Flood Propagation Characteristics in a Plain Lake: The Role of Multiple River Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Analysis
2.2.1. Hydrological Data
2.2.2. Topographic Data
2.2.3. Tributary Diversion Ratios
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Implementing a Special Open Boundary Condition
2.3.2. The Construction of the Hydrodynamic Flood Evolution Model
2.3.3. Combined Flooding
3. Analysis of Results
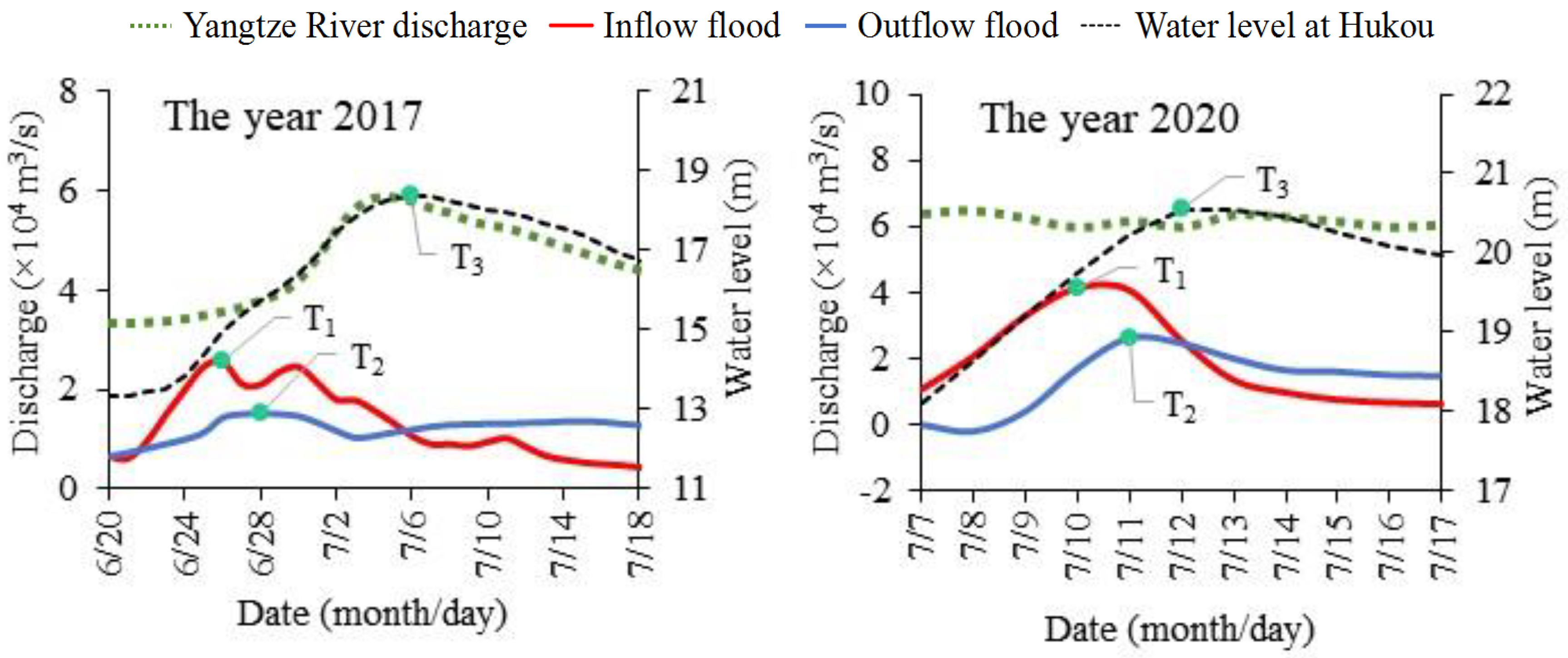
3.1. Interaction between River and Lake Floods
3.2. Changes in the Lake’s Water Level under River–Lake Interaction
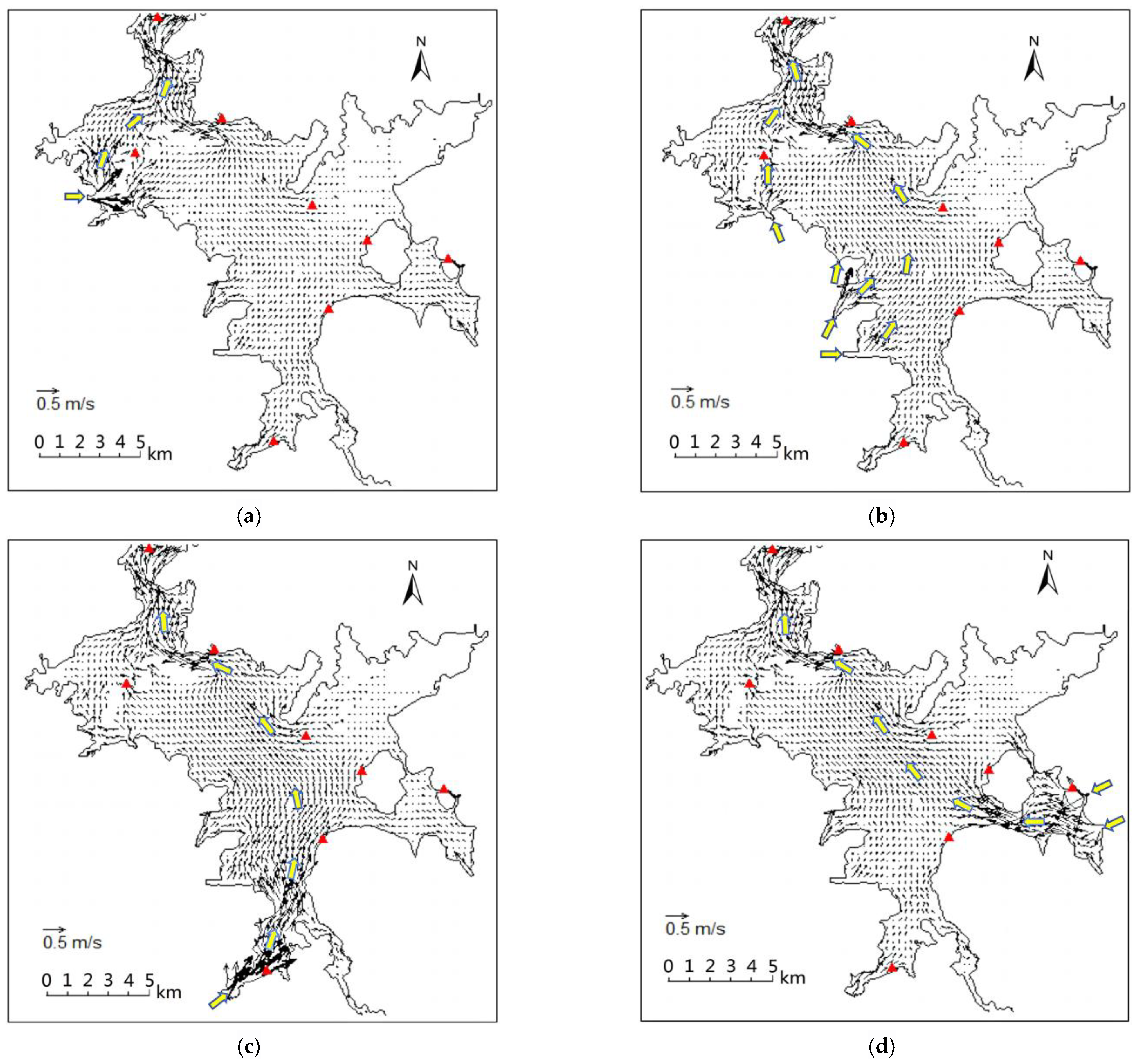
3.3. Propagation Characteristics of Floods from the “Five Rivers” into the Lake
4. Discussion and Suggestions
4.1. Reasonableness of the Results
4.2. Limitations and Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dou, H.; Jiang, J. China’s Five Largest Freshwater Lakes; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gierlowski-Kordesch, E.; Rust, B.R. The Jurassic East Berlin Formation, Hartford Basin, Newark Supergroup (Connecticut and Massachusetts): A Saline Lake Playa Alluvial Plain System; AAPG: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, M.F.; Jones, J.R. Trophic status of Missouri River Floodplain Lakes in Relation to Basin Type and connectivity. Wetlands 1997, 17, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, K.; Moeseneder, M.M.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J.; Peduzzi, P. Complexity of Bacterial Communities in a River-Floodplain system (Danube, Austria). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesack, L.F.; Marsh, P. River-to-Lake Connectivities, Water Renewal, and Aquatic Habitat Diversity in the Mackenzie River Delta. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummu, M.; Tes, S.; Yin, S.; Adamson, P.; Jozsa, J.; Koponen, J.; Richey, J.; Sarkkula, J. Water Balance Analysis for the Tonle Sap Lake-Floodplain System. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, A.G.; Bulcock, L.; Dessai, S.; Conway, D.; Jewitt, G.; Dougill, A.J.; Kolusu, S.R.; Mkwambisi, D. Lake Malawi’s threshold behaviour: A stakeholder-informed model to simulate sensitivity to climate change. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opere, A.; Ogallo, L.A. Natural Disasters in Lake Victoria Basin (Kenya): Causes and Impacts on Environment and Livelihoods; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP): Nairobi, Kenya, 2006; pp. 135–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, S. Review and Reflection on the Floods of Poyang Lake in 2020. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 37, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, S.-Q.; Jiang, C.; Sivakumar, M.; Enever, K.; Long, Y.; Deng, B.; Khalil, U.; Yin, L. Flood mitigation using an innovative flood control scheme in a large lake: Dongting Lake, China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, T.K.J. Global exposure to flood risk and poverty. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L. Wu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Deng, S. Hydrodynamic simulation of Poyang Lake under flooding in rivers and lakes. China Rural Water Resour. Hydropower 2023, 11, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Söderholm, K.; Pihlajamäki, M.; Dubrovin, T.; Veijalainen, N.; Vehviläinen, B.; Marttunen, M. Collaborative planning in daptive flood risk management under climate change. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 32, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, H. Risk assessment of flood disasters in the Poyang lake area. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2024, 100, 104208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsdorf, D.E.; Melack, J.M.; Dunne, T.; Mertes, L.A.K.; Hess, L.L.; Smith, L.C. Interferometric radar measurements of water level changes on the Amazon flood plain. Nature 2000, 404, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, G. Investigating Flood Characteristics and Mitigation Measures in Plain-Type River-Connected Lakes: A Case Study of Poyang Lake. Water 2024, 16, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Qin, Z. Calculation method for flood in the Poyang Lake section. Lake Sci. 1998, 10, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Setegn, S.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Dargahi, B. Hydrological modelling in the Lake Tana Basin, Ethiopia using SWAT model. Open Hydrol. J. 2008, 2, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaminie, A.A.; Amarnath, G.; Padhee, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Tilahun, S.A.; Mekonnen, M.A.; Assefa, G.; Seid, A.; Zimale, F.A.; Jury, M.R. Nested hydrological modeling for flood prediction using CMIP6 inputs around Lake Tana, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 