Novel Design of Double Slope Solar Distiller with Prismatic Absorber Basin, Linen Wicks, and Dual Parallel Spraying Nozzles: Experimental Investigation and Energic–Exergic-Economic Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
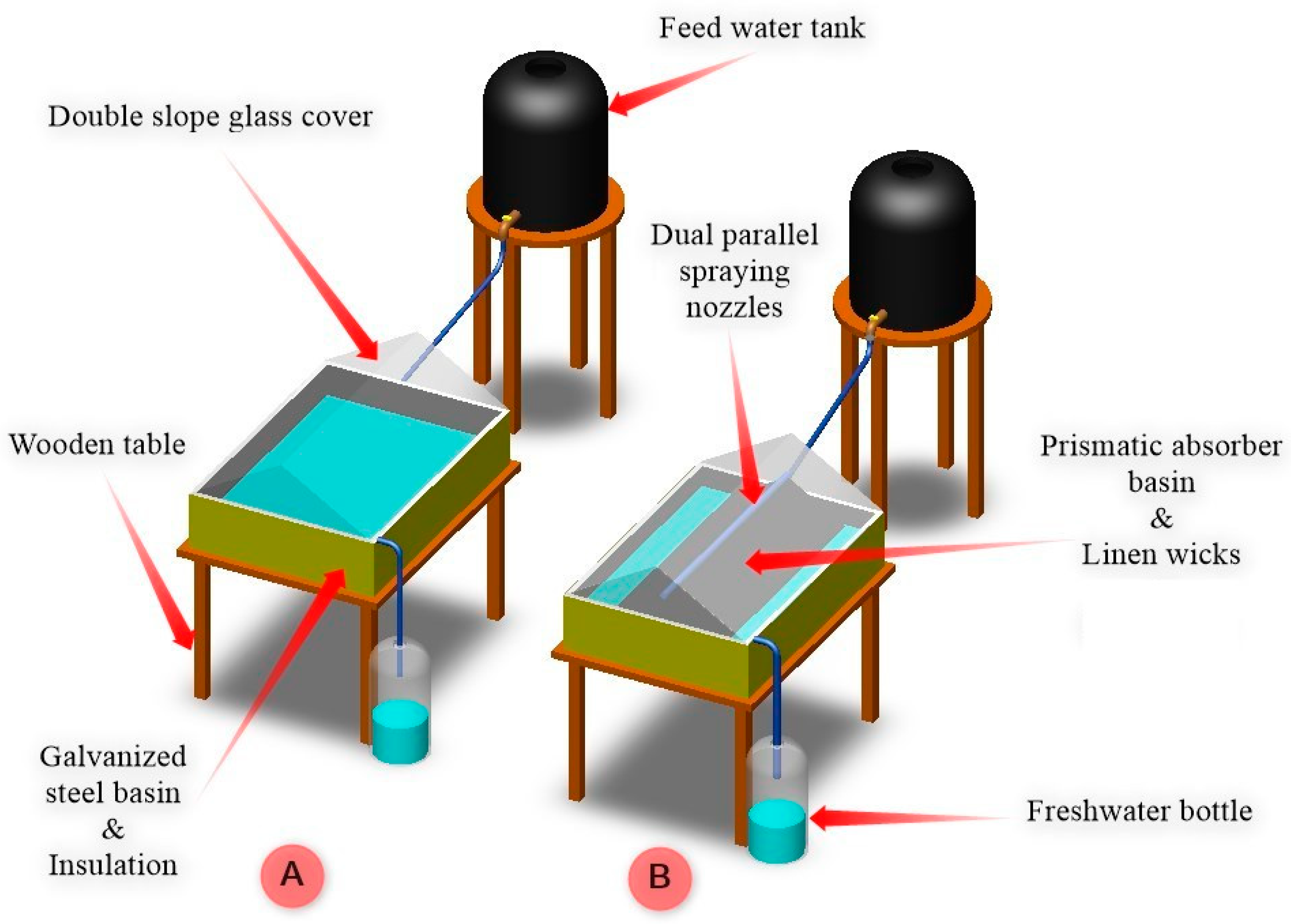
- A new double slope solar distiller with a wick prismatic basin and dual parallel spraying nozzles (DSSD-WPB&DPSN) is investigated for the first time and compared to the traditional double slope solar distiller (TDSSD).
- Modified DSSD-WPB&DPSN and TDSSD are designed, manufactured, and examined under the same weather conditions of Tanta (31° E and 30.5° N), Egypt.
