Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Propagation of Meteoro-Hydrological Drought in Yalong River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
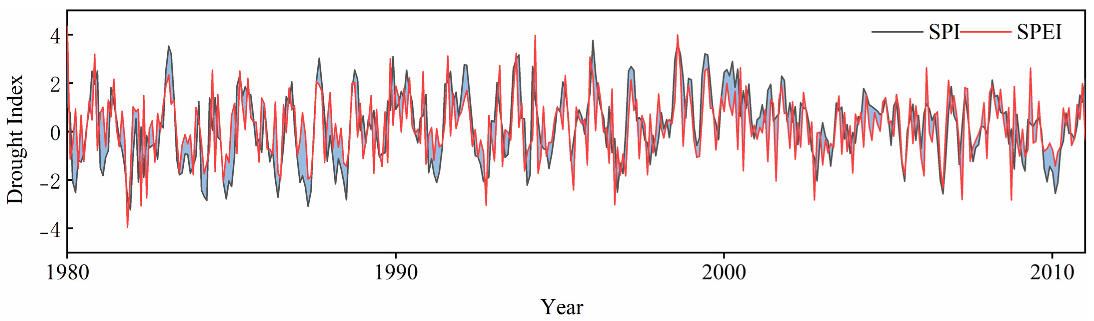
2.3.1. Drought Index
2.3.2. Indexes for Drought Evaluation
- (1)
- Calculate the SPEI on the time scale of 1–12 months (SPEI1, SPEI2, …, SPEI12);
- (2)
- Calculate the 1-month time scale SRI (SRI1);
- (3)
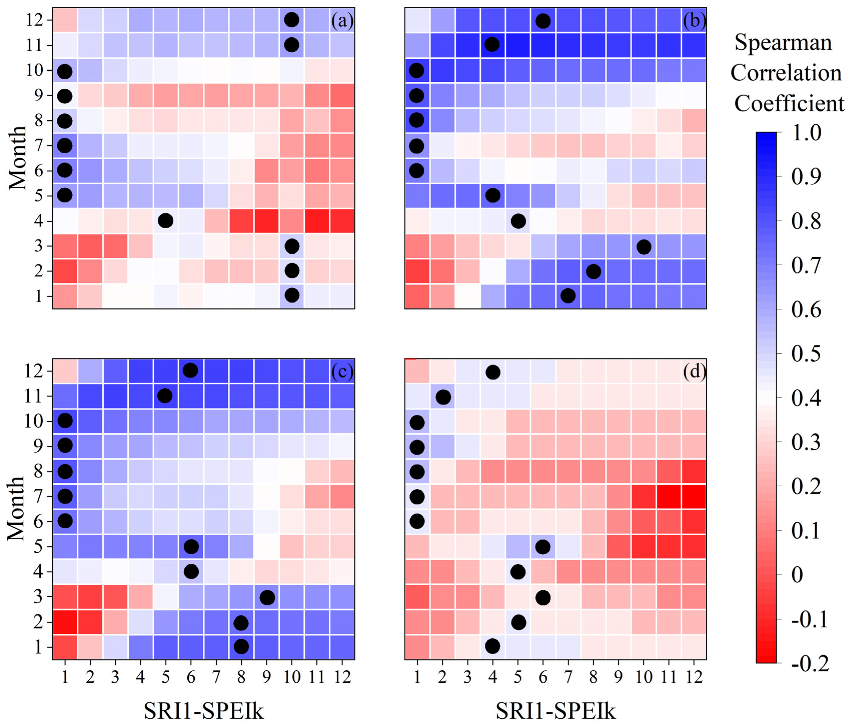
- Use the Spearman correlation test to analyze SPEI1, SPEI2, …, SPEI12, and SRI1;
- (4)
- Among the obtained correlation coefficients, the SPEIk-SRI1 sequence with the best correlation coefficient is further selected to analyze the propagation time of meteorological drought to hydrological drought, and 13 groups of lag time are set, which are 0, 1, 2, 3, …, 12 months. The results will show that the correlation coefficient is the highest when the lag time is n months, and the lag time is the drought propagation time of the basin.
