Large-Scale Two-Dimensional Cascade Modeling of the Odra River for Flood Hazard Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Large-Scale 2D Models
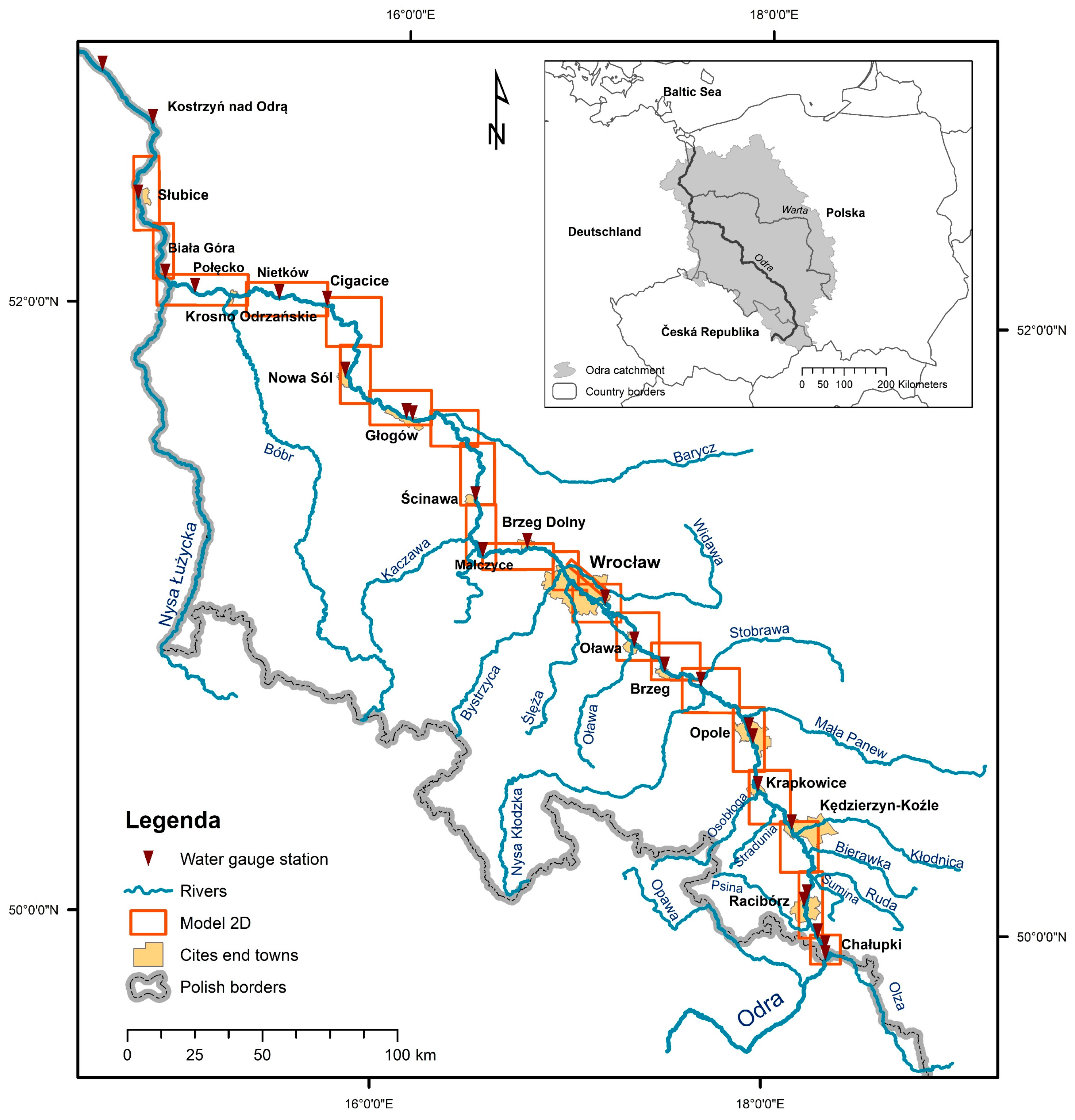
2. Case Study—The Odra River
3. The Concept of Two-Dimensional Flood Modeling
4. Model Set-Up
4.1. Bathymetry
4.2. Roughness
4.3. Calibration
5. Rating Curves and Verification of Flood Peak Discharges
6. Applications
6.1. Flood Hazard and Flood Risk Management
6.2. Modeling of the Wrocław Water Node
6.3. Dam Break Modeling
6.4. Ice Jam Flood Modeling
6.5. Feasibility Study for the Racibórz Reservoir
6.6. Flood Routing and Verification of the Design Discharges
7. Future Work
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K.; et al. Flood risk and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Arheimer, B.; Borga, M.; Brázdil, R.; Claps, P.; Kiss, A.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Kriaučiūnienė, J.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lang, M.; et al. Understanding flood regime changes in Europe: A state-of-the-art assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 2735–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranzoni, A.; D’Oria, M.; Rizzo, C. Quantitative flood hazard assessment methods: A review. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 16, e12855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritthart, M. Advanced Modeling Strategies for Hydraulic Engineering and River Research. Water 2021, 13, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, P.D. Flood Routing and Inundation Prediction. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences, Part 11, Rainfall-Runoff Modeling; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S. Flood inundation modelling: A review of methods, recent advances and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, K.V.; Caloiero, T.; Mehta, D.J.; Singh, K. Comprehensive Overview of Flood Modeling Approaches: A Review of Recent Advances. Hydrology 2023, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.; Liang, Q.; Bosher, L.; Chen, H.; Nicholson, A. A systematic review of natural flood management modelling: Approaches, limitations, and potential solutions. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2023, 16, e12899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, J.T.; Basnayaka, V.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Rathnayake, U. Comparing Combined 1D/2D and 2D Hydraulic Simulations Using High-Resolution Topographic Data: Examples from Sri Lanka—Lower Kelani River Basin. Hydrology 2022, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotti, M.; Maranzoni, A.; Tomirotti, M.; Velerio, G. 1923 Gleno Dam Break: Case Study and Numerical Modeling. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayefi, V.; Lane, S.N.; Hardy, R.J.; Yu, D. A comparison of one- and two-dimensional approaches to modelling flood inundation over complex upland floodplains. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3190–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armas, A.; Beillicci, R.; Beillicci, E. Numerical Limitations of 1D Hydraulic Models Using MIKE11 or HEC-RAS software—Case study of Baraolt River, Romania. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 072010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, P.; Vaes, G.; Popa, D.; Timbe, L.; Berlamont, J. Quasi 2D river flood modelling. In Proceedings of the River Flow 2002, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium, 4–6 September 2002; Bousmar, D., Zech, Y., Eds.; Swets & Zeitlinger: Lisse, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1253–1259, ISBN 90 5809 509 6. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267797546_Quasi_2D_river_flood_modelling (accessed on 3 October 2023).
