], all the ships engaged in international trade are required to manage their ballast water to avoid the introduction of alien species into coastal areas, including exchanging their ballast water (D-1 standard) or treating it using an approved ballast water management system (D-2 standard). All ships must carry a ballast water record book and an International Ballast Water Management Certificate. The D-1 standard requires ships to exchange their ballast water in open seas, away from coastal waters. Ideally, this means at least 200 nautical miles from land and in water at least 200 m deep. All ships will have to conform to the D-2 standard. For most ships, this involves installing special equipment. The ship should meet the D-2 standard at a date determined by its flag state, but not later than 8 September 2024. Until then, the introduction of new IAS is possible.
Moreover, biofouling, the unwanted colonization of aquatic organisms on ships’ hulls, may have a huge environmental and economic impact: not only on spread of non-indigenous species, but also on increasing vessel fuel consumption, operating costs for vessels, and greenhouse gas emissions [44]. Therefore, the guidelines for the control and management of ships’ biofouling to minimize the transfer of invasive aquatic species (Biofouling Guidelines) (resolution MEPC.207(62)) [45] are intended to provide a consistent approach to the management of biofouling. Management actions such as, ship cleaning, ship repair, and anti-fouling coatings should be implemented. The Guidelines were further supplemented by the guidance for minimizing the transfer of invasive aquatic species as biofouling (hull fouling) for recreational crafts, which was approved by the MEPC at its sixty-fourth session in October 2012 and circulated as MEPC.1/Circ.792 [46]. Therefore, biofouling control solutions, e.g., using coatings to protect vessels against biofouling, should be applied [47,48,49,50,51]. However, anti-fouling management actions are not always sufficient to prevent the introduction of alien species.
Aquatic species spread through the global shipping network [2,52] and the Trans-European Inland Waterway network [53,54]. The ‘Corridor’ pathway connects aquatic environments and emphasizes the role of large-scale canals that connect river catchments, waterways, basins, and seas. This means that there is still a considerable risk of species introduction by not only large cargo vessels but also by small, military, or recreational ships and boats [2] and from using vessel components, e.g., sailing/angling equipment and ropes [55]. Additionally, the introduction probability via biofouling as hitchhikers on ships using corridors is confirmed [3,4,32]. All these pathways of aquatic species introduction by shipping were implemented in the horizon scanning.
Under anthropopressure, during human-assisted ship transport, many organisms may spread beyond their native ranges. In fact, the species that were previously identified as potentially invasive for the Baltic region via shipping in 2015 [22], such as Dikerogammarus villosus, Palaemon macrodactylus, Neogobius gymnotrachelus, N. fluviatilis, and N. kessleri, are already present in the Baltic countries [26]. Our study predicted that the geographical origins of potential IAS in the Baltic Sea are Asia, North America, Indo-Pacific, Europe, and even warmer regions, such as the Mediterranean, Indonesia, Africa, and Australia. Our result about the potentiality of warmer regions to act as donors of IAS to the Baltic region confirm previous models [5], which predicted that climate warming will lead to elevated invasions in temperate regions. If water temperatures continue increasing under climate warming, many species from warm geographical regions will find appropriate environmental conditions at higher latitudes [56]. From the best of our knowledge, no aquatic species native to the Mediterranean Region have been recorded in the Baltic Sea. However, caution is needed as the horizon scanning we performed identified a potential invasive species of the Baltic Sea from the Mediterranean Sea, specifically, the commercial species of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. The potential impact of this species once it is established in the new ecosystem is uncertain, but it was reported that it can outcompete native mussels and the probability of establishment and spread is rather high due to its high adaptability to different environments and its high reproductive potential [26]. Prevention measures on this species should be based on prohibiting cultivation in foreign areas and monitoring unintentional introductions.
