Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
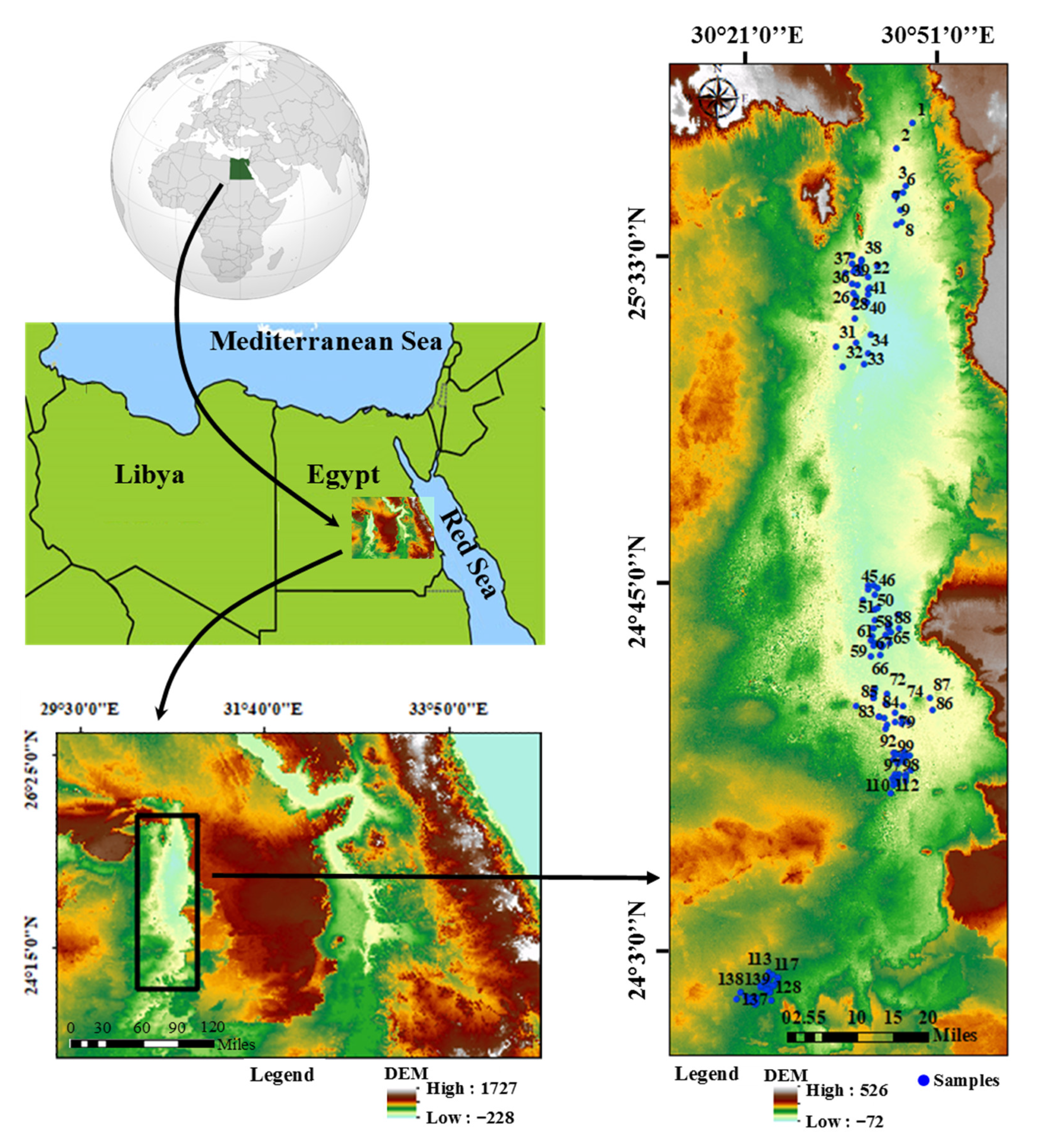
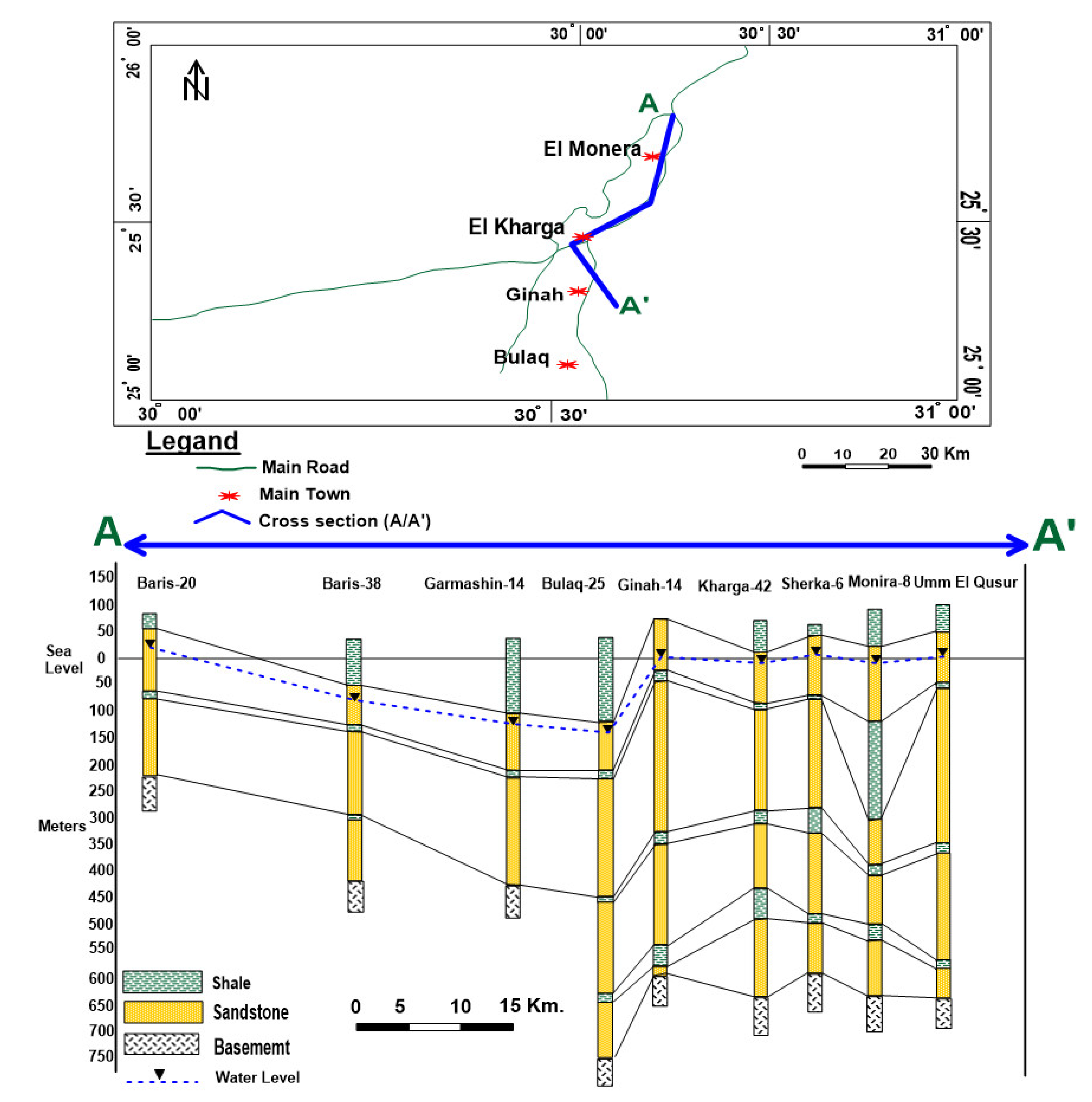
2.1. Description of the Site and Hydrogeological Characteristics
2.2. Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.3. Multivariate Statistical Methods and Data Treatments
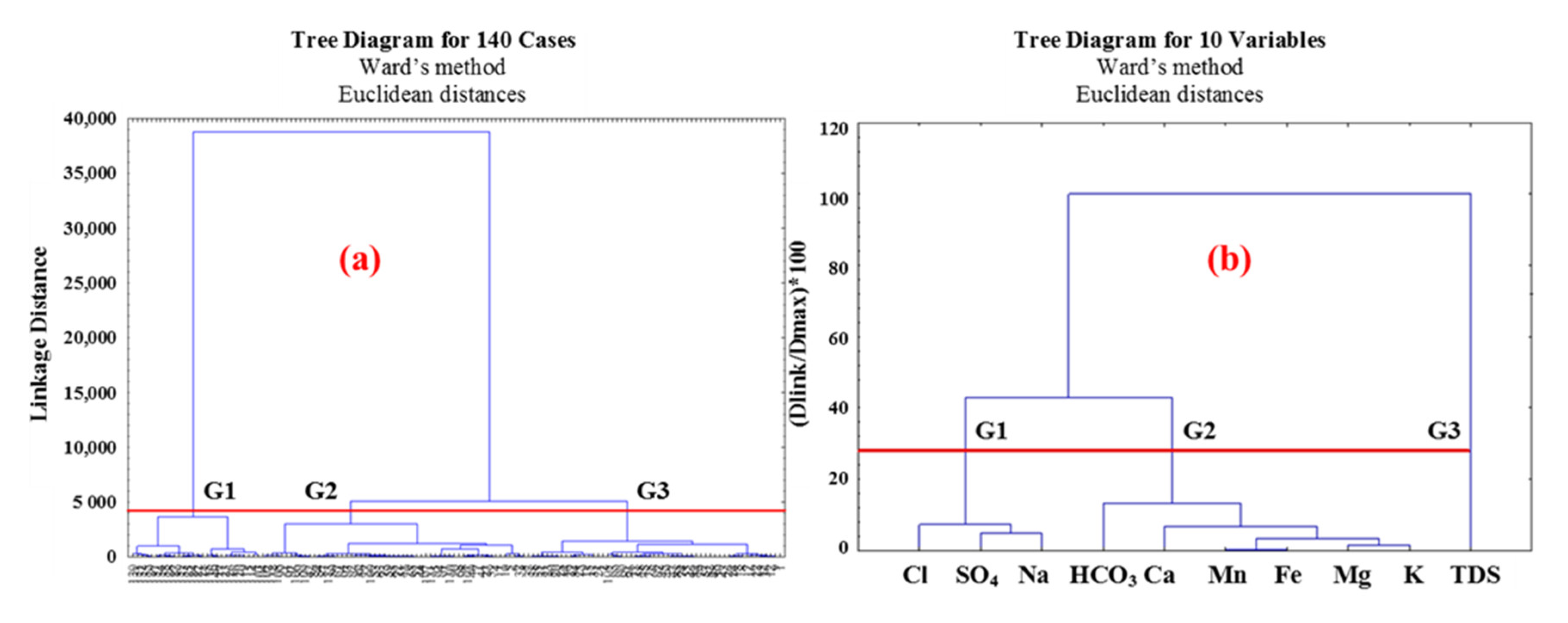
2.3.1. Cluster Analysis (CA)
2.3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.4. Indexing Approach
2.4.1. Drinking Water Quality Index (DWQI)
2.4.2. Health Risk Assessment Indices
Chronic Daily Intake (CDI)
Hazard Index (HI)
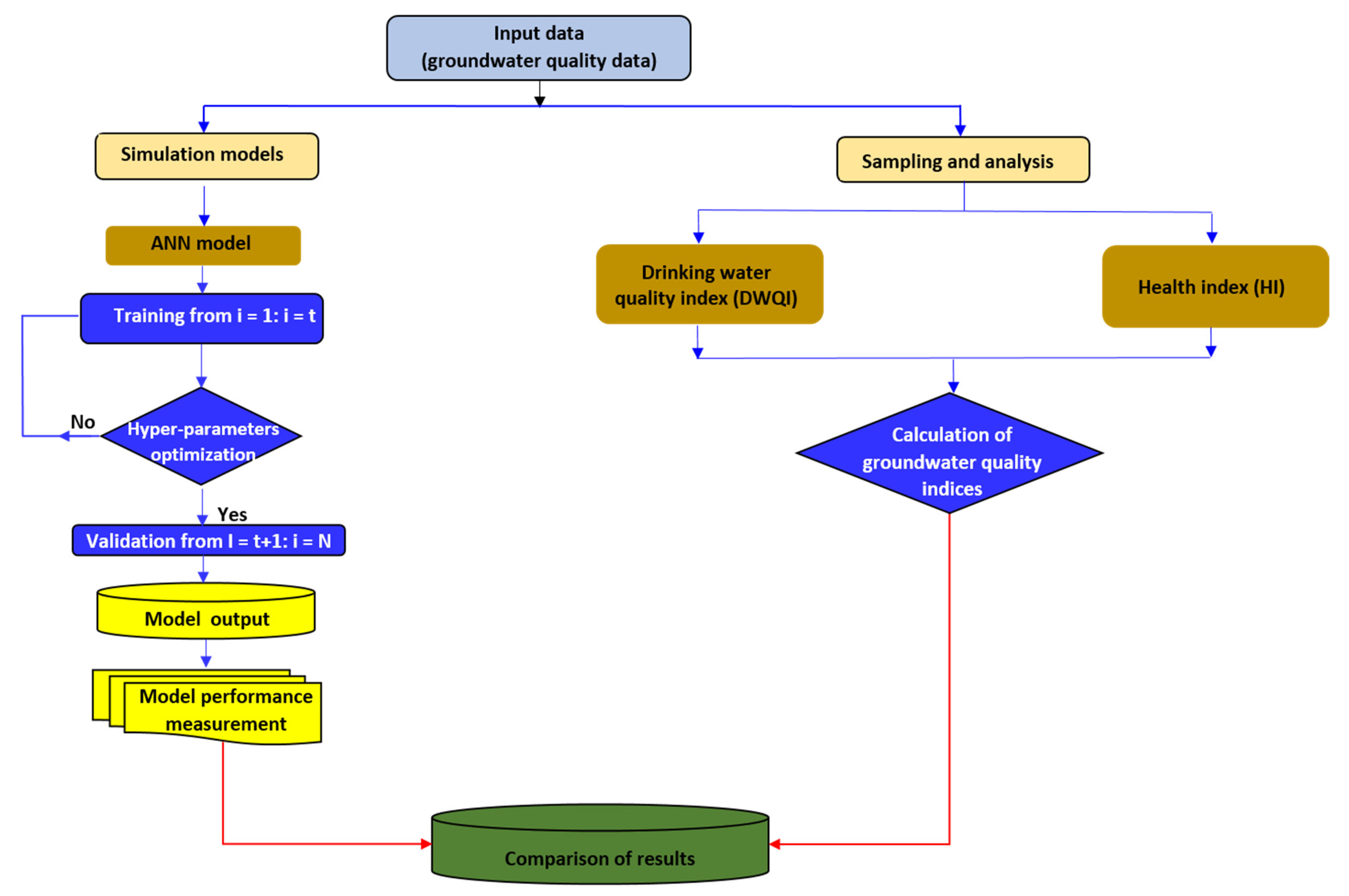
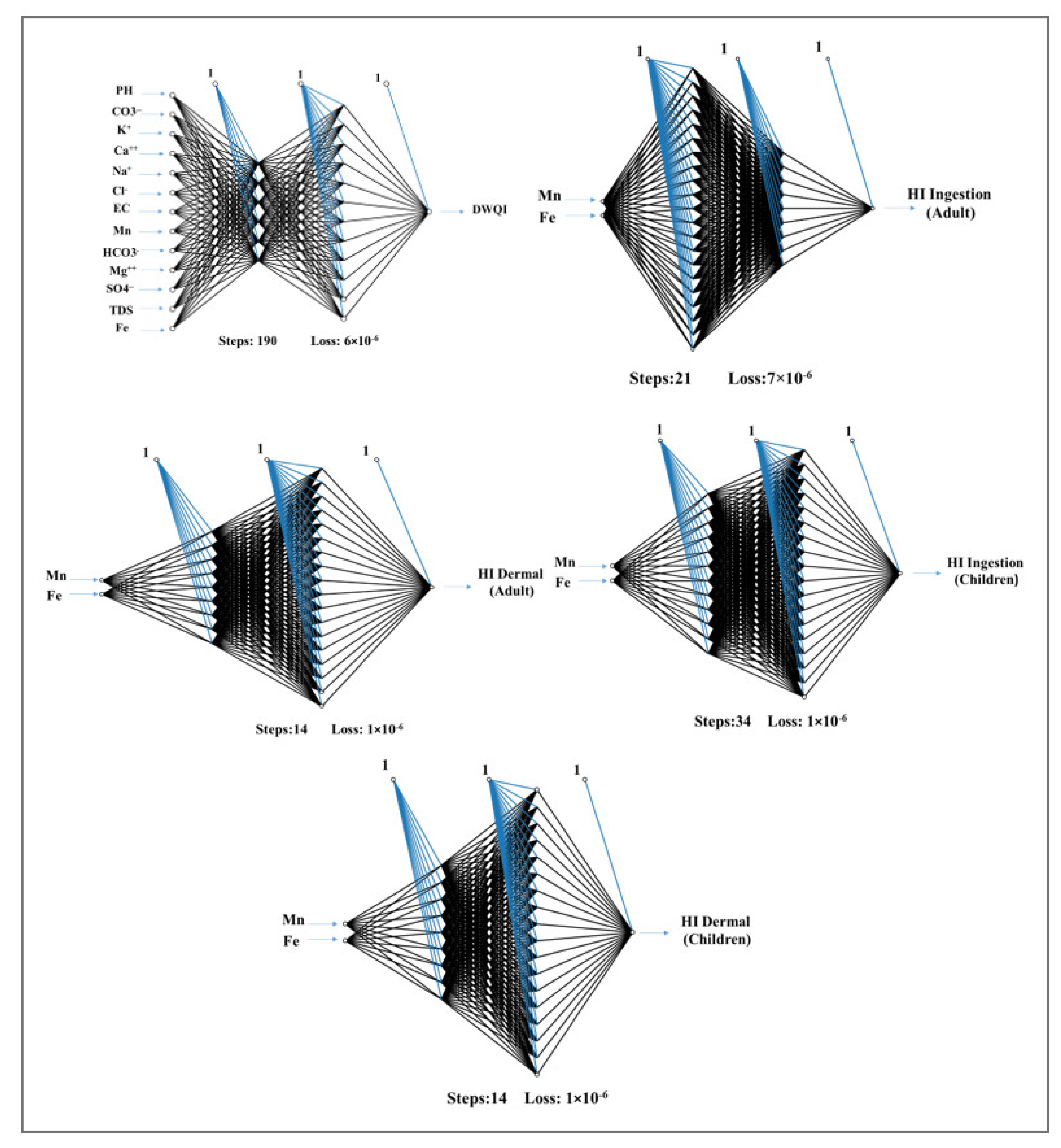
2.5. Back-Propagation Neural Network (BPNN)
Model Evaluation
- Root-mean-square error
- Coefficient of determination
2.6. Software and Datasets Used for Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Parameters
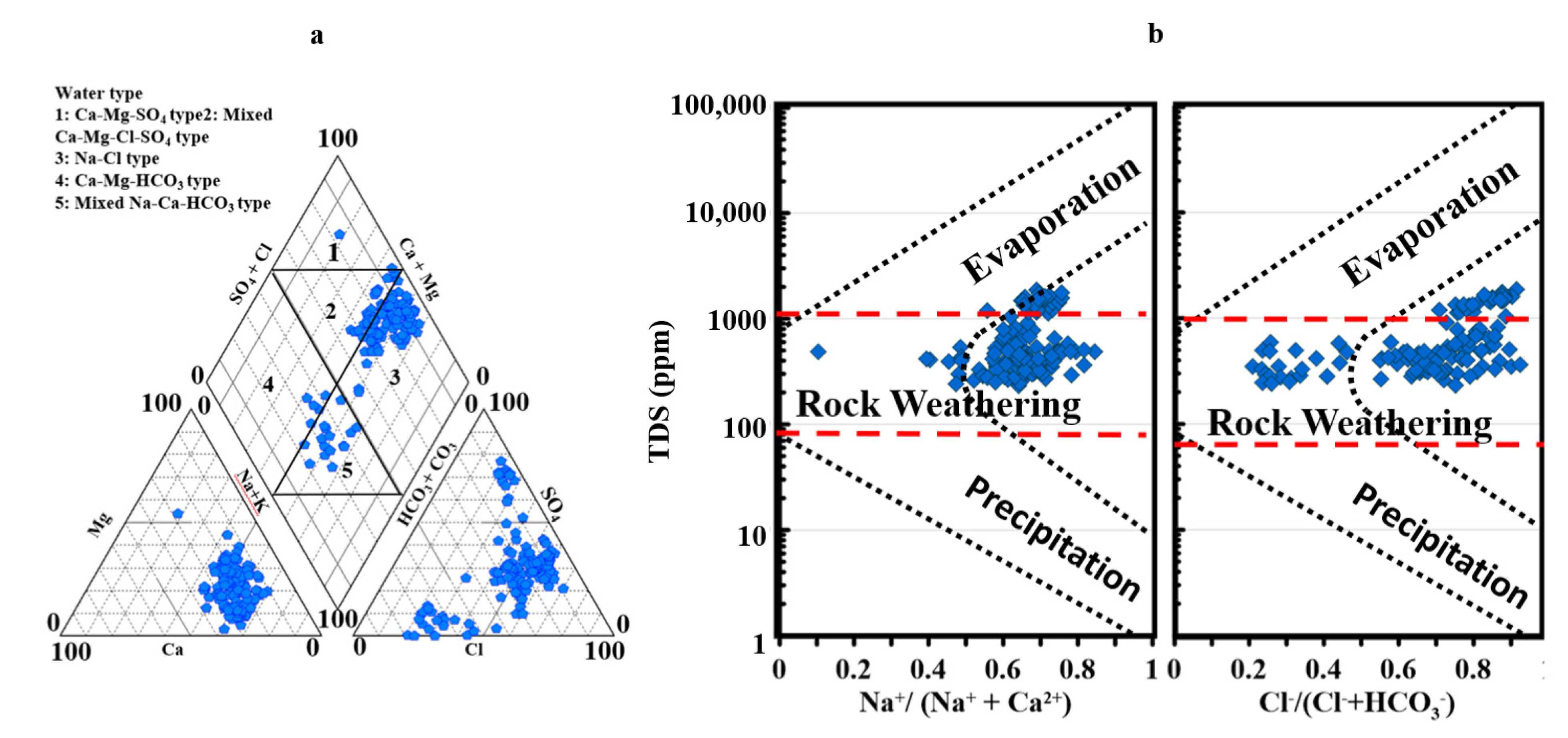
3.2. Geochemical Processes That Control GW Facies
3.3. Statistical Analysis
3.3.1. Cluster Analysis
3.3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
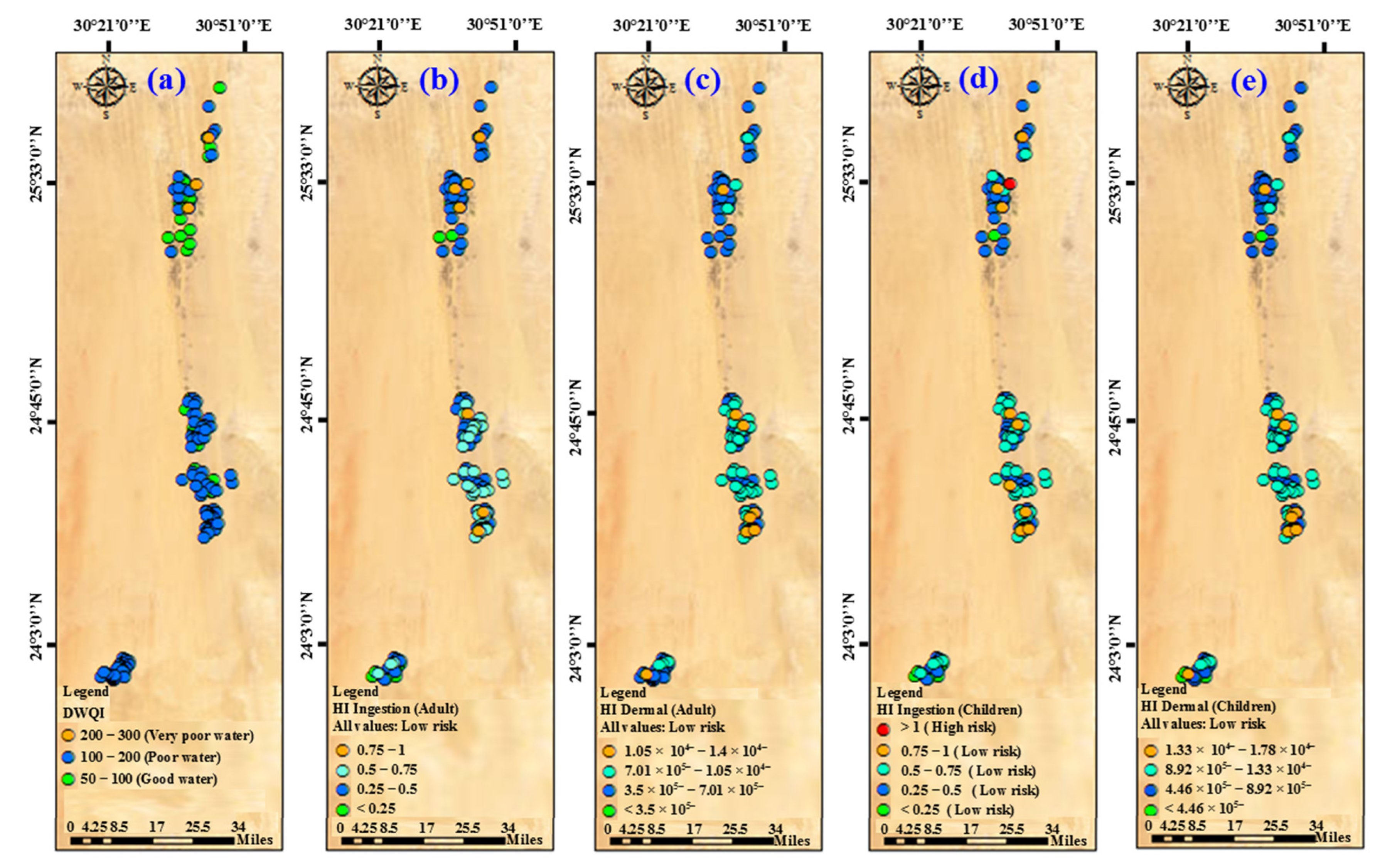
3.4. Water Quality Indices (WQIs)
3.5. Assessing Health Risk
3.6. The Performance of ANN to Predict Drinking Water Quality and Health Risk
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Gao, M.; Jin, D.; Wang, T.; Yang, J. Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Human Health Risk in the Aeolian-Sand Area of Yulin City, Northwest China. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snousy, M.G.; Wu, J.; Su, F.; Abdelhalim, A.; Ismail, E. Groundwater Quality and Its Regulating Geochemical Processes in Assiut Province, Egypt. Expo. Health 2022, 14, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P. To Make the Water Safer. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, M.T.B.; Alraggad, M.; Harahsheh, S.T. The Water Crisis and the Conflict in the Middle East. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Qiu, J.; Li, F.-F. Hybrid Models Combining EMD/EEMD and ARIMA for Long-Term Streamflow Forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Han, G. Distributions and Source Identification of the Major Ions in Zhujiang River, Southwest China: Examining the Relationships Between Human Perturbations, Chemical Weathering, Water Quality and Health Risk. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesari, T.; Roy, A.; Pant, D.; Sinha, U.K.; Kumar, P.V.N.; Rao, L.V. Major Ion, Trace Metal and Environmental Isotope Characterization of Groundwater in Selected Parts of Uddanam Coastal Region, Andhra Pradesh, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katla, S.; Gugulothu, S.; Dhakate, R. Spatial Assessment of Major Ion Geochemistry in the Groundwater around Suryapet Region, Southern Telangana, India. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, N.A.; Salem, Z.E.-S.; Ghorab, M.A.; Soliman, S.A.; Abdeldayem, A.L.; Moustafa, Y.M.; Ghazala, H.H. Evaluation of Groundwater Sensitivity to Pollution Using GIS-Based Modified DRASTIC-LU Model for Sustainable Development in the Nile Delta Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Dahab, K.; Ibrahim, H. Applying of a Geochemical Model on the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in Siwa Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.H.; Elbagory, M.; Tamma, A.A.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Hussein, H.; Moghanm, F.S.; Omara, A.E.-D.; Kovács, A.; Péter, S. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation in Deep Aquifers Using Multiple Graphical and Indexing Approaches Supported with Machine Learning Models and GIS Techniques, Souf Valley, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaagai, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Bencedira, S.; Hinge, G.; Athamena, A.; Haddam, S.; Gad, M.