Abstract
The increasing intensity of rainfall resulting from climate change is projected to worsen the inundation of urban areas by floods. As a viable alternative, stormwater harvesting presents an opportunity to enhance water supply reliability while reducing pressure on both water resources and urban stormwater drainage systems. The stored rainwater can be supplied with a radius of one kilometer around the storage facility, so less pumping energy is consumed compared to supplying the stored rainwater far away from the storage facilities. To visually depict the characteristics of the selected storage facility, land cover maps were created using ArcGIS. These maps were created for a circular region with a radius of one kilometer around each studied storage facility. In this study, a daily water balance model was formulated using spreadsheets to assess the potential of harvesting stormwater and rainwater for various pre-existing storage facilities. Five different types of storage facilities were selected for this study. The term “SRWH facility evaluation criteria” as a whole is used for the storm or rain (SR) water supply satisfaction rate, the SR guarantee rate, and the SR utilization rate. The results provide evidence that, for each selected studied storage facility, the SR water guarantee rate can potentially surpass 70% under conditions of low water demand. Moreover, we investigated the potential of the existing storage facilities to work as multifunctional resources, while the original purpose for which each facility was constructed remains un-affected.
1. Introduction
The demand for freshwater is increasing with urbanization, climate change, and population growth which have a significant impact on freshwater resources around the world [1,2,3]. Climate change induces shifts in precipitation patterns, elevating the occurrence of extreme storm events and drought [4,5,6]. The pervasive transformation of natural landscapes into impermeable expanses is a prevalent occurrence across global regions. Urbanization leads to the substitution of permeable terrains, primarily characterized by vegetated features such as agricultural lands and, green spaces, with impervious areas, including roadways, rooftops, and paved spaces, which also encompass parking lots [7]. Hence, the development of strategies such as low-impact development (LID) and transitioning to the Sponge City concept for the mitigation of stormwater on-site is essentially required [8,9,10].
The practice of stormwater harvesting, which involves the collection of runoff from urban areas to establish a supply of water suitable for non-potable usage and occasionally even for potable purposes, has gained recognition as a pivotal resource in urban development [11]. It has remarkable potential as an alternative water source, and stormwater possesses considerable abundance, frequently accessible in proximity to urban areas. Its utilization holds the promise of enhancing water security, fortifying resilience against the impacts of climate change in urban areas [12,13]. Stormwater runoff is usually channeled into streams through drainage systems, constituting a significant source of diverse pollutants. Consequently, it assumes a pivotal role as a principal contributor to the degradation of receiving water bodies, imparting considerable stress upon them [14,15,16]. Therefore, to make cities and towns the most resilient and livable in the world, stormwater pollution mitigation is therefore important for urban water management. Techniques of water sensitive urban design (WSUD) are used to reduce stormwater runoff and pollutant loads into the receiving environment [8,17]. Around the world, for WSUD concepts, different terminologies are used [18,19]. LID has emerged as a viable and environmentally sustainable alternative to traditional stormwater management systems within the realm of academic and practical discourse [20,21].
The treatment of stormwater is a prerequisite for its suitable utilization. The level of treatment is primarily dependent upon the specific characteristics of the catchment area and the ultimate intended end use of stormwater [22]. Pollutant loads are a key contributing factor to the degradation of aquatic ecosystems and environmental water bodies [23]. To achieve the design objectives of stormwater best management practices, a careful maintenance of infiltration facilities is required [24]. Irrigation stands out as one of the foremost and commonly sought-after applications for harvested stormwater [25]. The utilization of harvested stormwater for irrigation in parklands, open spaces, and sports fields plays a pivotal role in preserving and cultivating vibrant urban environments, yielding a multitude of advantages. These advantages encompass enhanced physical and mental well-being among the community through the enrichment of urban green spaces, augmented property values, increased amenity values, and significant freshwater conservation [26].
The evidence suggests that the use of stormwater harvesting for the irrigation of urban green spaces yields advantages across multiple dimensions, including environmental, social, and economic aspects [27,28,29]. Henceforth, it is reasonable that, through proper planning, precise design, and efficient execution, stormwater harvesting for reuse initiatives can be effectively implemented in appropriate locales, yielding manifold advantages. Heavy monsoons cause large stormwater runoff, which can be a resource if managed properly, but can also be a challenge if left mismanaged [30]. Numerous research studies have mentioned the process of site selection for stormwater harvesting, which encompasses the consideration of a diverse array of criteria, including social, economic, and environmental factors [31,32,33,34,35,36]. However, comprehensive studies to analyze the potential of stormwater harvesting and rainwater harvesting based on the SRWH facility evaluation criteria for different types of storage facilities are lacking. While there is an increase in research on the SRWH systems around the world, customizing these insights to the specific geographical, climatic, and urban context of Republic of Korea is a frontier that has yet to be fully explored [37].
The focus of this study is to investigate the potential of stormwater and rainwater harvesting for various existing storage facilities in Republic of Korea. Five different types of storage facilities were selected for this study. For a better visualization of the characteristics of each selected storage facility, land cover maps were created using ArcGIS. These maps were created for a circular region with a radius of one kilometer around each storage facility. The stored rainwater can be supplied to the area around the storage facility with a one-kilometer radius. A spreadsheet-based daily water balance model was developed to calculate the SRWH facility evaluation criteria for the selected studied storage facilities considering different water demand scenarios. It is hoped that this research, which focuses on stormwater and rainwater harvesting potential using a daily water balance model, will provide not only an academic contribution, but also a roadmap for efficient utilization of stormwater and rainwater in Republic of Korea.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
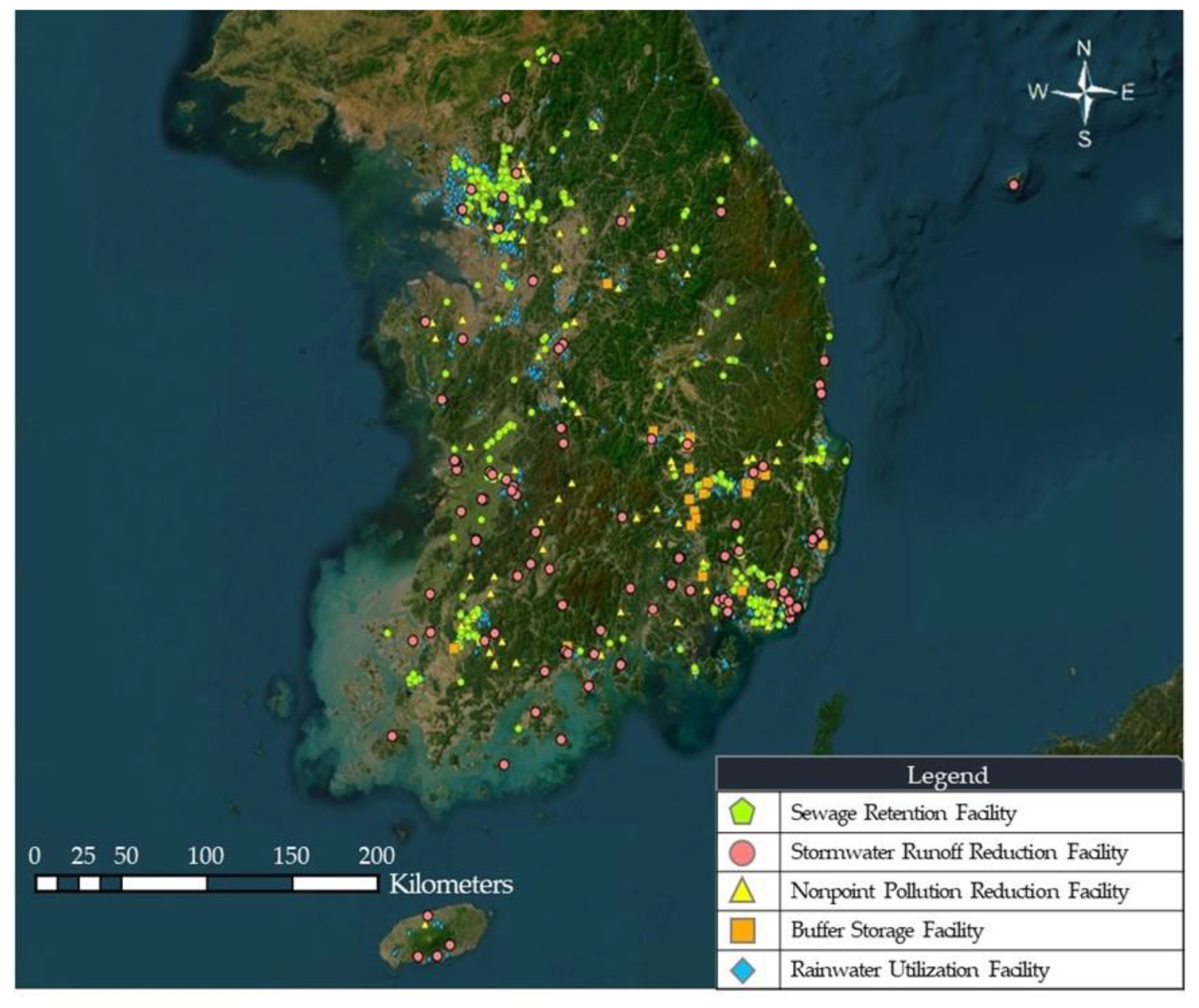
In the context of Republic of Korea, a multitude of stormwater and rainwater harvesting storage facilities have been established to effectively address both rainfall-runoff mitigation and the improvement of water quality. The comprehensive overview of these storage facilities can be observed in Figure 1, which provides a brief summary of five different categories of existing storage facilities. In addition, Table 1 includes information regarding each facility’s type, installation purpose, and number of storage facilities in the country.