- A comparative exergetic–energetic assessment of the two studied distillers is accomplished to explore the effects of the proposed applied modifications on the performance of the DSSD.
- A cost analysis is carried out to assess the production cost per liter of freshwater obtained by the two cases of DSSD.
2. Materials and Methods
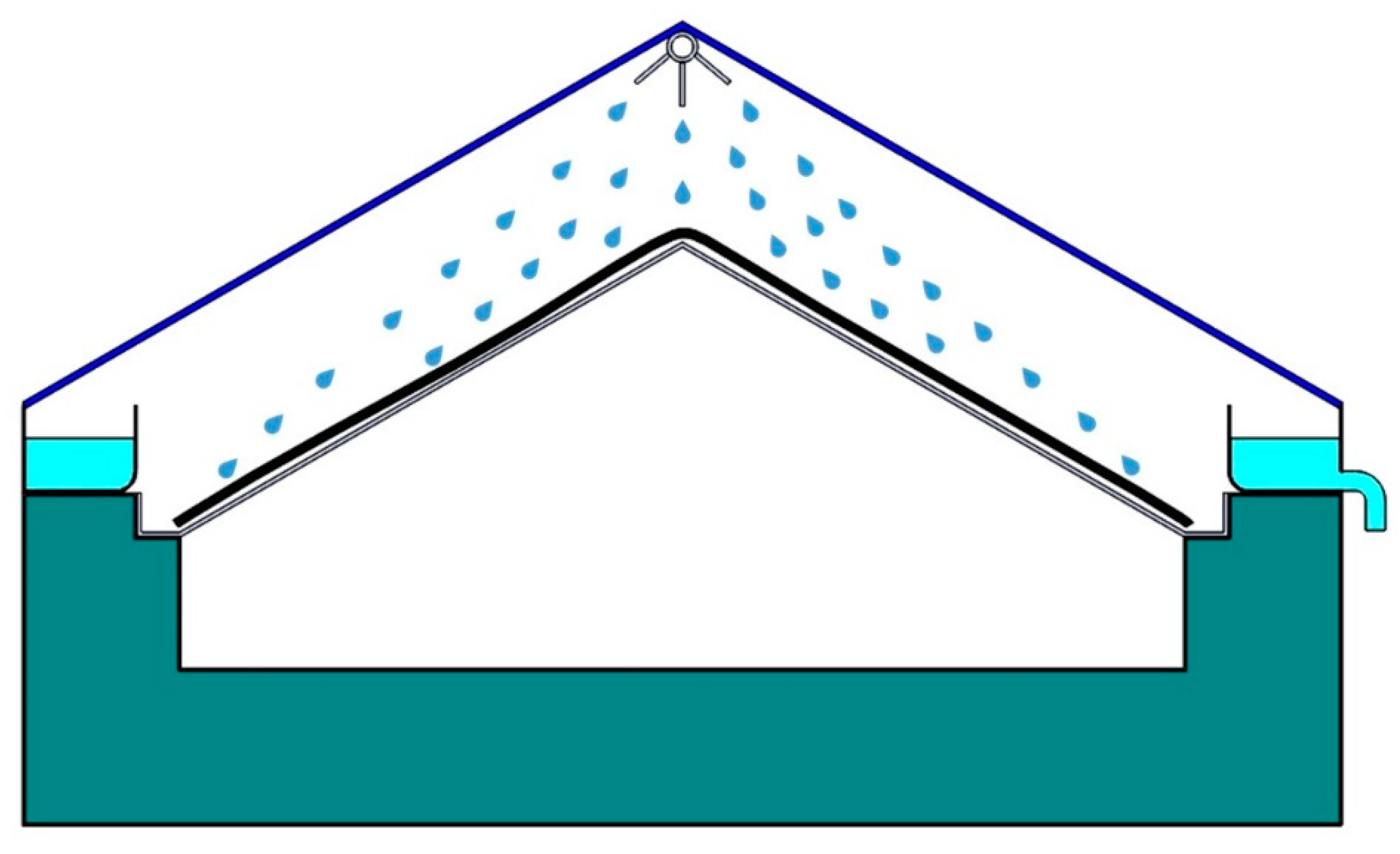
