Evaluation of Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios in the Buenaventura Bay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
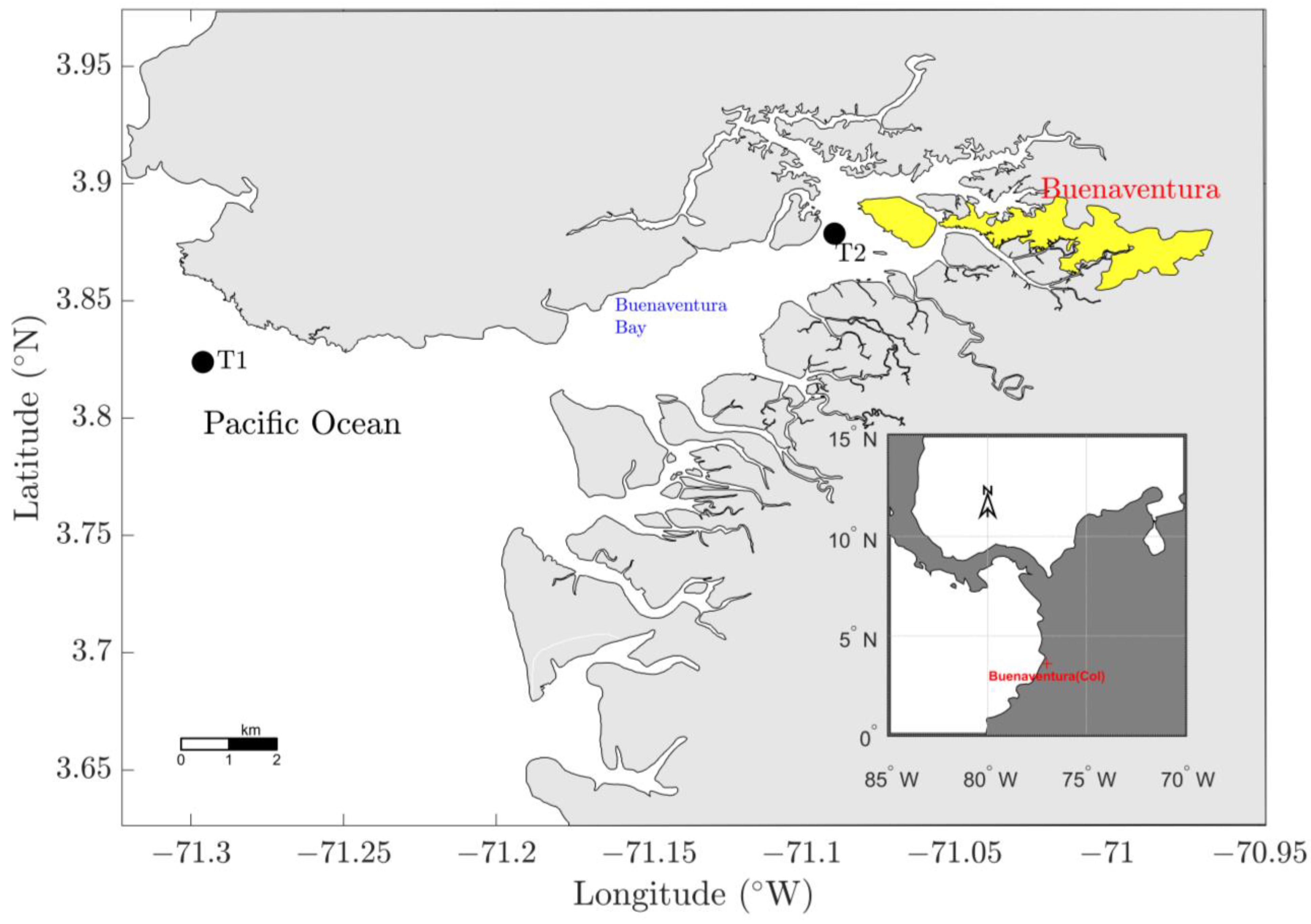
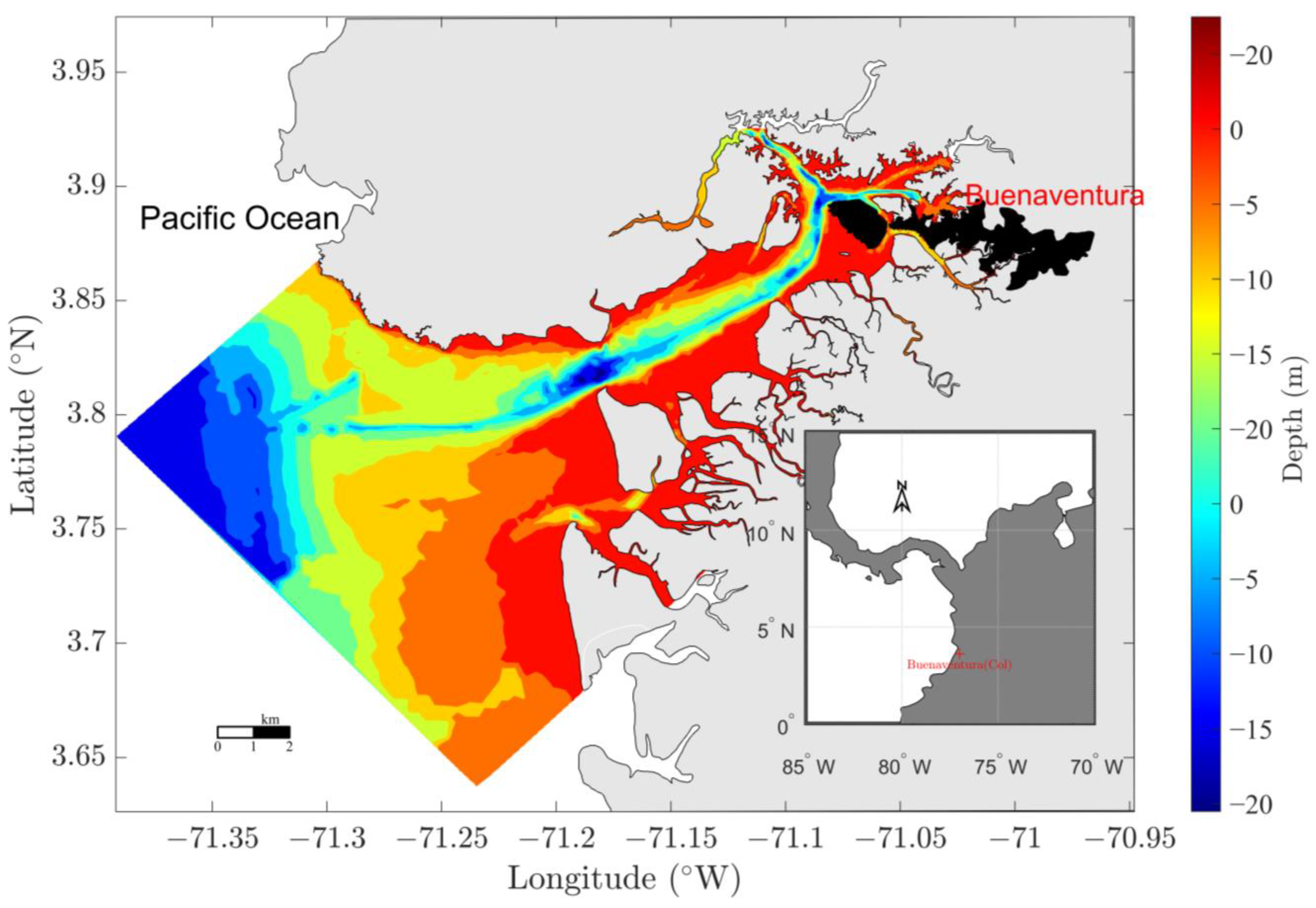
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Wastewater Characterization
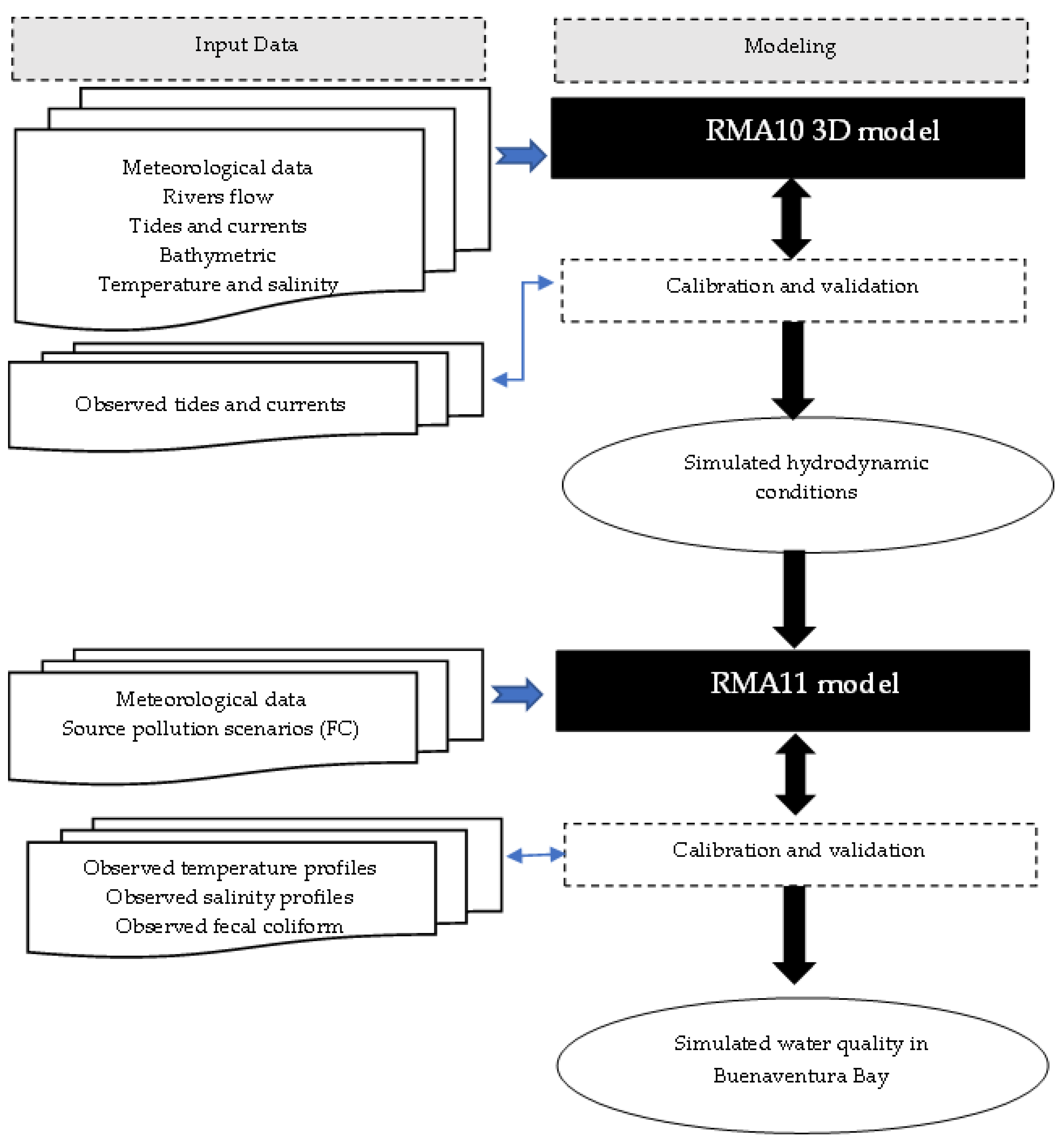
2.3. Hydrodynamic and Water Quality Models Description
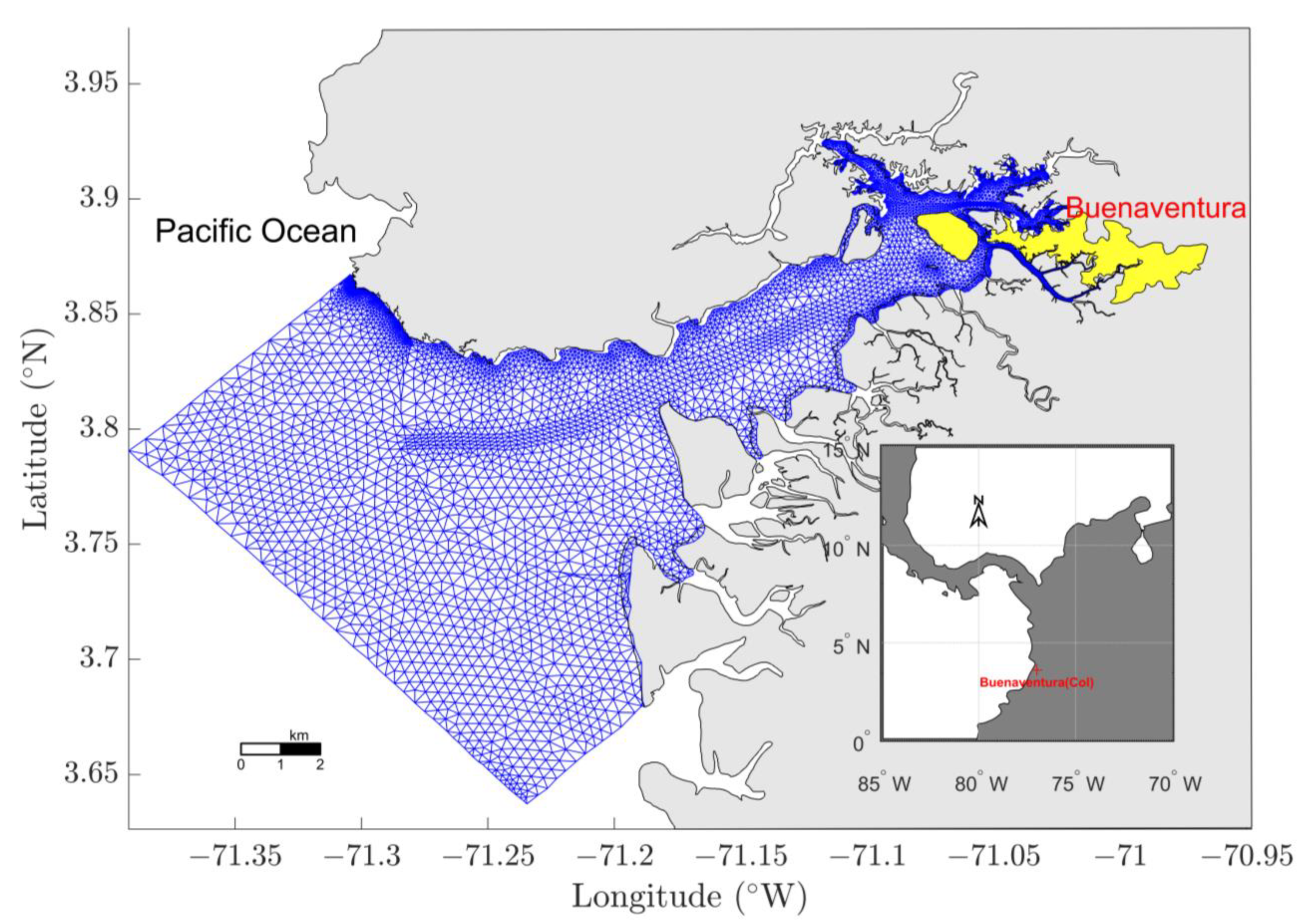
2.4. Model Set up for Buenaventura Bay
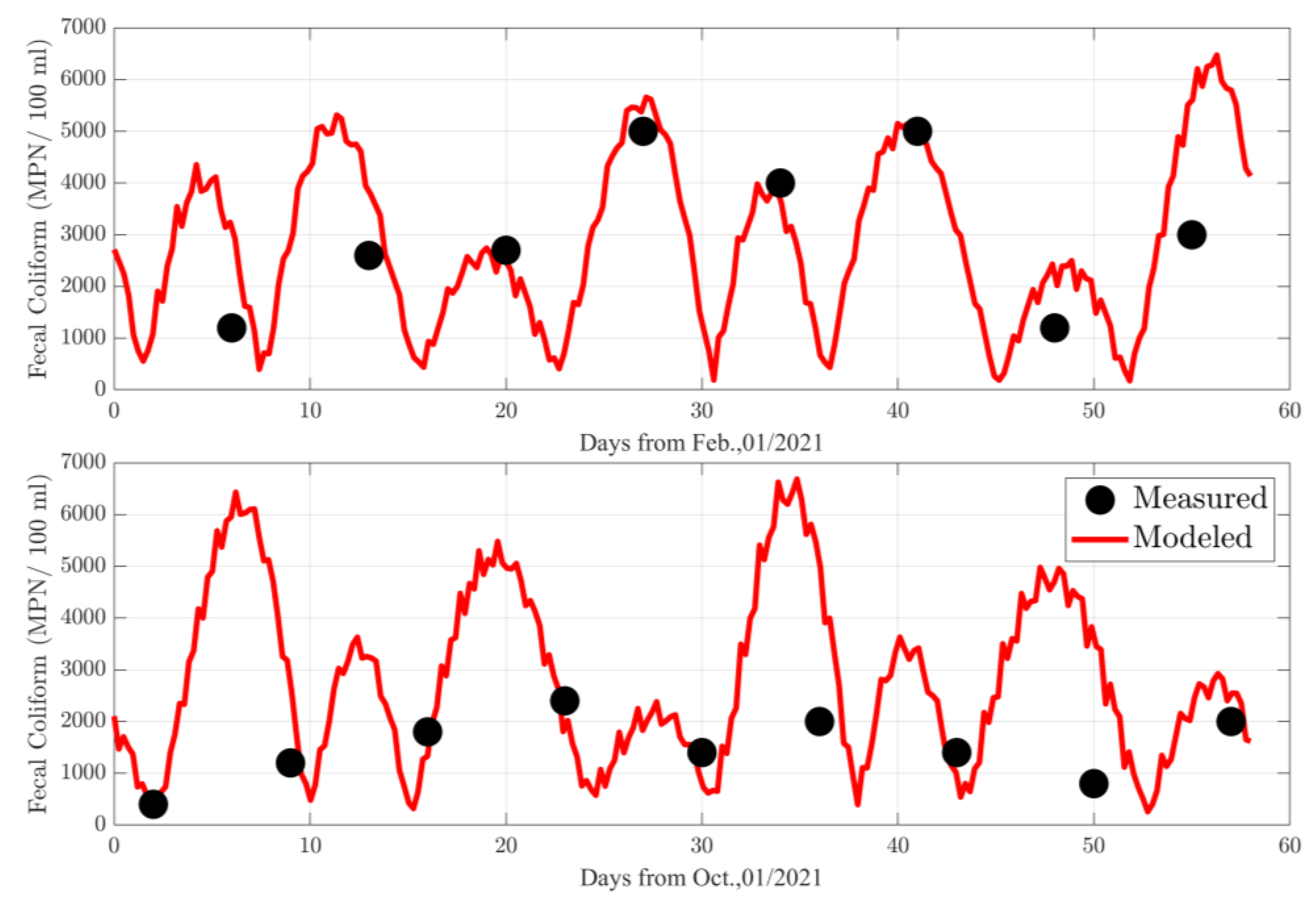
2.5. Calibration and Validation of Models
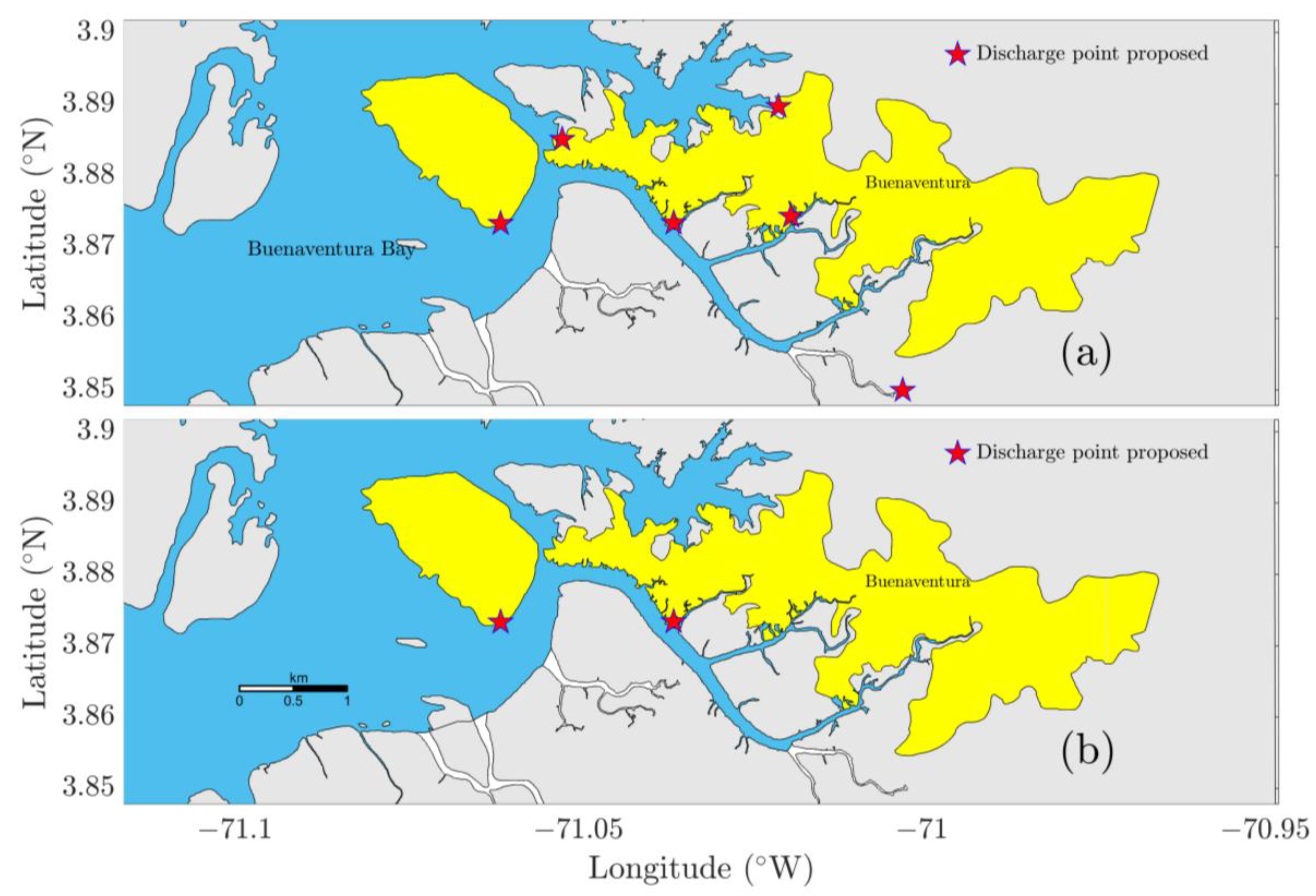
2.6. Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios
3. Results
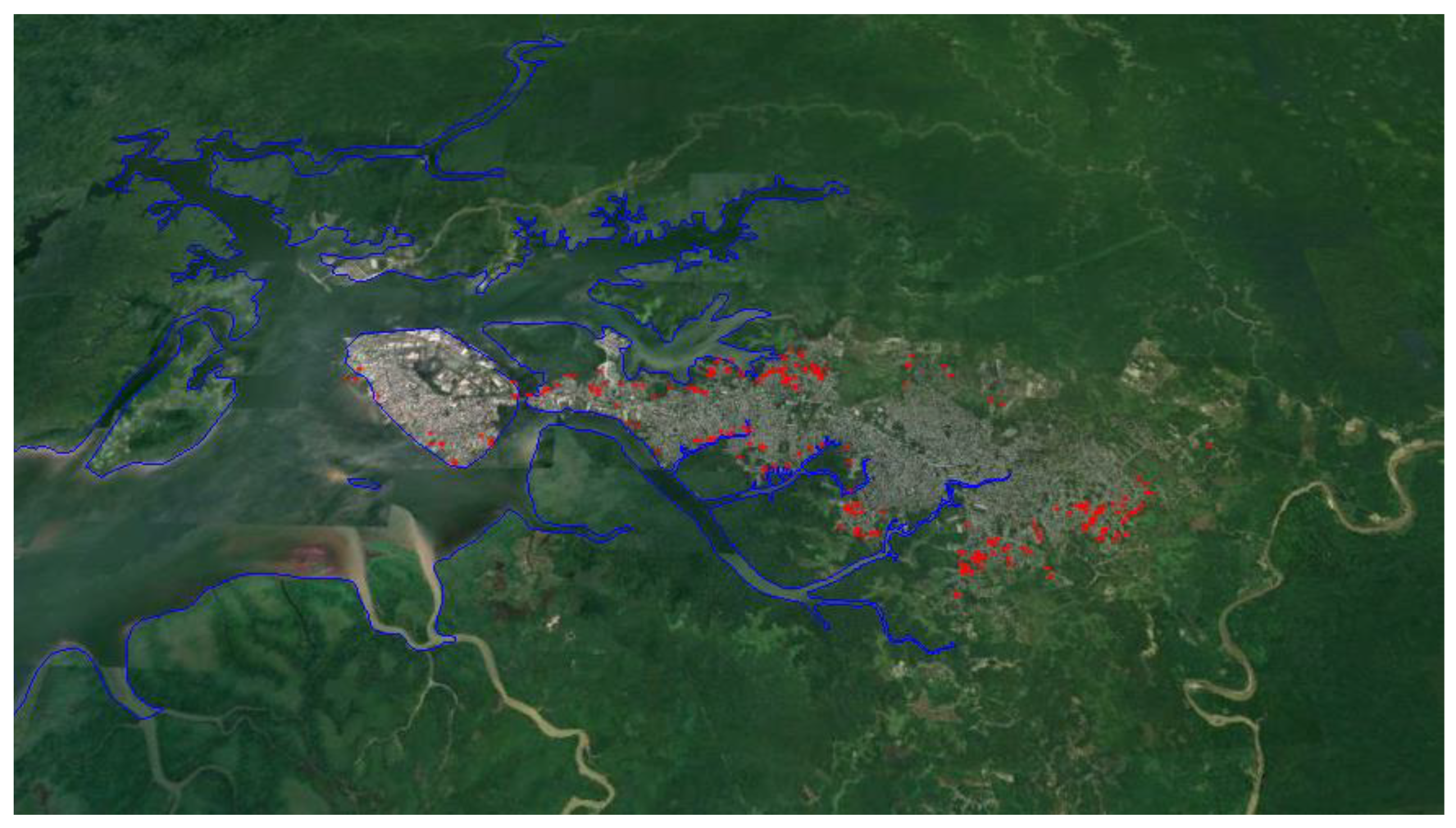
3.1. Characterization of Wastewater Discharges
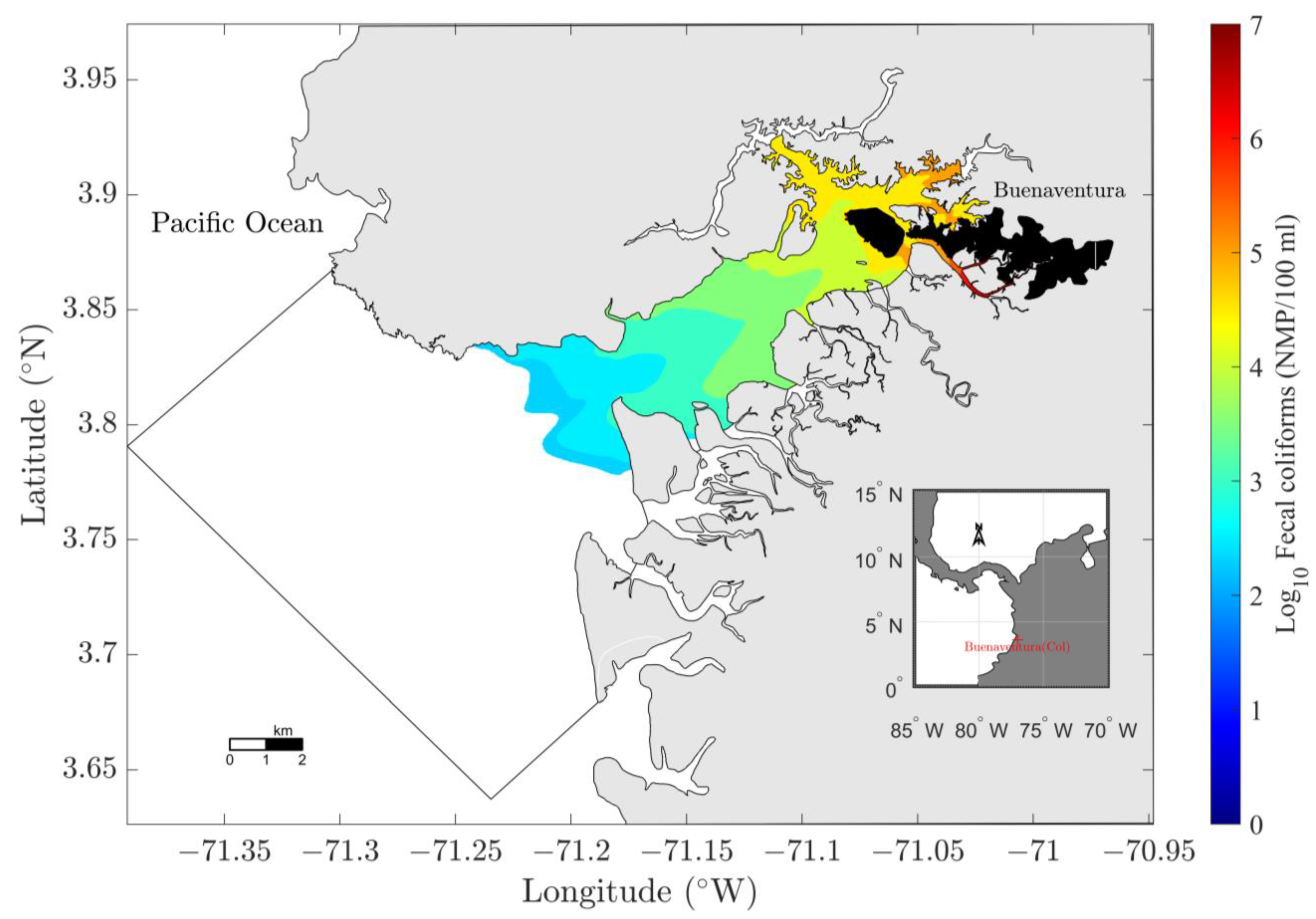
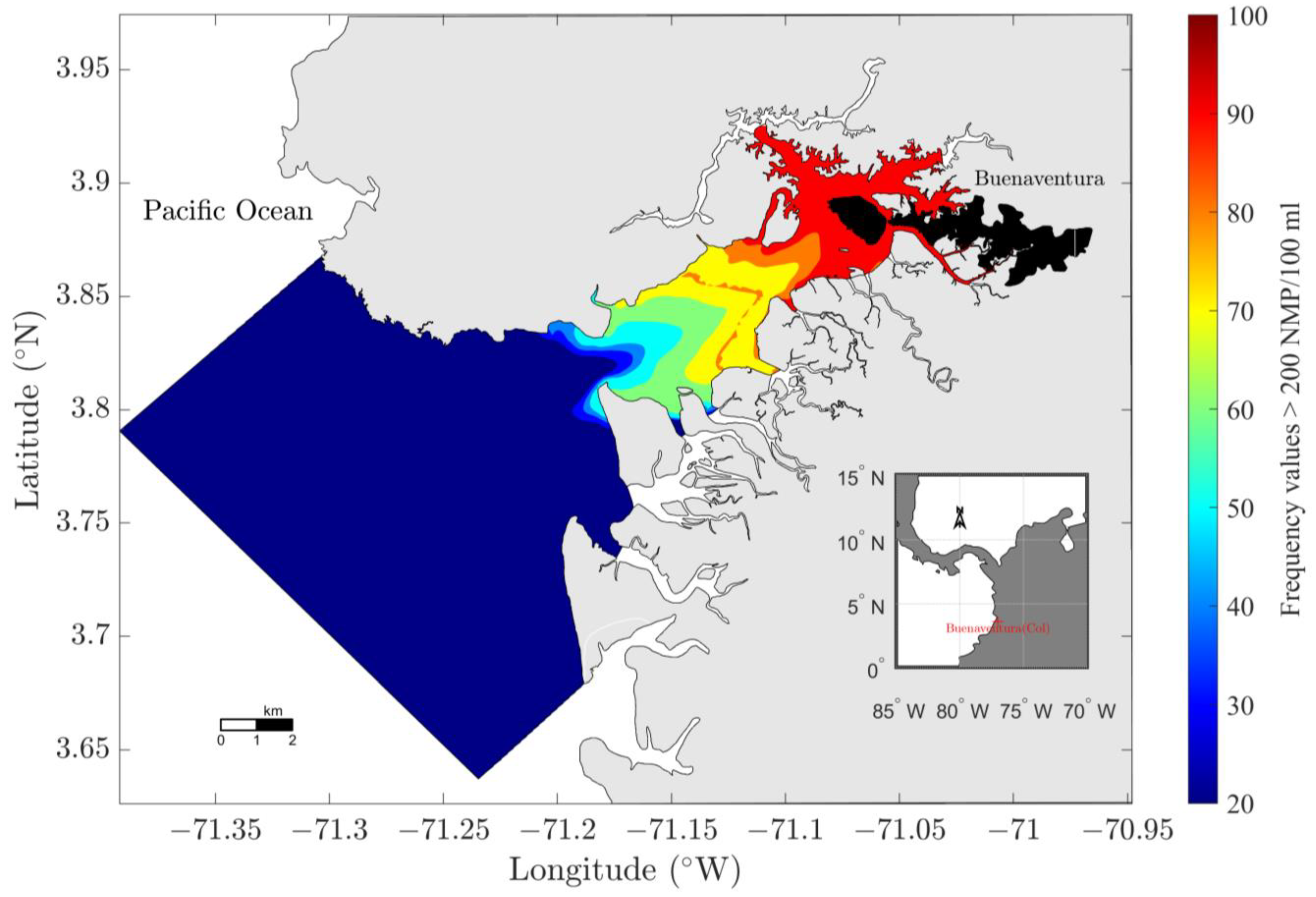
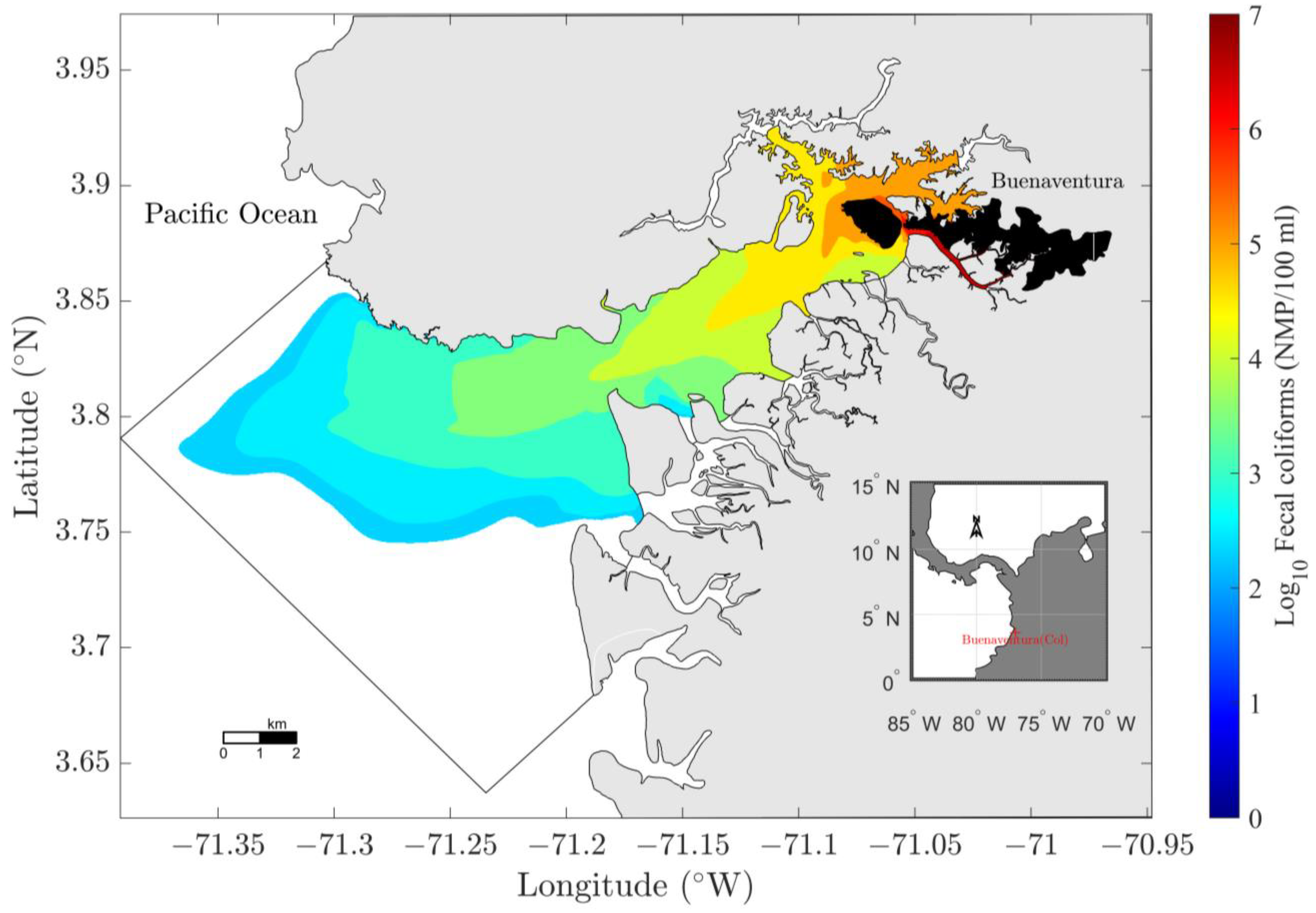
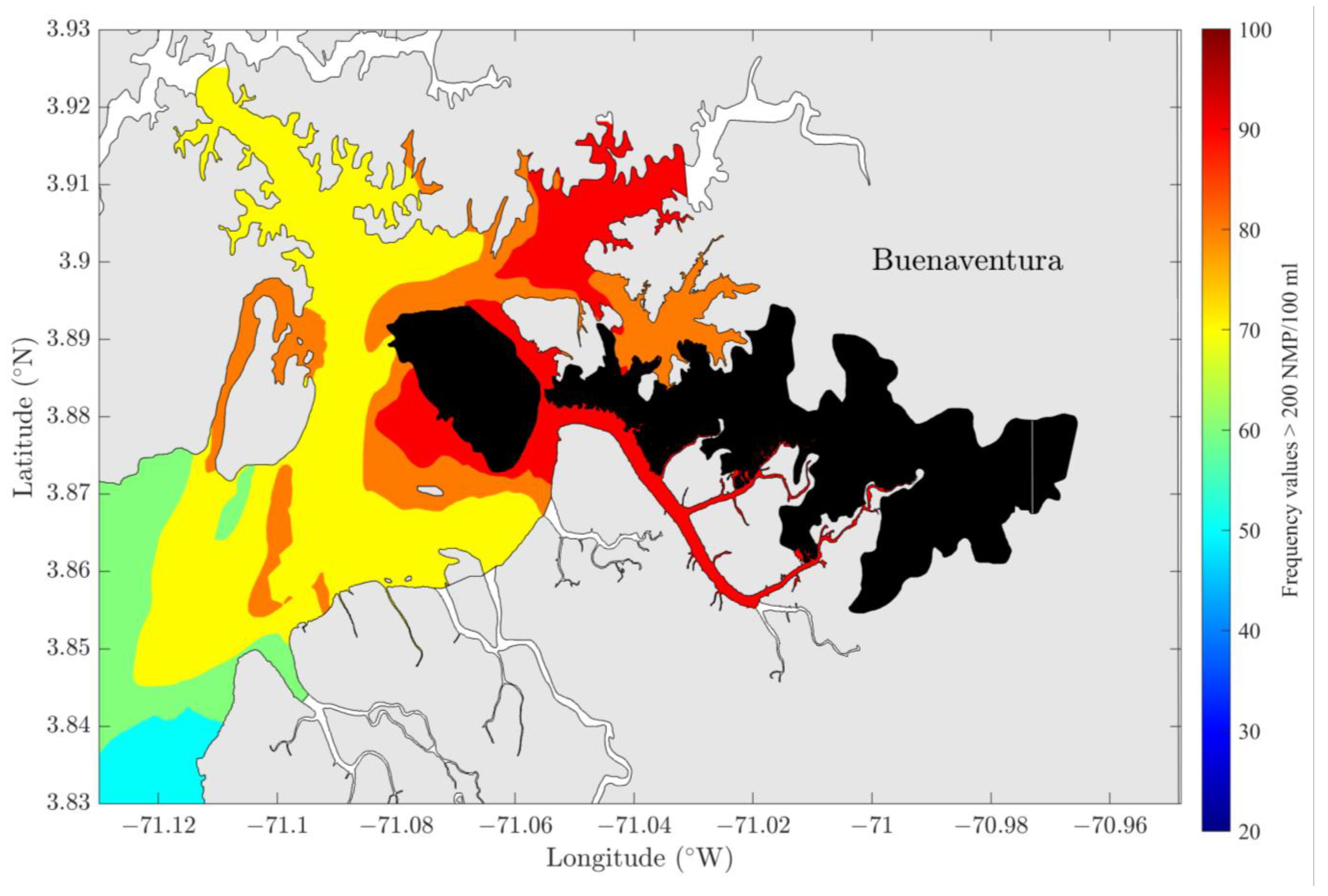
3.2. FC Concentration in the Water Column
3.3. Calibration Hydrodynamic Model
3.3.1. Sea Level
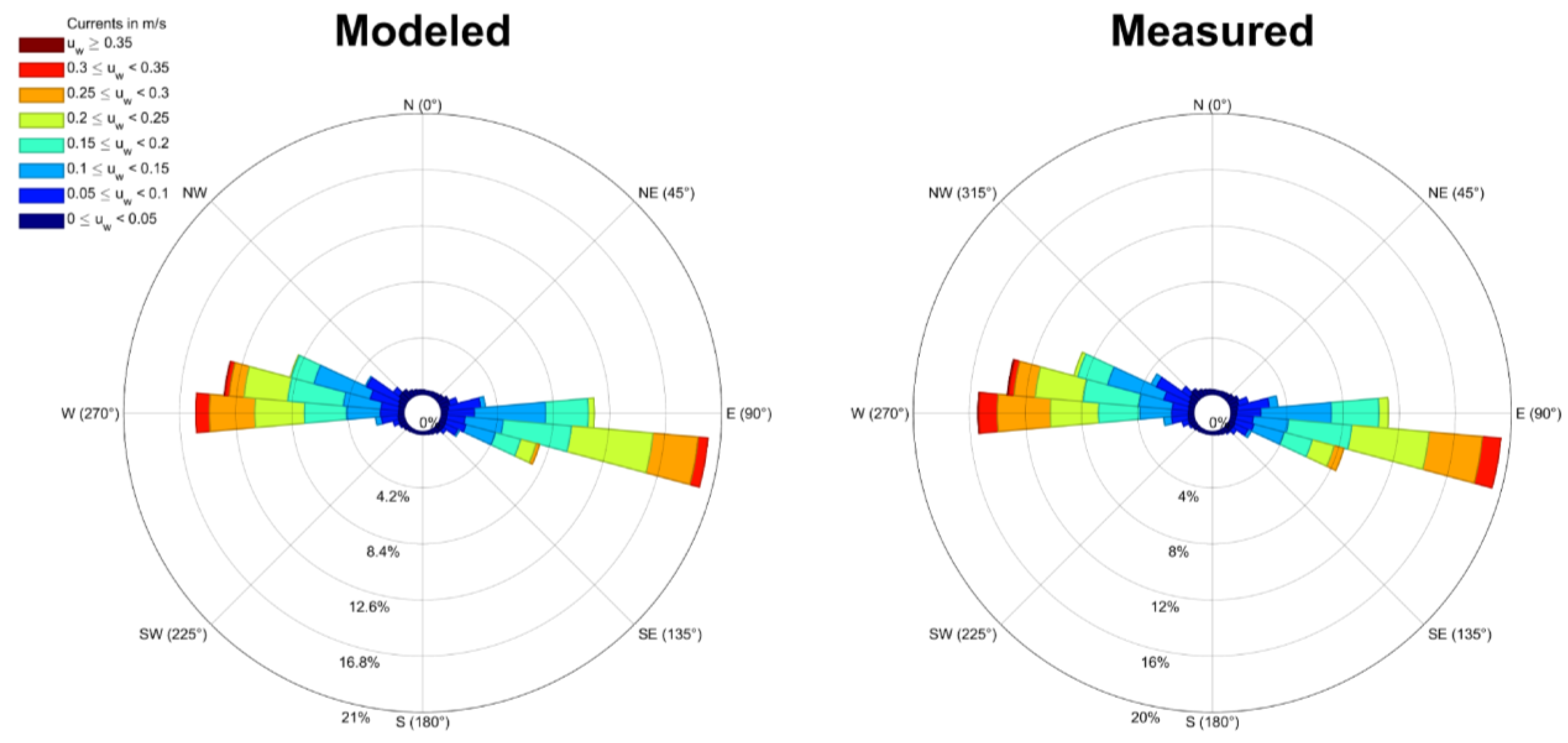
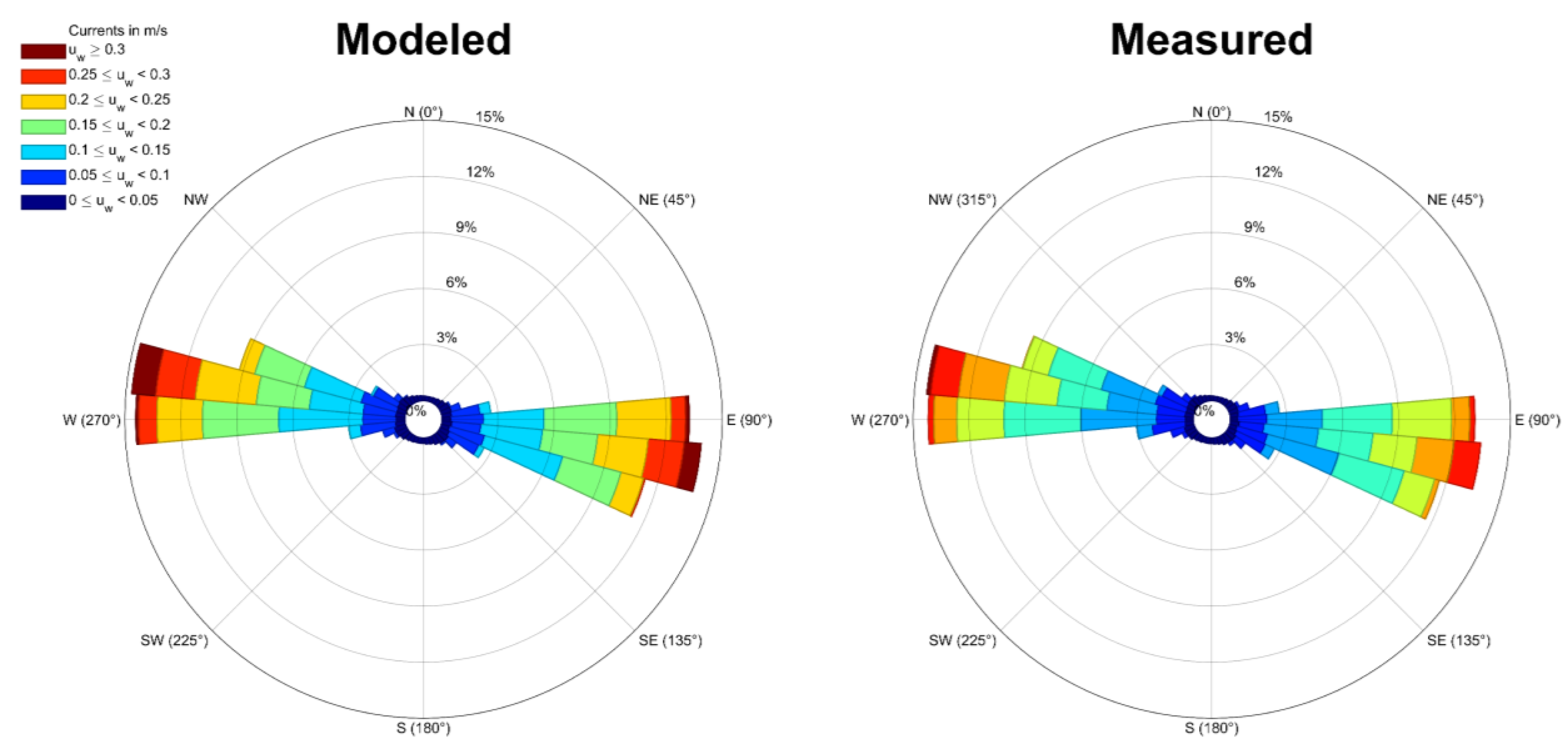
3.3.2. Currents
3.3.3. Water Quality Model
3.3.4. Discharge Reduction Scenario
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Superintendencia de Transporte. Ministerio de Transporte. Boletín Estadístico Tráfico Portuario en Colombia Año. 2020. Available online: https://www.supertransporte.gov.co/documentos/2021/Febrero/Puertos_04/BOLETIN-TRAFICO-PORTUARIO-2020.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- DANE. Available online: https://www.dane.gov.co/files/investigaciones/planes-desarrollo-territorial/100320-Info-Alcaldia-Buenaventura.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Gallego, B.E.; Josephraj, J. Evaluation of coastal vulnerability for the District of Buenaventura, Colombia: A geospatial approach. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 16, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, J.L. Determinación del régimen medio y extremal del nivel del mar para la bahía de Buenaventura. Boletín Científico Cent. Control Contam. Pac. 2004, 11, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, D.; Ramírez, L.F.; Segura-Quintero, C.; Castillo-Torres, P.; Díaz, J.M.; Walschburger, T.; Arango, N. Informe Técnico: Planificación Ecorregional para la Conservación in Situ de la Biodiversidad Marina y Costera en el Caribe y Pacifico Continental Colombiano, 1st ed.; INVEMAR Serie de documentos generales No. 41; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2009; 106p. [Google Scholar]
- INVEMAR. Informe Diagnóstico de la Situación Ambiental Marina de la Bahía de Buenaventura–Isla Cascajal y las Playas de Juanchaco, Ladrilleros y La Bocana. Available online: https://alfresco.invemar.org.co/share/s/sF3nl3iCRWa1THm9Dmc5-g (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Instituto de Hidrología, Meteorología y Estudios Ambientales (IDEAM). Estudio Nacional del Agua 2018. Bogotá: IDEAM. Available online: https://www.andi.com.co/Uploads/ENA_2018-comprimido.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Espinosa, S.; Delgado, B.; Orobio, L.M.; Mejía-Ladino, L.; Gil-Agudelo, D. Estado de la población y valoración de algunas estrategias de conservación del recurso piangüa Anadara tuberculosa (Sowerby) en sectores de Bazány Nerete, costa Pacífica nariñense de Colombia. Boletín Investig. Mar. Costeras 2010, 39, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas-Aguas, L.; Vargas-Morales, M.; Guillen, K.; Villarraga, D.; Sánchez, D. Vulnerabilidad de la Población Costera Frente a la Contaminación Orgánica y Microbiológica en la Bahía de Buenaventura; Serie de publicaciones generales del Invemar. No. 76; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2014; 24p. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, L. Application of the RMA10 3D model in simulating the water level and flow velocity in a river with complex terrain. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2019, 23, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Li, D. A review of hydrological/water–quality models. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.; Jun, S.-M.; Song, J.-H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Kang, M.-S. Application of the SWAT–EFDC Linkage Model for Assessing Water Quality Management in an Estuarine Reservoir Separated by Levees. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angello, Z.A.; Behailu, B.M.; Tränckner, J. Selection of Optimum Pollution Load Reduction and Water Quality Improvement Approaches Using Scenario Based Water Quality Modeling in Little Akaki River, Ethiopia. Water 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; de Almeida, R.; De Aguiar, E. Evaluation of reduction of external load of total phosphorus and total suspended solids for rehabilitation of urban lakes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113339. [Google Scholar]
- Me, W.; Hamilton, P.; McBride, C.; Abell, J.; Hicksa, B. Modelling hydrology and water quality in a mixed land use catchment and eutrophic lake: Effects of nutrient load reductions and climate change. Environ. Model. Softw. 2018, 109, 114–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Marthanty, D.R.; Soeryantono, H.; Carlier, E.; Sutjiningsih, D. Assessment of the capability of 3D stratified flow finite element model in characterizing meander dynamics. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2014, 8, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Fossati, M.; Piedra-Cueva, I. Numerical modelling of residual flow and salinity in the Rıo de la Plata. Appl. Math. Model. 