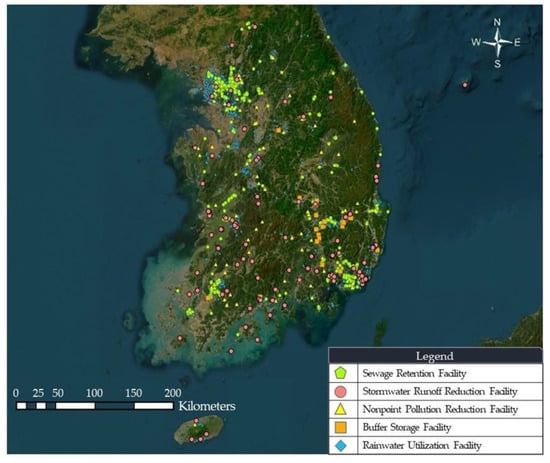
Figure 1.
Overview of different types of the existing storage facilities in Republic of Korea.

Table 1.
Summary of the selected storage facilities and the purpose of each type of facility.
2.2. Descriptions of the Studied Facilities
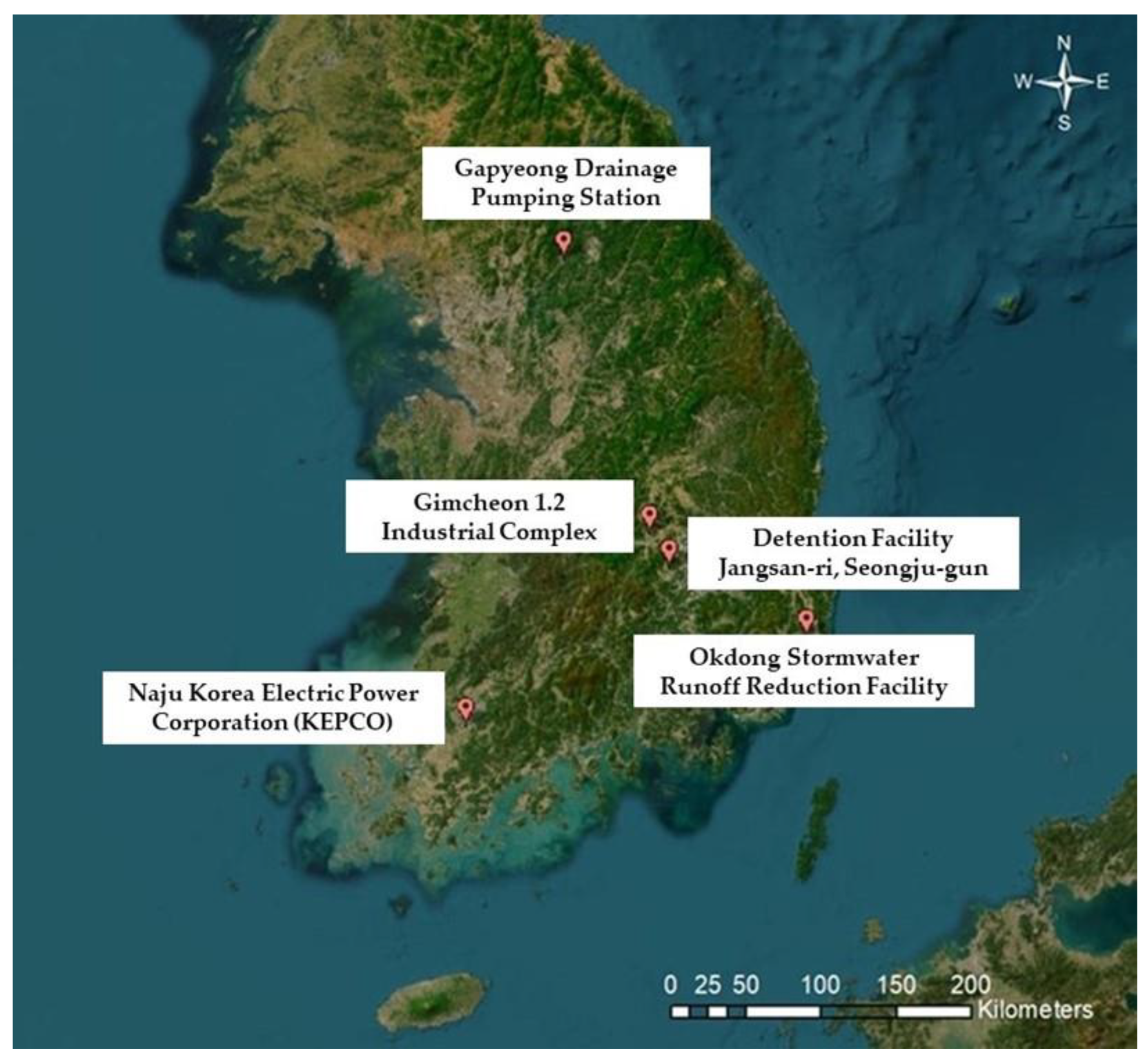
In this study, five different types of storage facilities were selected for investigation. The geographical distribution of these selected facilities is shown in Figure 2, which presents a regional map illustrating their respective locations. Additional comprehensive details are presented in Table 2, including essential information about the type and name of each storage facility, its precise geographic location specified through latitude and longitude coordinates, the name of the closest rain station, and the measured distance between the studied storage facility and the rain station, alongside the average rainfall for a decade-long period from January 2012 to December 2021. For a detailed understanding, Table 3 provides additional information, such as the rainfall capture area and size of the actual rainwater storage tanks for each of the selected studied storage facilities.
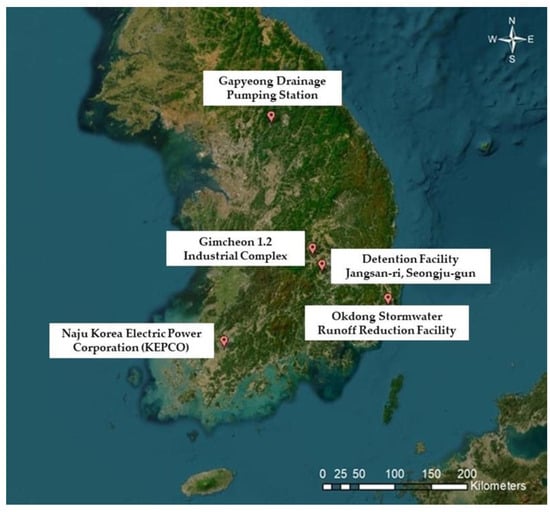
Figure 2.
The regional location map of the selected studied storage facilities.

Table 2.
Details of the selected storage facilities’ rainfall data and locations.

Table 3.
Summary of the selected storage facilities’ runoff catchment areas and storage tank sizes.
2.3. Methodology of the Present Study
In this research study, we developed a daily water balance model using spreadsheets, thereby facilitating an in-depth assessment of stormwater and rainwater harvesting potential for five distinct categories of existing storage facilities. The model developed in this investigation effectively computed the required water quantity and rate of rainwater availability for a period of 10 years (from January 2012 to December 2021). Additionally, it undertook an evaluation of the SRWH facility evaluation criteria score, considering various water demand scenarios, a different approach from conventional methodologies that exclusively consider rainfall data and rainwater tank size [38]. Our developed model, however, accounts for the capture of rainfall runoff from the facility’s designated catchment area, channeling it into the storage tank, while segregating the initial 10 mm of rainfall—laden with pollutants—into the first flush separation tank.
The first flush separation in stormwater runoff has drawn a lot of attention from experts in the field of non-point source pollution [39]. The attributes of the initial runoff event gained significance as a key determinant in the development of LID strategies, particularly in response to the compulsory implementation of stormwater treatment measures [40]. Within a research study in Republic of Korea, the initial runoff event served as a pivotal criterion in formulating and enhancing LID infrastructures. This primarily encompassed the design considerations for bioretention, green roofs, infiltration trenches, porous pavements, rain barrels, and vegetated swales [41]. Furthermore, an alternative research investigation proposed incorporating both the maximum effluent concentration and pollutant removal targets, discerned through the analysis of the first flush characteristics, as essential parameters in establishing the design of bio detention and retention facilities [42,43].
