Batik Effluent Treatment and Decolorization—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Production of Batik
| Dyes | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Maximum Absorption Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct dyes (Direct Black 38) |  | 760.8 | 520 |
| Indigo dyes (Vat blue 1) | 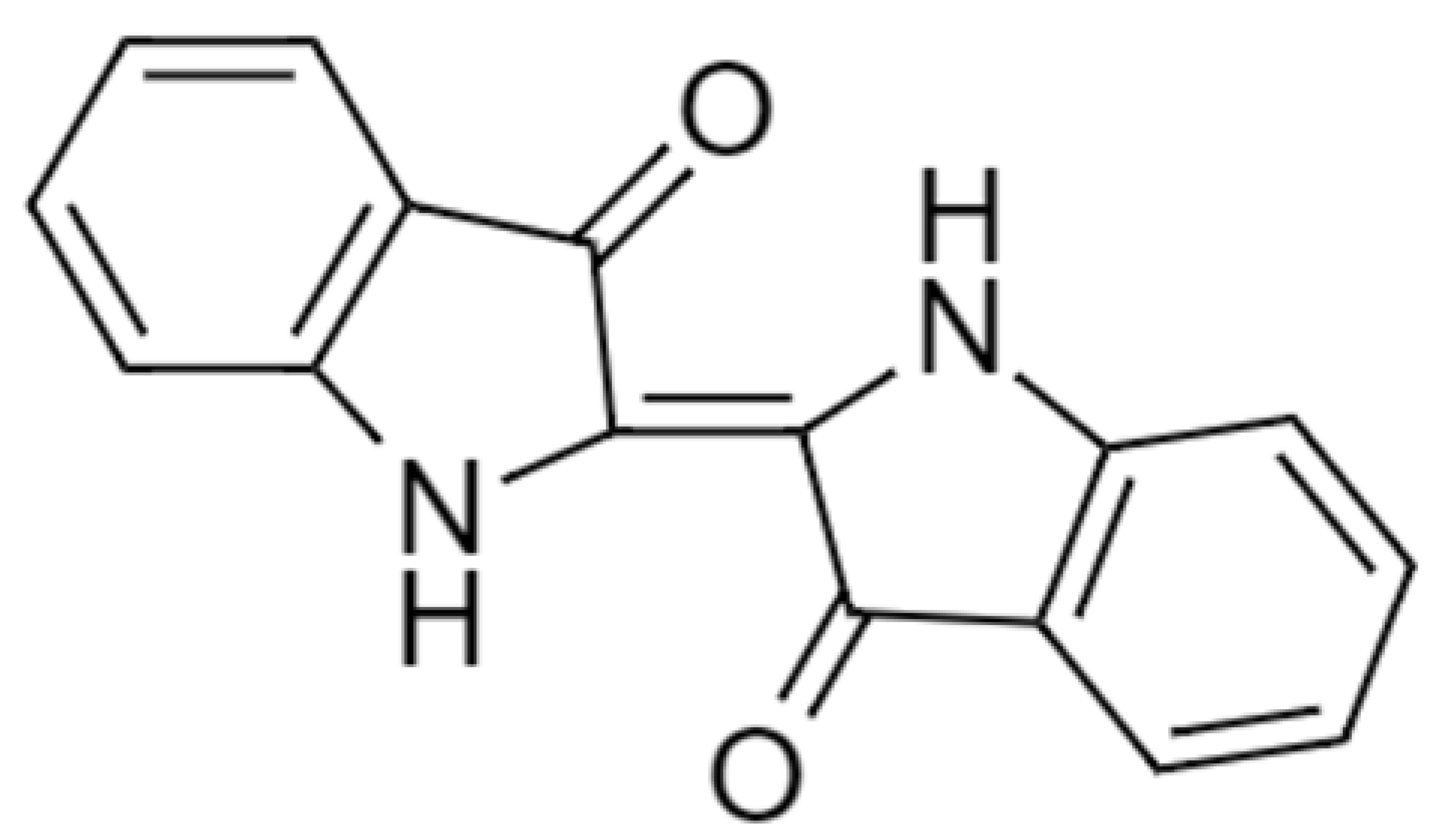 | 262.26 | 610 |
| Naphthol dyes (Acid Orange 20) |  | 350.3 | 488 |
| Dyes | Chemical Structure | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Maximum Absorption Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl sulfone (Reactive Red 239) | 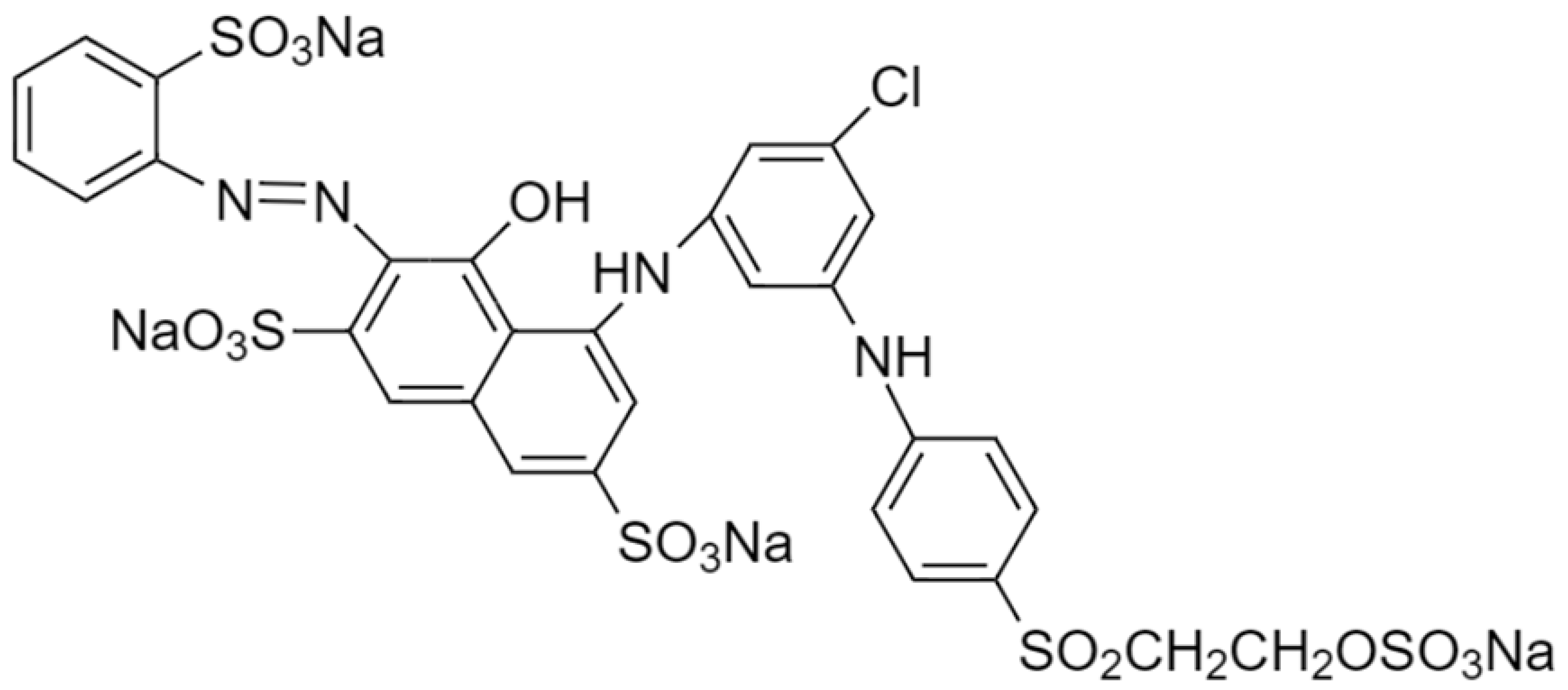 | 1050.37 | 555 |
| Procion MX (Reactive Red 3) | 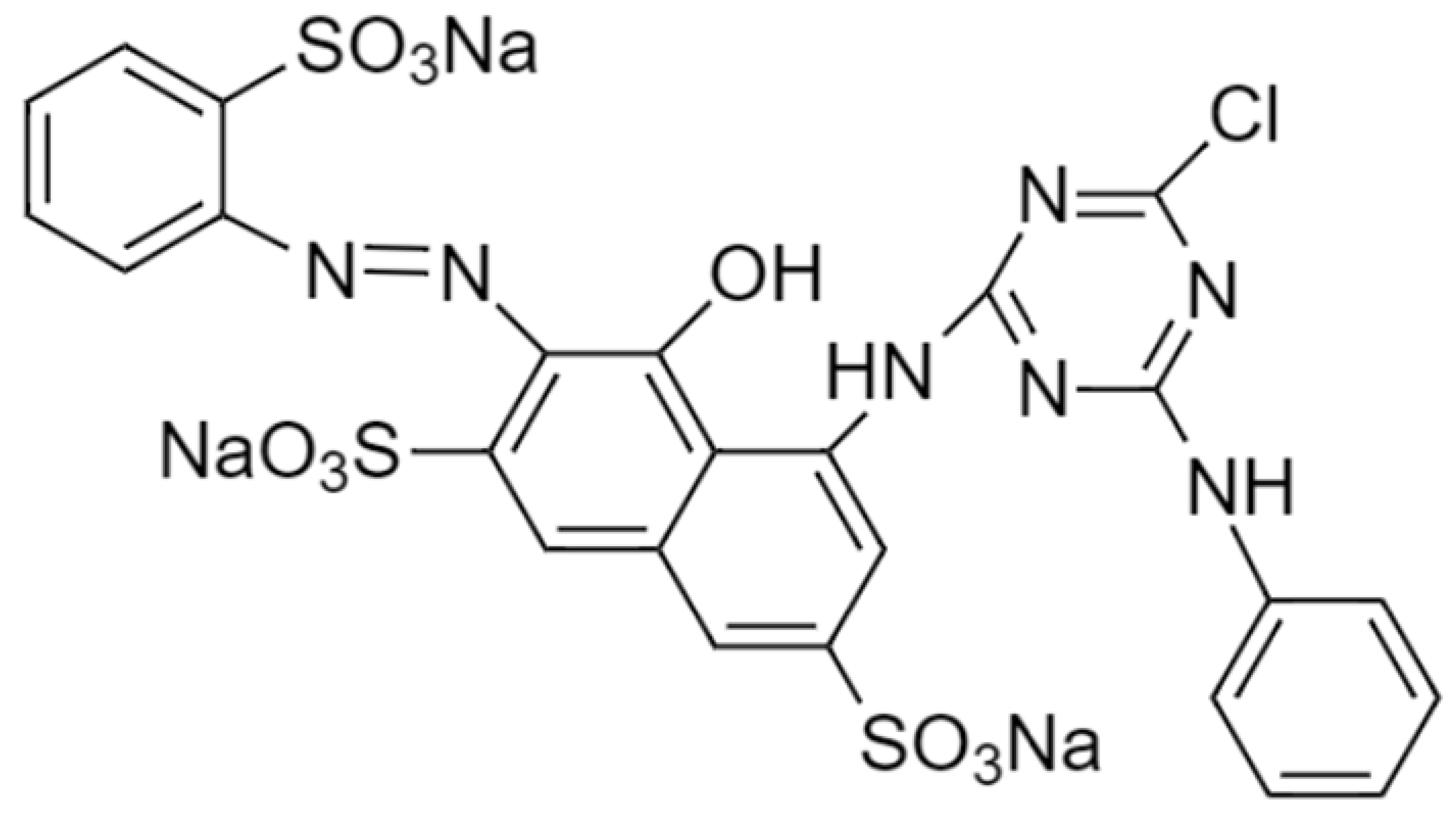 | 774.05 | 532 |
| Remazol (Reactive Blue 19) | 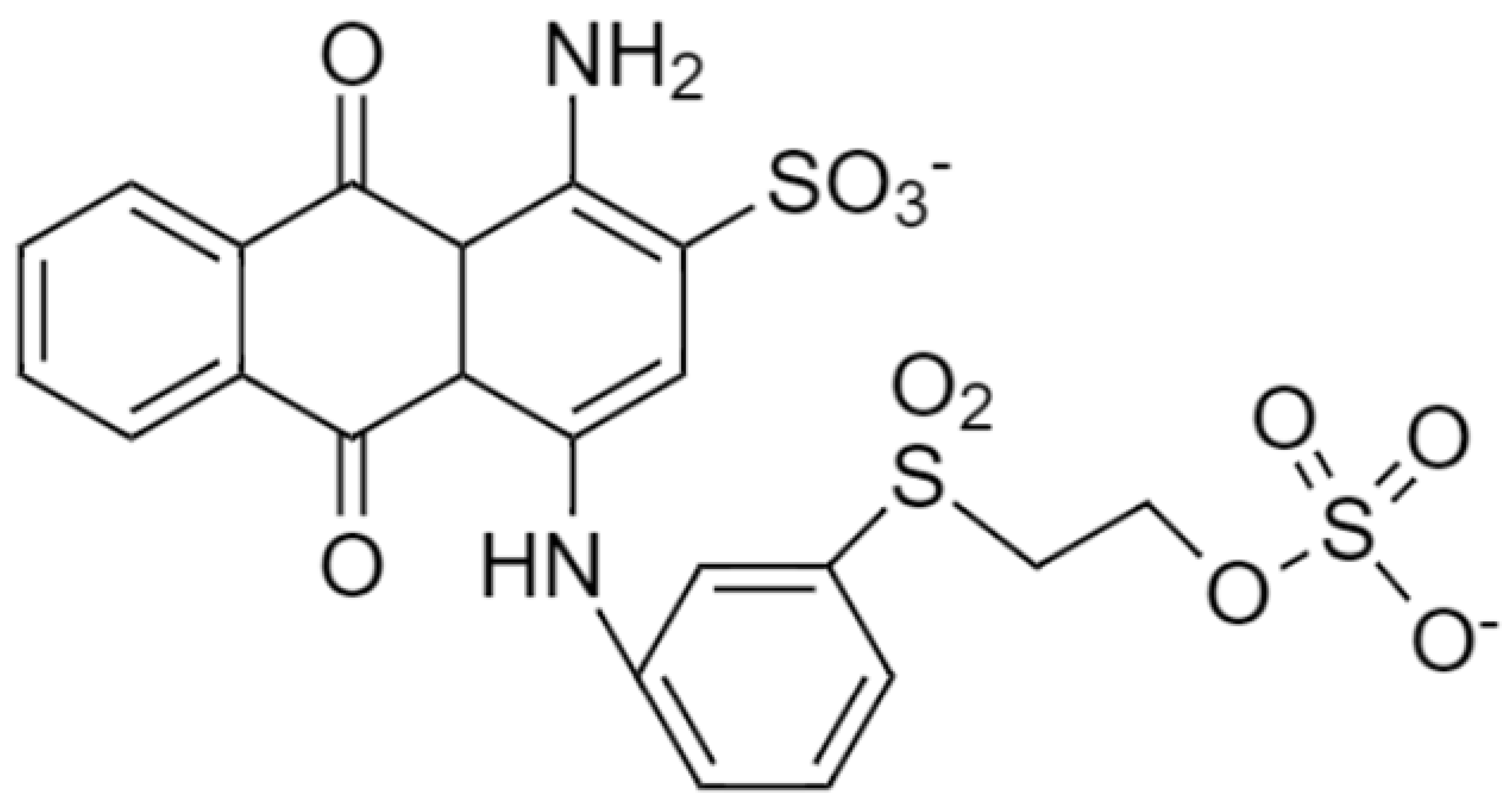 | 626.5 | 592 |
3. Characteristics of Batik Effluent
| No. | Parameter | Unit | Standard | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | |||
| 1. | Temperature | °C | 40 | 40 |
| 2. | pH Value | - | 6.0–9.0 | 5.5–9.0 |
| 3. | BOD at 20 °C | mg/L | 20 | 50 |
| 4. | Suspended Solids | mg/L | 50 | 100 |
| 5. | Mercury | mg/L | 0.005 | 0.05 |
| 6. | Cadmium | mg/L | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| 7. | Chromium, Hexavalent | mg/L | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| 8. | Chromium, Trivalent | mg/L | 0.20 | 1.0 |
| 9. | Arsenic | mg/L | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| 10. | Cyanide | mg/L | 0.05 | 0.10 |
| 11. | Lead | mg/L | 0.10 | 0.5 |
| 12. | Copper | mg/L | 0.20 | 1.0 |
| 13. | Manganese | mg/L | 0.20 | 1.0 |
| 14. | Nickel | mg/L | 0.20 | 1.0 |
| 15. | Tin | mg/L | 0.20 | 1.0 |
| 16. | Zinc | mg/L | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| 17. | Boron | mg/L | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| 18. | Iron (Fe) | mg/L | 1.0 | 5.0 |
| 19. | Silver | mg/L | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| 20. | Aluminum | mg/L | 10 | 15 |
| 21. | Selenium | mg/L | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| 22. | Barium | mg/L | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| 23. | Fluoride | mg/L | 2.0 | 5.0 |
| 24. | Formaldehyde | mg/L | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| 25. | Phenol | mg/L | 0.001 | 1.0 |
| 26. | Free Chlorine | mg/L | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| 27. | Sulfide | mg/L | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 28. | Oil and Grease | mg/L | 1.0 | 10 |
| 29. | Ammoniacal Nitrogen | mg/L | 10 | 20 |
| 30. | Color | ADMI * | 100 | 200 |
4. Discharge Standards for Industrial Effluents
5. Wastewater Treatment Techniques
5.1. Membrane Filtration
5.1.1. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
5.1.2. Nanofiltration (NF)
5.1.3. Ultrafiltration (UF)
5.1.4. Microfiltration (MF)
5.2. Coagulation-Flocculation Treatment
5.3. Adsorption
5.4. Fenton Reaction
5.5. Ozonation
5.6. Biological Treatment
5.6.1. Activated Sludge System
5.6.2. Trickling Filters
5.6.3. Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB)
5.6.4. Enzymatic Treatment
5.7. Electrical-Assisted Treatment
6. Summary of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Physical Chemical and Biological Methods
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angkawijaya, Y.; Agustina, I.A.; Tee Chuan, A.O. Batik as Part of Pop Culture. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium of Arts, Crafts & Design in South East Asia (ARCADESA), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 5 November 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, R.; Bakar, S.S.A. Malaysian Batik Industry: Protecting Local Batik Design by Copyright and Industrial Design Laws. Int. J. Bus. Soc. 2012, 13, 117–132. [Google Scholar]
- Fitri Samsuddin, M.; Nurul Akma Ahmad, S.; Hisham Johari, M.; Hanim Hamzah, A.; Abdul Samat, R. Promoting Malaysian “Batik” Pattern through Automotive Interior Design. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2018, 8, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E. Batik Making Process—MyBatik Kuala Lumpur. Available online: https://mybatik.org.my/batik/batik-making-process/ (accessed on 15 October 2022).
- Masrom, N.A. Projek Integrasi Pengeluaran Bersih Pembuatan Batik. Cleaner Production towards Environment Friendly Industries. 2012. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/353541199/Cleaner-Production-VOL-2-NO-2-2012 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Ramakreshnan, L.; Rajandra, A.; Aghamohammadi, N.; Fong, C.S.; Nalatambi, S. A Preliminary Insight into the Environmental Awareness of Community in the Vicinity of Batik Manufacturing Units in Kelantan, Malaysia. GeoJournal 2020, 85, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadi Batek Malaysia Batik|Jadi Batek. Available online: https://jadibatek.com/batik/ (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Buthiyappan, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A.; Daud, W.M.A.W. Development of an Advanced Chemical Oxidation Wastewater Treatment System for the Batik Industry in Malaysia. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 25222–25241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezagama, A.; Sutrisno, E.; Handayani, D.S. Pollution Model of Batik and Domestic Wastewater on River Water Quality. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 448, 012074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Ananthashankar, R.; Alhattab, M.V.V.R.; Ramakrishnan, V.V. Production, Characterization and Treatment of Textile Effluents: A Critical Review. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2013, 5, 1000182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, H.B.; Bouket, A.C.; Pourhassan, Z.; Alenezi, F.N.; Silini, A.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Oszako, T.; Luptakova, L.; Golińska, P.; Belbahri, L. Diversity of Synthetic Dyes from Textile Industries, Discharge Impacts and Treatment Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Meikandaan, T.P.; Gowrishankar, P.G.; Kanchanabhan, T.E. A Study on Treatment of Industrial Effluent (Dyeing) Using Moringa Oleifera, Tamarina Indica as Coagulants. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 2796–2811. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, H.R.; Sulaiman, N.M.N.; Hashim, N.A. Batik Industry Synthetic Wastewater Treatment Using Nanofiltration Membrane. Procedia Eng. 2012, 44, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’ rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. A Review on Classifications, Recent Synthesis and Applications of Textile Dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiyanto, S.A.; Purnaweni, H.; Sunoko, H.R. Environmental Analysis of the Impacts of Batik Waste Water Polution on the Quality of Dug Well Water in the Batik Industrial Center of Jenggot Pekalongan City. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 31, 09008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azha, S.F.; Ismail, S. Feasible and Economical Treatment of Real Hand-Drawn Batik/Textile Effluent Using Zwitterionic Adsorbent Coating: Removal Performance and Industrial Application Approach. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juliani, A.; Rahmawati, S.; Yoneda, M. Heavy Metal Characteristics of Wastewater from Batik Industry in Yogyakarta Area, Indonesia. Int. J. GEOMATE 2021, 20, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subki, N.S.; Rohasliney, H. A Preliminary Study on Batik Effluent in Kelantan State: A Water Quality Perspective. Int. Conf. Chem. Biol. Enviromental Sci. 2011, 1, 274–276. [Google Scholar]
- Khalik, W.F.; Ho, L.N.; Ong, S.A.; Wong, Y.S.; Yusoff, N.A.; Ridwan, F. Decolorization and Mineralization of Batik Wastewater through Solar Photocatalytic Process. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buthiyappan, A.; Abdul Raman, A.A. Energy Intensified Integrated Advanced Oxidation Technology for the Treatment of Recalcitrant Industrial Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.A.; Scholz, M. Textile Dye Wastewater Characteristics and Constituents of Synthetic Effluents: A Critical Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahmaniah, G.; Mahdi, C.; Safitri, A. Biosorption of Synthetic Dye from Batik Wastewater Using Trichoderma Viride Immobilized on Ca-Alginate. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1374, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masupha, T.M. Water Management at a Textile Industry: A Case Study in Lesotho. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lestari, S.; Sudarmadji; Tandjung, S.D.; Santosa, S.J. Improvement of Batik Wastewater Quality Using Biosorption Process. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 256, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.; El Nemr, A.; Hassaan, M.A. Health and Environmental Impacts of Dyes: Mini Review. Am. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Vacchi, F.I.; de Vendemiatti, J.A.S.; da Silva, B.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Umbuzeiro, G. de A. Quantifying the Contribution of Dyes to the Mutagenicity of Waters under the Influence of Textile Activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zafar, S.; Bukhari, D.A.; Rehman, A. Azo Dyes Degradation by Microorganisms—An Efficient and Sustainable Approach. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swarnkumar, R.; Osborne, W.J. Heavy Metal Determination and Aquatic Toxicity Evaluation of Textile Dyes and Effluents Using Artemia Salina. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 25, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odubanjo, G.O.; Oyetibo, G.O.; Ilori, M.O. Ecological Risks of Heavy Metals and Microbiome Taxonomic Profile of a Freshwater Stream Receiving Wastewater of Textile Industry. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment, M. of N.R. and the Environment Quality (Industrial Effluent) Regulations 2009. Available online: https://www.doe.