A Review of Drip Irrigation’s Effect on Water, Carbon Fluxes, and Crop Growth in Farmland
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
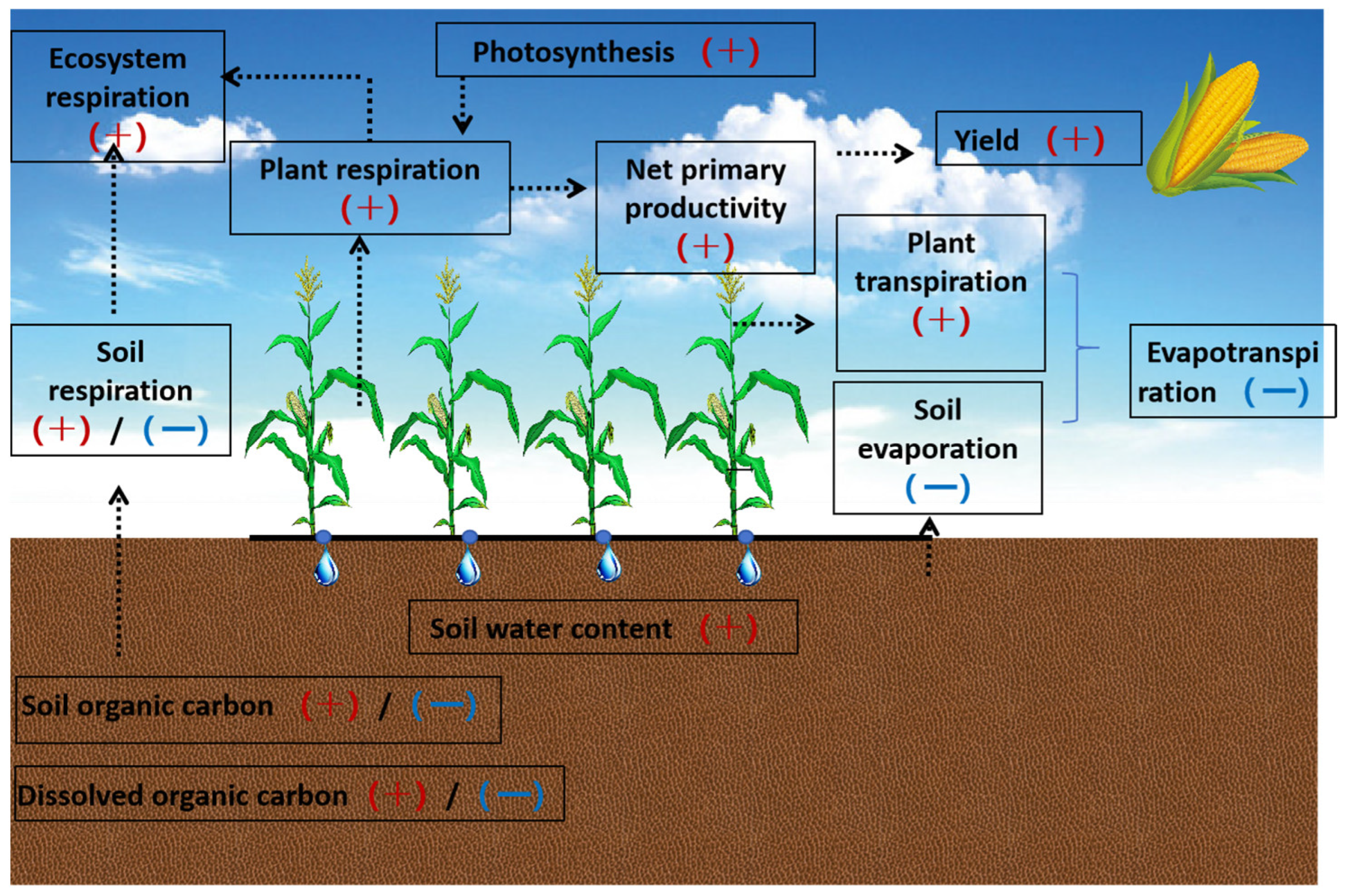
3. Drip Irrigation and Water Balance in Farmland
4. Drip Irrigation and Carbon Fluxes in Farmland
5. Effect of Drip Irrigation on Crop Growth
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elliott, J.; Deryng, D.; Mueller, C.; Frieler, K.; Konzmann, M.; Gerten, D.; Glotter, M.; Floerke, M.; Wada, Y.; Best, N.; et al. Constraints and Potentials of Future Irrigation Water Availability on Agricultural Production under Climate Change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3239–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famiglietti, J.S. The Global Groundwater Crisis. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Mekonnen, M.M. The Water Footprint of Humanity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3232–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Porkka, M.; Doell, P.; Ramankutty, N.; Scanlon, B.R. A Global Data Set of the Extent of Irrigated Land from 1900 to 2005. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1521–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermid, S.; Nocco, M.; Lawston-Parker, P.; Keune, J.; Pokhrel, Y.; Jain, M.; Jägermeyr, J.; Brocca, L.; Massari, C.; Jones, A.D.; et al. Irrigation in the Earth System. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 435–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Siebert, S.; Kummu, M.; Deng, Q.; Ali, T.; Marston, L.; Xie, W.; Davis, K.F. Half of Twenty-First Century Global Irrigation Expansion Has Been in Water-Stressed Regions. Nat. Water 2024, 2, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global Food Demand and the Sustainable Intensification of Agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mueller, C.; Elliot, J.; Mueller, N.D.; Ciais, P.; Jaegermeyr, J.; Gerber, J.; Dumas, P.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; et al. Global Irrigation Contribution to Wheat and Maize Yield. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Gao, Q. Water-Saving Irrigation Promotion and Food Security: A Study for China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, S.; Frances, F.; Garcia-Prats, A.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Sanchis-Ibor, C.; Schirmer, M.; Yang, H.; Jimenez-Martinez, J. From Flood to Drip Irrigation Under Climate Change: Impacts on Evapotranspiration and Groundwater Recharge in the Mediterranean Region of Valencia (Spain). Earth Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, G.V.; Bridjesh, P.; Prabhu Kishore, N.; Shiva Sai, N. Design and Development of a Drip Irrigation System. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, D.; Limbasia, B.; Mori, Y.; Imtiyazali Aglodiya, M.; Shah, M. A Comprehensive and Systematic Study in Smart Drip and Sprinkler Irrigation Systems. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, E.G.; Elliott, R.L. Design and Operation of Farm Irrigation Systems, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-1-892769-64-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, P.; Cheng, M.; Wu, L.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Qian, L. Review on Drip Irrigation: Impact on Crop Yield, Quality, and Water Productivity in China. Water 2023, 15, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Guan, B.; Huang, Q. Forty Years of Irrigation Development and Reform in China. Aust. J. Agr. Resour. Econ. 2020, 64, 126–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Agricultural Statistical Yearbook 2021: Comprehensive Data on the Development of China’s Agriculture; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Li, H.; Mei, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, F.; Hao, W.; Li, B. Drip Fertigation Significantly Increased Crop Yield, Water Productivity and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Respect to Traditional Irrigation and Fertilization Practices: A Meta-Analysis in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcon, F.; Navarro, N.; de-Miguel, M.D.; Balbo, A.L. Drip Irrigation Technology: Analysis of Adoption and Diffusion Processes. In Sustainable Solutions for Food Security: Combating Climate Change by Adaptation; Sarkar, A., Sensarma, S.R., vanLoon, G.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 269–285. ISBN 978-3-319-77878-5. [Google Scholar]
