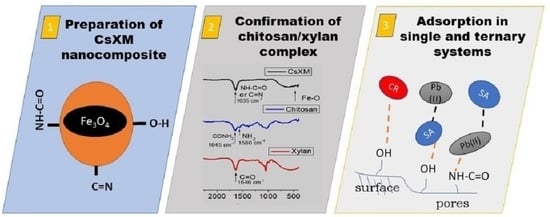
Multifunctional Chitosan/Xylan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Adsorption of the Emerging Contaminants Pb(II), Salicylic Acid, and Congo Red Dye
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of CsXM, CsM, and XnM
2.3. Characterization of CsXM, CsM, and XnM
2.4. Adsorption in Single Systems
2.5. Adsorption in Ternary Systems
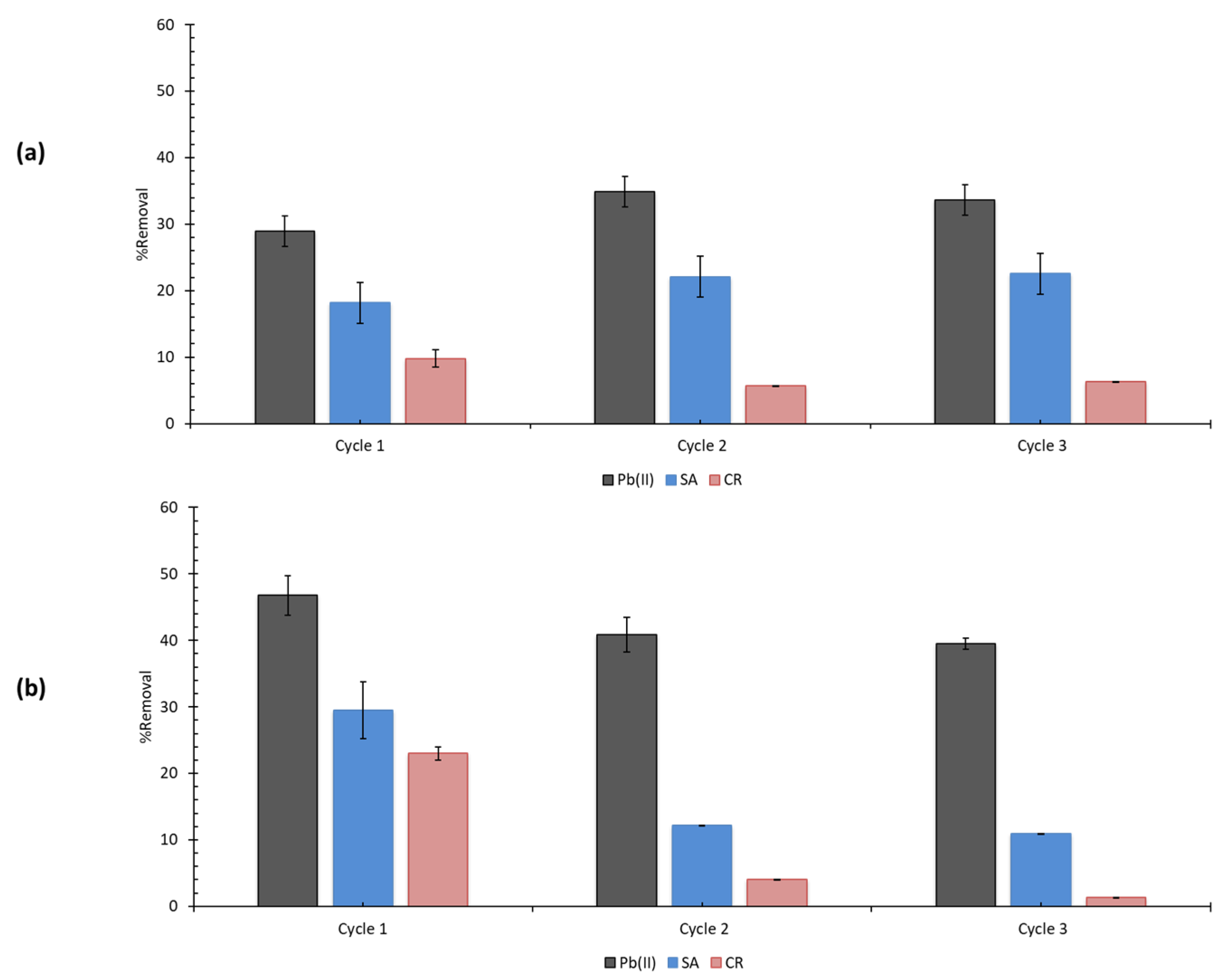
2.6. Regeneration
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics
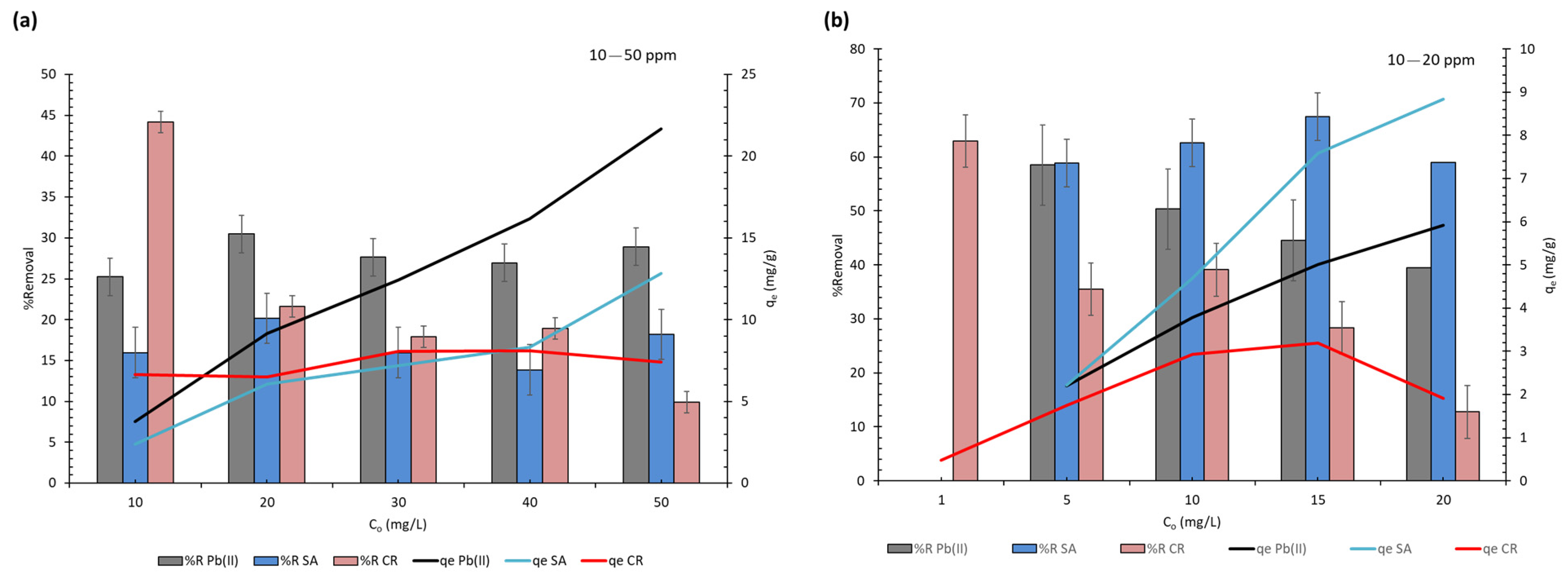
3.2. Adsorption Performance
3.3. Adsorption in Ternary System
3.4. Adsorption Mechanism
3.5. Regeneration
4. Comparison with Literature
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rout, P.R.; Zhang, T.C.; Bhunia, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. Treatment technologies for emerging contaminants in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaels, R.A. Legacy contaminants of emerging concern: Lead (Pb), flint (MI), and human health. Environ. Claims J. 2020, 32, 6–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; MMS, C.-P.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shabnam, A.A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Gupta, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; A Khan, S. Lead toxicity: Health hazards, influence on food chain, and sustainable remediation approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, Y.; Lei, D.; Ni, J.; Ren, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, H. Packed bed column studies on lead (II) removal from industrial wastewater by modified Agaricus bisporus. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadir, T.; Bakan, G.; Altas, L.; Buyukgungor, H. The investigation of lead removal by biosorption: An application at storage battery industry wastewaters. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 41, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosek, K.; Styszko, K.; Golas, J. Combined method of solid-phase extraction and GC-MS for determination of acidic, neutral, and basic emerging contaminants in wastewater (Poland). Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 961–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Baltrus, J.; Williams, C.; Knopf, A.; Zhang, L.; Baltrusaitis, J. Mesoporous Fe-doped MgO nanoparticles as a heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like catalyst for degradation of salicylic acid in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; Daković, A.; Obradović, M.; Ožegović, M.; Izzo, F.; Germinario, C.; de Gennaro, B. Application of Surfactant Modified Natural Zeolites for the Removal of Salicylic Acid—A Contaminant of Emerging Concern. Materials 2021, 14, 7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Mishra, V.; Sharma, R.S. Detoxification of azo dyes in the context of environmental processes. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekoye, J.N.; Wanyonyi, W.C.; Wangila, P.T.; Tonui, M.K. Kinetic and equilibrium studies of Congo red dye adsorption on cabbage waste powder. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 2, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, M.; Solís, A.; Pérez, H.I.; Manjarrez, N.; Flores, M. Microbial decolouration of azo dyes: A review. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1723–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, M.; Jin, B.; Dai, S.; Vimonses, V. Activating natural bentonite as a cost-effective adsorbent for removal of Congo-red in wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamoorthy, G.; Ali, D.; Yadav, V.K.; Dhinagaran, G.; Venkatachalam, K.; Narayanan, V. New construction of Fe3O4/rGO/ZnSnO3 nanocomposites enhanced photoelectro chemical properties. Opt. Mater. 2020, 109, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbani, P.; Tabatabaii, S.; Mehrizad, A. Removal of Congo red from textile wastewater by ozonation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Riquelme, C.L.; López-Maldonado, E.A.; Ochoa-Terán, A.; Alcántar-Zavala, E.; Trujillo-Navarrete, B.; Pérez-Sicairos, S.; Miranda-Soto, V.; Zizumbo-López, A. Chitosan-carbamoylcarboxylic acid grafted polymers for removal of metal ions in wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Rodriguez, L.; Miralles-Cuevas, S.; Oller, I.; Agüera, A.; Puma, G.L.; Malato, S. Treatment of emerging contaminants in wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) effluents by solar photocatalysis using low TiO2 concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 211, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, N.; Chen, C.; Ouyang, K.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z. Adsorption characteristics of directional cellulose nanofiber/chitosan/montmorillonite aerogel as adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 119120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. Adsorption characteristics of a novel carbon-nanotube-based composite adsorbent toward organic pollutants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2379–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Nebsen, M.; Salem, M.Y. Adsorptive removal of fluoroquinolones from water by pectin-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles: Process optimization using a spectrofluorimetric assay. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attallah, O.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Nebsen, M.; Salem, M.Y. Removal of cationic and anionic dyes from aqueous solution with magnetite/pectin and magnetite/silica/pectin hybrid nanocomposites: Kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 11461–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griggs, D.; Nilsson, M.; Stevance, A.; McCollum, D. A Guide to SDG Interactions: From Science to Implementation; International Council for Science: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Saheed, I.O.; Da Oh, W.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan modifications for adsorption of pollutants–A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, K.; Goda, T.; Yamada, T.; Nagoshi, M. Direct Ethanol Production from Xylan and Acorn Using the Starch-Fermenting Basidiomycete Fungus Phlebia acerina. Fermentation 2021, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtibe, A.; Motloung, M.P.; Bandyopadhyay, J.; Ray, S.S. Synthetic biopolymers and their composites: Advantages and limitations—An overview. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malesic-Eleftheriadou, N.; Evgenidou, E.; Lazaridou, M.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Yang, X.; Kyzas, G.Z.; Lambropoulou, D.A. Simultaneous removal of anti-inflammatory pharmaceutical compounds from an aqueous mixture with adsorption onto chitosan zwitterionic derivative. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, A. Adsorption characteristics of Congo Red onto the chitosan/montmorillonite nanocomposite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.M.; Eldin, T.A.S.; Hassan, M.A.; El-Anadouli, B.E. Efficient treatment of lead-containing wastewater by hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanostructures. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Tang, N.; Jin, X.; Gao, W. Fabrications and applications of hemicellulose-based bio-adsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalla, A.H.; Yaseen, Z.; Bhat, M.A.; Rangreez, T.A.; Maswal, M. Recent review for removal of metal ions by hydrogels. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Dong, X.; Wang, S.; Kong, F. Synthesis of nanocomposites using xylan and graphite oxide for remediation of cationic dyes in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananpattarachai, J.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Enhancement of chromium removal efficiency on adsorption and photocatalytic reduction using a bio-catalyst, titania-impregnated chitosan/xylan hybrid film. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 130, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.R.; Liang, H.; Dickinson, M.; Botchwey, E.A. Xylan hemicellulose improves chitosan hydrogel for bone tissue regeneration. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Hu, J.; Wei, L.; Du, Y.; Shi, X.; Deng, H.; Zhang, L. Construction of porous chitosan–xylan–TiO2 hybrid with highly efficient sorption capability on heavy metals. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Mohamed, I.M. A review on versatile applications of transition metal complexes incorporating Schiff bases. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nnadozie, E.C.; Ajibade, P.A. Green synthesis and characterization of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using Chromolaena odorata root extract for smart nanocomposite. Mater. Lett. 2020, 263, 127145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagbi, Y.; Sarswat, A.; Mohan, D.; Pandey, A.; Solanki, P.R. Lead (Pb2+) adsorption by monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles: Surface analysis and effects of solution chemistry. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4237–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, K.A. 5.5 the phenomenological theory of solvent effects in mixed solvent systems. In Handbook of Solvents; Chemtec Publishing: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2001; p. 281. [Google Scholar]
- Omraei, M.; Esfandian, H.; Katal, R.; Ghorbani, M. Study of the removal of Zn (II) from aqueous solution using polypyrrole nanocomposite. Desalination 2011, 271, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, N.-y.; Zhang, Q.-l. Thermodynamics and kinetics of cadmium adsorption onto oxidized granular activated carbon. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonin, J.-P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ofomaja, A.E. Intraparticle diffusion process for lead (II) biosorption onto mansonia wood sawdust. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5868–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.A.; El-Sayed, M.M.; Emam, A.N.; Abd-Rabou, A.A.; Dawood, R.M.; Oudadesse, H. Bioactive glass doped with noble metal nanoparticles for bone regeneration: In vitro kinetics and proliferative impact on human bone cell line. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 25628–25638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Saed, K. Possible utilization of silica gel sludge for the removal of phenol from aqueous solutions: Laboratory studies. Environmentalist 2003, 23, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyun, T.S.; Mseer, A.H. Comparison of the experimental results with the Langmuir and Freundlich models for copper removal on limestone adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teleman, A.; Tenkanen, M.; Jacobs, A.; Dahlman, O. Characterization of O-acetyl-(4-O-methylglucurono) xylan isolated from birch and beech. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleman, A.; Lundqvist, J.; Tjerneld, F.; Stålbrand, H.; Dahlman, O. Characterization of acetylated 4-O-methylglucuronoxylan isolated from aspen employing 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2000, 329, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, C.N.; Galván, M.V.; Zanuttini, M.A.; Mocchiutti, P. Hydrogels from xylan/chitosan complexes for the controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1465–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielii, I.; Gatenholm, P. Preparation and properties of hydrogels based on hemicellulose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 69, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Deen, M.J.; Kumar, S.; Selvaganapathy, P.R. Raman spectroscopy for in-line water quality monitoring—Instrumentation and potential. Sensors 2014, 14, 17275–17303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkin, P. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy: Principles and Spectral Interpretation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Asakura, M.; Okuno, M. Hyper-Raman Spectroscopic Investigation of Amide Bands of N-Methylacetamide in Liquid/Solution Phase. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 4780–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zając, A.; Hanuza, J.; Wandas, M.; Dymińska, L. Determination of N-acetylation degree in chitosan using Raman spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhong, L.; Hu, J.-F. Characterization of the surface properties of xylan by FT-Raman spectroscopy and wicking technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2004, 39, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoia, M.; Istratie, R.; Păcurariu, C. Investigation of magnetite nanoparticles stability in air by thermal analysis and FTIR spectroscopy. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, I.S.; Durmus, Z. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of magnetite (Fe 3 O 4)@ conducting polymer (pani, ppy, pt) composites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 2001708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donescu, D.; Raditoiu, V.; Spataru, C.I.; Somoghi, R.; Ghiurea, M.; Radovici, C.; Fierascu, R.C.; Schinteie, G.; Leca, A.; Kuncser, V. Superparamagnetic magnetite–divinylbenzene–maleic anhydride copolymer nanocomposites obtained by dispersion polymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2012, 48, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-kharrag, R.; Abdel Halim, S.S.; Amin, A.; Greish, Y.E. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan-coated magnetite nanoparticles using a modified wet method for drug delivery applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2019, 68, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Crist, R.M.; Clogston, J.D.; McNeil, S.E. Zeta potential: A case study of cationic, anionic, and neutral liposomes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5779–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Panda, A.; Kim, E.; Yoon, M. Biopolymer-coated magnetite nanoparticles and metal–organic framework ternary composites for cooperative Pb (II) adsorption. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 4198–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predescu, A.M.; Matei, E.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Pantilimon, C.; Drăgan, C.; Vidu, R.; Predescu, C.; Kuncser, V. Synthesis and characterization of dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; McClements, D.J.; Jian, L.; Han, Y.; Dai, L.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Core–shell biopolymer nanoparticles for co-delivery of curcumin and piperine: Sequential electrostatic deposition of hyaluronic acid and chitosan shells on the zein core. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38103–38115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha, R.K.; Kota, S. Removal of lead by adsorption with the renewable biopolymer composite of feather (Dromaius novaehollandiae) and chitosan (Agaricus bisporus). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 6, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, R.I. Acid–base properties of carboxylic acids, esters and amides. Acid Deriv. 1992, 2, 305–369. [Google Scholar]
- Schnell, C.N.; Galván, M.V.; Solier, Y.N.; Inalbon, M.C.; Zanuttini, M.A.; Mocchiutti, P. High strength biobased films prepared from xylan/chitosan polyelectrolyte complexes in the presence of ethanol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrache, Z.; Abbas, M.; Aksil, T.; Trari, M. Thermodynamic and kinetics studies on adsorption of Indigo Carmine from aqueous solution by activated carbon. Microchem. J. 2019, 144, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lei, B.; He, A.; Zhang, X.; Ma, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, C. Toward 3D graphene oxide gels based adsorbents for high-efficient water treatment via the promotion of biopolymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 467–478. [Google Scholar]
- Bayomie, O.S.; Kandeel, H.; Shoeib, T.; Yang, H.; Youssef, N.; El-Sayed, M.M. Novel approach for effective removal of methylene blue dye from water using fava bean peel waste. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, P.S.; Manteghi, F.; Tehrani, Z. Adsorption of Lead Ions by a Green AC/HKUST-1 Nanocomposite. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, V.S.; Sudhakar, B.; Prasad, K.; Sunadh, P.J.; Krishna, M. Adsorption of Congo red from aqueous solution onto Antigonon leptopus leaf powder: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 3197–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, F.-C. Inferring the favorable adsorption level and the concurrent multi-stage process with the Freundlich constant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Kamran, M.; Khan, S.A.; Shaheen, K.; Shah, Z.; Suo, H.; Khan, Q.; Shah, A.B.; Rehman, W.U.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O. Adsorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of methyl orange dye sequestration through chitosan composites films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Gao, B.; Dai, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, X. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution using salicylic acid type chelate adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, P.; Cai, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, H.; Li, A. Efficient adsorption of both methyl orange and chromium from their aqueous mixtures using a quaternary ammonium salt modified chitosan magnetic composite adsorbent. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weijiang, Z.; Yace, Z.; Yuvaraja, G.; Jiao, X. Adsorption of Pb (II) ions from aqueous environment using eco-friendly chitosan schiff’s base@ Fe3O4 (CSB@ Fe3O4) as an adsorbent; kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chai, K.; Yao, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, K.; Huang, Z.; Yan, J.; Qin, X.; Wei, W.; Ji, H. β-Cyclodextrin functionalized SBA-15 via amide linkage as a super adsorbent for rapid removal of methyl blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Liao, H.; Ma, X.; Xiao, M.; Liu, X.; Gong, S.; Shu, X.; Zhou, X. Adsorption performance of chitosan Schiff base towards anionic dyes: Electrostatic interaction effects. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2021, 780, 138958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; Long, F.; Huang, B.; Yang, B.; Pan, X. A magnetically recyclable chitosan composite adsorbent functionalized with EDTA for simultaneous capture of anionic dye and heavy metals in complex wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Bora, M.; Hao, S.; Tao, K.; Wu, J.; Hu, L.; Liao, J.; Lin, S.; Triantafyllou, M.S.; Li, X. Hyaluronic Acid Methacrylate Hydrogel-Modified Electrochemical Device for Adsorptive Removal of Lead (II). Biosensors 2022, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman Brohi, R.O.; Khuhawar, M.Y.; Mahar, R.B. Graphene oxide functionalized with a Schiff Base for the removal of Pb (II) ions from contaminated water: Experimental and modeling approach. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essandoh, M.; Kunwar, B.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Mohan, D.; Mlsna, T. Sorptive removal of salicylic acid and ibuprofen from aqueous solutions using pine wood fast pyrolysis biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Qiu, L.-G.; Su, H.-Z.; Cao, C.-l.; Jiang, J.-h. Schiff base–Chitosan grafted l-monoguluronic acid as a novel solid-phase adsorbent for removal of congo red. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez, T.; Pasquini, D.; de Faria Lima, A.; Rosa, E.V.; Sousa, M.H.; Cerqueira, D.A.; de Morais, L.C. Efficient removal of lead ions from water by magnetic nanosorbents based on manganese ferrite nanoparticles capped with thin layers of modified biopolymers. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hegazey, R. Utilization of waste aluminum cans in the fabrication of hydroxysodalite nanoparticles and their chitosan biopolymer composites for the removal of Ni (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions: Kinetic, equilibrium, and reusability studies. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, E.F.; Nunes, M.L.; Fajardo, A.R. Chitosan/waste coffee-grounds composite: An efficient and eco-friendly adsorbent for removal of pharmaceutical contaminants from water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahangdale, D.; Kumar, A. Chitosan as a substrate for simultaneous surface imprinting of salicylic acid and cadmium. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.-S.; Lee, D.-J. Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| BET Surface Area (m2/g) | BJH Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Langmuir Surface Area (m2/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsXM | 21.81 | 0.014 | 32.22 |
