Strategy for Adapting Environmental Flow Proposals to Situations with High Agricultural Demands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study of the Hydrological Alteration
2.3. Water Demand Calculation
- Main crop groups:
- Area occupied by each type of crop;
- Monthly water demand per surface area;
- List of demands associated with a specific water body [27].
2.4. Simulation Habitat Needs of Fish Species
2.5. Alternative Flow Regime Building
2.5.1. Rivers Where the Main Problem Is Seasonal Inversion Flow
- First, select the minimum flow for the driest month.
- Second, calculate the regime values for the remaining months by finding monthly variation rates that mimic the natural pattern.
- Third, modify the monthly variation indices with an exponent to adjust them according to the environmental criteria desired.
- The e-flow month rate is increased in months when a greater amount of water is required for irrigation.
- We calculate the amount of water that can be saved by implementing the alternative irrigation plan as compared with the current one. The saved water volume is transferred to non-irrigation months to augment the flow values in the winter months.
- In the months with the highest natural flow, the monthly coefficient (Im) was modified to exceed the flow rate values of the summer months; the winter months’ flow values must, as a condition, provide at least 80% of the WUA in the river.
2.5.2. Rivers Where There Has Been a Loss of Peak Flows
- The magnitude, duration, and frequency of peak natural flows are based on the hydrological analysis.
- Enough peak flows, replicating the natural flood occurrences in the river, will be formulated.
- To achieve this, the volume of water utilized during a normal flood has to be calculated. Timely points will be identified to discharge these peak flows from the regulation structures in the basin.
2.5.3. Rivers with Minor Problems
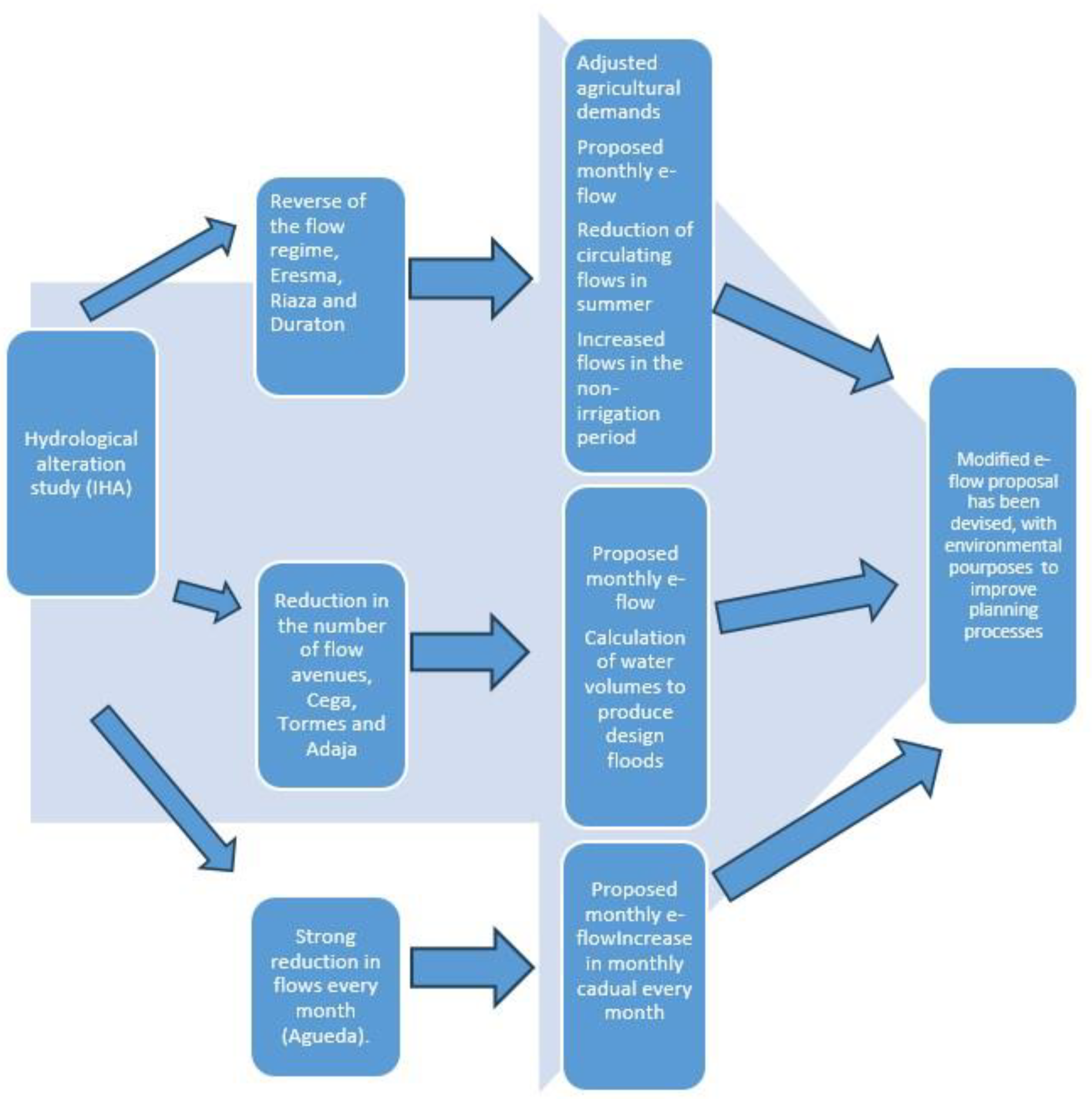
3. Results
3.1. Hydrological Alteration
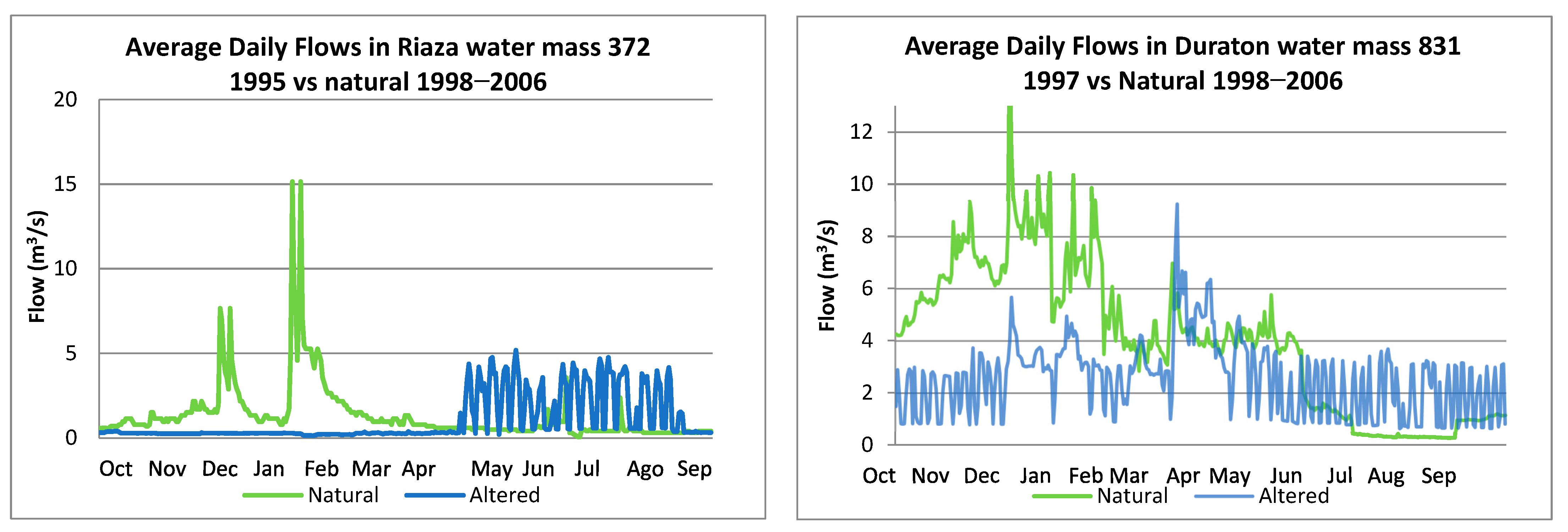
- Reverse of the flow regime (Eresma, Riaza, and Duratón); in the latter two rivers, hydropeaking is also present.
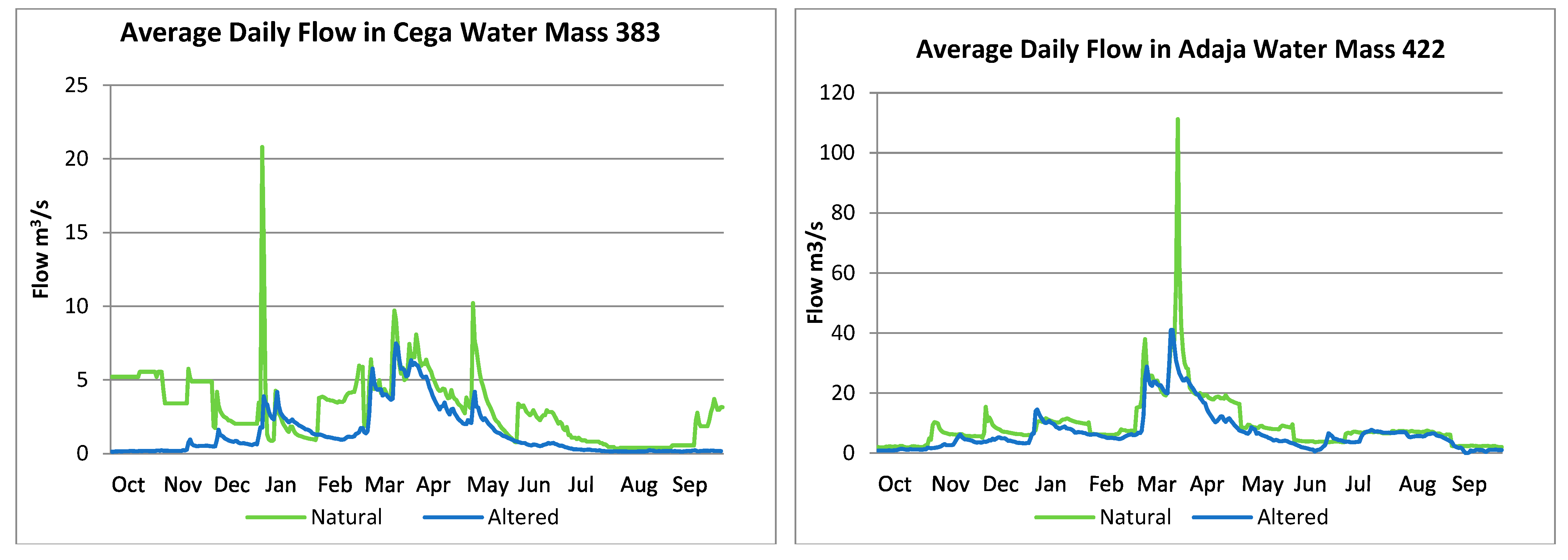
- Reduction in the number of flow avenues and general flow reduction (Cega, Tormes, and Adaja).
- Strong reduction in flows every month (Agueda).
