Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Work
2.1. Materials
2.2. Method
2.3. Adsorbent Characterisation
2.3.1. FTIR Analysis
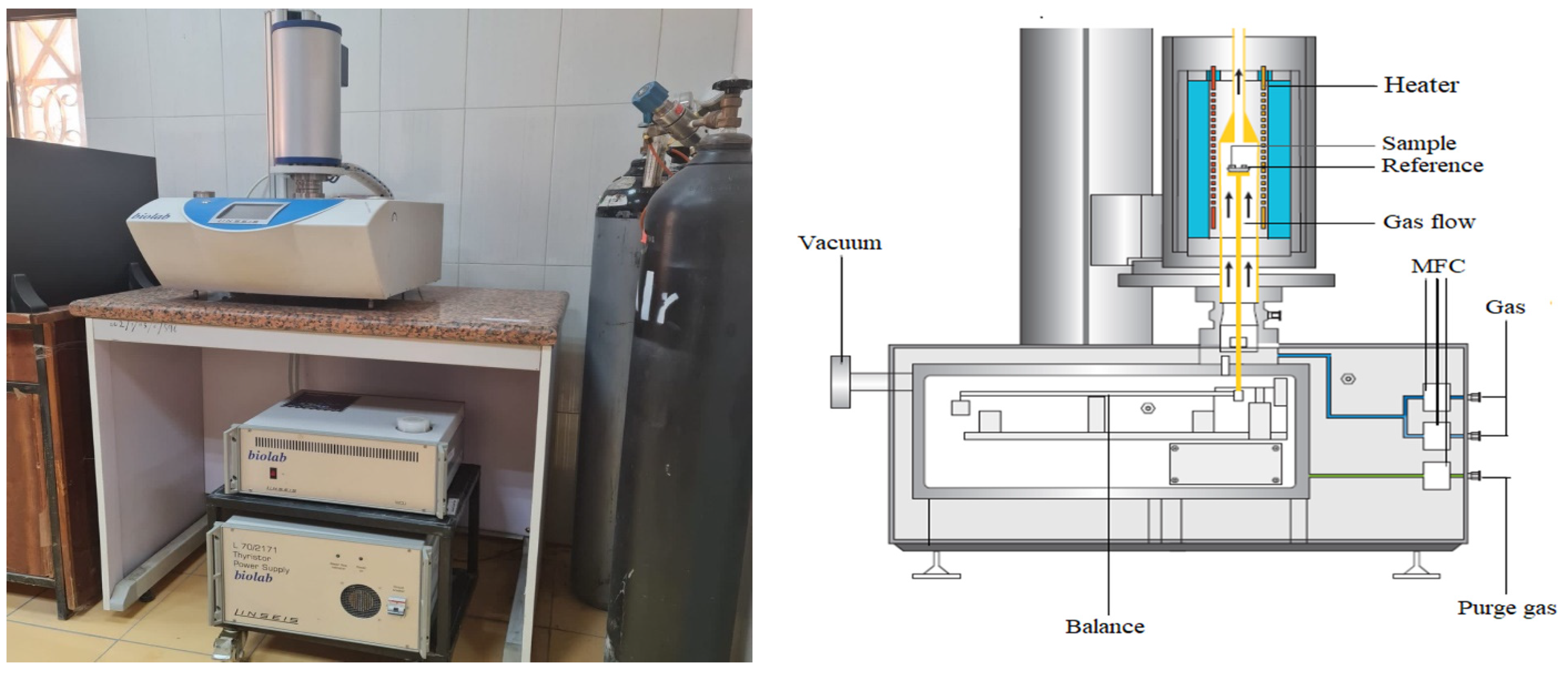
2.3.2. TGA Analysis
2.3.3. Contact Time Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
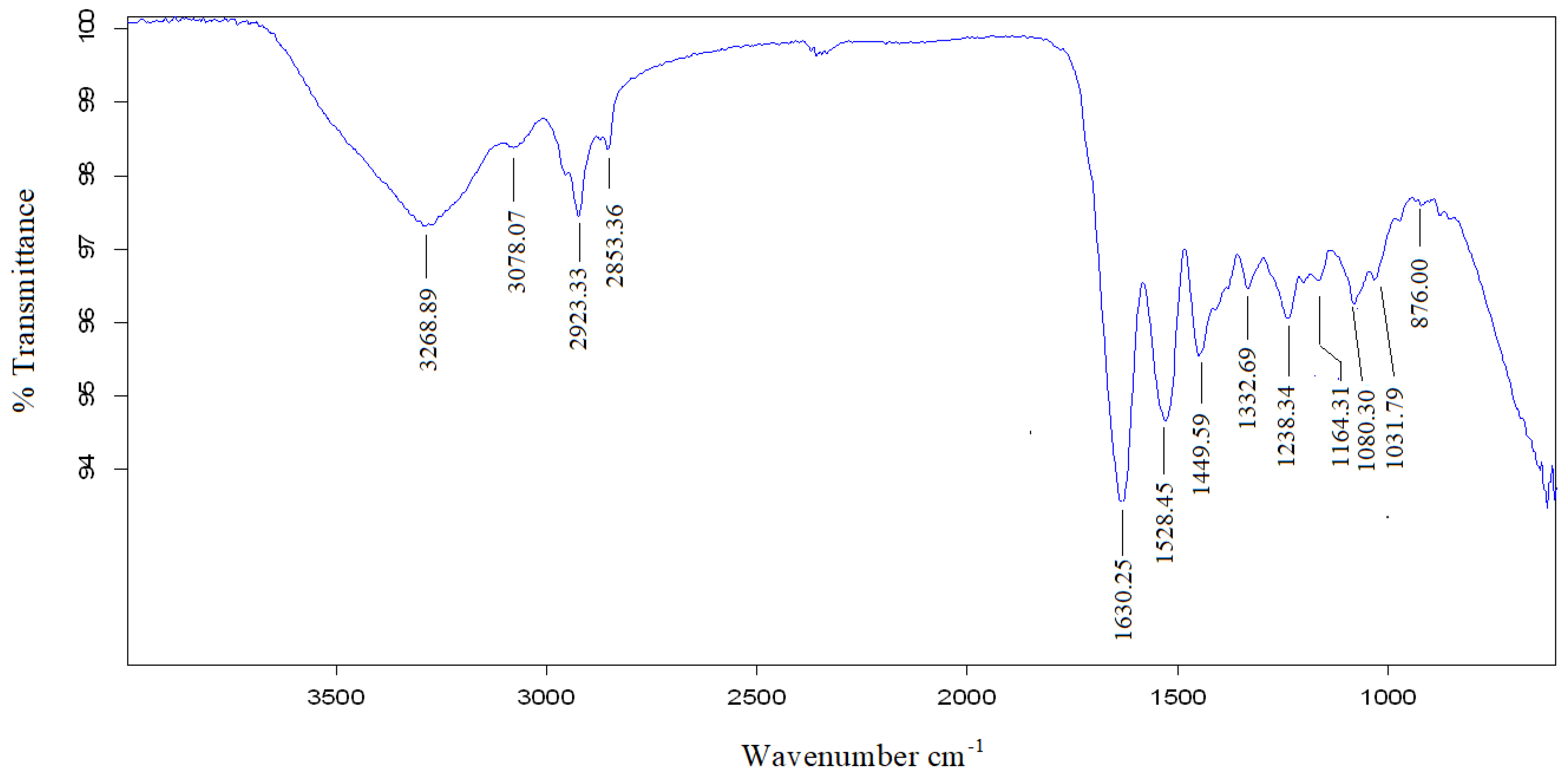
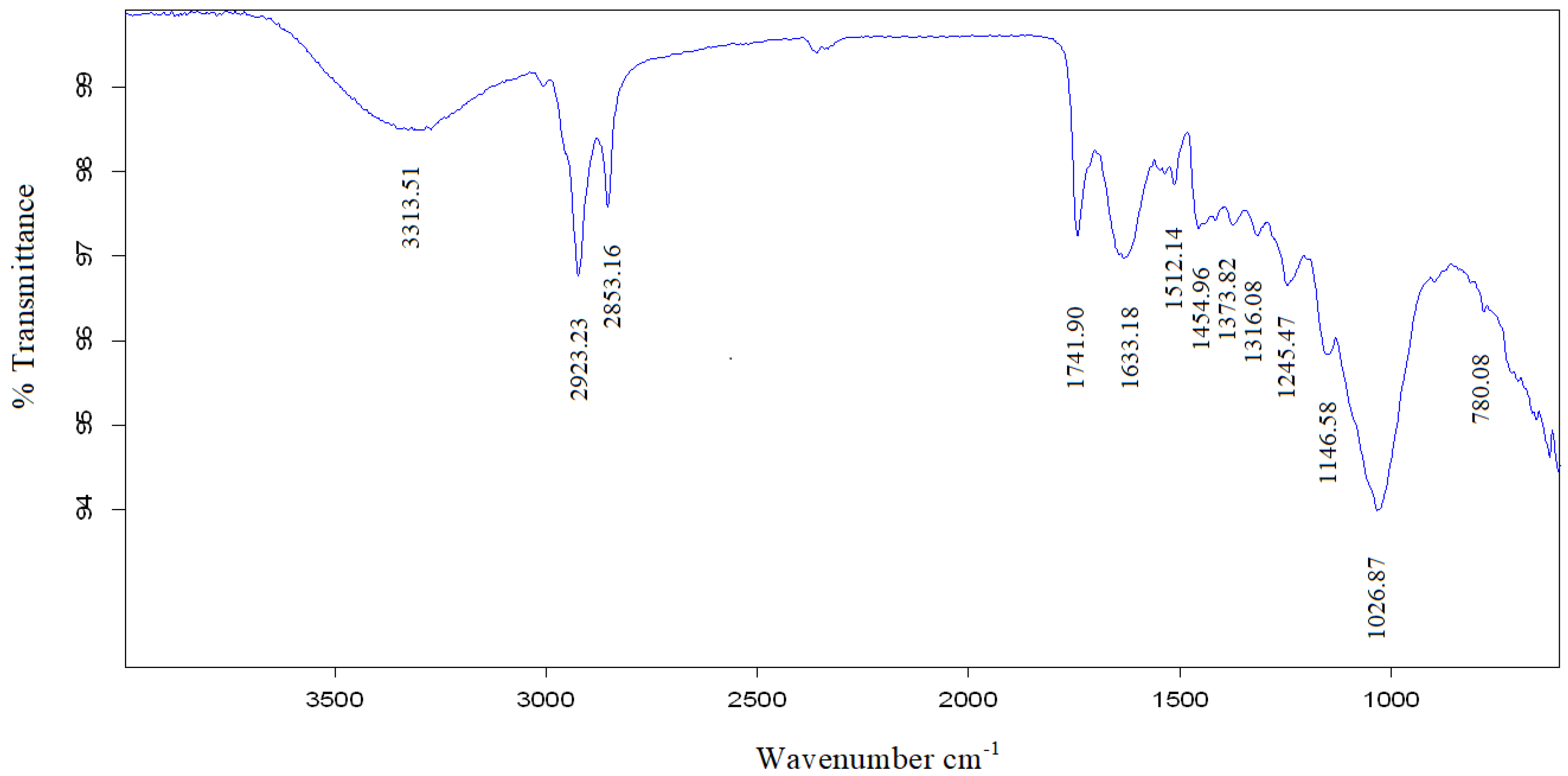
3.1. FTIR Analysis of Adsorbents
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.3. Contact Angle Measurement
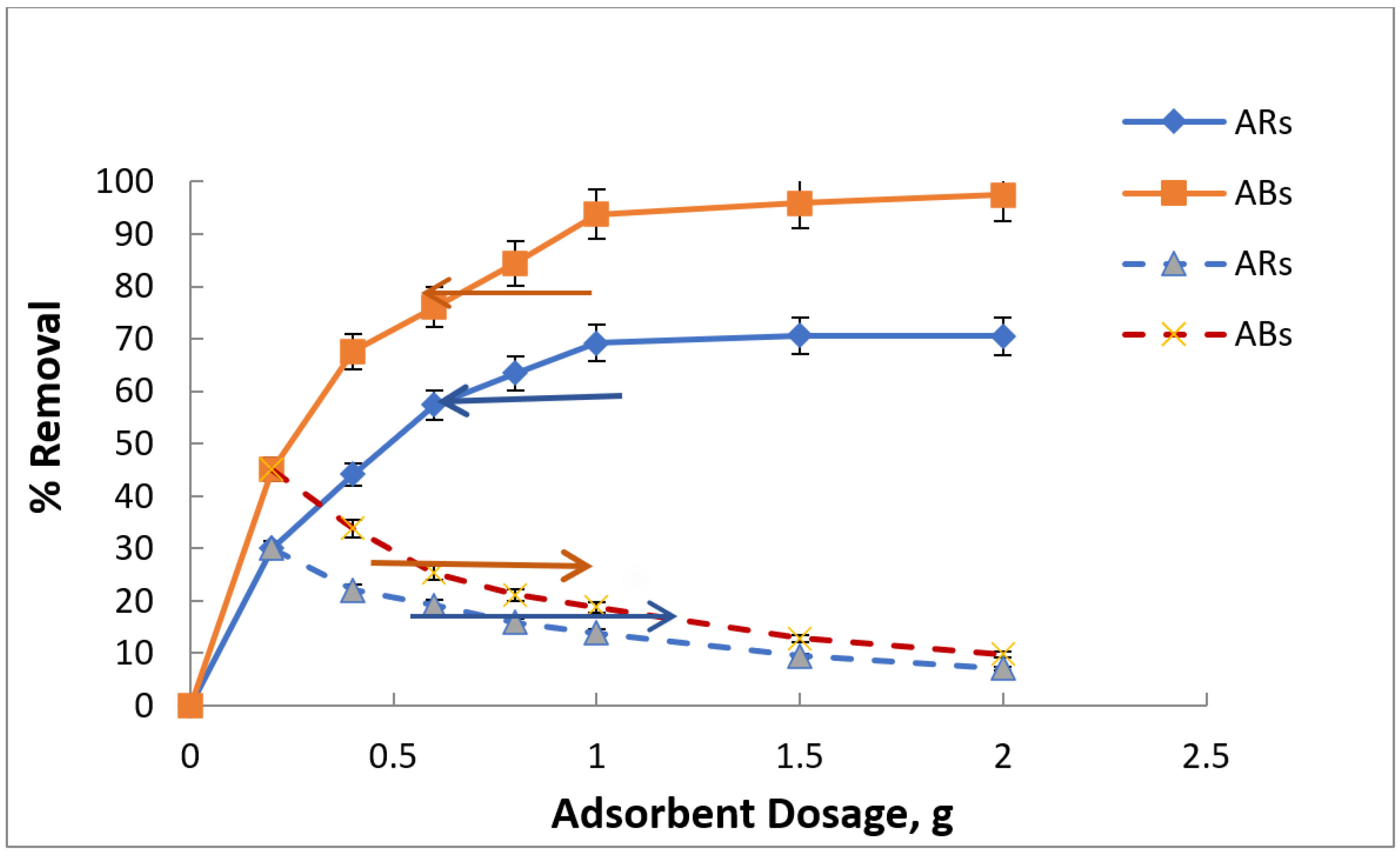
3.4. Adsorbent Dose Impact
3.5. Impact of Oil Concentration
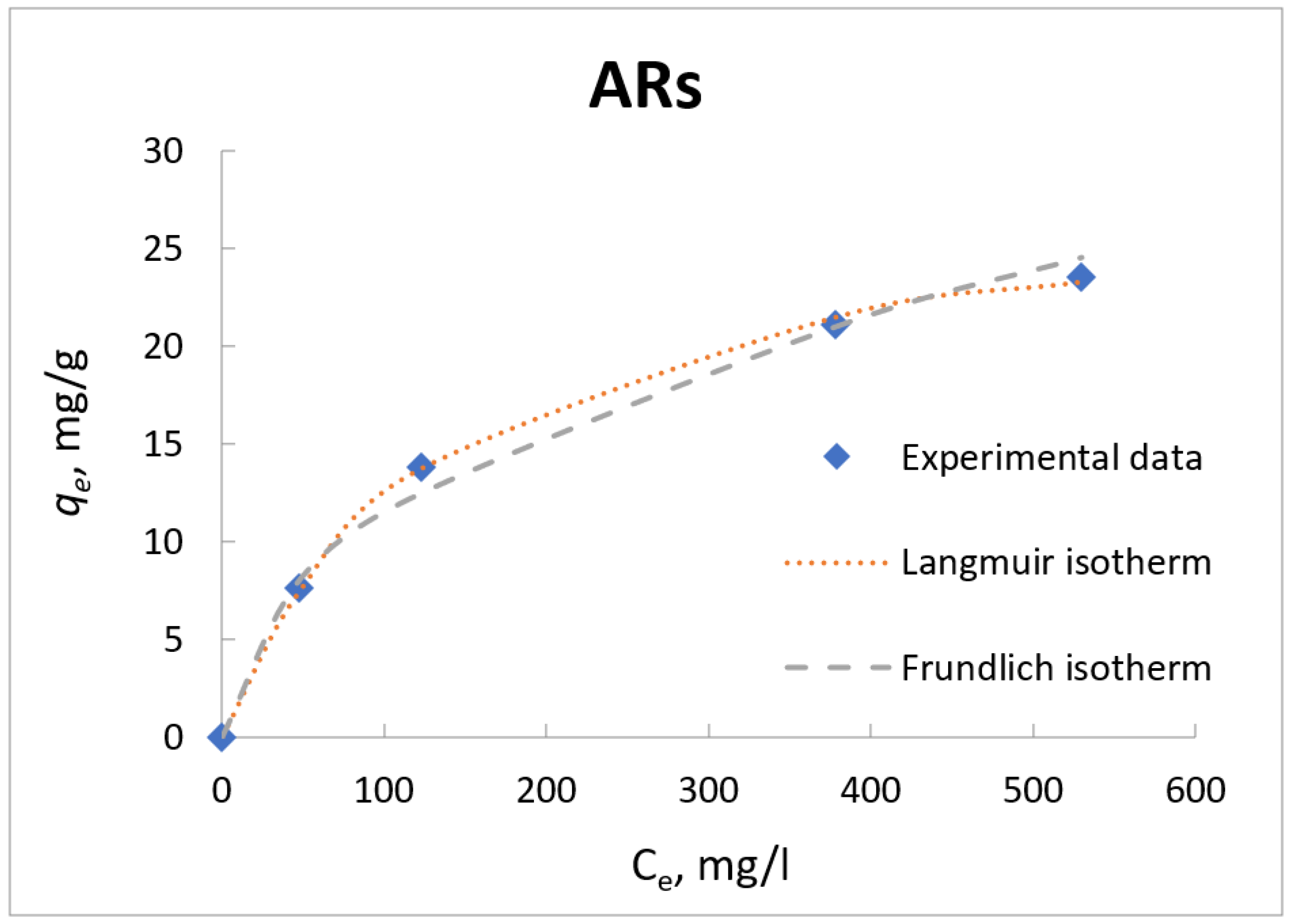
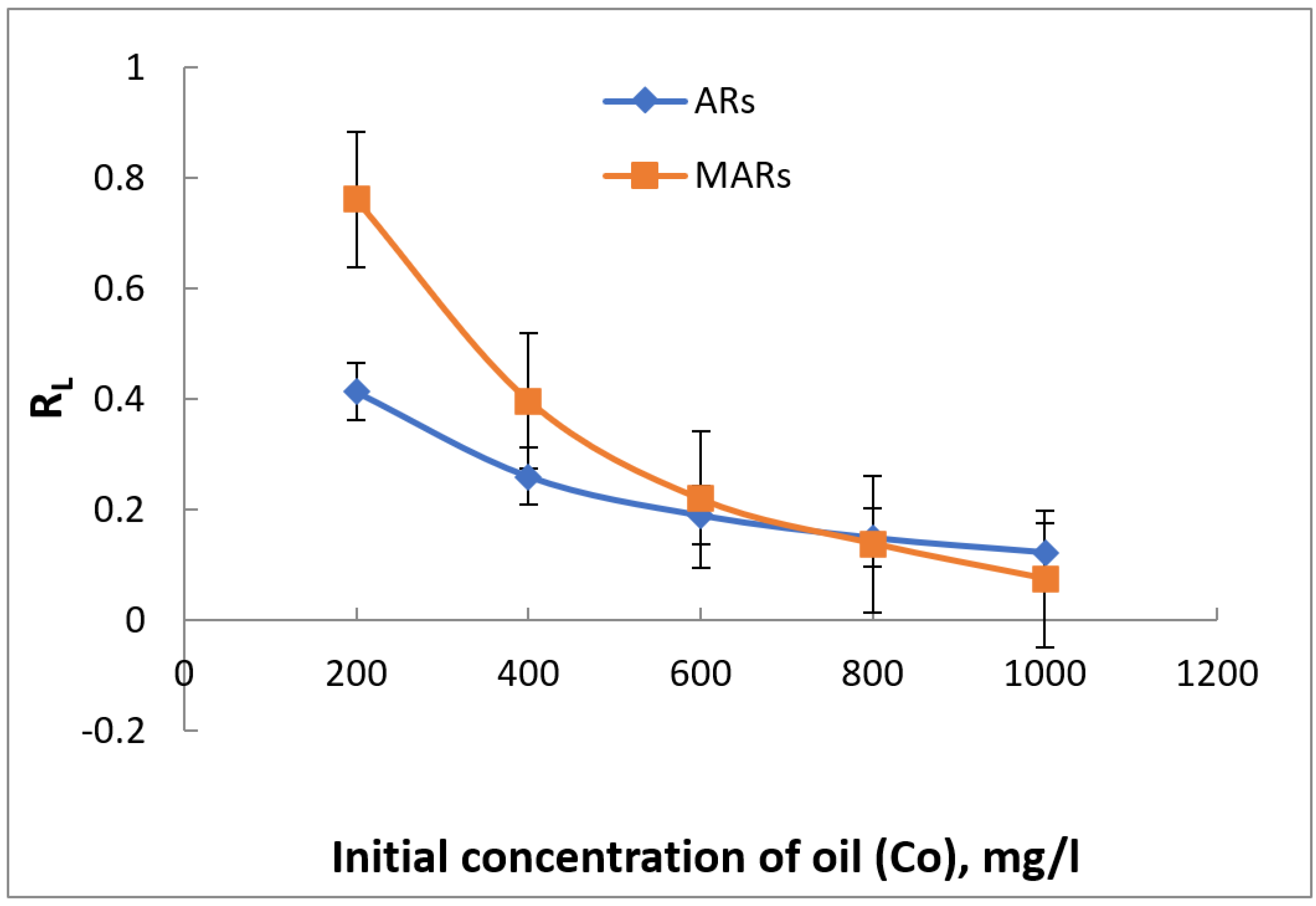
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm
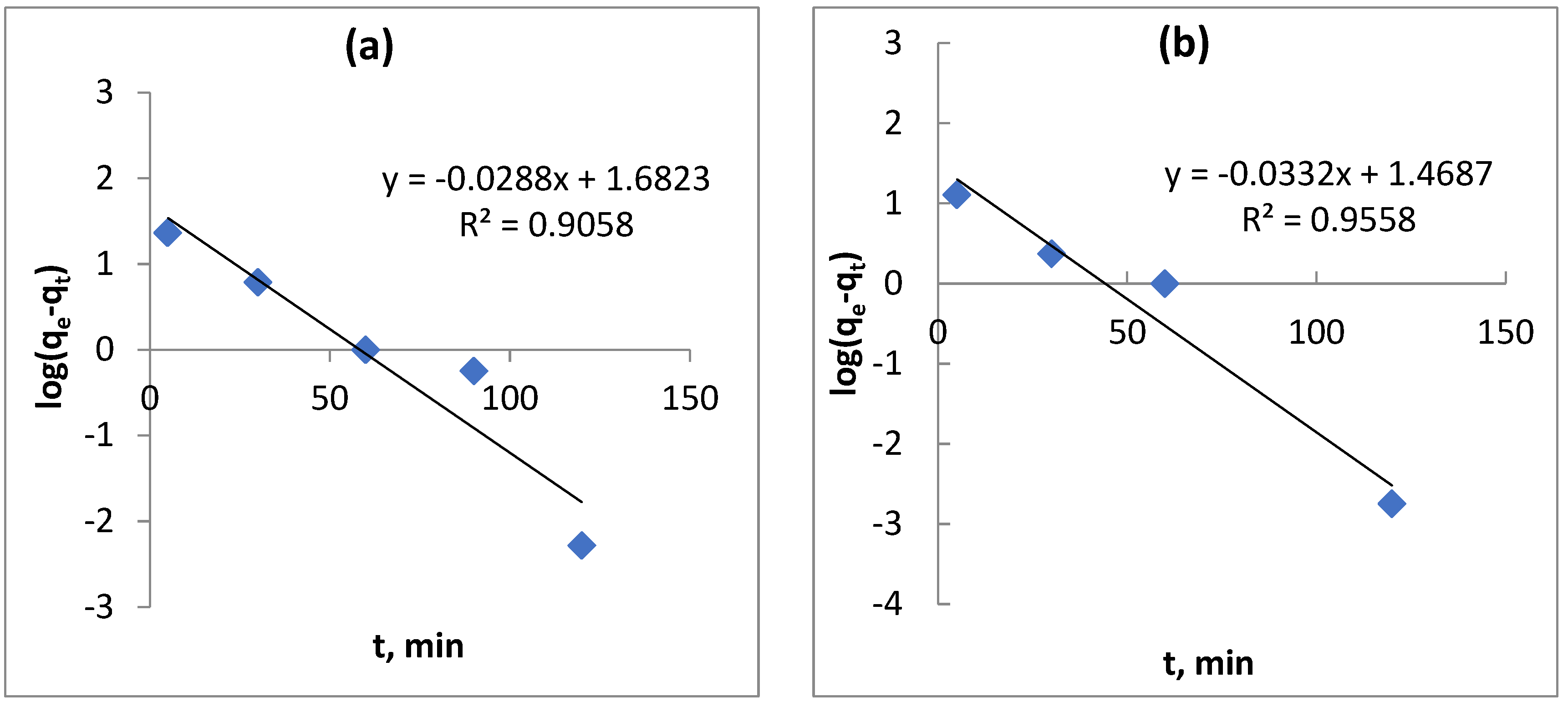
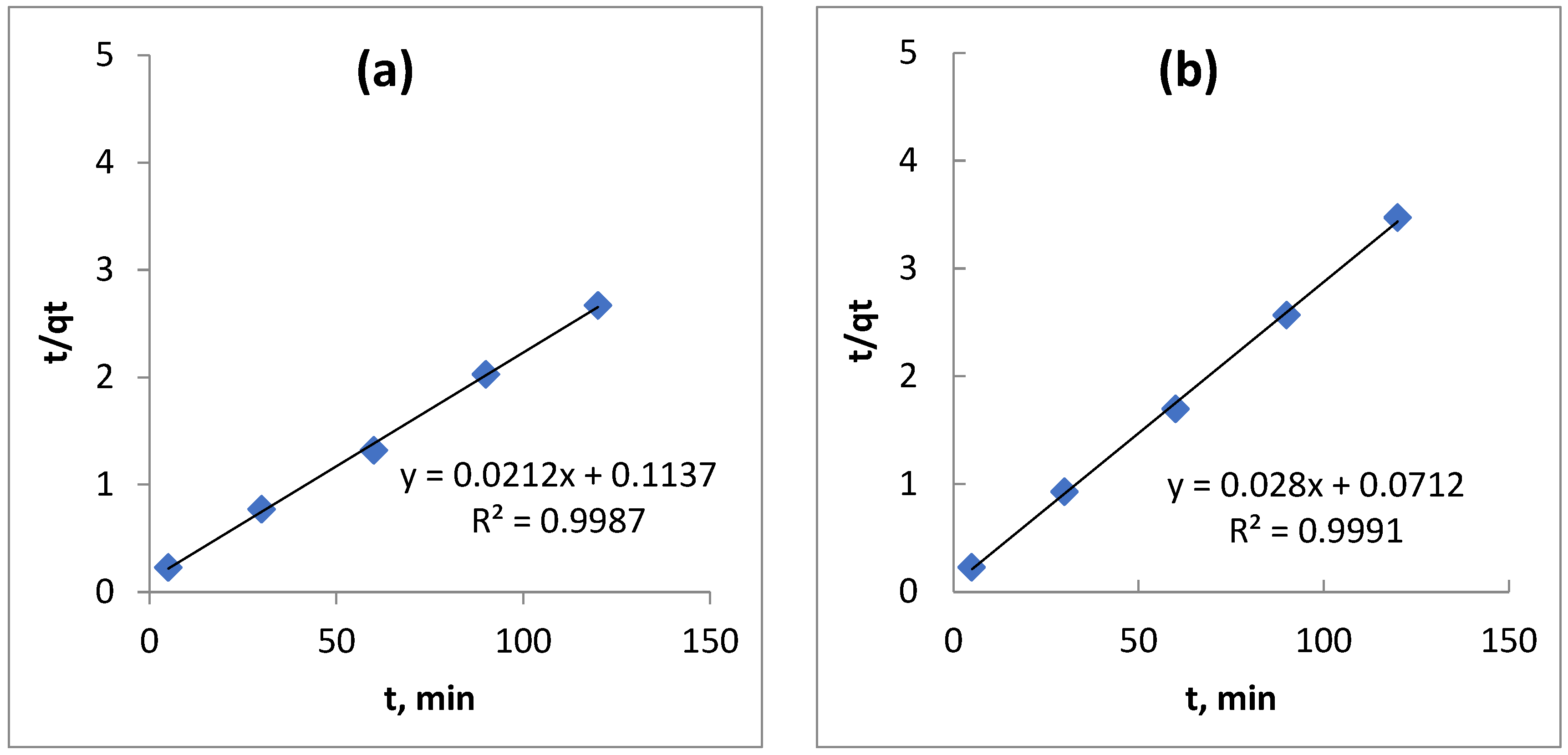
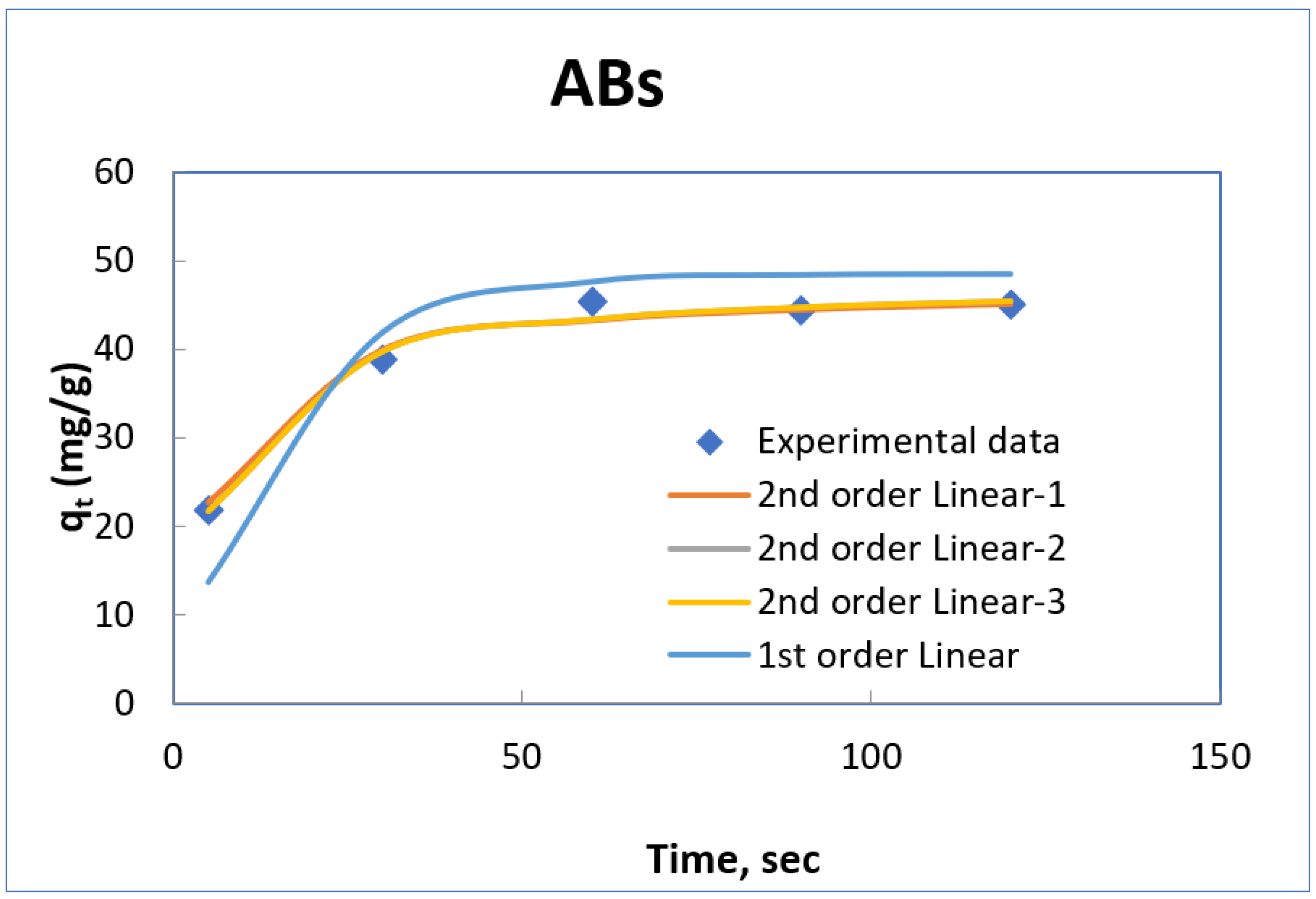
3.7. Adsorption Kinetic Study
3.8. BET Analsysis
3.9. Regeneration of Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sulyman, M.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Haponiuk, J.; Zalewski, S. New Approach for Adsorptive Removal of Oil in Wastewater using Textile Fibers as Alternative Adsorbent. Acta Sci. Agric. 2018, 2, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Hasmady, S.; Akhiar, A.; Ideris, F.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Mofijur, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Mahlia, T.M.I. A comprehensive review on anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, K.; Geed, S.R.; Mohanty, K. Chapter 23 - Hybrid biological processes for the treatment of oily wastewater. In Advances in Oil-Water Separation; Das, P., Manna, S., Pandey, J.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 423–435. [Google Scholar]
- Cisterna-Osorio, P.; Arancibia-Avila, P. Comparison of Biodegradation of Fats and Oils by Activated Sludge on Experimental and Real Scales. Water 2019, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherhan, B.Y.; Abbas, A.D.