Multi-Annual Dynamics of a Coastal Groundwater System with Soil-Aquifer Treatment and Its Impact on the Fate of Trace Organic Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
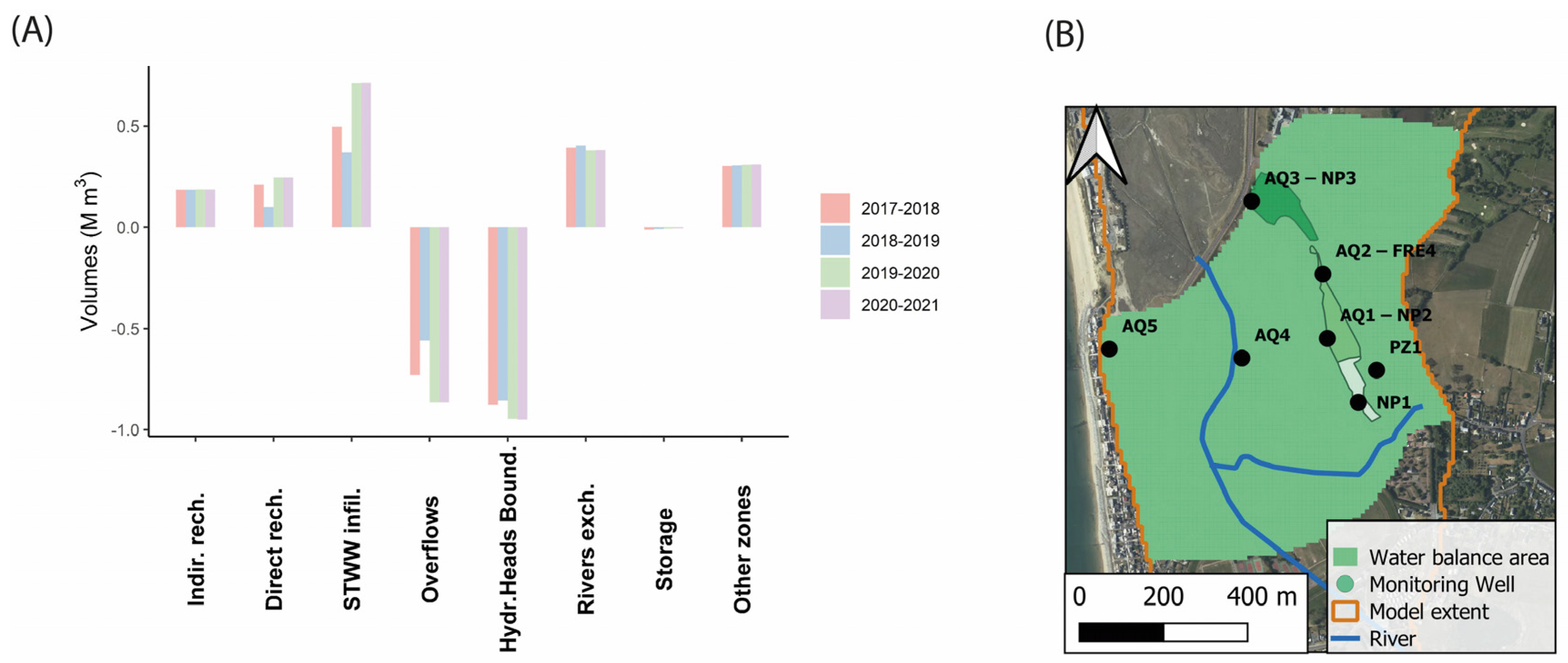
2.1. Study Area: Agon-Coutainville, Normandy, France
2.2. Available and Acquired Data
2.3. Methodological Approach
3. Modelling
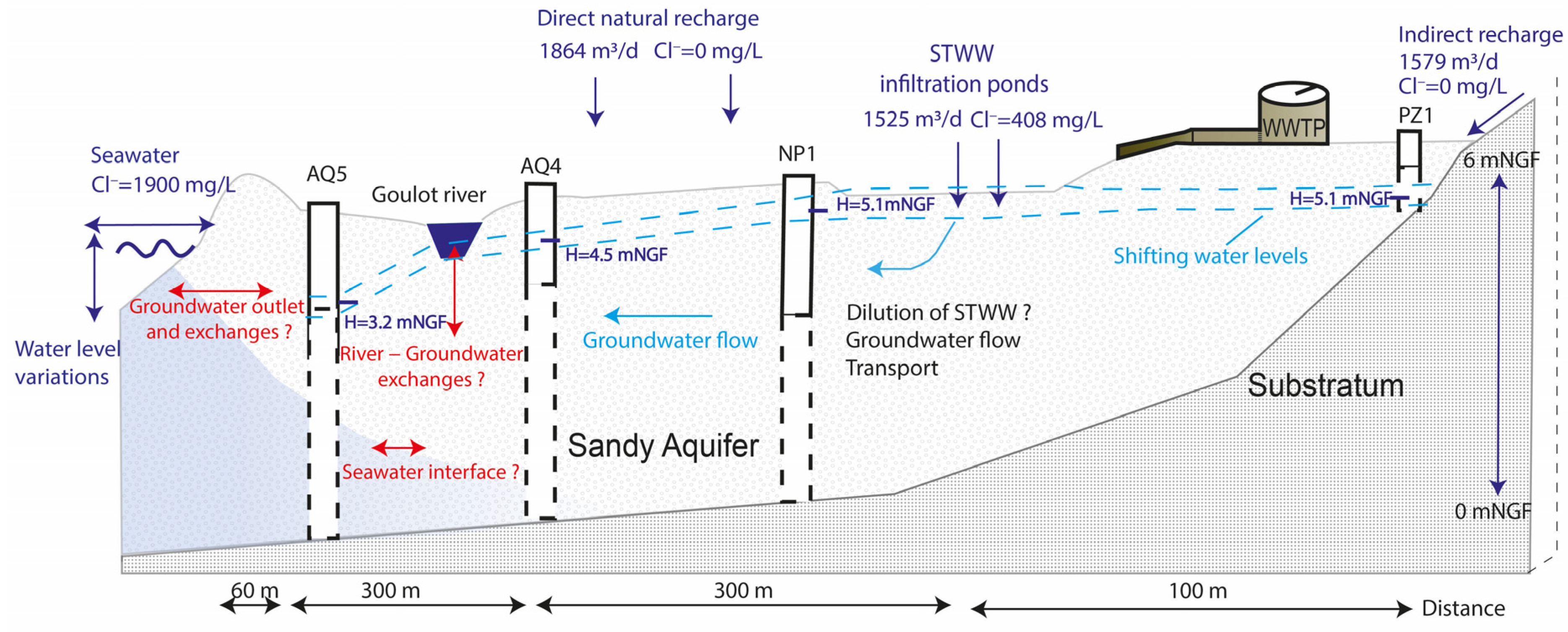
3.1. Conceptual Model: The Local SAT System in Its Hydrodynamic Aquifer Context
3.1.1. Coastal Sand Dune Aquifer
3.1.2. Natural Recharge and Runoff
3.1.3. Streams and Rivers
3.1.4. Sea and Harbour Effects
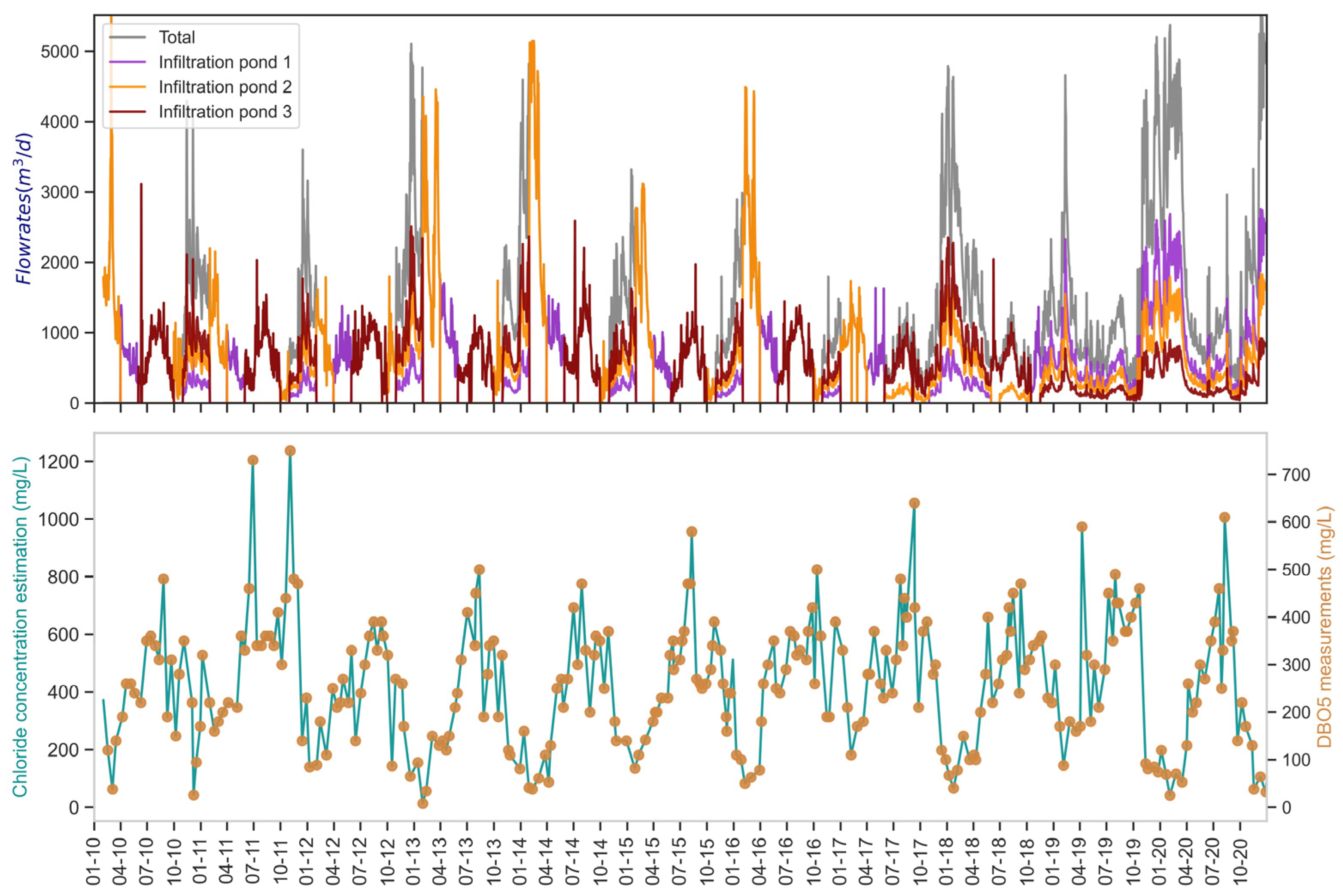
3.1.5. STWW Infiltrated in the SAT
- From April to May in pond 1;
- From June to September in pond 2;
- From October to March in pond 3.
3.1.6. Synthesis of the Conceptual Model
3.2. Flow and Solute Transport Equations
3.3. Numerical Modelling: The Local SAT System in Its Hydrodynamic Aquifer Context
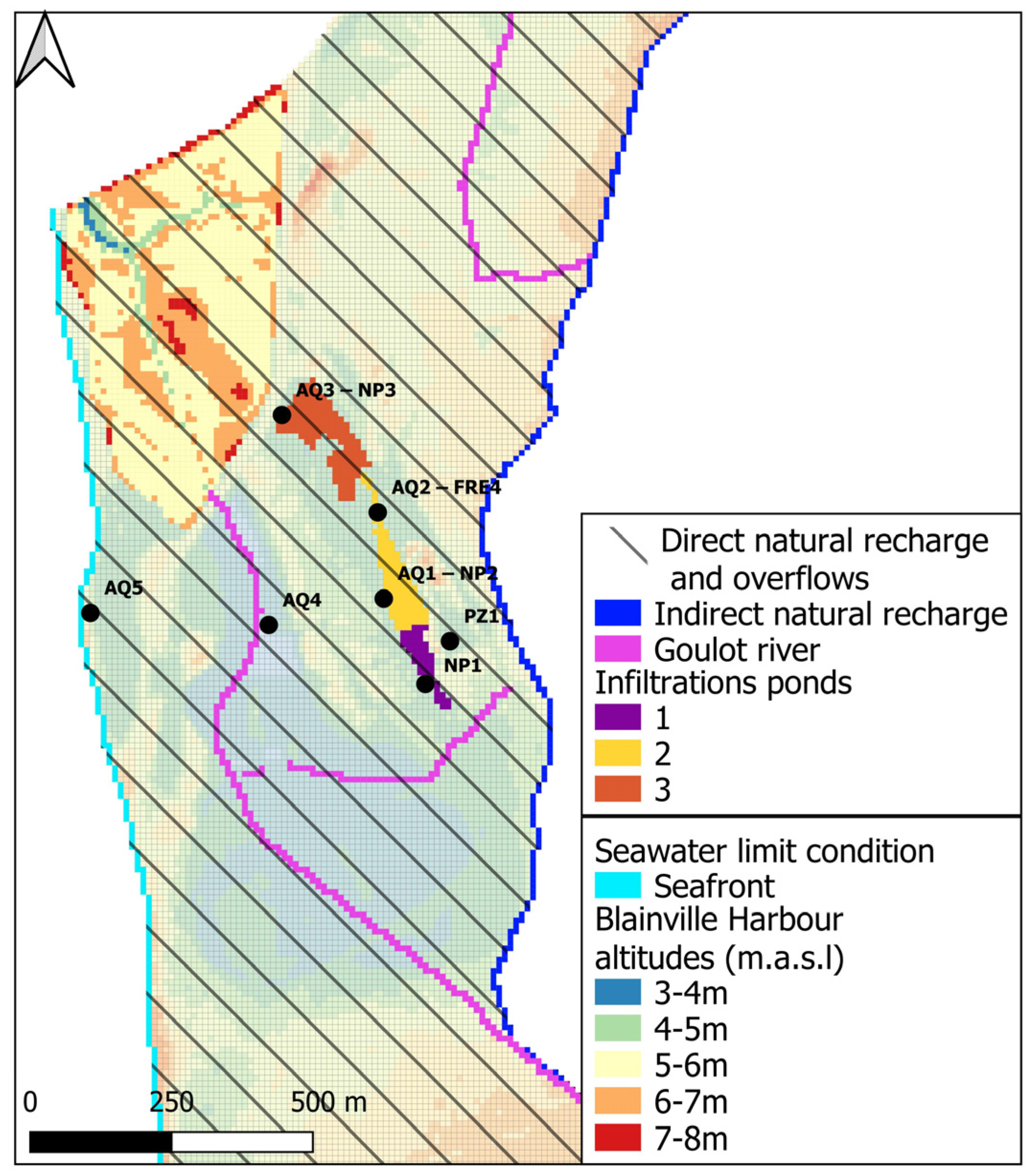
3.3.1. Geometry
3.3.2. Discretisation in Space and Time
3.3.3. Boundary Conditions
3.3.4. Initial Conditions
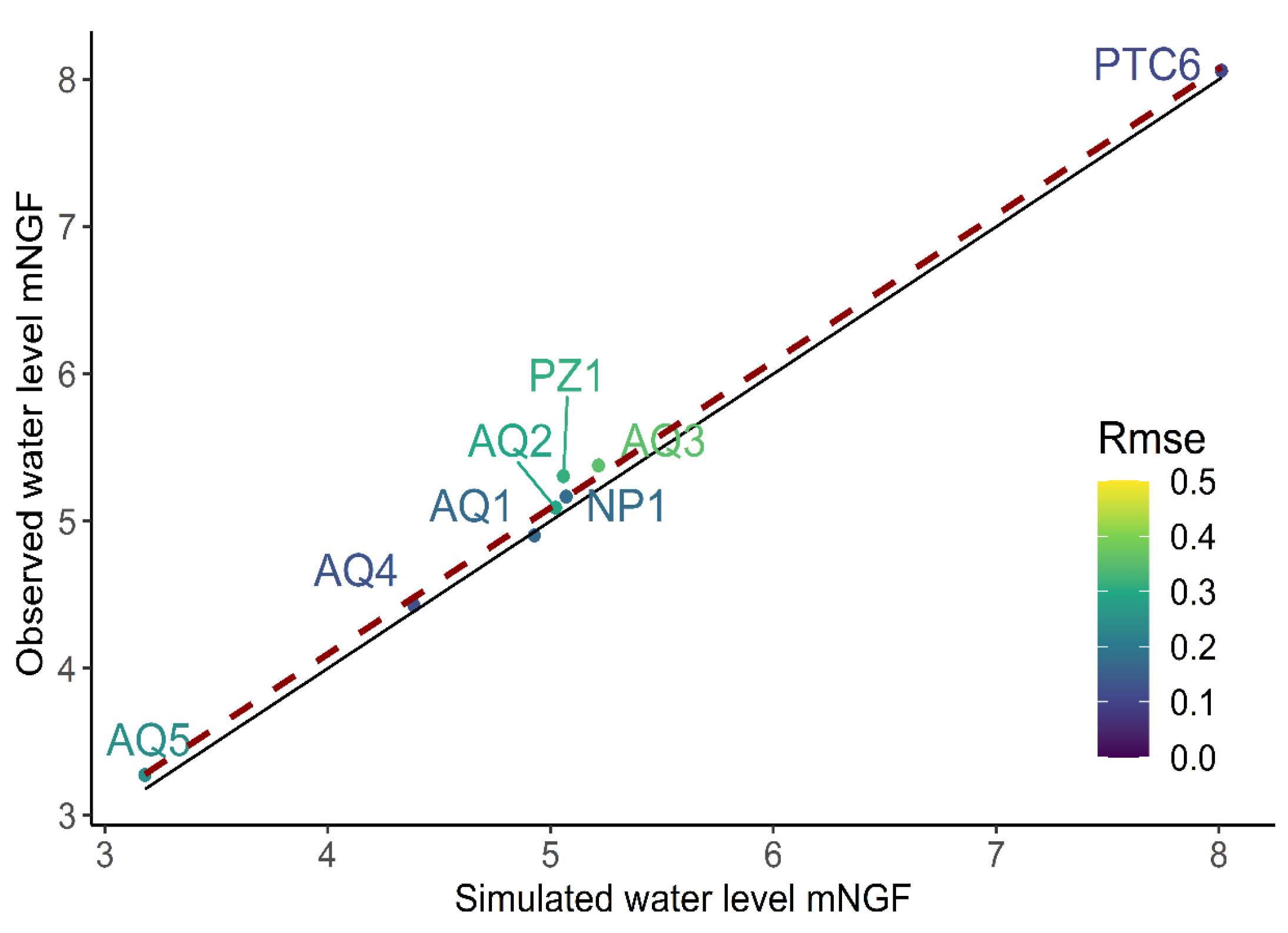
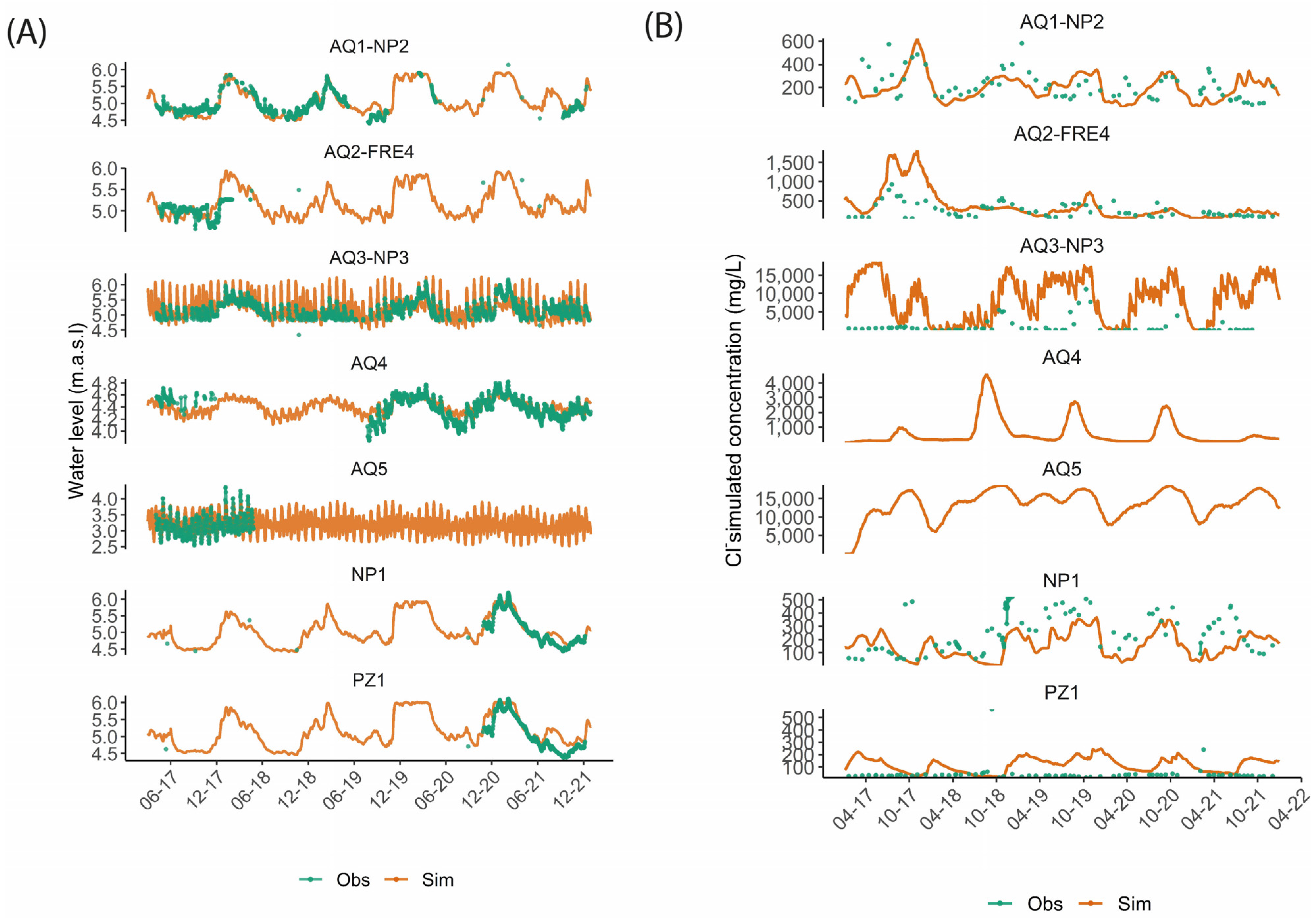
3.3.5. Model Calibration
3.3.6. Model Sensitivity
4. Results
4.1. Calibrated Hydrodynamic and Hydrodispersive Parameters