3. Results and Discussion
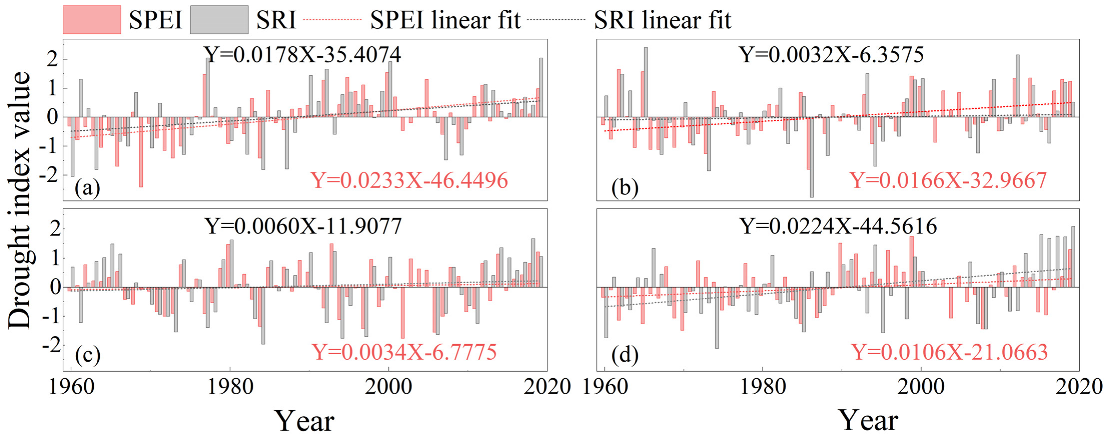
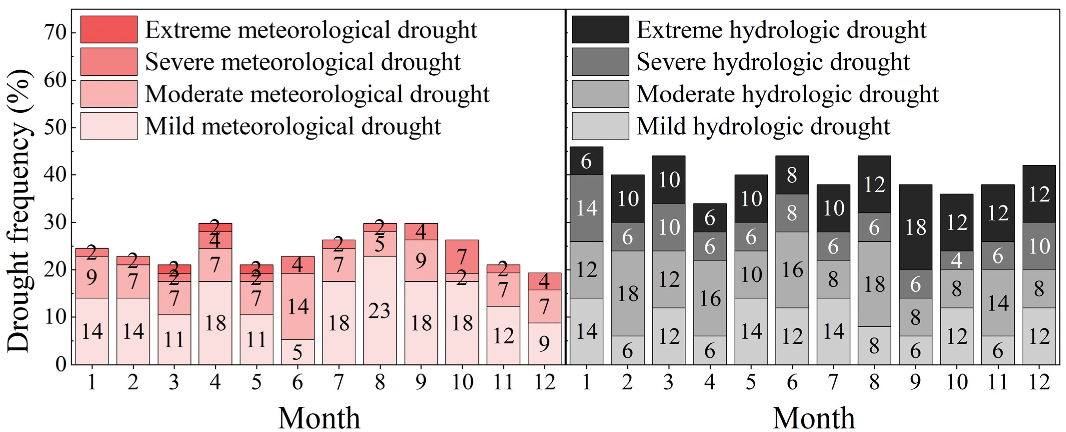
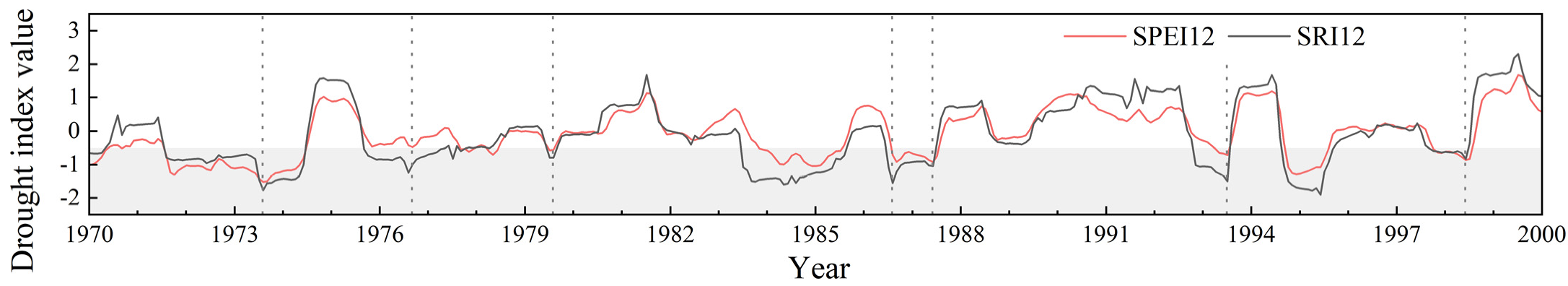
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Drought at Different Time Scales
3.1.1. The Annual Scale
3.1.2. The Seasonal Scale
3.1.3. The Monthly Scale
3.2. Analysis of Drought Propagation Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Meteorological Drought Index
4.2. The Impact of Drought Transmission in the Watershed on Hydropower Generation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Obasi, P.G. WMO’s Role in the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1994, 9, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Glantz, M.H. Understanding the drought phenomenon: The Role of Definitions. Water Int. 1985, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, F. Combination of multi-sensor remote sensing data for drought monitoring over Southwest China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 35, 270–283. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.B.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H.M.; Zhou, J.Z. Risk propagation from meteorological to hydrological droughts in achanging climate for main catchments in China. Adv. Water Sci. 2021, 32, 321–333. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.F.; Chen, X.W.; Love, C.A.; Yao, H.X.; Chen, H.X.; AghaKouchak, A. Determination of water required to recover from hydrological drought: Perspective from drought propagation and non-standardized indices. J. Hydrol. 2021, 590, 125227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltahir, E.A.B.; Yeh, P.J.F. On the asymmetric response of aquifer water level to floods and droughts in Illinois. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 4, 1199–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhou, T. Understanding and seasonal forecasting of hydrological drought in the Anthropocene. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 21, 5477–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alena, G.; Pedro, L.B.C.; Vinicius, B.P.C.; AghaKouchak, A. Spatial and temporal patterns of propagation from meteorological to hydrological droughts in Brazil. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126902. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.Q.; Huang, Q.; Guan, T.S.; Lu, J.; Zhou, H.C. Impact of climate change on the spatio-temporal characteristics of meteorological and hydrological drought over the Lancang-Mekong River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2021, 32, 508–519. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.L.; Zhu, S.N.; Liu, L.N.; Wan, Y.F.; Huang, Y.P. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Drought and Its Relationship with ENSO in Poyang Lake Basin Based on SPEI from 1958 to 2018. China Rural Water Hydropower 2020, 450, 116–123+128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F.H.; Hao, Z.C. Characteristics and risk analysis of drought propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought in Luanhe River Basin. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2022, 53, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.F.; He, P.F.; He, Y.C.; Han, X.Y.; Zeng, T.S.; Lu, G.B.; Wang, H.J. Investigation to the relation between meteorological drought and hydrological drought in the upper Shaying River Basin using wavelet analysis. Atmos. Res. 2019, 234, 104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Tang, H.; Qu, S.M.; Wen, T.; Zhao, L.L.; Li, Q.F. Propagation from meteorological drought to hydrological drought in Southwest China. Water Resour. Prot. 2023, 39, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.F.; Chen, X.H.; Yao, H.X.; Zhang, D.J. Multi-timescale assessment of propagation thresholds from meteorological to hydrological drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.L.; Zhu, X.F.; Pan, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Liu, X.F. Drought evaluation using the GRACE terrestrial water storage deficit over the Yangtze River Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Characteristics and trends in various forms of the Palmer Drought Severity Index during 1900–2008. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2011, 116, 0148–0227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mckee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.F. Impacts of Different Socioeconomic Development Levels on Extremely Wet/Dry Events in Mainland China. Water 2022, 14, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupesh, D. Is tree ring chronology of blue pine (Pinus wallichiana A. B. Jackson) prospective for summer drought reconstruction in the Western Himalaya? J. Asian Earth Sci. 2022, 229, 105142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndayiragije, J.M. Assessment of Two Drought Indices to Quantify and Characterize Drought Incidents. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lyu, A.; Wu, J.J. Impact of meteorological drought on streamflow drought in Jinghe River basinof China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Z.; Li, P.; Huang, Q. The propagation from meteorological to hydrological drought and its potential influence factors. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.F.; Chen, X.W.; Gao, L. Response of hydrological drought to meteorological drought and its critical conditions. Catastrophology 2017, 32, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C. Hydrological drought response to meteorological drought in the Iberian Peninsula. Clim. Res. 2013, 58, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; Liu, J.; Li, S.J. Attribution analysis of runoff variation in the upper-middle reaches of Yalong River. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K. Study on Climate Extreme Change and Runoff Response of Yalong River Basin under the Background of Climate Change; China Three Gorges University: Yichang, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Administration. Grades of Meteorological Drought. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=D2281945A96E8185F67EDC9E7A698049 (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.R.; Lu, F.; Xie, Z.B.; Zhu, K.; Song, X.Y. Characteristics and responses of hydrological and meteorological drought in Chaobai River Basin. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2019, 37, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.M.; Lyu, A.F.; Zhang, W.X. Response of hydrologic drought to meteorological drought in the Bayin River basin. South-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 459–467. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y. Detection and Attribution of Autumn Drought in China Based on SPI and SPEI; Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology: Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Mu, Z.X.; Zhou, Y.L. Applicability analysis of different hydrological drought indices in the western mountainous areas of the Tianshan Mountains. Water Resour. Power 2020, 38, 16–19,82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.P.; Lu, T.S.; Liu, M.C. Hydrological drought characteristics of the Shiyang River Basin based on standardized flow index (SDI). Chin. Desert 2020, 40, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Van, L.; Wanders, N.; Tallaksen, L.M. Hydrological drought across the world: Impact of climate and physical catchment structure. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1715–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.W.; Miao, C.Y.; Zheng, H. Meteorological and hydrological drought on the Loess Plateau, China: Evolutionary characteristics, impact, and propagation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 11569–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.S.; Tao, Y.Y. Research on the impact of human activities on the formation and development of hydrological droughts. Hydrology 2020, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Wang, H.M. Analysis of the characteristics and influencing factors of hydrological drought evolution in the Xilin River Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 178–184,192. [Google Scholar]