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Application of Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Approaches, and GIS to Identify Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Purposes: A Case Study of Sahara Aquifer, Doucen Plain, Algeria. Water 2023, 15, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; El Osta, M. Geochemical Controlling Mechanisms and Quality of the Groundwater Resources in El Fayoum Depression, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Scholz, M.; Ali, M.; Gad, M.; Elsayed, S.; Khadr, M.; Hussein, H.; Ibrahim, H.H.; Eid, M.H.; et al. Evaluation and Prediction of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation Using an Integrated Water Quality Indices, Machine Learning Models and GIS Approaches: A Representative Case Study. Water 2023, 15, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, T.; Szabó, G.; Bessenyei, É.; Karancsi, G.; Barkóczi, N.; Balla, D. The Effects of Uninsulated Sewage Tanks on Groundwater. A Case Study in an Eastern Hungarian Settlement. J. Water Land Dev. 2017, 33, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel-Galil, F.A.; Amro, M.A.; Abdel-Moniem, A.S.H.; El-Fandary, O.O. Population Fluctuations and Interspecific Competition between Tephritid Flies Attacking Fruit Crops in the New Valley Oases, Egypt. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2010, 43, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, E.G. Environmental Assessment Report for New Valley Governorate El Mounira and Naser El Thowra Villages, Kharga Oasis. 2007. Environmental Assessment Report. National Organization for Potable Water and Sanitary Drainage (NOPWASD). Available online: https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/Pnadj893.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- El Osta, M.; Hussein, H.; Tomas, K. Numerical Simulation of Groundwater Flow and Vulnerability in Wadi El-Natrun Depression and Vicinities, West Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.; Elhassan, B. Heavy Metals Pollution and Trend in the River Nile System. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2016, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Yang, W.; Nadine Ferrer, A.S.; Xiong, S.; Li, X.; Niu, G.; Lu, T. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Groundwater in Karst Areas of Southwest China: A Case Study of Bama, Guangxi. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 341, 130872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbo, J.N.; Isa, N.M.; Aris, A.Z.; Ramli, M.F.; Abubakar, M.B. Geochemometric Approach to Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals of Yankari Game Reserve and Its Environs, Northeast Nigeria. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, D.M.; Cherry, J.A. Groundwater Contamination: Pump-and-Treat Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, G.; West, L.J. Review of Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport Modelling Approaches for the Sherwood Sandstone Aquifer, UK; Insights from Analogous Successions Worldwide. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeol. 2022, 55, qjegh2021-176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; El-Hattab, M. Integration of Water Pollution Indices and DRASTIC Model for Assessment of Groundwater Quality in El Fayoum Depression, Western Desert, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 158, 103554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.; Dahab, K.; Ibrahim, H. Impact of Iron Concentration as a Result of Groundwater Exploitation on the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in El Kharga Oasis, Western Desert, Egypt. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2016, 5, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Sao, S. Evaluation of Water Quality by Physicochemical Parameters, Heavy Metal and Use of Metal Resistant Property of Bacteria for Bioremediation of Heavy Metals. World J. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 5, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Alqarawy, A.; El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance and Water Quality Indices to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking in Arid Regions, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Alqarawy, A.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Using Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling in Makkah Al-Mukarramah Province, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieszynska, M.; Wesolowski, M.; Bartoszewicz, M.; Michalska, M.; Nowacki, J. Application of Physicochemical Data for Water-Quality Assessment of Watercourses in the Gdansk Municipality (South Baltic Coast). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2017–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farid, S.; Baloch, M.K.; Ahmad, S.A. Water Pollution: Major Issue in Urban Areas. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2012, 4, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sadashivaiah, C.; Ramakrishnaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Hydrochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Groundwater Quality in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadr, M.; Gad, M.; El-Hendawy, S.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Dewir, Y.H.; Tahir, M.U.; Mubushar, M.; Elsayed, S. The Integration of Multivariate Statistical Approaches, Hyperspectral Reflectance, and Data-Driven Modeling for Assessing the Quality and Suitability of Groundwater for Irrigation. Water 2020, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batarseh, M.; Imreizeeq, E.; Tilev, S.; Al Alaween, M.; Suleiman, W.; Al Remeithi, A.M.; Al Tamimi, M.K.; Al Alawneh, M. Assessment of Groundwater Quality for Irrigation in the Arid Regions Using Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) and GIS-Zoning Maps: Case Study from Abu Dhabi Emirate, UAE. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 14, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Volume 1, ISBN 92-4-154638-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Levy, D.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; LoIacono, N.J.; et al. Water Manganese Exposure and Children’s Intellectual Function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kell, D.B. Towards a Unifying, Systems Biology Understanding of Large-Scale Cellular Death and Destruction Caused by Poorly Liganded Iron: Parkinson’s, Huntington’s, Alzheimer’s, Prions, Bactericides, Chemical Toxicology and Others as Examples. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 825–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powers, K.M.; Smith-Weller, T.; Franklin, G.M.; Longstreth, W.T.; Swanson, P.D.; Checkoway, H. Parkinson’s Disease Risks Associated with Dietary Iron, Manganese, and Other Nutrient Intakes. Neurology 2003, 60, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, A.S.; Jahin, H.S. Combinations of multivariate statistical analysis and analytical hierarchical process for indexing surface water quality under arid conditions. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 248, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athamena, A.; Gaagai, A.; Aouissi, H.A.; Burlakovs, J.; Bencedira, S.; Zekker, I.; Krauklis, A.E. Chemometrics of the Environment: Hydrochemical Characterization of Groundwater in Lioua Plain (North Africa) Using Time Series and Multivariate Statistical Analysis. Sustainability 2023, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubil, A.; El Ouali, A.; Bülbül, A.; Lahrach, A.; Mudry, J.; Mamouch, Y.; Essahlaoui, A.; El Hmaidi, A.; El Ouali, A. Groundwater Hydrochemical and Isotopic Evolution from High Atlas Jurassic Limestones to Errachidia Cretaceous Basin (Southeastern Morocco). Water 2022, 14, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaagai, A.; Boudoukha, A.; Boumezbeur, A.; Benaabidate, L. Hydrochemical Characterization of Surface Water in the Babar Watershed (Algeria) Using Environmetric Techniques and Time Series Analysis. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2017, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, N.H.; Duarte-Mermoud, M.A.; Soto Vicencio, V.A.; Salah, S.A.; Bustos, M.A. Chilean Wine Classification Using Volatile Organic Compounds Data Obtained with a Fast GC Analyzer. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2008, 57, 2421–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guyon, I.; Elisseeff, A. An Introduction to Variable and Feature Selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 1157–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, F.H.; Wolf, H.; Jansen, H.W.; van der Veer, P. Applications of Artificial Neural Networks in Integrated Water Management: Fiction or Future? Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 52, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ElMasry, G.; Sun, D.-W.; Allen, P. Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging for Predicting Colour, PH and Tenderness of Fresh Beef. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.-L.; Kneib, T.; Augustin, T.; Zeileis, A. Conditional Variable Importance for Random Forests. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glorfeld, L. A Methodology for Simplification and Interpretation of Backpropagation-Based Neural Network Models. Expert Syst. Appl. 1996, 10, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, G.; Dyer, C.; Blunsom, P. On the State of the Art of Evaluation in Neural Language Models. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J.; Yamins, D.; Cox, D. Making a Science of Model Search: Hyperparameter Optimization in Hundreds of Dimensions for Vision Architectures. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; Dasgupta, S., McAllester, D., Eds.; PMLR: Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. Volume 28, pp. 115–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, L.-D.; Lei, H.; Deng, S.-H. Hyperparameter Optimization for Machine Learning Models Based on Bayesian Optimization. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2019, 17, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Assaad, F.A. Hydrogeological Aspects and Environmental Concerns of the New Valley Project, Western Desert, Egypt, with Special Emphasis on the Southern Area. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1988, 12, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, H.; Bornkamm, R. Landscape Ecology and Vegetation Units of the Western Desert of Egypt. Catena. Suppl. 1993, Num. 26, pp. 155–178; Illustration; ref. 84 ref. ISSN 0722-0723. Available online: https://pascal-francis.inist.fr/vibad/index.php?action=getRecordDetail&idt=6318102 (accessed on 7 March 2023).
- Salman, A.B.; Howari, F.M.; El-Sankary, M.M.; Wali, A.M.; Saleh, M.M. Environmental Impact and Natural Hazards on Kharga Oasis Monumental Sites, Western Desert of Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoreaux, P.E.; Memon, B.A.; Idris, H. Groundwater Development, Kharga Oases, Western Desert of Egypt: A Long-Term Environmental Concern. Environ. Geol. Water Sci. 1985, 7, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewa, H.H.; Fathy, R.G.; Qaddah, A.A. The Contribution of Geographic Information Systems and Remote Sensing in Determining Priority Areas for Hydrogeological Development, Darb El-Arbain Area, Western Desert, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Rawy, M.; De Smedt, F. Estimation and Mapping of the Transmissivity of the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer in the Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2020, 12, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fathy, R.G.; El Nagaty, M.; Atef, A.; El Gammal, N. Contributions to the Hydrogeological and Hydrochemical Characteristics of Nubia Sandstone Aquifer in Darb Al-Arbeain, South Western Desert, Egypt. Al-Azhar. Bull. Sci. 2002, 13, 69–100. [Google Scholar]