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Abbas, T.K.; Mahdi, y.M.; Kareem, N.A.A.; Rashad, A.A.; Rashad, Z.W.; Shawkat, A.A. Produced Water Treatment Using Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration Membranes. Al-Khwarizmi Eng. J. 2016, 12, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alsulaili, A.D.F.; Asmaa, M. Oil removal from produced water by agriculture waste adsorbents. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2020, 25, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zuhairi, F.K.; Azeez, R.; Mahdi, S.A.; Kadhim, W.A.; Al-Naamee, M.K. Removal oil from produced water by using adsorption method with adsorbent a Papyrus reeds. Eng. Technol. J. 2019, 37, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa El-Din, G.; Amer, A.A.; Malsh, G.; Hussein, M. Study on the use of banana peels for oil spill removal. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, Z.H.; Naife, T.M. Demulsification of Water in Iraqi Crude Oil Emulsion. J. Eng. 2019, 25, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonte, V.; Prisciandaro, M.; Mascis, L.; Di Paola, L.; Barba, D. Reverse osmosis membranes for treatment of produced water: A process analysis. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Goh, P.S.; Abdul Karim, Z.; Ismail, A.F. Thin Film Composite Membrane for Oily Waste Water Treatment: Recent Advances and Challenges. Membranes 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, S.; Andreozzi, M.; Micó, M.M.; Álvarez, M.G.; Contreras, S. Produced water treatment by advanced oxidation processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, M.; Loudiyi, K.; Bellemharbet, K.; Djabbour, N. Electro-Coagulation Treatment and De-oiling of Wastewaters Arising from Petroleum Industries. J. Pet. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Ladner, D.A.; Popat, S.C. Electrocoagulation-electroflotation for primary treatment of animal rendering wastewater to enable recovery of fats. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remedhan, S.T. Experimental Investigation of Thermodynamics, Kinetics, and Equilibrium of Nickel Ion Removal from Wastewater Using Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as the Adsorbent. Eng. Technol. J. 2020, 38, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, S. Approach of Cost-Effective Adsorbents for Oil Removal from Oily Water. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1916–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansel, B.; Pascual, B. Removal of emulsified fuel oils from brackish and pond water by dissolved air flotation with and without polyelectrolyte use: Pilot-scale investigation for estuarine and near shore applications. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyu, U.M.; El-Nafaty, U.A.; Muhammad, I.M. Oil removal from crude oil polluted water using banana peel as sorbent in a packed column. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, I.M.; El-Nafaty, U.A.; Surajudeen, A.; Makarfi, Y.I. Oil Removal from Produced Water Using Surfactant Modified Eggshell. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Environmental, Energy and Biotechnology (ICEEB 2015), Madrid, Spain, 15–16 June 2015; pp. 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Sidik, S.M.; Jalil, A.A.; Triwahyono, S.; Adam, S.H.; Satar, M.A.H.; Hameed, B.H. Modified oil palm leaves adsorbent with enhanced hydrophobicity for crude oil removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutfee, T. Removal of Phenol From Aqueous Solution By Agriculture Waste. Eng. Technol. J. 2010, 28, 5938–5955. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin Daniel, A.; Zahir, E.; Asghar, M.A. On the practicability of a new bio sorbent: Lasani sawdust and coconut coir for cleanup of oil spilled on water. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 37, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwuka, J.C.; Agbaji, E.B.; Ajibola, V.O.; Okibe, F.G. Treatment of crude oil-contaminated water with chemically modified natural fiber. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pon-On, W.; Suntornsaratoon, P.; Charoenphandhu, N.; Thongbunchoo, J.; Krishnamra, N.; Tang, I.M. Hydroxyapatite from fish scale for potential use as bone scaffold or regenerative material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyanar, C.B.; Marimuthu, K.; Gayathri, B.; Sankarrajan. Characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of fish scale and seashell derived nano-hydroxyapatite high-density polyethylene composite. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 1534–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaii, A.; Abdollahi Fard, M. Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum. ISRN Pharm. 2012, 2012, 510795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Vishal, M.K.; Vishwakarma, R.K. Moisture Dependent Physical Properties of Anise Seeds. Int. J. Food Process. Technol. 2015, 2, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Katime, I.; Parada, L.; Meaurio, E.; Cesteros, L. Recent research developments in hydrogen bonding in polymer blends by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and calorimetry. Recent Res. Devel. Polym. Sci. 1997, 1, 91–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, M.D.; Muhammed, I.B.; Obayomi, K.S.; Olugbenga, A.G.; Abdullahi, U.B. Optimization of fixed bed column process for removal of Fe(II) and Pb(II) ions from thermal power plant effluent using NaoH-rice husk ash and Spirogyra. Sci. Afr. 2020, 10, e00649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, N.; Ibrahim, N.; Hamid, M.K.A.; Hasbullah, H.; Ali, R.R.; Sadikin, A.N.; Asli, U.A. Thermogravimetric analysis of rice husk and coconut pulp for potential biofuel production by flash pyrolysis. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2014, 18, 705–710. [Google Scholar]
- Jansson, I.; García-García, F.J.; Sánchez, B.; Suárez, S. Key factors to develop hybrid photoactive materials based on mesoporous carbon/TiO2 for removal of volatile organic compounds in air streams. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 623, 118281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didar, Z. Removal of impurities from waste oil using eggshell and its active carbon. J. Adv. Environ. Health Res. 2017, 5, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Ramalingam, S.; Senthamarai, C.; Niranjanaa, M.; Vijayalakshmi, P.