2.1. Design and Experimentation of the System
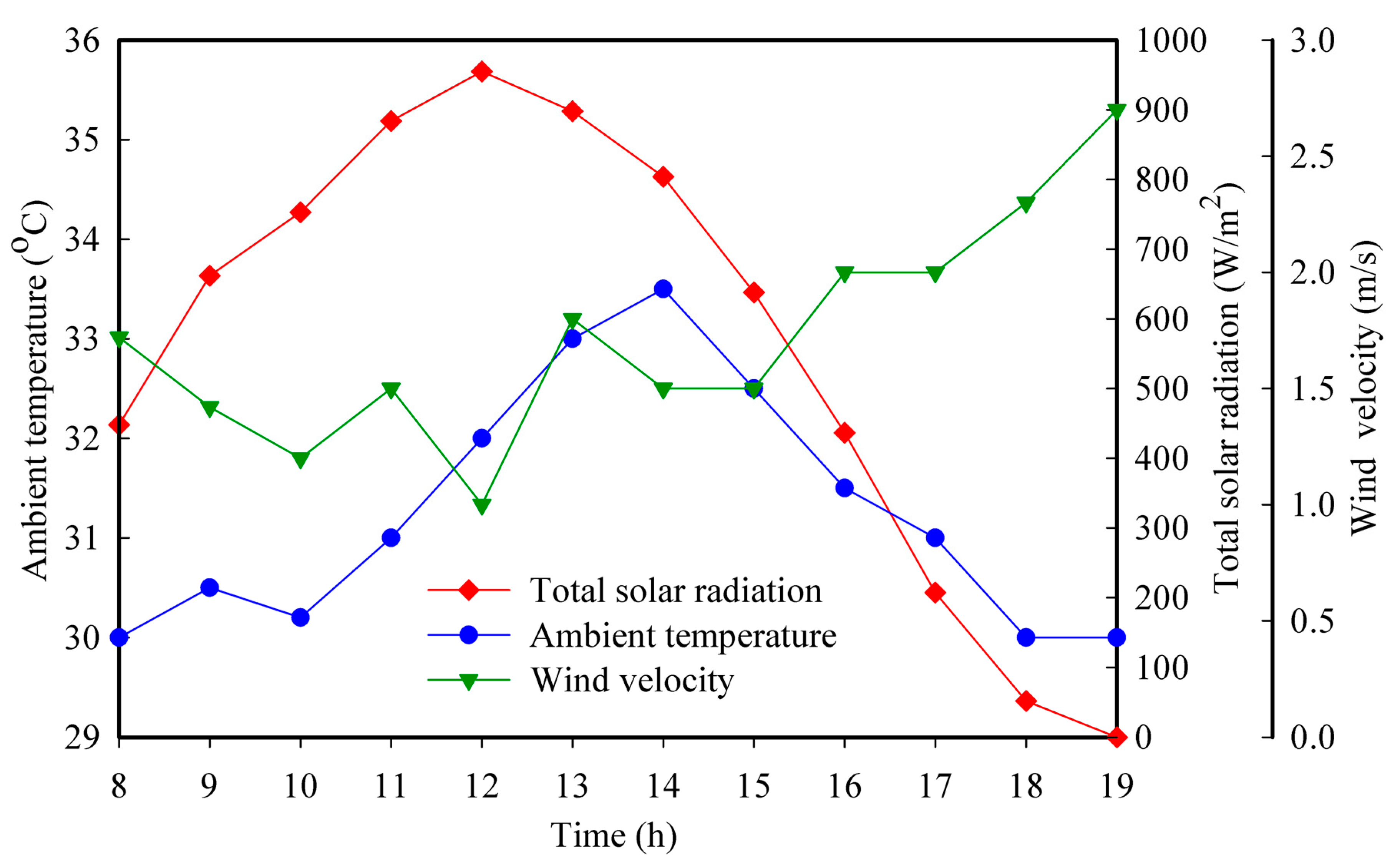
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
4. Comparison between the Present Work and Other Previous Studies
5. Life Cost Analysis
6. Conclusions
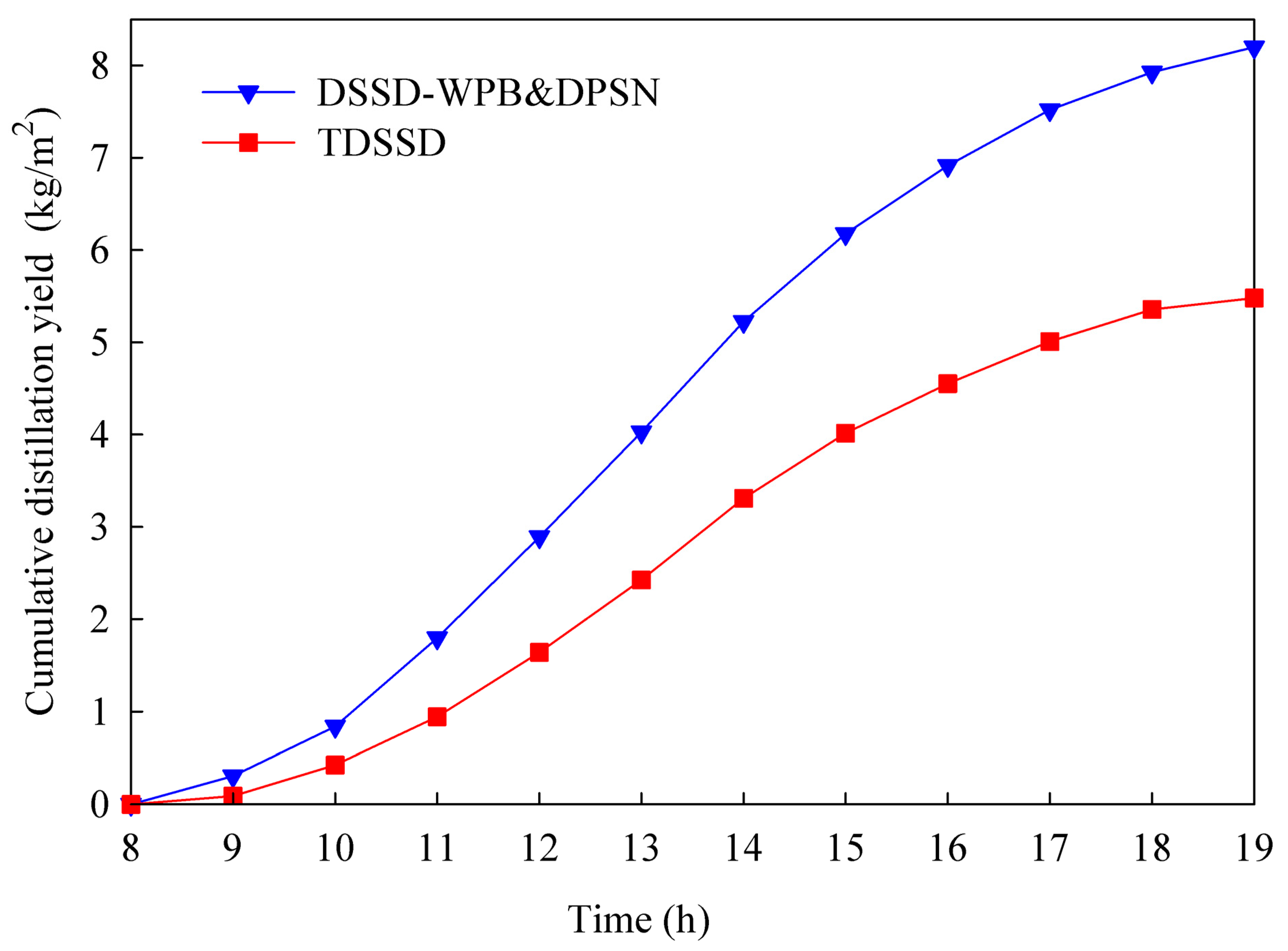
- The utilization of a wick prismatic absorber basin remarkably augmented the cumulative distillation yield by enhancing the vaporization rates via providing an increased heat transfer zone in the basin. In addition, the implementation of dual parallel spraying nozzles for the seawater feed supply helps in minimizing the saltwater film and augmenting the absorption of solar radiation, and enhancing the evaporation and condensation rates, thus significantly increasing the freshwater yields of the DSSD.