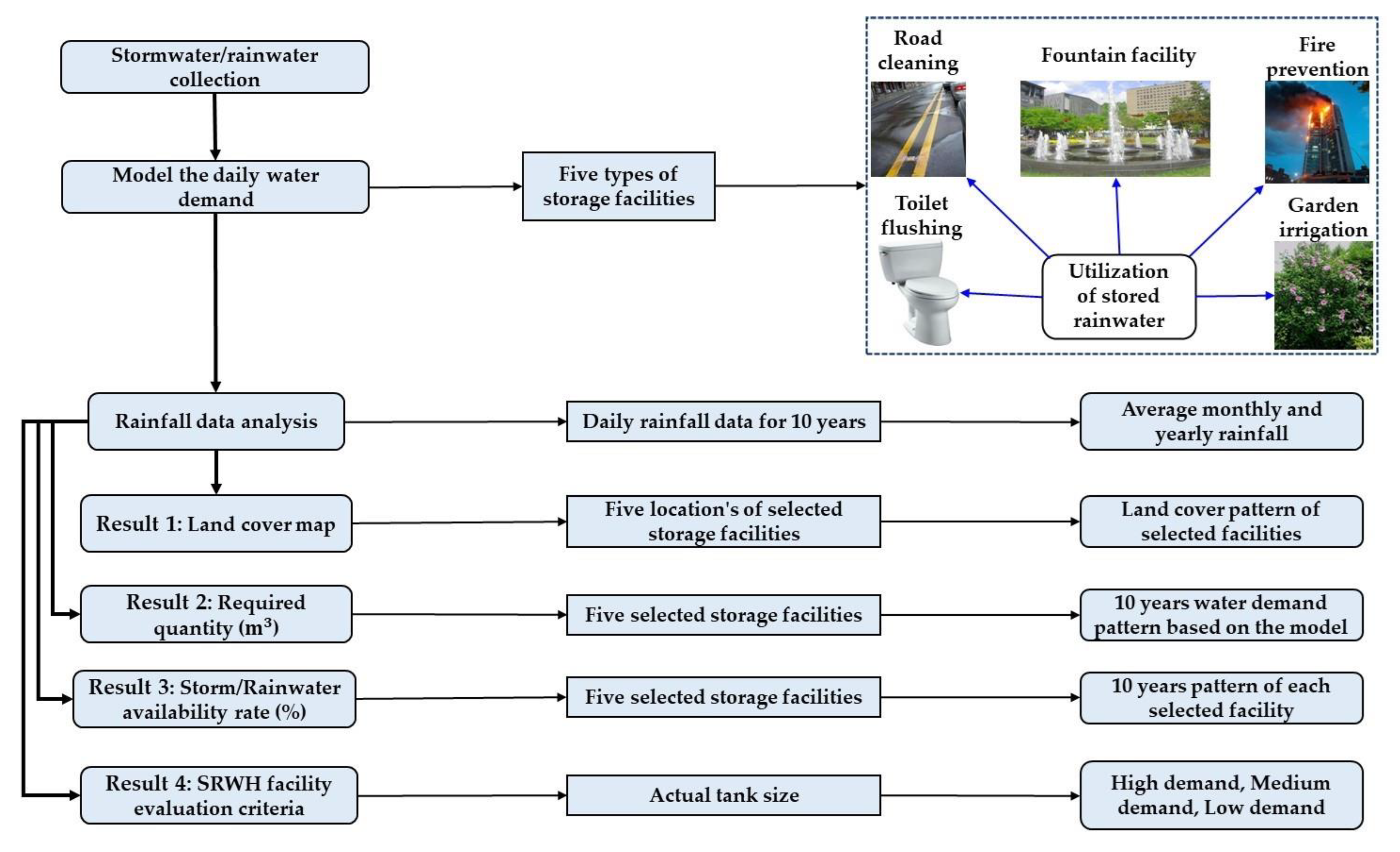
The accumulated rainwater, stored because of this process, finds applications for non-potable purposes [44], within a one-kilometer radius of the storage facility. This strategic localization minimizes the energy input required for pumping operations. A comprehensive land cover map for each analyzed storage facility was generated using ArcGIS, providing a detailed description of the respective sites. Pertinently, water demand was computed based on specific usage criteria, with Table 4 providing an extensive breakdown of water end-use categories for each storage facility type. Moreover, we assumed low, medium, and high demand scenarios, constituting 25%, 50%, and 75% of the model-calculated water demand, respectively. Furthermore, regional rainfall data were obtained from the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) [45] and subsequently integrated as inputs for our calculations. The methodological steps pursued throughout this study are shown in Figure 3.

Table 4.
Details of harvested SR water utilization water demand quantity and purpose in each type of the studied facility.
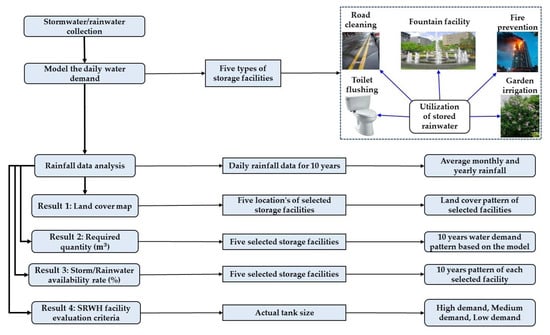
Figure 3.
The methodological flowchart for the present study.
2.4. Daily Water Balance Model Methodology
To evaluate the potential of stormwater and rainwater harvesting for five different storage facilities, we developed a daily water balance model in this study using spreadsheets. The simulation model utilizes input parameters such as the daily precipitation, the runoff catchment area, and the runoff coefficient. Additionally, variable input data were to consider the required water quantity pattern for a period of 10 years (from January 2012 to December 2021). The fundamental concept of the model lies in the sequential collection of rainwater from the catchment area: the initial rainfall is directed towards the first flush separation tank, followed by storage in a rainwater storage tank. For utilizing the minimum pumping energy during water distribution, the collected water from the storage tank serves the non-potable needs of a localized area within a one-kilometer radius of the storage facility. A more detailed land cover map of each studied storage facility was generated using ArcGIS. Moreover, a comprehensive insight into the specific applications of harvested rainwater and the corresponding water demand across the studied facility types are presented in Table 4.
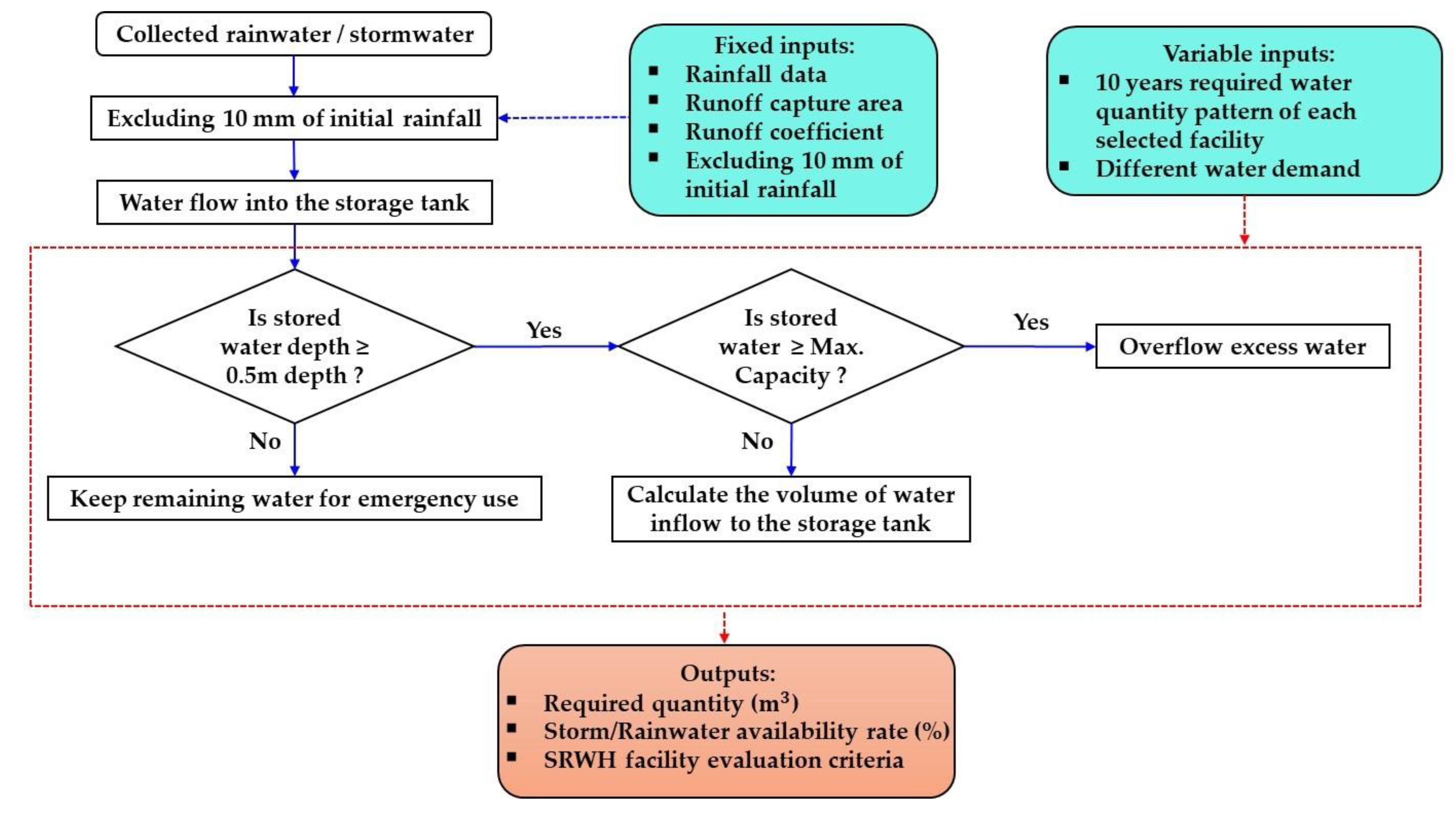
Figure 4 illustrates the logical schematic sequence of the simulation model, to compute the SRWH facility evaluation criteria for the selected studied storage facilities. Notably, the analysis assumes that the rainwater storage tank possesses sunlight-blocking characteristics, thus negating water losses because of evaporation from the water storage tank. Sunlight-blocking is important for the prevention of algae growth in the water storage tank. Since algae is like most plants that thrive off sunshine, depriving them of light prevents its growth. Moreover, a runoff coefficient of 0.75 was used in this study. Succinctly, the calculation model deducts the initial flush rainfall (10 mm) from the total precipitation. The remaining amount of rainfall is multiplied with the runoff capture area and the runoff coefficient to calculate the runoff volume. This procedure, articulated in Equation (1), culminates in the estimation of the runoff volume. The calculations proceed daily, with the runoff from the present day added with previously accumulated water in the storage tank. Every day, the amount of rainfall required by the model is decreased using the stored water (if available). However, in instances where the storage tank attains a full capacity, any subsequent runoff excessive amount is lost as an overflow. In case if no water is in the storage tank, the water demand is fulfilled through the city water supply.
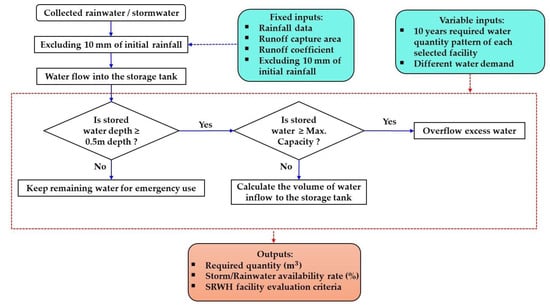
Figure 4.
The model methodology schematic procedure to visualize the daily water balance model developed in the present study based on the storage facility’s variable inputs, fixed inputs, and outputs.