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination 2010, 261, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okiel, K.; El-Sayed, M.; El-Kady, M.Y. Treatment of oil–water emulsions by adsorption onto activated carbon, bentonite and deposited carbon. Egypt. J. Pet. 2011, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husin, N.I.; Wahab, N.A.A.; Isa, N.; Boudville, R. Sorption Equilibrium and Kinetics of Oil from Aqueous Solution Using Banana Pseudostem Fibers. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation (ICEII 2011), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–5 June 2011; pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Podder, M.S.; Majumder, C.B. Bacteria immobilization on neem leaves/MnFe2O4 composite surface for removal of As(III) and As(V) from wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3263–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Sher, F.; Guleria, A.; Saeb, M.R.; Anastopoulos, I.; Tran, H.N.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A. Is one performing the treatment data of adsorption kinetics correctly? J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Chao, H.-P. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review. Water Res. 2017, 120, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sumathi, S.; Hameed, B.H. Chitosan: A Natural Biopolymer for the Adsorption of Residue Oil from Oily Wastewater. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2004, 22, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omorogie, M.O.; Babalola, J.O.; Unuabonah, E.I. Regeneration strategies for spent solid matrices used in adsorption of organic pollutants from surface water: A critical review. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 518–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, S.-H.; Fahmi, M.R.; Abidin, C.Z.A.; Ong, S.-A.; Ibrahim, N. Regeneration of spent activated carbon from industrial application by NaOH solution and hot water. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 29137–29142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Wavenumber cm−1 | Wavenumber Range cm−1 | Vibration | Functional Group Present | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | |||
