Wastewater Treatment for Nutrients and Pathogens in a Demonstration-Scale Outdoor Constructed Wetland System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Configuration
2.2. Characterization of the Reactive Material and Reaction Products
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Geochemical Modeling
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Reactive Materials
3.2. Flow Characteristics
3.3. pH and Alkalinity
3.4. Phosphorus Removal
3.4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4.2. XANES Spectroscopy
3.5. Ammonia and Nitrate
3.6. Carbonaceous Biochemical Oxygen Demand (cBOD5) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
3.7. Major Ion Chemistry
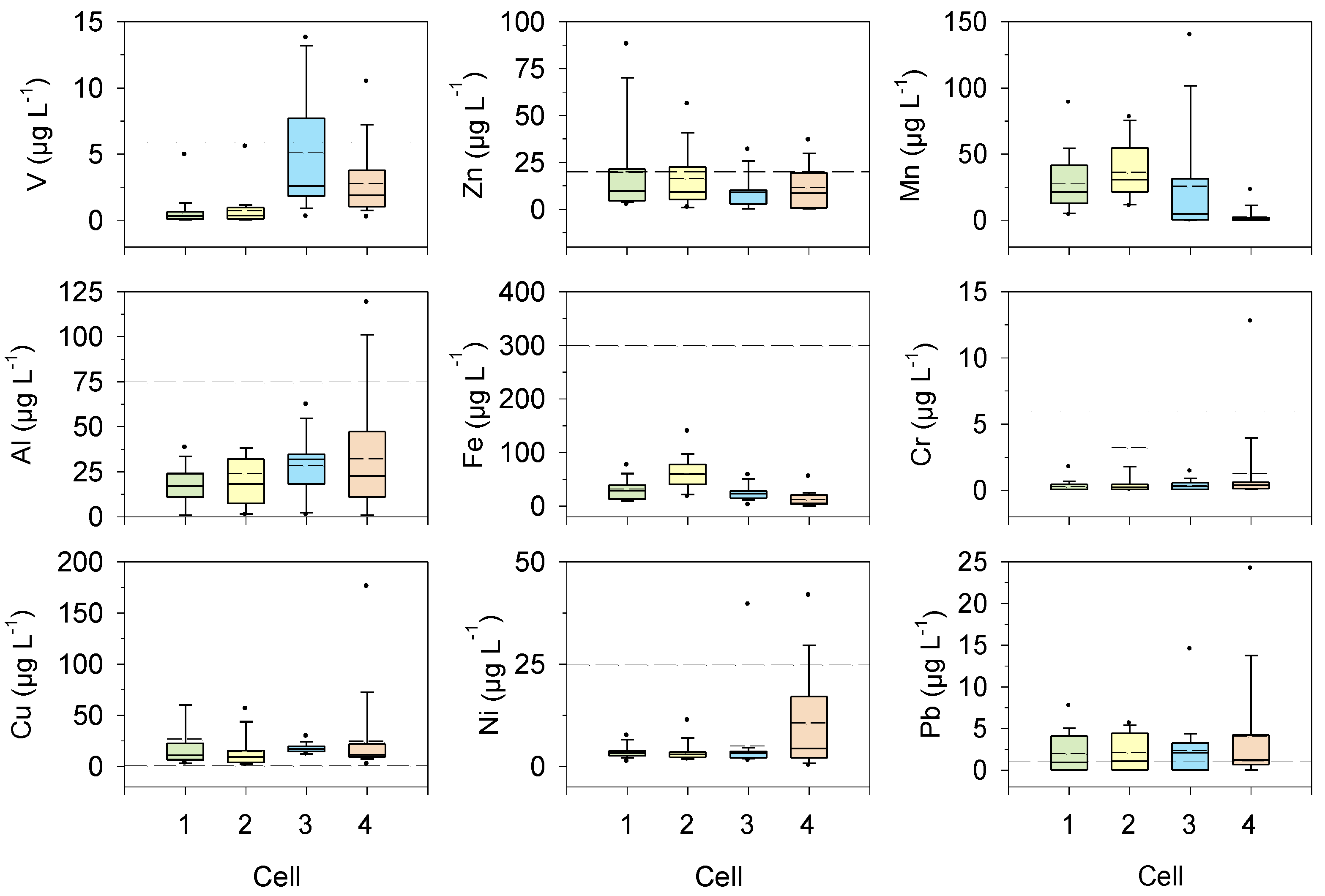
3.8. Trace Metals
3.9. Inactivation of Bacterial Indicators (E. coli and Total Coliforms)
3.10. Statistical Analysis and Interpretation
3.11. Statistical Comparison Using Dunn’s Method
3.12. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
3.13. Practical Implications and Potential Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA 910-R-07-002; Advanced Wastewater Treatment to Achieve Low Concentration of Phosphorus. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water and Watersheds: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Vymazal, J. Subsurface horizontal-flow constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: The Czech experience. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 1997, 4, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Hawkins, T.; Schoen, M.; Garland, J.; Ashbolt, N. Comparing the life cycle energy consumption, global warming and eutrophication potentials of several water and waste service options. Water 2016, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S. Controlling Nitrogen and Phosphorous in Wastewater. Chem. Eng. Prog. 2020, 116, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Preisner, M.; Neverova-Dziopak, E.; Kowalewski, Z. Mitigation of eutrophication caused by wastewater discharge: A simulation-based approach. Ambio 2020, 50, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P. Eutrophication in aquatic ecosystem. In Aquatic Environment Management; Pandey, P.K., Pande, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tat Wai, K.; O’Sullivan, A.D.; Bello-Mendoza, R. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal from Wastewater Using Calcareous Waste Shells—A Systematic Literature Review. Environments 2024, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of nutrients in various types of constructed wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; CRC Lewis Publishers Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment: Five decades of experience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Su, J.; Zhu, G.; Liu, L. Performance of vertical up-flow constructed wetlands on swine wastewater containing tetracyclines and tet genes. Water Res. 2015, 70, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of phosphorus in constructed wetlands with horizontal sub-surface flow in the Czech Republic. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2004, 4, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubernat, S.; Masłoń, A.; Czarnota, J.; Koszelnik, P. Reactive Materials in the Removal of Phosphorus Compounds from Wastewater—A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murujew, O.; Le Corre, K.; Wilson, A.; Bajón Fernández, Y.; Vale, P.; Jefferson, B.; Pidou, M. Reactive media constructed wetland for phosphorus removal: Assessing the opportunity and challenges. H2Open J. 2024, 7, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L. Industrial by-products and natural substrata as phosphorus sorbents. Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drizo, A.; Comeau, Y.; Forget, C.; Chapuis, R.P. Phosphorus saturation potential: A parameter for estimating the longevity of constructed wetland systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4642–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenssen, P.D.; Krogstad, T. Design of constructed wetlands using phosphorus sorbing lightweight aggregate (LWA). In Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment in Cold Climates; Mander, Ü., Jenssen, P.D., Eds.; WIT Press: Southampton, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 11, pp. 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Barca, C.; Troesch, S.; Meyer, D.; Drissen, P.; Andrès, Y.; Chazarenc, F. Steel slag filters to upgrade phosphorus removal in constructed wetlands: Two years of field experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansing, R.P.; Rout, P.D. Removal of phosphorus from sewage effluent by adsorption on laterite. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2, 551–559. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.I.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Jamieson-Hanes, J.H.; Wootton, B.; Balch, G.; Higgins, J. Mechanism of phosphorus removal in a pilot-scale constructed wetland/BOF slag wastewater treatment system. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 32, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Uddin, S.M.N.; Bai, X. Comparative research on phosphorus removal by pilot-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands using steel slag and modified steel slag as substrates. Water Sci. Technol. 2015, 71, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateus, D.M.R.; Vaz, M.M.N.; Capela, I.; Pinho, H.J.O. The potential growth of sugarcane in constructed wetlands designed for tertiary treatment of wastewater. Water 2016, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Ann, T.W.; Lee, S.M. Use of biochar to enhance constructed wetland performance in wastewater reclamation. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claveau-Mallet, D.; Boutet, É.; Comeau, Y. Steel slag filter design criteria for phosphorus removal from wastewater in decentralized applications. Water Res. 2018, 143, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehua, J.; Wenzhong, T.; Yuansheng, P. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drizo, A.; Forget, C.; Chapuis, R.P.; Comeau, Y. Phosphorus removal by electric arc furnace steel slag and serpentinite. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drizo, A.; Frost, C.A.; Grace, J.; Smith, K.A. Physico-chemical screening of phosphate-removing substrates for use in constructed wetland systems. Water Res. 1999, 33, 3595–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohla, C.; Kõiv, M.; Bavor, H.J.; Chazarenc, F.; Mander, Ü. Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands-A review. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, S.A.; Owens, D.R.; Wang, S.S.B.; Lastra, R.; Van Huyssteen, E. Characterization of Basic Oxygen Furnace Dust and Slag in Steelmaking; Report No. 94-18 (R); MSL Project; Mineral Sciences Laboratories, Canada Centre for Mineral and Energy Technology, Division: Ottawa, ON, USA, 1994; Volume 691, pp. 1–41.