The mathematical formulations for the cumulative runoff collected from the capture area is as presented in our previous study [37]:
where Vt is the harvested rainwater (m3) on day t from the catchment area, It is the rainfall (mm) on day t, If is the first flush rainfall (10 mm), A is the catchment area (m2), and Rc is the runoff coefficient (0.75). As the daily rainfall used in “Equation (1)” is in mm, the conversion factor 0.001 is used to convert “mm” into “m”. for .
The collected water volume held within the storage tank was computed utilizing the subsequent mathematical expression:
where St is the total water stored in the storage tank (m3) at the end of day t, Vt is the volume of harvested rainwater (m3) on day t, St−1 is the stored water in the tank (m3) at the start of day t, D is the daily rainwater demand (m3), and C is the capacity of the storage tank (m3). The term “SR water” is used for storm and rainwater.
The rainwater availability rate (%) was calculated using the following equation:
The mathematical formulations governing the computation of the SRWH facility evaluation criteria are as follows [37]:
2.5. Rainfall Data Summary
A complete investigation of rainfall patterns spanning a decade (January 2012 to December 2021) was carried out as part of the ongoing research. The rigorously obtained data from the KMA [40] provides vital insights into precipitation trends in selected Republic of Korea rainfall stations. The rain stations, which were chosen for their proximity to the studied storage facilities locations, were crucial in assuring the accuracy and usefulness of the collected data.
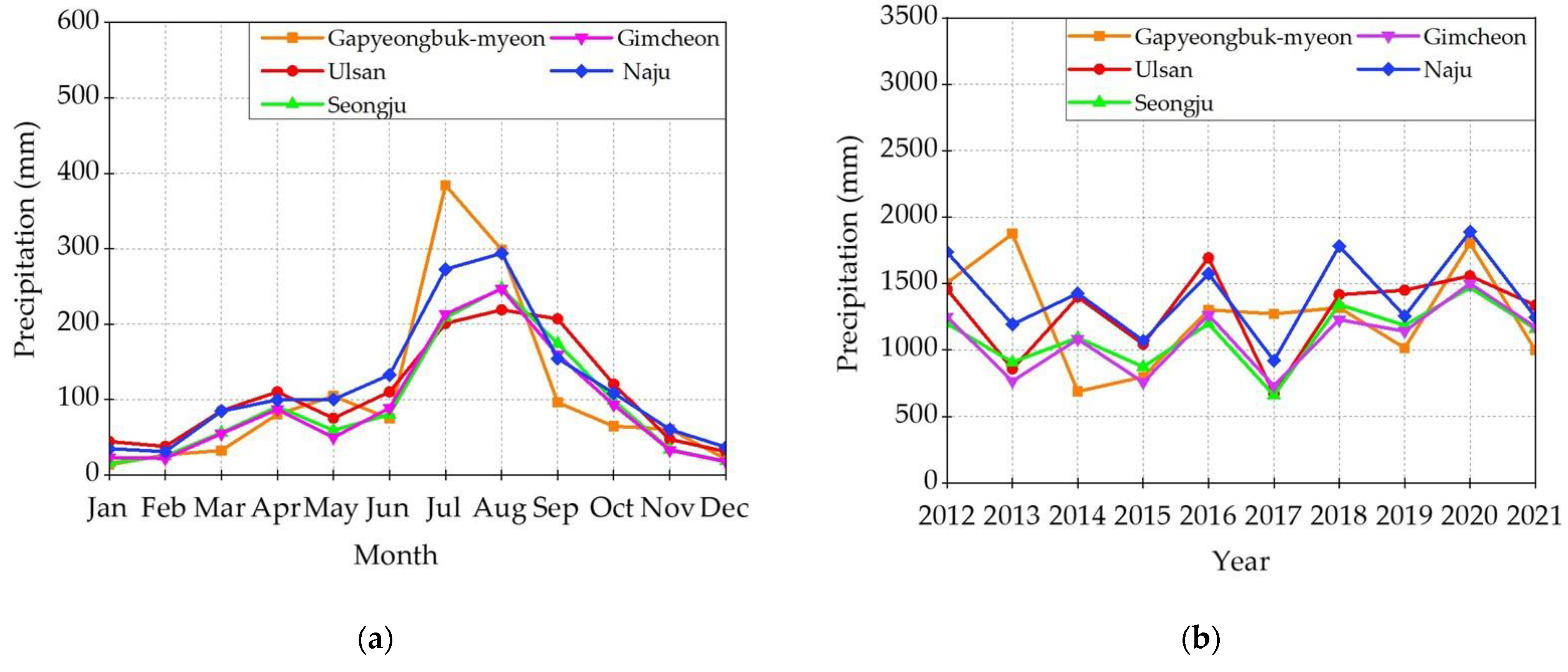
The monthly average rainfall across the five locations—Gapyeongbuk-myeon, Gimcheon, Ulsan, Naju, and Seongju—showed a distinct seasonal pattern, as shown in Figure 5a. This data-driven pattern emphasizes the importance of the Northern Hemisphere’s summer months on the region’s precipitation depth. The start of the monsoon season, usually in mid-June, heralds a period of increased rainfall that lasts about seven weeks, drastically impacting the water collection potential during this time.
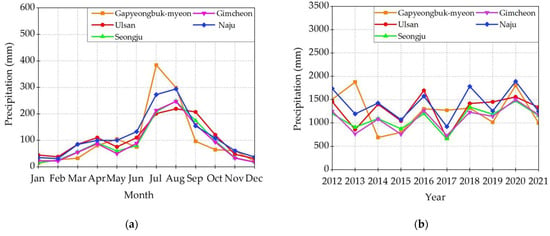
Figure 5.
Average rainfall of the rain station nearest to the locations of the selected storage facilities (years 2012–2021): (a) average monthly rainfall; (b) average annual rainfall.
Figure 5b, on the other hand, investigates the selected sites’ average yearly rainfall across the 10-year study period. A deeper look at the graph reveals that Naju received a comparatively higher annual average rainfall of 1410 mm while Ulsan, Gapyeongbuk-myeon, and Seongju received annual average rainfalls of 1288 mm, 1257 mm, and 1108 mm, respectively. This observation is compatible with the topographical and meteorological peculiarities of the locations, which favor more rainfall.
In contrast, Gimcheon had a comparatively low annual average of 1089 mm, which reflected its geographical location and the overall meteorological conditions that control the area. It is worth noting that, despite these variations, the general average yearly rainfall for the entire country was roughly 1250 mm. Such information highlights the need to understand microclimatic fluctuations when developing rainwater harvesting and stormwater harvesting techniques.
Finally, this decade-long study not only provides a comprehensive view of rainfall patterns across varied places, but also emphasizes the importance of seasonality that influences these patterns. Such findings are critical for legislators, urban planners, and environmentalists seeking to maximize rainwater harvesting efforts and ensure long-term rainwater management practices in the region.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selected Studied Storage Facilities Locations’ Land Cover Maps
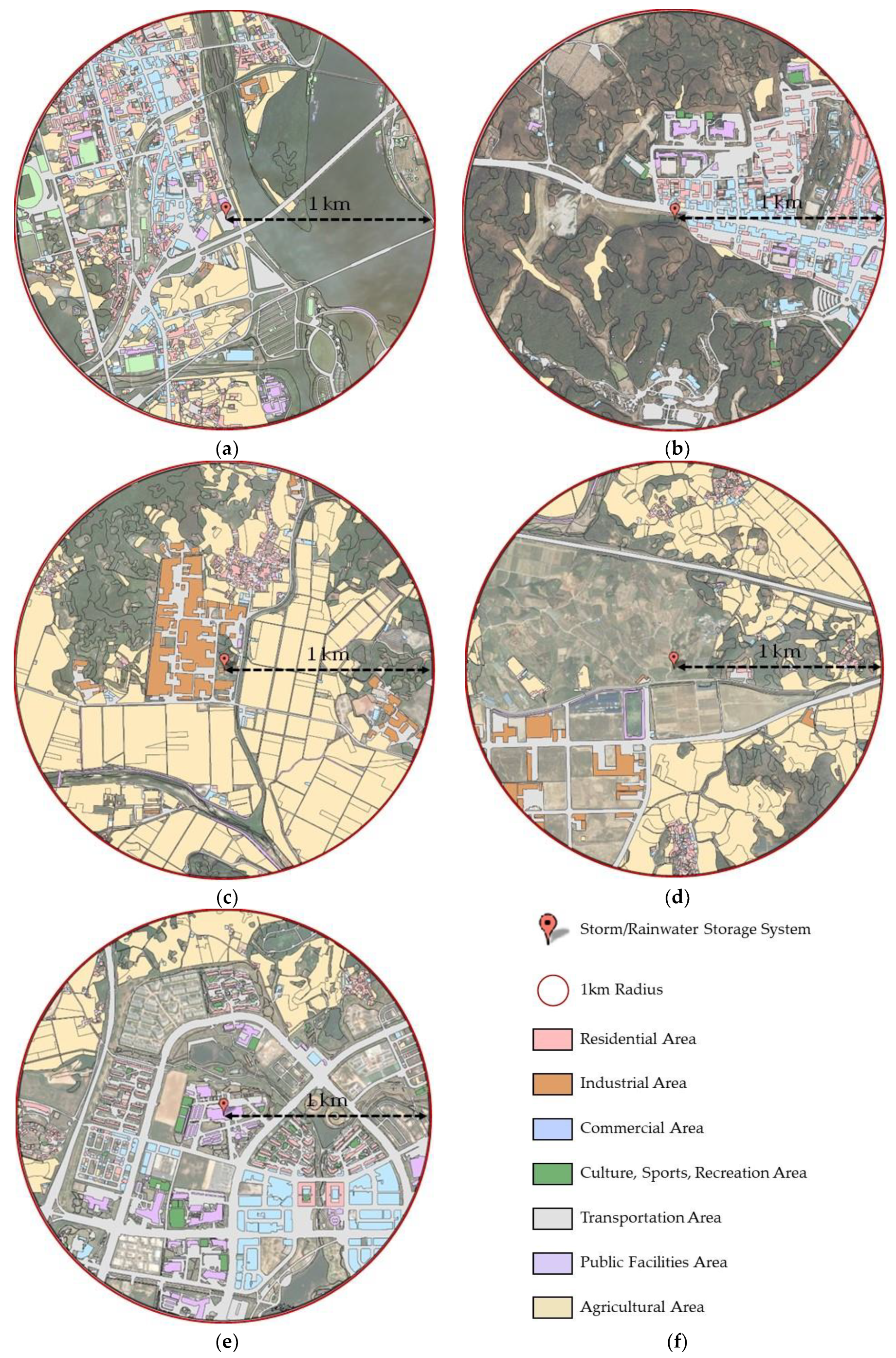
Figure 6a–e shows the land cover map for each storage facility, serving the purpose of providing a detailed characterization of the land cover within a one-kilometer circular region of the studied storage facility. Additionally, Figure 6f shows the legend key for reference. The resultant land cover maps, a fundamental outcome of our investigative efforts, offer a visual depiction of the spatial arrangement and constitution of diverse land cover classifications within a circular region of a one-kilometer radius. This cartographic representation assumes a pivotal role in unveiling the landscape’s diversity.