| 3305.6 | 3268.89 | 3200–2500 | O-H Stretching | Alcohol, phenols, Carboxylic acid |
| 3078.05 | 3078.07 | |||
| 2929.82 | 2923.33 | 2850–3000 | C-H Stretching | Alkenes |
| 2858.09 | 2853.36 | |||
| 1631.90 | 1630.25 | 1550–1650 | C=C Stretching | AromatiAB |
| 1519.45 | 1528.45 | 1475–1550 | N-O asymmetric stretching | Nitro compounds |
| 1446.45 | 1449.59 | 1400–1500 | C-C Stretching | AromatiAB |
| 1334.22 | 1332.69 | 1290–1400 | N-O Stretching | Nitro compounds |
| 1235.78 | 138.34 | 1000–1320 | C-O Stretching | Alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, ethers |
| 1156.56 | 1164.31 | 1150–1300 | C-H wag (-CH2X) Stretching | Alkyl halides |
| 1081.96 | 1080.30 | 1250–1020 | C-N Stretching | Aliphatic amines |
| 1028.30 | 1031.79 | |||
| 874.36 | 876.00 | 910–665 | N-H wag Stretching | Primary, and secondary amines |
| Wavenumber cm−1 | Wavenumber Range cm−1 | Vibration | Group Present | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | |||
| 3341.53 | 3313.51 | 3200–3500 | O-H stretching, H bond | Alcohol, phenols |
| 2923.48 | 2923.23 | 2850–3000 | C-H stretching | Alkanes |
| 2853.32 | 2853.16 | |||
| 1744.79 | 1741.90 | 1690–1760 | C=O stretching | Carbonyl, carboxylic acid |
| 1643.15 | 1633.18 | 1630–1680 | C=O stretching | Amides |
| 1511.49 | 1512.14 | 1475–1550 | N-O symmetric stretching | Nitro compounds |
| 1456.41 | 1454.96 | 1450–1470 | C-H bending | Alkanes |
| 1376.5 | 1373.82 | 1290–1400 | N-O stretching | Nitro compounds |
| 1318.92 | 1316.08 | 1000–1320 | C-O stretching | Alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, ethers |
| 1244.64 | 1245.47 | 1150–1300 m | C-H wag (-CH2X) | Alkyl halides |
| 1146.18 | 1146.58 | 1250–1020 | C-N stretching | Aliphatic amines |
| 1032.78 | 1026.87 | 1250–1020 | C-N stretching | Aliphatic amine |