46, 101343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Han, H.; Shu, Z. Bayesian model averaging by combining deep learning models to improve lake water level prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozdemir, S.; Yaqub, M.; Yildirim, S.O. A systematic literature review on lake water level prediction models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 163, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Variation of floods characteristics and their responses to climate and human activities in Poyang Lake, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Q.; Lotz, T. Evolution of flood regulation capacity for a large shallow retention lake: Characterization, mechanism, and impacts. Water 2020, 12, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Fu, J. Quantitative analysis of the hydrological relationship and evolution between the Yangtze River and Poyang Lake. J. Water Resour. 2018, 49, 570–579. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ni, Z. The Development and Evolution of Poyang Lake and the Impact of Changes in Jianghu Relations. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 35, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, B. Quantitative indicators for the causes and occurrence conditions of Yangtze River backflow into Poyang Lake. Prog. Water Sci. 2020, 31, 203–213. [Google Scholar]
- Lesack, L.F.; Melack, J.M. Flooding Hydrology and Mixture Dynamics of Lake Water Derived from MultipleSources in an Amazon Floodplain Lake. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Y. Flood mitigation effects of lake-reservoir group on the Poyang Lake watershed based on runoff-weighted model from multi-satellite weekly observation. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Li, X.W.; Xu, H. Effects of topographic changes on the water dynamics in flood season in the tail of Ganjiang River network. J. Hydropower Eng. 2022, 41, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Li, K. Influence of sand mining on river bed in middle and lower reaches of Ganjiang River. Hydropower New Energy 2010, 5, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, Z.C. Analysis of the influence of the evolution of the water channel into the river of Poyang Lake on the water level of the lake. Water Power 2021, 47, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.C.; Xu, X.F.; Huang, Z.W.; Wu, N.H.; Zhou, S.F. Siltation characteristics of the tail reach of Ganjiang river under the regulation of estuary gates. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2020, 20, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.Y.; Li, R.F.; Wang, Y.W. Analysis of flood control and disaster reduction situation in Poyang Lake District after removing embankments and returning farmland to the lake. Hydrology 2004, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.P.; Wang, S.G. Evolution of erosion and deposition in Poyang Lake and its hydrological and ecological effects. Water Resour. Hydropower Technol. 2022, 53, 66–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Hu, T. A study on the relationship between water level and flow rate at the mouth of Poyang Lake. China Rural Water Resour. Hydropower 2023, 11, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.Y.; Li, Z.Z. Direct fitting of water level flow relationship rope loop curve during flood season. Hydrology 1998, 5, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; An, X.; Zhang, Q. Finite element parallel numerical simulation of two-dimensional shallow water flow. J. Water Resour. 2002, 5, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, Z.; Chen, J. Study on the relationship between dynamic water level and area, water level and volume of Poyang Lake. Jiangxi Water Conserv. Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Keramidas, G.A. A hydrodynamic model for open channel flow problems. In Finite Elements in Water Resources; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.; Lei, S.; Wen, T. Simulation and Analysis of Flood Evolution in the Lianbei Dike Area of Poyang Lake under Active Flood Diversion. China Flood Drought Manag. 2024, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
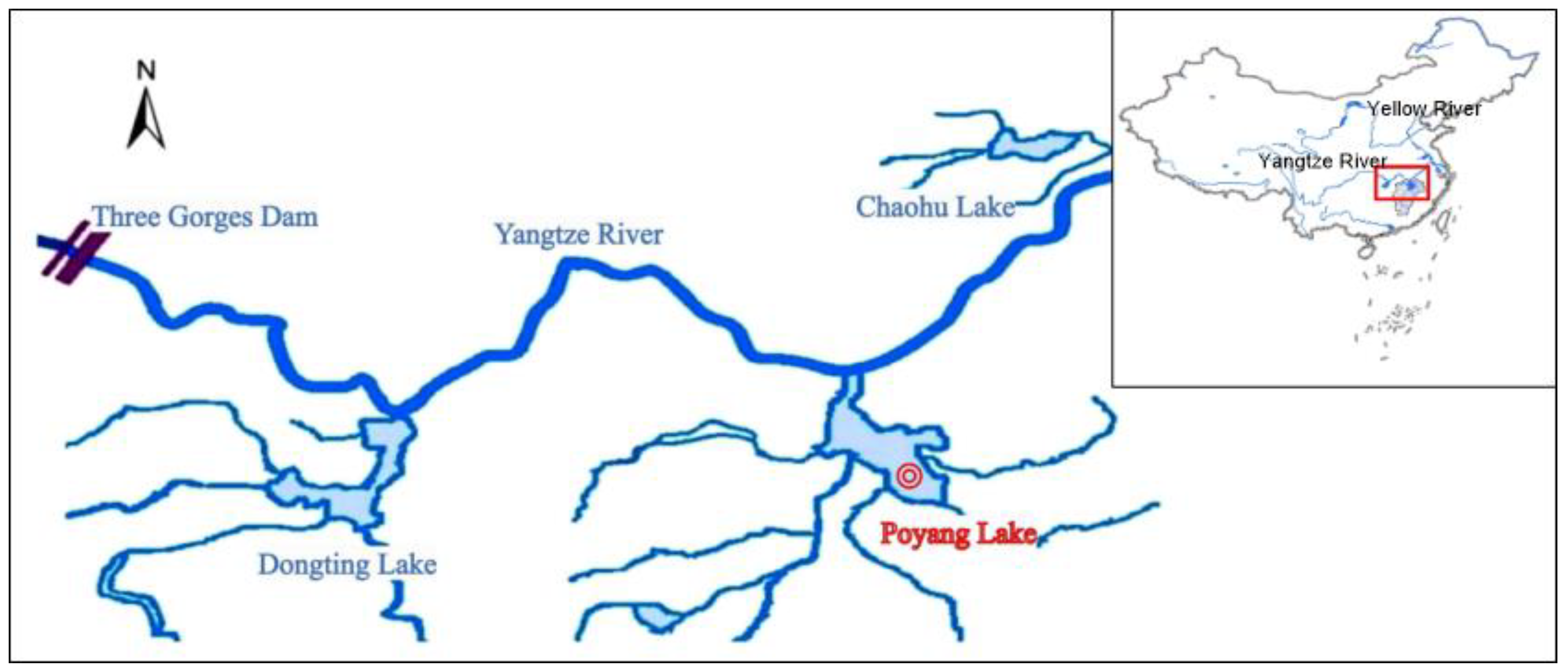








| Number | Hydrological Station | River System | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| ①, ② | Qiu Jin, Wanjiabu | Xiu River | Flow rate, water level |
| ③ | Waizhou | Gan River | Flow rate, water level |
| ④ | Lijiadu | Fu River | Flow rate, water level |
| ⑤ | Meigang | Xin River | Flow rate, water level |
| ⑥, ⑦ | Hushan, Dufengkeng | Rao River | Flow rate, water level |
| ⑧, ⑨ | Jiujiang, Hukou | Yangtze River | Flow rate, water level |
| ⑩ | Pengze | Water level | |
