Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
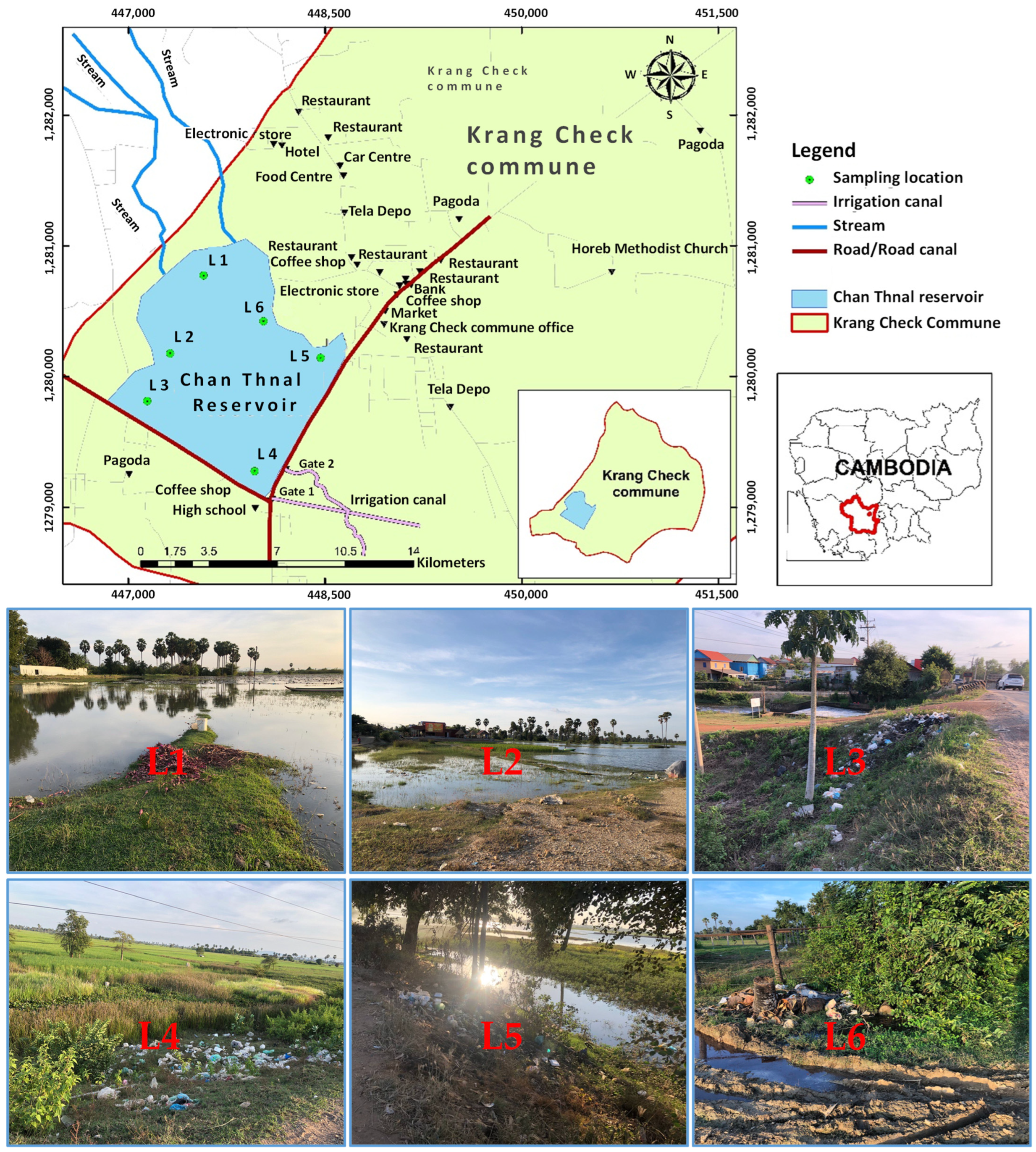
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Pollution Assessment Methods
2.4.1. Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo)
2.4.2. Ecological Risk (ER) and Potential Ecological Risk (PER)
2.4.3. Contamination Source Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Contamination Levels
| Locations | Mean Concentrations (mg/kg) in Sediment Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cu | Zn | Pb | As | Cr | Mn | Co | Fe | |
| L1 | 0.09 e | 8.39 d | 16.06 d | 3.33 f | 0.35 f | 11.52 f | 0.29 d | 2.45 e | 1794.70 b |
| L2 | 0.17 c | 8.51 d | 12.54 e | 9.77 d | 2.95 d | 14.42 d | 1.25 a | 6.68 d | 2236.00 a |
| L3 | 0.30 a | 25.11 a | 29.10 b | 16.04 a | 4.74 c | 20.25 b | 0.45 c | 12.79 a | 1990.00 b |
| L4 | 0.24 b | 16.84 c | 22.11 c | 14.45 b | 6.90 a | 22.37 a | 0.66 b | 8.56 c | 1388.60 c |
| L5 | 0.14 d | 9.90 d | 9.45 e | 8.14 e | 1.13 e | 17.14 c | 0.29 d | 7.60 c,d | 1160.20 c |
| L6 | 0.26 b | 22.00 b | 37.30 a | 11.95 c | 5.80 b | 13.28 d | 0.28 d | 10.76 b | 1386.60 c |
| Average ± SD | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 15.13 ± 0.98 | 21.09 ± 1.42 | 10.61 ± 0.72 | 3.64 ± 0.25 | 16.50 ± 0.72 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 8.14 ± 0.58 | 1659.35 ± 102.67 |
| CV (%) | 5 | 6.47 | 6.73 | 6.79 | 6.87 | 4.36 | 2.16 | 7.13 | 6.19 |
| Earth’s crust 1 | 0.09 | 28 | 67 | 17 | 4.8 | 92 | 950 | 20 | 41,000 |
| Bn 2 | 0.01 | 2.3 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 1.5 | 3.4 | 488 | 0.6 | 3500 |
| WHO 3 | 0.1 | 20 | <1 | 5 | 0.2–1.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | - | 5 |
| Thailand 4 | 0.16 | 21.5 | 80 | 36 | 10 | 45.5 | - | - | - |
3.2. Environmental Quality Evaluation of the Sediment from the Chan Thnal Reservoir
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
3.4. Identification of the Contamination Source
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chheang, L.; Thongkon, N.; Sriwiriyarat, T.; Thanasupsin, S.P. Heavy metal contamination and human health implications in the Chan Thnal reservoir, Cambodia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.B.; Singh, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Vegetables: A Threat to Human Health. Terr. Aquat. Environ. Toxicol. 2007, 1, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kladsomboon, S.; Jaiyen, C.; Choprathumma, C.; Tusai, T.; Apilux, A. Heavy metals contamination in soil, surface water, crops, and resident blood in Uthai District, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Thailand. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, H.B. Chapter 1 Sources and origins of heavy metals. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Agyeman, P.C.; Ahado, S.K.; John, K.; Kebonye, N.M.; Vašát, R.; Borůvka, L.; Kočárek, M.; Němeček, K. Health risk assessment and the application of CF-PMF: A pollution assessment–based receptor model in an urban soil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3117–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomirović, M.; Ćirović, Ž.; Maksin, D.; Bakić, T.; Lukić, J.; Stanković, S.; Onjia, A. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soil at a Former Painting Industry Facility. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 560415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adimalla, N.; Chen, J.; Qian, H. Spatial characteristics of heavy metal contamination and potential human health risk assessment of urban soils: A case study from an urban region of South India. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbueri, J.C.; Ukah, B.U.; Ubido, O.E.; Unigwe, C.O. A chemometric approach to source apportionment, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in industrial soils from southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 3399–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, H.; Gabarrón, M.; Abbaspour, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Faz, A.; Acosta, J.A. Environmental Impact Assessment of Industrial Activities on Heavy Metals Distribution in Street Dust and Soil; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Monged, M.H.E.; Hassan, H.B.; El-Sayed, S.A. Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Natural Radionuclides and Trace Elements in Agricultural Soil of Northeastern Nile Valley, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Fan, X.; Yang, Y. Ascertaining the pollution, ecological risk and source of metal(loid)s in the upstream sediment of Danjiang River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Shen, Z. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.I.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Mehmood, M.S.; Sajid, M.; Su, P.; Khan, A.J.K. Contamination Level, Ecological Risk, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Hyporheic Zone of the Weihe River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhien, H.T.H.; Nguyen, G.T. Environmental soil, water, and sediment quality of dong thang landfill in Can Tho City, Vietnam. Appl. Environ. Res. 2019, 41, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Kamani, H.; Shahsavani, S.; Hoseini, M. Environmental monitoring and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soils. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2021, 27, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongyuan, S.; Khantamoon, T.; Aendo, P.; Binot, A.; Tulayakul, P. Ecological and health risk assessment, carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects of heavy metals contamination in the soil from municipal solid waste landfill in Central, Thailand. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 27, 876–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, S.; Shen, L.; Li, S.; Cui, J.; Liu, Y. Bioaccumulation, trophic transfer, and human health risk of quinolones antibiotics in the benthic food web from a macrophyte-dominated shallow lake, North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defarge, N.; Spiroux de Vendômois, J.; Séralini, G.E. Toxicity of formulants and heavy metals in glyphosate-based herbicides and other pesticides. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.H.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Hu, G.C.; Chen, L.G.; Luo, J. An integrated approach to quantifying ecological and human health risks from different sources of soil heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerban, M.; Maihemuti, B.; Waili, Y.; Tuerhong, T. Ecological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metal pollution in vegetable bases of Urumqi, China, using the positive matrix factorization (PMF) method. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yi, L.; Lu, A.; Xie, B.; Peng, H. Evaluating Metal(loid)s Contamination in Soil of a Typical In-Dustry Smelting Site in South Central China: Levels, Possible Sources and Human Health Risk Analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhan, X.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, S. Effect of weathering on environmental behavior of microplastics: Properties, sorption and potential risks. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluhator, M.M.; Thomson, A.B.R.; Fedorak, R.N. Clinical aspects of trace elements: Zinc in human nutrition—Assessment of zinc status. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 1996, 10, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Paatero, P.; Malm, W.C.; Sisler, J.F. Atmospheric aerosol over Alaska 2. Elemental composition and sources. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 19045–19057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokcheng, S.; Socheat, K.; Molideth, S. Pesticide Use Practices in Cambodia’s Vegetable Farming; Cambodia Development Resource Institute (CDRI): Phnom Penh, Cambodia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.Q. Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Mao, L.; Sun, R.; Du, J.; Tan, Z.; Ding, M. Contamination evaluation and source identification of heavy metals in the sediments from the lishui river watershed, southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chand, V.; Prasad, S. ICP-OES assessment of heavy metal contamination in tropical marine sediments: A comparative study of two digestion techniques. Microchem. J. 2013, 111, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchuwararak, P.; Intamat, S.; Tengjaroenkul, B.; Neeratanaphan, L. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in local edible plants near a municipal landfill and the related human health risk assessment. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 25, 1549–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriuttha, M.; Tengjaroenkul, B.; Intamat, S.; Phoonaploy, U.; Thanomsangad, P.; Neeratanaphan, L. Cadmium, chromium, and lead accumulation in aquatic plants and animals near a municipal landfill. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Ali, M.L.; Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.Z. Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 5, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, T.O.; Yilmaz, F. Metal pollution assessment in water and sediment of Sarıcay stream in Mugla-Turkey. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 786–794. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, E.; Pandey, J. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water and surface sediment and evaluation of ecological risks associated with sediment contamination in the Ganga River: A basin-scale study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10926–10940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, G.; Ramasamy, V.; Meenakshisundaram, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Ponnusamy, V. Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Cao, Q.; Zheng, Y.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Zhu, Y.G. Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development, Publushing House: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; p. 136.
- Weber, P.; Behr, E.R.; De Lellis Knorr, C.; Secretti Vendruscolo, D.; Flores, E.M.M.; Dressler, V.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Wang, Y.; Tan, S.N.; Mohd Yusof, M.L.; Ghosh, S.; Chen, Z. Phytoremediation: A Promising Approach for Revegetation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Land. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abel, M.T.; Suedel, B.; Presley, S.M.; McDaniel, L.N.; Rigdon, R.; Goebel, T.; Lascano, R.J.; Zartman, R.; Anderson, T.A.; Cobb, G.P. Contribution of Soil Lead to Blood Lead in Children: A Study from New Orleans, LA. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarcinas, A.B.; Pongsakul, P.; McLaughlin, J.M.; Cozens, G. Heavy metals in soils and crops in Southeast Asia. 2. Thailand. Environ. Geochem. Health 2004, 26, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayinka-Olagunju, J.O.; Olatunji-Ojo, A.M. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Pelagic and Benthic Fishes of Ogbese River, Ondo State, South-Western Nigeria. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollution Control Department. Sediment Quality Criteria in Surface Water Resources; Pollution Control Department, Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Bangkok, Thailand, 2018.
- Zhu, D.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, J. Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of the Agriculture Soil in Xunyang Mining Area, Shaanxi Province, Northwestern China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimpour, M.; Mushrifah, I. Heavy metal concentrations in water and sediments in Tasik Chini, a freshwater lake, Malaysia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 141, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbassi, A.R.; Monavari, S.M.; Nabi Bidhendi, G.R.; Nouri, J.; Nematpour, K. Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 147, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlotman, D.E.; Ngila, J.C.; Ndlovu, T.; Malinga, S.P. Hyperbranched polymer integrated membrane for the removal of arsenic(III) in water. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2018, 4, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasumana, C.; Fonseka, S.; Fernando, A.; Jayalath, K.; Amarasinghe, M.; Siribaddana, S.; Gunatilake, S.; Paranagama, P. Phosphate fertilizer is a main source of arsenic in areas affected with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Marshall, G.; Liaw, J.; Yuan, Y.; Ferreccio, C.; Steinmaus, C. Mortality in young adults following in utero and childhood exposure to arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Preventing Disease through Healthy Environment—Exposure to Arsenic: A Major Public Health Concern; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–5.
- Plum, L.M.; Rink, L.; Hajo, H. The essential toxin: Impact of zinc on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1342–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasuluk, P.; Chotpantarat, S.; Siriwong, W.; Robson, M. Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Qin, J.; Peng, Z. Source identification, spatial distribution pattern, risk assessment and influencing factors for soil heavy metal pollution in a high-tech industrial development zone in Central China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2021, 27, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Uwizeyimana, H. Impacts of urbanization and landscape patterns on the accumulation of heavy metals in soils in residential areas in Beijing. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Prakash, J.; Habib, G.; Baudh, K.; Nasr, M. Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dust in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30413–30425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.J.; Rouillon, M.; Dong, C.; Ettler, V.; Handley, H.K.; Taylor, M.P.; Tyson, E.; Tennant, P.; Telfer, V.; Trinh, R. Geochemical sources, forms and phases of soil contamination in an industrial city. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Lv, J. Integrated receptor models and multivariate geostatistical simulation for source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in soils. Catena 2020, 194, 104638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehlić, E.; Nanić, H.; Jukić, H.; Aldžić, A. Determination of Heavy Metals in Hair Dyes by the Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2019, 42, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafaii, G.; Karamali, F.; abooSaedi, Z.; Atoof, F.; Hesami Arani, M.; Miranzadeh, M.B. Determination of Heavy Metals in Hair Dye Sale in Iranian Market: Dermal Sensitivity and Carcinogenicity Assessment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.A.M.; Goher, A.S.; Alzubaidi, A.A.A.M. Risk assessment of heavy metals content in different hair dyes and their users’ urine samples. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 101, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chheang, L.; Limsuwan, P.; Thongkon, N.; Sriwiriyarat, T.; Thanasupsin, S.P. Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia. Water 2023, 15, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081566
Chheang L, Limsuwan P, Thongkon N, Sriwiriyarat T, Thanasupsin SP. Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia. Water. 2023; 15(8):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081566
Chicago/Turabian StyleChheang, Lita, Pichet Limsuwan, Nisakorn Thongkon, Tongchai Sriwiriyarat, and Sudtida Pliankarom Thanasupsin. 2023. "Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia" Water 15, no. 8: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081566
APA StyleChheang, L., Limsuwan, P., Thongkon, N., Sriwiriyarat, T., & Thanasupsin, S. P. (2023). Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia. Water, 15(8), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081566