Special caution is needed for the worst potential aquatic IAS identified for the Baltic region, i.e., those with invasion scores of 125. All these species are easily established in the new ecosystem, able to rapidly spread, and they can cause important ecological and economical damages [26]. For instance, the species Faxonius rusticus of North American origin is considered one of the most aggressive crayfish, able to decrease biodiversity and cause cascading trophic interactions. In turn, Limnoperna fortunei from Asia, may cause environmental impact and great economic consequences connected with biofouling problems. The control measures for these species are extremely difficult and costly and for some of them, such as Grateloupia turuturu, Cabomba caroliniana, and Limnoperna fortunei, control measures are nearly ineffective [26]. Besides, control methods may have secondary undesirable effects because some of them, such as the chemical methods, are not species-specific. Prevention measures are essential to face these invasions, implementing, e.g., education campaigns informing about the importance to properly clean ships that may contains potential IAS species or involving citizens in detecting the presence of easily identifiable IAS, such as F. rusticus. It is also recommended to use Integrated Pest Management, considering a combination of different control measures at early stages of invasion. The research on the ecology and management of these species should be encouraged to create rapid response plans (RRP), as the one already available for the species Myriophyllum heterophyllum. Collaboration among countries is essential to effectively prevent the spread of IAS and implement RRPs. In the case of plants, it is important to know their dispersal period in the invaded area to implement control measures out of that period [26].
The water salinity of donor and recipient regions is one of the most important environmental factors when we consider potential distribution of species [57]. For an invasive species, it is important not only to spread, but also to establish permanent populations in the invaded areas. The species identified in this study as potential IAS in the Baltic Sea are mostly inhabitants of marine habitats, but some of them are euryhaline (prefer freshwater to saline environment) or may live in saline (brackish and marine) environments. The wide range of water salinity in the recipient region (the Baltic Sea) increases the possibility for the listed species to establish in the future. The salinity gradient in the Baltic Sea is from almost 0 ppt in the innermost parts of the large gulfs to 6–8 ppt in the Baltic proper and to about 35 ppt in the Kattegat (because the Kattegat is characterized by a quite sharp halocline at about 15 m depth dividing the surface mixed layer with a salinity of from 15 ppt to 25 ppt from the deep water with salinity from 32 ppt to about 35 ppt); this causes the Baltic Sea to be susceptible to invasions of freshwater, brackish, and marine species [42,58]. The salinity preferences of analyzed species were included in horizon scanning.
We should also remember that a successful invasion depends on multiple other factors such as, e.g., species interactions (e.g., [59]) and competition with native species (e.g., [60], which are still not included in the horizon-scanning tool. The Baltic Sea is a geologically young, species-poor system that is likely to have decreased biotic resistance to invasion [35], so the number of IAS is still growing [61]. Most of the species listed here as potential invaders of the Baltic Sea have elevated competitive abilities and are able to affect native diversity.
The present study represents the first step to establish potential IAS in the Baltic Sea, being essential to the development of future studies to experimentally identify the invasive potential of the listed species. However, predictions based on horizon scanning [25] should be compared to other risk assessments to obtain more information to implement monitoring programs and start processes of early warning and early detection. Climate matching among donor and recipient regions of IAS is an important step to identify potential IAS using horizon scanning. For instance, accounting for climate matching, we identified potential IAS that may be introduced via shipping in the Baltic region that were not previously identified. In addition, researchers could also use other methods, such as modeling future invasions, to prioritize the potential IAS [62]. Such a tool also provides a reliable method to identify possible IAS that could arrive in the future. Further steps, monitoring surveys, not yet performed in all Baltic ports, consequently, will be needed. The list of potential IAS provides a basis for cost-efficient management measures. The further spread of IAS into the Baltic Sea may have consequences for the economies of all the countries in the Baltic Sea Region.
5. Conclusions
Horizon scanning supports decision making and helps identify, categorize, and prioritize potential invasive species from regional to more local (e.g., country and city) levels. The horizon scanning presented here may be also applied in other regions, but it is necessary the use of available data on climatically matched countries for the potential IAS. We identified eight aquatic species with high probabilities of invasion (establishment, spread, and impact) in the Baltic Sea, being good candidates in which managers may start applying prevention measures. Horizon scanning provides a starting point for the design of the early identification and rapid action measures for the effective management of potential IAS. If some species are unsuitable to be in the Baltic Sea, then ways to prevent their spread should be found. Therefore, further steps and monitoring surveys will be needed.