- Puy, A.; Garcia Aviles, J.M.; Balbo, A.L.; Keller, M.; Riedesel, S.; Blum, D.; Bubenzer, O. Drip Irrigation Uptake in Traditional Irrigated Fields: The Edaphological Impact. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibragimov, N.; Evett, S.R.; Esanbekov, Y.; Kamilov, B.S.; Mirzaev, L.; Lamers, J.P.A. Water Use Efficiency of Irrigated Cotton in Uzbekistan under Drip and Furrow Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 90, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ren, A.; Yang, J.; Yu, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Q. Soil water and salt movement and spatial distribution of fine alfalfa roots under drip irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, G.; Tian, J.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Mulched Drip Irrigation Increases Cotton Yield and Water Use Efficiency via Improving Fine Root Plasticity. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, K.N.; Singh, A.; Mal, P.K. Effect of Drip Irrigation on Yield of Cabbage (Brassica Oleracea L. Var. Capitata) under Mulch and Non-Mulch Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, G.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, Q. Corn Production: A Subsurface Drip Irrigation Approach. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 666, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonteyne, S.; Flores García, Á.; Verhulst, N. Reduced Water Use in Barley and Maize Production Through Conservation Agriculture and Drip Irrigation. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 734681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpute, S.; Singh, M.C. Improved Irrigation and Groundwater Management for Reducing CO2 Emissions: A Case Study of Indian Punjab. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2024, 29, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathi, T.; Vanitha, K.; Mohandass, S.; Vered, E. Evaluation of Drip Irrigation System for Water Productivity and Yield of Rice. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 2378–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Influence of Mulched Drip Irrigation on Landscape Scale Evapotranspiration from Farmland in an Arid Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Qin, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, C. Effect of Drip Irrigation on Soil Water Balance and Water Use Efficiency of Maize in Northwest China. Water 2021, 13, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Li, S.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Ding, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Transpiration of Female and Male Parents of Seed Maize in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, R.; Hu, Z.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. Simulating Drip Irrigation in Large-Scale and High-Resolution Ecohydrological Models: From Emitters to the Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, M.; Fan, Y.; Yan, L.; Wang, F. Effects of Mulched Drip Irrigation on Soil Moisture and Groundwater Recharge in the Xiliao River Plain, China. Water 2018, 10, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Stokvis, B.; Galindo, A.; Blatchford, M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Water Scarcity Alleviation through Water Footprint Reduction in Agriculture: The Effect of Soil Mulching and Drip Irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Hussain, T.; Jiang, H.; Ahmad, A.; Yao, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Min, L.; Shen, Y. Water-Saving Potential of Subsurface Drip Irrigation For Winter Wheat. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Liang, Y.; Duan, A. Root Development and Water Uptake in Winter Wheat under Different Irrigation Methods and Scheduling for North China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 182, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hao, W.; Mei, X.; Guo, R. Effect of different irrigation and fertilization managements on N2O emissions and yeild in summer maize-winter wheat field. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moursy, M.a.M.; ElFetyany, M.; Meleha, A.M.I.; El-Bialy, M.A. Productivity and Profitability of Modern Irrigation Methods through the Application of On-Farm Drip Irrigation on Some Crops in the Northern Nile Delta of Egypt. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 62, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, M.g.; Pawar, D.d.; Kale, K.d.; Dingre, S.k. Performance of Cabbage at Different Irrigation Levels under Drip and Microsprinkler Irrigation Systems. Irrig. Drain. 2021, 70, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Timsina, J.; Mandal, K.G.; Naorem, A. Effects of Different Irrigation Methods and Mulching on Yield, Growth and Water Use Efficiency of Strawberry. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Shi, X.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, F. Effects of Irrigation Level and Method on Soil Salt Balance and Crop Water Use Efficiency in Arid Oasis Regions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 16, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zou, Y.; Kisekka, I.; Biswas, A.; Cai, H. Comparison of Different Irrigation Methods to Synergistically Improve Maize’s Yield, Water Productivity and Economic Benefits in an Arid Irrigation Area. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, I.; Buttar, G.S.; Brar, A.S. Drip Irrigation and Fertigation Improve Economics, Water and Energy Productivity of Spring Sunflower (Helianthus Annuus L.) in Indian Punjab. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 185, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, K.; Fan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lin, S.; Wang, J. Simulating the Fate of Nitrogen and Optimizing Water and Nitrogen Management of Greenhouse Tomato in North China Using the EU-Rotate_N Model. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 128, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malash, N.M.; Flowers, T.J.; Ragab, R. Plant–Water Relations, Growth and Productivity of Tomato Irrigated by Different Methods with Saline and Non-Saline Water. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 60, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yuan, B.; Hu, X.; Yin, C. Drip Irrigation Enhances Water Use Efficiency without Losses in Cucumber Yield and Economic Benefits in Greenhouses in North China. Irrig. Sci. 2022, 40, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin, F.; Nortes, P.A.; Dominguez, A.; Sanchez, J.M.; Intrigliolo, D.S.; Alarcon, J.J.; Lopez-Urrea, R. Comparing Evapotranspiration and Yield Performance of Maize under Sprinkler, Superficial and Subsurface Drip Irrigation in a Semi-Arid Environment. Irrig. Sci. 2020, 38, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Wang, J.; Gong, S.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q. Assessment of Maize Yield-Increasing Potential and Optimum N Level under Mulched Drip Irrigation in the Northeast of China. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; Ortuno, M.F.; Chaves, M.M. Deficit Irrigation as a Strategy to Save Water: Physiology and Potential Application to Horticulture. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 1421–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, T.J.; DeJonge, K.C. Water Productivity of Maize in the US High Plains. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Lopez-Urrea, R.; Dona, C.; Caselles, V.; Gonzalez-Piqueras, J.; Niclos, R. 5 Modeling Evapotranspiration in a Spring Wheat from Thermal Radiometry: Crop Coefficients and E/T Partitioning. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Qin, S.; Guo, H.; Yang, D.; Lam, H.