Microplastic Toxicity and Trophic Transfer in Freshwater Organisms: Ecotoxicological and Genotoxic Assessment in Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. and Echinogammarus veneris (Heller, 1865) Treated with Polyethylene Microparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Microplastic, Reagent and Chemical Characteristics
2.2. Spirodela polyrhiza–Growth and Experimental Treatment
2.3. Echinogammarus veneris–Growth and Experimental Treatment
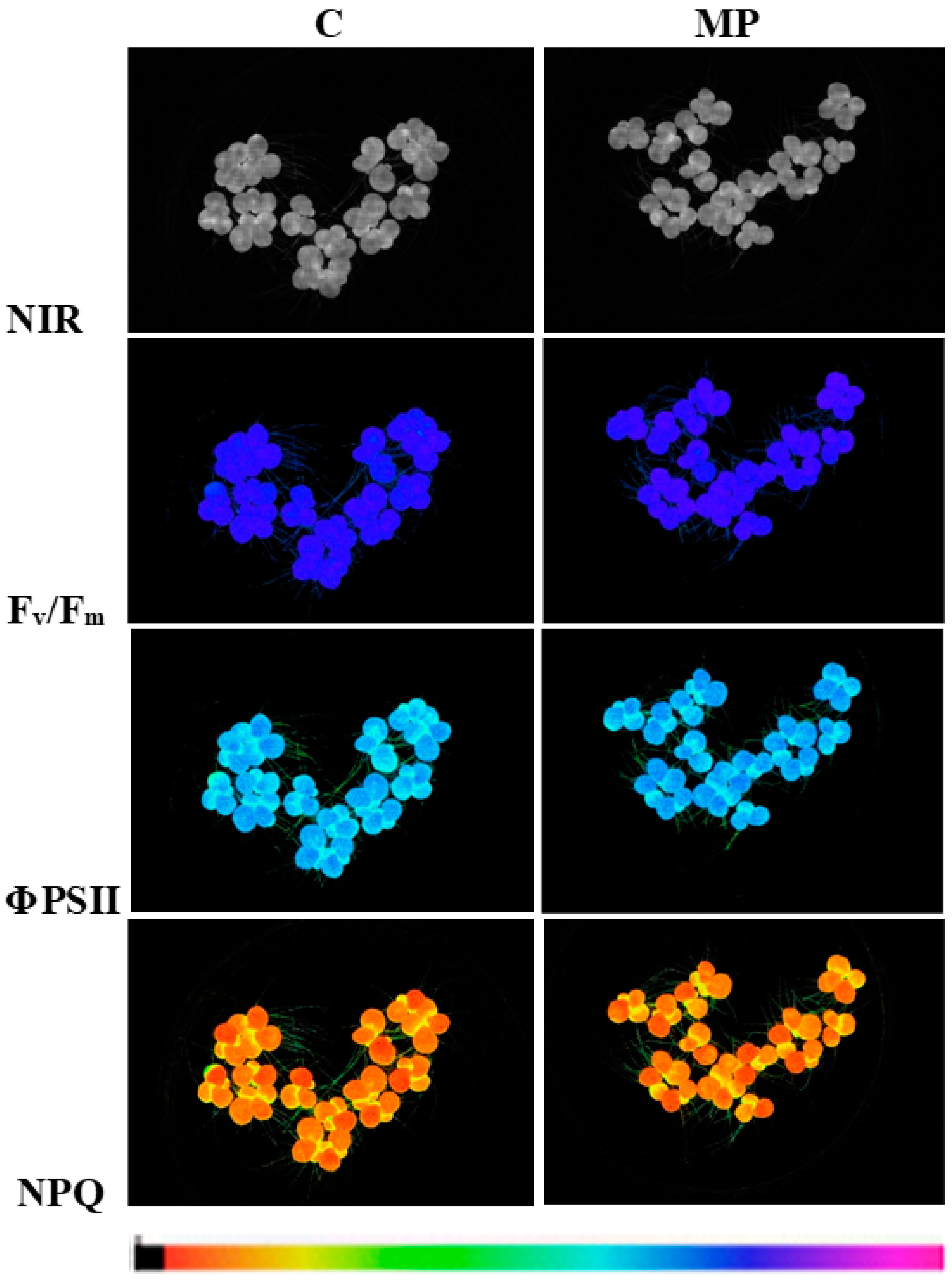
2.4. Plant Biometric and Physiological Traits Evaluation
- -
- Photochemical Reflectance Index (PRI) = (R531 − R570)/(R531 + R570) [62]
- -
- Pigment Specific Simple Ratio a (PSSRa) = (R800)/(R680) [63]
- -
- Pigment Specific Simple Ratio b (PSSRb) = (R800)/(R635) [63]
- -
- Pigment Specific Simple Ratio c (PSSRc) = (R800)/(R470) [63]
- -
- Normalized Phaeophytinization Index (NPQI) = (R415 − R435)/(R415 + R435) [64]
- -
- Anthocyanin Reflectance Index (ARI) = (1/R550)/(1/R700) [65].