- El Saeed, G.H.; Abdelmageed, N.B.; Riad, P.; Komy, M. Confined aquifer piezometric head depletion in the dynamic state. Jokull 2019, 69, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gummadi, S.; Swarnalatha, G.; Vishnuvardhan, Z.; Harika, D. Statistical Analysis of the Groundwater Samples from Bapatla Mandal, Guntur District, Andhra Pradesh, India. IOSR J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. Food Technol. 2014, 8, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuş, C.B. Evaluation of Water Quality of Kızılırmak River (Sivas/Turkey) Using Geo-Statistical and Multivariable Statistical Approaches. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 4735–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkat, A.; Bouaicha, F.; Bouteraa, O.; Mester, T.; Ata, B.; Balla, D.; Rahal, Z.; Szabó, G. Assessment of Complex Terminal Groundwater Aquifer for Different Use of Oued Souf Valley (Algeria) Using Multivariate Statistical Methods, Geostatistical Modeling, and Water Quality Index. Water 2021, 13, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yu, S.; Ma, T.; Ding, J.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, G. Modeling the Water and Nitrogen Management Practices in Paddy Fields with HYDRUS-1D. Agriculture 2022, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-C.; Choi, H.; Lee, M.-G.; Kim, S.-H.; Im, J.-K. Identification and Apportionment of Potential Pollution Sources Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and APCS-MLR Model to Assess Surface Water Quality in Imjin River Watershed, South Korea. Water 2022, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chounlamany, V.; Tanchuling, M.A.; Inoue, T. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Water Quality of a Segment of Marikina River Using Multivariate Statistical Methods. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, C.R.; Nayak, S.K. Assessment of Seasonal Variations in Water Quality of Brahmani River Using PCA. Adv. Environ. Res. 2017, 6, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H. Hydrochemical Characterization of Drinking Groundwater with Special Reference to Fluoride in an Arid Area of China and the Control of Aquifer Leakage on Its Concentrations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 8575–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Shang, J.; Zhao, J.; Guo, H. Factor Analysis and Dynamics of Water Quality of the Songhua River, Northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2003, 144, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, F.B.; Yarnold, P.R. Principal-Components Analysis and Exploratory and Confirmatory Factor Analysis. In Reading and Understanding Multivariate Statistics; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, V.B.B.; Pinto, S.M.; Govindaraju, T.; Hebbalu, V.S.; Bhat, V.; Kannanur, L.N. Multivariate Statistics and Water Quality Index (WQI) Approach for Geochemical Assessment of Groundwater Quality—A Case Study of Kanavi Halla Sub-Basin, Belagavi, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 2667–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.M.; McClelland, N.I.; Deininger, R.A.; Tozer, R.G. A Water Quality Index-Do We Dare. Water Sew. Work. 1970, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Human Health Risk Assessment via Drinking Water Pathway Due to Metal Contamination in the Groundwater of Subarnarekha River Basin, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.K.; Kumar, B. Pathways of Heavy Metals Contamination and Associated Human Health Risk in Ajay River Basin, India. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Sarkar, S.K.; Raja, P.; Biswas, J.K.; Murugan, K. Dissolved Trace Elements in Hooghly (Ganges) River Estuary, India: Risk Assessment and Implications for Management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhao, D.Y.; Jia, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, S.P. Preliminary Risk Assessment of Trace Metal Pollution in Surface Water from Yangtze River in Nanjing Section, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 82, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial Metal Pollution in Water and Probabilistic Assessment of Human Health Risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N. Spatial Distribution, Exposure, and Potential Health Risk Assessment from Nitrate in Drinking Water from Semi-Arid Region of South India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 26, 310–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part E, Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment); USEPA/540/R/99; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- NSCEP. Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; Volume 12, pp. 1–187. [Google Scholar]
- Exposure Factors Handbook—Front Matter; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Kopylev, L.; Kadry, A.-R. Approaches to Cancer Assessment in EPA’s Integrated Risk Information System. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2011, 254, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Schalkoff, R.J. Artificial Neural Networks; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-07-057118-X. [Google Scholar]
- Haykin, S. Self-Organizing Maps. In Neural Networks—A Comprehensive Foundation; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 443–483. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yoder, R.E.; Odhiambo, L.O.; Zhang, J. Simulation of Nitrate Distribution under Drip Irrigation Using Artificial Neural Networks. Irrig. Sci. 2004, 23, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, B.P.; Styc, Q.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Digital Soil Mapping of Soil Carbon at the Farm Scale: A Spatial Downscaling Approach in Consideration of Measured and Uncertain Data. Geoderma 2017, 290, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. Reference Evapotranspiration Estimation and Modeling of the Punjab Northern India Using Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, G. Mapping Forest Ecosystem Biomass Density for Xiangjiang River Basin by Combining Plot and Remote Sensing Data and Comparing Spatial Extrapolation Methods. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freeze, R.A.; Cherry, J. Physical Properties and Principles. Groundwater; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 14–79. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Trans. AGU 1944, 25, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeller, H. Geochemistry of Groundwater. In Groundwater Studies, an International Guide for Research and Practice; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1977; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Güler, C.; Thyne, G.D.; McCray, J.E.; Turner, K.A. Evaluation of Graphical and Multivariate Statistical Methods for Classification of Water Chemistry Data. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 455–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles and Practice of Numerical Classification; A Series of books in biology; W. H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973; ISBN 978-0-7167-0697-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mustapha, A.; Aris, A.Z.; Ramli, M.F.; Juahir, H. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Surface Water Quality in the Downstream Region of the Jakara River, North-Western Nigeria: A Statistical Approach. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2012, 47, 1551–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinge, G.; Bharali, B.; Baruah, A.; Sharma, A. Integrated Groundwater Quality Analysis Using Water Quality Index, GIS and Multivariate Technique: A Case Study of Guwahati City. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Ramanathan, A.L. Geochemical Assessment of GroundwaterQuality in Vicinity of Bhalswa Landfill, Delhi, India, Using Graphical and Multivariate Statistical Methods. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1509–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraiem, Z.; Zouari, K.; Chkir, N.; Agoune, A. Geochemical Characteristics of Arid Shallow Aquifers in Chott Djerid, South-Western Tunisia. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, O.; Zhou, L.; Feng, L.; Qiu, Z. Integration of Visible and Thermal Imagery with an Artificial Neural Network Approach for Robust Forecasting of Canopy Water Content in Rice. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Weight (wi) | WHO 2017 (mg/L) | Relative Weight (Wi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 3 | 8.5 | 0.076923077 |
| EC | 5 | 1500 | 0.128205128 |
| TDS | 5 | 500 | 0.128205128 |
| K+ | 2 | 12 | 0.051282051 |
| Na+ | 3 | 200 | 0.076923077 |
| Ca2+ | 2 | 50 | 0.051282051 |
| Mg2+ | 2 | 75 | 0.051282051 |
| Cl− | 3 | 250 | 0.076923077 |
| SO42− | 4 | 250 | 0.102564103 |
| HCO3− | 2 | 120 | 0.051282051 |
| CO32− | 2 | 350 | 0.051282051 |
| Fe | 2 | 0.3 | 0.051282051 |
| Mn | 4 | 0.1 | 0.102564103 |
| ∑wi = 39 | ∑Wi = 1 |
| Factors | Fe | Mn | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ingestion rate (IngR) | Child: 0.78 L/day | [76] | |
| Adult: 2.5 L/day | |||
| Exposure frequency (EF) | 350 days/year | [77] | |
| Exposure duration (ED) | Child: 6 years | [77] | |
| Adult: 30 years | |||
| Body weight (BW) | Child: 15 kg | [71] | |
| Adult: 52 kg | |||
| Average time (AT) | Child: 2190 day | [75] | |
| Adult: 10,950 days | |||
| Exposed skin area (SA) | Child: 0.66 m2 | [78] | |
| Adult: 1.8 m2 | |||
| Adherence factor (AF) | 0.07 | [78] | |
| Dermal absorption fraction (ABSd) | 0.03 | [78] | |
| Exposure time (ET) | 0.58 h/ day | [74] | |
| Conversion factor (CF) | 10−2 kg/mg | [79] | |
| Ingestion reference dose (RFD) | 0.7 | 0.024 | [79] |
| Dermal reference dose (RFD) | 0.14 | 96 × 10−5 | |
| Parameters | Unit | WHO (2017) | Min. | Max. | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp. | °C | - | 29.0 | 38.0 | 33.5 |
| pH | - | 8.5 | 6.10 | 8.10 | 6.99 |
| EC | μS/cm | 1500 | 214 | 2610 | 931.2 |
| TDS | mg/L | 500 | 203 | 1870 | 628.4 |
| K+ | mg/L | 12 | 3.50 | 53.00 | 25.51 |
| Na+ | mg/L | 200 | 4.00 | 460.0 | 115.23 |
| Mg2+ | mg/L | 75 | 1.45 | 68.10 | 21.9 |
| Ca2+ | mg/L | 50 | 8.00 | 180.0 | 48.14 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 250 | 23.25 | 620.0 | 175.53 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 250 | 0.06 | 575.0 | 143.47 |
| HCO3− | mg/L | 120 | 10.98 | 300.0 | 107.08 |
| CO32− | mg/L | 350 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Fe | mg/L | 0.3 | 0.12 | 10.0 | 2.27 |
| Mn | mg/L | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.31 | 0.15 |
| Parameter | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TDS | −0.967 | −0.071 | −0.030 | 0.042 |
| K+ | 0.756 | −0.335 | −0.155 | −0.107 |
| Na+ | −0.981 | −0.022 | 0.007 | 0.073 |
| Mg2+ | −0.744 | 0.282 | −0.126 | −0.033 |
| Ca2+ | −0.962 | −0.017 | −0.016 | 0.038 |
| Cl− | −0.980 | 0.022 | −0.075 | 0.069 |
| SO42− | −0.929 | −0.070 | −0.251 | 0.127 |
| HCO3− | −0.432 | 0.151 | 0.814 | −0.321 |
| Fe | 0.433 | 0.372 | 0.246 | 0.768 |
| Mn | 0.259 | 0.835 | −0.299 | −0.300 |
| Indices | Min | Max | Mean | Range | Class | No. of Samples (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <50 | Excellent water | 0.0 (0.0%) | |||||
