Motion Characteristics of Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow of Microbubbles in a Labyrinth Channel Used for Aerated Drip Irrigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Micro-Nanobubble Water
2.2. Labyrinth Channels and Their Pressure-Flow Relationship
2.3. Aerated Drip Irrigation System
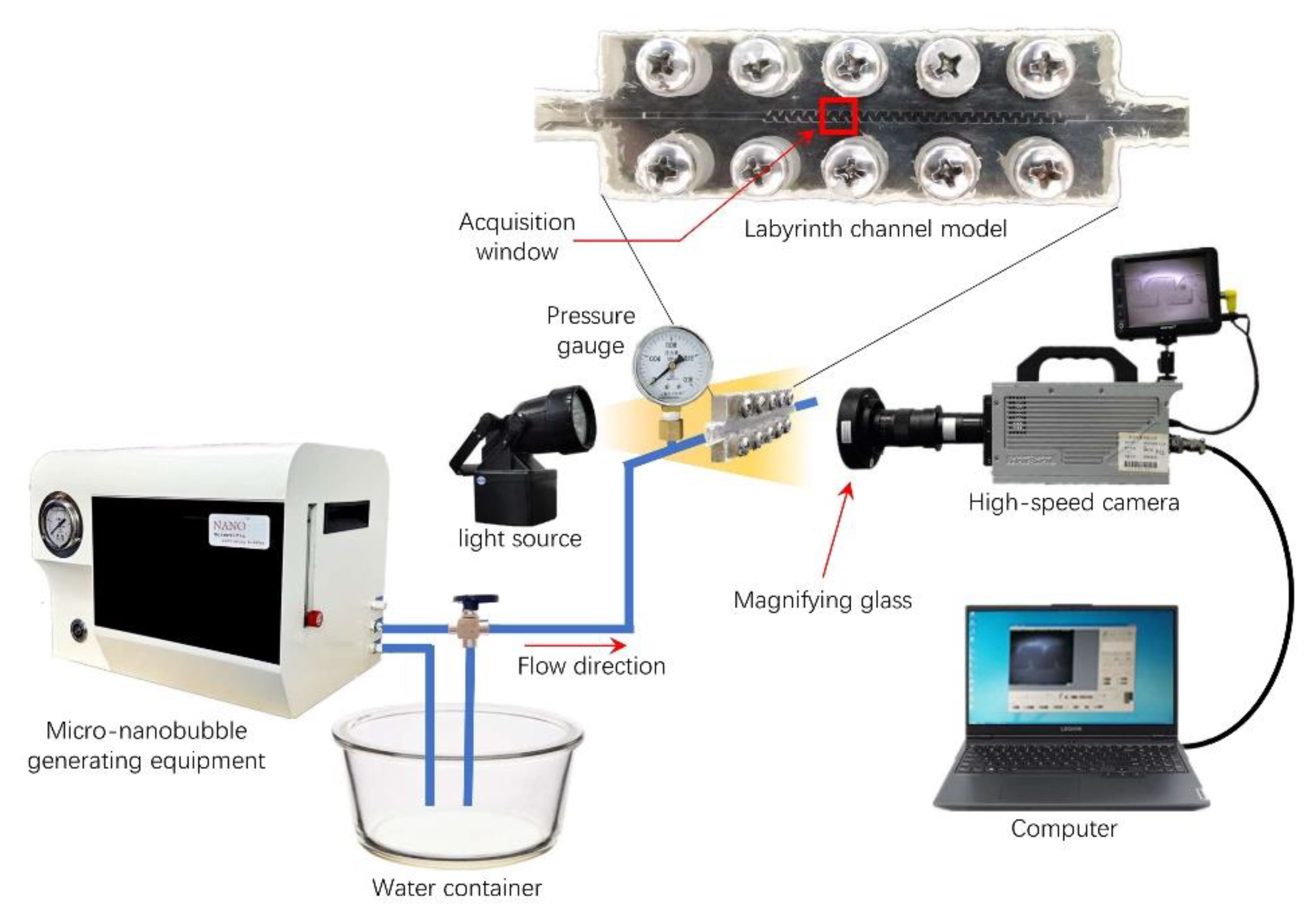
2.4. Imaging of the Labyrinth Channels
2.4.1. Equipment
2.4.2. Image Processing
2.5. Test Design and Data Processing
3. Results
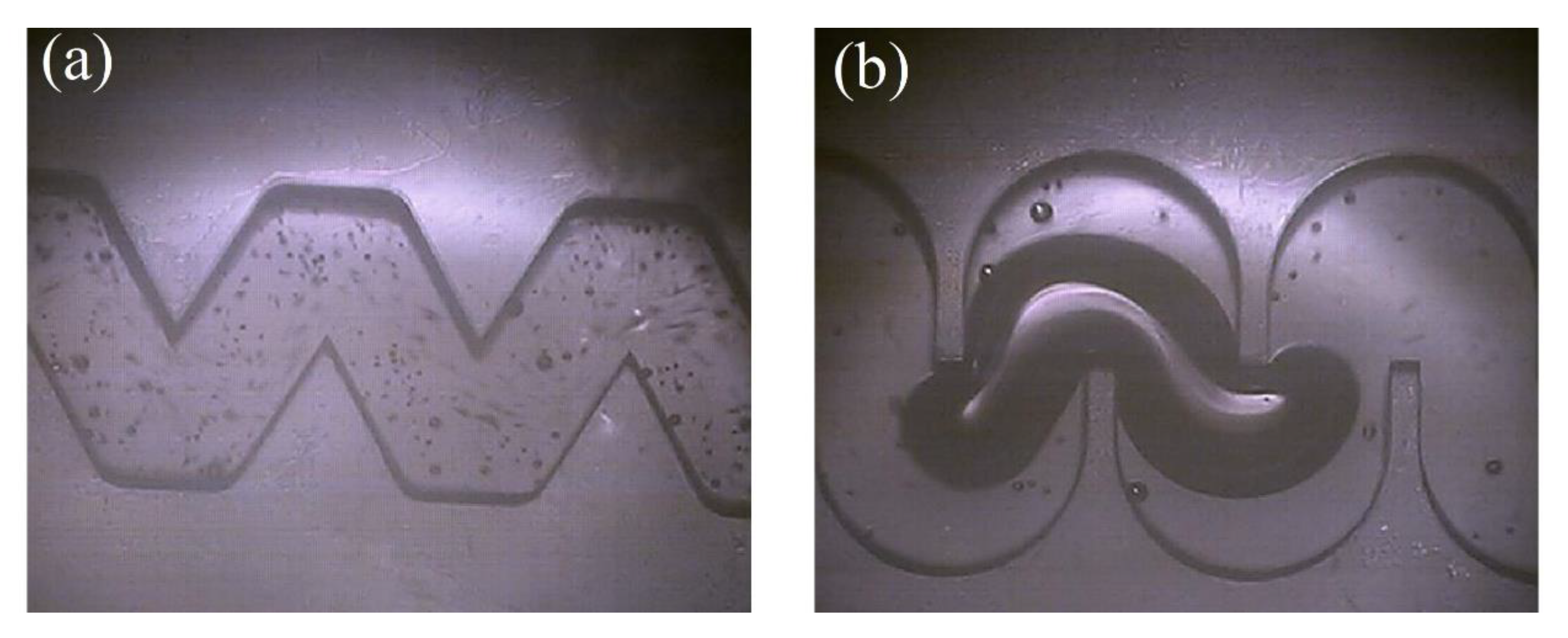
3.1. Flow Pattern of Gas-Liquid Two-Phase in a Labyrinth Channel
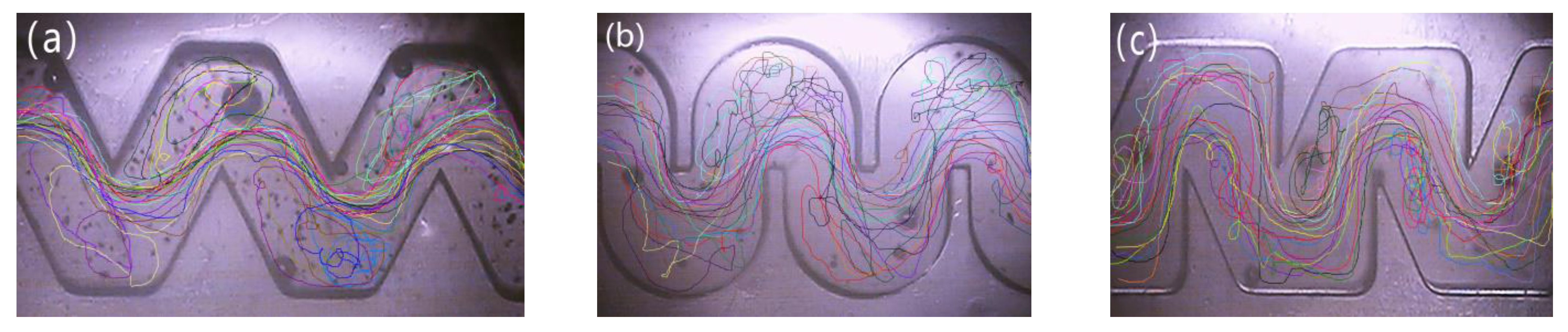
3.2. Bubble Trajectory
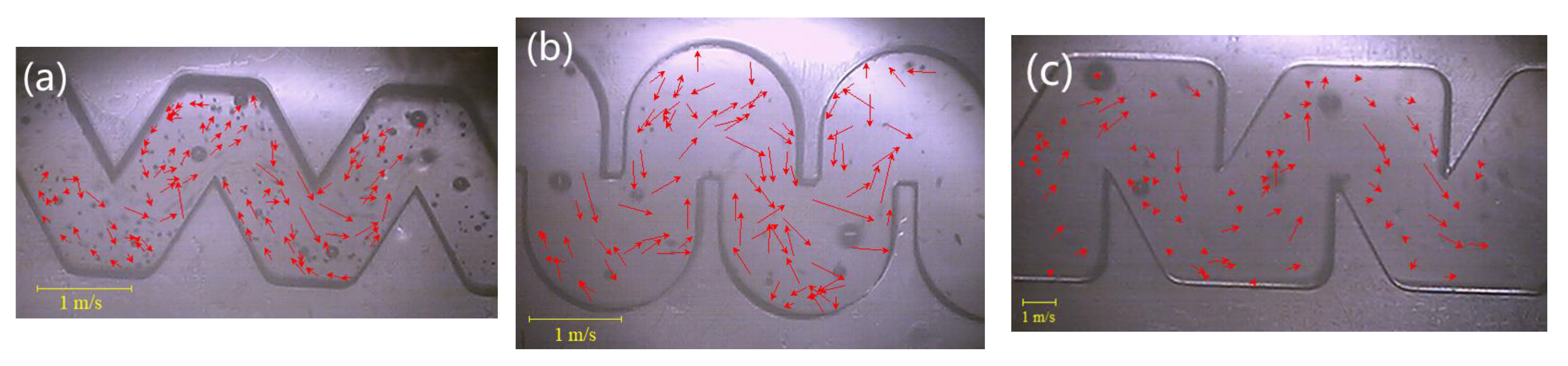
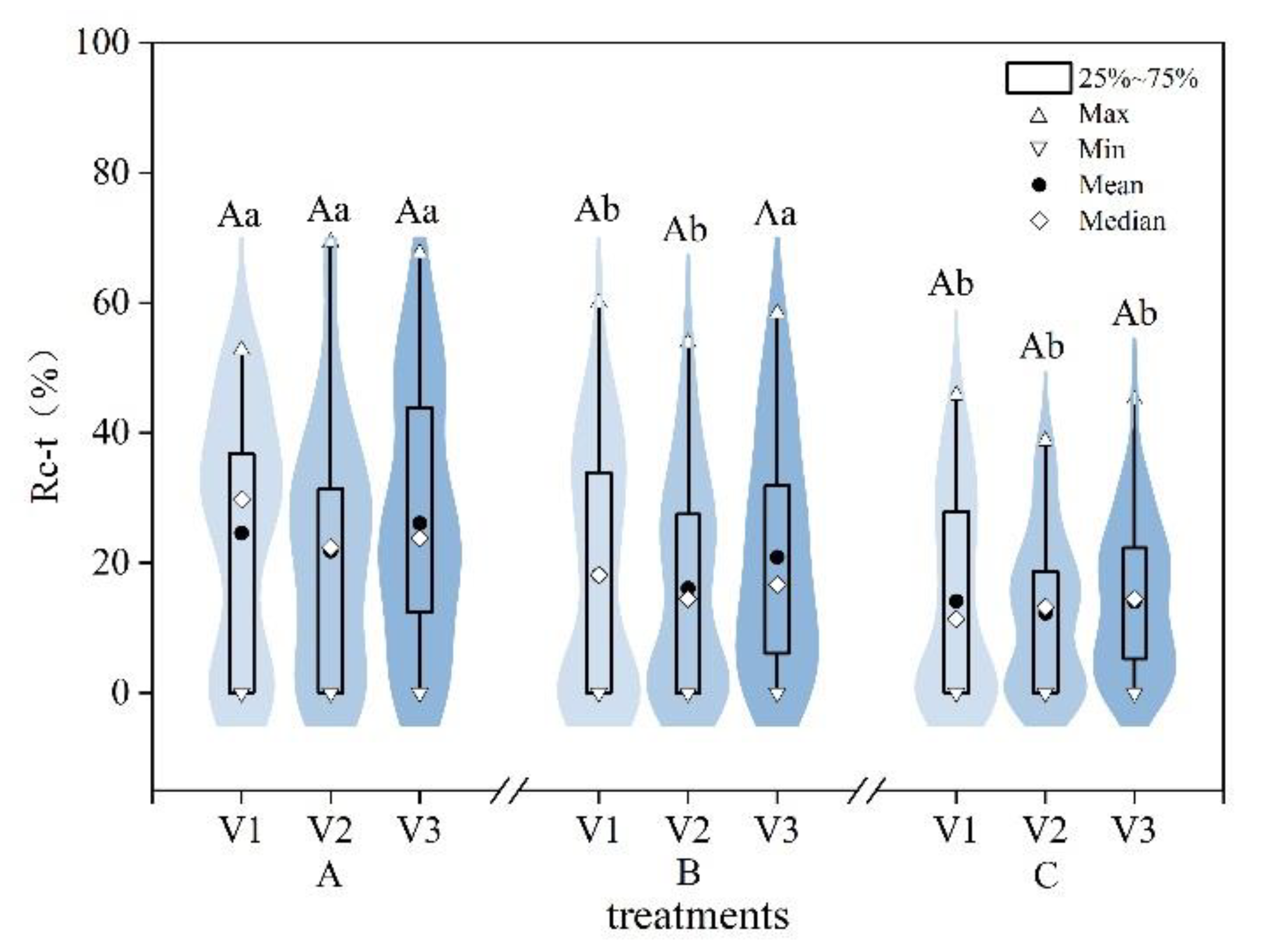
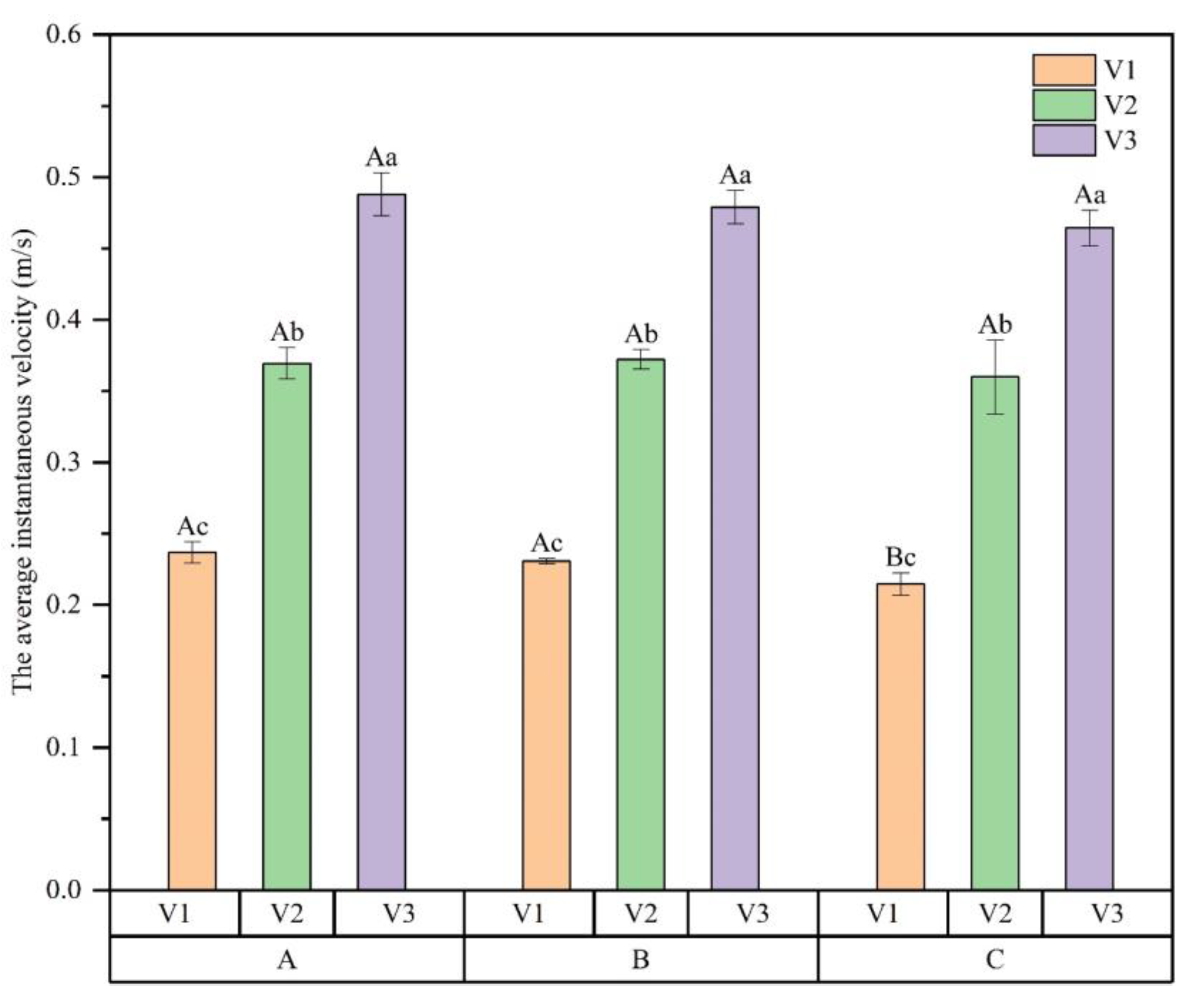
3.3. Bubble Velocity Vector
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abuarab, M.; Mostafa, E.; Ibrahim, M. Effect of air injection under subsurface drip irrigation on yield and water use efficiency of corn in a sandy clay loam soil. J. Adv. Res. 2013, 4, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Pendergast, L.; Midmore, D.J. Root aeration improves yield and water use efficiency of tomato in heavy clay and saline soils. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 108, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goorahoo, D.; Carstensen, G.; Zoldoske, D.F.; Mazzei, A. Using air in subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) to increase yields in bell pepper. In Proceedings of the 2002 California Plant and Soil Conference. Energy and Agriculture: Now and the Future; Fresno, CA, USA, 5–6 February 2002, California Chapter of American Society of Agronomy and California Plant Health Association: Fresno, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Bagatur, T. Evaluation of Plant Growth with Aerated Irrigation Water Using Venturi Pipe Part. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2014, 39, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Noah, I.; Friedman, S.P. Aeration of clayey soils by injecting air through subsurface drippers: Lysimetric and field experiments. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, H. Influence of micro/nanobubbles on clogging in drip irrigation systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 42338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Si, B. Behavior characteristics of micro-bubbles along labyrinth channels under different inlet pressures of micro-nano aeration drip irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. Trans. CSAE 2022, 38, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Zhang, E.; Gan, H.; Niu, W.; Ali, S.; Dong, A.; Zhang, W.; Wu, M.; Sun, D. Aerated drip irrigation increased the emitter clogging risk of the Yellow River water drip irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2023, 72, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuarab, M.E.; El-Mogy, M.M.; Hassan, A.M.; Abdeldaym, E.A.; Abdelkader, N.H.; El-Sawy, M.B.I. The Effects of Root Aeration and Different Soil Conditioners on the Nutritional Values, Yield, and Water Productivity of Potato in Clay Loam Soil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Muhammad, J.; Tomas, S.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; Amielh, M.; Anselmet, F. Experimental and numerical characterization of the vortex zones along a labyrinth milli-channel used in drip irrigation. Int. J. Heat Fluid Fl. 2019, 80, 108500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Huber, S.; Midmore, D.J. Aerated subsurface irrigation water gives growth and yield benefits to zucchini, vegetable soybean and cotton in heavy clay soils. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2004, 144, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Saddique, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cai, H. The effects of aeration and irrigation regimes on soil CO2 and N2O emissions in a greenhouse tomato production system. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Niu, W.; Gu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, B.; Zhao, Y. Crop yield and water use efficiency under aerated irrigation: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 210, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Kou, C.; Christie, P.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, F. Changes in the soil environment from excessive application of fertilizers and manures to two contrasting intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 145, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pendergast, L.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Midmore, D.J. Evaluation of aerated subsurface drip irrigation on yield, dry weight partitioning and water use efficiency of a broad-acre chickpea (Cicer arietinum, L.) in a vertosol. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xu, F.; Muhammad, T.; Li, Y. Appropriate dissolved oxygen concentration and application stage of micro-nano bubble water oxygation in greenhouse crop plantation. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 223, 105713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, M.; Midmore, D.J.; Walsh, K.B.; Bhattarai, S.P.; Tait, L. Analysis of factors affecting the availability of air bubbles to subsurface drip irrigation emitters during oxygation. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Bhattarai, S.; Balsys, R.; Midmore, D.J.; Holmes, T.; Zimmerman, W. Temporal and spatial dimension of dissolved oxygen saturation with fluidic oscillator and Mazzei air injector in soil-less irrigation systems. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Liu, H.; Balsys, R.; Midmore, D.J.; Zang, M.; Bhattarai, S. Factors of relevance for improving the uniformity of oxygen distribution in drip irrigation water. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabi, M.; Midmore, D.J.; Walsh, K.B.; Bhattarai, S.P. Improving the Uniformity of Emitter Air Bubble Delivery during Oxygation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 140, 06014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Liu, H.; Bhattarai, S.; Balsys, R.; Pan, H. Impacts of gas source and surfactant on gas-water coupling transmission along a long-distance drip tape in one or two line layout under aerated drip irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Balsys, R.J.; Eichler, P.; Midmore, D.J.; Wassink, D. Dynamic changes in bubble profile due to surfactant and tape orientation of emitters in drip tape during aerated water irrigation. Int. J. Multiphas. Flow 2015, 75, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, S.P.; Balsys, R.J.; Wassink, D.; Midmore, D.J.; Torabi, M. The total air budget in oxygenated water flowing in a drip tape irrigation pipe. Int. J. Multiphas. Flow 2013, 52, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, T.; Ren, S.; Lin, X.; Wei, R.; Xu, H. CFD and digital particle tracking to assess flow characteristics in the labyrinth flow path of a drip irrigation emitter. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Cao, M.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Lu, B. Flow behaviour analysis and experimental investigation for emitter micro-channels. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2012, 25, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Li, Z.; Long, J. Influence of Dentation Angle of Labyrinth Channel of Drip Emitters on Hydraulic and Anti-Clogging Performance. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhammad, J.; Tomas, S.; Ait-Mouheb, N.; Amielh, M.; Anselmet, F. Micro-PIV characterization of the flow in a milli-labyrinth-channel used in drip irrigation. Exp. Fluids 2018, 59, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhammad, J.; Tomas, S.; Anselmet, F. Modeling a weak turbulent flow in a narrow and wavy channel: Case of micro-irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2016, 34, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroud, C.N.; Gallaire, F.; Dangla, R. Dynamics of microfluidic droplets. Lab. Chip 2010, 10, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerdeira, A.T.S.; Campos, J.B.L.M.; Miranda, J.M.; Araújo, J.D.P. Review on Microbubbles and Microdroplets Flowing through Microfluidic Geometrical Elements. Micromachines 2020, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, M.; Das, S.K.; Balakrishnan, A.R. Effect of tube diameter on two-phase flow patterns in mini tubes. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 88, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisorn, S.; Wongwises, S. A review of two-phase gas–liquid adiabatic flow characteristics in micro-channels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liang, F.; Huang, N.; Cheng, C.; Lei, L. Visualization and void fraction of gas-liquid interfaces in minicircular tubes. J. Chem. Eng. Chin. Univ. 2021, 35, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, G.; Ye, C.; Yuan, Q. Gas–liquid two-phase flow in microchannel at elevated pressure. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 87, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Liao, Q.; Ding, Y.; Feng, H. Migration behavior of bubble cluster emerging from micro-orifice with liquid cross flow in mini-channel. CIESC J. 2014, 65, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, Z.; Wanhua, Z.; Yiping, T.; Zhengying, W.; Bingheng, L. Numerical investigation of the clogging mechanism in labyrinth channel of the emitter. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2007, 70, 1598–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, P.; Ren, S.; Wei, R.; Xu, H. Flow Characteristics in Energy Dissipation Units of Labyrinth Path in the Drip Irrigation Emitters with DPIV Technology. J. Hydrodyn. 2010, 22, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Numerical simulation of flow fields and particle movement characteristics in labyrinth channel emitter using different turbulence models. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 120–128. [Google Scholar]


| Indexes | Value |
|---|---|
| Average bubble diameter (nm) | 200.2 |
| Median bubble diameter (nm) | 155.2 |
| AD10 (nm) | 108.0 |
| D50 (nm) | 164.1 |
| D90 (nm) | 297.8 |
| Concentration (particles/mL) | 3.44 × 108 |
| Labyrinth Channel | q-H Relationship |
|---|---|
| A | q = 6.2554H0.4734 |
| B | q = 6.9107H0.4705 |
| C | q = 8.2504H0.4988 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Si, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Motion Characteristics of Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow of Microbubbles in a Labyrinth Channel Used for Aerated Drip Irrigation. Water 2023, 15, 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071432
Liu Y, Wang G, Zhang X, Li H, Si B, Liu W, Zhang Z. Motion Characteristics of Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow of Microbubbles in a Labyrinth Channel Used for Aerated Drip Irrigation. Water. 2023; 15(7):1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071432
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanfang, Guocui Wang, Xianna Zhang, Hongchen Li, Bingcheng Si, Wenqian Liu, and Zhenhua Zhang. 2023. "Motion Characteristics of Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow of Microbubbles in a Labyrinth Channel Used for Aerated Drip Irrigation" Water 15, no. 7: 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071432
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, G., Zhang, X., Li, H., Si, B., Liu, W., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Motion Characteristics of Gas–Liquid Two-Phase Flow of Microbubbles in a Labyrinth Channel Used for Aerated Drip Irrigation. Water, 15(7), 1432. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15071432






