Reverse Salt Flux Effect on Dewatering Chlorella vulgaris in a Forward Osmosis System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FO System
2.2. Algal Species and Cultivation
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Experimental Protocol
3. Results
3.1. pH
3.2. Conductivity
3.3. Lipid Content
3.4. Settling Velocity
3.5. Algal Biomass
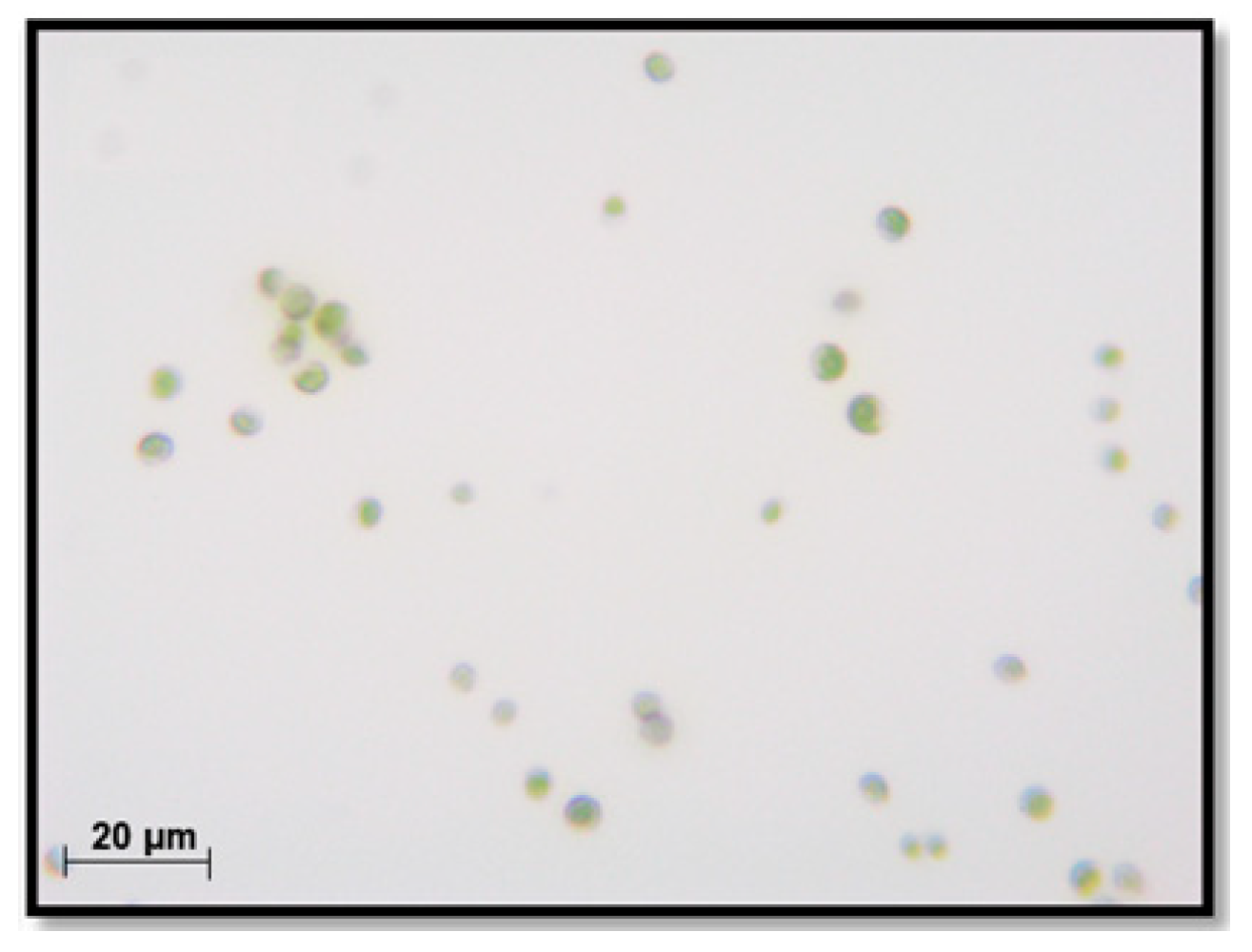
3.6. Microscopic Investigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, J.-M.; Cheng, L.-H.; Xu, X.-H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.-L. Enhanced lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris by adjustment of cultivation conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6797–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Yen, H.-W.; Ho, S.-H.; Lo, Y.-C.; Cheng, C.-L.; Ren, N.; Chang, J.-S. Cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris JSC-6 with swine wastewater for simultaneous nutrient/COD removal and carbohydrate production. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Church, J.; Lee, S.-J.; Park, J.; Lee, W.H. Use of microalgae for advanced wastewater treatment and sustainable bioenergy generation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azov, Y. Effect of pH on inorganic carbon uptake in algal cultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 43, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Ling, M.; Chung, T.-S. Draw solutions for forward osmosis processes: Developments, challenges, and prospects for the future. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K.; Hong, S.; Lee, S.; Vigneswaran, S. A novel low energy fertilizer driven forward osmosis desalination for direct fertigation: Evaluating the performance of fertilizer draw solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, F.M.; Church, J.; McLean, R.; Maier, N.; Sadmani, A.H.M.A.; Duranceau, S.J.; Lee, W.H. Dewatering algae using an aquaporin-based polyethersulfone forward osmosis membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 204, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferby, M.; Zou, S.; He, Z. Reduction of reverse solute flux induced solute buildup in the feed solution of forward osmosis. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeesang, C.; Cheirsilp, B. Effect of nitrogen, salt, and iron content in the growth medium and light intensity on lipid production by microalgae isolated from freshwater sources in Thailand. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.; Hwang, J.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; McLean, R.; Oh, Y.-K.; Nam, B.; Joo, J.C.; Lee, W.H. Effect of salt type and concentration on the growth and lipid content of Chlorella vulgaris in synthetic saline wastewater for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.-L.; Chang, J.-S. Effects of cultivation conditions and media composition on cell growth and lipid productivity of indigenous microalga Chlorella vulgaris ESP-31. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 105, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Discart, V.; Bilad, M.R.; Marbelia, L.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Impact of changes in broth composition on Chlorella vulgaris cultivation in a membrane photobioreactor (MPBR) with permeate recycle. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 152, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, P.; Murthy, S.D.S. Effects of salt stress on basic processes of photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 2004, 42, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillip, W.A.; Yong, J.S.; Elimelech, M. Reverse Draw Solute Permeation in Forward Osmosis: Modeling and Experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5170–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, L.M.; Hayes, D.G.; Womac, A.R.; Labbe, N. Simplified determination of lignin content in hard and soft woods via UV-spectrophotometric analysis of biomass dissolved in ionic liquids. BioResources 2010, 5, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, J.R. Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements; CUP Archive: Cambridge, UK, 1979; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, P.; Cook, C. Effects of host feeding and dissolved ammonium on cell division and nitrogen status of zooxanthellae in the hydroid Myrionema amboinense. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.; Whitton, B. Effect of pH on growth of acid stream algae. Br. Phycol. J. 1976, 11, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayo, A.W. Effects of temperature and pH on the kinetic growth of unialga Chlorella vulgaris cultures containing bacteria. Water Environ. Res. 1997, 69, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Li, T.; Huang, H. Bioaccumulation and ecophysiological responses to copper stress in two populations of Rumex dentatus L. from Cu contaminated and non-contaminated sites. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2004, 52, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimer, Y.M. The effects of sodium chloride, potassium chloride and glycerol on the activity of nitrate reductase of a salt-tolerant and two non-tolerant plants. Planta 1973, 113, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia-Arroyo, T.; Wei, W.; Ruan, R.; Hu, B. Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris and its potential application for the oil accumulation from non-sugar materials. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeliovich, A.; Azov, Y. Toxicity of ammonia to algae in sewage oxidation ponds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1976, 31, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, M.K.H.; Bassin, J.P.; Kleerebezem, R.; van der Lans, R.G.J.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Temperature and salt effects on settling velocity in granular sludge technology. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5445–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Draw Solution (mM) | Draw Solution (mg L−1) | Feed Solution (g L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | KCl | NH4Cl | ||
| 8 | 467.5 | 596.4 | 427.9 | 0.37 dry C. vulgaris biomass |
| 32 | 1870.1 | 2385.6 | 1711.7 | |
| 80 | 4675.2 | 5964.1 | 4279.3 | |
| KCl | NH4Cl | NaCl | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mM | 0.379 ± 0.023 | 0.358 ± 0.014 | 0.382 ± 0.009 |
| 32 mM | 0.377 ± 0.015 | 0.361 ± 0.007 | 0.382 ± 0.009 |
| 80 mM | 0.366 ± 0.012 | 0.358 ± 0.014 | 0.385 ± 0.013 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munshi, F.M.; Hwang, J.-H.; Stoll, S.; Lee, W.H. Reverse Salt Flux Effect on Dewatering Chlorella vulgaris in a Forward Osmosis System. Water 2023, 15, 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081462
Munshi FM, Hwang J-H, Stoll S, Lee WH. Reverse Salt Flux Effect on Dewatering Chlorella vulgaris in a Forward Osmosis System. Water. 2023; 15(8):1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081462
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunshi, Faris M., Jae-Hoon Hwang, Stephanie Stoll, and Woo Hyoung Lee. 2023. "Reverse Salt Flux Effect on Dewatering Chlorella vulgaris in a Forward Osmosis System" Water 15, no. 8: 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081462
APA StyleMunshi, F. M., Hwang, J.-H., Stoll, S., & Lee, W. H. (2023). Reverse Salt Flux Effect on Dewatering Chlorella vulgaris in a Forward Osmosis System. Water, 15(8), 1462. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081462