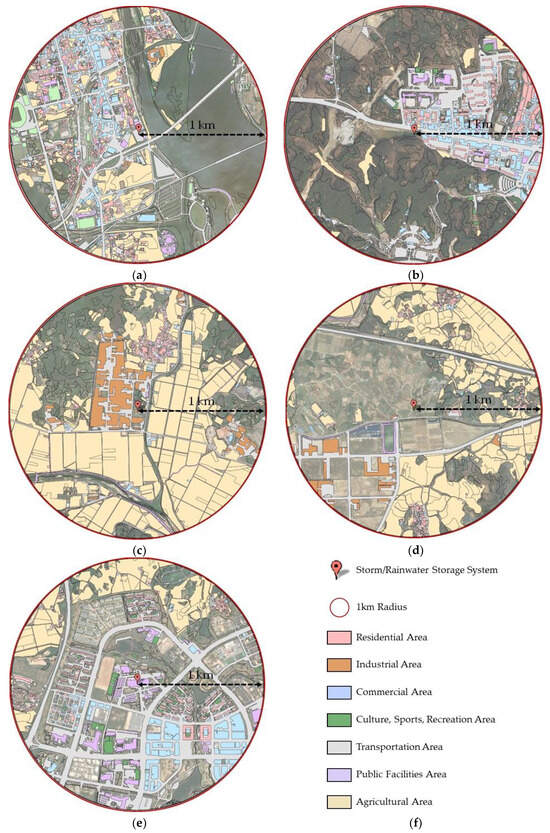
Figure 6.
Land cover maps of the selected studied storage facilities’ locations: (a) sewage retention facility (Gapyeong Drainage Pumping Station); (b) stormwater runoff reduction facility (storm-water runoff reduction facility in Okdong); (c) non-point pollution reduction facility (detention facility in Jangsan-ri, Seongju-gun); (d) buffer storage facility (Gimcheon 1.2 Industrial Complex); (e) rainwater utilization facility (Naju Korea Electric Power Corporation); (f) legend land cover map.
Using remote sensing data and advanced geospatial methodologies, we generated these land cover maps, prioritizing the attainment of precision and reliability, using ArcGIS. The classification endeavor entailed the systematic grouping of terrestrial surfaces into discrete categories, spanning residential, industrial, commercial, cultural, sports and recreational, transportation, public facilities, and agricultural areas. This nuanced categorization serves not only to foster a holistic comprehension of land usage trends, but also lays the foundation for subsequent analytical pursuits exploring the detailed effect of land cover dynamics on water demand.
3.2. Selected Studied Locations’ Required Water Quantities
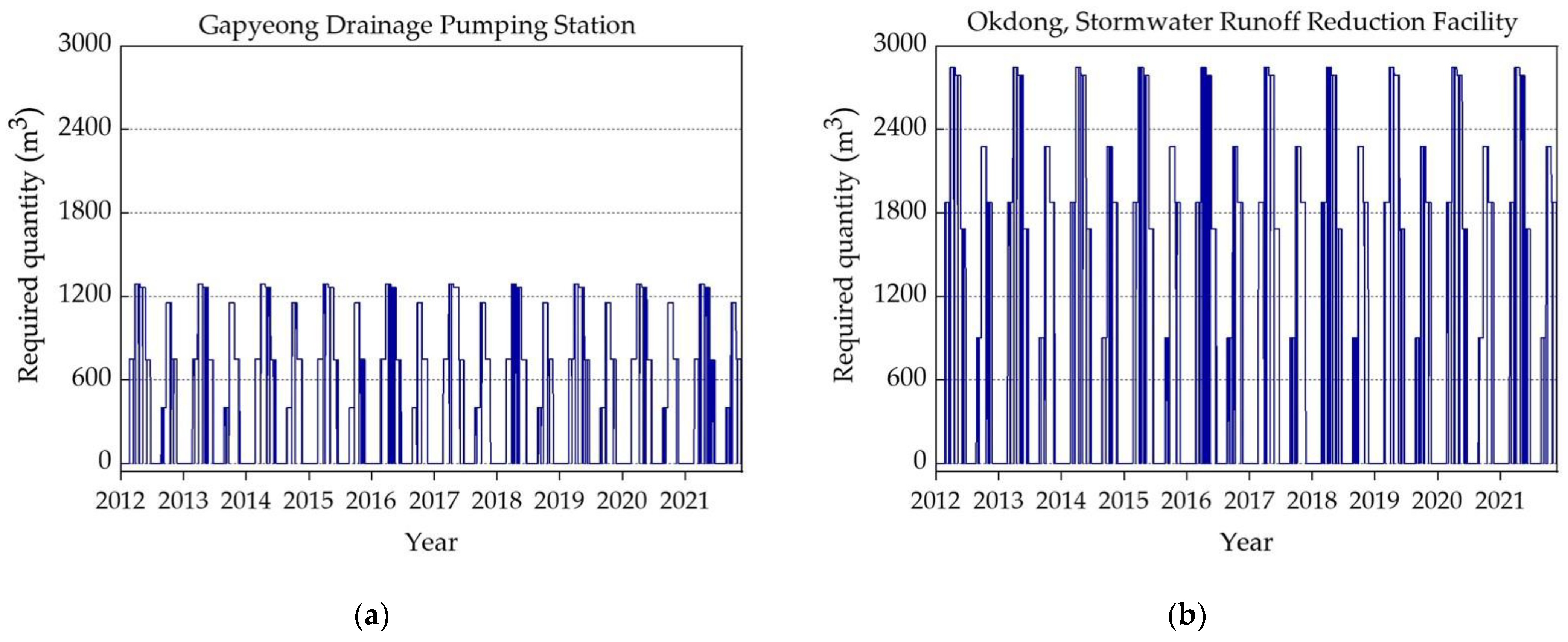
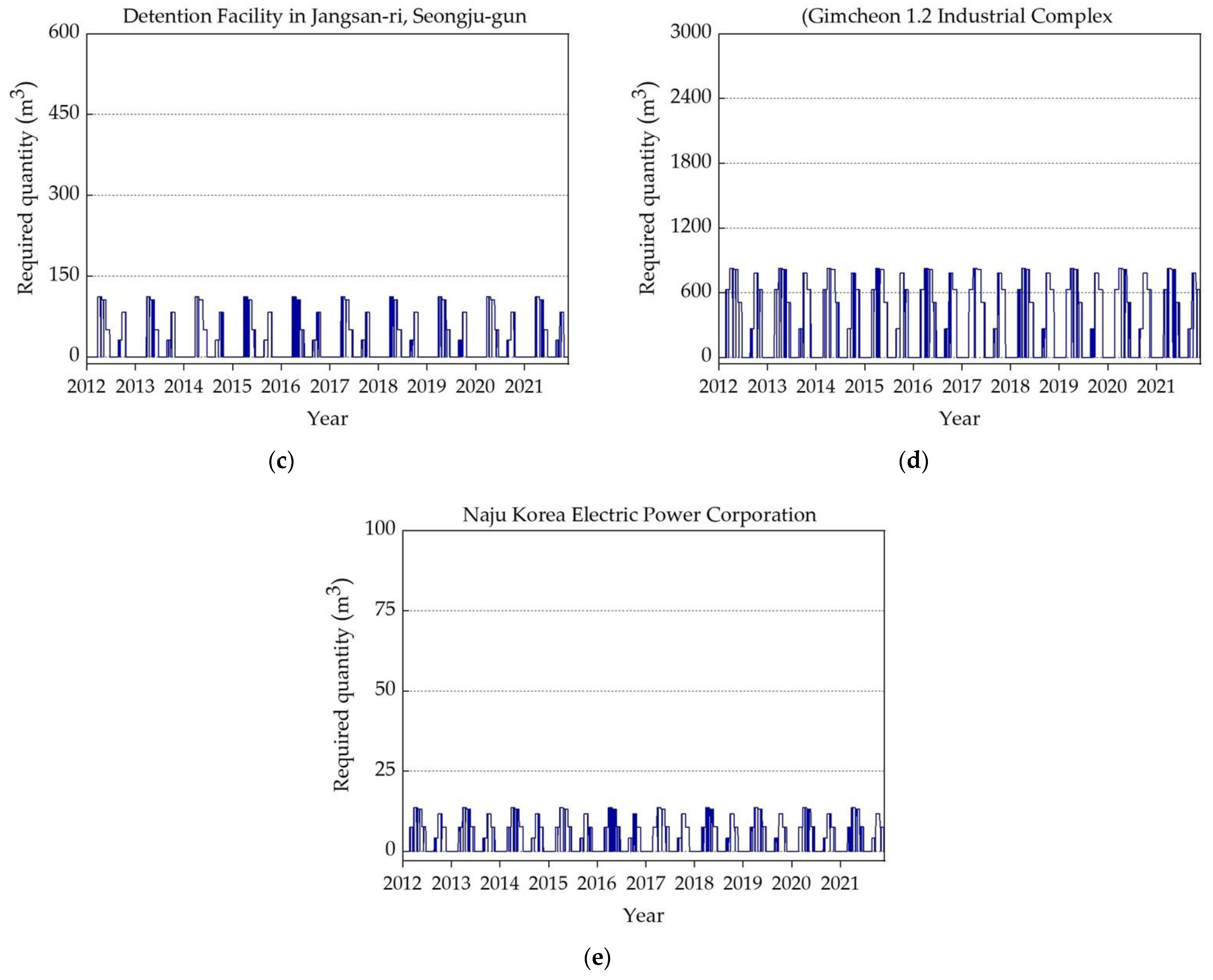
Figure 7a–e illustrates the temporal water requirements over a 10-year period (January 2012 to December 2021) for the five selected storage facilities. The water demand quantity was calculated daily for each facility as shown in Figure 7a–e. The computation of the required water quantity was calculated based on the specific use; a detailed exposition of water end usage for each studied storage facility type is provided in Table 4. Upon the study of the outcomes shown in Figure 7a–e, it becomes evident that among the selected studied facilities, the stormwater runoff reduction facility in Okdong required the highest demand of water quantity. Conversely, the Naju Korea Electric Power Corporation required the lowest water quantity. It is worth noting that, despite these variations, the general pattern of required water quantity for each selected facility showed that in the rainy season less water quantity was needed because of the low irrigation water demand. Ultimately, this extensive decade-long analysis of water requirements not only offers a holistic perspective of the water demands for the five selected facilities under study, but also emphasizes the pivotal role of seasonality in influencing these demand patterns.
