Experimental Study on the Purification Mechanism of Mine Water by Coal Gangue
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.1.1. Coal Gangue
2.1.2. Mine Water
2.2. Methods
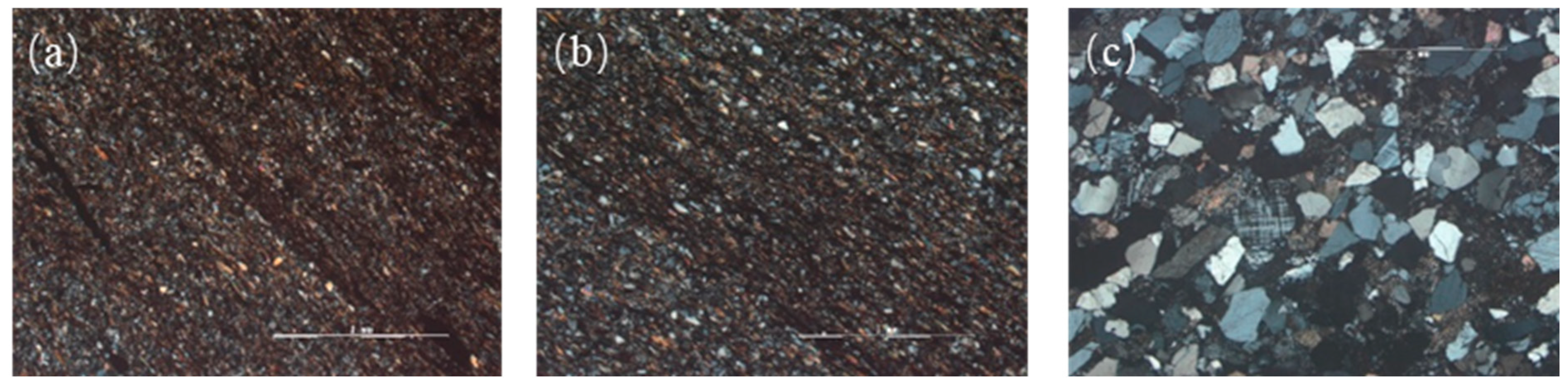
2.2.1. Microscopic Observation of Thin Sections of Rock
2.2.2. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.2.3. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) Spectroscopy
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
2.2.5. Ion Concentration Test
2.2.6. Static Leaching of Gangue
2.2.7. Dynamic Leaching of Gangue
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Ions in Mine Water
3.2. Microscopic Characteristics of Gangue
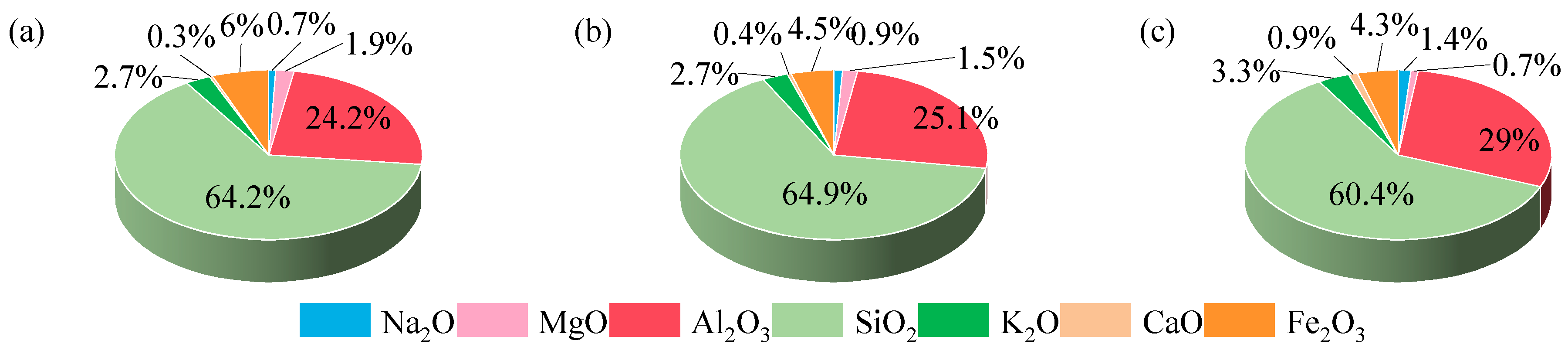
3.3. Chemical Composition of Gangue
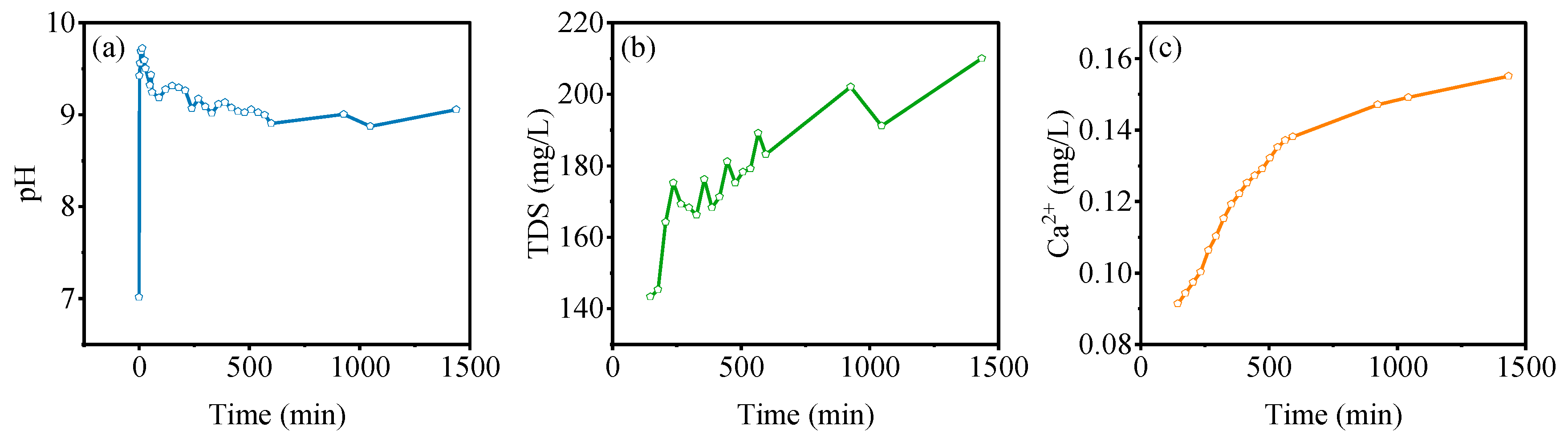
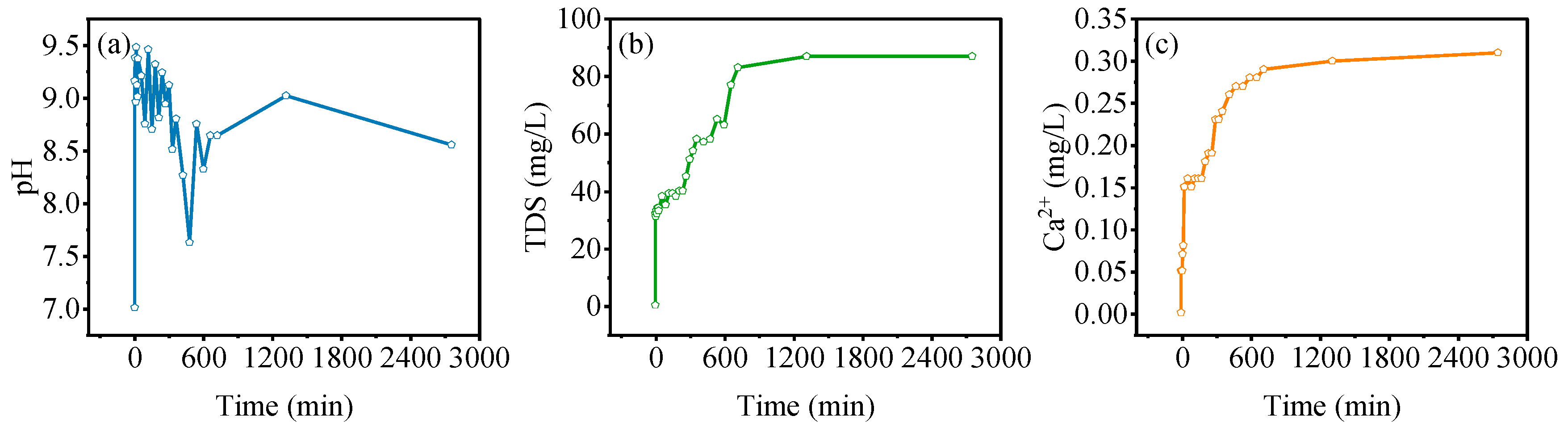
3.4. Static Adsorption Characteristics of Gangue
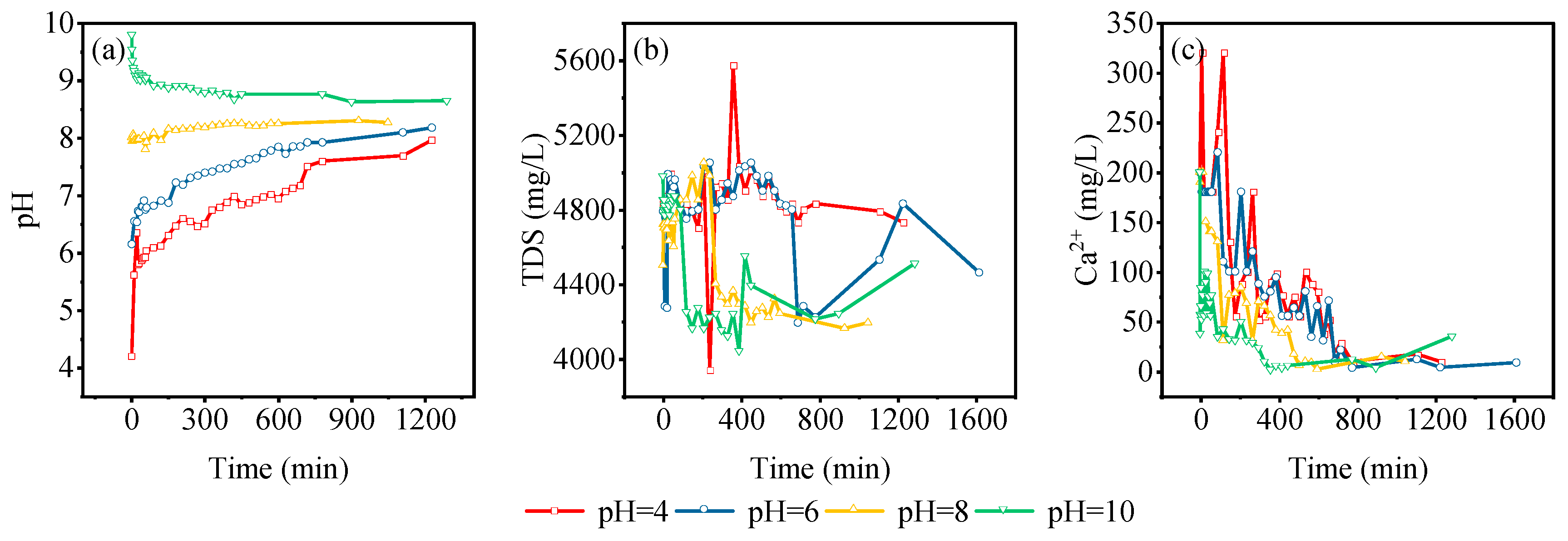
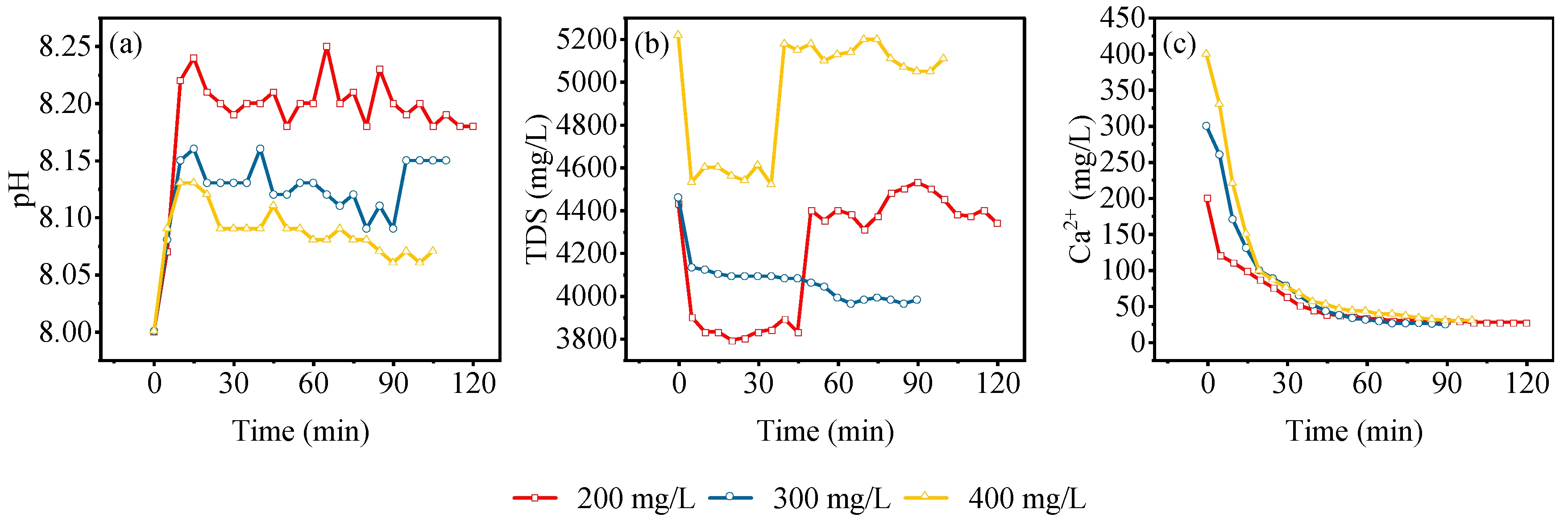
3.5. Adsorption Characteristics of Dynamic Leaching of Gangue
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, D.Z.; Li, J.F.; Cao, Z.G.; Wu, B.Y.; Jiang, B.B.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.P. Technology and engineering development strategy of water protection and utilization of coal mine in China. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 3079–3089. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, B.S.; Kharel, G. Acid mine drainage from coal mining in the United States—An overview. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Zhai, X.; Huang, K.; Liu, W. Water Abundance Comprehensive Evaluation of Coal Mine Aquifer Based on Projection Pursuit Model. Lithosphere 2022, 2021, 3259214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Guo, X.; Zhou, Z. Characteristics of Water Hazards in China’s Coal Mines: A Review. Mine Water Environ. 