Nitrate Source and Transformation in Groundwater under Urban and Agricultural Arid Environment in the Southeastern Nile Delta, Egypt
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Distribution of NO3− in the Shallow Groundwaters
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Hydrogeochemical Parameters
3.3. Groundwater Recharge
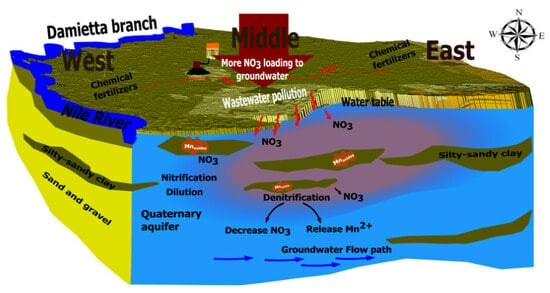
3.4. Sources and Transformations of NO3−
3.5. Identification of NO3− Transformation Process Coupled with Mn Oxides Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Karunanidhi, D.; Subramani, T.; Srinivasamoorthy, K. Sources and Consequences of Groundwater Contamination. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 80, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Tang, Y.; Liu, M.; Van Zwieten, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Song, Z. Carbon-Nitrogen Isotope Coupling of Soil Organic Matter in a Karst Region under Land Use Change, Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breida, M.; Alami Younssi, S.; Ouammou, M.; Bouhria, M.; Hafsi, M. Pollution of Water Sources from Agricultural and Industrial Effluents: Special Attention to NO3−, Cr(VI), and Cu(II). In Water Chemistry; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zendehbad, M.; Cepuder, P.; Loiskandl, W.; Stumpp, C. Source Identification of Nitrate Contamination in the Urban Aquifer of Mashhad, Iran. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 25, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, J.; Li, Y. How Rapid Urbanization Drives Deteriorating Groundwater Quality in a Provincial Capital of China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 29, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Liu, C.Q. Water Geochemistry Controlled by Carbonate Dissolution: A Study of the River Waters Draining Karst-Dominated Terrain, Guizhou Province, China. Chem. Geol. 2004, 204, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shinawi, A.; Zeleňáková, M.; Nosair, A.M.; Abd-Elaty, I. Geo-Spatial Mapping and Simulation of the Sea Level Rise Influence on Groundwater Head and Upward Land Subsidence at the Rosetta Coastal Zone, Nile Delta, Egypt. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elewa, H.H.; Shohaib, R.E.; Qaddah, A.A.; Nousir, A.M. Determining Groundwater Protection Zones for the Quaternary Aquifer of Northeastern Nile Delta Using GIS-Based Vulnerability Mapping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.; Biagioni, R.N.; Alarcón-Herrera, M.T.; Rivas-Lucero, B.A. An Overview of Nitrate Sources and Operating Processes in Arid and Semiarid Aquifer Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z.; Yuan, L. Nitrate in Groundwater and the Unsaturated Zone in (Semi)Arid Northern China: Baseline and Factors Controlling Its Transport and Fate. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Xue, C.; Wu, J. Progress, Opportunities, and Key Fields for Groundwater Quality Research under the Impacts of Human Activities in China with a Special Focus on Western China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 13224–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Sickman, J.O.; Fargher, L.; Herrera-Silveira, J.; Lucero, D.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; Lamas-Cosío, E.; Robledo-Ardila, P.A. Groundwater Quality in the Yucatan Peninsula: Insights from Stable Isotope and Metals Analysis. Groundwater 2021, 59, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddau, R.; Dore, E.; Da Pelo, S.; Lorrai, M.; Botti, P.; Testa, M.; Cidu, R. Geochemistry, Stable Isotopes and Statistic Tools to Estimate Threshold and Source of Nitrate in Groundwater (Sardinia, Italy). Water Res. 2023, 232, 119663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, K.O.; Gomo, M.; Oke, S.A. Groundwater Quality Assessment of Shallow Aquifer Hand Dug Wells in Rural Localities of Ilorin Northcentral Nigeria: Implications for Domestic and Irrigation Uses. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 9, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeman, A.J.; Barreteau, O.; Hunt, R.J.; Rinaudo, J.-D.; Ross, A.; Arshad, M.; Hamilton, S. Integrated Groundwater Management: An Overview of Concepts and Challenges in Integrated Groundwater Management: Concepts, Approaches and Challenges; Jakeman, A.J., Barreteau, O., Hunt, R.J., Rinaudo, J.-D., Ross, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 3–20. ISBN 978-3-319-23576-9. [Google Scholar]
- Puckett, L.J. Nonpoint and Point Sources of Nitrogen in Major Watersheds of the United States; Water-Resources Investigations Report 94-4001; US Geological Survey: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1994; Volume 94.