Author Contributions
A.D.-K.—conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data duration, writing—original draft preparation, review and editing, visualization, and supervision. S.M.-V.—methodology, formal analysis, investigation, and writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Ricciardi, A. Tracking marine alien species by ship movements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5470–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saebi, M.; Xu, J.; Grey, E.K.; Lodge, D.M.; Corbett, J.J.; Chawla, N. Higher-order patterns of aquatic species spread through the global shipping network. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0220353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupak, J.; Hałupka, M.; Gruszka, P. Porastanie kadłubów małych statków jako sposób rozprzestrzeniania się makrozoobentosu. Inż. Ekol. 2014, 37, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppäkoski, E.; Gollasch, S.; Gruszka, P.; Ojaveer, H.; Olenin, S.; Panov, V. The Baltic—A sea of invaders. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seebens, H.; Schwartz, N.; Schupp, P.J.; Blasius, B. Predicting the spread of marine species introduced by global shipping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinskaya, T.; Semenchenko, V.; Minchin, D. A pathways risk assessment of aquatic non-indigenous macroinvertebrates passing to, and through, the Central European invasion corridor. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2020, 11, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.E.; Adriaens, T.; Aldridge, D.C.; Bacher, S.; Bishop, J.D.D.; Blackburn, T.M.; Branquart, E.; Brodie, J.; Carboneras, C.; Cook, E.J.; et al. Invasive Alien Species—Prioritising Prevention Efforts through Horizon Scanning; ENV.B.2/ETU/2014/0016; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015; p. 227.
- CBD. Convention on Biological Diversity. 1993. Available online: http://www.cbd.int/ (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melillo, J.M. Human Domination of Earth’s Ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagne, C.; Leroy, B.; Gozlan, R.E.; Vaissière, A.-C.; Assailly, C.; Nuninger, L.; Roiz, D.; Jourdain, F.; Jarić, I.; Courchamp, F. InvaCost, a public database of the economic costs of biological invasions worldwide. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, A.; Oficialdegui, F.J.; Cuthbert, R.N.; Kourantidou, M.; South, J.; Tricarico, E.; Gozlan, R.E.; Courchamp, F.; Haubrock, P.J. Identifying economic costs and knowledge gaps of invasive aquatic crustaceans. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colautti, R.I.; Bailey, S.A.; Van Overdijk, C.D.A.; Amundsen, K.; MacIsaac, H.J. Characterised and projected costs of nonindigenous species in Canada. Biol. Invasions 2006, 8, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilà, M.; Basnou, C.; Pyšek, P.; Josefsson, M.; Genovesi, P.; Gollasch, S.; Nentwig, W.; Olenin, S.; Roques, A.; Roy, D.; et al. How well do we understand the impacts of alien species on ecosystem services? A pan-European, cross-taxa assessment. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinden, J.; Gong, W.; Jones, R. Estimating the costs of protecting native species from invasive animal pests in New South Wales, Australia. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 50, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, S.M.; Kark, S. Amassing efforts against alien invasive species in Europe. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyšek, P.; Hulme, P.E. Spatio-temporal dynamics of plant invasions: Linking pattern to process. Ecoscience 2005, 12, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Regulation (EU) No 1143/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 October 2014 on the prevention and management of the introduction and spread of invasive alien species. Off. J. Eur. Union 2014, 317, 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, B.; Lodge, D.M.; Finnoff, D.; Shogren, J.F.; Lewis, M.A.; Lamberti, G. An ounce of prevention or a pound of cure: Bioeconomic risk analysis of invasive species. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Berthou, E.; Alcaraz, C.; Pou-Rovira, Q.; Zamora, L.; Coenders, G.; Feo, C. Introduction pathways and establishment rates of invasive aquatic species in Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, C.; Kettunen, M.; Genovesi, P.; Essl, F.; Gollasch, S.; Rabitsch, W.; Scalera, R.; Starfinger, U.; Ten Brink, P. Assessment to Support Continued Development of the EU Strategy to Combat Invasive Alien Species; Final Report for the European Commission; Institute for European Environmental Policy (IEEP): Brussels, Belgium, 2010; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, M.H. Biological Invasions; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1996; p. 244. [Google Scholar]