| 50–100 | Good water | 37 (26.4%) | |||||
| DWQI | 55.06 | 239.03 | 121.19 | 100–200 | Poor water | 100(71.5%) | |
| 200–300 | Very poor water | 3.0 (2.1%) | |||||
| >300 | Unsuitable | 0.0 (0.0%) | |||||
| Children | HI (ingestion) | 0.084 | 1.045 | 0.467 | <1 | Low risk | 139 (99.2%) 1.0 (0.8%) |
| >1 | High risk | ||||||
| HI (dermal) | 1.72 × 10−5 | 1.78 × 10−4 | 8.74 × 10−5 | <1 | Low risk | 140 (100%) 0.0 (0.0%) | |
| >1 | High risk | ||||||
| Adult | HI (ingestion) | 0.08 | 0.97 | 0.43 | <1 | Low risk | 140 (100%) 0.0 (0.0%) |
| >1 | High risk | ||||||
| HI (dermal) | 1.4 × 10−5 | 1.4 × 10−4 | 6.9 × 10−5 | <1 | Low risk | 140 (100%) 0.0 (0.0%) | |
| >1 | High risk |
| Parameters | Type | Min | Max | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDI ingestion (Fe) | Child | 0.006 | 0.499 | 0.113 |
| Adult | 0.006 | 0.46 | 0.105 | |
| CDI ingestion (Mn) | Child | 0.001 | 0.015 | 0.007 |
| Adult | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.007 | |
| CDI dermal (Fe) | Child | 6.2 × 10−8 | 5.1 × 10−6 | 1.2 × 10−6 |
| Adult | 4.9 × 10−8 | 4 × 10−6 | 9.2 × 10−7 | |
| CDI dermal (Mn) | Child | 1.5 × 10−8 | 1.6 × 10−7 | 7.6 × 10−8 |
| Adult | 1.2 × 10−8 | 1.3 × 10−7 | 6 × 10−8 | |
| HQ ingestion (Fe) | Child | 0.009 | 0.712 | 0.162 |
| Adult | 0.008 | 0.659 | 0.147 | |
| HQ ingestion (Mn) | Child | 0.06 | 0.64 | 0.31 |
| Adult | 0.06 | 0.6 | 0.28 | |
| HQ dermal (Fe) | Child | 4.4 × 10−7 | 3.7 × 10−5 | 8.3 × 10−6 |
| Adult | 3.5 × 10−7 | 2.9 × 10−5 | 6.6 × 10−6 | |
| HQ dermal (Mn) | Child | 1.6 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 10−4 | 7.9 × 10−5 |
| Adult | 1.3 × 10−5 | 1.3 × 10−4 | 6.2 × 10−5 |
| Parameters | Training | Cross-Validation | Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Ranking * | (h1, h2, fn) | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE |
| DWQI | pH, CO32−, K+, Ca2+, Na+, Cl−, EC, Mn, HCO3−, Mg2+, SO42−, TDS, Fe | (6, 12, relu) | 0.999 *** | 0.00024 | 0.999 | 0.00018 | 0.999 *** | 0.00044 |
| HI ingestion (adult) | Mn, Fe | (21, 9, identity) | 1.000 *** | 4.031 × 10−7 | 1.0 | 1.609 × 10−7 | 1.000 *** | 3.995 × 10−7 |
| HI dermal (adult) | Mn, Fe | (9, 18, identity) | 0.999 *** | 1.859 × 10−6 | 0.999 | 2.233 × 10−6 | 0.999 *** | 1.641 × 10−6 |
| HI ingestion (children) | Mn, Fe | (12, 18, identity) | 1.000 *** | 2.406 × 10−7 | 1.0 | 1.413 × 10−7 | 1.000 *** | 1.259 × 10−7 |
| HI dermal (children) | Mn, Fe | (9, 18, identity) | 0.999 *** | 1.777 × 10−6 | 0.999 | 1.601 × 10−6 | 0.999 *** | 1.584 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gad, M.; Gaagai, A.; Eid, M.H.; Szűcs, P.; Hussein, H.; Elsherbiny, O.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Moustapha, M.E.; et al. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water 2023, 15, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061216
Gad M, Gaagai A, Eid MH, Szűcs P, Hussein H, Elsherbiny O, Elsayed S, Khalifa MM, Moghanm FS, Moustapha ME, et al. Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water. 2023; 15(6):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061216
Chicago/Turabian StyleGad, Mohamed, Aissam Gaagai, Mohamed Hamdy Eid, Péter Szűcs, Hend Hussein, Osama Elsherbiny, Salah Elsayed, Moataz M. Khalifa, Farahat S. Moghanm, Moustapha E. Moustapha, and et al. 2023. "Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt" Water 15, no. 6: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061216
APA StyleGad, M., Gaagai, A., Eid, M. H., Szűcs, P., Hussein, H., Elsherbiny, O., Elsayed, S., Khalifa, M. M., Moghanm, F. S., Moustapha, M. E., Tolan, D. A., & Ibrahim, H. (2023). Groundwater Quality and Health Risk Assessment Using Indexing Approaches, Multivariate Statistical Analysis, Artificial Neural Networks, and GIS Techniques in El Kharga Oasis, Egypt. Water, 15(6), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15061216












