Promotion of Sugar Extraction from Sewage Sludge by Microwave Combined with Thermal-Alkaline Pretreatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Analysis
2.2.1. Sludge Pretreatment Test
2.2.2. Extraction of Crude Sugar
2.2.3. Purity of Crude Sugar
2.2.4. Response Surface Analysis
2.2.5. Characterization
2.3. Data Definition
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Pretreatment Conditions on Sugar Extraction
3.1.1. Effect of NaOH Dosage
3.1.2. Effect of Alkali Extraction Time
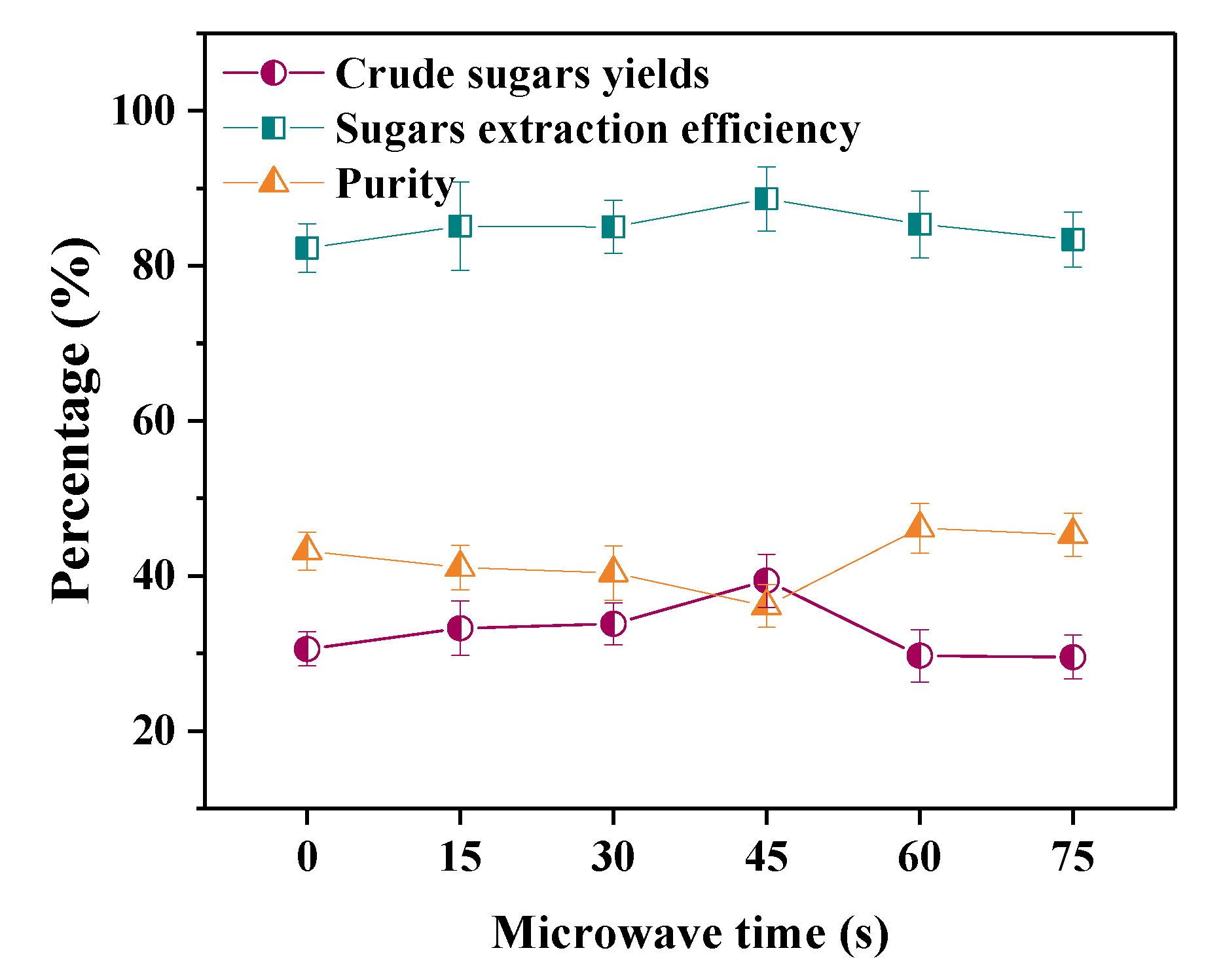
3.1.3. Effect of Microwave Time on Sugar Extraction
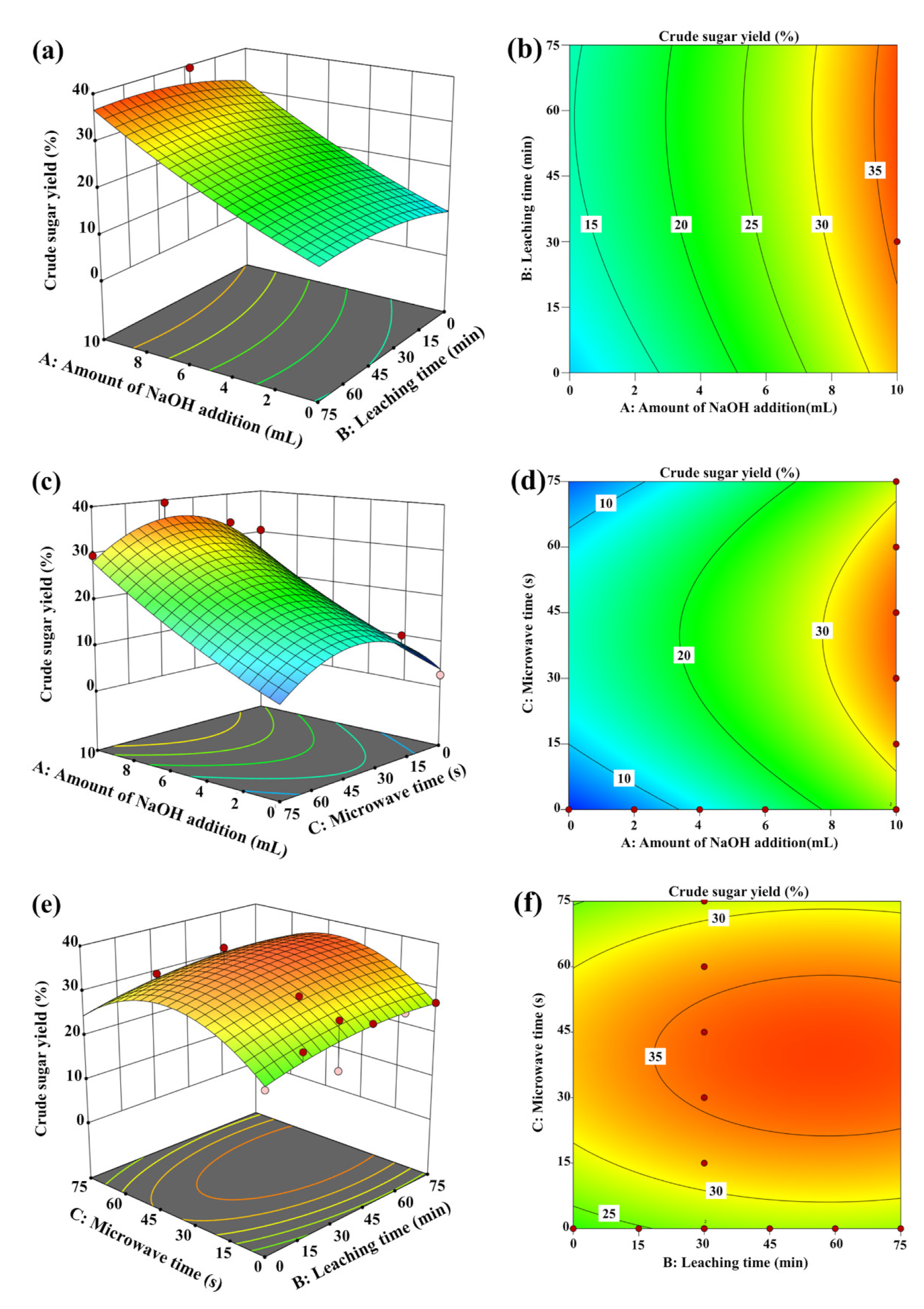
3.2. Response Surface Analysis
3.3. Characterization of Sludge and Crude Sugar
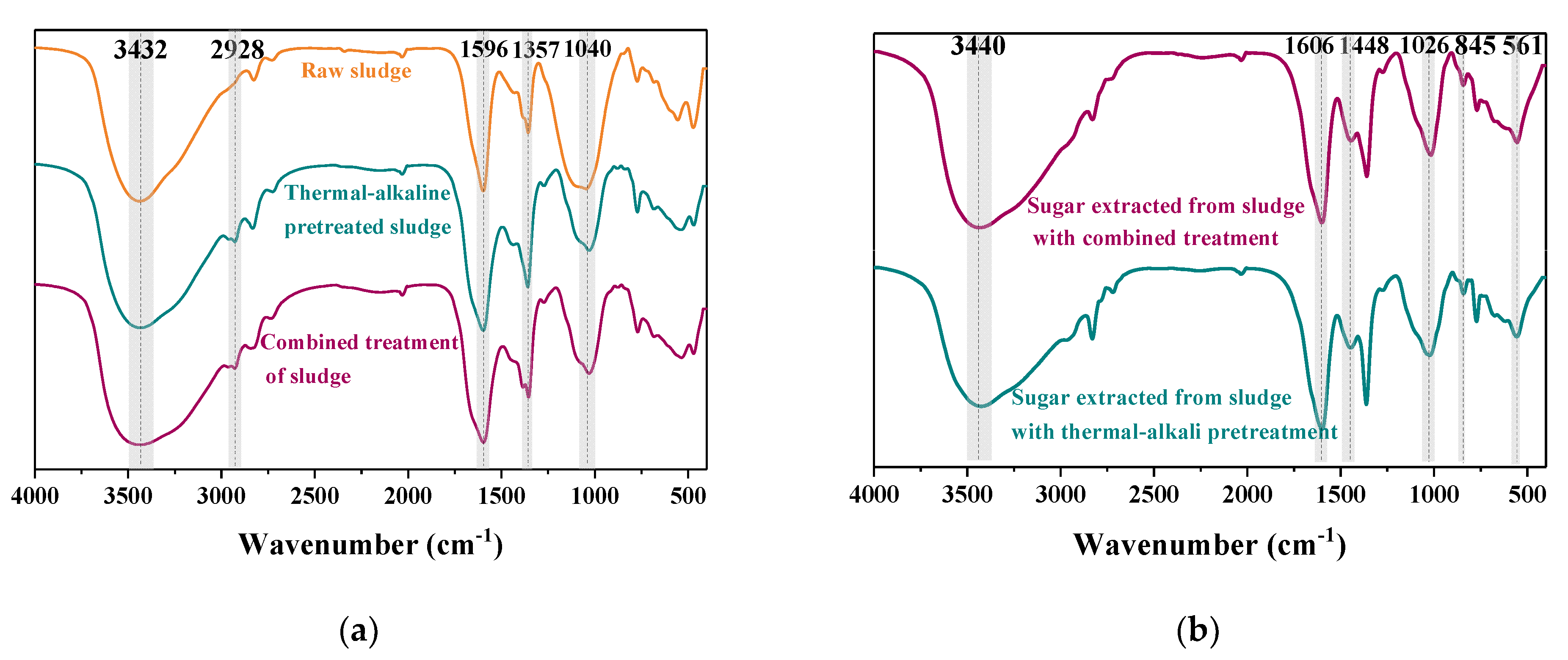
3.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectra
3.3.2. Sludge Surface Morphology
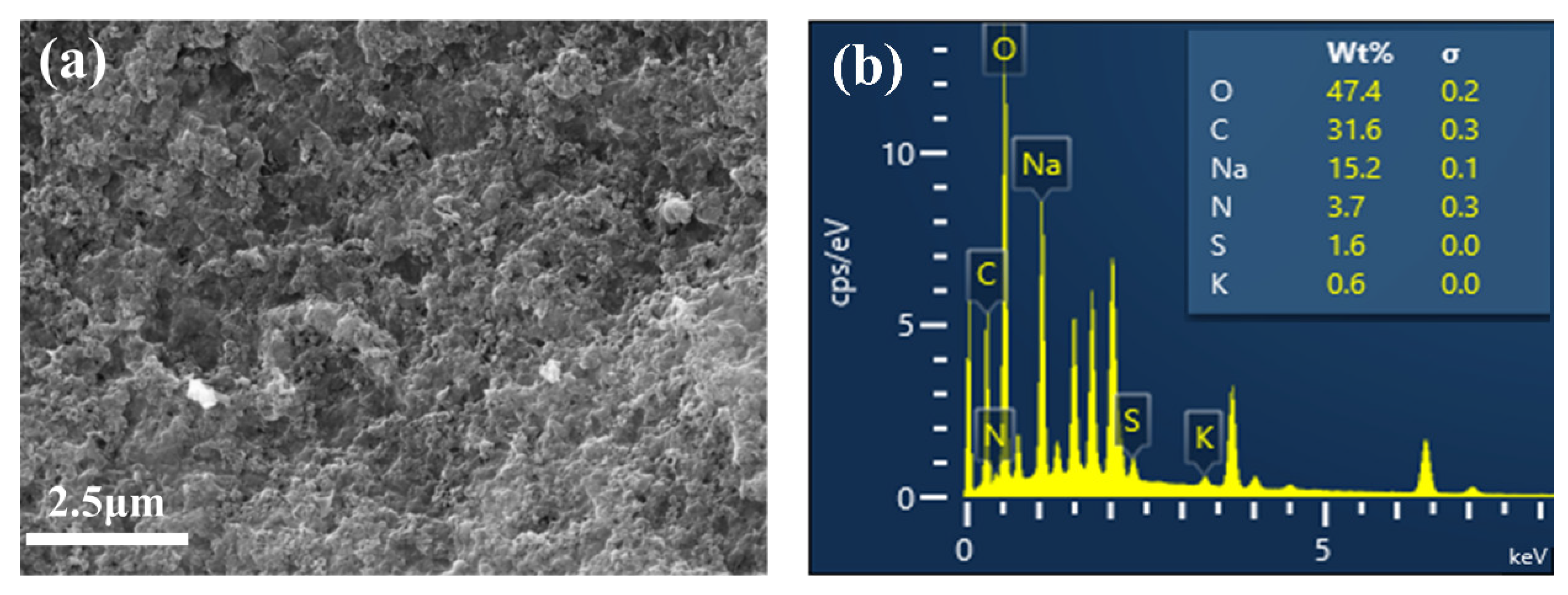
3.3.3. Crude Sugar Surface Morphology and Composition
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, L.; Qi, J. Recent Progress on Biodiesel Production from Municipal Sewage Sludge. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgun, S.; Semerci, N. Combined and Individual Applications of Ozonation and Microwave Treatment for Waste Activated Sludge Solubilization and Nutrient Release. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 241, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, A.; Ren, W. A New Mechanical Cutting Pretreatment Approach towards the Improvement of Primary Sludge Fermentation and Anaerobic Digestion. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fan, Y.; Hornung, U.; Zhu, W.; Dahmen, N. Char and Tar Formation during Hydrothermal Treatment of Sewage Sludge in Subcritical and Supercritical Water: Effect of Organic Matter Composition and Experiments with Model Compounds. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, O.K.; Oh, D.; Lee, K.; Park, Y.; Kim, D. Stimulation of Lipid Extraction Efficiency from Sewage Sludge for Biodiesel Production through Hydrothermal Pretreatment. Energies 2020, 13, 6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, Z. Ultrasonic-Alkali Method for Synergistic Breakdown of Excess Sludge for Protein Extraction. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccia, J.; Westerhoff, P. We Should Expect More out of Our Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8271–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imman, S.; Kreetachat, T.; Khongchamnan, P.; Laosiripojana, N.; Champreda, V.; Suwannahong, K.; Sakulthaew, C.; Chokejaroenrat, C.; Suriyachai, N. Optimization of Sugar Recovery from Pineapple Leaves by Acid-Catalyzed Liquid Hot Water Pretreatment for Bioethanol Production. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6945–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Başar, İ.A.; Perendeci, N.A. Optimization of Zero-Waste Hydrogen Peroxide—Acetic Acid Pretreatment for Sequential Ethanol and Methane Production. Energy 2021, 225, 120324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, C.K.; Qin, F.; Mussatto, S.I. Advances and Opportunities in Biomass Conversion Technologies and Biorefineries for the Development of a Bio-Based Economy. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Dai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, X.; Liu, J.; Xiao, B. Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge by Thermal or Alkaline-Thermal Pretreatments: Influence of Hydraulic Retention Time Reduction. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Shim, H.; Qiu, R.; Wang, S. Sludge Pre-Treatments Change Performance and Microbiome in Methanogenic Sludge Digesters by Releasing Different Sludge Organic Matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xiao, K.; Chen, Y.; Soh, Y.N.A.; Zhou, Y. Transformation of Dissolved Organic Matters Produced from Alkaline-Ultrasonic Sludge Pretreatment in Anaerobic Digestion: From Macro to Micro. Water Res. 2018, 142, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudhoo, A.; Sharma, S.K. Microwave Irradiation Technology in Waste Sludge and Wastewater Treatment Research. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 999–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Huang, S.; Dai, W.; Liang, J.; Sun, S. A Rapid Fenton Treatment Technique for Sewage Sludge Dewatering. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perendeci, N.A.; Ciggin, A.S.; Kökdemir Ünşar, E.; Orhon, D. Optimization of Alkaline Hydrothermal Pretreatment of Biological Sludge for Enhanced Methane Generation under Anaerobic Conditions. Waste Manag. 2020, 107, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; Zhou, J.; Jin, R. Proteins Recovery from Waste Activated Sludge by Thermal Alkaline Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.Q.; Zheng, X.J.; Hu, Z.H.; Gu, G.W. High-Rate Anaerobic Hydrolysis and Acidogenesis of Sewage Sludge in a Modified Upflow Reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thungklin, P.; Reungsang, A.; Sittijunda, S. Hydrogen Production from Sludge of Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment Plant Pretreated with Microwave. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 8751–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostas, E.T.; Beneroso, D.; Robinson, J.P. The Application of Microwave Heating in Bioenergy: A Review on the Microwave Pre-Treatment and Upgrading Technologies for Biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fonseca, F.G.; Gong, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Hornung, U.; Dahmen, N. Energy Valorization of Integrating Lipid Extraction and Hydrothermal Liquefaction of Lipid-Extracted Sewage Sludge. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Feng, A.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; Fan, Y. Coupling of Hydrothermal Pretreatment and Supercritical Water Gasification of Sewage Sludge for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 17914–17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Niu, T.; Lü, X.; Liu, M. Effects of Monosaccharide Composition on Quantitative Analysis of Total Sugar Content by Phenol-Sulfuric Acid Method. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 963318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Ye, G.; Li, G.; Cao, H.; Wang, Z.; Ji, S. RID Serve as a More Appropriate Measure than Phenol Sulfuric Acid Method for Natural Water-Soluble Polysaccharides Quantification. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, S.; Dong, B. The Neglected Effects of Polysaccharide Transformation on Sludge Humification during Anaerobic Digestion with Thermal Hydrolysis Pretreatment. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, N.M.G.; Droste, R.L.; Kennedy, K.J. Microwave Effects on Soluble Substrate and Thermophilic Digestibility of Activated Sludge. Water Environ. Res. 2013, 86, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, A. Organic Matter Release from Primary Sludge by Mechanical Cutting. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Felz, S.; Lin, Y.; van Lier, J.B.; de Kreuk, M. Structural Extracellular Polymeric Substances Determine the Difference in Digestibility between Waste Activated Sludge and Aerobic Granules. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Song, Y. Adsorption and Recovery of Phosphate from Water by Amine Fiber, Effects of Co-Existing Ions and Column Filtration. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 87, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Silva, J.; Filho, G.R.; Da Silva Meireles, C.; Ribeiro, S.D.; Vieira, J.G.; Da Silva, C.V.; Cerqueira, D.A. Thermal Analysis and FTIR Studies of Sewage Sludge Produced in Treatment Plants. The Case of Sludge in the City of Uberlândia-MG, Brazil. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 528, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, T.; Gao, B.; Meng, R.; Zhou, P.; Chen, G.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, H. Comparison between Hydrogen-Rich Biogas Production from Conventional Pyrolysis and Microwave Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge: Is Microwave Pyrolysis Always Better in the Whole Temperature Range? Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 23322–23333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Moisture (wt.%) | Ash (wt.% dry) | Elemental Compositions (wt.%) 1 | HHVs 2 (MJ/kg) | Organic Compositions (wt.% daf.) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O 1 | N | S | Carbohydrates | Proteins | Lipids | Others | |||
| 97.98 ± 1.2 | 39.75 ± 0.6 | 29.54 ± 0.2 | 5.61 ± 0.3 | 18.84 ± 0.5 | 5.26 ± 0.4 | 0.79 ± 0.1 | 14.77 ± 0.5 | 16.04 ± 0.8 | 44.08 ± 1.1 | 17.37 ± 0.7 | 22.51 ± 0.9 |
| Number | NaOH Addition (mL) | Leaching Time (min) | Microwave Time(s) | Crude Sugar Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 30 | 0 | 2.60 |
| 2 | 2 | 30 | 0 | 10.04 |
| 3 | 4 | 30 | 0 | 10.52 |
| 4 | 6 | 30 | 0 | 14.72 |
| 5 | 8 | 30 | 0 | 18.16 |
| 6 | 10 | 30 | 0 | 19.91 |
| 7 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 21.82 |
| 8 | 10 | 15 | 0 | 26.65 |
| 9 | 10 | 45 | 0 | 27.31 |
| 10 | 10 | 60 | 0 | 27.07 |
| 11 | 10 | 75 | 0 | 26.92 |
| 12 | 10 | 30 | 0 | 30.55 |