4.2. Hydrodynamic Balances in 2017–2021
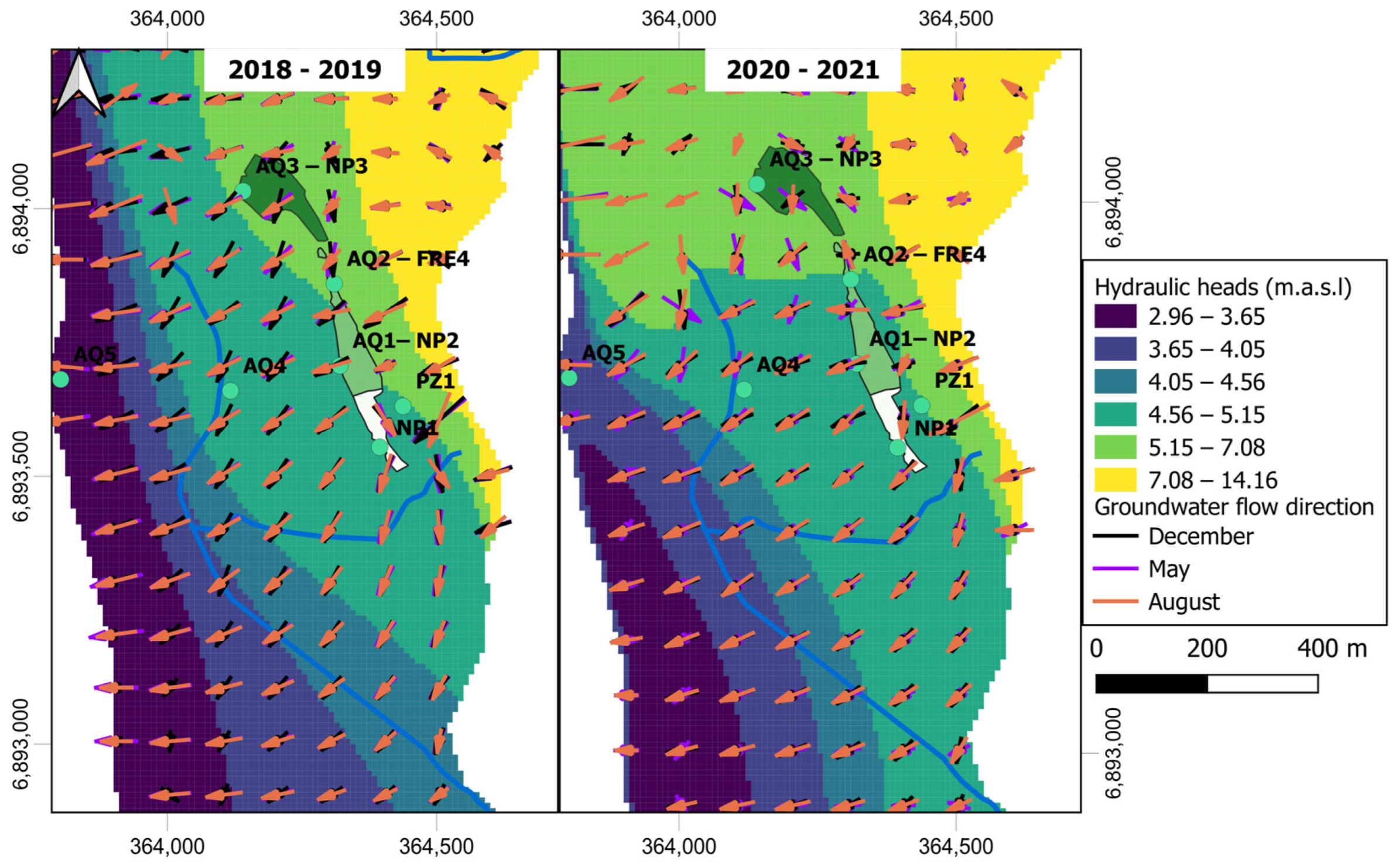
4.3. Calculated Piezometric Maps and Main Flow Lines
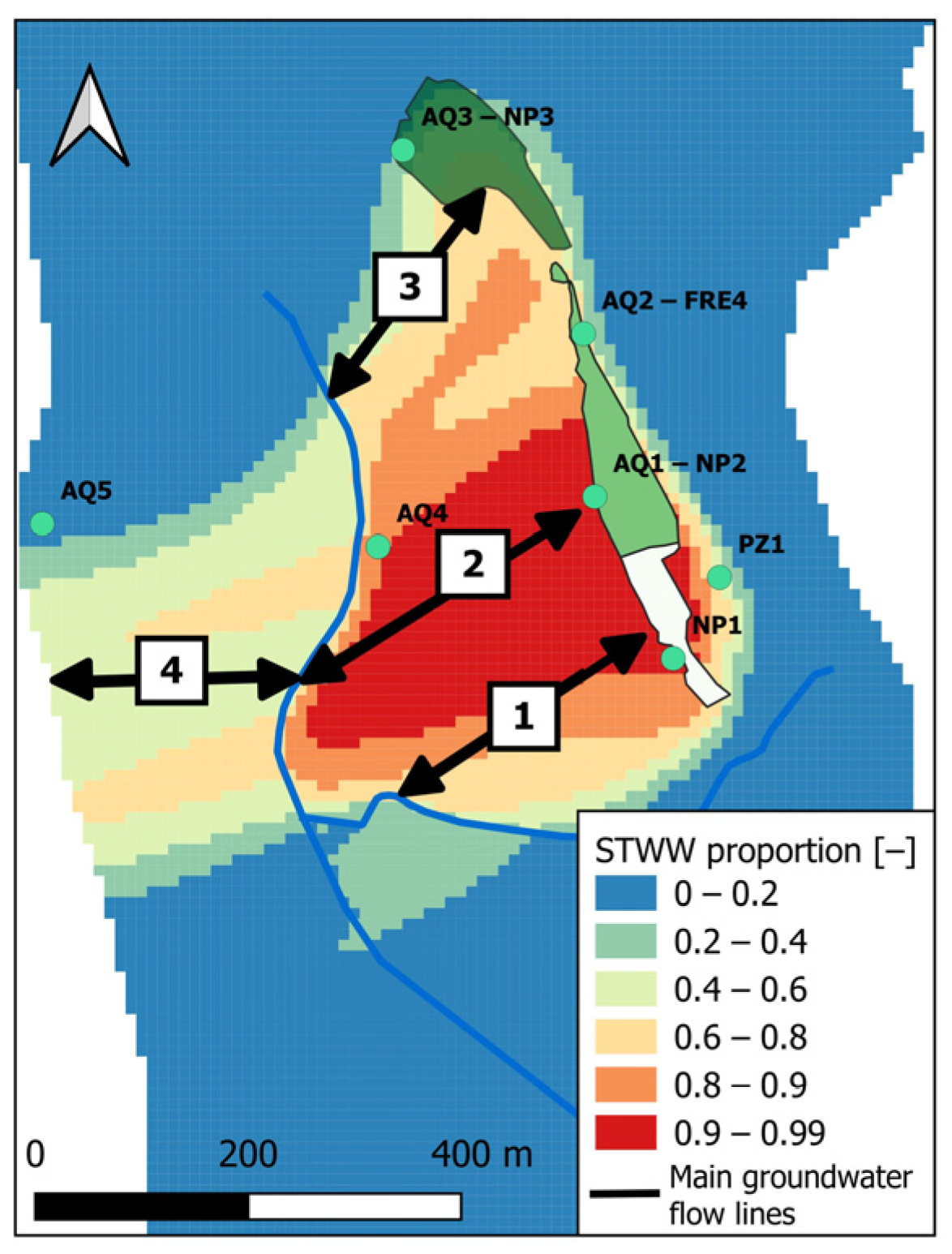
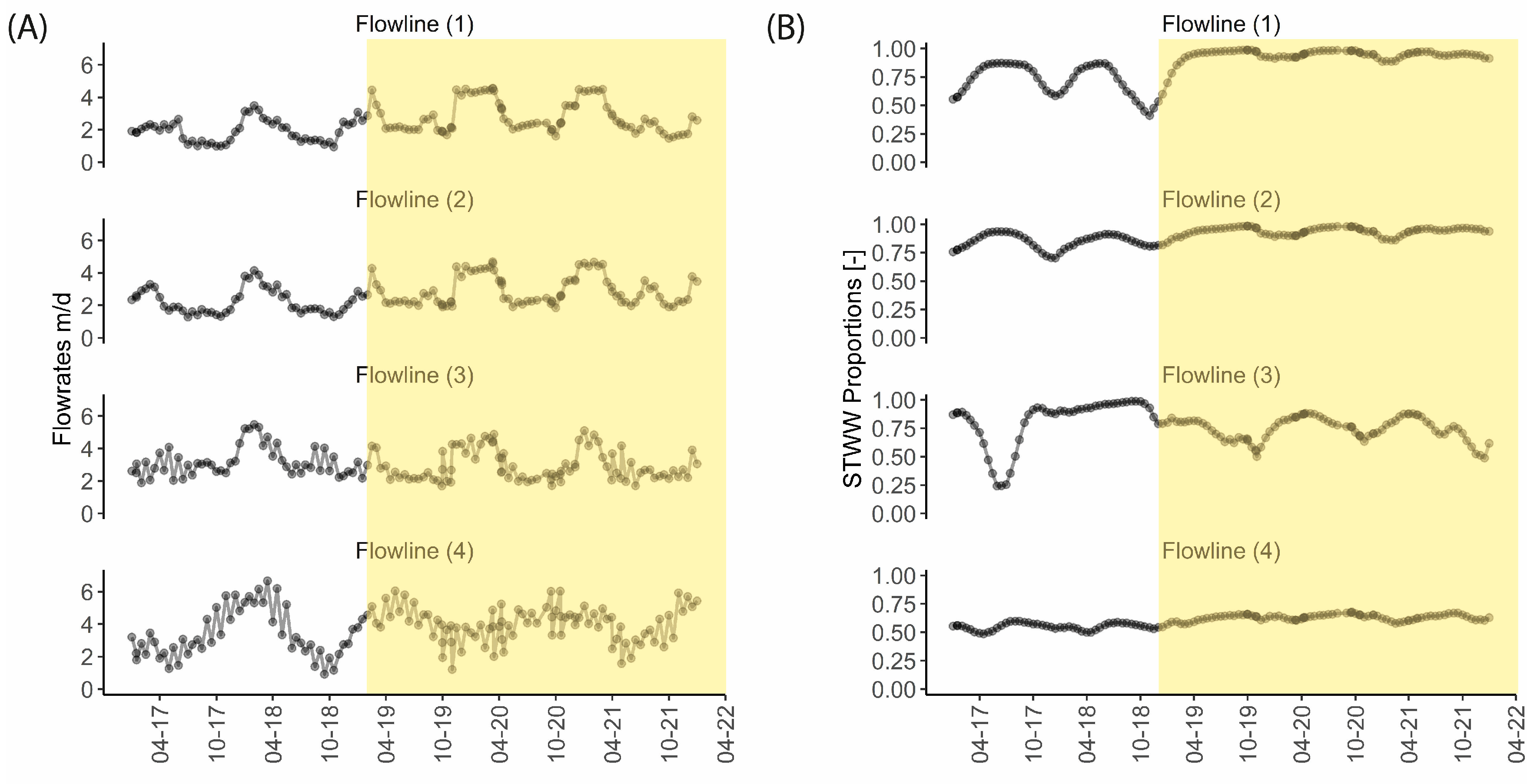
4.4. Spatialised Variations in Flow Velocities and Proportions of STWW
5. Discussion
5.1. Interactions between SAT and Surrounding Natural and Anthropic Dynamics
5.2. Effects of SAT Variations on the Fate of TrOCs at the Hydrosystem Scale
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dillon, P.; Fern, E.; Massmann, G. Managed Aquifer Recharge for Water Resilience. Water 2020, 12, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kennedy, M.D. Soil Aquifer Treatment for Wastewater Treatment and Reuse. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloppmann, W.; Aharoni, A.; Chikurel, H.; Dillon, P.; Gaus, I.; Guttman, J.; Kraitzer, T.; Kremer, S.; Masciopinto, C.; Pavelic, P.; et al. Use of Groundwater Models for Prediction and Optimisation of the Behaviour of MAR Sites. In Water Reclamation Technologies for Safe Managed Aquifer Recharge; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; Chapter 8; pp. 311–349. [Google Scholar]