2008, 32, 1066–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Simulation of hydrodynamic conditions at Santa Marta coastal area (Colombia). Dyna 2012, 174, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, F.F.; Palacio, C.; Garcia, U. Calibración y validación de un modelo 3D para el área costera de Santa Marta (Colombia). Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioq. 2012, 62, 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Li, Y. Application of the RMA10 3D model to simulate flood events in an urban area. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X. Application of the RMA10 3D model to simulate sediment transport in the Yangtze River. Water Sci. Eng. 2018, 11, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Song, J. Simulation of water quality in a river using the RMA10 3D model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 3584–3594. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Zhang, Z. Application of the RMA10 3D model in simulating the thermal environment of a river. J. Waterw. Port Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021002. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzatti, P.; Fossati, M.; Piedra-Cueva, I. An efficient version of the RMA-11 model. CLEI Electron. J. 2011, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glamore, W.; Mitrovic, S.; Ruprecht, J.; Dafforn, K.; Scanes, P.; Ferguson, A.; Rayner, D.; Miller, B.; Dieber, M.; Tucker, T. The Hunter River Estuary Water Quality Model. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports 2019 Conference, Hobart, Australia, 10–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ruprecht, J.; King, I.P.; Mitrovic, S.; Dafforn, K.A.; Miller, B.M.; Deiber, M.; Westhorpe, D.P.; Hitchcock, J.N.; Harrison, A.J.; Glamore, W.C. Assessing the validity and sensitivity of microbial processes within a hydrodynamic model. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fu, X.; Wang, G. Simulation of wind-driven circulation and temperature in the near-shore region of southern Lake Michigan by using a channelized model. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2013, 25, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Barnwell, T.O. The Enhanced Stream Water Quality Models QUAL2E and QUAL2E–UNCAS: Documentation and Users Manual; EPA/600/3-87/007; Environmental Research Laboratory, Office of Research and Development, US Environmental Protection Agency: Athens, GA, USA, 1987; Available online: https://webpages.charlotte.edu/~jdbowen/6141/qual2e_info/qual2e_sect1-1.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Thomann, R.V.; Mueller, J.A. Principles of Surface Water Quality and Control; Harper Collins: New York, NY, USA, 1987; 644p. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, A.M.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Hamza, W. Assessment of water quality and eutrophication of Rosetta Branch using RMA11 water quality model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 571. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zahrani, M.; Alharbi, S.; Almazroui, M.; Ghulam, A. Use of RMA11 water quality model to assess the impact of treated sewage discharge on coastal water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 30508–30521. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, J.; Yu, D. Simulation of the spatial and temporal variation of water quality in the Jialing River using the RMA11 model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Yang, L.; Qiu, C.; Chen, B. Application of the RMA11 model to simulate water quality and ecological responses in a shallow lake. Water Sci. Eng. 2017, 10, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Shi, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, J. A three-dimensional RMA11 water quality model for the Lower Yellow River. Ecol. Model. 