| Category | Wet | No Drought | Mild Drought | Moderate Drought | Severe Drought | Exceptional Drought |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPEI | (0.5, +∞) | (−0.5, 0.5] | (−1.0, −0.5] | (−1.5, −1.0] | (−2.0, −1.5] | (−∞, −2.0] |
| Basin | Meteorological Drought Frequency/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drought | Mild Drought | Moderate Drought | Severe Drought | Exceptional Drought | |
| GZB | 35.0 | 23.3 | 8.3 | 3.3 | 0.0 |
| DFB | 33.3 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| YJB | 31.7 | 21.7 | 8.3 | 1.7 | 0.0 |
| LNB | 28.3 | 18.3 | 10.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Basin | Hydrological DroughtFrequency/% | ||||
| Drought | Mild Drought | Moderate Drought | Severe Drought | Exceptional Drought | |
| GZB | 31.8 | 11.4 | 13.6 | 6.8 | 0.0 |
| DFB | 29.1 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 5.5 | 1.8 |
| YJB | 34.0 | 13.2 | 15.1 | 3.8 | 1.9 |
| LNB | 39.6 | 20.8 | 12.5 | 6.3 | 0.0 |
| Basin | SPEI and SRI at Different Time Scales | Number of Months Lagged | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| GZB | 0.494 ** | 0.610 ** | 0.698 ** | 0.740 ** | 0.756 ** | 0.756 ** | 0.727 ** | 0.662 ** | 0.576 ** |
| DFB | 0.401 ** | 0.490 ** | 0.569 ** | 0.575 ** | 0.569 ** | 0.569 ** | 0.565 ** | 0.530 ** | 0.474 ** |
| YJB | 0.488 ** | 0.613 ** | 0.780 ** | 0.834 ** | 0.837 ** | 0.837 ** | 0.819 ** | 0.755 ** | 0.665 ** |
| LNB | 0.474 ** | 0.589 ** | 0.749 ** | 0.808 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.818 ** | 0.761 ** | 0.672 ** |
| Basin | Number of Months Lagged | ||||||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| GZB | 0.489 ** | 0.406 ** | 0.323 ** | 0.243 ** | 0.163 ** | 0.08 | −0.003 | −0.081 | −0.144 ** |
| DFB | 0.419 ** | 0.368 ** | 0.320 ** | 0.275 ** | 0.230 ** | 0.183 ** | 0.133 ** | 0.089 * | 0.06 |
| YJB | 0.575 ** | 0.491 ** | 0.408 ** | 0.327 ** | 0.246 ** | 0.165 ** | 0.089 * | 0.017 | −0.044 |
| LNB | 0.581 ** | 0.492 ** | 0.405 ** | 0.320 ** | 0.235 ** | 0.153 ** | 0.077 | 0.009 | −0.048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, K.; Xu, Y.; Lu, F.; Sun, X.; Gao, M.; Han, X.; Li, D.; Jiang, M. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Propagation of Meteoro-Hydrological Drought in Yalong River Basin. Water 2023, 15, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061025
Zhu K, Xu Y, Lu F, Sun X, Gao M, Han X, Li D, Jiang M. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Propagation of Meteoro-Hydrological Drought in Yalong River Basin. Water. 2023; 15(6):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061025
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Kui, Yang Xu, Fan Lu, Xueying Sun, Mingxing Gao, Xuhang Han, Dongsheng Li, and Ming Jiang. 2023. "Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Propagation of Meteoro-Hydrological Drought in Yalong River Basin" Water 15, no. 6: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061025
APA StyleZhu, K., Xu, Y., Lu, F., Sun, X., Gao, M., Han, X., Li, D., & Jiang, M. (2023). Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Propagation of Meteoro-Hydrological Drought in Yalong River Basin. Water, 15(6), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061025