- Masciopinto, C.; Carrieri, C. Assessment of Water Quality After 10 Years of Reclaimed Water Injection: The Nardò Fractured Aquifer (Southern Italy). Ground Water Monit. Remediat. 2002, 22, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shammas, M.I. The Effectiveness of Artificial Recharge in Combating Seawater Intrusion in Salalah Coastal Aquifer, Oman. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbohede, A.; Van Houtte, E.; Lebbe, L. Groundwater Flow in the Vicinity of Two Artificial Recharge Ponds in the Belgian Coastal Dunes. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, J.E.; Heberer, T.; Reddersen, K. Fate of Pharmaceuticals during Indirect Potable Reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 46, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of Drugs in German Sewage Treatment Plants and Rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, S.Y.; Lapworth, D.J.; Crane, E.J.; Grima-Olmedo, J.; Koroša, A.; Kuczynska; Mali, N.; Rosenqvist, L.; van Vliet, M.E.; Togola, A.; et al. Emerging Organic Compounds in European Groundwater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aemig, Q.; Hélias, A.; Patureau, D. Impact Assessment of a Large Panel of Organic and Inorganic Micropollutants Released by Wastewater Treatment Plants at the Scale of France. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.C.; de Souza, A.O.; Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Tasso, M.J.; Pereira, P.H.; Dorta, D.J. A Perspective on the Potential Risks of Emerging Contaminants to Human and Environmental Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 13800–13823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G.; Drewes, J. Soil Aquifer Treatment (SAT) as a Natural and Sustainable Wastewater Reclamation/Reuse Technology: Fate of Wastewater Effluent Organic Matter (EfOM) and Trace Organic Compounds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 129, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeng, S.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Abel, C.D.T.; Magic-Knezev, A.; Amy, G.L. Role of Biodegradation in the Removal of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds with Different Bulk Organic Matter Characteristics through Managed Aquifer Recharge: Batch and Column Studies. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4722–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greskowiak, J.; Hamann, E.; Burke, V.; Massmann, G. The Uncertainty of Biodegradation Rate Constants of Emerging Organic Compounds in Soil and Groundwater—A Compilation of Literature Values for 82 Substances. Water Res. 2017, 126, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheytt, T.J.; Mersmann, P.; Heberer, T. Mobility of Pharmaceuticals Carbamazepine, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, and Propyphenazone in Miscible-Displacement Experiments. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2006, 83, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheytt, T.; Mersmann, P.; Lindstädt, R.; Heberer, T. Determination of Sorption Coefficients of Pharmaceutically Active Substances Carbamazepine, Diclofenac, and Ibuprofen, in Sandy Sediments. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnery, J.; Lee, J.; Drumheller, Z.W.; Drewes, J.E.; Illangasekare, T.H.; Kitanidis, P.K.; McCray, J.E.; Smits, K.M. Trace Organic Chemical Attenuation during Managed Aquifer Recharge: Insights from a Variably Saturated 2D Tank Experiment. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picot-Colbeaux, G.; Mathurin, F.; Pettenati, M.; Nakache, F.; Guillemoto, Q.; Baïsset, M.; Devau, N.; Gosselin, M.; Allain, D.; Neyens, D.; et al. Sustainable Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR)—Soil Aquifer Treatment System to Protect Coastal Ecosystem in Agon-Coutainville (Normandy), France. In Exemplary case Studies of Sustainable and Economic Managed Aquifer Recharge; Zheng, Y., Ross, A., Villholth, K., Dillon, P., Eds.; UNESCO-IAH-GRIPP Publication: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pettenati, M.; Picot, G.; Thomas, L.; Aurouet, A.; Baïsset, M.; Appels, J.; Wünsch, R.; Hochstrat, R.; Aharoni, A.; Raanan, H.; et al. Combined Natural and Engineered Systems (CNES) for Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) & Soil Aquifer Treatment (SAT) System with Water Storage and Quality Improvement, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Managed Aquifer Recharge (ISMAR 10). In Managed Aquifer Recharge: Local Solutions to the Global Water Crisis. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Managed Aquifer Recharge (ISMAR 10); TRAGSA Group: Madrid, Spain, 2019; ISBN 13 978-84-09-15736-5. [Google Scholar]
- Guillemoto, Q.; Picot-Colbeaux, G.; Valdes, D.; Devau, N.; Mathurin, F.A.; Pettenati, M.; Kloppmann, W.; Mouchel, J.-M. Transfer of Trace Organic Compounds in an Operational Soil-Aquifer Treatment System Assessed through an Intrinsic Tracer Test and Transport Modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupret, L.; Poncet, J.; Lautribou, J.P.; Hommeril, P. Carte Géol. France (1/50000), Feuille COUTANCES (142)—Orléans: Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières, 58 p. Carte Géologique par DUPRET L., PONCET J., LAUTRIDOU J.P, HOMMERIL P. et coll. (1987); BRGM: Paris, France, 1987.