3.2. Assessment of Agricultural Demands
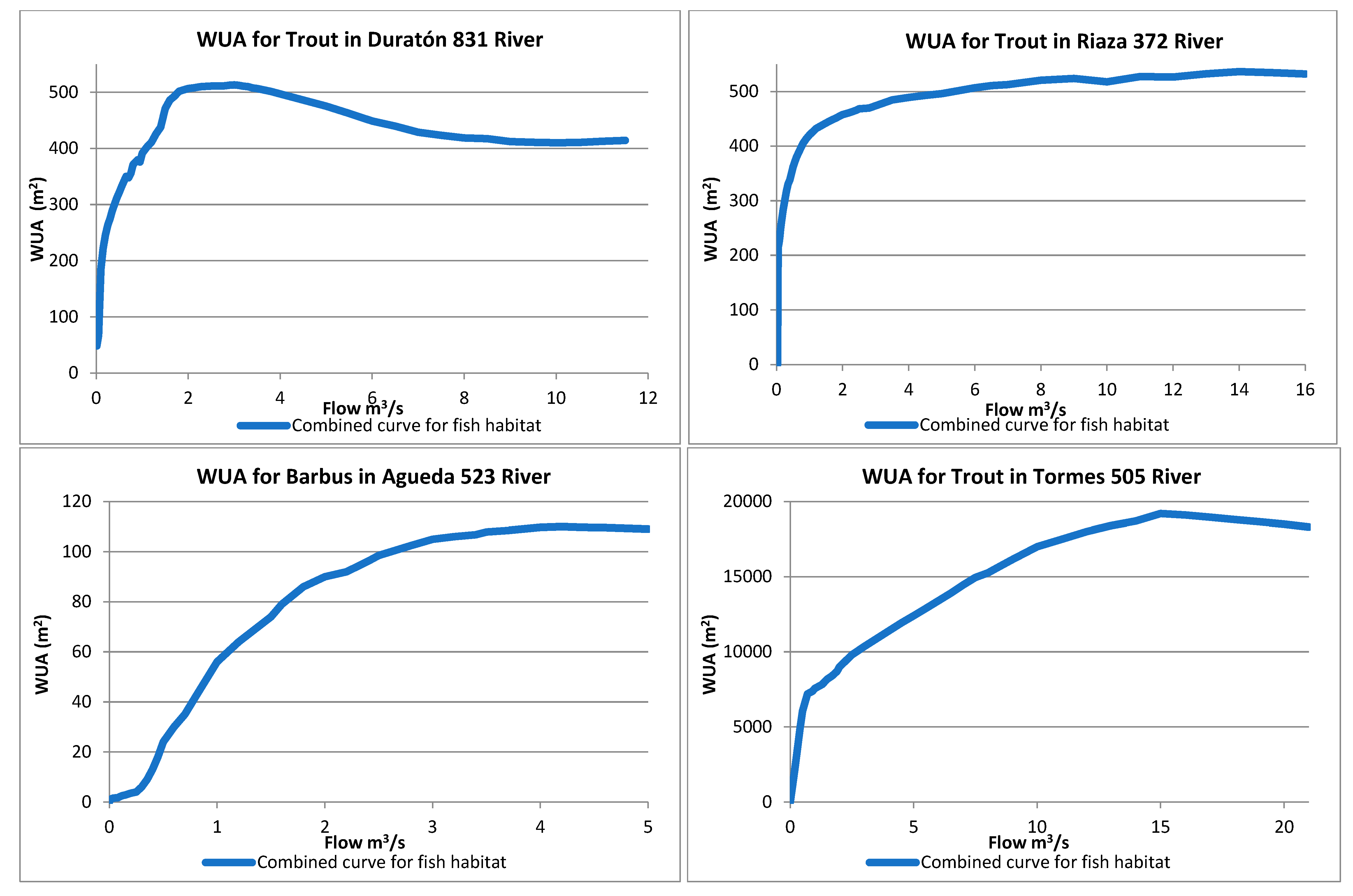
3.3. Potential Habitat of Indigenous Fish Species versus Flow
Basic e-Flow Structure Estimation
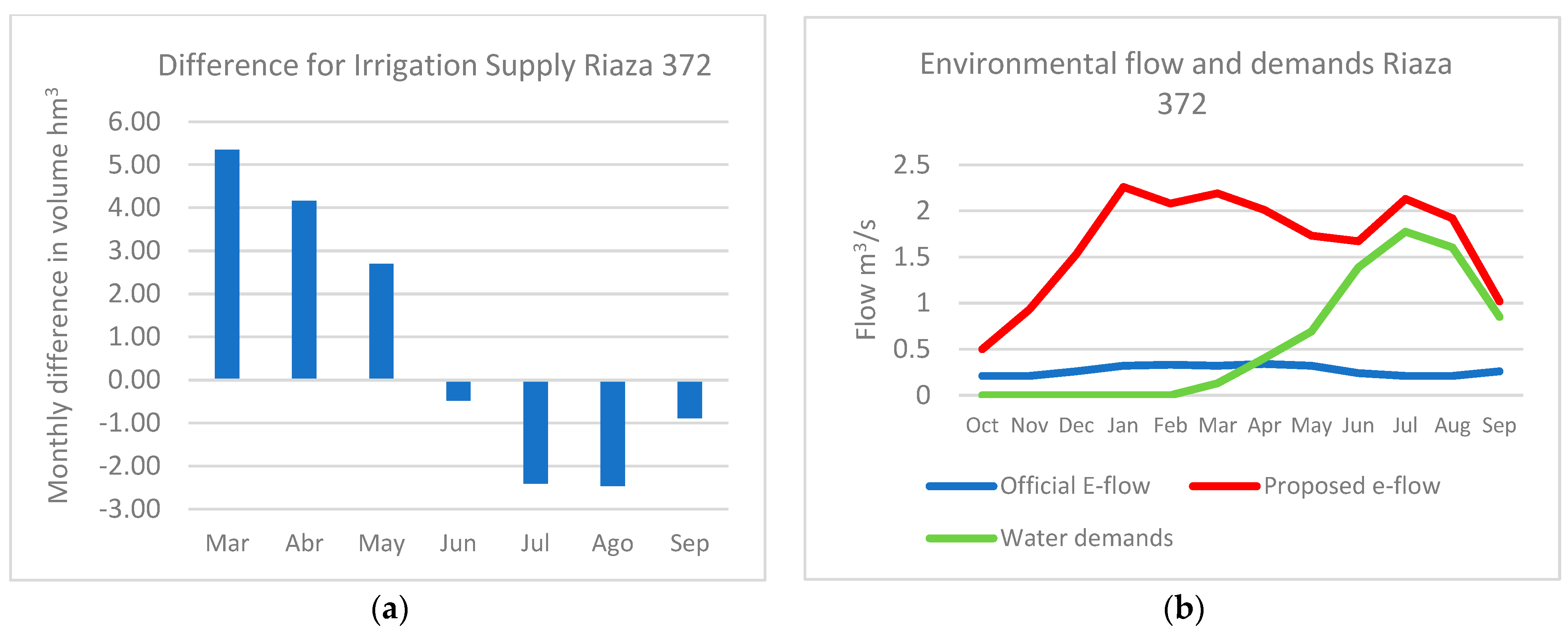
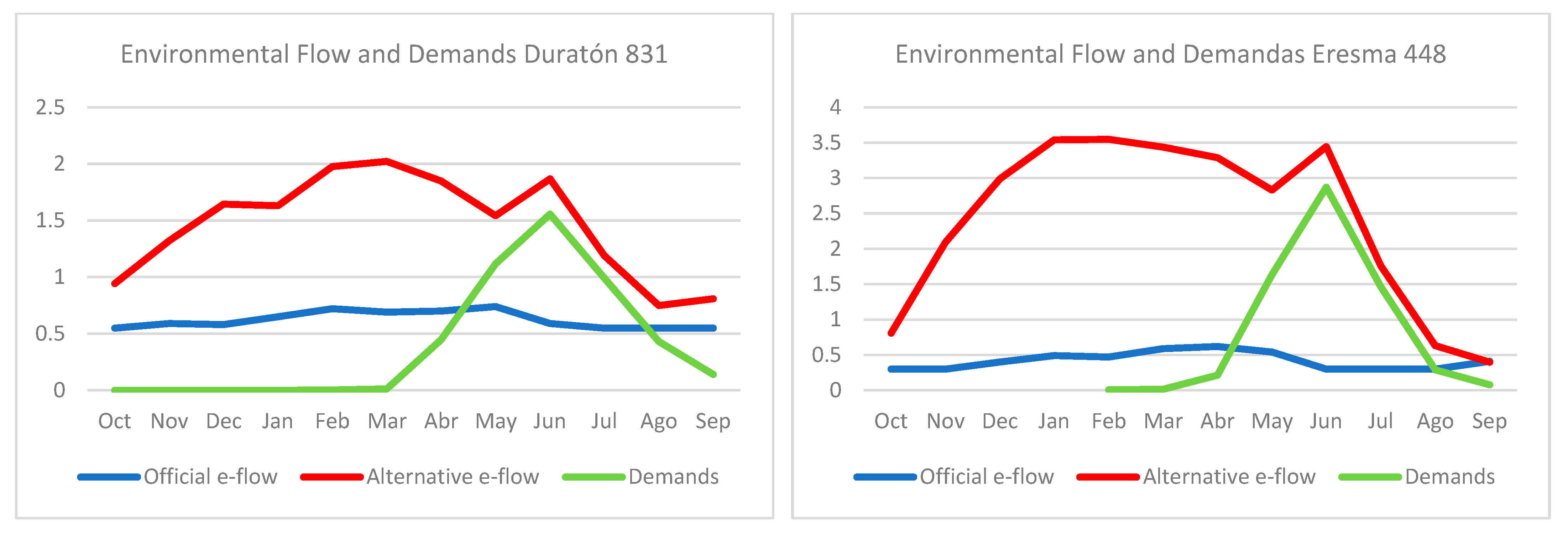
3.4. Strategy to Offer an Alternative Environmental Regime
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme). Global Environment Outlook 3: Past, Present and Future Perspectives; Earthscan: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arévalo-Mejía, R.; Leblois, E.; Mastachi-Loza, C.A.; Salinas-Tapia, H.; Khalidou, M.B.; Yadira, A.; Vilchis-Francés, A.Y.; Becerril-Piña, R.; Díaz-Delgado, C. Integrated hydro informatics tool to assess hydrological alteration on gauged sites: Hydra-Eflow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 160, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Zimmerman, J.K.H. Ecological responses to altered flow regimes: A literature review to inform the science and management of environmental flows. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.; Tharme, R.; Arthington, A. Evolution of Environmental Flows Assessment Science, Principles, and Methodologies. In Water for the Environment; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 203–236. [Google Scholar]
- Meitzen, K.M.; Martin, W.D.; Martin, C.T.; Burns, C.E. Geomorphology within the interdisciplinary science of environmental flows. Geomorphology 2013, 200, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcázar, J.; Palau, A. Establishing environmental flow regimes in a Mediterranean watershed based on a regional classification. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovee, K.D. A Guide to Stream Habitat Analysis Using the Instream Flow Incremental Methodology; US Fish and Wildlife Service: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1982; 248p. [Google Scholar]
- García de Jalón, D. The Spanish Experience in Determining Minimum Flow regimes in Regulated Streams. Can. Water Resour. J. 2003, 28, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Acreman, M.C.; Dunbar, M.J. Defining environmental river flow requirements—A review. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2004, 8, 861–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Wigington, R.; Braun, D.P. How much water does a river need? Freshw. Biol. 1997, 37, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharme, R.E.; King, J.M. Development of the Building Block Methodology for Instream Flow Assessments, and Supporting Research on the Effects of Different Magnitude Flows on Riverine Ecosystems; Water Research Commission Report No. 576/1/98; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- King, J.M.; Tharme, R.E.; De Villiers, M. (Eds.) Environmental Flow Assessments for Rivers: Manual for the Building Block Methodology; Water Research Commission Technology Transfer Report No. TT131/00; Water Research Commission: Pretoria, South Africa, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L.; Richter, B.D.; Arthington, A.H.; Bunn, S.E.; Naiman, R.J.; Kendy, E.; Acreman, M.; Apse, C.; Bledsoe, B.P.; Freeman, M.C. The ecological limits of hydrologic alteration (ELOHA): A new framework for developing regional environmental flow standards. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 55, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManamay, R.A.; Orth, D.J.; Dolloff, C.A.; Mathews, D.C. Application of the ELOHA framework to regulated rivers in the upper Tennessee River Basin: A case study. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthington, A.H.; Rall, J.L.; Kennard, M.J.; Pusey, B.J. Environmental flow requirements of fish in Lesotho rivers using the DRIFT methodology. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 641–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, A.V.; Ludwig, F.; Biemans, H.; Hoff, H.; Kabat, P. Accounting for environmental flow requirements in global water assessments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 5041–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreman, M.C.; Overton, I.C.; King, J.; Wood, P.J.; Cowx, I.G.; Dunbar, M.J.; Kendy, E.; Young, W.J. The changing role of ecohydrological science in guiding environmental flows. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.H.; Bernardo, J.M. Caudais Ecológicos em Portugal; INAG, Ministério das Cidades, Ordenamento do Território e Ambiente: Lisboa, Portugal, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Alcácer, C.; Ballester, A.; De Stefano, L.; Hernández, J.M.; Lacalle, A.; Magdaleno, F.; Schmidt, G. Recomendaciones Para la Concertación de Regímenes Ecológicos de Caudales en el Marco de la Planificación Hidrológica Española; Contributions from experts of the Working Group on Environmental Flows (GTCA); Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Madrid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hirji, R.; Davis, R. Recommendations Environmental Flows in Water Resources Policies, Plans, and Projects. Case Studies; The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kampa, E.; Schmidt, G. Implementation of e-flows in the EU. Developed under the Framework Contract ‘Water for the Green Deal’. In EU Strategy on Adaptation to Climate Change and Common Implementation Strategy Work Programme for the Water Directives (2022–2024); European Commission Report 2023; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Snelder, T.; Booker, D.; Lamouroux, N. A Method to Assess and Define Environmental Flow Rules for Large Jurisdictional Regions. J. Am. Water Resour. As. 2011, 47, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, F.; Costa, C.; Pinheiro, P.; Reis, F.; Pinheiro, A. Integrated Procedure for Environmental Flow Assessment in Rivers. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, C.; Schmidt, G. Analysis of the Implementation of Environmental Flows in the Wider Context of the River Basin Management Plans (Report Drafted in the Framework of the Comparative Study of Pressures and Measures in the Major River Basin Management Plans. Task 3d: Water Abstraction and Water Use); European Commission Report 2012; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- WFD. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 Establishing a Framework for Community Action in the Field of Water Policy; WFD, European Parliament and of the Council: Luxemburg, 2000.
- González del Tánago, M.; García de Jalón, D.G.; Román, M. River restoration in Spain: Theoretical and practical approach in the context of the European Water Framework Directive. Environ. Manag. 2012, 50, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Arquiola, J.; Martinez-Capel, F.; Solera, A.; Aguilella, V. Implementing environmental flows in complex water resources systems—Case study: The Duero river basin, Spain. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsch, M.; Popp, A.; Biewald, A.; Rolinski, S.; Schmitz, C.; Weindl, I.; Stevanovic, M.; Högner, K.; Heinke, J.; Ostber, S.; et al. Environmental flow provision: Implications for agricultural water and land-use at the global scale. Global Environ. Chang. 