- NOBANIS. Invasive Alien Species Pathway Analysis and Horizon Scanning for Countries in Northern Europe; TemaNord 2015:517; Nordic Council of Ministers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2015; p. 229. Available online: https://www.nobanis.org/globalassets/nobanis-projects/invasive-alien-species---pathway-analysis-and-horizon-scanning-for-countries-in-northern-europe.pdf (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Roy, H.E.; Bacher, S.; Essl, F.; Adriaens, T.; Aldridge, D.C.; Bishop, J.D.D.; Blackburn Tim, M.; Branquart, E.; Brodie, J.; Carboeras, C.; et al. Developing a list of invasive alien species likely to threaten biodiversity and ecosystems in the European Union. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1032–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, D.; Roy, S.; Baker, R.; Cannon, R.; Eyre, D.; Hill, M.; Wagner, M.; Preston, C.; Roy, H.; Beckmann, B.; et al. Horizon Scanning for New Invasive Non-Native Animal Species in England; Natural England: Sheffield, UK, 2009; p. 111.
- CABI. Horizon Scanning Tool. 2022. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/horizonscanningtool (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- CABI. CABI Compendium; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2023; Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/journal/cabicompendium (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. 2022. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/ (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Venice System. The Venice system for the classification of marine waters according to salinity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1958, 3, 245–352. [Google Scholar]
- AquaNIS. Information System on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species. 2020. Available online: http://www.corpi.ku.lt/databases/index.php/aquanis (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- EUSBSR. EU Strategy for the Baltic Sea Region. 2009. Available online: https://www.euro-access.eu/regions/eusbsr_-_baltic_sea_region (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- UNEP. Pathways of Introduction of Invasive Species, Their Prioritization and Management. 2014. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/doc/meetings/sbstta/sbstta-18/official/sbstta-18-09-add1-en.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2022).
- Tsiamis, K.; Cardoso, A.C.; Gervasini, E. The European Alien Species Information Network on the Convention on Biological Diversity pathways categorization. NeoBiota 2017, 32, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraufvelin, P.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z.; Bergstr, U.; Florin, A.B.; Lehikoinen, A.; Mattila, J.; Arula, T.; Briekmane, L.; Brown, E.J.; Celmer, Z.; et al. Essential coastal habitats for fish in the Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 204, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; Lieberum, C.; Bock, G.; Karez, R. Environmental parameters of shallow water habitats in the SW Baltic Sea. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaveer, H.; Jaanus, A.; MacKenzie, B.R.; Martin, G.; Olenin, S.; Radziejewska, T.; Telesh, I.; Zettler, M.L.; Zaiko, A. Status of biodiversity in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuorinen, I.; Hänninen, J.; Rajasilta, M.; Laine, P.; Eklund, J.; Montesino-Pouzols, F.; Corona, F.; Junker, K.; Meier, M.H.E.; Dippner, J.W. Scenario simulations of future salinity and ecological consequences in the Baltic Sea and adjacent North Sea areas—Implications for environmental monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 50, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feistel, R.; Weinreben, S.; Wolf, H.; Seitz, S.; Spitzer, P.; Adel, G.; Nausch, B.; Schneider, D.; Wright, D. Density and absolute salinity of the Baltic Sea 2006–2009. Ocean Sci. 2010, 6, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASIN. European Alien Species Information Network 2022. Available online: https://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu/easin (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Fishbase. Global Information System on Fishes 2022. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- GISD. Global Invasive Species Database 2022. Available online: http://www.iucngisd.org/gisd/ (accessed on 2 October 2022).