- Shi, C. Steel slag—Its production, processing, characteristics, and cementitious properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2004, 16, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. Laboratory development of permeable reactive mixtures for the removal of phosphorus from onsite wastewater disposal systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2308–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, L.I.; Jarvis, A.P.; Younger, P.L.; Johnson, K.L. Phosphorus removal from waste waters using basic oxygen steel slag. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.I.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Olding, D. Phosphorus removal from lake water using basic oxygen furnace slag: System performance and characterization of reaction products. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Y.; Yu, X.; Ding, S.; Yan, J.; Min, Y. Vegetated Steel Slag Substrate Constructed Wetlands can Achieve High Efficiency Simultaneous Nitrogen and Phosphorus Removal. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 947783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, D.M.; Fehling, K.A.; Shay, E.C.; Wittenborn, J.L.; Green, J.J.; Avent, C.; Bigham, R.D.; Connolly, M.; Lee, B.; Shepker, T.O.; et al. Physical and chemical characteristics of blast furnace, basic oxygen furnace, and electric arc furnace steel industry slags. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, W.; Kim, J.; Choi, H. Evaluation of steel slag for organic and inorganic removals in soil aquifer treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-H.; Hwang, H.-K.; Yim, S.-B. Phosphorus removal characteristics in hydroxyapatite crystallization using converter slag. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2006, 41, 2531–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Hou, H.; Zhu, S. Characteristics and mechanisms of phosphate adsorption onto basic oxygen furnace slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, C.; Diaz, M.; Villa-Garcia, M.A. Physico-chemical characterization of steel slag study of its behavior under simulated environmental conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 5383–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieux, P.; Aubert, J.; Escadeillas, G. Utilization of weathered basic oxygen furnace slag in the production of hydraulic road binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimson, J.; Chae, G.; Ptacek, C.J.; Emelko, M.B.; Mesquita, M.M.; Hirata, R.A.; Blowes, D.W. Basic oxygen furnace slag as a treatment material for pathogens: Contribution of inactivation and attachment in virus attenuation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, I.Z.; Prezzi, M. Chemical mineralogical and morphological properties of steel slag. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2011, 2011, 463638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, E.; Diliberto, C.; Lecomte, A. Characterization and activation of Basic Oxygen Furnace slag. Cement. Concrete. Comp. 2012, 34, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J. Phosphorous adsorption and precipitation in a permeable reactive wall: Applications for wastewater disposal systems. Land Contam. Reclam. 1997, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Benner, S.G.; McRae, C.W.T.; Bennett, T.A.; Puls, R.W. Treatment of inorganic contaminants using permeable reactive barriers. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2000, 45, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Xue, X. Removal kinetics of phosphorus from synthetic wastewater using basic oxygen furnace slag. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 30, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, D.J.A.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Baker, M.J.; Ford, G.; Foss, S.; Bernstene, E. Removal of phosphate and waterborne pathogens from wastewater effluent using permeable reactive materials. In Proceedings of the 55th Canadian Geotechnical and 3rd Joint IAH-CNC and CGS Groundwater Specialty Conference, Niagara Falls, ON, Canada, 20–23 October 2002; pp. 1123–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Suhogusoff, A.V.; Hirata, R.; Ferrari, L.C.K.M.; Robertson, W.D.; Stimson, J.; Forbes, D.; Blowes, D.W. Field performance of two on-site wastewater treatment systems using reactive media layers for nutrient and pathogen removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Baker, M.J. Treatment of Wastewater. G.B. Patent 2,306,954, 1 December 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Baker, M.J. Treatment of Wastewater. Canadian Patent 2,190,933, 11 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Baker, M.J. Treatment of Wastewater. U.S. Patent 5,876,606, 9 March 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Phosphex™ Canadian Trademark Registration. Canadian Patent 1,051,185, 17 March 2000.