| 13 | 10 | 30 | 15 | 33.24 |
| 14 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 33.79 |
| 15 | 10 | 30 | 45 | 39.38 |
| 16 | 10 | 30 | 60 | 29.68 |
| 17 | 10 | 30 | 75 | 29.50 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1395.73 | 6 | 232.62 | 19.84 | 0.0001 | Significant |
| A | 465.68 | 1 | 465.68 | 39.72 | 0.0001 | |
| B | 12.69 | 1 | 12.69 | 1.08 | 0.3253 | |
| C | 4.16 | 1 | 4.16 | 0.3544 | 0.5663 | |
| A2 | 2.69 | 1 | 2.69 | 0.2296 | 0.6433 | |
| B2 | 4.13 | 1 | 4.13 | 0.3524 | 0.5674 | |
| C2 | 101.52 | 1 | 101.52 | 8.66 | 0.0164 | |
| Residual | 105.52 | 9 | 11.72 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 48.92 | 8 | 6.11 | 0.1080 | 0.9840 | Not Significant |
| Pure Error | 56.60 | 1 | 56.60 | |||
| Cor. Total | 1501.26 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, P.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y. Promotion of Sugar Extraction from Sewage Sludge by Microwave Combined with Thermal-Alkaline Pretreatment. Water 2023, 15, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071291
Cheng P, Yang L, Liu Y, Liu J, Fan Y. Promotion of Sugar Extraction from Sewage Sludge by Microwave Combined with Thermal-Alkaline Pretreatment. Water. 2023; 15(7):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071291
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Peng, Lei Yang, Yu Liu, Jiaxin Liu, and Yujie Fan. 2023. "Promotion of Sugar Extraction from Sewage Sludge by Microwave Combined with Thermal-Alkaline Pretreatment" Water 15, no. 7: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071291
APA StyleCheng, P., Yang, L., Liu, Y., Liu, J., & Fan, Y. (2023). Promotion of Sugar Extraction from Sewage Sludge by Microwave Combined with Thermal-Alkaline Pretreatment. Water, 15(7), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071291