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Fidalgo, M.L. Euryhalinity and geographical origin aid global crayfish invasion. Water 2023. Under review. [Google Scholar]
- Gollasch, S.; Leppäkoski, E. Risk assessment and management scenarios for ballast water mediated species introductions into the Baltic Sea. Aquat. Invasions 2007, 2, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. International Convention for the Control and Management of Ships Ballast Water and Sediments of IMO; IMO: London, UK, 2004; Available online: http://www.imo.org/home.asp (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Nakano, D.; Strayer, D.L. Biofouling animals in freshwater: Biology, impacts, and ecosystem engineering. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine Environment Protection Committee. Guidelines for the Control and Management of Ships’ Biofouling to Minimize the Transfer of Invasive Aquatic Species; Resolution MEPC.207(62) Adopted on 15 July 2011; Marine Environment Protection Committee: Oxfordshire, UK, 2011; Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/OurWork/Environment/Documents/RESOLUTION%20MEPC.207[62].pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- IMO. Guidance for Minimizing the Transfer of Invasive Aquatic Species as Biofouling (Hull Fouling) for Recreational Craft; MEPC.1/Circ.792; IMO: London, UK, 2012; Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/OurWork/Environment/Documents/MEPC.1-Circ.792.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Pelletier, E.; Bonnet, C.; Lemarchand, K. Biofouling growth in cold estuarine waters and evaluation of some chitosan and copper ant-fouling paints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 3209–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magin, C.M.; Cooper, S.P.; Brennan, A. Non-toxic antifouling strategies. Mater. Today 2010, 13, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobosz, K.M.; Kolewe, K.W.; Schiffman, J.D. Green materials science and engineering reduces biofouling: Approeches for medical and membrane-based technologies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nir, S.; Reches, M. Bio-inspired antifouling approaches: The quest towards non-toxic and non-biocidal materials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 39, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faÿ, F.; Horel, G.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K. 2018 Effect of biocidal coatings on microfouling: In Vitro and In Situ results. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 114, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, P.; Kölzsch, A.; Gastner, T.; Blasius, B. The complex network of global ship movements. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bij de Vaate, A.; Jażdżewski, K.; Ketelaars, H.A.M.; Gollasch, S.; Van der Velde, G. Geographical patterns in range extension of Ponto-Caspian macroinvertebrate species in Europe. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B.S.; Nehring, S.; Panov, V.E. Waterways as invasion highways: Impact of climate change and globalization. In Biological Invasions; Ecological Studies No. 193; Nentwig, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 59–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bącela-Spychalska, K. Attachment ability of two invasive amphipod species may promote their spread by overland transport. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2016, 26, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Medina-Villar, S. Alien species of Mediterranean origin in the Baltic Sea Region: Current state and risk assessment. Environ. Rev. 2020, 28, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Graca, B. Laboratory study of the effect of salinity and ionic composition of water on the mortality and osmoregulation of the gammarid amphipod Dikerogammarus haemobaphes (Eichwald, 1841): Implications for understanding its invasive distribution pattern. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2014, 47, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svansson, A. Physical and Chemical Oceanography of the Skagerrak and the Kattegat; Fishery Board of Sweden, Institute of Marine Research: Lysekil, Sweden, 1975; Volume 1, p. 88. [Google Scholar]
- Dueñas, M.-A.; Ruffhead, H.J.; Wakefield, N.H.; Roberts, P.D.; Hemming, D.J.; Diaz-Soltero, H. The role played by invasive species in interactions with endangered and threatened species in the United States: A systematic review. Biodivers. Conserv. 2018, 27, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiec, J.; Dobrzycka-Krahel, A. New data on the non-indigenous gammarids in the Vistula Delta and the Vistula Lagoon. Oceanologia 2008, 50, 443–447. [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A.; Bogalecka, M. The Baltic Sea under anthropopressure—The sea of paradoxes. Water 2022, 14, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paini, D.R.; Yemshanov, D. Modelling the arrival of invasive organisms via the international marine shipping network: A Khapra beetle study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).