2018, 384, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Ye, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y. The spatial–temporal distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in a typical urban river using RMA11 model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 5966–5978. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Ke, X. Three-dimensional RMA11 model for water quality simulation in a typical urban river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 543. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q. Assessment of the water quality in the Weihe River basin based on RMA11 model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7192–7202. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z. Investigation of river water quality based on the RMA11 model in a rural area of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26047–26060. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Wu, B.; Zhou, X. Evaluation of the effectiveness of water environment protection measures in the upper Han River Basin using the RMA11 model. Water 2019, 11, 967. [Google Scholar]
- Engwirda, D. Locally–Optimal Delaunay-Refinement and Optimisation-Based Mesh Generation. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Mathematics and Statistics, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Engwirda, D. Conforming Restricted Delaunay Mesh Generation for Piecewise Smooth Complexes. Procedia Eng. 2016, 163, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Smedstad, O.M.; Halliwell, G.R.; Hogan, P.J.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Baraille, R.; Bleck, R. The HYCOM (HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model) data assimilative system. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 65, 60–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, A.; Duque, G.; Cogua, P. Influences of environmental conditions in the fish assemblage structure of a tropical estuary. Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, K.; Kuang, C.; Zhu, D.Z.; He, L.; Mao, X.; Liang, H.; Song, H. Influence of sea level rise on saline water intrusion in the Yangtz River Estuary, China. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 54, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondragón-Díaz, L.; Molina, A.; Duque, G. Influence of environmental variables on the spatiotemporal dynamics of water quality in Buenaventura Bay, Colombian Pacific. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

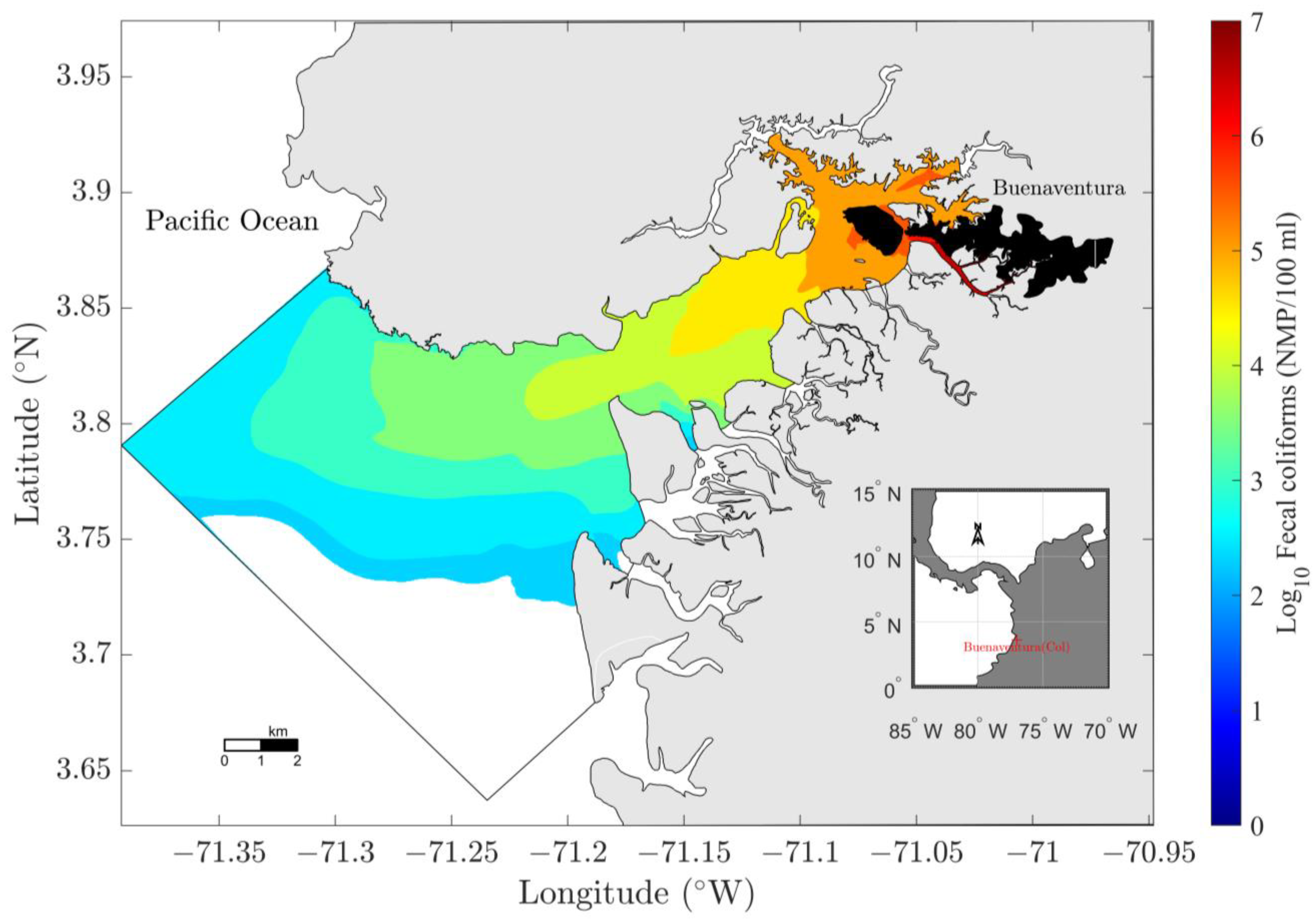
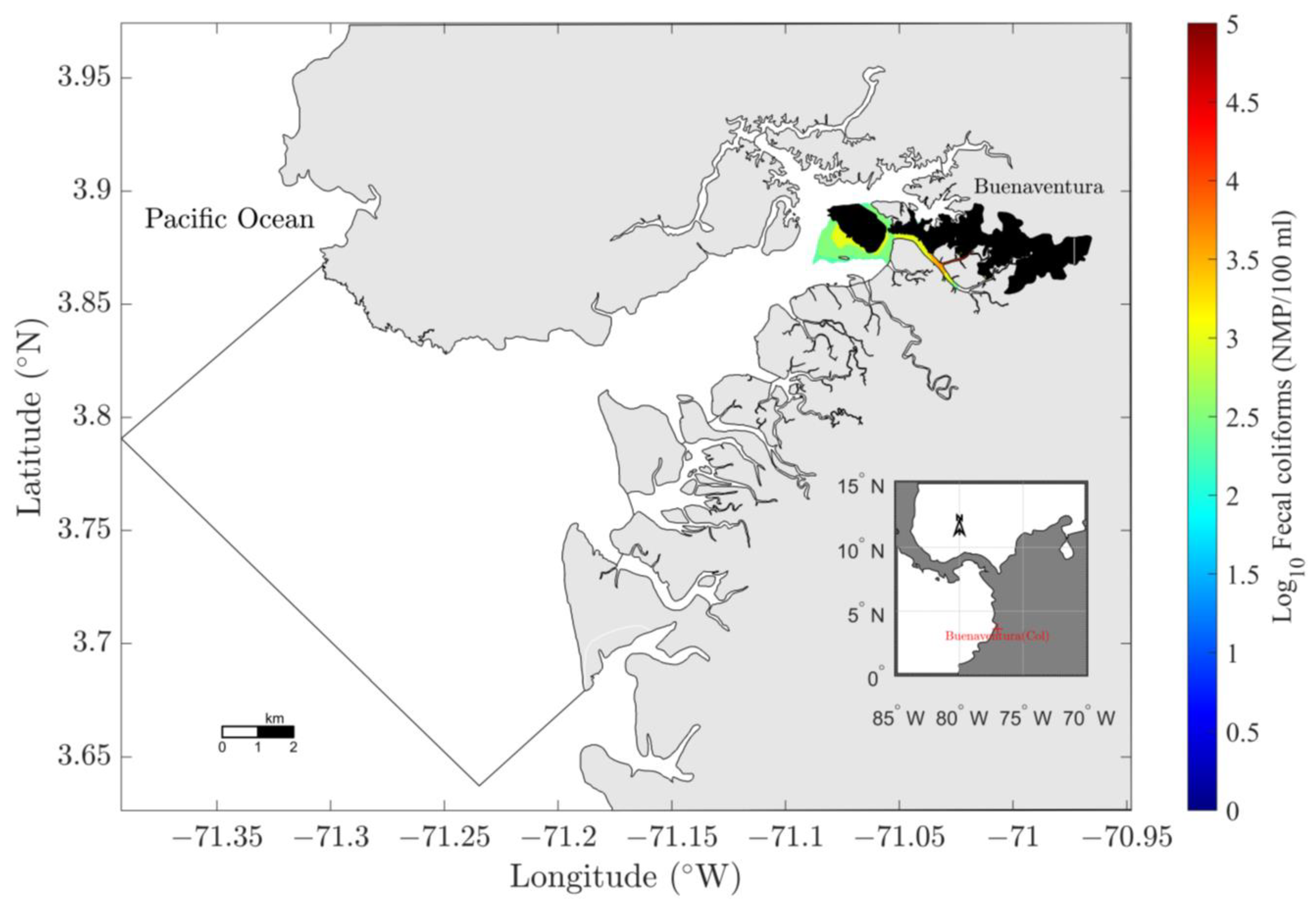
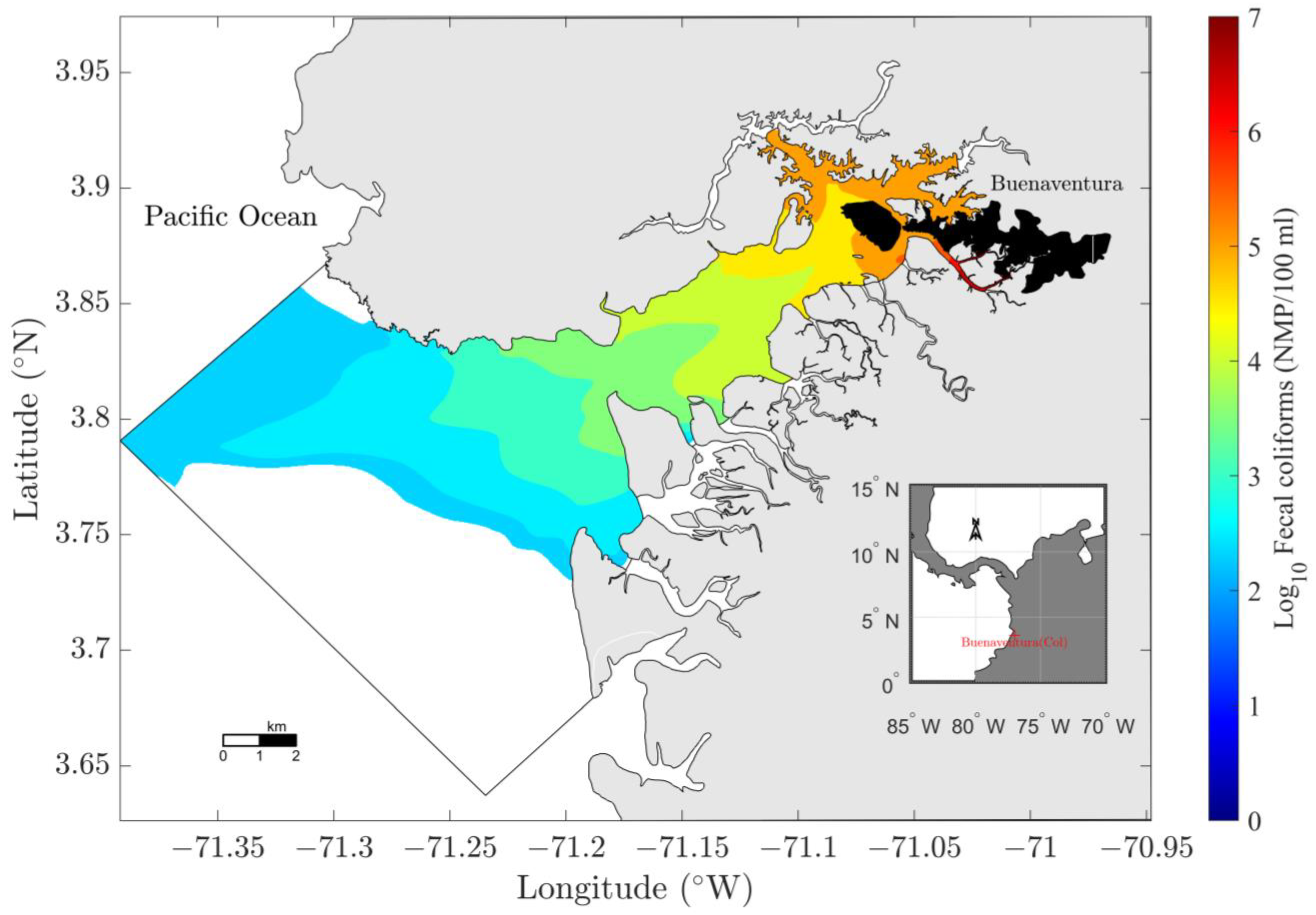
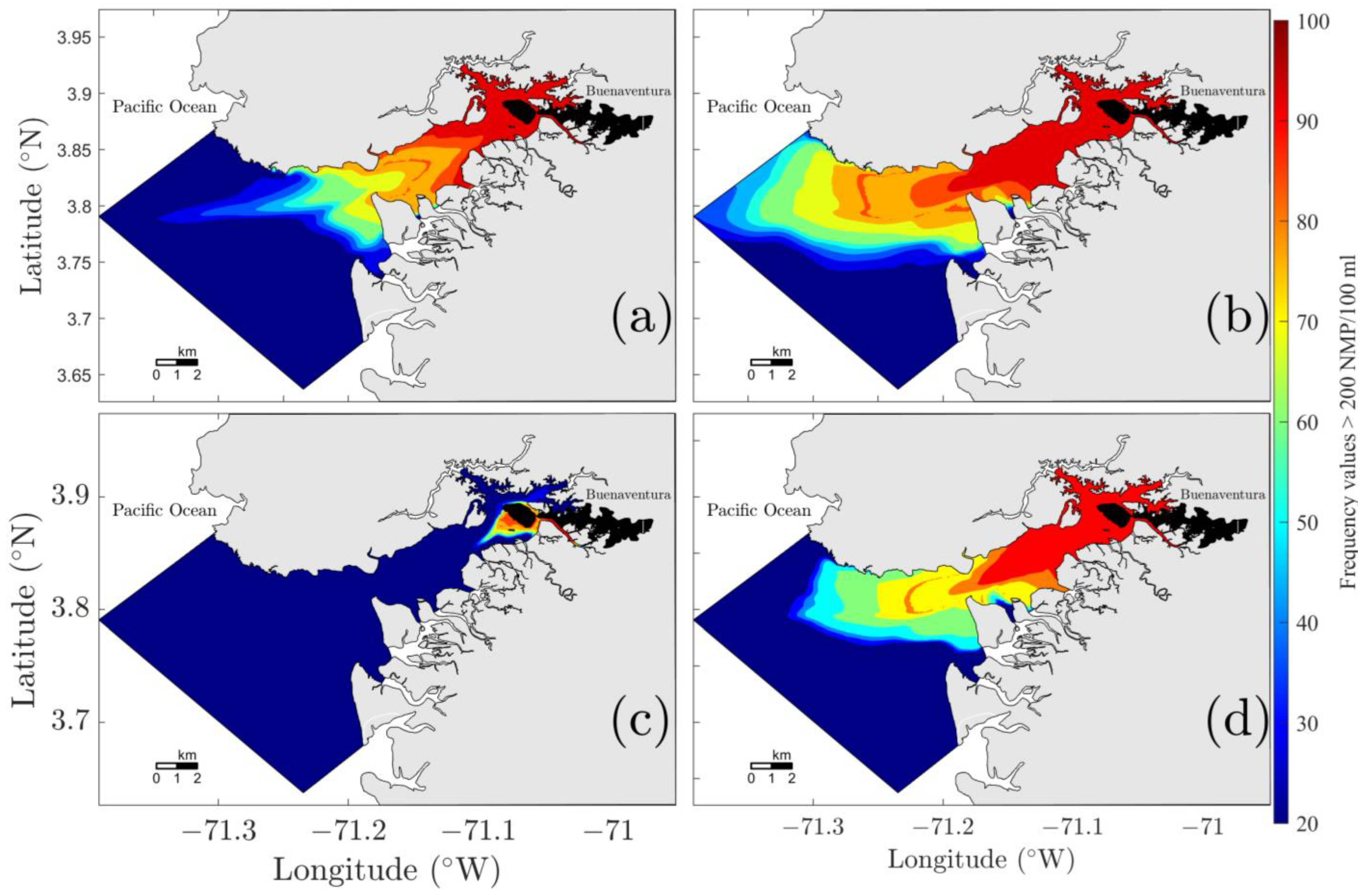
| Discharge Type | Mean Flow (L/S) | Flow Range (L/S) | Number of Discharge Points | Total Flow (L/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 0.74 | 0.11–0.93 | 316 | 233.84 |
| Medium | 1.01 | 0.94–1.42 | 252 | 254.52 |
| High | 1.62 | 1.43–1.83 | 127 | 205.74 |
| Scenario Number | Number of Discharges Considered | Time of Implementation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| One | 695 | Current Situation | A total of 695 discharges of untreated wastewater. |
| Two | 6 | 10 years | The collection of all discharges in the sewage system to pass to six unique discharges that concentrate the flow of these. Six new concentrated discharges of untreated wastewater. |