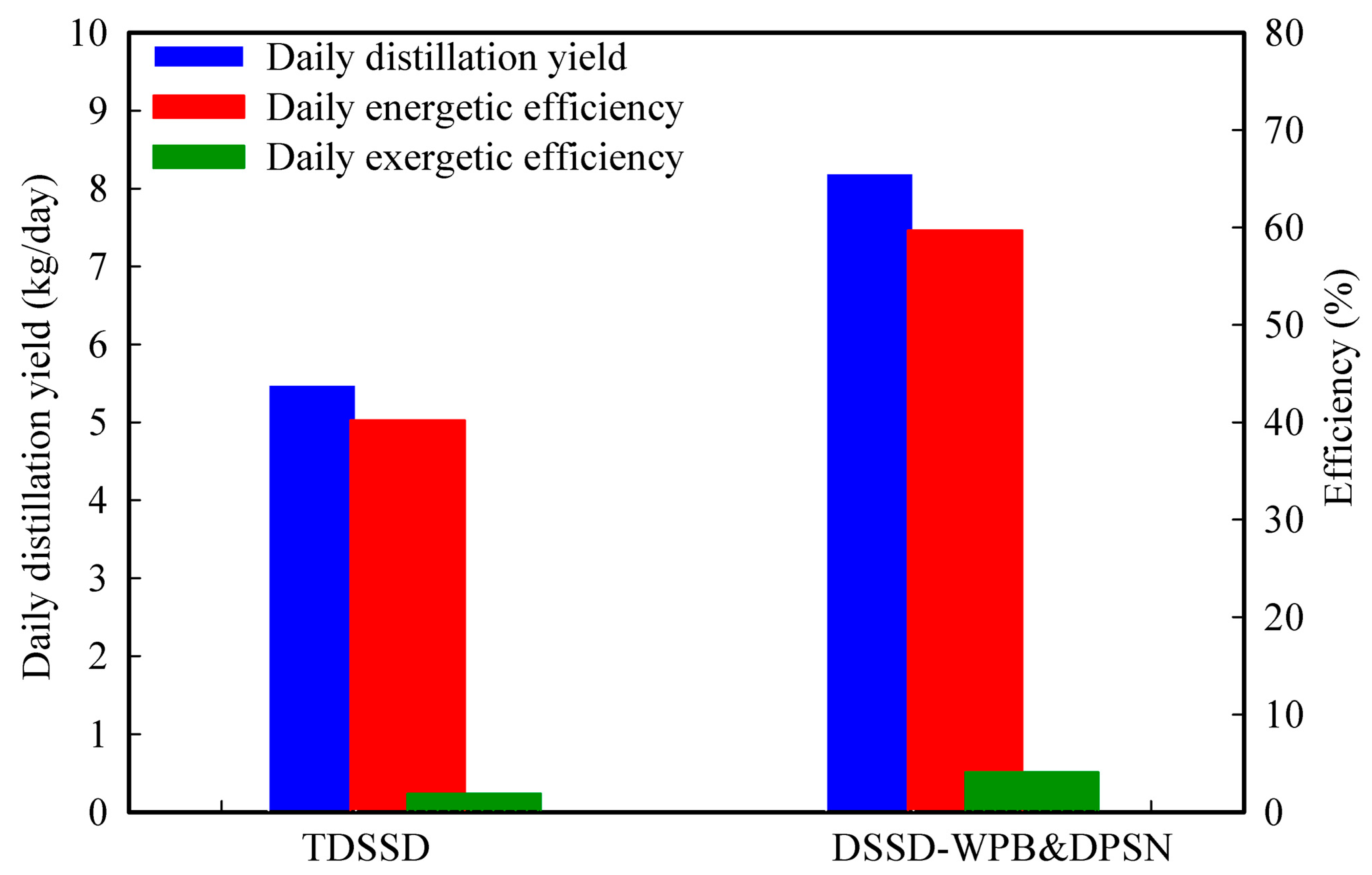
- The modified DSSD with a wick prismatic basin and dual parallel spraying nozzles (DSSD-WPB&DPSN) obtained an augmentation in the cumulative distillation yield by 49.64% (8.20 kg/day·m2) over the TDSSD (5.48 kg/day·m2) at a fixed saltwater deepness of 2.0 cm.
- The diurnal energetic efficiency of the DSSD-WPB&DPSN was computed to be 59.60% compared to 40.20% for TDSSD, respectively, representing a 48.51% improvement in the energetic efficiency.
- The daily exergetic efficiency of the DSSD-WPB&DPSN was obtained as 4.10% compared to 1.82% for TDSSD, respectively, representing 118.10% augmentation in the daily exergy efficacy.
- The life cost assessment reveals that the cost per liter of the distilled yield of the DSSD-WPB&DPSN and TDSSD were estimated to be 0.01820 USD/kg and 0.01330 USD/kg, respectively, representing a reduction in the freshwater production cost of 11.13%.