- Toombes, L.; Chanson, H. Numerical limitations of hydraulic models. In Proceedings of the 34th IAHR World Congress, 33rd Hydrology and Water Resources Symposium and 10th Conference on Hydraulics in Water Engineering, Brisbane, Australia, 26 June–1 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkimpen, P.; Peeters, P. Flood modeling for risk evaluation: A MIKE FLOOD sensitivity analysis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics (River Flow 2008), Izmir, Turkey, 3–5 September 2008; pp. 2335–2344. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, O.; Dorfman, C.; Zenz, G. 2-D hydraulic modelling of a dam break scenario. In Proceedings of the ICOLD 2013, Graz, Austria, 2–4 October 2013; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311807694 (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Yakti, B.P.; Adityawan, M.B.; Farid, M.; Suryadi, Y.; Nugroho, J.; Hadihardaja, I.K. 2D Modeling of Flood Propagation due to the Failure of Way Ela Natural Dam. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Sustainable Infrastructure and Built Environment (SIBE 2017), Bandung, Indonesia, 26–27 September 2018; Volume 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozinaki, A.-E.K.; Morianou, G.G.; Alexakis, D.D.; Tsanis, I.K. Comparing 1D and combined 1D/2D hydraulic simulations using high-resolution topographic data: A case study of the Koiliaris basin, Greece. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2017, 62, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecki, S.; Banasiak, R. The Catastrophe of the Niedów Dam—The Causes of the Dam’s Breach, Its Development, and Consequences. Water 2021, 13, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M.S.; Bates, P.D. Evaluation of 1D and 2D numerical models for predicting river flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 268, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, A.; Merwade, V. Effect of topographic data, geometric configuration and modeling approach on flood inundation mapping. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falter, D.; Dung, N.V.; Vorogushyn, S.; Schröter, K.; Hundecha, Y.; Kreibich, H.; Apel, H.; Theisselmann, F.; Merz, B. Continuous, large-scale simulation model for flood risk assessments: Proof-of-concept. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2016, 9, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandlburger, G.; Hauer, C.; Hofle, B.; Habersack, H.; Pfeifer, N. Optimisation of LiDAR derived terrain models for river flow modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fewtrell, T.J.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.; Hunter, N.M. Evaluating the effect of scale in flood inundation modelling in urban environments. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 107–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.P.; Neal, J.C.; Voisin, N.; Andreadis, K.M.; Pappenberger, F.; Phanthuwongpakdee, N.; Hall, A.C.; Bates, P.D. A first large-scale flood inundation forecasting model. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6248–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overton, I.C. Modelling floodplain inundation on a regulated river: Integrating GIS, remote sensing and hydrological models. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitková, B.V.; Pekárová, P.; Miklánek, P.; Pekár, J. Hydrological simulation of flood transformations in the upper Danube River: Case study of large flood events. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2016, 64, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, R.C.D.; Buarque, D.C.; Collischonn, W.; Bonnet, M.P.; Frappart, F.; Calmant, S.; Bulhões Mendes, C.A. Large-scale hydrologic and hydrodynamic modeling of the Amazon River basin. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, J.; Schmalz, B.; Brown, G.L.; Fohrer, N. Application of a hydrological-hydraulic modelling cascade in lowlands for investigating water and sediment fluxes in catchment, channel and reach. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2013, 61, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Chung, M.K.; Yang, S.Y.; Hsu, C.T.; Wu, S.J. Improving the Computational Performance of an Operational Two-Dimensional Real-Time Flooding Forecasting System by Active-Cell and Multi-Grid Methods in Taichung City, Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajib, A.; Liu, Z.; Merwade, V.; Tavakoly, A.A.; Follum, M.L. Towards a large-scale locally relevant flood inundation modeling framework using SWAT and LISFLOOD-FP. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.R.M.; Sidek, L.M.; Yalit, M.R.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Basri, H.; Yaacob, K.M. 2D Hydraulic Modelling of Dam Break Analysis Using MIKE FLOOD for Kenyir Dam. In ICDSME 2019, Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Dam Safety Management and Engineering; Sidek, L., Salih, G.H.A., Boosroh, M.H., Eds.; Water Resources Development and Management; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondia, J.; Stelling, G. Application of one-dimensional-two-dimensional integrated hydraulic model for flood simulation and damage assessment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydroinformatics, Cardiff, UK, 1–5 July 2002; pp. 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Pasquier, U.; He, Y.; Hooton, S.; Goulden, M.; Hiscock, K.M. An integrated 1D–2D hydraulic modelling approach to assess the sensitivity of a coastal region to compound flooding hazard under climate change. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 915–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhe, P.; Mitchell, B.; Bates, P.D.; Addor, N.; Neal, J.; Beck, H.E. Model cascade from meteorological drivers to river flood hazard: Flood-cascade v1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 4865–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poretti, I.; De Amicis, M. An approach for flood hazard modelling and mapping in the medium Valtellina. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission for the Protection of the Odra River against Pollution (ICPO). A Concept for Hydraulic Modelling of the Lusatian Neisse River. Work Group G2 “Flood”; Technical Report; ICPO: Wrocław, Poland, in press; (In Polish, Czech and German).