| 721.70 | 780.08 | 910–665 | N-H wag Stretching | Primary, secondary amines |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | %Removal | qe (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Textile fiber (TF) | Oil | 95.2 | 4400 | [1] |
| Walnut shells and date pits | Oil | 80 and 87 | - | [6] |
| Papyrus reed | Oil | 94.5 | 229.726 | [6] |
| Banana peel | Oil | 97.45 | [18] | |
| Eggshell | Oil | 100 | 108.69 | [19] |
| Modified oil palm leaves (OPL) | Oil | - | 1176 | [20] |
| Sawdust | Oil | - | 1282 | [22] |
| Coconut coir | Oil | - | 360 | [22] |
| Anise residues | Oil | 70 | 30 | Present work |
| Animal bone | Oil | 94 | 45 | Present work |
| Adsorbents | Isotherm Model | Isotherm Parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Unit | Values | |||
| ABs | Langmuir | Linear-1 | qm | mg/g | 48.0769 |
| KL | L/mg | 0.0244 | |||
| R2 | ------- | 0.9983 | |||
| MPSD | ------- | 3.2762 | |||
| Linear-2 | qm | mg/g | 46.5116 | ||
| KL | L/mg | 0.0267 | |||
| R2 | ------- | 0.9920 | |||
| MPSD | ------- | 4.0258 | |||
| Linear-3 | qm | mg/g | 47.121 | ||
| KL | L/mg | 0.0258 | |||
| R2 | ------- | 0.9752 | |||
| MPSD | ------- | 3.8978 | |||
| Freundlich | Kf | (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 5.9038 | ||
| n | -------- | 2.7064 | |||
| R2 | -------- | 0.9736 | |||
| MPSD | ------- | 5.3534 | |||
| ARs | Langmuir | Linear-1 | qm | mg/g | 29.4985 |
| KL | L/mg | 0.0071 | |||
| R2 | ----- | 0.9991 | |||
| MPSD | ----- | 1.7490 | |||
| Linear-2 | qm | mg/g | 29.1545 | ||
| KL | L/mg | 0.0073 | |||
| R2 | ----- | 0.9998 | |||
| MPSD | ----- | 1.4910 | |||
| Linear-3 | qm | mg/g | 29.395 | ||
| KL | L/mg | 0.0072 | |||
| R2 | ----- | 0.9988 | |||
| MPSD | ----- | 1.5277 | |||
| Freundlich | Kf | (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 1.3464 | ||
| n | ----- | 2.1450 | |||
| R2 | ----- | 0.9797 | |||
| MPSD | ----- | 8.7582 | |||
| RL Value | Adsorption Nature |
|---|---|
| RL > 1 | Unfavourable |
| RL = 1 | Linear |
| 0 < RL < 1 | Favourable |
| RL = 0 | Irreversible |