- Wakida, F.T.; Lerner, D.N. Non-Agricultural Sources of Groundwater Nitrate: A Review and Case Study. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, G.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y. Driving Mechanism and Sources of Groundwater Nitrate Contamination in the Rapidly Urbanized Region of South China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 182, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, E.A.; David, M.B.; Galloway, J.N.; Goodale, C.L.; Haeuber, R.; Harrison, J.A.; Howarth, R.W.; Jaynes, D.B.; Lowrance, R.R.; Thomas, N.B.; et al. Excess Nitrogen in the U.S. Environment: Trends, Risks, and Solutions. Issues Ecol. 2011, 15, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dan-Hassan, M.A.; Olasehinde, P.I.; Amadi, A.N.; Yisa, J.; Jacob, J.O. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Nitrate Pollution in Groundwater of Abuja, Nigeria. Int. J. Chem. 2012, 4, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.H.; de Kok, T.M.; Levallois, P.; Brender, J.; Gulis, G.; Nolan, B.T.; VanDerslice, J. Workgroup Report: Drinking-Water Nitrate and Health—Recent Findings and Research Needs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 113, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Howard, K.; Qian, H. Use of Multiple Isotopic and Chemical Tracers to Identify Sources of Nitrate in Shallow Groundwaters along the Northern Slope of the Qinling Mountains, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 113, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality; Fourth Edition Incorporating The First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Mondal, N.C.; Tiwari, K.K. Anthropogenic Nitrate in Groundwater and Its Health Risks in the View of Background Concentration in a Semi Arid Area of Rajasthan, India. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerkhatibi, M.; Mosaferi, M.; Pourakbar, M.; Ahmadnejad, M.; Safavi, N.; Banitorab, F. Comprehensive Investigation of Groundwater Quality in the North-West of Iran: Physicochemical and Heavy Metal Analysis. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šrajbek, M.; Kranjčević, L.; Kovač, I.; Biondić, R. Groundwater Nitrate Pollution Sources Assessment for Contaminated Wellfield. Water 2022, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, A.; Soto, D.X.; Matiatos, I.; Martínez, D.E.; Esquius, S. A Biological and Nitrate Isotopic Assessment Framework to Understand Eutrophication in Aquatic Ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastén-Zapata, E.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R.; Harter, T.; Ramírez, A.I.; Mahlknecht, J. Assessment of Sources and Fate of Nitrate in Shallow Groundwater of an Agricultural Area by Using a Multi-Tracer Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.M.; Choi, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.K.; Hamm, S.Y. Characterizing Land Use Effect on Shallow Groundwater Contamination by Using Self-Organizing Map and Buffer Zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hu, Q.; Shen, W.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, L. Identification of Nitrate Sources of Groundwater and Rivers in Complex Urban Environments Based on Isotopic and Hydro-Chemical Evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 162026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Kagabu, M.; Nakata, H.; Orishikida, T.; Lin, I.-T.; Shimada, J. The Use of Δ15N and Δ18O Tracers with an Understanding of Groundwater Flow Dynamics for Evaluating the Origins and Attenuation Mechanisms of Nitrate Pollution. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2661–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Qin, X.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Li, F. Using Dual Isotopes to Evaluate Sources and Transformations of Nitrate in the West Lake Watershed, Eastern China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2015, 177–178, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorette, G.; Sebilo, M.; Buquet, D.; Lastennet, R.; Denis, A.; Peyraube, N.; Charriere, V.; Studer, J.-C. Tracing Sources and Fate of Nitrate in Multilayered Karstic Hydrogeological Catchments Using Natural Stable Isotopic Composition (Δ15N-NO3− and Δ18O-NO3−). Application to the Toulon Karst System (Dordogne, France). J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Liu, W. Using Dual Isotopes to Identify Sources and Transformations of Nitrogen in Water Catchments with Different Land Uses, Loess Plateau of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, F.