- Costabile, P.; Macchione, F. Enhancing river model set-up for 2-D dynamic flood modelling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 67, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.; Schumann, G.; Bates, P. A subgrid channel model for simulating river hydraulics and floodplain inundation over large and data sparse areas. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazzi, S.; Shustikova, I.; Domeneghetti, A.; Castellarin, A.; Vacondio, R. Comparison of two modelling strategies for 2D large-scale flood simulations. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 146, 105225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nádudvari, Á.; Czajka, A.; Wyżga, B.; Zygmunt, M.; Wdowikowski, M. Patterns of Recent Changes in Channel Morphology and Flows in the Upper and Middle Odra River. Water 2023, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubicki, A.; Malinowska-Małek, M.; Strońska, K. Flood hazards in the upper and middle Odra River basin—A short review over the last century. Limnologica 2005, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligenza, P.; Tokarczyk, T.; Adynkiewicz-Piragas, M. (Eds.) Przebieg i Skutki Wybranych Powodzi w Dorzeczu Odry od XIX Wieku do Czasów Współczesnych; Monografie IMGW-PIB; IMGW-PIB: Szczecin, Poland, 2021; 132p, ISBN 978-83-64979-45-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zalewski, J.; Winter, J. Programme for the Odra River. Strategy for the Modernization of the Odra River System; PWN: Wrocław, Poland, 2000; 159p, ISBN 83-01-13384-8. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W. Adapting flood preparedness tools to changing flood risk conditions: The situation in Poland. Oceanologia 2014, 56, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://odrapcu.pl/en/project-orfpp/about-project-orfpp/# (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- DHI. MIKE 11—A modeling system for Rivers and Channels. In User Manual; DHI Water Environment Health: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McCowan, A.D.; Rasmussen, E.B.; Berg, P. Improving the Performance of a Two-dimensional Hydraulic Model for Floodplain Applications. In The State of Hydraulics, Proceedings of the 6th Conference on Hydraulics in Civil Engineering; Institution of Engineers: Barton, Australia, 2001; Available online: https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.521741235414023 (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- DHI. MIKE21 Flow Model & MIKE 21 Flood Screening Tool. In Hydrodynamic Module; Scientific Documentation; DHI Water Environment Health: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Banasiak, R. Hydrodynamic 2D model of the City Centre Hydrosystem of the city of Wrocław and its flood capacity analysis. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 18, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.G.F.; Hunter, N.M.; Bates, P.D. Identifiability of distributed floodplain roughness values in flood extent estimation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcement, G.J.; Schneider, V.R. Guide for Selecting Manning’s Roughness Coefficients for Natural Channels and Flood Plains; Water Supply Paper 2339; U.S. Government Publishing Office, Federal Center: Denver, CO, USA, 1989.
- Morvan, H.; Knight, D.; Wright, N.; Tang, X.; Crossley, A. The concept of roughness in fluvial hydraulics and its formulation in 1D, 2D and 3D numerical simulation models. J. Hydraul. Res. 2008, 46, 191–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczegielniak, C. Analiza hydraulicznych warunków przebiegu wezbrania Odry w 1985 roku na podstawie pomiarów hydrometrycznych. Mater. I Stud. Opol. 1988, XXX, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Banasiak, R.; Krzyżanowski, M.; Gierczak, J.; Wdowikowski, M. Bathymetric changes, roughness and conveyance of a compound, regulated by groynes river channel during low and high water conditions. In Proceedings of the River Flow 2014, Lausanne, Switzerland, 3–5 September 2014; Shleiss, A.J., de Cesare, G., Pfister, M.J., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2014; pp. 369–374, ISBN 978-1-138-02674-2. [Google Scholar]
- Molinari, D.; De Bruijn, K.M.; Castillo-Rodríguez, J.T.; Aronica, G.T.; Bouwer, L.M. Validation of flood risk models: Current practice and possible improvements. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2019, 33, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, R. Verification of the peak flow rates of the July 1997 flood in the upper and middle Odra river. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasiak, R.; Krzyżanowski, M. Flood flows in the Odra river in 2010—Quantitative and qualitative assessment of the ADCP data. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. 2015, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubicki, A.; Słota, H.; Zieliński, J. Dorzecze Odry: Monografia Powodzi, Lipiec 1997; IMGW-PIB: Warszawa, Poland, 1999; 164p, ISBN 978-8361102-60-1. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission for the Protection of the Odra River against Pollution (ICPO). The Odra Basin. Flood in 1997; ICPO: Wrocław, Poland, 2009; 150p, ISBN 83-916202-6-3. Available online: www.mkoo.pl/download.php?fid=3918&lang=PL (accessed on 9 November 2023)(In Polish, Czech and German).