- Phosphex™, U.S. Trademark Registration. U.S. Patent 78/015,068, 30 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.I.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Liu, Y.; Wootton, B.C.; Balch, G.; Higgins, J. Transport and attenuation of an artificial sweetener and six pharmaceutical compounds in a sequenced wetland-steel slag wastewater treatment system. Water 2023, 15, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravel, B.; Newville, M. Athena, Artemis, Hephaestus: Data analysis for X-ray absorption spectroscopy using IFEFFIT. J. Synchrotron Rad. 2005, 12, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, J.; Vallet-Regi, M. Hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate and biphasic materials prepared by a liquid mix technique. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation: Washington DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Inorganic Ventures. “7 Anion Calibration Standard (125 mL).” Inorganic Ventures, n.d. Web. Available online: https://www.inorganicventures.com/7-anion-calibration-std-125ml (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Inorganic Ventures. “26 Element ICP Calibration/Quality Control Standard.” Inorganic Ventures, n.d. Web. Available online: https://www.inorganicventures.com/qcplus-qc-solution-26-125ml (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Inorganic Ventures. “10 ppm 43 Element ICP Calibration/Quality Control Standard.” Inorganic Ventures, n.d. Web. Available online: https://www.inorganicventures.com/icp-ms-complete-std-125ml (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Hach Company. Method 10031: Nitrogen, Ammonia-Salicylate HR Method, Test ‘N Tube™ Vials. DOC316.53.01079. Available online: https://www.hach.com/p-nitrogen-ammonia-reagent-set-tnt-amver-salicylate-high-range/2606945 (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Users Guide to PHREEQC (Version2)—A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Resources Investigations Report 99-4259: 312; U.S. Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Knight, R.L.; Payne, V.W.E., Jr.; Borer, R.E.; Clarke, R.A., Jr.; Pries, J.H. Constructed wetlands for livestock wastewater management. Ecol. Eng. 2000, 15, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Ontario. “F-5-1 Determination of Treatment Requirements for Municipal and Private Sewage Treatment Works.” Ontario.ca. Available online: https://www.ontario.ca/page/f-5-1-determination-treatment-requirements-municipal-and-private-sewage-treatment-works#section-2 (accessed on 24 July 2024).
- Aregu, M. Industrial wastewater treatment efficiency of mixed substrate (pumice and scoria) in horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland: Comparative experimental study design. Air Soil Water Res. 2022, 15, 117862212110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, R.G.; Richardson, C.J. Forms of soil phosphorus along a nutrient enrichment gradient in the northern everglades. Soil Sci. 1995, 160, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1981; 780p. [Google Scholar]
- Parks, G.A. The isoelectric points of solid oxides, solid hydroxides, and aqueous hydroxo complex systems. Chem. Rev. 1965, 65, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. Surface Charging and Points of Zero Charge; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Kayama, M.; Saito, K.; Hara, M. A fundamental research on phosphate removal by using slag. Water Res. 1986, 20, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Remmers, J.C.; Saakes, M.; Buisman, C.J. Is there a precipitation sequence in municipal wastewater induced by electrolysis? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 8399–8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, I.; Bonfield, W. Characterization of hydroxyapatite and carbonated apatite by photo acoustic FTIR spectroscopy. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. M. 1997, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.C.; Gibson, I.; Barbosa, M.A. The uptake of titanium ions by hydroxyapatite particles—Structural changes and possible mechanisms. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, R.N.; Hsieh, M.F.; Chung, R.J.; Chin, T.S. FTIR, XRD, SEM and solid state NMR investigations of carbonate-containing hydroxyapatite nano-particles synthesized by hydroxide-gel technique. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 2003, 64, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Purohit, K.M. Chemical synthesis, characterization and bioactivity evaluation of hydroxyapatite prepared from Garden snail (Helix aspersa). J. Bioprocess. Biotechniq. 2011, 1, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matković, I.; Maltar-Strmecki, N.; Babić-Ivancić, V.; Dutour Sikirić, M.; Noethig-Laslo, V. Characterisation of b-tricalcium phosphate-based bone substitute materials by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Ugarte, J.F.; De Sena, L.Á.; De Castro Pérez, C.A.; De Aguiar, P.F.; Rossi, A.M.; Soares, G.A. Influence of processing parameters on structural characteristics of porous calcium phosphate samples: A study using an experimental design method. Mat. Res. 2005, 8, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.R.B.; de Lima-Neto, P.; Sales, F.A.M.; da Silva, E.E.; Ladeira, L.O.; Freire, V.N.; Caetano, E.W.S. Phosphate group vibrational signatures of the osteoporosis drug alendronate. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2014, 45, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, P.; McMillan, P.; Schott, J.; Badro, J.; Grzechnik, A. Thermodynamic properties and isotopic fractionation of calcite from vibrational spectroscopy of 18O-substituted calcite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1996, 60, 3471–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongsavat, V.; Winotai, P.; Meejoo, S. Phase transitions of natural corals monitored by ESR spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 2006, 243, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatzber, M.; Stemmer, M.; Spiegel, H.; Katzlberger, C.; Haberhauer, G.; Gerzabek, M.H. An alternative method to measure carbonate in soils by FT-IR spectroscopy. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Anbalagan, G. Spectroscopic study of phase transitions in natural calcite mineral. Spectrochim. Acta. A 2008, 69, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, D.; Zhou, W.; Hutchison, K.J.; Beauchemin, S.; Sayers, D.E. XAFS study of adsorbed and mineral forms of phosphate. J. Synchrotron Rad. 1999, 6, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Solomon, D.; Hyland, C.; Ketterings, Q.M.; Lehmann, J. Phosphorus speciation in manure and manure-amended soils using XANES spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7485–7491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shober, A.L.; Hesterberg, D.L.; Sims, J.T.; Gardner, S. Characterization of phosphorus species in biosolids and manures using XANES spectroscopy. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, K.; Jürgensen, A.; Karthikeyan, K.G. Determination of phosphorus speciation in dairy manure using XRD and XANES spectroscopy. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandes, J.A.; Ingall, E.; Paterson, D. Characterization of minerals and organic phosphorus species in marine sediments using soft X-ray fluorescence spectromicroscopy. Mar. Chem. 2007, 103, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peak, D.; Sims, J.T.; Sparks, D.L. Solid-state speciation of natural and alum-amended poultry litter using XANES spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4253–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, R.; Hormes, J. The P K-near edge absorption spectra of phosphates. Phys. B Phys. Condens. Matter 1995, 216, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajiboye, B.; Akinremi, O.O.; Hu, Y.; Jürgensen, A. XANES speciation of phosphorus in organically amended and fertilized Vertisol and Mollisol. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2008, 72, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveborn, D.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Hillier, S. XANES speciation of P in environmental samples: An assessment of filter media for on-site wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6515–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, S.; Hesterberg, D.; Chou, J.; Beauchemin, M.; Simard, R.R.; Sayers, D.E. Speciation of phosphorus in phosphorus-enriched agricultural soils using X-ray absorption near-edge structure spectroscopy and chemical fractionation. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, N.; Hesterberg, D.; Beauchemin, S.; Wang, S. XANES determination of adsorbed phosphate distribution between ferrihydrite and boehmite in mixtures. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 68, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.I.; Phillips, L.A.; Hu, Y.; Frey, S.K.; Geuder, D.S.; Edwards, M.; Lapen, D.R.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W. Differences in phosphorus biogeochemistry and mediating microorganisms in the matrix and macropores of an agricultural clay loam soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.; Friedler, E.; Safrai, I. Enhancing nitrification in vertical flow constructed wetland utilizing a passive air pump. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3513–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Li, Y. Enhancement of nitrogen removal in towery hybrid constructed wetland to treat domestic wastewater for small rural communities. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Agrawal, A. Reduction of nitrate and nitrite by iron metal: Implications for ground water remediation. In Proceedings of the 213th ACS National meeting, Sanfrancisco, CA, USA, 13–17 April 1997; Volume 37, pp. 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W. Treatment of dissolved perchlorate, nitrate, and sulfate using zero-valent iron and organic carbon. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Mara, D.D. Aerated rock filters for enhanced nitrogen and faecal coliform removal from facultative waste stabilization pond effluents. Water Sci. Technol. 2005, 51, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, H.; Arias, C.A. The use of vertical flow constructed wetlands for on-site treatment of domestic wastewater: New Danish guidelines. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Arias, C.; Brix, H.; Bayona, J.M. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from urban wastewater in a pilot vertical flow constructed wetland and a sand filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8171–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, S.; Scholz, M.; Li, J. Nutrient removal in pilot-scale constructed wetlands treating eutrophic river water: Assessment of plants, intermittent artificial aeration and polyhedron hollow polypropylene balls. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOEE (Ministry of Environment and Energy). Water Management Policies, Guidelines, Provincial Water Quality Objectives; Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1994; pp. 9–28.