-J.; Li, S.-L.; Liu, C.-Q.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Ding, H. Tracing Nitrate Sources with Dual Isotopes and Long Term Monitoring of Nitrogen Species in the Yellow River, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Tracing Nitrate Pollution Sources and Transformations in the Over-Exploited Groundwater Region of North China Using Stable Isotopes. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, Q. Tracing Nitrate Pollution Sources and Transformation in Surface- and Ground-Waters Using Environmental Isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, C.; Elliott, E.M.; Wankel, S.D. Tracing Anthropogenic Inputs of Nitrogen to Ecosystems. In Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science, 2nd ed.; Michener, R., Lajtha, K., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 375–449. [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, R.F.; Hirsh, A.J.; Exner, M.E.; Little, N.A.; Kloppenborg, K.L. Applicability of the Dual Isotopes Δ15N and Δ18O to Identify Nitrate in Groundwater beneath Irrigated Cropland. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2019, 220, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Hu, A.; Gad, M.; Adyari, B.; Qin, D.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Yu, C.P. Domestic Wastewater Causes Nitrate Pollution in an Agricultural Watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, E.P.; Goodhue, R.; Meier-Augenstein, W.; Kalin, R.M.; Fenton, O.; Richards, K.G.; Coxon, C.E. Combining Stable Isotopes with Contamination Indicators: A Method for Improved Investigation of Nitrate Sources and Dynamics in Aquifers with Mixed Nitrogen Inputs. Water Res. 2017, 124, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q. From Soil to River: Revealing the Mechanisms Underlying the High Riverine Nitrate Levels in a Forest Dominated Catchment. Water Res. 2023, 241, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Su, J.; Ali, A.; Wang, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Denitrification Strategy of Pantoea Sp. MFG10 Coupled with Microbial Dissimilatory Manganese Reduction: Deciphering the Physiological Response Based on Extracellular Secretion. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 355, 127278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, N.; Parent, S.; Villemur, R. Addition of Trace Metals Increases Denitrification Rate in Closed Marine Systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Q.; Li, S.-L.; Lang, Y.-C.; Xiao, H.-Y. Using Δ15N- and Δ18O-Values To Identify Nitrate Sources in Karst Ground Water, Guiyang, Southwest China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6928–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, S.V.; Hackley, K.C.; Hwang, H.H.; Greenberg, S.E.; Krapac, I.G.; Landsberger, S.; O’Kelly, D.J. Characterization and Identification of Na-Cl Sources in Ground Water. Groundwater 2006, 44, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Song, X.; Ma, Y. Identification of Nitrate Source Using Isotopic and Geochemical Data in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River Irrigation District (China). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Alday, J.J.; Hussein, S.; Arman, H.; Alshamsi, D.; Murad, A.; Elhaj, K.; Aldahan, A. A Multi-Isotopic Evaluation of Groundwater in a Rapidly Developing Area and Implications for Water Management in Hyper-Arid Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elagouz, M.H.; Abou-Shleel, S.M.; Belal, A.A.; El-Mohandes, M.A.O. Detection of Land Use/Cover Change in Egyptian Nile Delta Using Remote Sensing. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2020, 23, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, M.; Ali, M.; Zaghlool, E.; Stash, O.S. Hydrochemical and Stable Isotopes Indicators for Detecting Sources of Groundwater Contamination Close to Bahr El-Baqar Drain, Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water Sci. 2019, 33, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, R.; Ahmed, M.; Aly, A.I. Tracking Anthropogenic Nitrogen-Compound Sources of Surface and Groundwater in Southwestern Nile Delta: Hydrochemical, Environmental Isotopes, and Modeling Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22115–22136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAPMAS. Arab. Republic of Egypt—General. Census for Population, Housing and Establishments. 2017. Available online: https://censusinfo.capmas.gov.eg/metadata-en-v4.2/index.php/catalog/621 (accessed on 17 December 2023).
