Binary Coati Optimization Algorithm- Multi- Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine-Extreme Learning Machine Model (BCOA-MKLSSVM-ELM): A New Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Predicting Reservoir Water Level
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The MKLSSVM model is introduced to predict the water level of a reservoir in Malaysia.
- The LLSVM and MKLSSVM model is coupled with the extreme learning machine (ELM) model to predict water level fluctuations. In addition, the hybrid model boosts the learning ability of the LLSVM and MKLSSVM models.
- This study introduces a novel binary optimization algorithm for choosing input data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Structure of the LLSVM Model
2.2. Structure of the Multi-Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine Model (MKLSSVM)
- Radial basis function (LSSVM-RBF)
- Linear Kernel Function (LSSVM-LKF)
- Polynomial Kernel Function (LSSVM-PKF)where c, and : kernel parameters, and d (power of equation) = 3. Equation (9) shows a combination of kernel functions:where qi: ith input qj: jth: input , , and : Weight coefficients, , , and : RBF, LKF, and PKF. Since there is no priority, we assign equal weights to the kernel functions. Kernel parameters are set using an optimization algorithm.
2.3. Structure of Extreme Learning Machine (ELM)
2.4. Optimization Algorithm
2.5. Structure of Coati Optimization Algorithm—ELM-MKLSSVM
3. Case Study
- 1
- Root mean square error (RMSE)
- 2
- Mean absolute error (MAE)
- 3
- Nash–Sutcliff efficiency (NSE)
- 4
- Willmott indexwhere, : Estimated Water level, : Observed Water Level, : Average observed Water level, n: number of data. Ideal models have high WI and NSE values.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Determination of Optimal Input Scenario
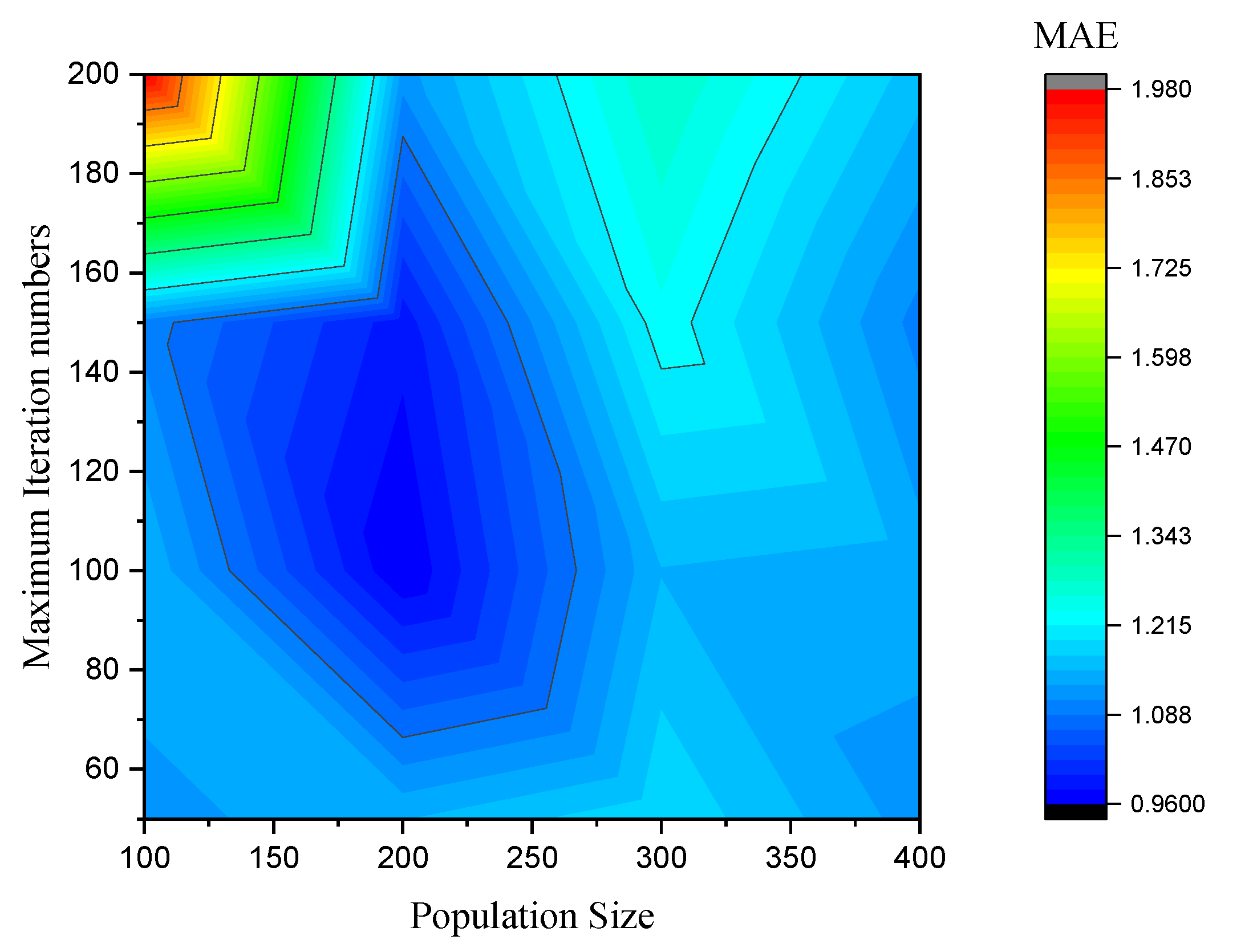
4.2. Determination of Random Parameters
4.3. Evaluation of the Accuracy of LSSVM Models
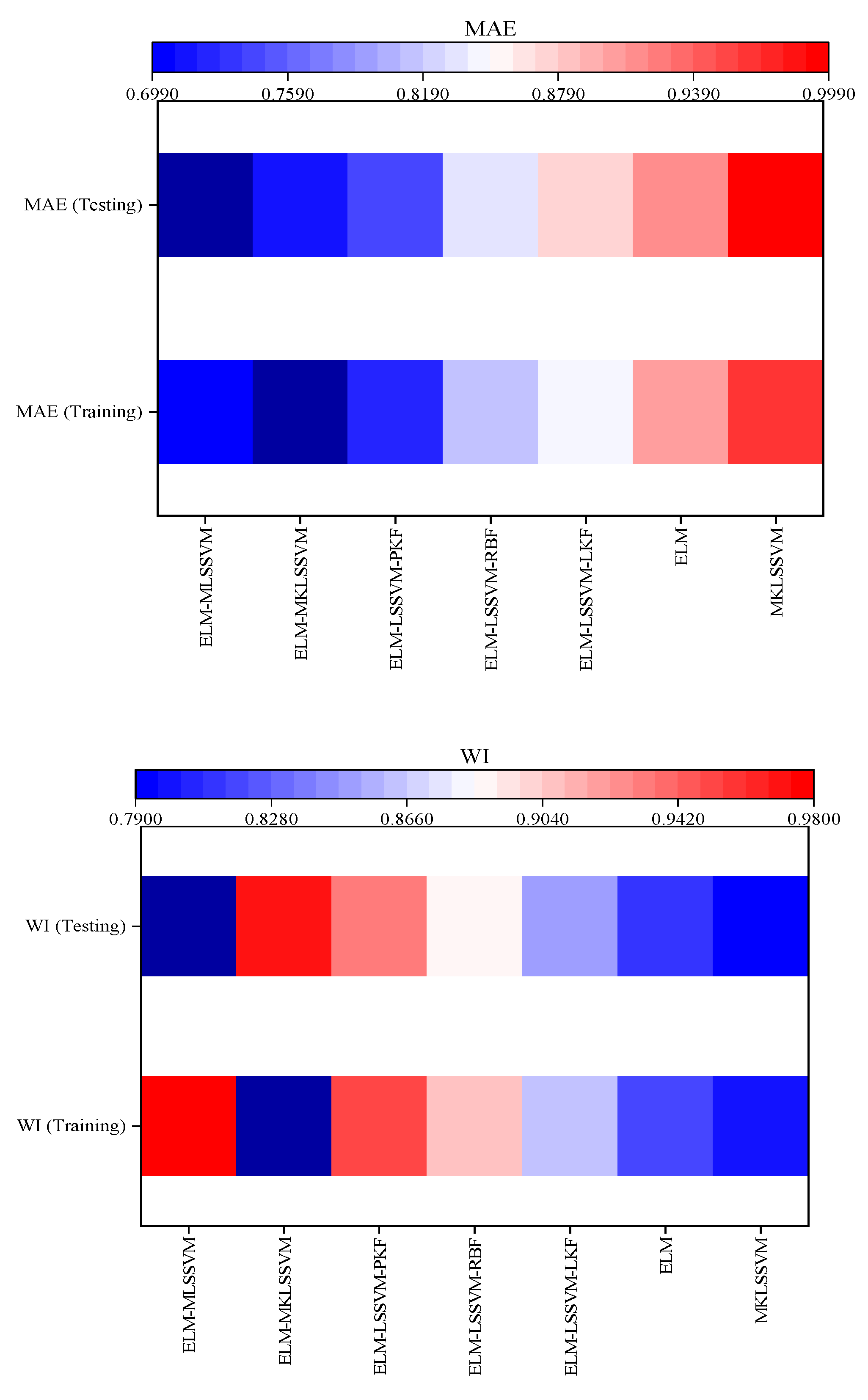
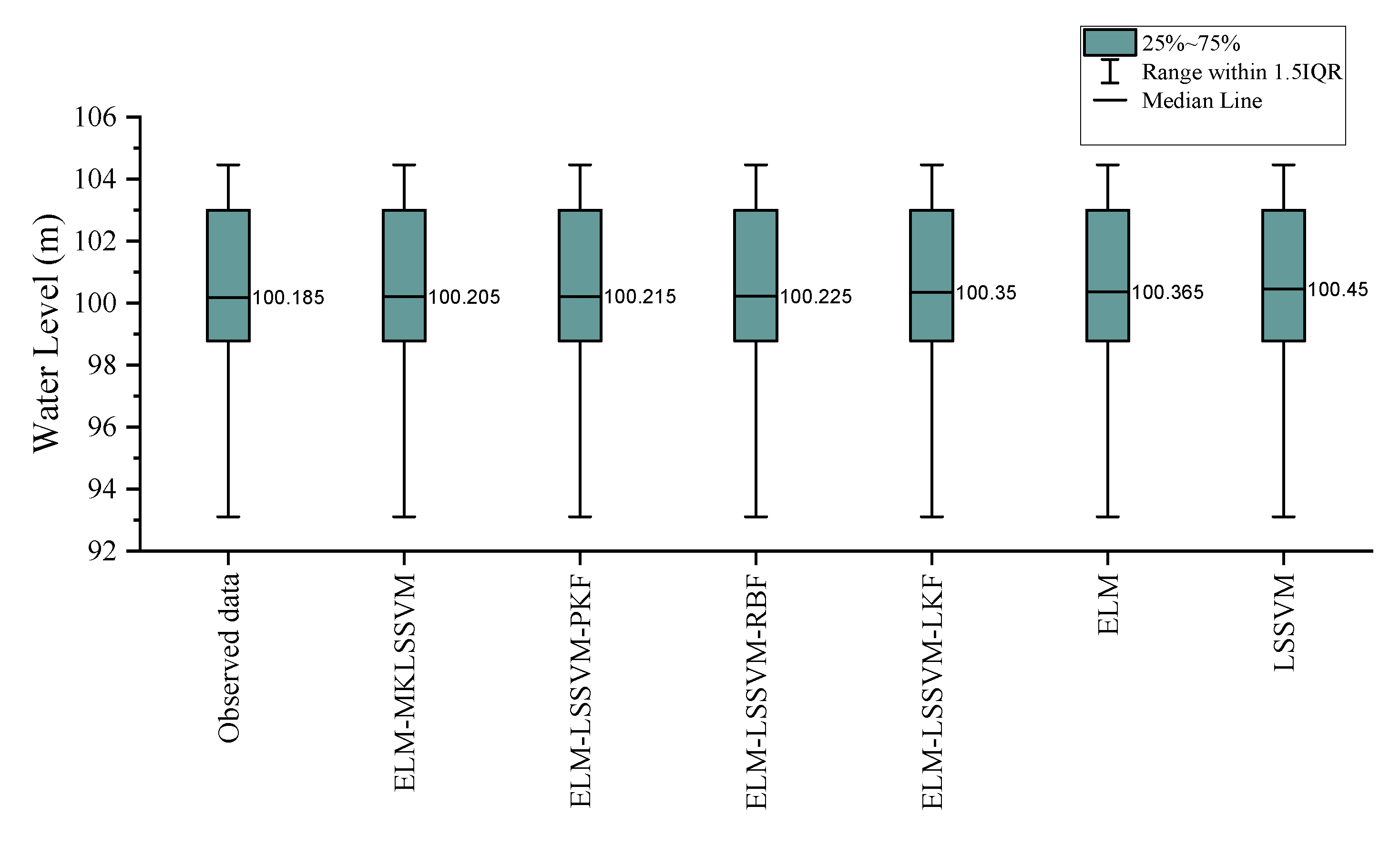
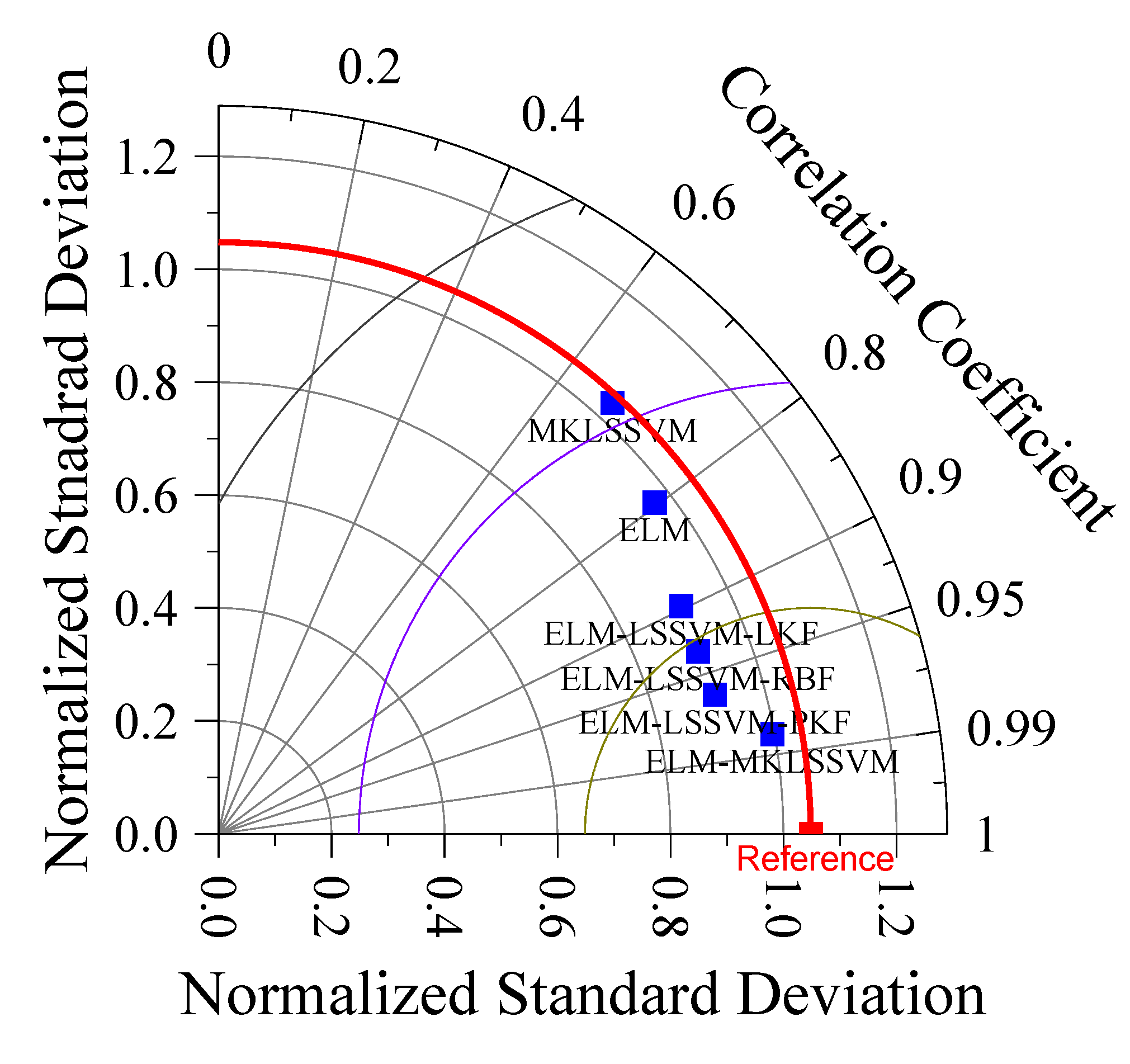
4.4. Evaluation of the Accuracy of Hybrid Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kusudo, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kimura, M.; Matsuno, Y. Development and Assessment of Water-Level Prediction Models for Small Reservoirs Using a Deep Learning Algorithm. Water 2022, 14, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Liu, X.; Niu, J.; Lei, X.; Zhang, Z. Real-time water level prediction of cascaded channels based on multilayer perception and recurrent neural network. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.S.; Sokkalingam, R.; Daud, H.; Adhikary, S.K.; Khurshid, H.; Mazlan, S.N.A.; Rabbani, M.B.A. Water Level Prediction through Hybrid SARIMA and ANN Models Based on Time Series Analysis: Red Hills Reservoir Case Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Jung, Y.; Seong, Y.; Lee, S. Development of Deep Learning Models to Improve the Accuracy of Water Levels Time Series Prediction through Multivariate Hydrological Data. Water 2022, 14, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; He, W.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, X.; Malekian, R.; Li, Z. An Improved LSSVM Model for Intelligent Prediction of the Daily Water Level. Energies 2019, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zang, C.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, M. Data-Driven Modeling of Groundwater Level with Least-Square Support Vector Machine and Spatial–Temporal Analysis. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravej, M.; Amani, P.; Hosseini-Moghari, S.-M. Groundwater level simulation and forecasting using interior search algorithm-least square support vector regression (ISA-LSSVR). Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorain, I.S.; Ismail, S.; Sadon, A.N.; Yasin, S.M. Application of box-jenkins, artificial neural network and support vector machine model for water level prediction. In Recent Advances in Soft Computing and Data Mining, Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Soft Computing and Data Mining (SCDM 2022), Virtual Event, 30–31 May 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bemani, A.; Xiong, Q.; Baghban, A.; Habibzadeh, S.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Doranehgard, M.H. Modeling of cetane number of biodiesel from fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) information using GA-, PSO-, and HGAPSO-LSSVM models. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.B.; Yang, T.C.; Kuo, C.M.; Tseng, H.W.; Yu, P.S. Combing Random Forest and Least Square Support Vector Regression for Improving Extreme Rainfall Downscaling. Water 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranian, A.; Abdollahzade, M. Developing a Local Least-Squares Support Vector Machines-Based Neuro-Fuzzy Model for Nonlinear and Chaotic Time Series Prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Tian, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Tang, H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. Interval prediction of landslide displacement with dual-output least squares support vector machine and particle swarm optimization algorithms. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 4013–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, C.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tan, Q. Short-Term Wind Power Prediction Based on LSSVM-GSA Model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 101, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.L.; Chia, M.Y.; Koo, C.H.; Huang, Y.F. Integration of advanced optimization algorithms into least-square support vector machine (LSSVM) for water quality index prediction. Water Supply 2022, 22, 1951–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, J.; Shamshirband, S.; Kisi, O.; Karimi, S.; Bateni, S.M.; Nezhad, S.H.H.; Hashemi, A. Prediction of Water-Level in the Urmia Lake Using the Extreme Learning Machine Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 5217–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C.; Şahin, M. An extreme learning machine model for the simulation of monthly mean streamflow water level in eastern Queensland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabio, D.N.; Abba, S.I.; Pham, B.Q.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Talukdar, S.; Francesco, G. Groundwater level forecasting in Northern Bangladesh using nonlinear autoregressive exogenous (NARX) and extreme learning machine (ELM) neural networks. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardabili, S.F.; Najafi, B.; Alizamir, M.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Rabczuk, T. Using SVM-RSM and ELM-RSM Approaches for Optimizing the Production Process of Methyl and Ethyl Esters. Energies 2018, 11, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonakdari, H.; Ebtehaj, I.; Samui, P.; Gharabaghi, B. Lake Water-Level fluctuations forecasting using Minimax Probability Machine Regression, Relevance Vector Machine, Gaussian Process Regression, and Extreme Learning Machine. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 33, 3965–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidu, J.; Ewusi, A.; Kuma, J.S.Y.; Ziggah, Y.Y.; Voigt, H.-J. A hybrid groundwater level prediction model using signal decomposition and optimised extreme learning machine. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 3607–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Li, P.; Li, M.; He, Q.; Chao, H.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J. Load Prediction Based on Hybrid Model of VMD-mRMR-BPNN-LSSVM. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6940786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.H.; Sadatsakkak, S.A.; Feidt, M. Connectionist intelligent model estimates output power and torque of stirling engine. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 50, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Le, J.; Liao, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, Y. A novel combination forecasting model for wind power integrating least square support vector machine, deep belief network, singular spectrum analysis and locality-sensitive hashing. Energy 2019, 168, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Deo, R.C.; Chau, K.-W. An enhanced extreme learning machine model for river flow forecasting: State-of-the-art, practical applications in water resource engineering area and future research direction. J. Hydrol. 2019, 569, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, S.; Alatas, B. Plant intelligence based metaheuristic optimization algorithms. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2017, 47, 417–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Montazeri, Z.; Trojovská, E.; Trojovský, P. Coati Optimization Algorithm: A new bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 259, 110011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, R.; Chau, K.-W. Data-driven input variable selection for rainfall–runoff modeling using binary-coded particle swarm optimization and Extreme Learning Machines. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Qu, J.; Fang, W. Examination and comparison of binary metaheuristic wrapper-based input variable selection for local and global climate information-driven one-step monthly streamflow forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ren, K.; Shi, X. Binary Grey Wolf Optimization-Regularized Extreme Learning Machine Wrapper Coupled with the Boruta Algorithm for Monthly Streamflow Forecasting. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Kaur, B.; Sharma, S. Quantum based Whale Optimization Algorithm for wrapper feature selection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 89, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.M.A.; Ariffin, W.N.H.W.; Sidek, L.M.; Basri, H.; Khambali, M.H.M.; Ahmed, A.N. Hydrological Analysis of Batu Dam, Malaysia in the Urban Area: Flood and Failure Analysis Preparing for Climate Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, R.; Torkzadeh, P.; Noori, M. A machine-learning approach for structural damage detection using least square support vector machine based on a new combinational kernel function. Struct. Health Monit. 2016, 15, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ye, S.; Wang, P.; Chevallier, J.; Wei, Y. Forecasting carbon price using a multi-objective least squares support vector machine with mixture kernels. J. Forecast. 2022, 41, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
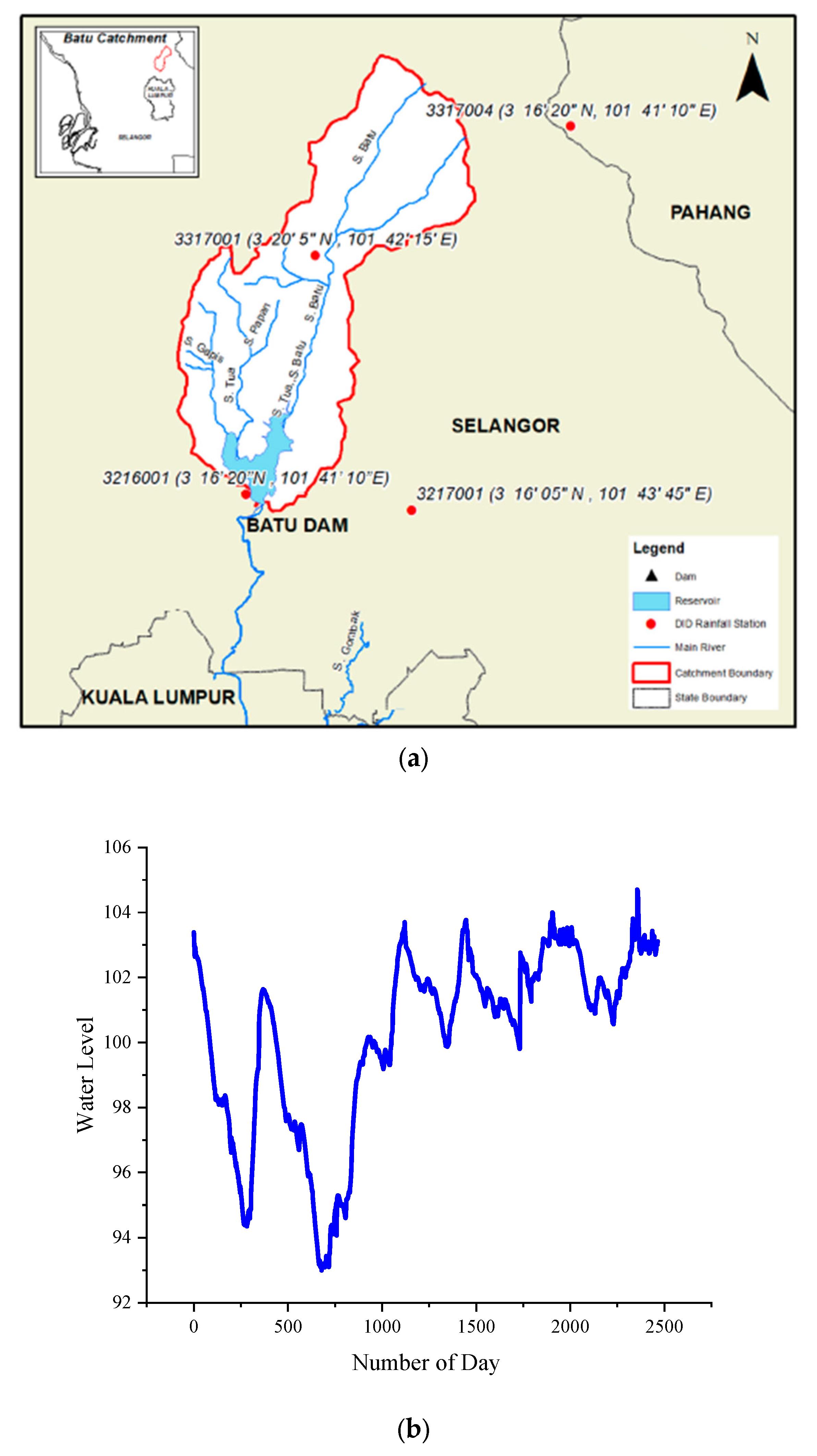


| Parameter | Maximum | Average | Minimum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Level (m) | 104.46 | 99.23 | 93.11 |
| Rainfall (mm) | 50.5 | 34.56 | 0.50 |
| Input Combination | Components |
|---|---|
| First best input combination | rainfall (t−1), rainfall (t−2), water level (t−1), water level (t−2), water level (t−3) |
| Second best input combination | rainfall (t−1), rainfall (t−2), water level (t−1), water level (t−2), water level (t−3), rainfall (t−4) |
| Third-best input combination | rainfall (t−1), rainfall (t−2), water level (t−1), water level (t−2), water level (t−3), rainfall (t−3), water level (t−5) |
| Model | MAE (Training) | MAE (Testing) | RMSE (Training) | RMSE (Testing) | NSE (Training) | NSE (Testing) | WI (Training) | WI (Testing) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MKLSSVM | 0.96 | 0.99 | 1.67 | 1.78 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.79 |
| LSSVM-PKF | 1.02 | 1.12 | 1.97 | 1.98 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.76 |
| LSSVM-RBF | 1.14 | 1.23 | 1.99 | 2.01 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.74 |
| LSSVM-LKF | 1.18 | 1.28 | 2.12 | 2.24 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.73 | 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sammen, S.S.; Ehteram, M.; Sheikh Khozani, Z.; Sidek, L.M. Binary Coati Optimization Algorithm- Multi- Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine-Extreme Learning Machine Model (BCOA-MKLSSVM-ELM): A New Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Predicting Reservoir Water Level. Water 2023, 15, 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081593
Sammen SS, Ehteram M, Sheikh Khozani Z, Sidek LM. Binary Coati Optimization Algorithm- Multi- Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine-Extreme Learning Machine Model (BCOA-MKLSSVM-ELM): A New Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Predicting Reservoir Water Level. Water. 2023; 15(8):1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081593
Chicago/Turabian StyleSammen, Saad Sh., Mohammad Ehteram, Zohreh Sheikh Khozani, and Lariyah Mohd Sidek. 2023. "Binary Coati Optimization Algorithm- Multi- Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine-Extreme Learning Machine Model (BCOA-MKLSSVM-ELM): A New Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Predicting Reservoir Water Level" Water 15, no. 8: 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081593
APA StyleSammen, S. S., Ehteram, M., Sheikh Khozani, Z., & Sidek, L. M. (2023). Binary Coati Optimization Algorithm- Multi- Kernel Least Square Support Vector Machine-Extreme Learning Machine Model (BCOA-MKLSSVM-ELM): A New Hybrid Machine Learning Model for Predicting Reservoir Water Level. Water, 15(8), 1593. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081593