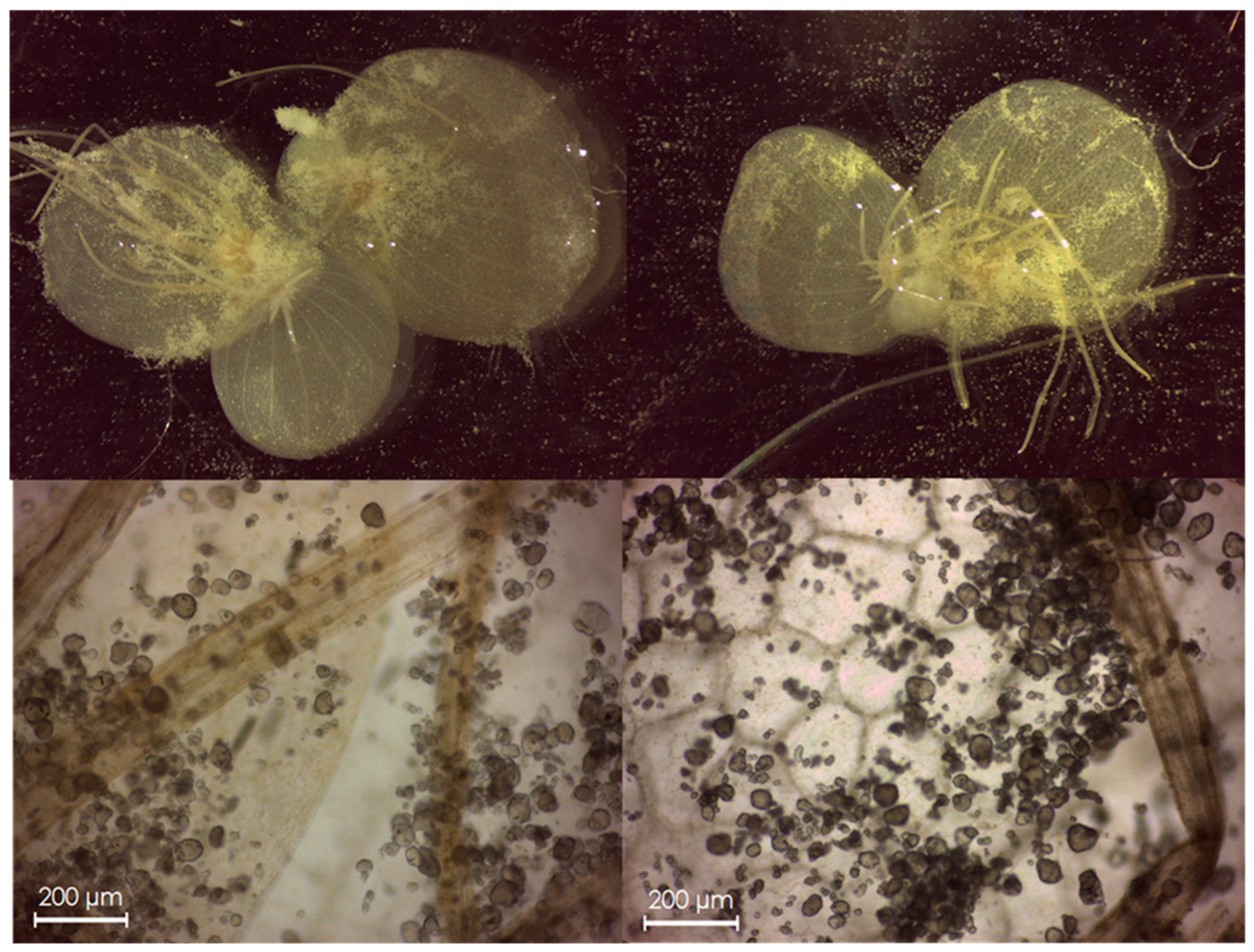
2.5. Evaluation of MP Transfer from S. polyrhiza to E. veneris
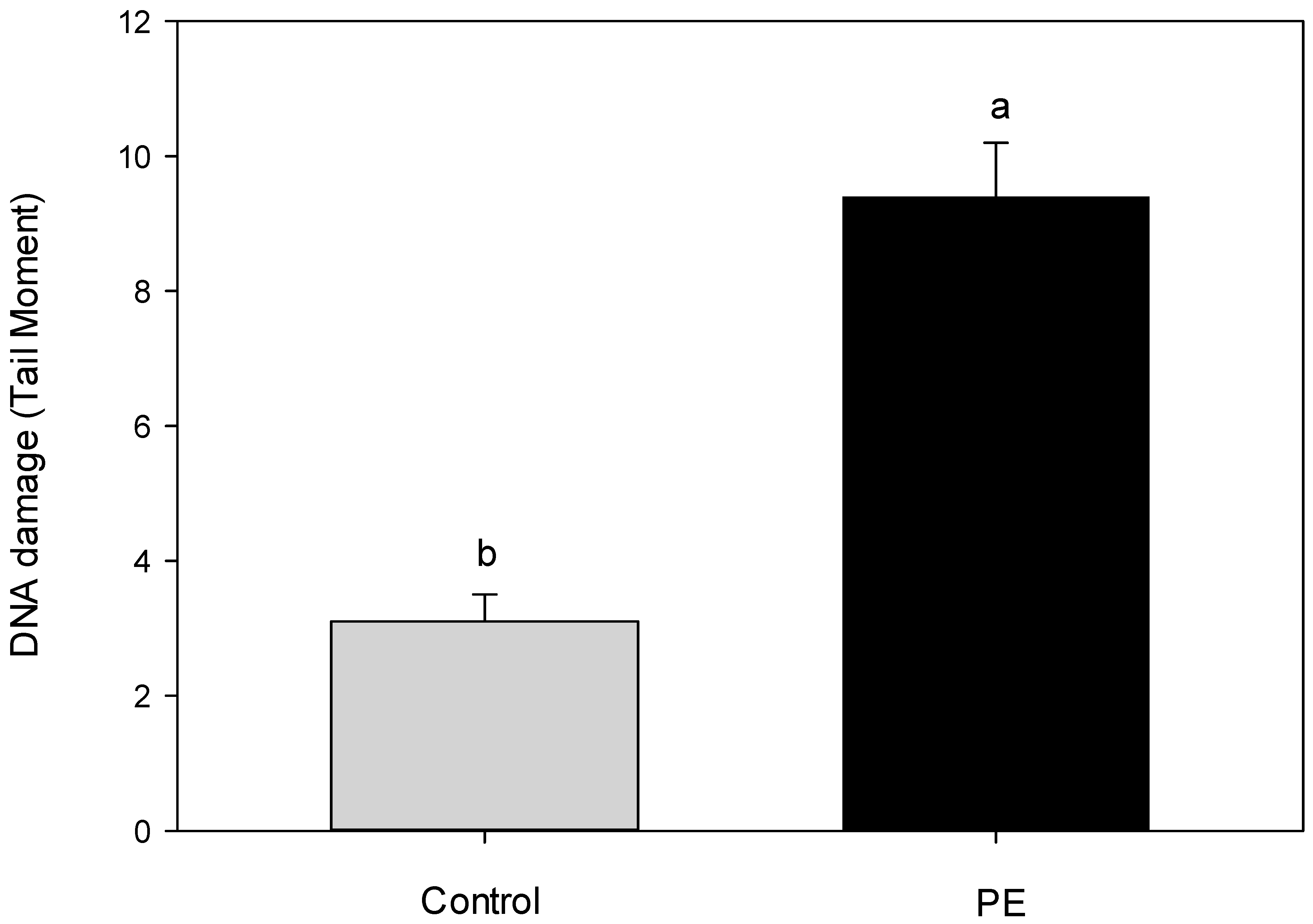
2.6. Genotoxicity Test in E. veneris
2.7. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maheswaran, B.; Karmegam, N.; Al-Ansari, M.; Subbaiya, R.; Al-Humaid, L.; Raj, J.S.; Govarthanan, M. Assessment, characterization, and quantification of microplastics from river sediments. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, V.; Pasquali, V.; Setini, A.; Corami, F. First evidence of microplastics ingestion in benthic amphipods from Svalbard. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, J.; Mishra, P.P. Microplastics in polar regions: An early warning to the world’s pristine ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiano, V.; Compa, M.; Alomar, C.; Rios-Fuster, B.; Morató, M.; Capó, X.; Deudero, S. Breaking the paradigm: Marine sediments hold two-fold microplastics than sea surface waters and are dominated by fibers. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 858, 159722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; van Pelt, F.N.; O’Halloran, J.; Jansen, M.A. Adsorption, uptake and toxicity of micro- and nanoplastics: Effects on terrestrial plants and aquatic macrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.; Nash, R. Microplastics: Finding a consensus on the definition. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 138, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.M.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIvor, A.J.; Pires, R.; Lopes, C.; Raimundo, J.; Campos, P.F.; Pais, M.P.; Canning-Clode, J.; Dinis, A. Assessing microplastic exposure of the Critically Endangered Mediterranean monk seal (Monachus monachus) on a remote oceanic island. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Fu, D.; Qi, H.; Lan, C.Q.; Yu, H.; Ge, C. Micro-and nano-plastics in marine environment: Source, distribution and threats—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Coffin, S.; Sun, C.; Schlenk, D.; Gan, J. Negligible effects of microplastics on animal fitness and HOC bioaccumulation in earthworm Eisenia fetida in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, F.; Cryder, Z.; Huang, D.; Lu, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, Z.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J. Microplastics in the soil environment: Occurrence, risks, interactions and fate–a review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2175–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Thompson, R. Occurrence, fate, and effect of microplastics in freshwater systems. In Microplastic Contamination in Aquatic Environments; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 95–132. [Google Scholar]
- Koutnik, V.S.; Leonard, J.; Alkidim, S.; DePrima, F.J.; Ravi, S.; Hoek, E.M.; Mohanty, S.K. Distribution of microplastics in soil and freshwater environments: Global analysis and framework for transport modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, V.; Di Gennaro, A.; Lecce, F.; Sighicelli, M.; Falconieri, M.; Pietrelli, L.; Poeta, G.; Battisti, C. Microplastics in Talitrus saltator (Crustacea, Amphipoda): New evidence of ingestion from natural contexts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28725–28729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corami, F.; Rosso, B.; Iannilli, V.; Ciadamidaro, S.; Bravo, B.; Barbante, C. Occurrence and Characterization of Small Microplastics (<100 μm), Additives, and Plasticizers in Larvae of Simuliidae. Toxics 2022, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanalp, M.; Kokturk, M.; Gündüz, F.; Parlak, V.; Ucar, A.; Alwazeer, D.; Alak, G. The Use of Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) as a Sentinel Species for the Microplastic Pollution of Freshwater: The Case of Beyhan Dam Lake, Turkey. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannilli, V.; Corami, F.; Grasso, P.; Lecce, F.; Buttinelli, M.; Setini, A. Plastic abundance and seasonal variation on the shorelines of three volcanic lakes in Central Italy: Can amphipods help detect contamination? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14711–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, U.; Kalčíková, G. The Response of Duckweed Lemna minor to Microplastics and Its Potential Use as a Bioindicator of Microplastic Pollution. Plants 2022, 11, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovidat, L.C.; Brinkmann, B.W.; Vijver, M.G.; Bosker, T. Plastic particles adsorb to the roots of freshwater vascular plant Spirodela polyrhiza but do not impair growth. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; Scott, D.T.; Seitmaganbetova, G.; van Pelt Frank NA, M.; O’Halloran, J.; Jansen Marcel, A.K. Polyethylene microplastics adhere to Lemna minor (L.), yet have no effects on plant growth or feeding by Gammarus duebeni (Lillj.). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos-Cárdenas, A.; O’Halloran, J.; van Pelt, F.N.A.M.; Jansen, M.A.K. Rapid fragmentation of microplastics by the freshwater amphipod Gammarus duebeni (Lillj.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudo, R.; Foudoulakis, M.; Arapis, G.; Perdaen, K.; Lanneau, W.; Paxinou, A.C.; Kouvdou, S.; Persoone, G. History and sensitivity comparison of the Spirodela polyrhiza microbiotest and Lemna toxicity tests. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2015, 416, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietrini, F.; Di Baccio, D.; Aceña, J.; Pérez, S.; Barceló, D.; Zacchini, M. Ibuprofen exposure in Lemna gibba L.: Evaluation of growth and phytotoxic indicators, detection of ibuprofen and identification of its metabolites in plant and in the medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkandawire, M.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Dudel, E.G. The Lemna Bioassay: Contemporary Issues as the Most Standardized Plant Bioassay for Aquatic Ecotoxicology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 154–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceschin, S.; Bellini, A.; Scalici, M. Aquatic plants and ecotoxicological assessment in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 4975–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalčíková, G. Aquatic vascular plants—A forgotten piece of nature in microplastic research. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokalj, A.J.; Kuehnel, D.; Puntar, B.; Gotvajn, A.; Kalčikova, G. An exploratory ecotoxicity study of primary microplastics versus aged in natural waters and wastewaters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozman, U.; Kokalj, A.J.; Dolar, A.; Drobne, D.; Kalčíková, G. Long-term interactions between microplastics and floating macrophyte Lemna minor: The potential for phytoremediation of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 831, 154866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Feng, L.J.; Sun, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhu, F.P.; Yuan, X.Z. Do Polystyrene Nanoplastics Have Similar Effects on Duckweed (Lemna minor L.) at Environmentally Relevant and Observed-Effect Concentrations? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4071–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, L.; Nack, F.; Zimmermann, T.; Pröfrock, D. Microplastics as a Trojan horse for trace metals. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ivy, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dey, A.; Sharma, P. Coupled effects of microplastics and heavy metals on plants: Uptake, bioaccumulation, and environmental health perspectives. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 836, 155619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Cao, Y. Antidote or Trojan horse for submerged macrophytes: Role of microplastics in copper toxicity in aquatic environments. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Wei, L.; Li, Z. Microplastics and co-pollutant with ciprofloxacin affect interactions between free-floating macrophytes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Peng, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Qi, W. Effects of microplastics and glyphosate on growth rate, morphological plasticity, photosynthesis, and oxidative stress in the aquatic species Salvinia cucullata. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 279, 116900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfriso, A.A.; Tomio, Y.; Juhmani, A.-S.; Sfriso, A.; Munari, C.; Mistri, M. Macrophytes: A Temporary Sink for Microplastics in Transitional Water Systems. Water 2021, 13, 3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Vargas, D. Toxicity of Agrochemicals on Fresh- water Invertebrates—A Short Review. In Toxicity and Hazard of Agrochemicals; Larramendy, M.L., Soloneski, S., Eds.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welton, J.S. Life-history and production of the amphipod Gammarus pulex in a Dorset chalk stream. Freshw. Biol. 1979, 9, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, R.R.; Woodward, J.C.; Rothwell, J.J. Ingestion of Microplastics by Freshwater Tubifex Worms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12844–12851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, A.J.; Brooks, L.S.R.; Reid, W.D.K.; Piertney, S.B.; Narayanaswamy, B.E.; Linley, T.D. Microplastics and synthetic particles ingested by deep-sea amphipods in six of the deepest marine ecosystems on Earth. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 180667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blarer, P.; Burkhardt-Holm, P. Microplastics affect assimilation efficiency in the freshwater amphipod Gammarus fossarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 23522–23532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, A. Effects of New and Aged Polyethylenterephthalat and Polylactic Acid on Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea: Amphipoda) during Long-Term Exposures. J. Environ. Prot. 2020, 11, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Ecological Effects Test Guidelines: OPPTS 850.1020 Guideline Gammarid Acute Toxicity Test; 712–C–96–130; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Garcia-Galan, M.J.; Sordet, M.; Buleté, A.; Garric, J.; Vulliet, E. Evaluation of the influence of surfactants in the bioaccumulation kinetics of sulfamethoxazole and oxazepam in benthic invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokota, K.; Waterfield, H.; Hastings, C.; Davidson, E.; Kwietniewski, E.; Wells, B. Finding the missing piece of the aquatic plastic pollution puzzle: Interaction between primary producers and microplastics. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2017, 2, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietrini, F.; Zacchini, M. A New Ecotoxicity Assay for Aquatic Plants: Eco-Tox Photosystem Tool (ETPT). Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 1266–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davolos, D.; Chimenti, C.; Ronci, L.; Setini, A.; Iannilli, V.; Pietrangeli, B.; De Matthaeis, E. An integrated study on Gammarus elvirae (Crustacea, Amphipoda): Perspectives for toxicology of arsenic-contaminated freshwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15563–15570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.; Botelho, M.T.; Vannuci-Silva, M.; Artal, M.C.; Vacchi, F.I.; Magalhães, G.R.; Gomes, V.; Henry, T.B.; Umbuzeiro, G.D.A. The amphipod Parhyale hawaiensis as a promising model in ecotoxicology. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, L.; Serranti, S.; Mazziotti, C.; Riccardi, E.; Benzi, M.; Bonifazi, G. Classification and distribution of freshwater microplastics along the Italian Po river by hyperspectral imaging. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 48588–48606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzanti, M.; Mastrantuono, L.; Solimini, A.G. Selecting macroinvertebrate taxa and metrics to assess eutrophication in different depth zones of Mediterranean lakes. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2012, 180, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronci, L.; Meccoli, L.; Iannilli, V.; Menegoni, P.; De Matthaeis, E.; Setini, A. Comparison between active and pas- sive biomonitoring strategies for the assessment of genotoxicity and metal bioaccumulation in Echinogammarus veneris (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Ital. J. Zool. 2016, 83, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genomic Resources Development Consortium; Baratti, M.; Cattonaro, F.; Di Lorenzo, T.; Galassi, D.M.P.; Iannilli, V.; Iannucci, A.; Jensen, J.; Larsen, P.; Nielsen, R.O.; et al. Genomic Resources Notes Accepted 1 October 2014–30 November 2014. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 458–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, S.; Aureli, F.; Iannilli, V. Bisphenols A and its analogues induce genotoxic damage in marine and freshwater amphipods. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrini, F.; Passatore, L.; Fischetti, E.; Carloni, S.; Ferrario, C.; Polesello, S.; Zacchini, M. Evaluation of morpho-physiological traits and contaminant accumulation ability in Lemna minor L. treated with increasing perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) concentrations under laboratory conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence: A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baccio, D.; Pietrini, F.; Bertolotto, P.; Pérez, S.; Barcelò, D.; Zacchini, M.; Donati, E. Response of Lemna gibba L. to high and environmentally relevant concentrations of ibuprofen: Removal, metabolism and morpho-physiological traits for biomonitoring of emerging contaminants. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584–585, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J. Photosynthetic Acclimation and Nitrogen Partitioning Within a Lucerne Canopy. II. Stability Through Time and Comparison With a Theoretical Optimum. Funct. Plant Biol. 1993, 20, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrini, F.; Iannilli, V.; Passatore, L.; Carloni, S.; Sciacca, G.; Cerasa, M.; Zacchini, M. Ecotoxicological and genotoxic effects of dimethyl phthalate (DMP) on Lemna minor L. and Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. plants under a short-term laboratory assay. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 806, 150972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platt, T.; Gallegos, C.L.; Harrison, W.G. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J. Mar Res. 1980, 38, 687–701. [Google Scholar]
- Gamon, A.; Serrano, L.; Surfus, S. The photochemical reflectance index: An optical indicator of photosynthetic radiation use efficiency across species, functional types, and nutrient levels. Oecologia 1997, 112, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.A. Quantifying chlorophylls and carotenoids at leaf and canopy scales: An evaluation of some hyperspectral approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Lloret, P.; Mun Oz, F.; Vilajeliu, M. Reflectance assessment of mite effects on apple trees. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 2727–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Merzlyak, M.N.; Chivkunova, O.B. Optical properties and nondestructive estimation of anthocyanin content in plant leaves. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 74, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugolini, A.; Ungherese, G.; Ciofini, M.; Lapucci, A.; Camaiti, M. Microplastic debris in sandhoppers. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P. The comet assay: Reflections on its development, evolution and applications. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2016, 767, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bivehed, E.; Hellman, B. Flash-comet assay. Methodsx 2020, 7, 101161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD guideline 221. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals: Revised Proposal for a New Guideline 221, Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test; Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kalčíková, G.; Gotvajn, A.; Kladnik, A.; Jemec, A. Impact of polyethylene microbeads on the floating freshwater plant duckweed Lemna minor. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozman, U.; Turk, T.; Skalar, T.; Zupančič, M.; Korošin, N.Č.; Marinšek, M.; Kalčíková, G. An extensive characterization of various environmentally relevant microplastics–Material properties, leaching and ecotoxicity testing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewez, D.; Goltsev, V.; Kalaji, H.M.; Oukarroum, A. Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles on photosystem II performance in Lemna gibba probed by chlorophyll fluorescence. Curr. Plant Biol. 2018, 16, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, V.; Hepp, A.; Irfan, M.; Mészáros, I. Chlorophyll fluorescence imaging-based duckweed phenotyping to assess acute phytotoxic effects. Plants 2021, 10, 2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriel, A.; Dundas, G.; Cirelli, A.F.; Lagorio, M.G. Effect of arsenic on reflectance spectra and chlorophyll fluorescence of aquatic plants. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I. Visible and near-infrared reflectance techniques for diagnosing plant physiological status. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováč, D.; Veselovská, P.; Klem, K.; Večeřová, K.; Ač, A.; Peñuelas, J.; Urban, O. Potential of Photochemical Reflectance Index for Indicating Photochemistry and Light Use Efficiency in Leaves of European Beech and Norway Spruce Trees. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, D.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chao, D.-Y.; Messing, J.; et al. Plant evolution and environmental adaptation unveiled by long-read whole-genome sequencing of Spirodela. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18893–18899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cochran-Biederman, J.L.; Vondracek, B. Seasonal feeding selectivity of brown trout Salmo trutta in five groundwater-dominated streams. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2017, 32, 653–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lollobrigidi, R.; Procacciante, M.; D’orsi, A.; Seminara, M. Feeding habits of Salmo cettii (Rafinesque, 1810) in Central Italy: Studying a residual population of an endangered species using non-invasive methods. Ital. J. Freshw. Ichtyol. 2017, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Lopes, C.; Oliveira, P.; Bessa, F.; Otero, V.; Henriques, B.; Raimundo, J.; Caetano, M.; Vale, C.; Guilhermino, L. Microplastics in wild fish from North East Atlantic Ocean and its potential for causing neurotoxic effects, lipid oxidative damage, and human health risks associated with ingestion exposure. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 717, 134625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhdoumi, P.; Hossini, H.; Nazmara, Z.; Mansouri, K.; Pirsaheb, M. Occurrence and exposure analysis of microplastic in the gut and muscle tissue of riverine fish in Kermanshah province of Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 112915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagorti, G.; Kaya, B. Genotoxic effect of microplastics and COVID-19: The hidden threat. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber, A.A. Genotoxic Evaluation Of Polystyrene Microplastic. Sak. Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 23, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, F.; Garcia, A.R.; Pereira, B.P.; Fonseca, M.; Mestre, N.C.; Fonseca, T.G.; Ilharco, L.M.; Bebianno, M.J. Microplastics effects in Scrobicularia plana. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; D’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubowska, M.; Białowąs, M.; Stankevičiūtė, M.; Chomiczewska, A.; Pažusienė, J.; Jonko-Sobu´s, K.; Hallmann, A.; Urban-Malinga, B. Effects of chronic exposure to microplastics of different polymer types on early life stages of sea trout Salmo trutta. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 139922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannetier, P.; Morin, B.; Le Bihanic, F.; Dubreil, L.; Clérandeau, C.; Chouvellon, F.; Van Arkel, K.; Danion, M.; Cachot, J. Environmental samples of microplastics induce significant toxic effects in fish larvae. Environ. Int. 2019, 134, 105047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revel, M.; Lagarde, F.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Mouneyrac, C. Tissue-specific biomarker responses in the blue mussel Mytilus spp. exposed to a mixture of microplastics at environmentally relevant concentrations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Biometric Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFA (mm2) | MFA (mm2) | FN | MR | Td | μ(t0–7) | |