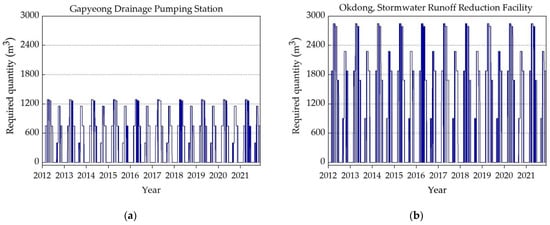
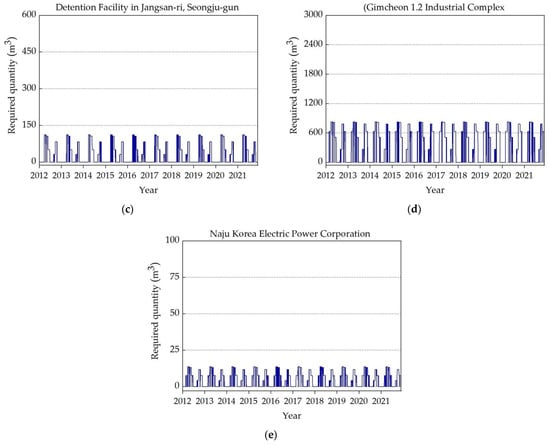
Figure 7.
Selected studied locations’ required water quantities (m3): (a) sewage retention facility; (b) stormwater runoff reduction facility; (c) non-point pollution reduction facility; (d) buffer storage facility; (e) rainwater utilization facility.
3.3. Selected Studied Locations’ Storm/Rainwater (SR Water) Availability Rates
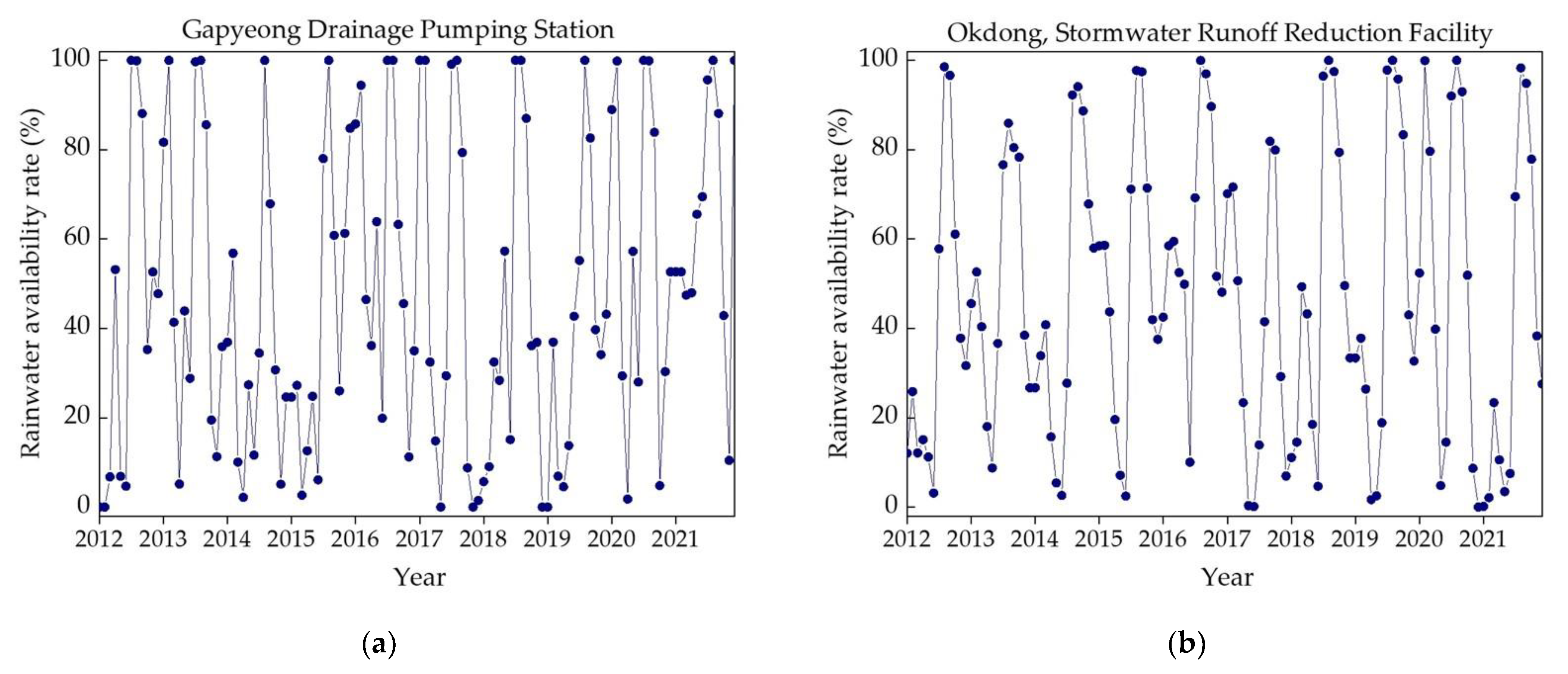
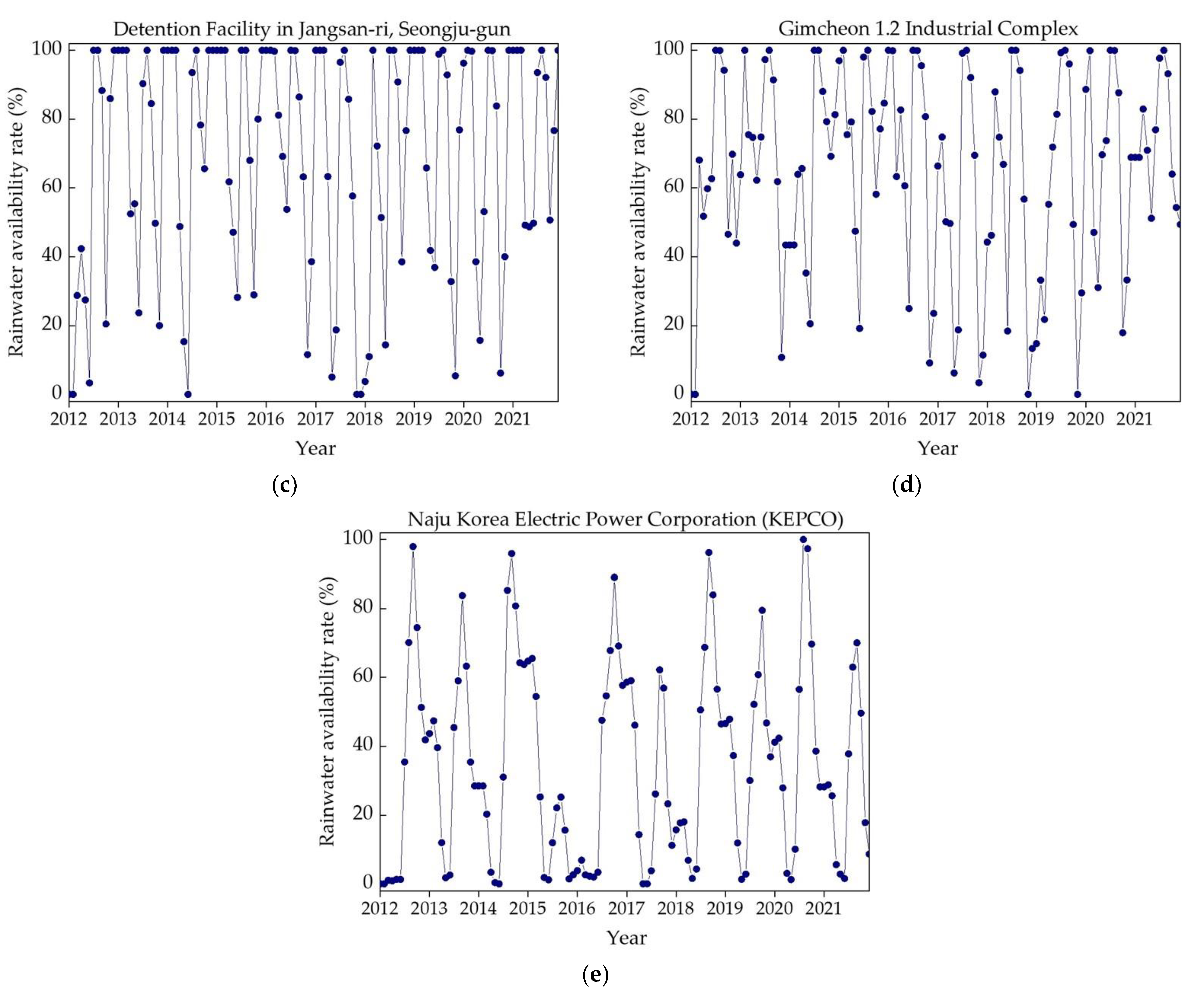
Illustrated in Figure 8a–e are the patterns of SR water availability rates for a period of 10 years (January 2012 to December 2021) for the five studied storage facilities. During the monsoon season, each facility exhibited an available SR water volume surpassing the demand, leading to surplus water overflowing from the storage tanks. Consequently, the rainwater availability rate was inherently capped at 100%. Conversely, the dry season was characterized by the scant rainwater volume, causing the SR water availability rate to reduce to 0%. As shown in Figure 8a–e, the SR water availability rate for each chosen storage facility followed a reasonable and consistent pattern over the 10-year timeframe (January 2012 to December 2021). The findings suggest that, during the monsoon season, water should be released safely after storms events and space should be kept for water available while during the dry season water should only be released if the storage is full.