- It can be inferred that the wick prismatic absorber basin and dual parallel spraying nozzles can be regarded as an effective strategy for augmenting the freshwater distillation and energic, exergetic, and economic performances of the double-slope solar distillers.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Fang, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. The growing water crisis in Central Asia and the driving forces behind it. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; El-Said, E.M.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Fujii, M.; El-Tahan, H.R. Water distillation tower: Experimental investigation, economic assessment, and performance prediction using optimized machine-learning model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Panchal, H.N.; Sengottain, S.; Alsaleh, N.A.; Ahmadein, M. Applications of Heat Exchanger in Solar Desalination: Current Issues and Future Challenges. Water 2022, 14, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, C.; Biswas, A.K. Achieving universal access to clean water and sanitation in an era of water scarcity: Strengthening contributions from academia. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 34, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, B. Water crisis: From conflict to cooperation—An overview. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelmaaref, M.M.; Zayed, M.E.; Zhao, J.; Li, W.; Askalany, A.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Ali, E.S. Hybrid solar desalination systems driven by parabolic trough and parabolic dish CSP technologies: Technology categorization, thermodynamic performance and economical assessment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 220, 113103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Agouz, S.; Zayed, M.E.; Ghazala, A.M.A.; Elbar, A.R.A.; Shahin, M.; Zakaria, M.; Ismaeil, K.K. Solar thermal feed preheating techniques integrated with membrane distillation for seawater desalination applications: Recent advances, retrofitting performance improvement strategies, and future perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 164, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Katekar, V.P.; Muskens, O.L.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Elaziz, M.A.; Dabour, S.M. Utilization of LSTM neural network for water production forecasting of a stepped solar still with a corrugated absorber plate. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.N.; Sahota, L. Review on the energy and economic efficiencies of passive and active solar distillation systems. Desalination 2017, 401, 151–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, A.O.; Moustafa, E.B.; Alhumade, H.; Abulkhair, H.; Elsheikh, A. A coupled artificial neural network with artificial rabbits optimizer for predicting water productivity of different designs of solar stills. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2023, 175, 103315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Shanmugan, S.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Thakur, A.K.; Issa, M.; Panchal, H.; Muthuramalingam, T.; Kumar, R.; Sharifpur, M. Low-cost bilayered structure for improving the performance of solar stills: Performance/cost analysis and water yield prediction using machine learning. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 49, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.A.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Elsheikh, A.H. Prediction of power consumption and water productivity of seawater greenhouse system using random vector functional link network integrated with artificial ecosystem-based optimization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 144, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevada, D.; Panchal, H.; Ahmadein, M.; Zayed, M.E.; Alsaleh, N.A.; Djuansjah, J.; Moustafa, E.B.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Sadasivuni, K.K. Investigation and performance analysis of solar still with energy storage materials: An energy- exergy efficiency analysis. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 29, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandourah, E.; Panchal, H.; Fallatah, O.; Ahmed, H.M.; Moustafa, E.B.; Elsheikh, A.H. Performance enhancement and economic analysis of pyramid solar still with corrugated absorber plate and conventional solar still: A case study. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 35, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, F.A.; Shalaby, S.M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Zayed, M.E. Experimental investigation and thermo-economic performance analysis of a modified solar distiller design with thermal storage material and v-corrugated absorber basin. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, L.; Tiwari, G.N. Exergoeconomic and enviroeconomic analyses of hybrid double slope solar still loaded with nanofluids. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 148, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SD, U.M.; Meena, M.; Nagaraju, V.; Yakkala, B.; Vinod, D.; Mageshbabu, D.; Madhu, B.; Sathyamurthy, R. Effect of energy storage material on a triangular pyramid solar still operating with constant water depth. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, N.T.; Majeed, M.H.; Shcheklein, S.E.; Ali, O.M.; PraveenKumar, S. Experimental Study of a Tilt Single Slope Solar Still Integrated with Aluminum Condensate Plate. Inventions 2021, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammoodi, K.A.; Dhahad, H.A.; Alawee, W.H.; Omara, Z.M. A detailed review of the factors impacting pyramid type solar still performance. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 66, 123–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.B.; Hammad, A.H.; Elsheikh, A.H. A new optimized artificial neural network model to predict thermal efficiency and water yield of tubular solar still. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 30, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, O.; Hussein, A.K.; Attia, M.E.H.; Rashid, F.L.; Kolsi, L.; Biswal, U.; Abderrahmane, A.; Mourad, A.; Alazzam, A. Hemispherical solar still: Recent advances and development. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 8236–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.M.; Shanmugan, S.; Gorjian, S.; Pruncu, C.I.; Sivakumar, S.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Essa, F.A.; Omara, Z.M.; Panchal, H. Performance enhancement of stepped basin solar still based on OSELM with traversal tree for higher energy adaptive control. Desalination 2021, 502, 114926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.S.; Alarjani, A.; Abou Al-Sood, M.M.; Omara, Z.M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Essa, F.A. Rotating-wick solar still with mended evaporation technics: Experimental approach. Alex. Eng. J. 2019, 58, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z. Diffusion of single-effect vertical solar still fixed with inclined wick still: An experimental study. Fuel 2022, 329, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, M.A.; Pasha, G.; Ebrahimpour, B.; Guodarzi, A.M.; Morshedsolouk, F.; Roshan, H.H.; Shafaghat, R. Experimental investigation of a novel single-slope tilted wick solar still with an affordable channeled absorber sheet, an external condenser, and a reflector. Sol. Energy 2022, 241, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.M.; Alshammari, F.; Alqsair, U.F.; Alhadri, M.; Abdullah, A.S.; Elashmawy, M. Experimental study on the effect of the black wick on tubular solar still performance. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbuShanab, W.S.; Elsheikh, A.H.; Ghandourah, E.I.; Moustafa, E.B.; Sharshir, S.W. Performance improvement of solar distiller using hang wick, reflectors and phase change materials enriched with nano-additives. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 31, 101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangasamy, G.; Mani, S.; Kolandavelu, S.K.S.; Alsoufi, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.M.M.; Muthusamy, S.; Panchal, H.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Elsheikh, A.H. An extensive analysis of mechanical, thermal and physical properties of jute fiber composites with different fiber orientations. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, G.; Shanmugan, S.; Chithambaram, V.; Gorjian, S.; Pruncu, C.I.; Essa, F.A.; Kabeel, A.E.; Panchal, H.; Janarthanan, B.; Ebadi, H.; et al. Thermal investigation of a solar box-type cooker with nanocomposite phase change materials using flexible thermography. Renew. Energy 2021, 178, 260–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Sharshir, S.W.; Ali, M.K.A.; Shaibo, J.; Edreis, E.M.; Abdelhamid, T.; Du, C.; Haiou, Z. Thin film technology for solar steam generation: A new dawn. Sol. Energy 2019, 177, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Sharshir, S.W.; Mostafa, M.E.; Essa, F.A.; Ali, M.K.A. Applications of nanofluids in solar energy: A review of recent advances. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 3483–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, T.; Murugavel, K.K. The effect of the water depth on the productivity for single and double basin double slope glass solar stills. Desalination 2015, 359, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanaraj, S.J.P.; Velmurugan, V. Experimental investigation on the performance of modified single basin double slope solar stills. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2022, 43, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jani, H.K.; Modi, K.V. Experimental performance evaluation of single basin dual slope solar still with circular and square cross-sectional hollow fins. Sol. Energy 2019, 179, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, R.; Singh, H.N.; Tiwari, G.N. Characteristic equation of double slope passive solar still. Desalination 2011, 267, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, L.; Tiwari, G.N. Effect of nanofluids on the performance of passive double slope solar still: A comparative study using characteristic curve. Desalination 2016, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugavel, K.K.; Srithar, K. Performance study on basin type double slope solar still with different wick materials and minimum mass of water. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobrane, M.; Kopmeier, A.; Kahn, A.; Cauchie, H.-M.; Kharroubi, A.; Penny, C. Internal and external improvements of wick type solar stills in different configurations for drinking water production– A review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 12, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuly, S.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.R.I.; Beg, R.A. Combined influence of fin, phase change material, wick, and external condenser on the thermal performance of a double slope solar still. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharshir, S.W.; Eltawil, M.A.; Algazzar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kandeal, A.W. Performance enhancement of stepped double slope solar still by using nanoparticles and linen wicks: Energy, exergy and economic analysis. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 174, 115278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveenkumar, S.; Agyekum, E.B.; Kumar, A.; Velkin, V.I. Thermo-enviro-economic analysis of solar photovoltaic/thermal system incorporated with u-shaped grid copper pipe, thermal electric generators and nanofluids: An experimental investigation. J. Energy Storage 2023, 60, 106611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PraveenKumar, S.; Agyekum, E.B.; Kumar, A.; Velkin, V.I. Performance evaluation with low-cost aluminum reflectors and phase change material integrated to solar PV modules using natural air convection: An experimental investigation. Energy 2023, 266, 126415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffat, R.J. Describing the uncertainties in experimental results. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1988, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.E.; Katekar, V.P.; Tripathy, R.K.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Elsheikh, A.H. Predicting the yield of stepped corrugated solar distiller using kernel-based machine learning models. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 213, 118759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; Sharshir, S.W.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Kabeel, A.E.; Guilan, W.; Haiou, Z. Modeling of solar energy systems using artificial neural network: A comprehensive review. Sol. Energy 2019, 180, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.B.; Elsheikh, A. Predicting Characteristics of Dissimilar Laser Welded Polymeric Joints Using a Multi-Layer Perceptrons Model Coupled with Archimedes Optimizer. Polymers 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A. Bistable Morphing Composites for Energy-Harvesting Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandourah, E.I.; Sangeetha, A.; Shanmugan, S.; Zayed, M.E.; Moustafa, E.B.; Tounsi, A.; Elsheikh, A.H. Performance assessment of a novel solar distiller with a double slope basin covered by coated wick with lanthanum cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 32, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Measurement Device | Accuracy | Range | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-type thermocouples | ±0.10 °C | 0–100 °C | 0.197 |
| SR05 solarimeter | ±1 W/m2 | (0–5000) W/m2 | 0.462 |
| Testo 410i Vane anemometer | ±0.1 m/s | 0.4–30 m/s | 2.45 |
| Graduated beaker | ±5.0 mL | 0–500 mL | 0.260 |
| Ref. | SD Design | Modifications and Additives | Daily Yield (kg/m2·day) | Yield Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33] | DSSD | - With black granite storage material - With external reflectors | 3.76 4.98 | 23.08 62.90 |
| [34] | DSSD | Circular hollow fins | 1.50 | 43.80 |
| [36] | DSSD | - Water + Al2O3 nanofluid - Water + TiO2 nanofluid - Water + CuO nanofluid | 7.46 7.05 6.90 | 16.0 9.66 7.30 |
| [39] | DSSD | Rectangular fins + paraffin wax + wicks + exterior condenser | 2.82 | 13.12 |
| [48] | DSSD | Nano LaCoO3/black paint | 5.40 | 40.20 |
| This study | DSSD | Wick prismatic absorber basin and dual parallel spraying nozzles | 8.20 | 49.64 |
| Cost Parameter | TDSSD | DSSD-WPB&DPSN |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing and Materials (USD) | 80.0 | 80.0 |
| Wick prismatic absorber basin cost (USD) | - | 20 |
| Dual parallel spraying nozzles cost (USD) | - | 15 |
| Capitalized total cost, P (USD) | 80.0 | 115.00 |
| First annual cost, FAC (USD) | 14.1587 | 20.3531 |
| Annual maintenance cost, AMC, (USD) | 4.2476 | 6.1059 |
| Annual salvage value, ASV (USD) | 0.9117 | 1.3106 |
| Total yearly cost, TYC (USD) | 17.495 | 25.148 |
| Daily distillation yield (kg/m2·d) | 5.4800 | 8.2000 |
| Annual distillation yield (kg/m2·yr) | 1479.6 | 2214.0 |
| Cost of 1.0 L of distilled yield, CLDY (USD/kg) | 0.01820 | 0.01135 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zayed, M.E.; Kamal, A.; Diab, M.R.; Essa, F.A.; Muskens, O.L.; Fujii, M.; Elsheikh, A.H. Novel Design of Double Slope Solar Distiller with Prismatic Absorber Basin, Linen Wicks, and Dual Parallel Spraying Nozzles: Experimental Investigation and Energic–Exergic-Economic Analyses. Water 2023, 15, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030610
Zayed ME, Kamal A, Diab MR, Essa FA, Muskens OL, Fujii M, Elsheikh AH. Novel Design of Double Slope Solar Distiller with Prismatic Absorber Basin, Linen Wicks, and Dual Parallel Spraying Nozzles: Experimental Investigation and Energic–Exergic-Economic Analyses. Water. 2023; 15(3):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030610
Chicago/Turabian StyleZayed, Mohamed E., Abdallah Kamal, Mohamed Ragab Diab, Fadl A. Essa, Otto L. Muskens, Manabu Fujii, and Ammar H. Elsheikh. 2023. "Novel Design of Double Slope Solar Distiller with Prismatic Absorber Basin, Linen Wicks, and Dual Parallel Spraying Nozzles: Experimental Investigation and Energic–Exergic-Economic Analyses" Water 15, no. 3: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030610
APA StyleZayed, M. E., Kamal, A., Diab, M. R., Essa, F. A., Muskens, O. L., Fujii, M., & Elsheikh, A. H. (2023). Novel Design of Double Slope Solar Distiller with Prismatic Absorber Basin, Linen Wicks, and Dual Parallel Spraying Nozzles: Experimental Investigation and Energic–Exergic-Economic Analyses. Water, 15(3), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15030610