| Three | 2 | 15 years | The collection of six discharges in the sewage system to pass to two unique discharges that concentrate the flow of these. Two new concentrated discharges of untreated wastewater. |
| Four | 2 | 30 years | Two wastewater discharges, removing 90% of the wastewater contaminants with the treatment plants in operation. Two effluents of treated wastewater. |
| Five | 695 | 30 years | A future scenario without a sanitation solution for the Bay of Buenaventura, considering an increase in the discharge flow. A total of 695 discharges of untreated wastewater. |
| Parameter | Unit | Maximum | Mean | Minimum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fecal Coliform | MPN/100 mL | 2 × 1010 | 8 × 108 | 7 × 103 |
| Unit | Maximum | Mean | Minimum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | MPN/100 mL | 5 × 103 | 2.8 × 103 | 1.2 × 103 |
| Validation | MPN/100 mL | 2.4 × 103 | 1.8 × 103 | 4 × 102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Rentería, F.-F.; Nieto, G.A.C.; Cortez, G.H. Evaluation of Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios in the Buenaventura Bay. Water 2023, 15, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061027
García-Rentería F-F, Nieto GAC, Cortez GH. Evaluation of Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios in the Buenaventura Bay. Water. 2023; 15(6):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Rentería, Francisco-Fernando, Gustavo Ariel Chang Nieto, and Gustavo Hernández Cortez. 2023. "Evaluation of Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios in the Buenaventura Bay" Water 15, no. 6: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061027
APA StyleGarcía-Rentería, F.-F., Nieto, G. A. C., & Cortez, G. H. (2023). Evaluation of Wastewater Discharge Reduction Scenarios in the Buenaventura Bay. Water, 15(6), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061027