| C | 1376 ± 54 | 23.349 ± 0.001 | 59.0 ± 2.6 | 79.5 ± 2.8 | 2.39 ± 0.03 | 0.171 ± 0.005 |
| MP | 1275 ± 50 | 23.322 ± 0.001 | 54.6 ± 2.1 | 74.8 ± 2.3 | 2.45 ± 0.03 | 0.160 ± 0.005 |
| P | 0.241 | 0.891 | 0.263 | 0.268 | 0.272 | 0.246 |
| Treatment | Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Chlorophyll Content | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fv/Fm (rel. un.) | Φ PSII (rel. un.) | NPQ (rel. un.) | ETR (µmol Elect m−2 s−1) | Abs (rel. un.) | Chl (g m−2) | |
| C | 0.780 ± 0.003 | 0.634 ± 0.005 | 0.423 ± 0.043 | 16.15 ± 0.06 | 0.857 ± 0.003 a | 0.400 ± 0.010 a |
| MP | 0.777 ± 0.003 | 0.633 ± 0.008 | 0.421 ± 0.075 | 15.83 ± 0.19 | 0.829 ± 0.002 b | 0.328 ± 0.007 b |
| P | 0.626 | 0.928 | 0.978 | 0.110 | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| Treatment | Light Response Curves Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| α | ETRmax | Ek | |
| C | 0.358 ± 0.003 | 29.31 ± 0.91 | 81.74 ± 2.81 |
| MP | 0.351 ± 0.008 | 28.04 ± 0.50 | 80.05 ± 3.31 |
| P | 0.449 | 0.289 | 0.716 |
| Treatment | Spectral Index Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRI | PSSRa | PSSRb | PSSRc | NPQI | ARI | |
| C | 0.029 ± 0.001 | 12.35 ± 0.58 a | 5.39 ± 0.22 a | 12.21 ± 0.55 a | 0.065 ± 0.005 | −0.148 ± 0.026 |
| MP | 0.024 ± 0.002 | 9.45 ± 0.28 b | 4.35 ± 0.19 b | 9.42 ± 0.19 b | 0.055 ± 0.012 | −0.085 ± 0.029 |
| P | 0.100 | 0.011 | 0.024 | 0.009 | 0.531 | 0.157 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannilli, V.; Passatore, L.; Carloni, S.; Lecce, F.; Sciacca, G.; Zacchini, M.; Pietrini, F. Microplastic Toxicity and Trophic Transfer in Freshwater Organisms: Ecotoxicological and Genotoxic Assessment in Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. and Echinogammarus veneris (Heller, 1865) Treated with Polyethylene Microparticles. Water 2023, 15, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050921
Iannilli V, Passatore L, Carloni S, Lecce F, Sciacca G, Zacchini M, Pietrini F. Microplastic Toxicity and Trophic Transfer in Freshwater Organisms: Ecotoxicological and Genotoxic Assessment in Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. and Echinogammarus veneris (Heller, 1865) Treated with Polyethylene Microparticles. Water. 2023; 15(5):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050921
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannilli, Valentina, Laura Passatore, Serena Carloni, Francesca Lecce, Giulia Sciacca, Massimo Zacchini, and Fabrizio Pietrini. 2023. "Microplastic Toxicity and Trophic Transfer in Freshwater Organisms: Ecotoxicological and Genotoxic Assessment in Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. and Echinogammarus veneris (Heller, 1865) Treated with Polyethylene Microparticles" Water 15, no. 5: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050921
APA StyleIannilli, V., Passatore, L., Carloni, S., Lecce, F., Sciacca, G., Zacchini, M., & Pietrini, F. (2023). Microplastic Toxicity and Trophic Transfer in Freshwater Organisms: Ecotoxicological and Genotoxic Assessment in Spirodela polyrhiza (L.) Schleid. and Echinogammarus veneris (Heller, 1865) Treated with Polyethylene Microparticles. Water, 15(5), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050921