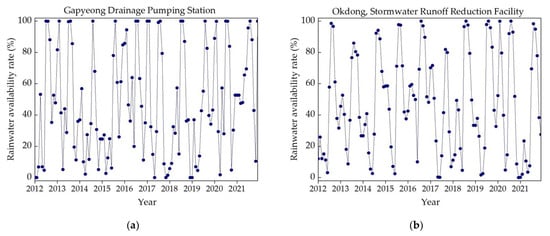
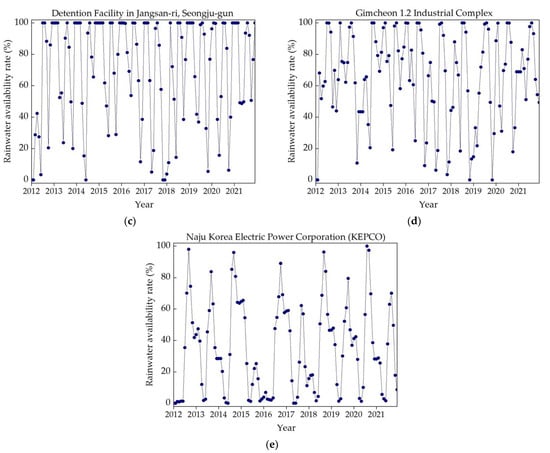
Figure 8.
Selected studied locations’ SR water availability rates (%): (a) sewage retention facility; (b) stormwater runoff reduction facility; (c) non-point pollution reduction facility; (d) buffer storage facility; (e) rainwater utilization facility.
3.4. Effects of the Water Demand Scenarios on the SRWH Facility Evaluation Criteria
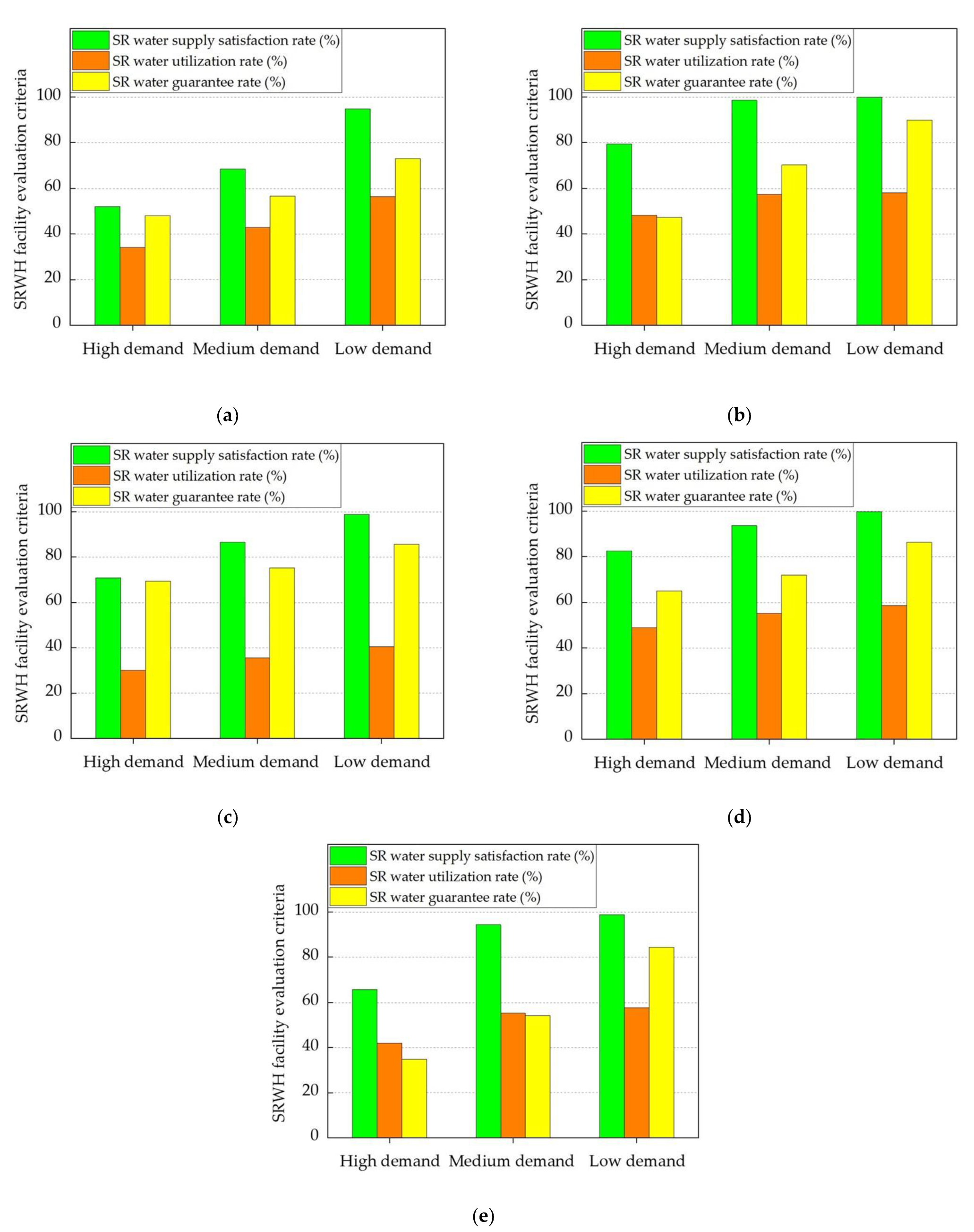
Figure 9a–e shows the SRWH facility evaluation criteria for the designated storage facilities under study. The SRWH facility evaluation criteria were determined based on the actual storage tank size, accounting for different water demand scenarios. The specifics details of the catchment area and the storage tank size for each of the chosen storage facilities are presented in Table 3. The graphical representations in Figure 9a–e collectively demonstrate that, across all selected storage facilities, the SRWH facility evaluation criteria consistently exhibited their peak values under conditions of low water demand. Moreover, our analysis of the presented results indicates that the Gapyeong Drainage Pumping Station (depicted in Figure 9a) exhibited an SR water guarantee rate that could surpass 70% under conditions of low water demand. Conversely, among the examined facilities illustrated in Figure 9b–e, the SR water guarantee rate can potentially exceed 80%.
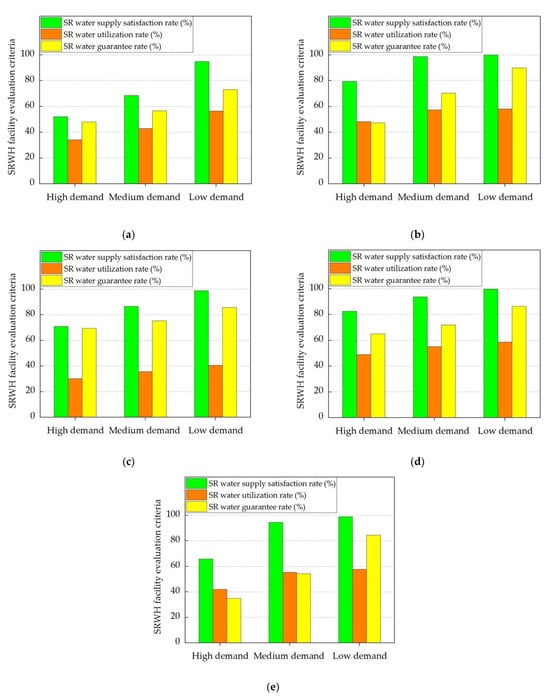
Figure 9.
SRWH facility evaluation criteria considering high, medium, and low water demand scenarios for the selected studied storage facilities: (a) sewage retention facility (Gapyeong Drainage Pumping Station); (b) stormwater runoff reduction facility (stormwater runoff reduction facility in Okdong); (c) non-point pollution reduction facility (detention facility in Jangsan-ri, Seongju-gun); (d) buffer storage facility (Gimcheon 1.2 Industrial Complex); (e) rainwater utilization facility (Naju Korea Electric Power Corporation).
Furthermore, of paramount significance is our investigation into the potential of the existing storage facilities to serve as multifunctional resources, thereby enhancing on-site water management. Notably, the primary objectives underlying the construction of each facility, as detailed in Table 1, will remain unaffected. By utilizing the stored rainwater within a one-kilometer circular radius of the storage facility, the demand for pumping energy will be substantially reduced in comparison to the transportation of stored rainwater over greater distances. Moreover, as many storage facilities in Republic of Korea have been constructed already, no cost for the initial construction will be required.