- RIGW-IWACO Hydrogeological Map of Egypt, 1:2000,000; Research Institute of Groundwater, Water Research Center, Ministry of Public Works and Water Resources, Arab Republic of Egypt: Cairo, Egypt, 1992.
- Hefny, K.; Khalil, J.B. General Hydrogeological Condition of Greater Cairo Area. Water Sci. J Oct. 1989, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.M.; Tokunaga, T.; Yousef, A.F. Insights from Stable Isotopes and Hydrochemistry to the Quaternary Groundwater System, South of the Ismailia Canal, Egypt. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; El Arabi, N.E.; Hamza, M.S. Use of Solute Chemistry and Isotopes to Identify Sources of Ground-Water Recharge in the Nile Aquifer System, Upper Egypt. Groundwater 1997, 35, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Salem, H.; Gemail, K.S.; Nosair, A.M. A Multidisciplinary Approach for Delineating Wastewater Flow Paths in Shallow Groundwater Aquifers: A Case Study in the Southeastern Part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 236, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; Rice, E.W., Bridgewater, L., American Public Health Association, Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sigman, D.M.; Casciotti, K.L.; Andreani, M.; Barford, C.; Galanter, M.; Böhlke, J.K. A Bacterial Method for the Nitrogen Isotopic Analysis of Nitrate in Seawater and Freshwater. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4145–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, M.A.; Foriel, J.; Barnett, B.; Oleynik, S.; Sigman, D.M. Updates to Instrumentation and Protocols for Isotopic Analysis of Nitrate by the Denitrifier Method. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2016, 30, 1365–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Fakharany, M.A.; Mansour, N.M.; Yehia, M.M.; Monem, M. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality of the Quaternary Aquifer through Multivariate Statistical Techniques at the Southeastern Part of the Nile Delta, Egypt. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 3, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, D.; Abotalib, A.Z.; El-Bastaweesy, M.; El-Said, M.A.; Melegy, A.; Garamoon, H. Geo-Environmental Impacts of Hydrogeological Setting and Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality in the Quaternary Aquifer Southeast of the Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2020, 172, 103947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.; Sun, H.; Xu, Z. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Recharge Sources Identification Based on Isotopic Tracing of Alpine Rivers in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Hamza, M.S.; Farid, M.S. Studies on the Recharge of the Aquifer Systems in the Southern Portion of the Nile Delta Using Radioisotopes and Hydro Chemistry. Isot. Radiat. Res. 1994, 26, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, M.S.; Aly, A.I.M.; Swailem, F.M.; Nada, A. Environmentally Stable Isotopes and Groundwater Recharge in the Eastern Nile Delta. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1987, 3, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jiang, H.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Unexpectedly High Nitrate Levels in a Pristine Forest River on the Southeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 132047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widory, D.; Petelet-Giraud, E.; Négrel, P.; Ladouche, B. Tracking the Sources of Nitrate in Groundwater Using Coupled Nitrogen and Boron Isotopes: A Synthesis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, J. Delineation of Hydrochemical Characteristics and Tracing Nitrate Contamination of Groundwater Based on Hydrochemical Methods and Isotope Techniques in the Northern Huangqihai Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Mahlknecht, J.; Daesslé, L.W.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.A.; Ledesma-Ruiz, R. Estimation of Nitrate Pollution Sources and Transformations in Groundwater of an Intensive Livestock-Agricultural Area (Comarca Lagunera), Combining Major Ions, Stable Isotopes and MixSIAR Model. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoelstra, J.; Leal, K.A.; Senger, N.D.; Schiff, S.L.; Post, R. Isotopic Characterization of Sulfate in a Shallow Aquifer Impacted by Agricultural Fertilizer. Groundwater 2021, 59, 658–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Martínez, J.A.; Mora, A.; Knappett, P.S.K.; Ornelas-Soto, N.; Mahlknecht, J. Tracking Nitrate and Sulfate Sources in Groundwater of an Urbanized Valley Using a Multi-Tracer Approach Combined with a Bayesian Isotope Mixing Model. Water Res. 2020, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papazotos, P.; Vasileiou, E.; Perraki, M. The Synergistic Role of Agricultural Activities in Groundwater Quality in Ultramafic Environments: The Case of the Psachna Basin, Central Euboea, Greece. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Abdel Samie, S.G.; Badawy, H.A. Factors Controlling Mechanisms of Groundwater Salinization and Hydrogeochemical Processes in the Quaternary Aquifer of the Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.; Awad, S.R.; Salam, M.A.; Smidt, E. Monitoring of Groundwater in Gabal El Asfar Wastewater Irrigated Area (Greater Cairo). Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 32, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gamal, S.; El-Sayed, S.; Atta, E. Exploring Surface-and Groundwater Interactions in East Delta Aquifer Using Conventional and Nonconventional Techniques. J. Appl. Geol. Geophys. 2018, 6, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, P.R.; Urup, J.; Helstrup, T.; Jensen, M.B.; Eiland, F.; Vinther, F.P. Transport and Reduction of Nitrate in Clayey till underneath Forest and Arable Land. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 73, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desireddy, S.; Pothanamkandathil Chacko, S. A Review on Metal Oxide (FeOx/MnOx) Mediated Nitrogen Removal Processes and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 697–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, M.H. Nitrogen: Environmental and Wastewater Concerns. In Nitrification and Denitrification in the Activated Sludge Process; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Barzegar, R.; Moghaddam, A.A.; Tziritis, E.; Fakhri, M.S.; Soltani, S. Identification of Hydrogeochemical Processes and Pollution Sources of Groundwater Resources in the Marand Plain, Northwest of Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Lian, X.; Feng, F.; Shang, C.; Zang, Y.; Xi, B. Anthropogenic Perturbation Enhances the Release of Geogenic Mn to Groundwater: Evidence from Hydrogeochemical Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shu, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Shang, X.; Yang, Y.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M. Nitrate Pollution Source Apportionment, Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis across a Rural-Urban River Network Based on Δ15N/Δ18O-NO3− Isotopes and SIAR Modeling. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Isotope Tracers in Catchment Hydrology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; ISBN 008092915X. [Google Scholar]
- Wankel, S.D.; Kendall, C.; Francis, C.A.; Paytan, A. Nitrogen Sources and Cycling in the San Francisco Bay Estuary: A Nitrate Dual Isotopic Composition Approach. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivett, M.O.; Buss, S.R.; Morgan, P.; Smith, J.W.N.; Bemment, C.D. Nitrate Attenuation in Groundwater: A Review of Biogeochemical Controlling Processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4215–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. Multiple Isotopes Reveal a Hydrology Dominated Control on the Nitrogen Cycling in the Nujiang River Basin, the Last Undammed Large River Basin on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4610–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michener, R.; Lajtha, K. (Eds.) Stable Isotopes in Ecology and Environmental Science; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; ISBN 9780470691854. [Google Scholar]
- Homoncik, S.C.; MacDonald, A.M.; Heal, K.V.; Ó Dochartaigh, B.É.; Ngwenya, B.T. Manganese Concentrations in Scottish Groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2467–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoch, D.C. Manganese, an Essential Trace Element for N2 Fixation by Rhodospirillum rubrum and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata: Role in Nitrogenase Regulation. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 140, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.C.; El Shishtawy, A.M.; Sharp, J.M.; Atwia, M.G. Source and Migration of Dissolved Manganese in the Central Nile Delta Aquifer, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2014, 96, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Elevated Manganese Concentrations in Shallow Groundwater of Various Aquifers in a Rapidly Urbanized Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.G.; El-Awady, M.H.; Amin, E. Enhanced Removal of Dissolved Iron and Manganese from Nonconventional Water Resources in Delta District, Egypt. Energy Procedia 2012, 18, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimi, Z.; El-Barkooky, A.; Martínez Frías, J.; Fritz, H.; Abd El-Rahman, Y. (Eds.) The Geology of Egypt, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-15264-2. [Google Scholar]
- EEBS. Geological, Hydrological and Geomorphological Properties of Soil for Egyptian Governorates. In Soil Atlas of Egypt; Part Egyptian Education Building Society Publication: Cairo, Egypt, 2004; pp. 1–290. [Google Scholar]
- Egyptian Geological Survey. Geologic Map of Egypt, Scale 1:2,000,000; Egyptian Geological Survey and Mining Authority: Cairo, Egypt, 1981.