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/Environmental_Quality_Industrial_Effluent_Regulations_2009_-_P.U.A_434-2009.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and Disadvantages of Techniques Used for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, M.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z. Textile Dyeing Wastewater Treatment. In Advances in Treating Textile Effluent; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Istirokhatun, T.; Susanto, H.; Budihardjo, M.A.; Septiyani, E.; Wibowo, A.R.; Karamah, E.F. Treatment of Batik Industry Wastewater Plant Effluent Using Nanofiltration. Int. J. Technol. 2021, 12, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradihamedani, P. Recent Advances in Dye Removal from Wastewater by Membrane Technology: A Review. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 2603–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinperi, N.C.; Ozturk, E.; Yigit, N.O.; Kitis, M. Treatment of Woolen Textile Wastewater Using Membrane Bioreactor, Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis for Reuse in Production Processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, X.; Feng, S.; Wan, Y.; Luo, J. Nanofiltration for Decolorization: Membrane Fabrication, Applications and Challenges. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 19858–19875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmen, Z.; Daniel, S. Textile Organic Dyes—Characteristics, Polluting Effects and Separation/Elimination Procedures from Industrial Effluents—A Critical Overview. In Organic Pollutants Ten Years After the Stockholm Convention Environmental and Analytical Update; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; ISBN 978-953-307-917-2. [Google Scholar]
- Trishitman, D.; Cassano, A.; Basile, A.; Rastogi, N.K. Reverse Osmosis for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. In Current Trends and Future Developments on (Bio-) Membranes: Reverse and Forward Osmosis: Principles, Applications, Advances; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 207–228. ISBN 9780128167779. [Google Scholar]
- Kurt, E.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Dizge, N.; Chellam, S.; Koyuncu, I. Pilot-Scale Evaluation of Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis for Process Reuse of Segregated Textile Dyewash Wastewater. Desalination 2012, 302, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Ang, W.L.; Teow, Y.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N. Nanofiltration Membrane Processes for Water Recycling, Reuse and Product Recovery within Various Industries: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Purkait, M.K.; DasGupta, S.; De, S.; Basu, J.K. Nanofiltration of Textile Plant Effluent for Color Removal and Reduction in COD. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 31, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Z.; Sun, S.P.; Li, F.Y.; Ong, Y.K.; Chung, T.S. Treatment of Highly Concentrated Wastewater Containing Multiple Synthetic Dyes by a Combined Process of Coagulation/Flocculation and Nanofiltration. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 469, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. Batik Effluent Reclamation through a Task-Orientated Coupling Process of Nanofiltration Membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 27557–27572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryanti, P.T.P.; Nugroho, F.A.; Widiasa, I.N.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Wenten, I.G. Preparation of Highly Selective PSf/ZnO/PEG400 Tight Ultrafiltration Membrane for Dyes Removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramutshatsha-Makhwedzha, D.; Nomngongo, P.N. Application of Ultrafiltration Membrane Technology for Removal of Dyes from Wastewater. In Membrane Based Methods for Dye Containing Wastewater; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 37–47. ISBN 10.1007/9789811. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumawati, N.; Wijiastuti, A. Erina Rahmadyanti Operating Conditions Optimization on Indonesian ‘Batik’ Dyes Wastewater Treatment by Fenton Oxidation and Separation Using Ultrafiltration Membrane. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 1, 672. [Google Scholar]
- Nadeem, K.; Guyer, G.T.; Keskinler, B.; Dizge, N. Investigation of Segregated Wastewater Streams Reusability with Membrane Process for Textile Industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkanlı, M.; Yilmaz, L.; Çulfaz-Emecen, P.Z.; Yetis, U. Brackish Water Recovery from Reactive Dyeing Wastewater via Ultrafiltration. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćurić, I.; Dolar, D.; Karadakić, K. Textile Wastewater Reusability in Knitted Fabric Washing Process Using UF Membrane Technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Canbolat, Ç.B.; Lin, J.; Luis, P. The Potential of Membrane Technology for Treatment of Textile Wastewater. In Sustainable Membrane Technology for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 349–380. [Google Scholar]
- Alventosa-Delara, E.; Barredo-Damas, S.; Zuriaga-Agustí, E.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.I.; Iborra-Clar, M.I. Ultrafiltration Ceramic Membrane Performance during the Treatment of Model Solutions Containing Dye and Salt. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 129, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, I.N.H.M.; Nizam, M.H.M. Assessment of Membrane Fouling Indices during Removal of Reactive Dye from Batik Wastewater. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2016, 6, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Vigneswaran, S. Fouling Control of Membranes with Pretreatment. In Membrane Technology and Environmental Applications; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 533–580. ISBN 9780784476895. [Google Scholar]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Microfiltration Membrane Processes: A Review of Research Trends over the Past Decade. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgada, A.; Charik, F.Z.; Achiou, B.; Ntambwe Kambuyi, T.; Alami Younssi, S.; Beniazza, R.; Dani, A.; Benhida, R.; Ouammou, M. Optimization of Phosphate/Kaolinite Microfiltration Membrane Using Box-Behnken Design for Treatment of Industrial Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, A.; Achiou, B.; Karim, A.; Harrati, A.; Sadik, C.; Ouammou, M.; Alami Younssi, S.; El Bouari, A. New Low-Cost Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane Made from Natural Magnesite for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homem, N.C.; de Camargo Lima Beluci, N.; Amorim, S.; Reis, R.; Vieira, A.M.S.; Vieira, M.F.; Bergamasco, R.; Amorim, M.T.P. Surface Modification of a Polyethersulfone Microfiltration Membrane with Graphene Oxide for Reactive Dyes Removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 486, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.H.B.R.; Paixão, R.M.; Bergamasco, R.; Vieira, A.M.S.; Vieira, M.F. Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly of Polyethersulphone Microfiltration Membranes for Dye Removal and Flux Recovery Improvement. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 100, 1920–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Bulasara, V.K.; Reddy, A.S. Performance of a New Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane Based on Kaolin in Textile Industry Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 206, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.S.D.; Madeira, L.M.; Boaventura, R.A.R. Treatment of Textile Dye Wastewaters Using Ferrous Sulphate in a Chemical Coagulation/Flocculation Process. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhi, D.; Elmchaouri, A.; Rakhila, Y.; Abouri, M.; Souabi, S.; Hamdani, M.; Jada, A. Optimization of the Treatment of a Real Textile Wastewater by Coagulation– Flocculation Processes Using Central Composite Design. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 196, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonal, S.; Mishra, B.K. Role of Coagulation/Flocculation Technology for the Treatment of Dye Wastewater: Trend and Future Aspects. In Water Pollution and Management Practices; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 303–331. ISBN 10.1007/9789811. [Google Scholar]
- Dotto, J.; Fagundes-Klen, M.R.; Veit, M.T.; Palácio, S.M.; Bergamasco, R. Performance of Different Coagulants in the Coagulation/Flocculation Process of Textile Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 208, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.K.F.S.; Oliveira, V.M.; de Souza, M.T.F.; Geraldino, H.C.L.; Almeida, V.C.; Fávaro, S.L.; Garcia, J.C. Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation Process for Treatment of Industrial Textile Wastewater Using Okra (A. Esculentus) Mucilage as Natural Coagulant. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Feng, N. Removal of Reactive Dyes from Wastewater Assisted with Kaolin Clay by Magnesium Hydroxide Coagulation Process. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 494, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinew, B. Textile Effluent Treatment and Decolorization Techniques—A Review. Chemistry 2012, 21, 434–456. [Google Scholar]
- Teh, C.Y.; Budiman, P.M.; Shak, K.P.Y.; Wu, T.Y. Recent Advancement of Coagulation-Flocculation and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4363–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, J.M.; Fredrick, S.; Shadrack, M.S. Potential of Moringa Oleifera Seeds and Fuel Wood Ash as Adsorbent of Dye and Organic Matter in Wastewater from Batik Producing Enterprises. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2021, 13, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soedjono, E.S.; Slamet, A.; Fitriani, N.; Sumarlan, M.S.; Supriyanto, A.; Mitha Isnadina, D.R.; Othman, N.B. Residual Seawater from Salt Production (Bittern) as a Coagulant to Remove Lead (Pb2+) and Turbidity from Batik Industry Wastewater. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtekar, V.S.; Bhandari, V.M.; Shirsath, S.R.; Sai Chandra, P.L.V.N.; Jolhe, P.D.; Ghodke, S.A. Dye Wastewater Treatment: Removal of Reactive Dyes Using Inorganic and Organic Coagulants. J. Ind. Pollut. Control 2014, 30, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Iqbal, M.J.; Hussain, M. A State-of-the-Art Review on Wastewater Treatment Techniques: The Effectiveness of Adsorption Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nazli, Z.; Nouren, S. Dyes Adsorption Using Clay and Modified Clay: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H. Charcoal as an Adsorbent for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2797–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husien, S.; El-taweel, R.M.; Salim, A.I.; Fahim, I.S.; Said, L.A.; Radwan, A.G. Review of Activated Carbon Adsorbent Material for Textile Dyes Removal: Preparation, and Modelling. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 5, 100325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Bakhoum, E.S.; Zaher, K. Sustainable Evaluation of Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron and Activated Carbon for Real Textile Effluent Remediation. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 10365–10380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, T.M.; Haeger, A.; Biffinger, J.C.; Ren, Z.J. Granular Biochar Compared with Activated Carbon for Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery. Water Res. 2016, 94, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, T.W.; Lourenço, L.A.; Scheibe, A.S.; De Souza, S.M.A.G.U.; De Souza, A.A.U. Textile Wastewater Treatment Using Low-Cost Adsorbent Aiming the Water Reuse in Dyeing Process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2705–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, M.Z. Study on Removal of Pollutant from Batik Wastewater Using Coal Bottomash (CBA). Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 476, 012033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.D.N.; Santana, C.S.; Velloso, C.C.V.; da Silva, A.H.M.; Magalhães, F.; Aguiar, A. A Review on the Treatment of Textile Industry Effluents through Fenton Processes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 155, 366–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Gandhimathi, R.; Ramesh, S.T. Degradation of Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Fenton Processes: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2099–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P. A Review on Fenton-like Processes for Organic Wastewater Treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 762–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Kapoor, S.; Christian, R.A. Effect of Fenton Process on Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1665–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkay, O.; Barişçi, S.; Sillanpää, M. E-Peroxone Process for the Treatment of Laundry Wastewater: A Case Study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4282–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucan-Altuntas, K.; Ilhan, F. Enhancing Biodegradability of Textile Wastewater by Ozonation Processes: Optimization with Response Surface Methodology. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, X. Effect of Wastewater Particles on Catalytic Ozonation in the Advanced Treatment of Petrochemical Secondary Effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilińska, L.; Blus, K.; Gmurek, M.; Ledakowicz, S. Coupling of Electrocoagulation and Ozone Treatment for Textile Wastewater Reuse. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramugani, A.; Shimizu, T.; Goto, S.; Argo, T.A.; Soda, S. Decolorization and Biodegradability Enhancement of Synthetic Batik Wastewater Containing Reactive Black 5 and Reactive Orange 16 by Ozonation. Water 2022, 14, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Cuevas, S.; Oller, I.; Agüera, A.; Llorca, M.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A.; Malato, S. Combination of Nanofiltration and Ozonation for the Remediation of Real Municipal Wastewater Effluents: Acute and Chronic Toxicity Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paździor, K.; Wrębiak, J.; Klepacz-Smółka, A.; Gmurek, M.; Bilińska, L.; Kos, L.; Sójka-Ledakowicz, J.; Ledakowicz, S. Influence of Ozonation and Biodegradation on Toxicity of Industrial Textile Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, M.T.F.; Glasser, D.; Hildebrandt, D. Wastewater Treatment of Reactive Dyestuffs by Ozonation in a Semi-Batch Reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 166, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Cuevas, S.; Oller, I.; Agüera, A.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A.; Sánchez-Moreno, R.; Malato, S. Is the Combination of Nanofiltration Membranes and AOPs for Removing Microcontaminants Cost Effective in Real Municipal Wastewater Effluents? Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, D.; Sharma, N.R.; Singh, J.; Kanwar, R.S. Biological Methods for Textile Dye Removal from Wastewater: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1836–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhartini, S.; Hidayat, N.; Permatasari, V.R.; Herera, A.C.E. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Batik Wastewater with Macroalgae. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 475, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, R.S.; Kasiamdari, R.S.; Martani, E.; Purwestri, Y.A. Efficiency of Aspergillus Sp. 3 to Reduce Chromium, Sulfide, Ammonia, Phenol, and Fat from Batik Wastewater. Proc. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 308, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshabib, M.; Onaizi, S.A. A Review on Phenolic Wastewater Remediation Using Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Enzymatic Processes: Current Status and Potential Challenges. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 219, 186–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A Critical Review on Textile Wastewater Treatments: Possible Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kang, H.J.; Park, H.D. Influence of Influent Wastewater Communities on Temporal Variation of Activated Sludge Communities. Water Res. 2015, 73, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Abid, S.; Hamdi, M.; Bouallagui, H. Reduction of Adsorbed Dyes Content in the Discharged Sludge Coming from an Industrial Textile Wastewater Treatment Plant Using Aerobic Activated Sludge Process. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrati, L.; El Achaby, M.; Chatoui, H.; Laqbaqbi, M.; El Kharraz, J.; Aziz, F. Inhibiting Effect of Textile Wastewater on the Activity of Sludge from the Biological Treatment Process of the Activated Sludge Plant. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1753–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirbagheri, S.A.; Charkhestani, A. Pilot-Scale Treatment of Textile Wastewater by Combined Biological-Adsorption Process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 9082–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janet Joshiba, G.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Femina, C.C.; Jayashree, E.; Racchana, R.; Sivanesan, S. Critical Review on Biological Treatment Strategies of Dairy Wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 160, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irum, A.; Mumtaz, S.; Rehman, A.; Naz, I.; Ahmed, S. Treatment of Simulated Textile Wastewater Containing Reactive Azo Dyes Using Laboratory Scale Trickling Filter. Citeseer 2015, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watari, T.; Hata, Y.; Hirakata, Y.; Nguyet, P.N.; Nguyen, T.H.; Maki, S.; Hatamoto, M.; Sutani, D.; Setia, T.; Yamaguch, T. Performance Evaluation of Down-Flow Hanging Sponge Reactor for Direct Treatment of Actual Textile Wastewater; Effect of Effluent Recirculation to Performance and Microbial Community. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 39, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Shen, C.; Ma, C.; Tian, Q.; Song, X.; Sand, W. Recent Advances in Anaerobic Biological Processes for Textile Printing and Dyeing Wastewater Treatment: A Mini-Review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Goi, D. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (Uasb) Technology for Energy Recovery: A Review on State-of-the-Art and Recent Technological Advances. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Khan, S.J.; Nawaz, M.S.; Saleem, M.U. Effect of Intermittent Operation of Lab-Scale Upflow Anaerobic Slublanket (UASB) Reactor on Textile Wastewater Treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 136, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Bhunia, P.; Dash, R.R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Zhang, T.C. Effects of Physico-Chemical Pre-Treatment on the Performance of an Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Reactor Treating Textile Wastewater: Application of Full Factorial Central Composite Design. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, R.S.; Ilyas, M.; Sari, A.A. Ligninolitic Enzyme Immobilization from Pleurotus Ostreatus for Dye and Batik Wastewater Decolorization. J. Pendidik. IPA Indones. 2019, 8, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanto, D.H.Y.; Guntoro, M.A.; Nurhayat, O.D.; Anita, S.H.; Oktaviani, M.; Ramadhan, K.P.; Pradipta, M.F.; Watanabe, T. Biodegradation and Biodetoxification of Batik Dye Wastewater by Laccase from Trametes Hirsuta EDN 082 Immobilised on Light Expanded Clay Aggregate. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.K.H.; Tan, H.K.; Lau, S.Y.; Yap, P.S.; Danquah, M.K. Potential and Challenges of Enzyme Incorporated Nanotechnology in Dye Wastewater Treatment: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.L.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.P. Enzymatic Decolorization and Degradation of Azo Dyes—A Review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 104, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiong, T.; Lau, S.Y.; Lek, Z.H.; Koh, B.Y.; Danquah, M.K. Enzymatic Treatment of Methyl Orange Dye in Synthetic Wastewater by Plant-Based Peroxidase Enzymes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami-Borujeni, F.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Alimohammadi, M. Enzymatic Treatment and Detoxification of Acid Orange 7 from Textile Wastewater. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 165, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwesh, O.M.; Matter, I.A.; Eida, M.F. Development of Peroxidase Enzyme Immobilized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Bioremediation of Textile Wastewater Dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyung, K.S.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H.; Indarto, A. Gliding Arc Plasma Processing for Decomposition of Chloroform. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2005, 87, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarto, A.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H. Oxidation of Chloroform in a Gliding-Arc Plasma: Observation of Molecular Vibrations. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2009, 37, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarto, A.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H.; Song, H.K. Treatment of CCl4 and CHCl3 Emission in a Gliding-Arc Plasma. Plasma Devices Oper. 2006, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarto, A.; Yang, D.R.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H.; Song, H.K. CCl4 Decomposition by Gliding Arc Plasma: Role of C2 Compounds on Products Distribution. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2007, 194, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indarto, A.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, H.; Song, H.K. Decomposition of CCl4 and CHCl3 on gliding arc plasma. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Manoj Kumar Reddy, P.; Rama Raju, B.; Karuppiah, J.; Linga Reddy, E.; Subrahmanyam, C. Degradation and Mineralization of Methylene Blue by Dielectric Barrier Discharge Non-Thermal Plasma Reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 217, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojčinović, B.P.; Roglić, G.M.; Obradović, B.M.; Kuraica, M.M.; Kostić, M.M.; Nešić, J.; Manojlović, D.D. Decolorization of Reactive Textile Dyes Using Water Falling Film Dielectric Barrier Discharge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.C.; Fernandes, L.R.; Simões, R.M.S. Oxidation Rates of Two Textile Dyes by Ozone: Effect of PH and Competitive Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 189–190, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichonovas, M.; Krugly, E.; Racys, V.; Hippler, R.; Kauneliene, V.; Stasiulaitiene, I.; Martuzevicius, D. Degradation of Various Textile Dyes as Wastewater Pollutants under Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 229, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, N.A.; Shaban, S.A.; Ibrahim, F.A.; Mahmoud, A.S. Degradation of Methyl Orange Using Fenton Catalytic Reaction. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benincá, C.; Peralta-Zamora, P.; Tavares, C.R.G.; Igarashi-Mafra, L. Degradation of an Azo Dye (Ponceau 4R) and Treatment of Wastewater from a Food Industry by Ozonation. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2013, 35, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ye, K.; Deng, J.; Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Zhao, S.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Conventional Ultrafiltration as Effective Strategy for Dye/Salt Fractionation in Textile Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10698–10708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Baltaru, M.C.; Tang, Y.P.; Bernstein, N.J.; Gao, P.; Balta, S.; Vlad, M.; Volodin, A.; Sotto, A.; et al. Tight Ultrafiltration Membranes for Enhanced Separation of Dyes and Na2SO4 during Textile Wastewater Treatment. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 514, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, G.; Trabelsi, R.; Ellouze, E.; Amar, R.B. New Treatment at Source Approach Using Combination of Microfiltration and Nanofiltration for Dyeing Effluents Reuse. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Dash, R.R.; Bhunia, P. A Review on Chemical Coagulation/Flocculation Technologies for Removal of Colour from Textile Wastewaters. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 93, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
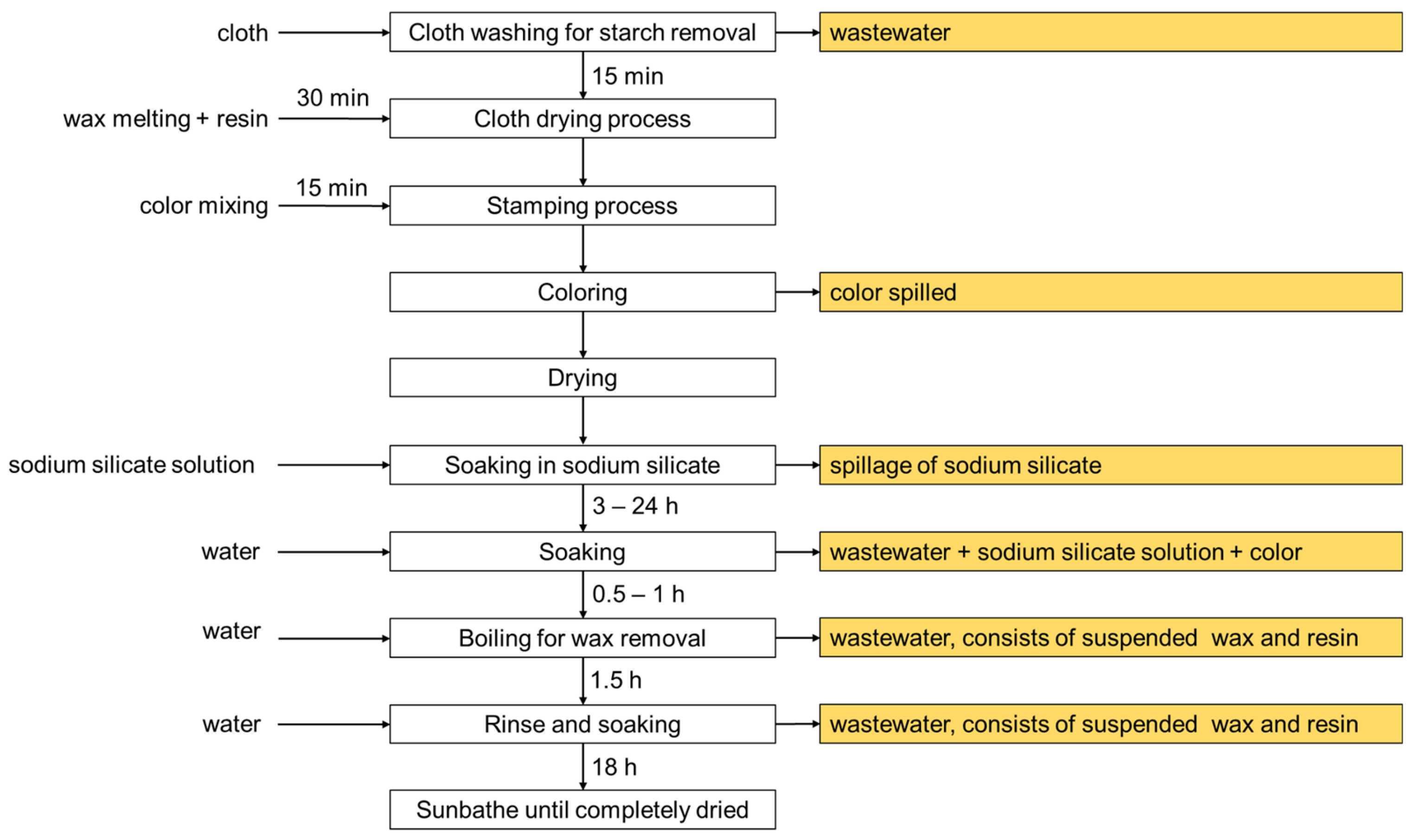


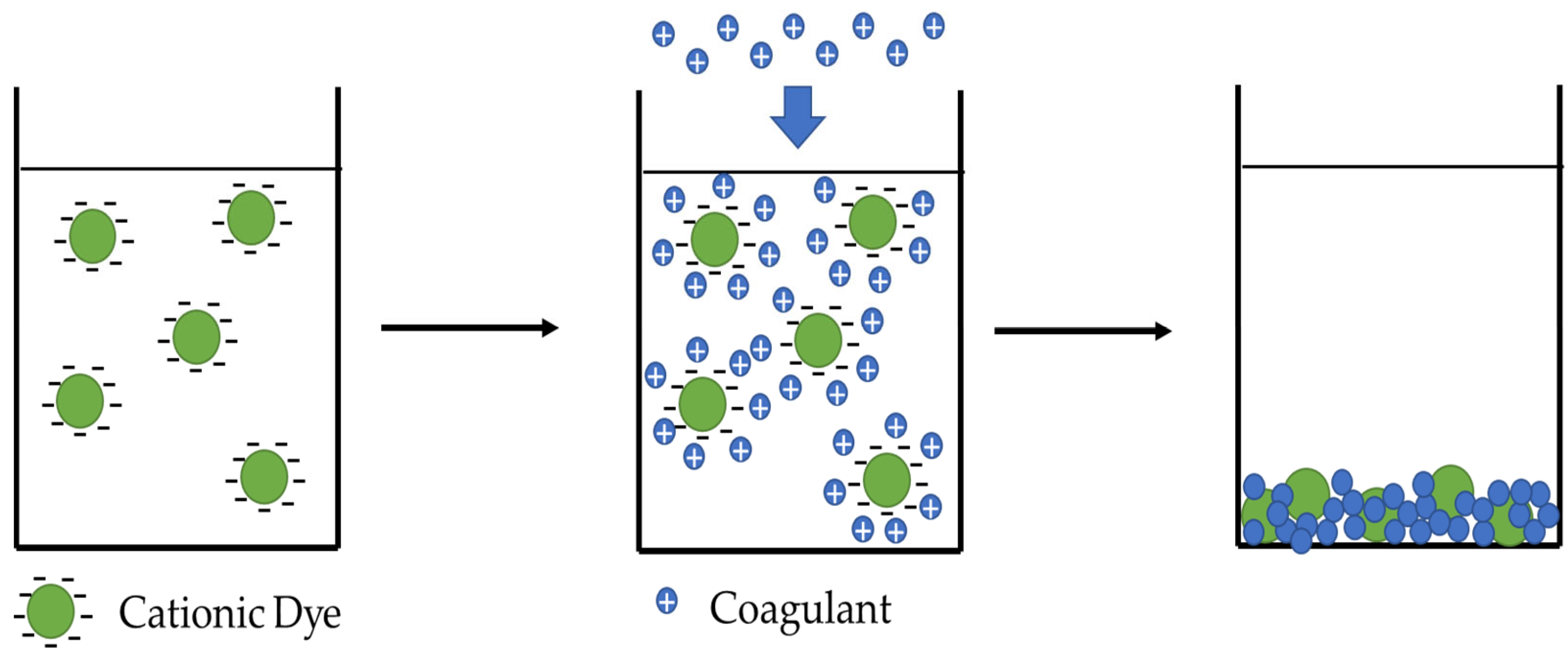
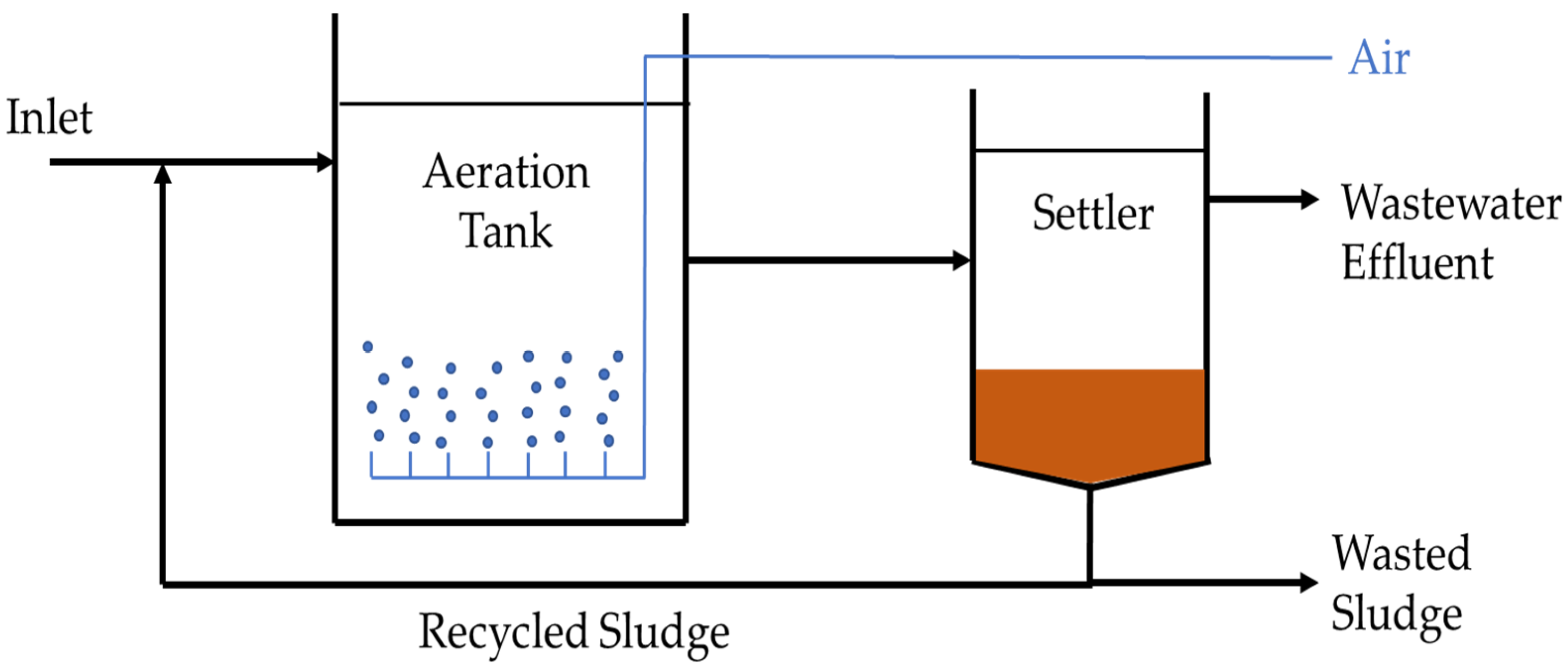

| Parameter | Batik Effluent 1 | Textile Effluent 2 | Permitted Value 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.65–12.5 | 5.5–10.5 | 5.5–9.0 |
| Dissolved Oxygen (DO) (mg/L) | 1.7–2.25 | - | 3 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 340 | 80–6000 | 50 |
| COD (mg/L) 4 | 1600–4090 | 150–30,000 | 250 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 305 | 15–8000 | 100 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 217 | - | - |
| Trade/Industry | Unit | Standard A | Standard B |
|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L mg/L mg/L | 80 80 80 | 350 250 300 |
| mg/L | 80 | 250 |
| mg/L | 400 | 400 |
| mg/L | 80 | 200 |
| Treatment Methods | Method Description | Dye Removal Performance | Advantages | Disadvantages | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fenton reagent | Decompose contaminants using strong oxidizing agents and iron ions as catalyst | 81.35–97.8% |
|
| [83,125] |
| Ozonation | Dissolving ozone in wastewater that acts as a strong oxidizing agent | 95–100% |
|
| [87,126] |
| Membrane filtration | Utilizes pore sizes and pressure to separate contaminants in wastewater |
|
|
| [33,39,59,127,128,129] |
| Coagulation | Adding coagulant as aggregation aid to increase the sedimentation rate of contaminants | 58–100% |
|
| [63,130] |
| Activated sludge | Utilizes sludge-like bacteria colony to degrade contaminants with aid of aeration | 89–95% |
|
| [99] |
| Trickling filter | Spraying wastewater over a filter bed that contains microorganism film on its surface | 72–99.8% |
|
| [103,104] |
| Physical/Chemical Method | Method Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photochemical | This process involves the use of a photochemical oxidant, such as hydrogen peroxide or ozone, which is activated by UV or visible light to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). | No sludge production | Formation of by-products |
| NaOCl | NaOCl is a strong oxidizing agent that can react with the chromophoric groups of dyes to break down their chemical structure and remove them from the water. | Initiates and accelerates azo-bond cleavage | Release of aromatic amine |
| Cucurbituril | Cucurbituril is a macrocyclic molecule with a hydrophobic cavity that can selectively bind to and trap guest molecules, including dyes. | Good sorption capacity for various dyes | High cost |
| Electrochemical destruction | The process relies on the application of an electric current to the contaminated water, which initiates a series of oxidation and reduction reactions that ultimately result in the destruction of the dye molecules. | Breakdown compounds are non-hazardous | High cost of electricity |
| Peat | Wastewater is pumped through a bed containing peat that allows for dye adsorption. | Good adsorbent due to the cellular structure | Specific surface area for adsorption is lower than activated carbon |
| Wood chips | The adsorption of dye molecules onto the surface of wood chips, that act as a natural adsorbent material. | Good sorption capacity for acid dyes | Requires long retention times |
| Silica gels | Silica gel is a synthetic, amorphous form of silicon dioxide with a high surface area and surface reactivity, making it an efficient adsorbent for various pollutants. | Effective for basic dye removal | Side reaction prevents commercial application |
| Ion exchange | The process relies on the selective affinity of ion exchange resins for specific ions or molecules. | Regeneration; no adsorbent loss | Not effective for all dyes |
| Irradiation | The process relies on the ability of certain wavelengths of radiation to initiate a series of chemical reactions that ultimately result in the degradation and destruction of the dye molecules. | Effective oxidation at lab scale | Requires a lot of dissolved oxygen |
| Microorganism | Method Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria (aerobic) | The process relies on the ability of aerobic bacteria to break down and convert the organic pollutants into carbon dioxide, water, and other harmless byproducts. |
|
|
| Bacteria (anaerobic) | The process relies on the ability of anaerobic bacteria to use alternative electron acceptors, such as nitrate, sulfates, or carbon dioxide to metabolize organic pollutants. |
|
|
| Fungi | The process relies on the ability of fungi to secrete enzymes that can degrade organic pollutants, including dyes and pesticides. |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakaria, N.; Rohani, R.; Wan Mohtar, W.H.M.; Purwadi, R.; Sumampouw, G.A.; Indarto, A. Batik Effluent Treatment and Decolorization—A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071339
Zakaria N, Rohani R, Wan Mohtar WHM, Purwadi R, Sumampouw GA, Indarto A. Batik Effluent Treatment and Decolorization—A Review. Water. 2023; 15(7):1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071339
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakaria, Nuriah, Rosiah Rohani, Wan Hanna Melini Wan Mohtar, Ronny Purwadi, Giovanni Arneldi Sumampouw, and Antonius Indarto. 2023. "Batik Effluent Treatment and Decolorization—A Review" Water 15, no. 7: 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071339
APA StyleZakaria, N., Rohani, R., Wan Mohtar, W. H. M., Purwadi, R., Sumampouw, G. A., & Indarto, A. (2023). Batik Effluent Treatment and Decolorization—A Review. Water, 15(7), 1339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071339