4. Conclusions
This research analyzed the potential of harvesting stormwater and rainwater for five distinct types of existing storage facilities, using a spreadsheet-driven daily water balance model. The investigation incorporated a decade-long dataset of daily rainfall, obtained from the KMA, spanning from January 2012 to December 2021. This comprehensive collection of daily rainfall figures served as the foundational input for the computation of the SRWH facility evaluation criteria. Derived from an in-depth study of the outcomes, we can draw the following conclusions:
- For every scrutinized storage facility, the detailed generated land cover map through ArcGIS shows the potential utilization of SR water for multiple non-potable applications within the one-kilometer circular vicinity;
- Opting for releasing water safely after storms events and keeping space for water available during the monsoon season and releasing water only if the storage is full in the dry season is recommended;
- For each examined facility depicted in Figure 9a–e, the SR water guarantee rate can potentially surpass 70% under conditions of low water demand.
Moreover, our investigation holds profound importance in investigating the potential of existing storage facilities to function as multifunctional resources, thereby enhancing on-site water management strategies. It is noteworthy that the primary objectives underlying the construction of each facility, as outlined in Table 1, will remain unaffected. By utilizing the stored rainwater within a one-kilometer circular radius of the storage facility, the demand for pumping energy will be substantially reduced in comparison to the transportation of stored rainwater over greater distances. Moreover, as many storage facilities in Republic of Korea have been constructed already, the need for initial construction expenses is obviated. Our formulated methodology for assessing the potential of stormwater and rainwater harvesting will be of great interest to policymakers and practitioners working on urban stormwater and rainwater management.
However, future studies should focus on a comprehensive investigation of stored rainwater quality, accompanied by the development of optimized treatment train systems aimed at aligning water quality with required end-usage standards. Furthermore, a more detailed quantification of pumping energy associated with the water supply needs further attention.
Author Contributions
The paper was guided by R.K.; A.K. and Y.P. monitored the data and analyzed the results. J.P. and I.S. developed the spreadsheet-based model. The whole manuscript was written and composed by A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research for this paper was carried out under the KICT Research Program (Project No. 20230306-001) and Research on the Development of Design-Construction-Operation Technology to Build a Microgrid System based on Renewable Energy, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Data Availability Statement
The rainfall data used can be collected from Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) https://data.kma.go.kr/, accessed on 11 November 2023.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very thankful to the Ministry of Science and ICT for project funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Jongpyo Park, Inkyeong Sim were employed by the company HECOREA Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Whitmee, S.; Haines, A.; Beyrer, C.; Boltz, F.; Capon, A.G.; de Souza Dias, B.F.; Ezeh, A.; Frumkin, H.; Gong, P.; Head, P. Safeguarding human health in the Anthropocene epoch: Report of The Rockefeller Foundation–Lancet Commission on planetary health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1973–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayeni, A.; Kapangaziwiri, E.; Soneye, A.; Engelbrecht, F. Assessing the impact of global changes on the surface water resources of Southwestern Nigeria. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 1956–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacoli, C.; McGranahan, G.; Satterthwaite, D. Urbanisation, Rural-Urban Migration and Urban Poverty; IIED: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, B.I.; Mankin, J.S.; Anchukaitis, K.J. Climate change and drought: From past to future. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Climate change and drought: A perspective on drought indices. Curr. Clim. Chang. Rep. 2018, 4, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, E.; Gao, X. Climate change impacts on extreme events in the United States: An uncertainty analysis. Clim. Chang. 2015, 131, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sanciolo, P.; Behroozi, A.; Navaratna, D.; Muthukumaran, S. Stormwater Harvesting Potential for Local Reuse in an Urban Growth Area: A Case Study of Melton Growth Area in the West of Melbourne. Water 2023, 15, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, A. Water sensitive urban design approaches and their description. In Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R. Low impact development practices: A review of current research and recommendations for future directions. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2015, 22, 543–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevenbergen, C.; Fu, D.; Pathirana, A. Transitioning to sponge cities: Challenges and opportunities to address urban water problems in China. Water 2018, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthy, R.G.; Sharvelle, S.; Dillon, P. Urban stormwater to enhance water supply. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5534–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Jeffes, L.; Carden, K.; Armitage, N.P.; Winter, K. Stormwater harvesting: Improving water security in South Africa’s urban areas. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2017, 113, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, A.; Mills, K.; Tanner, C.; Hamlyn-Harris, D. Climate change impacts on stormwater harvesting yields. Water J. Aust. Water Assoc. 2015, 42, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- King, R.S.; Baker, M.E.; Kazyak, P.F.; Weller, D.E. How novel is too novel? Stream community thresholds at exceptionally low levels of catchment urbanization. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1659–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietz, G.J.; Sammonds, M.J.; Walsh, C.J.; Fletcher, T.D.; Rutherfurd, I.D.; Stewardson, M.J. Ecologically relevant geomorphic attributes of streams are impaired by even low levels of watershed effective imperviousness. Geomorphology 2014, 206, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.A.; Davies, P.J.; Findlay, S.J.; Jonasson, O.J. A new type of water pollution: Concrete drainage infrastructure and geochemical contamination of urban waters. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gardner, T.; Begbie, D. Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design: Potential, Design, Ecological Health, Urban Greening, Economics, Policies, and Community Perceptions; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, J.C. History of water sensitive urban design/low impact development adoption in Australia and internationally. In Approaches to Water Sensitive Urban Design; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Abdeljaber, A.; Adghim, M.; Abdallah, M.; Ghanima, R.; ALjassem, F. Comparative performance and cost-integrated life cycle assessment of low impact development controls for sustainable stormwater management. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.; Kim, R. Recent progress in low-impact development in South Korea: Water-management policies, challenges and opportunities. Water 2018, 10, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, M.; McMahon, J.; Heyenga, S.; Marinoni, O.; Jenkins, G.; Maheepala, S.; Greenway, M. Review of stormwater harvesting practices. In Urban Water Security Research Alliance; Technical Report No. 9; UWSRA: City East, QLD, Australia, 2008; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, T.C.; Pomeroy, C.A.; Burian, S.J. Hydrologic modeling analysis of a passive, residential rainwater harvesting program in an urbanized, semi-arid watershed. J. Hydrol. 2014, 508, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, G.; Roberts, L.; Page, W. Inspection and maintenance of infiltration facilities. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 47, 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.K.; Sharma, A.K. Stormwater harvesting infrastructure systems design for urban park irrigation: Brimbank Park, Melbourne case study. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2020, 69, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, D.; Mosley, E.; Lopes, A.; Mathieson, L.; Morison, J.; Connellan, G. Irrigation of Urban Green Spaces: A Review of the Environmental, Social and Economic Benefits; CRC for Irrigation Futures Technical Report; CRC for Irrigation Futures: Toowoomba, QLD, Canada, 2008; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Fryd, O.; Zhang, S. Blue-green infrastructure for sustainable urban stormwater management—Lessons from six municipality-led pilot projects in Beijing and Copenhagen. Water 2019, 11, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sadiq, R.; Zhu, Y. Climate change impacts on water resources and sustainable water management strategies in North America. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 37, 2771–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaitah, T.; Appleby, M.; Rosenblat, H.; Drake, J.; Joksimovic, D. The potential of Blue-Green infrastructure as a climate change adaptation strategy: A systematic literature review. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 3, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Geronimo, F.K.F.; Jeon, M.; Kim, L.-H. Investigation of the factors affecting the treatment performance of a stormwater horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland treating road and parking lot runoff. Water 2021, 13, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Garg, R.D.; Jato-Espino, D.; Lakshmi, V.; Ojha, C.; Asce, F. Evaluating hotspots for stormwater harvesting through participatory sensing. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaeizadeh, A.; Geza, M.; McCray, J.; Hogue, T.S. Site-scale integrated decision support tool (i-DSTss) for stormwater management. Water 2019, 11, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandy, G.C.; Marchi, A.; Maier, H.R.; Kandulu, J.; MacDonald, D.H.; Ganji, A. An integrated framework for selecting and evaluating the performance of stormwater harvesting options to supplement existing water supply systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Ariza, S.L.; Martínez, J.A.; Muñoz, A.F.; Quijano, J.P.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Camacho, L.A.; Díaz-Granados, M. A multicriteria planning framework to locate and select sustainable urban drainage systems (SUDS) in consolidated urban areas. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, P.M.; Sharma, A.; Cook, S.; Perera, B. Evaluation of stormwater harvesting sites using multi criteria decision methodology. J. Hydrol. 2018, 562, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Alazba, A.; Adamowski, J.; El-Gindy, A. GIS methods for sustainable stormwater harvesting and storage using remote sensing for land cover data-location assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Park, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, R. Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting Facilities Tank Size Based on a Daily Water Balance Model: The Case of Korea. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Jeong, Y.K. A study on the rational scale estimation of rainwater harvesting facilities on condominium complex. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2017, 17, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniquiz-Redillas, M.; Robles, M.E.; Cruz, G.; Reyes, N.J.; Kim, L.H. First flush stormwater runoff in urban catchments: A bibliometric and comprehensive review. Hydrology 2022, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringler, S. First Flush Characterization of Storm Water Runoff. Master’s Thesis, University of New Orleans, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2007. Available online: https://scholarworks.uno.edu/td/537 (accessed on 14 November 2023).
- Baek, S.S.; Choi, D.H.; Jung, J.W.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.; Yoon, K.S.; Cho, K.H. Optimizing low impact development (LID) for stormwater runoff treatment in urban area, Korea: Experimental and modeling approach. Water Res. 2015, 86, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q. A review of sustainable urban drainage systems considering the climate change and urbanization impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombes, P.J.; Argue, J.R.; Kuczera, G. Figtree Place: A case study in water sensitive urban development (WSUD). Urban Water 2000, 1, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolavani, N.J.; Kolavani, N.J. Technical feasibility analysis of rainwater harvesting system implementation for domestic use. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Meteorogical Administration. Meteorological Information. Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/ (accessed on 11 November 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).