- Karra, K.; Kontgis, C.; Statman-Weil, Z.; Mazzariello, J.C.; Mathis, M.; Brumby, S.P. Global Land Use/Land Cover with Sentinel 2 and Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 4704–4707. [Google Scholar]








| Parameter | Fresh Surface Water (n = 7) | Agricultural Drain (n = 2) | Polluted Lake (n = 2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | |
| Total depth (m) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| pH | 7.39 | 0.36 | 6.70 | 7.73 | 7.68 | 0.67 | 7.20 | 8.15 | 8.41 | 0.30 | 8.20 | 8.62 |
| Temp (°C) | 18.31 | 0.80 | 17.00 | 19.20 | 18.60 | 2.26 | 17.00 | 20.20 | 21.00 | 0.00 | 21.00 | 21.00 |
| EC (µS/cm) | 498 | 24 | 475 | 540 | 1980 | 665 | 1510 | 2450 | 17,555 | 1648 | 16,390 | 18,720 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 324 | 15 | 309 | 351 | 1287 | 432 | 982 | 1593 | 11,411 | 1071 | 10,654 | 12,168 |
| SiO2 (mg/L) | 1.03 | 0.59 | 0.45 | 2.07 | 17.49 | 5.85 | 13.36 | 21.63 | 13.54 | 18.92 | 0.17 | 26.92 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 6.10 | 0.42 | 5.66 | 6.60 | 24.58 | 2.84 | 22.57 | 26.60 | 74.11 | 5.17 | 70.45 | 77.76 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 11.74 | 12.45 | 6.46 | 39.97 | 112.21 | 90.13 | 48.48 | 175.94 | 1650 | 141.42 | 1550 | 1750 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 41.09 | 2.01 | 36.77 | 43.05 | 119.63 | 68.46 | 71.22 | 168.03 | 617 | 316 | 393 | 840 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 16.12 | 1.39 | 13.31 | 17.58 | 59.05 | 34.92 | 34.36 | 83.74 | 269.7 | 4.52 | 266.5 | 272.9 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 186.74 | 11.98 | 173.17 | 203.33 | 254.66 | 108.36 | 178.04 | 331.28 | 550.07 | 352.30 | 300.95 | 799.18 |
| F− (mg/L) | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.39 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.19 | 0.28 | – | – | – | – |
| Cl− (mg/L) | 31.02 | 2.60 | 27.33 | 35.24 | 263.39 | 143.39 | 161.99 | 364.78 | 4272.9 | 1074.7 | 3513 | 5032.8 |
| NO2− (mg/L) | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| NO3− (mg/L) | 1.86 | 1.33 | 0.80 | 4.59 | 35.58 | 13.80 | 25.82 | 45.33 | 0.68 | 0.03 | 0.66 | 0.70 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 34.3 | 1.4 | 32.4 | 36.3 | 308.5 | 92.4 | 243.2 | 373.8 | 3700 | 132.9 | 3606 | 3794 |
| Mn (mg/L) | 0.004 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.198 | 0.198 | 0.058 | 0.338 | 0.072 | 0.099 | 0.001 | 0.142 |
| Fe (mg/L) | 0.045 | 0.005 | 0.037 | 0.053 | 0.137 | 0.093 | 0.071 | 0.203 | 0.171 | 0.004 | 0.168 | 0.174 |
| As (mg/L) | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0002 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.021 | 0.001 | 0.021 | 0.022 |
| B (mg/L) | 0.056 | 0.039 | 0.026 | 0.134 | 0.072 | 0.006 | 0.068 | 0.076 | 2.438 | 0.477 | 2.100 | 2.775 |