2015, 30, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunna, S.M.; Stalham, M.; Chalmers, N.; Crabtree, B. Adjusting irrigation abstraction to minimise the impact on stream flow in the East of Scotland. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 68, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, A.; Li, C.; Sun, T. Trade-Off Analysis to Determine Environmental Flows in a Highly Regulated Watershed. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Bautista, A.; Baeza, D.; Herrera, T.; La Calle, A.; Martínez, J. Los caudales ecológicos, en el olvido en la Red Natura 2000. Quercus 2021, 427, 34. [Google Scholar]
- Tharme, R.E. A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: Emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 397–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OPH-CHD (Confederación Hidrográfica del Duero). Plan hidrológico de la parte española de la Demarcación Hidrográfica del Duero. In Plan Hidrológico de Cuenca; Anejo 4. Caudales ecológicos; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Belmar, O.; Velasco, J.; Martínez-Capel, F. Hydrological classification of natural flow regimes to support environmental flow assessments in intensively regulated Mediterranean rivers, Segura River Basin (Spain). Environ. Manag. 2011, 47, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jowett, I.G.; Hayes, J.W.; Duncan, M.J. A Guide to Instream Habitat Survey Methods and Analysis; NIWA Science and Technology Series No. 54; NIWA: Wellington, New Zealand, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Parasiewicz, P. The mesoHABSIM model revisited. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-García, J.M. Modelo Distribuido Para la Evaluación de Recursos Hídricos; Ministry of Public Works, Monografía del CEDEX n° M-67; Ministerio de Fomento: Madrid, Spain, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Santa-María, C.; Fernández Yuste, J.A. IAHRIS Índices de Alteración Hidrológica en Ríos. Manual de Referencia Metodológica; Versión 1; Dirección General del Agua (MITECORD): Madrid, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Black, A.R.; Rowan, J.S.; Duck, R.W.; Bragg, O.M.; Clelland, B.E. DHRAM: A method for classifying river flow regime alterations for the EC Water Framework Directive. Aquat. Conserv. 2005, 15, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Baumgartner, J.V.; Powell, J.; Braun, D.P. A method for assessing hydrologic alteration within ecosystems. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Tecnológico Agrario de Castilla y León. Inforiego. 2019. Available online: https://www.inforiego.org/opencms/opencms/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2023).
- Brouwer, C.; Prins, K.; Heibloem, M. Irrigation Water Management: Irrigation Scheduling; Training Manual No. 4; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1989; 43p. [Google Scholar]
- García de Jalón, D.; Gutierrez, B.; Morillo, M.; Martínez, F.; Baselga, S.; Baeza, D. Realización del Cálculo de Aportaciones Ambientales y Caudales Ecológicos Mínimos en la Cuenca Hidrográfica del Río Tajo; Departamento de Ingeniería Forestal E.T.S.I. Montes; Universidad Politécnica de Madrid. CEDEX: Madrid, Spain, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Bovee, K.D.; Cochnauer, T. Development and Evaluation of Weighted Criteria: Probability-of-Use Curves for Instream Flow Assessments: Fisheries; United States Fish and Wildlife Service, Instream Flow Information Paper 3, FWS/OBS-77; U.S. Geological Survey: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1977.