- Available online: https://wody.isok.gov.pl/imap_kzgw/?gpmap=gpMZP (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Banasiak, R. Evaluation of the Wrocław Water Node flow capacity before and after modernisation. Gospod. Wodna 2018, 2, 44–50. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Banasiak, R. Two-dimensional hydrodynamic modelling of the Wrocław Water Node and the May 2010 flood. Gospod. Wodna 2017, 10, 297–302. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Najninger, S. Is it safe after years? (Czy po latach jest bezpiecznie?). In 15 Years after the Flood on the Lower Silesia; Sobota, J., Ed.; Centre for Modelling of Hydrological Processes, Wrocław University of Environmental and Life Sciences: Wrocław, Poland, 2012; 197p, ISBN 978-83-932321-4-7. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Grześ, M. Ice jams hazard on the Polish rivers. In Monographs of the Water Management Committee Polish Academy of Sciences; Polish Academy of Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, 2014; Volume I, pp. 107–116. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Lü, H.; Lindenschmidt, K.-E.; Xü, K.; Zhu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Xie, B. Hazard assessment and prediction of ice-jam flooding for a river regulated by reservoirs using an integrated probabilistic modelling approach. J. Hydrol. 2022, 615 Pt A, 128611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenschmidt, K.-E.; Alfredsen, K.; Carstensen, D.; Choryński, A.; Gustafsson, D.; Halicki, M.; Hentschel, B.; Karjalainen, N.; Kögel, M.; Kolerski, T.; et al. Assessing and Mitigating Ice-Jam Flood Hazards and Risks: A European Perspective. Water 2023, 15, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research Institute. Wytypowanie Newralgicznych Miejsc Zagrożenia Powodzią Zatorową na Odrze od Stopnia Wodnego Malczyce do Ujścia Nysy Łużyckiej Wraz z Oszacowaniem Potencjalnych Strat Powodziowych na tym Odcinku Rzeki; Technical Report; Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research: Wrocław, Poland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research Institute. Analizy Hydrologiczne i Hydrauliczne na Potrzeby Opracowania Instrukcji Eksploatacji Zbiornika Racibórz; Technical Report; Institute of Meteorology and Water Management—National Research: Wrocław, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Marine Economy and Inland Navigation (MGMiŻŚ). Assumptions for the Development Plans of Inland Waterways in Poland for 2016–2020 with 2030 Perspective. 2017. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/gospodarkamorska/publikacje-i-materialy-informacyjne (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Şen, Z. Flood Design Discharge and Case Studies. In Flood Modeling, Prediction and Mitigation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guganesharajah, K.; Lyons, D.J.; Parsons, S.B.; Lloyd, B.J. Influence of Uncertainties in the Estimation Procedure of Floodwater Level. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2006, 132, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogger, M.; Kohl, B.; Pirkl, H.; Viglione, A.; Komma, J.; Kirnbauer, R.; Merz, R.; Blöschl, G. Runoff models and flood frequency statistics for design flood estimation in Austria—Do they tell a consistent story? J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berends, K.D.; Straatsma, M.W.; Warmink, J.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Uncertainty quantification of flood mitigation predictions and implications for interventions. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Environmental Protection—National Research Institute (IEP-NRI). Final Report on the Situation of the Odra River. 191p. Available online: https://ios.edu.pl/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/raport-konczacy-prace-zespolu-ds-sytuacji-w-odrze-2.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Free, G.; Van De Bund, W.; Gawlik, B.; Van Wijk, L.; Wood, M.; Guagnini, E.; Koutelos, K.; Annunziato, A.; Grizzetti, B.; Vigiak, O.; et al. An EU Analysis of the Ecological Disaster in the Oder River of 2022; JRC Technical Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2023; 44p. [Google Scholar]







| Chałupki (km 20.7) | Opole (km 152.2) | Brzeg (km 199.1) | Wrocław (km 242) | Ścinawa (km 331.9) | Głogów (km 392.9) | Połęcko (km 530.3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 2160 | 3100 (3500) | 3530 | 3640 | 3000 | 3040 | 3200 |
| Based on 2D model | 2950 | 3400 | 4200 | 3900 | 3000 | 2300 | 2250 |
| % change | 35.6 | 9.7 (−2.9) | 19.0 | 7.1 | 0.0 | −24.3 | −29.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banasiak, R. Large-Scale Two-Dimensional Cascade Modeling of the Odra River for Flood Hazard Management. Water 2024, 16, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010039
Banasiak R. Large-Scale Two-Dimensional Cascade Modeling of the Odra River for Flood Hazard Management. Water. 2024; 16(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanasiak, Robert. 2024. "Large-Scale Two-Dimensional Cascade Modeling of the Odra River for Flood Hazard Management" Water 16, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010039
APA StyleBanasiak, R. (2024). Large-Scale Two-Dimensional Cascade Modeling of the Odra River for Flood Hazard Management. Water, 16(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010039