| Li (mg/L) | 0.001 | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.0004 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.033 | 0.009 | 0.027 | 0.039 |
| Sr (mg/L) | 0.324 | 0.023 | 0.298 | 0.362 | 0.859 | 0.342 | 0.617 | 1.100 | 7.845 | 0.148 | 7.740 | 7.950 |
| Al (mg/L) | 0.117 | 0.098 | 0.010 | 0.266 | 0.056 | 0.057 | 0.016 | 0.097 | 0.016 | 0.001 | 0.016 | 0.017 |
| Cr (mg/L) | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.012 | 0.033 | 0.023 | 0.017 | 0.050 |
| Co (mg/L) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.002 |
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.011 |
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.000 | 0.011 | 0.011 |
| Ba (mg/L) | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.032 | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.041 | 0.019 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.020 |
| Ni (mg/L) | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.027 | 0.002 | 0.025 | 0.029 |
| δ18O-H2O (‰) | 2.00 | 0.13 | 1.74 | 2.13 | 1.29 | 0.65 | 0.83 | 1.75 | 6.31 | 0.59 | 5.89 | 6.73 |
| δ2H-H2O (‰) | 18.49 | 1.19 | 15.94 | 19.20 | 14.02 | 4.72 | 10.69 | 17.36 | 31.16 | 4.36 | 28.08 | 34.25 |
| δ15N-NO3 (‰) | 5.03 | 8.47 | −12.76 | 11.52 | 11.43 | 4.60 | 8.18 | 14.68 | 6.45 | 2.51 | 4.68 | 8.23 |
| δ18O-NO3 (‰) | 9.02 | 6.65 | −4.69 | 14.24 | 5.51 | 1.67 | 4.33 | 6.70 | 3.28 | 1.52 | 2.20 | 4.35 |
| Parameter | Wastewater Drain (n = 4) | Groundwater (n = 55) | ||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | |||||
| Total depth (m) | – | – | – | – | 32.11 | 20.74 | 9.00 | 156.00 | ||||
| pH | 7.24 | 0.48 | 6.56 | 7.70 | 7.08 | 0.36 | 6.20 | 7.75 | ||||
| Temp (°C) | 19.38 | 0.85 | 18.50 | 20.50 | 20.29 | 6.63 | 18.50 | 25.30 | ||||
| EC (µS/cm) | 1410 | 276 | 1080 | 1680 | 1476 | 688 | 700 | 3650 | ||||
| TDS (mg/L) | 917 | 179 | 702 | 1092 | 960 | 447 | 455 | 2373 | ||||
| SiO2 (mg/L) | 8.99 | 3.65 | 4.16 | 13.02 | 63.53 | 65.57 | 18.70 | 237.32 | ||||
| K+ (mg/L) | 17.97 | 6.79 | 7.79 | 21.50 | 11.64 | 6.50 | 4.64 | 31.61 | ||||
| Na+ (mg/L) | 132.45 | 88.85 | 7.87 | 200.78 | 147.27 | 108.88 | 7.47 | 579.77 | ||||
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 62.39 | 11.73 | 46.16 | 71.24 | 102.65 | 49.69 | 19.07 | 366.72 | ||||
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 21.67 | 3.10 | 17.02 | 23.47 | 35.50 | 16.05 | 9.63 | 85.81 | ||||
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 306.25 | 66.54 | 246.29 | 367.02 | 390.90 | 120.78 | 165.16 | 753.35 | ||||
| F− (mg/L) | 0.28 | 0.01 | 0.27 | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 1.38 | ||||
| Cl− (mg/L) | 208.16 | 88.72 | 129.54 | 312.22 | 170.34 | 110.86 | 33.31 | 603.98 | ||||
| NO2− (mg/L) | 107.24 | 63.74 | 50.13 | 176.01 | – | – | – | – | ||||
| NO3− (mg/L) | 18.24 | 34.58 | 0.67 | 70.11 | 49.90 | 109.22 | 0.42 | 651.79 | ||||