| Chitosan | 1.82 | 0.007 | 2.93 |
| Xylan | 0.59 | 0.001 | 0.88 |
| Chitosan/xylan | 22.78 | 0.018 | 177.24 |
| CsM | 79.31 | 0.109 | 114.27 |
| XnM | 41.67 | 0.043 | 60.08 |
| Pb(II) | SA | CR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsM | 22.9 ± 0.1 | 16.5 ± 0.0 | 17.6 ± 0.1 |
| XnM | 49.5 ± 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 11.1 ± 0.2 |
| CsXM | 28.9 ± 2.3 | 18.1 ± 3.1 | 9.8 ± 1.3 |
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | Intra-Particle Diffusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe mg/g | k1 min−1 | R2 | qe mg/g | k2 G·mg−1·min−1 | R2 | vi min−1 | C | kid mg·g−1·min−0.5 | R2 | |
| Pb(II) | 22.26 | 0.014 | 0.9916 | 29.06 | 0.0007 | 0.9982 | 9.272 | 0 | 1.630 | 0.9923 |
| SA | 5.50 | 0.009 | 0.6971 | 13.49 | 0.0026 | 0.9920 | 3.037 | 0 | 1.107 | 0.9895 |
| CR | 0.82 | 0.004 | 0.08 | 8.10 | 0.0220 | 0.9948 | 1.445 | −6.624 | 2.665 | 0.9519 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm mg/g | Kd | R2 | RMSE | Kf (mg/g) (L/mg) n | 1/n | R2 | RMSE | |
| Pb(II) | 434.78 | 784.56 | 0.0433 | 0.131 | 0.51 | 1.04 | 0.9859 | 0.074 |
| SA | 4.31 | 13.06 | 0.3681 | 0.400 | 0.35 | 0.92 | 0.9649 | 0.133 |
| CR | 13.23 | 8.91 | 0.7676 | 0.673 | 1.32 | 0.60 | 0.9833 | 0.443 |
| A/B | ||
|---|---|---|
| pH 5.5 | pH 4.0 | |
| Pb(II)/SA | 3.85 | 1.06 |
| Pb(II)/CR | 7.83 | 4.96 |
| SA/CR | 2.03 | 4.70 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | qm (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxymethyl starch-coated manganese ferrite | Pb(II) | 34.15 (Freundlich) | [83] |
| Hydroxysodalite-chitosan composites | Pb(II) | 17.85 (Langmuir) | [84] |
| Crosslinked acrylamide grafted chitosan-based mimic SA and cadmium dual imprinted polymer | SA | 40.80 (Langmuir) | [86] |
| Chitosan/waste coffee grounds composite | Acetyl-SA | 9.97 (Freundlich) | [85] |
| Chitosan/montmorillonite | CR | 54.52 (Langmuir) | [27] |
| Orange peel | CR | 14.00 (Langmuir) | [87] |
| CsXM | Pb(II) SA CR | 25.20 (Freundlich) 11.34 (Freundlich) 13.01 (Freundlich) | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farghal, H.H.; Nebsen, M.; El-Sayed, M.M.H. Multifunctional Chitosan/Xylan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Adsorption of the Emerging Contaminants Pb(II), Salicylic Acid, and Congo Red Dye. Water 2023, 15, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040829
Farghal HH, Nebsen M, El-Sayed MMH. Multifunctional Chitosan/Xylan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Adsorption of the Emerging Contaminants Pb(II), Salicylic Acid, and Congo Red Dye. Water. 2023; 15(4):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040829
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarghal, Hebatullah H., Marianne Nebsen, and Mayyada M. H. El-Sayed. 2023. "Multifunctional Chitosan/Xylan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Adsorption of the Emerging Contaminants Pb(II), Salicylic Acid, and Congo Red Dye" Water 15, no. 4: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040829
APA StyleFarghal, H. H., Nebsen, M., & El-Sayed, M. M. H. (2023). Multifunctional Chitosan/Xylan-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Adsorption of the Emerging Contaminants Pb(II), Salicylic Acid, and Congo Red Dye. Water, 15(4), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15040829