- Martínez-Capel, F.; García de Jalón, D.; Werentzky, D.; Baeza Sanz, D.; Rodilla-Alamá, M. Microhabitat use by three endemic Iberian cyprinids in Mediterranean rivers (Tagus river basin, Spain). Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2009, 16, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffler, P.; Blackburn, J. River2D: Two-Dimensional Depth Averaged Model of River Hydrodynamics and Fish Habitat. Introduction to Depth Averaged Modeling and User’s Manual; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- HPR. The Instruction for Hydrologic Planning in B.O.E. Orden ARM/2656/2008, de 10 de Septiembre, Por la Que se Aprueba la Instrucción de Planificación Hidrológica; Spanish Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2008.
- King, J.; Brown, C.; Sabet, H. A scenario-based holistic approach to environmental flow assessments for rivers. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Batlles-de la Fuente, A.; Fidelibus, M.D. Sustainable Irrigation in Agriculture: An Analysis of Global Research. Water 2019, 11, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, M.; Webb, R.H.; Schmidt, J.C. Dams and Rivers: Primer on the Downstream Effects of Dams; US Geological Survey Circular nr 1126; United States Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1996.
- Kondolf, G.M.; Batalla, R.J. Hydrological effects of dams and water diversions on rivers of Mediterranean-climate regions: Examples from California. In Catchment Dynamics and River Processes: Mediterranean and Other Climate Regions; Garcia, C., Batalla, R.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 197–211. [Google Scholar]
- Growns, I. The implementation of an environmental flow regime results in ecological recovery of regulated rivers. Restor. Ecol. 2016, 24, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Peña-Gallardo, M.; Hannaford, J.; Murphy, C.; Lorenzo-Lacruz, J.; Dominguez-Castro, F.; López-Moreno, J.I.; Beguería, S.; Noguera, I.; Harrigan, S.; et al. Climate, Irrigation, and Land Cover Change Explain Streamflow Trends in Countries Bordering the Northeast Atlantic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 10821–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González del Tánago, M.; Martínez-Fernández, V.; García de Jalón, D. Diagnosing problems produced by flow regulation and other disturbances in Southern European Rivers: The Porma and Curueño Rivers (Duero Basin, NW Spain). Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalla, R.J.; Gomez, C.M.; Kondolf, G.M. Reservoir-induced hydrological changes in the Ebro River basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaroli, R.; Muñoz-Mas, R.; Martínez-Capel, F. Fish community responses to antecedent hydrological conditions based on long-term data in Mediterranean river basins (Iberian Peninsula). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benejam, L.; Angermeier, P.L.; Munné, A.; García Berthou, E. Assessing effects of water abstraction on fish assemblages in Mediterranean streams. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 628–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, T.E.; Viers, J.H.; Moyle, P.B. Systematic Screening of Dams for Environmental Flow Assessment and Implementation. BioScience 2014, 64, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Navarro, R.; Stewardson, M.; Breil, P.; García de Jalón, D.; Eisele, M. Hydrological impacts affecting endangered fish species: A Spanish case study. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-González, C.; Gortázar, J.; Baeza Sanz, D.; García de Jalón, D. Dam function rules based on brown trout flow requirements: Design of environmental flow regimes in regulated streams. Hydrobiologia 2008, 609, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, A.; Mul, M.; van der Zaag, P.; Slinger, J. Re-operating dams for environmental flows: From recommendation to practice. River Res. Appl. 2020, 37, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivaes, R.; Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Ferreira, T. Importance of considering riparian vegetation requirements for the long-term efficiency of environmental flows in aquatic microhabitats. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5763–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, D.M.; Scott, M.L.; Poff, N.L.; Auble, G.T.; Lytle, D.A. Theory, methods and tools for determining environmental flows for riparian vegetation: Riparian vegetation-flow response guilds. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piqué, G.; Batalla, R.J.; Sabater, S. Hydrological characterization of dammed rivers in the NW Mediterranean region. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1691–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, M.A.; Mellado-Díaz, A. A Landscape-based Regionalization of Natural Flow Regimes in the Ebro River Basin and its Biological Validation. River Res. Appl. 2015, 31, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñas, F.J.; Barquín, J.; Snelder, T.H.; Booker, D.J.; Álvarez, C. The influence of methodological procedures on hydrological classification performance. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3393–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keeffe, J.; Quesne, T.L. Cómo Conservar Los Ríos Vivos; WWF—World Wildlife Fund, Serie Seguridad Hídrica de WWF: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, A.; Malano, H.M. Managing irrigation demand to improve seasonality of river flows. Irrig. Drain. 2009, 58, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confederación Hidrográfica del Duero. Resumen de los resultados Cuantitativos del Estudio Sobre Tenencia de Recursos Hídricos Para FAO: Caso de Estudio de la Modernización de la Comunidad de Regantes de Cabecera del río Riaza; Confederación Hidrográfica del Duero: Valladolid, Spain, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kennard, M.; Arthington, A.H.; Thompson, C. Flow requirements of freshwater fish. In Environmental Flow Requirements of the Brisbane River Downstream from Wivenhoe Dam; South East Queensland Water Corporation and Centre for Catchment and In-Stream Research: Brisbane, Australia, 2000; pp. 265–330. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.J.; Gawne, B.; Beesley, L.; Koehn, J.D.; Nielsen, D.L.; Amina Price. Improving ecological response monitoring of environmental flows. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bêche, L.; Loire, R.; Barillier, A.; Archambaud, G.; Morel, A. Flow restoration of the Durance River: Implementation and monitoring of targeted water releases to reduce clogging and improve river function. In Proceedings of the REFORM International Conference on River and Stream Restoration D7.5 “Novel Approaches to Assess and Rehabilitate Modified Rivers”, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 29 June–2 July 2015; pp. 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Capra, H.; Sabaton, C.; Gouraud, V.; Souchon, Y.; Lim, P. A Population Dynamics Model and Habitat Simulation as a Tool to Predict Brown Trout Demography in Natural and Bypassed Stream Reaches. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, I.G.; Biggs, B.J.F. Flow regime requirements and the biological effectiveness of habitat-based minimum flow assessments for six rivers. Intl. J. River Basin Manag. 2006, 4, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.; Brown, N.; Grantham, C.M.; Matthews, T.E.; Palmer, J.H.; Wilby, M.A.; Spence, R.L.; Haasnoot, C.M.; Mendoza, M.; Dominique, G.F.; et al. Sustainable water management under future uncertainty with eco-engineering decision scaling. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
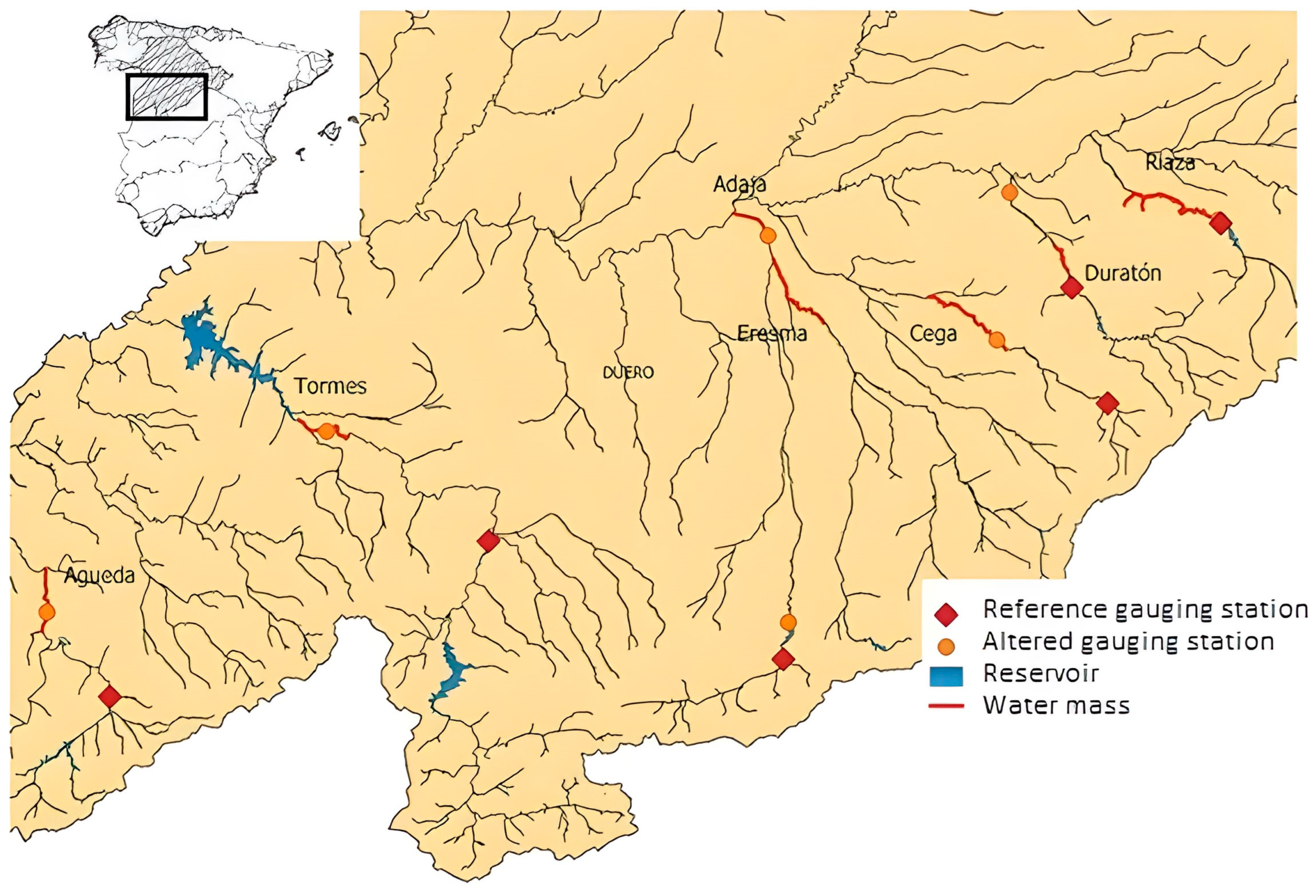




| River | Water Body Code According to the Water Administration | Gauging Station for Natural Flow | Gauging Station for Altered Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duratón | 831 | 2110 | 2161 |
| Riaza | 372 | 2010 | 2010 |
| Eresma | 448 | 2016 | 2048 |
| Adaja | 422 | 2073 | 2056 |
| Agueda | 523 | 2046 | 2091 |
| Cega | 383 | 2016 | 2714 |
| Tormes | 505 | 2086 | 2088 |
| River and Water Mass Code | Main Alterations | Possible Causes of the Alteration | IHA Result (DHRAM Value) | Principal Modified Hydrological Characters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duratón 831 | The peak flows disappear, as well as the river flow regime has many fluctuations. | Hydroelectric production, conditioned by irrigation. | 17, high risk of impact | Timing of annual extremes. Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Riaza 372 | Inverted river flow regime. | Agricultural demand and electricity production. One reservoir for electrical production. | 17, high risk of impact | Magnitude of monthly water conditions. Timing of annual extremes. Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Eresma 448 | River flow inverted regime, lower annual flow than natural. | High irrigation demands, altered flow reduction compared with natural, almost dried in summer. It has five reservoirs. | 10, moderate risk of impact | Magnitude of monthly water conditions. Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Adaja 422 | Not very intense, reduction of the annual flow, smaller number of peak flows. | Demand is not high compared with the total water contribution; the regime differs a little from natural. Receives the Eresma river, and it has one more reservoir than that river. | 6, moderate risk of impact | Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Agueda 523 | Severe reduction in the annual flow. | Agriculture does not explain the reduction in river flow; the agricultural demands are very low. It has two dams for urban supply. | 15, high risk of impact | Magnitude of monthly water conditions. Timing of annual extremes. Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Cega 383 | Small annual flow reduction. The period of more alteration and lower flow is autumn. | Relatively low agricultural demand; there are no dams upstream. | 11, high risk of impact | Magnitude of monthly water conditions. Timing of annual extremes. Frequency and duration of high and low pulses. |