| SO42− (mg/L) | 114.88 | 57.77 | 58.31 | 165.67 | 200.66 | 175.32 | 2.47 | 827.15 | ||||
| Mn (mg/L) | 0.227 | 0.150 | 0.102 | 0.429 | 0.831 | 0.720 | 0.0019 | 3.380 | ||||
| Fe (mg/L) | 0.088 | 0.020 | 0.069 | 0.108 | 0.089 | 0.060 | 0.040 | 0.430 | ||||
| As (mg/L) | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.006 | ||||
| B (mg/L) | 0.137 | 0.038 | 0.090 | 0.177 | 0.094 | 0.112 | 0.016 | 0.577 | ||||
| Li (mg/L) | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.023 | ||||
| Sr (mg/L) | 0.928 | 0.535 | 0.425 | 1.410 | 0.986 | 0.947 | 0.128 | 6.590 | ||||
| Al (mg/L) | 0.030 | 0.005 | 0.024 | 0.036 | 0.012 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.046 | ||||
| Cr (mg/L) | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.023 | ||||
| Co (mg/L) | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.003 | ||||
| Cu (mg/L) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.025 | ||||
| Zn (mg/L) | 0.020 | 0.014 | 0.010 | 0.041 | 0.022 | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.404 | ||||
| Ba (mg/L) | 0.023 | 0.005 | 0.019 | 0.030 | 0.122 | 0.087 | 0.011 | 0.341 | ||||
| Ni (mg/L) | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.005 | 0.023 | ||||
| δ18O-H2O (‰) | 2.08 | 0.15 | 1.93 | 2.29 | 1.23 | 1.46 | −1.86 | 3.32 | ||||
| δ2H-H2O (‰) | 19.10 | 0.87 | 18.19 | 20.20 | 13.99 | 8.83 | −4.46 | 26.61 | ||||
| δ15N-NO3 (‰) | 8.13 | 6.10 | −0.16 | 13.86 | 8.92 | 16.87 | −23.40 | 75.42 | ||||
| δ18O-NO3 (‰) | −1.69 | 13.54 | −13.25 | 13.20 | 10.53 | 12.85 | −14.32 | 39.79 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasem, A.M.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Nosair, A.M. Nitrate Source and Transformation in Groundwater under Urban and Agricultural Arid Environment in the Southeastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water 2024, 16, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010022
Kasem AM, Xu Z, Jiang H, Liu W, Zhang J, Nosair AM. Nitrate Source and Transformation in Groundwater under Urban and Agricultural Arid Environment in the Southeastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water. 2024; 16(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasem, Alaa M., Zhifang Xu, Hao Jiang, Wenjing Liu, Jiangyi Zhang, and Ahmed M. Nosair. 2024. "Nitrate Source and Transformation in Groundwater under Urban and Agricultural Arid Environment in the Southeastern Nile Delta, Egypt" Water 16, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010022
APA StyleKasem, A. M., Xu, Z., Jiang, H., Liu, W., Zhang, J., & Nosair, A. M. (2024). Nitrate Source and Transformation in Groundwater under Urban and Agricultural Arid Environment in the Southeastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Water, 16(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010022