-M. How Can Drip Irrigation Save Water and Reduce Evapotranspiration Compared to Border Irrigation in Arid Regions in Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, P.; Kang, S.; Li, S.; Tong, L.; Ding, R.; Lu, H. Comparison of Evapotranspiration and Energy Partitioning Related to Main Biotic and Abiotic Controllers in Vineyards Using Different Irrigation Methods. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C. Photosynthetic Carbon Fixation in Relation to Net Co2 Uptake. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Molec. Biol. 1973, 24, 253–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raich, J.W.; Tufekcioglu, A. Vegetation and Soil Respiration: Correlations and Controls. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Nadal, M. Linking Water Relations and Hydraulics with Photosynthesis. Plant J. 2020, 101, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, E.; Singandhupe, R.B. Impact of Drip and Surface Irrigation on Growth, Yield and WUE of Capsicum (Capsicum Annum L.). Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D. Temporal and Spatial Variation of Morpho-Physiological Characteristics of Spring Maize under Mulched Drip Irrigation in Northeastern China. Crop Pasture Sci. 2022, 73, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, D.; Gong, S.; Wu, Z.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Plastic Film Mulching with Drip Irrigation Promotes Maize (Zea Mays L.) Yield and Water-Use Efficiency by Improving Photosynthetic Characteristics. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2021, 67, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, C. Effects of Drip Irrigation and Fertilization Frequency on Yield, Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Medium and Strong Gluten Wheat in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghari, S.J.; Hu, K.; Wei, Y.; Wang, T.; Bhutto, T.A.; Buriro, M. Modelling Water Consumption, N Fates and Maize Yield under Different Water-Saving Management Practices in China and Pakistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hendawy, S.E.; Hokam, E.M.; Schmidhalter, U. Drip Irrigation Frequency: The Effects and Their Interaction with Nitrogen Fertilization on Sandy Soil Water Distribution, Maize Yield and Water Use Efficiency Under Egyptian Conditions. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2008, 194, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Cui, N.; Wei, W. Effect of Different Irrigation Methods on Dissolved Organic Carbon and Microbial Biomass Carbon in the Greenhouse Soil. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, K.R.; Malik, A.A.; Muscarella, C.; Blankinship, J.C. Irrigation Alters Biogeochemical Processes to Increase Both Inorganic and Organic Carbon in Arid-Calcic Cropland Soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2023, 187, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Han, W.; Peng, M. Effects of Drip and Flood Irrigation on Carbon Dioxide Exchange and Crop Growth in the Maize Ecosystem in the Hetao Irrigation District, China. J. Arid Land 2024, 16, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Huang, G. Impact of Irrigation and Fertilization Regimes on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Soil of Mulching Cultivated Maize (Zea Mays L.) Field in the Upper Reaches of Yellow River, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, H.M.; Homyak, P.M.; Oikawa, P.Y.; Wang, J.; Jenerette, G.D. Water-Conscious Management Strategies Reduce per-Yield Irrigation and Soil Emissions of CO2, N2O, and NO in High-Temperature Forage Cropping Systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 332, 107944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Effects of Cotton Field Management Practices on Soil CO2 Emission and C Balance in an Arid Region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land 2014, 6, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, C.; Luo, N.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, P. Mitigating Global Warming Potential While Coordinating Economic Benefits by Optimizing Irrigation Managements in Maize Production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Xavier, F.A.; da Silva Pereira, B.L.; Souza, E.d.A.; Borges, A.L.; