Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
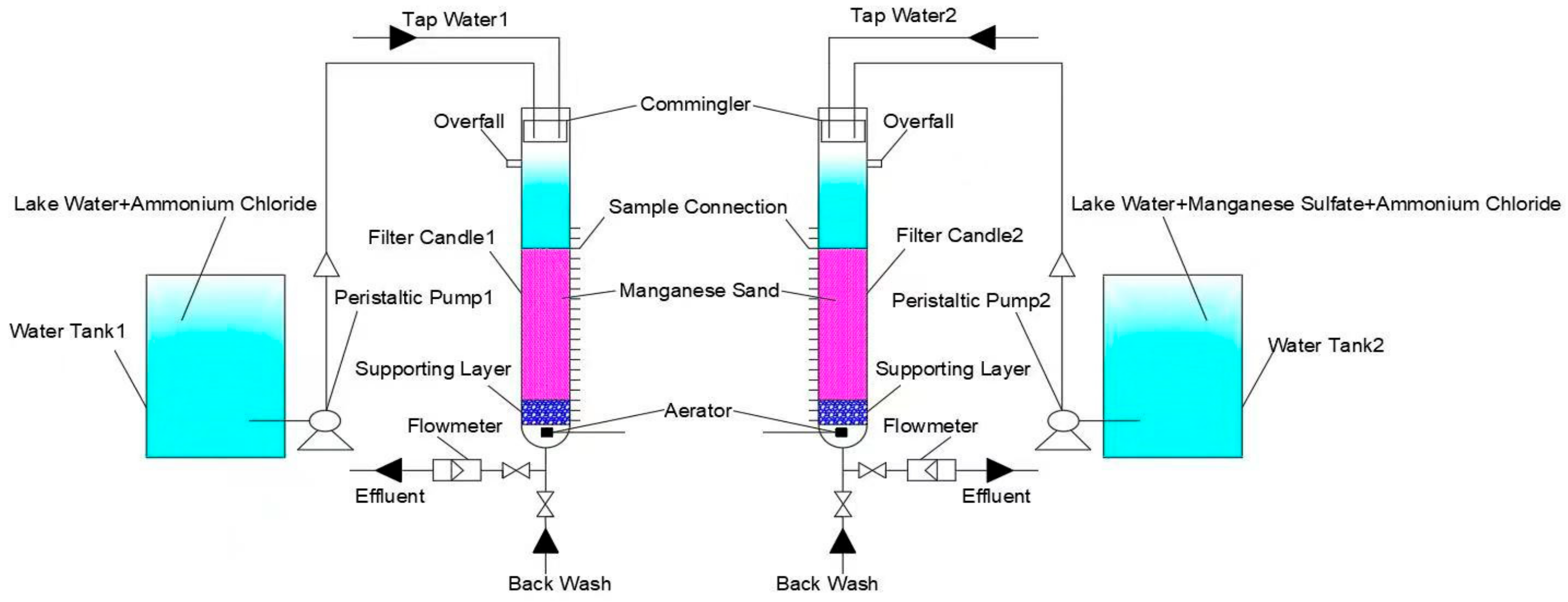
2.1. Testing Device
2.2. Inlet Water Quality
2.3. Test Methods
2.4. Detection Methods
2.5. The Kinetics of Biological CODMn, NH4+-N, and Mn2+ Oxidation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Biological Manganese Oxide on CODMn and Ammonia Nitrogen
3.1.1. The Impact of Biological Manganese Oxide on the Use Reduction in CODMn
3.1.2. The Effect of Biological Manganese Oxide on Ammonia Nitrogen Removal
3.1.3. The Removal Effect of Manganese Using the Aerated Aeration Biofilter #2 Column
3.2. Changes in and Kinetic Analysis of CODMn, Ammonia Nitrogen, and Manganese along the Filter Layers
3.2.1. Along-Filter Changes in CODMn and Kinetic Analysis
3.2.2. Changes in and Kinetic Analysis of Ammonia Nitrogen along the Treatment Path
3.2.3. Changes in and Kinetic Characteristics of Manganese along the Treatment Pathway
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tröger, R.; Köhler, S.J.; Franke, V.; Bergstedt, O.; Wilberg, K. A case study of organic micropollutants in a major Swedish water source—Removal efficiency in seven drinking water treatment plants and influence of operational age of granulated active carbon filters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshorifi, F.T.; Ali, S.L.; Salama, R.S. Promotional Synergistic Effect of Cs–Au NPs on the Performance of Cs–Au/MgFe2O4 Catalysts in Catalysis 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-Ones and Degradation of RhB Dye. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 3765–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakry, A.M.; Alamier, W.M.; Salama, R.S.; El-Shall, M.S.; Awad, F.S. Remediation of water containing phosphate using ceria nanoparticles decorated partially reduced graphene oxide (CeO2-PRGO) composite. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 31, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasseh, N.; Arghavan, F.S.; Daglioglu, N.; Asadi, A. Fabrication of novel magnetic CuS/Fe3O4/GO nanocomposite for organic pollutant degradation under visible light irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19222–19233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshorifi, F.T.; Alswat, A.A.; Salama, R.S. Gold-selenide quantum dots supported onto cesium ferrite nanocomposites for the efficient degradation of rhodamine B. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.S.; Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Design and Development of Novel Composites Containing Nickel Ferrites Supported on Activated Carbon Derived from Agricultural Wastes and Its Application in Water Remediation. Materials 2023, 16, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mazari Moghaddam, N.S.; Rahimi, S.M.; Amarzadeh, M.; Nasseh, N. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of metronidazole in wastewater under simulated sunlight using surfactant- and CuS-activated zeolite nanoparticles. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.S.; Panahi, A.H.; Moghaddam, S.M.N.; Allahyari, E.; Nasseh, N. Breaking down of low-biodegradation Acid Red 206 dye using bentonite/Fe3O4/ZnO magnetic nanocomposite as a novel photo-catalyst in presence of UV light. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 794, 139480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carra, I.; Lozano, J.F.; Autin, O.; Bolton, J.R.; Jarvis, P. Disinfection by-product formation during UV/Chlorine treatment of pesticides in a novel UV-LED reactor at 285 nm and the mitigation impact of GAC treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Gu, X. Pilot study of nitrogen removal from landfill leachate by stable nitritation-denitrification based on zeolite biological aerated filter. Waste Manag. 2019, 12, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B. Pretreatment and Removal of Ammonia Nitronia from Micro-Polluted Water Source in North China. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, D.; Li, X.K.; Zhang, X. Rapid Start-up of Biofilter Purifying Groundwater Containing High Concentrations of lron, Manganese and Ammonia Nitrogen. China Water Wastewater 2013, 29, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bargar, J.R.; Fuller, C.C.; Marcus, M.A.; Brearley, A.J.; Perez De la Rosa, M.; Webb, S.M.; Caldwell, W.A. Structural Characterization of Terrestrial Microbial Mn Oxides from Pinal Creek, AZ. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 889–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, S.M.; Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R. Structural Influences of Sodium and Calcium Ions on the Biogenic Manganese Oxides Produced by The Marine Bacillus Sp., Strain SG-1. Geomicrobiol. J. 2005, 22, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, M.; Lanson, B.; Manceau, A.; Toner, B.; Sposito, G. Structural Model for the Biogenic Mn Oxide Produced by Pseudomonas putida. Am. Mineral. 2006, 91, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Performance and Mechanism of the Oxidation of Typical Organic Pollutants by Nanoscale Hydrous Manganese Dioxide. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Forrez, I.; Carballa, M.; Verbeken, K.; Vanhaecke, L.; Schlüsener, M.; Ternes, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Diclofenac Oxidation by Biogenic Manganese Oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3449–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrez, I.; Carballa, M.; Fink, G.; Wick, A.; Hennebel, T.; Vanhaecke, L.; Ternes, T.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Biogenic Metals for the Oxidative and Reductive Removal of Pharmaceuticals, Biocides and Iodinated Contrast Media in a Polish Membrane Bioreactor. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, F.; Nengzi, L.; Zhang, J. Influence of temperature on CODMn and Mn2+ removal and microbial community structure in pilot-scale biofilter. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Yu, J.; Nengzi, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Xin, X.; Zhang, J. Effects of ammonia on efficiency of iron, manganese and ammonia removal in biological purifying filter. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 10, 6371–6377. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Q.; Nengzi, L.; Xu, D.; Guo, J.; Yu, J. Influence of nitrite on the removal of Mn(II) using pilot-scale biofilters. J. Water Reuse Desalination 2017, 7, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Nengzi, L.; Xu, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Simultaneous Removal of lron, Manganese, Ammonia and Turbidity from Groundwater Using Two-stage Biofilters. China Water Wastewater 2016, 32, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Biological treatment of Mn(II) and Fe(II) containing groundwater: Kinetic considerations and product characterization. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Li, D.; Liang, Y.W.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, J. Effective start-up biofiltration method for Fe, Mn, and ammonia removal and bacterial community analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 176, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Hasan, H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Kofli, N.T.; Anuar, N. Kinetic evaluation of simultaneous cod, ammonia and manganese removal from drinking water using a biological aerated filter system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 130, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Item | CODMn (mg/L) | NH4+-N (mg/L) | Mn (mg/L) | pH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intake water quality | range | 5.82~8.23 | 0.98~1.42 | 0.42~2.21 | 6.79~7.94 |
| average value | 6.83 | 1.24 | 1.12 | 7.28 | |
| Filter Layer Thickness (m) | CODMn (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1/86 Days | #2/69 Days | #2/101 Days | #2/159 Days | |
| 0 | 6.81 | 6.88 | 6.22 | 6.91 |
| 0.4 | 6.23 | 5.96 | 5.04 | 5.49 |
| 0.8 | 5.14 | 4.58 | 3.78 | 3.92 |
| 1.2 | 4.47 | 3.71 | 2.95 | 2.87 |
| 1.5 | 4.05 | 3.07 | 2.47 | 2.42 |
| Filter/Time | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Half-Reaction Time t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1–86 days | 0.0194 | 35.73 | y = −0.0194x + 0.0511 | 0.992 |
| #2–69 days | 0.0297 | 23.34 | y = −0.0297x + 0.0861 | 0.998 |
| #2–101 days | 0.0323 | 21.46 | y = −0.0323x + 0.0360 | 0.998 |
| #2–159 days | 0.0376 | 18.43 | y = −0.0376x + 0.0521 | 0.995 |
| Filter Layer Thickness (m) | Ammonia Nitrogen (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1–86 Days | #2–69 Days | #2–101 Days | #2–159 Days | |
| 0 | 1.29 | 1.37 | 1.19 | 1.28 |
| 0.4 | 0.65 | 0.58 | 0.49 | 0.51 |
| 0.8 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.16 |
| 1.2 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.082 | 0.073 |
| 1.5 | 0.064 | 0.053 | 0.042 | 0.038 |
| Time | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Half-Reaction Time t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1–86 days | 0.1007 | 6.88 | y = −0.1007x + 0.1383 | 0.981 |
| #2–69 days | 0.1059 | 6.55 | y = −0.1059x − 0.0070 | 0.994 |
| #2–101 days | 0.1096 | 6.32 | y = −0.1096x − 0.0762 | 0.994 |
| #2–159 days | 0.1162 | 5.97 | y = −0.1162x − 0.0792 | 0.992 |
| Filter Layer Thickness (m) | Manganese (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 69 Days | 101 Days | 159 Days | |
| 0 | 0.55 | 1.13 | 2.03 |
| 0.4 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 1.30 |
| 0.8 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.53 |
| 1.2 | 0.051 | 0.049 | 0.12 |
| 1.5 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.034 |
| Time | Kinetic Constant k (min−1) | Half-Reaction Time t1/2 (min) | Formula | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2–69 days | 0.114 | 6.08 | y = −0.114x + 0.1819 | 0.983 |
| #2–101 days | 0.1579 | 4.39 | y = −0.1579x + 0.713 | 0.987 |
| #2–159 days | 0.1668 | 4.16 | y = −0.1668x + 1.0812 | 0.982 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nengzi, L.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Qiu, G.; Li, H. Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water 2023, 15, 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081624
Nengzi L, Jiang Y, Fang Z, Hu Q, Qiu G, Li H. Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water. 2023; 15(8):1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081624
Chicago/Turabian StyleNengzi, Lichao, Ying Jiang, Zhirong Fang, Qiyuan Hu, Guanglei Qiu, and Haitao Li. 2023. "Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water" Water 15, no. 8: 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081624
APA StyleNengzi, L., Jiang, Y., Fang, Z., Hu, Q., Qiu, G., & Li, H. (2023). Influence of Biological Manganese Oxides on the Removal of Organic Matter and Ammonia in Micro-Polluted Source Water. Water, 15(8), 1624. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081624