2021, 40, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Yan, H.; Ju, F.; Mei, X.; Wang, X. Influential factors and control of water inrush in a coal seam as the main aquifer. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2018, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, F.; Xing, Z.; Wang, L. Impacts of Underground Reservoir Site Selection and Water Storage on the Groundwater Flow System in a Mining Area—A Case Study of Daliuta Mine. Water 2022, 14, 3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, D.; Gao, H.; Guo, Y.; Ouyang, S. Triaxial compression behaviour of gangue solid wastes under effects of particle size and confining pressure. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Cao, G. Study on dynamic adsorption characteristics of broken coal gangue to heavy metal ions under leaching condition and its cleaner mechanism to mine water. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Tang, C.; Xia, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Chong, Z.; Hui, X. Mechanisms of failure in coal samples from underground water reservoir. Eng. Geol. 2020, 267, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madlener, R.; Specht, J. An Exploratory Economic Analysis of Underground Pumped-Storage Hydro Power Plants in Abandoned Deep Coal Mines. Energies 2020, 13, 5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, J.; Loredo, J.; Galdo, M.; Fernández-Oro, J.M. Energy storage in underground coal mines in NW Spain: Assessment of an underground lower water reservoir and preliminary energy balance. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Xu, J.; Fang, J.; Cao, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, T. Potential for mine water disposal in coal seam goaf: Investigation of storage coefficients in the Shendong mining area. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 244, 118646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Reduction and utilization of coal mine waste rock in China: A case study in Tiefa coalfield. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 83, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, S.; Kibort, K.; Mioduska, J.; Lieder, M.; Małachowska, A. Waste management in the mining industry of metals ores, coal, oil and natural gas—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 304, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriens, B.; Plante, B.; Seigneur, N.; Jamieson, H. Mine Waste Rock: Insights for Sustainable Hydrogeochemical Management. Minerals 2020, 10, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibee, N.; Osanloo, M.; Rahmanpour, M. Adverse effects of coal mine waste dumps on the environment and their management. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, Z.Q.; Li, C.M. Waste rock filling in fully mechanized coal mining for goaf-side entry retaining in thin coal seam. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Meng, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Germain, D.M. Sensitivity analysis of key factors influencing compression-induced deformation of waste rocks for backfilling to reduce environmental pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 