- Vernhet, Y. Carte Géologique Harmonisée du Département de la Manche; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2003; 228p.
- Garceran, R. Installation Report of Three Imageau “Subsurface Monitoring Device” (SMD) and Two Data Loggers in Agon-Coutainville, Littoral of Manche Department in France, Aquanes; imaGeau: Nîmes, France, 2017; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Refsgaard, J.C.; Henriksen, H.J. Modelling Guidelines––Terminology and Guiding Principles. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lithologic, Mise En Place de Trois Nouveaux Piézomètres de Contrôle Au Sein de La Roselière de La Station D’épuration d’Agon-Coutainville; Agon-Coutainville Municipalité: Agon-Coutainville, France, 2014; p. 33.
- de Marsily, G. Hydrogéologie Quantitative. 216 Pp., 11 P1. Paris, New York, Milan, Mexico, Rio de Janeiro: Masson. ISBN 2 225 75504 3 (Paperback). Geol. Mag. 1983, 120, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelo, C.A.J.; Postma, D. Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, 2nd ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-415-36421-8. [Google Scholar]
- Thiéry, D. Reservoir Models in Hydrogeology. In Mathematical Models Volume 2; Environmental Hydraulics Series; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 13; pp. 409–418. ISBN 978-1-84821-154-4. [Google Scholar]
- Seguin, J.-J. Méthodes d’évaluation de La Recharge Des Nappes; Rapport BRGM/RP-65635-FR; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2016.
- Millero, F.J.; Feistel, R.; Wright, D.G.; McDougall, T.J. The Composition of Standard Seawater and the Definition of the Reference-Composition Salinity Scale. Deep Sea Res. Part Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2008, 55, 50–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiéry, D. Hydrogeologic Models. In Mathematical Models Volume 2; Environmental Hydraulics Series; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Chapter 4; pp. 71–92. ISBN 978-1-84821-154-4. [Google Scholar]
- Thiéry, D.; Picot-Colbeaux, G.; Guillemoto, Q. Guidelines for MARTHE v7.8 Computer Code for Hydro-Systems Modelling (English Version); Rapport BRGM/RP-69660-FR; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2020.
- Thiéry, D. Software MARTHE, Release 4.3; Modelling of Aquifers with a Rectangular Grid in Transient State for Hydrodynamic Calculations of HEads and Flows; BRGM: Orléans, France, 1990.
- Thiéry, D. Code de Calcul CATHERINE—Principe et Mode d’Emploi. Rapport BRGM RP-61430-FR; Figure 16, Table 5; BRGM: Orléans, France, 2012; p. 41.
- Lyard, F.H.; Allain, D.J.; Cancet, M.; Carrère, L.; Picot, N. FES2014 Global Ocean Tide Atlas: Design and Performance. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelhar, L.W.; Welty, C.; Rehfeldt, K.R. A Critical Review of Data on Field-Scale Dispersion in Aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1955–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Makuch, D. Longitudinal Dispersivity Data and Implications for Scaling Behavior. Groundwater 2005, 43, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaj, M.; Javadi, A.A.; Akrami, M.; Ke, K.-Y.; Farmani, R.; Tan, Y.-C.; Chen, A.S. Modelling Seawater Intrusion in the Pingtung Coastal Aquifer in Taiwan, under the Influence of Sea-Level Rise and Changing Abstraction Regime. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.T.; Fenstemaker, T.R.; Sharp, J.M. Variable-Density Groundwater Flow and Solute Transport in Heterogeneous Porous Media: Approaches, Resolutions and Future Challenges. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2001, 52, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, J.; Cheng, A.; Sorek, S.; Ouazar, D.; Herrera, I. Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers: Concepts, Methods, and Practices; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999; ISBN 978-90-481-5172-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, J.E.; Heberer, T.; Rauch, T.; Reddersen, K. Fate of Pharmaceuticals During Ground Water Recharge. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2003, 23, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regnery, J.; Wing, A.D.; Alidina, M.; Drewes, J.E. Biotransformation of Trace Organic Chemicals during Groundwater Recharge: How Useful Are First-Order Rate Constants? J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 179, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntau, M.; Schulz, M.; Jewell, K.S.; Hermes, N.; Hübner, U.; Ternes, T.; Drewes, J.E. Evaluation of the Short-Term Fate and Transport of Chemicals of Emerging Concern during Soil-Aquifer Treatment Using Select Transformation Products as Intrinsic Redox-Sensitive Tracers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crampon, M.; Soulier, C.; Sidoli, P.; Hellal, J.; Joulian, C.; Charron, M.; Guillemoto, Q.; Picot-Colbeaux, G.; Pettenati, M. Dynamics of Soil Microbial Communities During Diazepam and Oxazepam Biodegradation in Soil Flooded by Water From a WWTP. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 742000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alidina, M.; Li, D.; Ouf, M.; Drewes, J.E. Role of Primary Substrate Composition and Concentration on Attenuation of Trace Organic Chemicals in Managed Aquifer Recharge Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe-Jones, C.; Dickenson, E.R.V.; Drewes, J.E. The Role of Microbial Adaptation and Biodegradable Dissolved Organic Carbon on the Attenuation of Trace Organic Chemicals during Groundwater Recharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 437, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch-Williams, T.; Hoppe-Jones, C.; Drewes, J.E. The Role of Organic Matter in the Removal of Emerging Trace Organic Chemicals during Managed Aquifer Recharge. Water Res. 2009, 44, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, V.; Greskowiak, J.; Asmuß, T.; Bremermann, R.; Taute, T.; Massmann, G. Temperature Dependent Redox Zonation and Attenuation of Wastewater-Derived Organic Micropollutants in the Hyporheic Zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzler, A.F.; Greskowiak, J.; Massmann, G. Seasonality of Temperatures and Redox Zonations during Bank Filtration—A Modeling Approach. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greskowiak, J.; Prommer, H.; Vanderzalm, J.; Pavelic, P.; Dillon, P. Modeling of Carbon Cycling and Biogeochemical Changes during Injection and Recovery of Reclaimed Water at Bolivar, South Australia: Modeling Carbon Cycling. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greskowiak, J.; Prommer, H.; Massmann, G.; Nützmann, G. Modeling Seasonal Redox Dynamics and the Corresponding Fate of the Pharmaceutical Residue Phenazone During Artificial Recharge of Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6615–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefetz, B.; Mualem, T.; Ben-Ari, J. Sorption and Mobility of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Soil Irrigated with Reclaimed Wastewater. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, M.; Kröger, K.F.; Nödler, K.; Ayora, C.; Carrera, J.; Hernández, M.; Licha, T. Influence of a Compost Layer on the Attenuation of 28 Selected Organic Micropollutants under Realistic Soil Aquifer Treatment Conditions: Insights from a Large Scale Column Experiment. Water Res. 2015, 74, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Peng, P.; Yu, Z.; Fu, J. Effects of Organic Matter Heterogeneity on Sorption and Desorption of Organic Contaminants by Soils and Sediments. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 955–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, B.V.; Dickenson, E.R.V.; Johnson, T.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Drewes, J.E. Attenuation of Contaminants of Emerging Concern during Surface-Spreading Aquifer Recharge. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maoz, A.; Chefetz, B. Sorption of the Pharmaceuticals Carbamazepine and Naproxen to Dissolved Organic Matter: Role of Structural Fractions. Water Res. 2010, 44, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benotti, M.J.; Brownawell, B.J. Microbial Degradation of Pharmaceuticals in Estuarine and Coastal Seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuyfzand, P.J. Hydrogeochemical Processes During Riverbank Filtration and Artificial Recharge of Polluted Surface Waters: Zonation, Identification, and Quantification. In Riverbank Filtration for Water Security in Desert Countries; Shamrukh, M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 97–128. ISBN 978-94-007-0026-0. [Google Scholar]
- Henzler, A.F.; Greskowiak, J.; Massmann, G. Modeling the Fate of Organic Micropollutants during River Bank Filtration (Berlin, Germany). J. Contam. Hydrol. 2014, 156, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Prat, A.; Greskowiak, J.; Burke, V.; Rivera Villarreyes, C.A.; Krause, J.; Monninkhoff, B.; Sperlich, A.; Schimmelpfennig, S.; Duennbier, U.; Massmann, G. A Model-Based Analysis of the Reactive Transport Behaviour of 37 Trace Organic Compounds during Field-Scale Bank Filtration. Water Res. 2020, 173, 115523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, M.; Licha, T. A Framework for Assessing the Retardation of Organic Molecules in Groundwater: Implications of the Species Distribution for the Sorption-Influenced Transport. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nham, H.T.T.; Greskowiak, J.; Nödler, K.; Rahman, M.A.; Spachos, T.; Rusteberg, B.; Massmann, G.; Sauter, M.; Licha, T. Modeling the Transport Behavior of 16 Emerging Organic Contaminants during Soil Aquifer Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Data | Location | Measurements and Frequencies | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| Groundwater level | AQ1-NP2, AQ2-FRE4, AQ3-NP3, AQ4, AQ5, | Probes 15 min, 2017–2022 * | Projects AQUANES (April 2017 to April 2019) + EVIBAN (April 2019 to December 2022) |
| NP1, AQ1-NP2, AQ2-FRE4, AQ3-NP3, AQ4, AQ5, PZ1 **, PTC6 ** | 9 Manual measurements from 2017 to 2021 | Projects AQUANES (6 from April 2017 to April 2019) + EVIBAN (3 from April 2019 to December 2022) | |
| NP1, PZ1 | Probes 15 min, 2020–2022 | EVIBAN project | |
| GW analysis of Cl− | NP1, AQ1-NP2, AQ2-FRE4, AQ3-NP3, PZ1 | 12–14 per year | SAUR operator |
| NP1, AQ1-NP2, AQ2-FRE4, AQ3-NP3, PZ1 | 9 field campaigns from 2016 to 2021 | Projects AQUANES (6 from April 2017 to April 2019) + EVIBAN (3 from April 2019 to December 2022) | |
| STWW analysis of DBO5 | WWTP outlet | 24 per year | SAUR operator (2006 to 2022) |
| STWW Flow | WWTP outlet | Radar venturi channel, hourly | SAUR operator (2010–2022) |
| Meteorology | Gouville | Precipitation and PET, daily | METEO-FRANCE |
| Geology | Normandie | Maps—cross-section | [21,22] |
| NP1, AQ1-NP2, AQ2-FRE4, AQ3-NP3, AQ4, AQ5, PZ1, (PTC6) | logs | SAUR Operator | |
| Topography | Normandy Agon-Coutainville | Normalised to elevation (asl) 25 m Normalised to elevation (asl) 1 m | Region Region |
| Rivers | France | Map—streams—network | BDTOPO® (IGN, France) |
| Name Length (m) | Flowline 1 265 | Flowline 2 325 | Flowline 3 250 | Flowline 3 190 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Velocity (m/d) | ||||
| Mean | 2.48 | 2.67 | 3.03 | 3.77 |
| Min | 0.94 | 1.28 | 1.69 | 0.92 |
| Max | 4.55 | 4.69 | 5.48 | 6.67 |
| Residence time (d) | ||||
| Mean | 107 | 122 | 82 | 50 |
| Min | 58 | 69 | 46 | 28 |
| Max | 282 | 254 | 148 | 207 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guillemoto, Q.; Picot-Colbeaux, G.; Valdes, D.; Devau, N.; Thierion, C.; Idier, D.; Mathurin, F.A.; Pettenati, M.; Mouchel, J.-M.; Kloppmann, W. Multi-Annual Dynamics of a Coastal Groundwater System with Soil-Aquifer Treatment and Its Impact on the Fate of Trace Organic Compounds. Water 2023, 15, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050934
Guillemoto Q, Picot-Colbeaux G, Valdes D, Devau N, Thierion C, Idier D, Mathurin FA, Pettenati M, Mouchel J-M, Kloppmann W. Multi-Annual Dynamics of a Coastal Groundwater System with Soil-Aquifer Treatment and Its Impact on the Fate of Trace Organic Compounds. Water. 2023; 15(5):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050934
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuillemoto, Quentin, Géraldine Picot-Colbeaux, Danièle Valdes, Nicolas Devau, Charlotte Thierion, Déborah Idier, Frédéric A. Mathurin, Marie Pettenati, Jean-Marie Mouchel, and Wolfram Kloppmann. 2023. "Multi-Annual Dynamics of a Coastal Groundwater System with Soil-Aquifer Treatment and Its Impact on the Fate of Trace Organic Compounds" Water 15, no. 5: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050934
APA StyleGuillemoto, Q., Picot-Colbeaux, G., Valdes, D., Devau, N., Thierion, C., Idier, D., Mathurin, F. A., Pettenati, M., Mouchel, J.-M., & Kloppmann, W. (2023). Multi-Annual Dynamics of a Coastal Groundwater System with Soil-Aquifer Treatment and Its Impact on the Fate of Trace Organic Compounds. Water, 15(5), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15050934