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | qe mg/g | k1 min−1 | R2 | qe mg/g | k2 mg/g.min | R2 |
| ABs | 48.5400 | 0.0666 | 0.9045 | 47.1698 | 0.00395 | 0.9987 |
| ARs | 29.4239 | 0.0765 | 0.9558 | 35.4610 | 0.0112 | 0.9992 |
| Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbent | qe mg/g | k2 mg/g.min | R2 | |
| ABs | Linear-1 | 47.1698 | 0.00395 | 0.9987 |
| Linear-2 | 47.6190 | 0.00352 | 0.9965 | |
| Linear-3 | 47.751 | 0.00349 | 0.9861 | |
| ARs | Linear-1 | 35.7143 | 0.0112 | 0.9992 |
| Linear-2 | 36.2319 | 0.00829 | 0.9995 | |
| Linear-3 | 36.169 | 0.0083 | 0.9861 | |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area (Micropore Surface Area), m2/g | Pore Volume (Micropore Volume), cm3/ g | Pore Size (nm) | Particle Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anise Residue (AR) | ---- | 0.00115 | ------ | 0.6 |
| Animal Bond (AB) | 5.5389 | 0.005477 | 3.95534 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Najar, J.A.; Al-Humairi, S.T.; Lutfee, T.; Balakrishnan, D.; Veza, I.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Fattah, I.M.R. Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water. Water 2023, 15, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061186
Al-Najar JA, Al-Humairi ST, Lutfee T, Balakrishnan D, Veza I, Soudagar MEM, Fattah IMR. Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water. Water. 2023; 15(6):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061186
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Najar, Jenan A., Shurooq Talib Al-Humairi, Tagreed Lutfee, Deepanraj Balakrishnan, Ibham Veza, Manzoore Elahi M. Soudagar, and Islam M. R. Fattah. 2023. "Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water" Water 15, no. 6: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061186
APA StyleAl-Najar, J. A., Al-Humairi, S. T., Lutfee, T., Balakrishnan, D., Veza, I., Soudagar, M. E. M., & Fattah, I. M. R. (2023). Cost-Effective Natural Adsorbents for Remediation of Oil-Contaminated Water. Water, 15(6), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061186