| Tormes 505 | Moderate flow reduction, severe loss of peak flow. | It has two reservoirs upstream. High agricultural demands. | 9, moderate risk of impact | Timing of annual extremes. Frequency and duration of high and low. |
| River and Water Mass Code | Water Volume Demanded (Hm3) | Actual Irrigated Area (ha) | Adjusted Agrarian Demands (Hm3) | Percentage of Agricultural Demands against Total Resources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duratón 831 | 16 | 2900 | 12.2 | 16.00 |
| Riaza 372 | 31.52 | 6767 | 18.1 | 45.9 |
| Eresma 448 | 17.04 | 2465 | 16.47 | 6.14 |
| Adaja 422 | 36.9 | 7000 | 34.5 | 8.61 |
| Agueda 523 | 30.27 | 2030 | 23.1 | 5.53 |
| Cega 383 | 24.9 | 4564 | 18.5 | 25.78 |
| Tormes 505 | 125.01 | 20,462 | 121.8 | 12.72 |
| Official e-Flow m3/s | WUA (m2) Official | Proposed e-Flow m3/s | WUA (m2) Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| October | 0.21 | 282.94 | 0.50 | 361.96 |
| November | 0.21 | 282.94 | 0.93 | 413.66 |
| December | 0.26 | 301.81 | 1.53 | 442.42 |
| January | 0.32 | 317.72 | 2.26 | 461.12 |
| February | 0.33 | 317.72 | 2.08 | 457.54 |
| March | 0.32 | 317.72 | 2.19 | 457.54 |
| April | 0.34 | 317.72 | 2.01 | 457.54 |
| May | 0.32 | 317.72 | 1.73 | 445.66 |
| June | 0.24 | 282.94 | 1.67 | 445.66 |
| July | 0.21 | 282.94 | 2.13 | 457.54 |
| August | 0.21 | 282.94 | 1.92 | 451.53 |
| September | 0.26 | 301.81 | 1.02 | 420.89 |
| Total | 3606.924 | 5273.058 |
| Official River Water Body | Min Flow (m3/s) | Exponent in Monthly Index | 80% WUA Flow (m3/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duratón 831 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| Riaza 372 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.7 |
| Eresma 448 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 1.05 |
| Adaja 422 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Agueda 523 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1.8 |
| Cega 383 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Tormes 505 | 7 | 0.5 | 8 |
| River Water Body Mass | Magnitude of the High Flow (m3/s) | Duration Days | Number of Events per Year | Volume Required to Generate 6-Day Flood (Hm3) | Volume Required for the Season (Hm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adaja 422 | 27.9 | 6.6 | 5 | 6.00 | 11.99 |
| Cega 383 | 10.5 | 12.8 | 4 | 2.33 | 4.66 |
| Tormes 505 | 74 | 12 | 4 | 16.43 | 32.87 |
| e-Flow in m3/s | Riaza | Duratón | Eresma | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months | e-Flow Initial | e-Flow Modified | e-Flow Initial | e-Flow Modified | e-Flow Initial | e-Flow Modified |
| October | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.86 | 0.94 | 0.66 | 0.81 |
| November | 0.75 | 0.93 | 1.07 | 1.32 | 1.30 | 2.09 |
| December | 1.05 | 1.53 | 1.22 | 1.64 | 1.68 | 2.99 |
| January | 1.37 | 2.26 | 1.22 | 1.63 | 1.90 | 3.54 |
| February | 1.29 | 2.08 | 1.37 | 1.98 | 1.90 | 3.55 |
| March | 1.34 | 2.19 | 1.39 | 2.02 | 1.86 | 3.44 |
| April | 1.26 | 2.01 | 1.32 | 1.85 | 1.80 | 3.29 |
| May | 1.15 | 1.73 | 1.18 | 1.54 | 1.62 | 2.83 |
| June | 0.90 | 1.67 | 0.98 | 1.87 | 1.22 | 3.44 |
| July | 0.71 | 2.13 | 0.79 | 1.19 | 0.82 | 1.76 |
| August | 0.60 | 1.92 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 0.63 |
| September | 0.50 | 1.02 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Adaja 422 | Agueda 523 | Cega 383 | Tormes 505 | |||
| October | 1.18 | 2.06 | 1.29 | 9.47 | ||
| November | 2.03 | 3.26 | 1.46 | 13.07 | ||
| December | 2.52 | 3.87 | 1.48 | 14.31 | ||
| January | 2.96 | 4.05 | 1.43 | 13.88 | ||
| February | 3.22 | 3.25 | 1.28 | 14.49 | ||
| March | 3.20 | 2.86 | 1.35 | 15.10 | ||
| April | 3.04 | 2.59 | 1.37 | 15.37 | ||
| May | 2.67 | 2.36 | 1.50 | 14.75 | ||
| June | 1.98 | 1.58 | 1.03 | 11.56 | ||
| July | 1.32 | 1.00 | 0.61 | 8.43 | ||
| August | 0.92 | 0.60 | 0.50 | 7.00 | ||
| September | 0.80 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 7.57 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baeza, D.; Chacón, P.; Rico, E. Strategy for Adapting Environmental Flow Proposals to Situations with High Agricultural Demands. Water 2024, 16, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152106
Baeza D, Chacón P, Rico E. Strategy for Adapting Environmental Flow Proposals to Situations with High Agricultural Demands. Water. 2024; 16(15):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152106
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaeza, Domingo, Patricia Chacón, and Eugenio Rico. 2024. "Strategy for Adapting Environmental Flow Proposals to Situations with High Agricultural Demands" Water 16, no. 15: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152106
APA StyleBaeza, D., Chacón, P., & Rico, E. (2024). Strategy for Adapting Environmental Flow Proposals to Situations with High Agricultural Demands. Water, 16(15), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152106