- Chaurand, P.; Rose, J.; Briois, V.; Olivi, L.; Hazemann, J.-L.; Proux, O.; Domas, J.; Bottero, J.-Y. Environmental impacts of steel slag reused in road construction: A crystallographic and molecular (XANES) approach. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, B139, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Cell ID | Cell Type | Cell Description | Cell Volume (m3) | Media Volume (m3) | Porosity (θ) | Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT) (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell 1 | Pre-treatment septic tank effluent chamber | The influent of the treatment system, wastewater, was received from this pre-treatment septic tank and periodically pumped to Cell 2. | 1 | - | - | - |
| Cell 2 | Subsurface flow constructed wetland (HSSF CW Cell) | Filled with granitic gravel and vegetated with cattails (Typha spp.). | 24 | 19.4 | 0.35 | 7.64 |
| Cell 3 | Subsurface flow aerated constructed wetland (Aerated VSSF CW Cell) | Filled with granitic gravel and vegetated with cattails (Typha spp.). | 24.2 | 19.3 | 0.35 | 7.61 |
| Cell 4 | Downward vertical flow cell (BOFS Cell) | Filled with BOFS and ZVI to remove phosphate. BOFS media were covered by a granitic gravel layer and then a plastic tarp and a sand layer to avoid atmospheric oxygen ingress. A sacrificial BOFS chamber was placed before cell four to prevent the formation of a CaCO3 scale around the Cell 4 inlet. | 27.4 | 13.3 | 0.4 | 5.97 |
| Cell 5 | pH adjustment unit | Equipped with a CO2 sparger and an adjusted pH between 6.5 and 8.5 before being released into the City of Kawartha Lakes sewer system. | 2 | - | - | - |
| Band Type | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Description | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonate ν4 | 712–713 | Sharp carbonate band | [79,80,81,82] |
| Carbonate ν2 | 872–874 | Sharp carbonate band | |
| Carbonate ν3 | 1422–1426 | Broad distinct carbonate band | |
| Carbonate ν1 + ν4 | 1797–1800 | Combination band | [79,80,82] |
| Carbonate ν1 + ν3 | 2514–2515 | Combination band | [80] |
| Carbonate 2 ν2 + ν4 | 2514–2515 | Combination band | [82] |
| Carbonate overtones | 2874–2876, 2980–2982 | Weaker carbonate overtones | [82] |
| Phosphate ν3 | 1030–1039 | Broad phosphate band | [37,56,70,71,72,73,76,77,78] |
| Phosphate ν4 | 632–635, 602–608, 595–597, 583–588, 567–575 | Several weak to very weak phosphate bands | |
| Phosphate ν2 | 450–461, 475 | Phosphate band |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, S.I.; Blowes, D.W.; Ptacek, C.J.; Wootton, B.C.; Balch, G.; Higgins, J. Wastewater Treatment for Nutrients and Pathogens in a Demonstration-Scale Outdoor Constructed Wetland System. Water 2024, 16, 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152198
Hussain SI, Blowes DW, Ptacek CJ, Wootton BC, Balch G, Higgins J. Wastewater Treatment for Nutrients and Pathogens in a Demonstration-Scale Outdoor Constructed Wetland System. Water. 2024; 16(15):2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152198
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Syed I., David W. Blowes, Carol J. Ptacek, Brent C. Wootton, Gordon Balch, and James Higgins. 2024. "Wastewater Treatment for Nutrients and Pathogens in a Demonstration-Scale Outdoor Constructed Wetland System" Water 16, no. 15: 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152198
APA StyleHussain, S. I., Blowes, D. W., Ptacek, C. J., Wootton, B. C., Balch, G., & Higgins, J. (2024). Wastewater Treatment for Nutrients and Pathogens in a Demonstration-Scale Outdoor Constructed Wetland System. Water, 16(15), 2198. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152198