16707–16717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stracher, G.B.; Taylor, T.P. Coal fires burning out of control around the world: Thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2004, 59, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, T.-C. Reactivity activation of waste coal gangue and its impact on the properties of cement-based materials—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 234, 117424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, G.; Guo, L.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, K. Utilization of coal gangue as coarse aggregates in structural concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 268, 121212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Guo, X.; Guan, J.; Yao, X.; Hao, Y. Activation Mechanism of Coal Gangue and Its Impact on the Properties of Geopolymers: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yao, X.; Han, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, M. Using Chinese Coal Gangue as an Ecological Aggregate and Its Modification: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.J.; Ajalloeian, R.; Hajiannia, A. Preparation and application of alkali-activated materials based on waste glass and coal gangue: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, C.; Barbour, S.L.; Hendry, M.J. The geochemistry and hydrology of coal waste rock dumps: A systematic global review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilha, C.; Melo, A.; Flores, D.; Ribeiro, J.; Rocha, J.R.; Martins, V.; Santos, P.; Marques, J.E. Irrigation with Coal Mining Effluents: Sustainability and Water Quality Considerations (São Pedro da Cova, North Portugal). Water 2021, 13, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; He, H.-Y. Glass-ceramics fabricated by efficiently utilizing coal gangue. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 8, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Application of Coal Gangue as a Coarse Aggregate in Green Concrete Production: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Road performance analysis of cement stabilized coal gangue mixture. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanovych, A.; Balloy, M.; Olszewski, T.K.; Petit, E.; Grison, C. Depollution of mining effluents: Innovative mobilization of plant resources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 19327–19334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Guo, Z.; Yang, W.; Song, W. Durability of Concrete With Coal Gasification Slag and Coal Gangue Powder. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 791178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, F.; Li, B.; Guo, S.; Xiao, M. Dynamic characteristics of gangues during vertical feeding in solid backfill mining: A case study of the Wugou coal mine in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Qiao, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, T.; Kong, G.; Gao, H.; Guo, L. Effects of Water Soaked Height on the Deformation and Crushing Characteristics of Loose Gangue Backfill Material in Solid Backfill Coal Mining. Processes 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Zhou, N. Reutilisation of coal gangue and fly ash as underground backfill materials for surface subsidence control. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hao, Y. Experimental Study and Application of Rheological Properties of Coal Gangue-Fly Ash Backfill Slurry. Processes 2020, 8, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, X.M. Performance of cemented coal gangue backfill. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2007, 14, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Li, F.; Pang, Z. Investigation of Hydraulic-Mechanical Properties of Paste Backfill Containing Coal Gangue-Fly Ash and Its Application in an Underground Coal Mine. Energies 2017, 10, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letina, D.; Letshwenyo, W. Investigating waste rock, tailings, slag and coal ash clinker as adsorbents for heavy metals: Batch and column studies. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 105, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Gao, X.; Hou, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Occurrence and environmental impact of coal mine goaf water in karst areas in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Gao, J.; Du, K.; Deng, X.; Zhang, K. Insight into the water–rock interaction process and purification mechanism of mine water in underground reservoir of Daliuta coal mine in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 28538–28551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zou, W.; Wang, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Adsorption and interaction mechanisms of Chi-g-P(AM-DMDAAC) assisted settling of kaolinite in a two-step flocculation process. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 816, 151576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Wang, C.; Gong, L.; Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, W. Potential Application of Discarded Natural Coal Gangue for the Removal of Tetracycline Hydrochloride (TC) from an Aqueous Solution. Toxics 2023, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
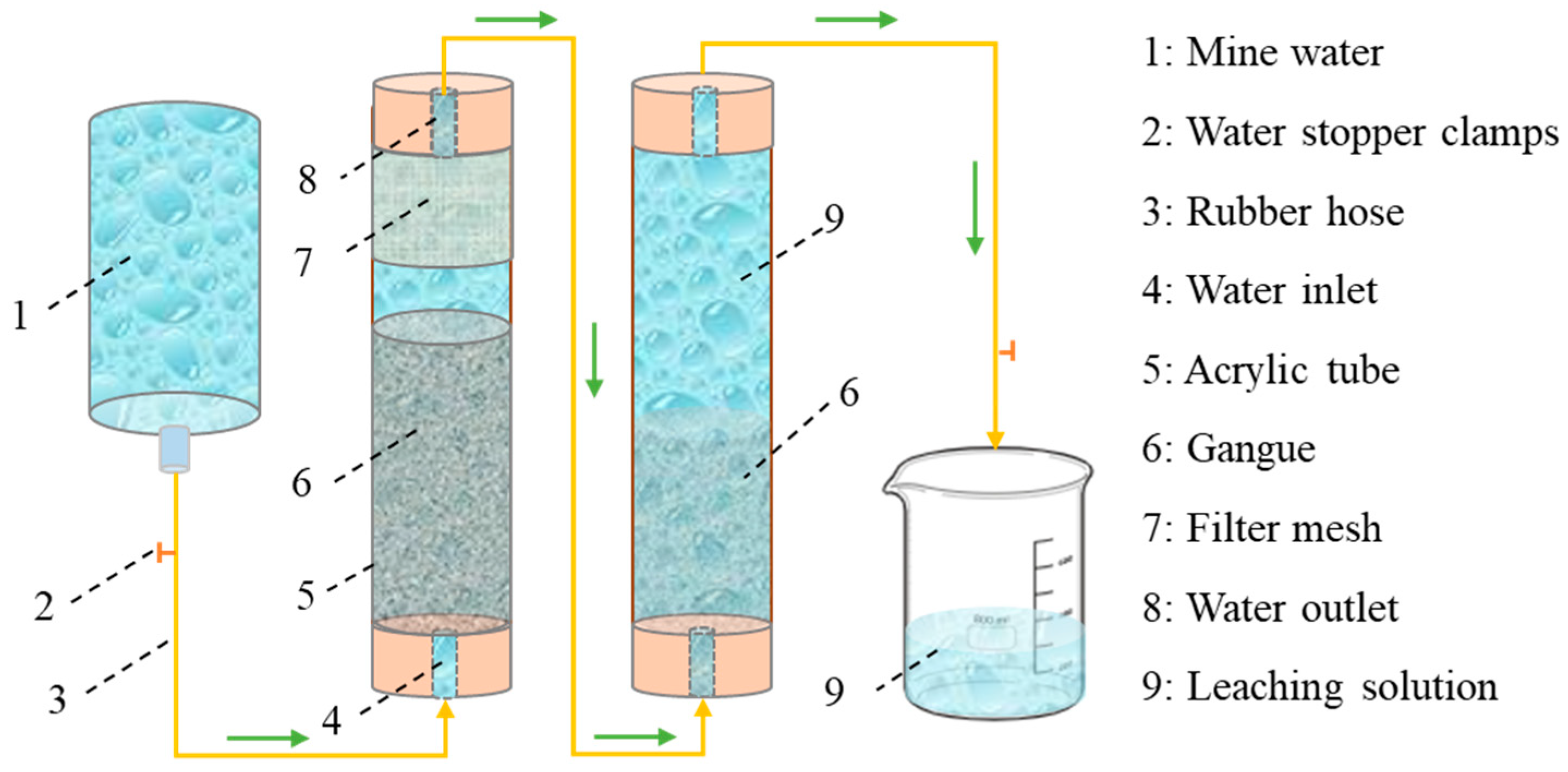
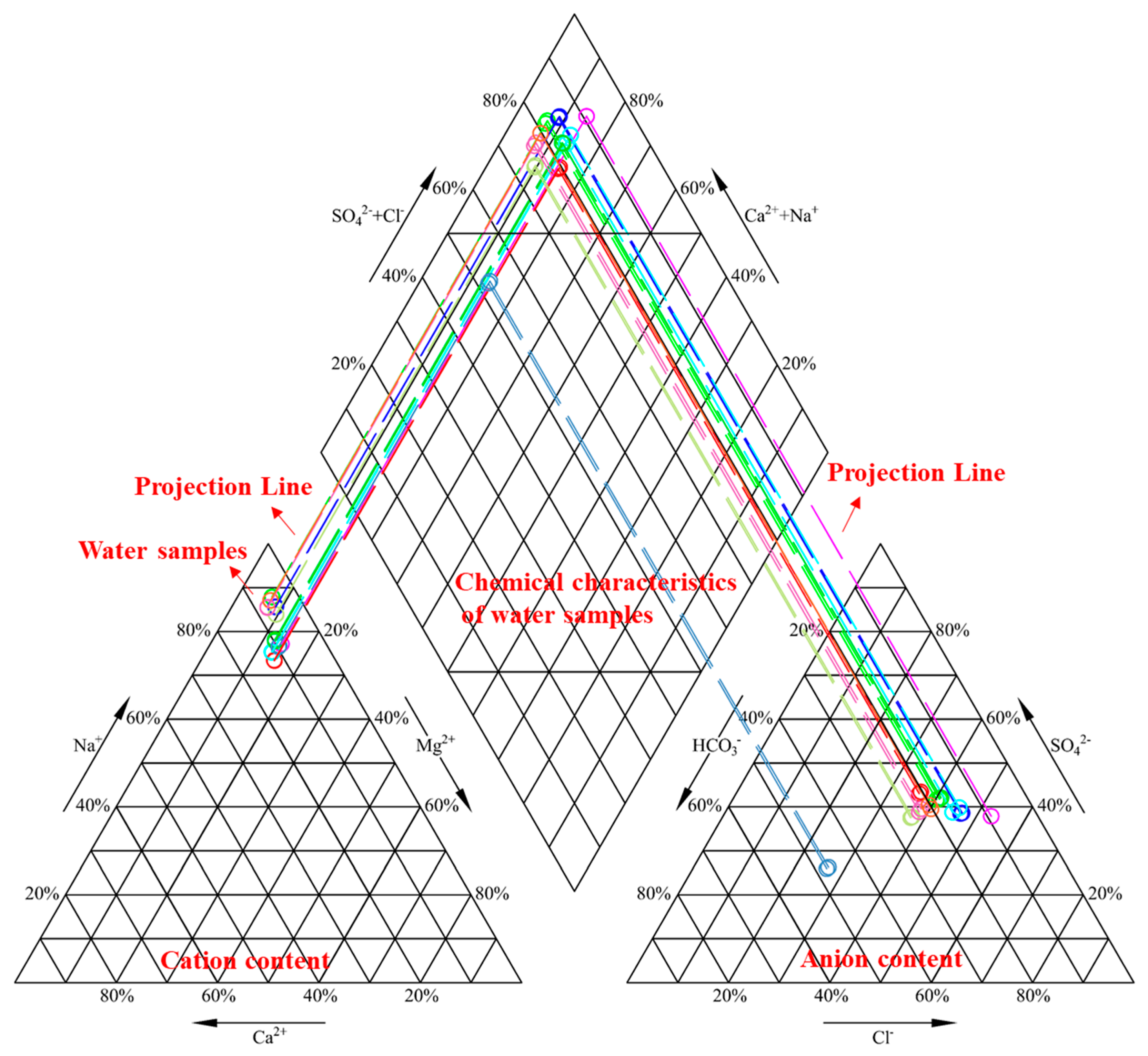

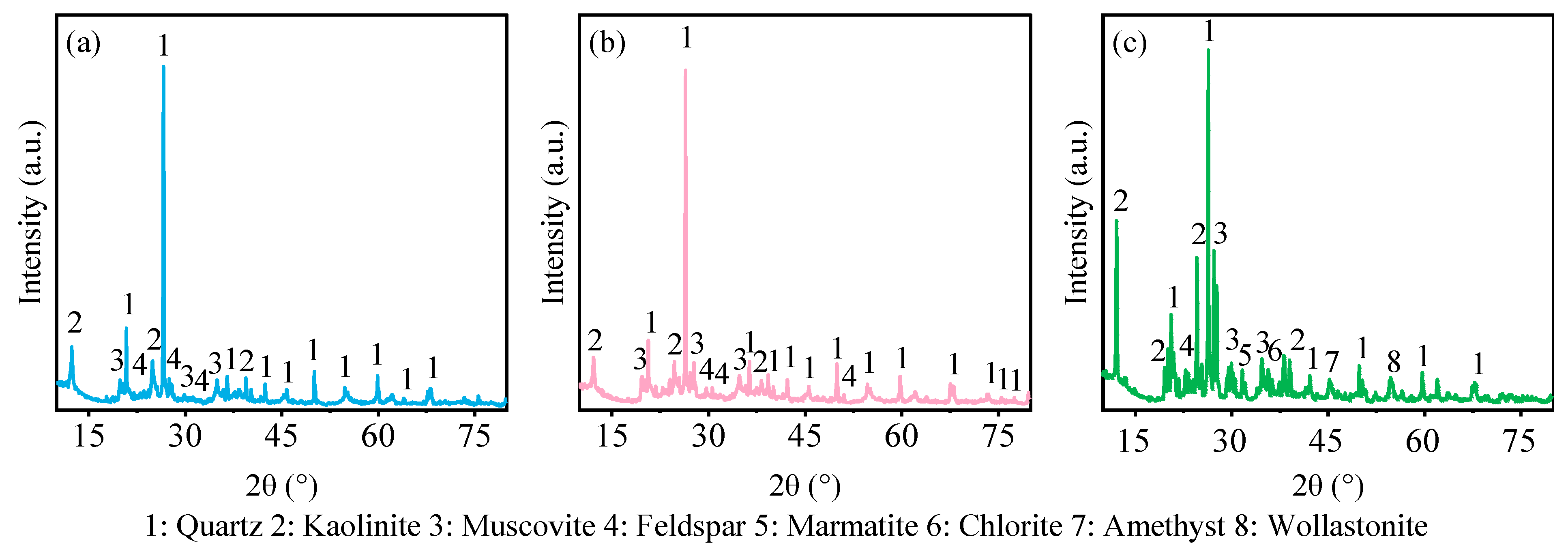
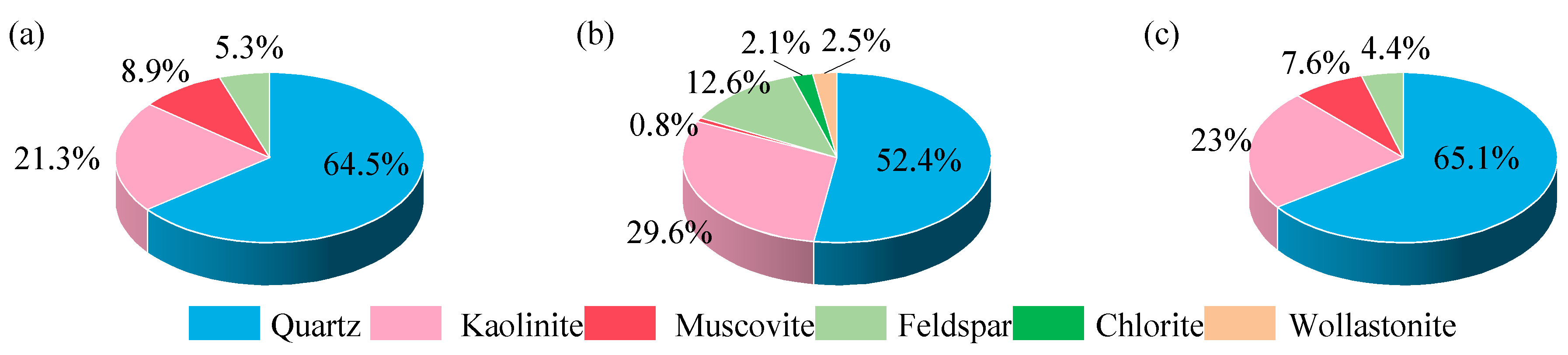
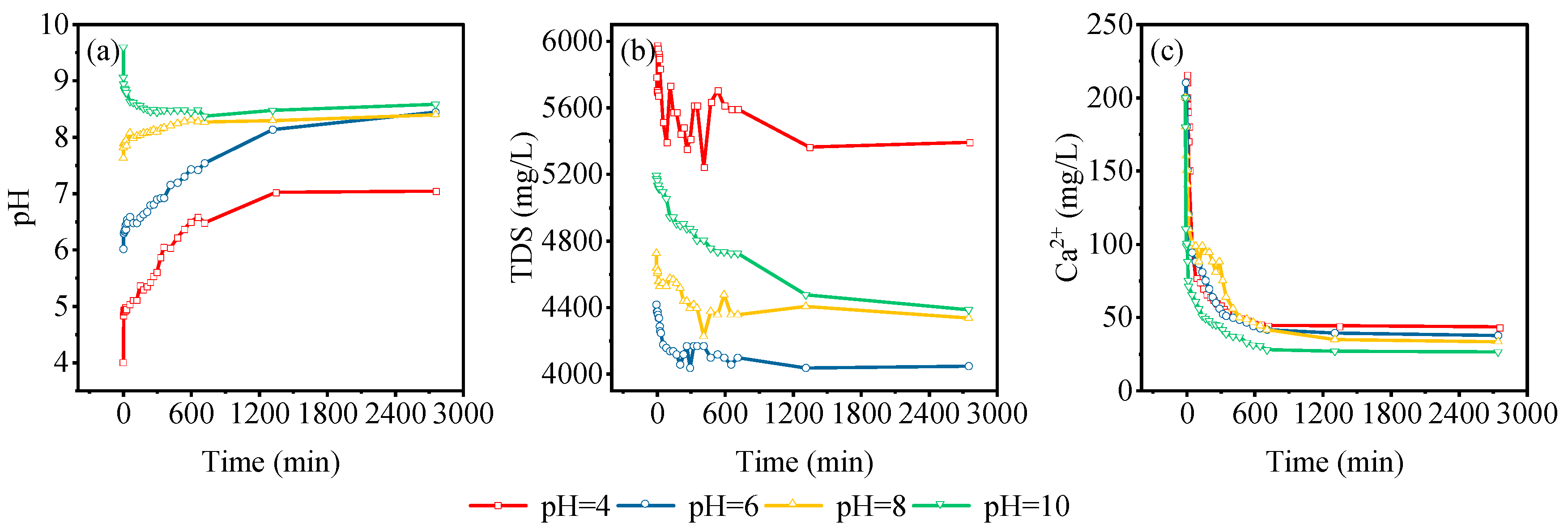


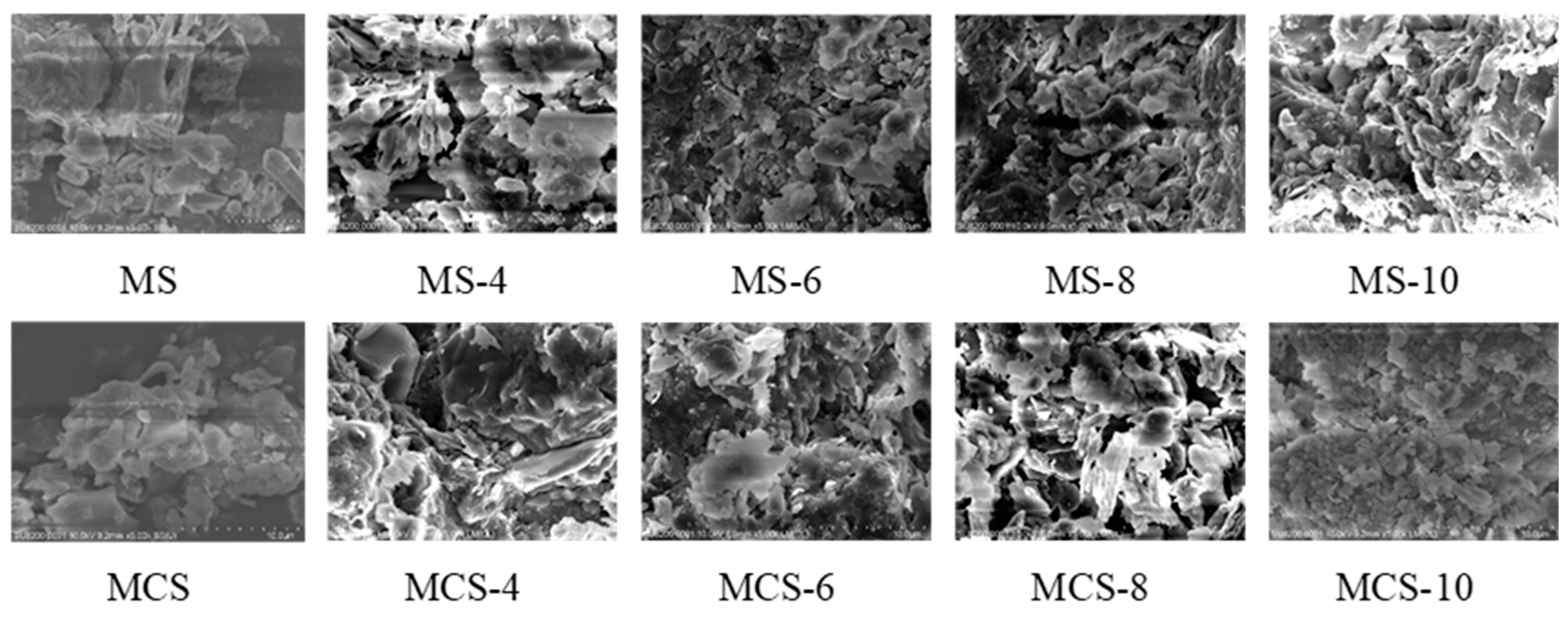
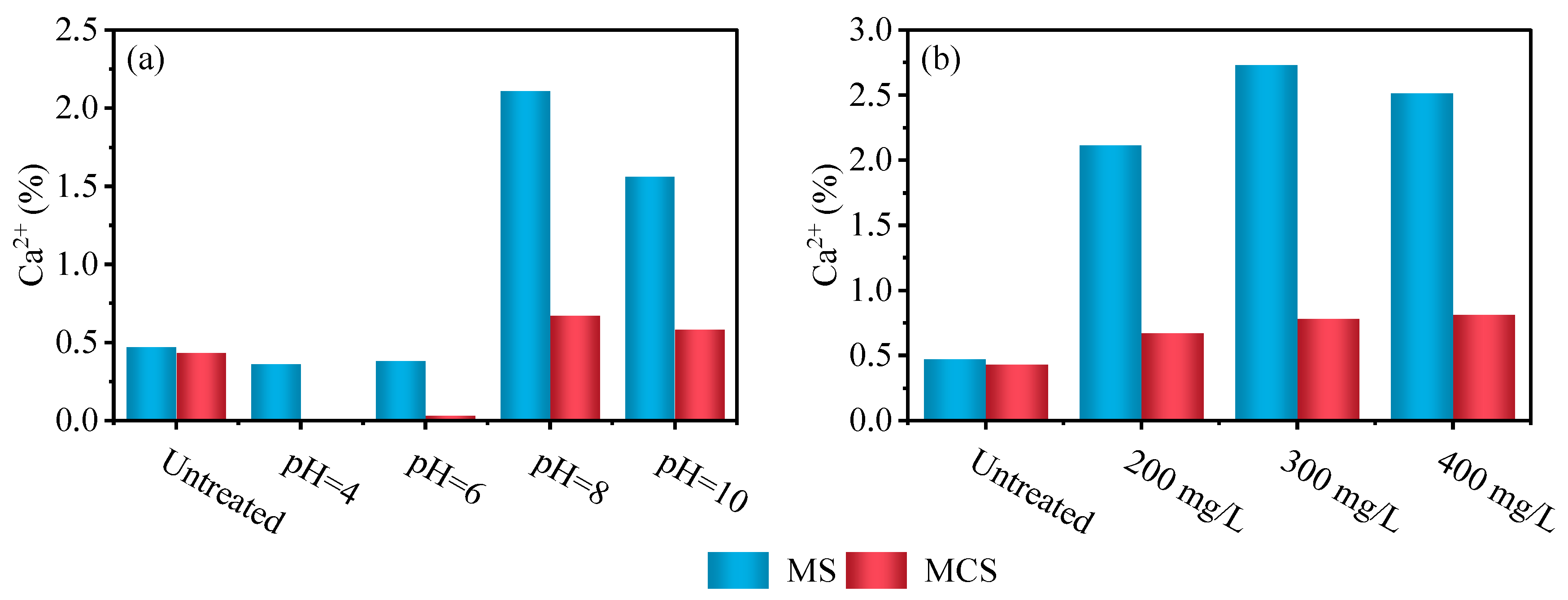
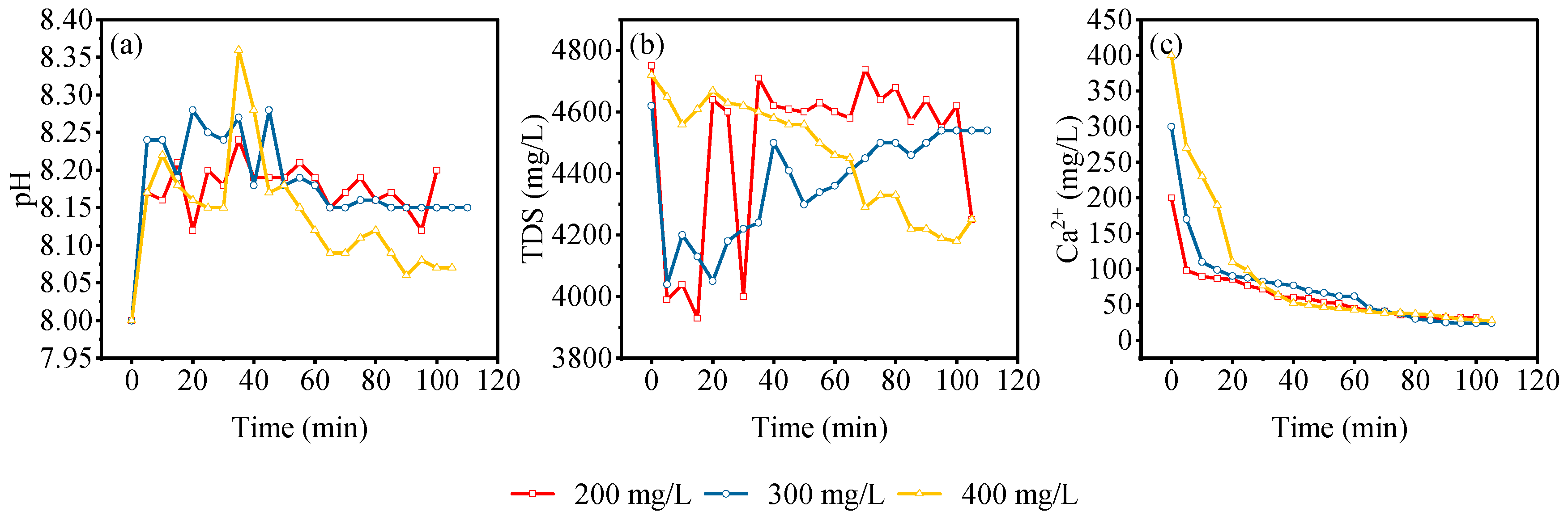
| Experiment Number | Lithology | pH | Grain Size (mesh) | Solid-to-Liquid Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL-MS-pH-4 | Muddy siltstone | 4 | 200 | 1:10 |
| SL-MS-pH-6 | 6 | |||
| SL-MS-pH-8 | 8 | |||
| SL-MS-pH-10 | 10 | |||
| SL-MS-pH-7 | Deionized water | |||
| SL-MCS-pH-4 | Medium-grained coarse sandstone | 4 | 200 | 1:10 |
| SL-MCS-pH-6 | 6 | |||
| SL-MCS-pH-8 | 8 | |||
| SL-MCS-pH-10 | 10 | |||
| SL-MCS-pH-7 | Deionized water |
| Experiment Number | Lithology | Grain Size (mesh) | pH | Ca2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL-MS-4 | Muddy siltstone | 20–30 | 4.0 | 200 |
| DL-MS-6 | 6.0 | |||
| DL-MS-8 | 8.0 | |||
| DL-MS-10 | 10.0 | |||
| DL-MCS-4 | Medium-grained coarse sandstone | 20–30 | 4.0 | 200 |
| DL-MCS-6 | 6.0 | |||
| DL-MCS-8 | 8.0 | |||
| DL-MCS-10 | 10.0 | |||
| DL-MS-200 | Muddy siltstone | 20–30 | 8.0 | 200 |
| DL-MS-300 | 300 | |||
| DL-MS-400 | 400 | |||
| DL-MCS-200 | Medium-grained coarse sandstone | 20–30 | 8.0 | 200 |
| DL-MCS-300 | 300 | |||
| DL-MCS-400 | 400 |
| Experiment Number | Ca/mg/L | Mg/mg/L | K/mg/L | Fe/mg/L | Al/mg/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL-PS-4 | 22.78 | 192.4 | 23.11 | 0.174 | 1.049 |
| DL-PS-6 | 21.9 | 193 | 19.27 | 0.164 | 1.047 |
| DL-PS-8 | 31.5 | 279.7 | 40.1 | 1.056 | 2.037 |
| DL-PS-10 | 10.53 | 161.3 | 19.15 | 0.16 | 1.103 |
| DL-MCS-4 | 21.21 | 202.7 | 7.992 | 0.166 | 1.099 |
| DL-MCS-6 | 19.08 | 203 | 7.451 | 0.163 | 1.88 |
| DL-MCS-8 | 26.67 | 276.7 | 11.06 | 0.506 | 1.638 |
| DL-MCS-10 | 0.97 | 188.7 | 7.078 | 0.208 | 1.006 |
| DL-PS-200 | 31.5 | 279.7 | 40.1 | 1.056 | 2.037 |
| DL-PS-200 | 24.18 | 195.1 | 19.33 | 0.221 | 1.221 |
| DL-PS-200 | 27.48 | 208.6 | 19.02 | 0.143 | 1.112 |
| DL-MCS-200 | 26.67 | 276.7 | 11.06 | 0.506 | 1.638 |
| DL-MCS-300 | 23.56 | 201.3 | 7.669 | 0.411 | 1.279 |
| DL-MCS-400 | 29.29 | 197.4 | 7.716 | 0.284 | 1.412 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, L.; Yao, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Experimental Study on the Purification Mechanism of Mine Water by Coal Gangue. Water 2023, 15, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040697
Zhu L, Yao Q, Xu Q, Li Y, Li X. Experimental Study on the Purification Mechanism of Mine Water by Coal Gangue. Water. 2023; 15(4):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040697
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Liu, Qiangling Yao, Qiang Xu, Yinghu Li, and Xuehua Li. 2023. "Experimental Study on the Purification Mechanism of Mine Water by Coal Gangue" Water 15, no. 4: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040697
APA StyleZhu, L., Yao, Q., Xu, Q., Li, Y., & Li, X. (2023). Experimental Study on the Purification Mechanism of Mine Water by Coal Gangue. Water, 15(4), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040697