| ⑪, ⑫, ⑬, ⑭, ⑮,⑯, ⑰, ⑱ | Xingzi, Wucheng, Duchang, Tangyin, Longkou, Kangshan, Sanyang, Poyang | Poyang Lake | Water level |
| Year | Time of Incoming Flood Peak T1 (month/day) | Time of Peak Outflow T2 (month/day) | T2–T1 (days) | Time of Water Level Peak T3 (month/day) | T3–T1 (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1998 | 6/26 | 6/26 | 0 | 7/1 | 5 |
| 2010 | 6/21 | 6/23 | 2 | 6/29 | 8 |
| 2017 | 6/26 | 6/28 | 2 | 7/6 | 10 |
| 2020 | 7/10 | 7/11 | 1 | 7/12 | 2 |
| Flood Source | Lake Outlet | Xingzi | Duchang | Wucheng | Tangyin | Kangshan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gan River | 52 | 50 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 46 |
| Xiu River | 50 | 48 | 47 | 46 | 49 | 50 |
| Fu River | 56 | 55 | 54 | 55 | 51 | 47 |
| Xin River | 56 | 55 | 54 | 55 | 51 | 48 |
| Rao River | 56 | 54 | 52 | 52 | 49 | 48 |
| Name | Xiu River Flood | Gan River Flood | Fu River Flood | Xin River Flood | Rao River Flood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time of Peak Outflow (h) | 44 | 46 | 52 | 51 | 49 |
| Propagation Distance (km) | 99 | 102–162 | 177 | 166 | 155 |
| Flood Source | Xingzi Station | Tangyin Station | Kangshan Station |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gan River | 1.05 | 1.11 | 1.11 |
| Xiu River | 1.05 | 1.08 | 1.07 |
| Fu River | 1.07 | 1.14 | 1.16 |
| Xin River | 1.07 | 1.14 | 1.15 |
| Rao River | 1.06 | 1.14 | 1.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z.; Wen, T.; You, W.; Xia, Y. Flood Propagation Characteristics in a Plain Lake: The Role of Multiple River Interactions. Water 2024, 16, 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101447
Wu Q, Wang Z, Xu X, Huang Z, Wen T, You W, Xia Y. Flood Propagation Characteristics in a Plain Lake: The Role of Multiple River Interactions. Water. 2024; 16(10):1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101447
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qiuqin, Zhichao Wang, Xinfa Xu, Zhiwen Huang, Tianfu Wen, Wensun You, and Yang Xia. 2024. "Flood Propagation Characteristics in a Plain Lake: The Role of Multiple River Interactions" Water 16, no. 10: 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101447
APA StyleWu, Q., Wang, Z., Xu, X., Huang, Z., Wen, T., You, W., & Xia, Y. (2024). Flood Propagation Characteristics in a Plain Lake: The Role of Multiple River Interactions. Water, 16(10), 1447. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101447






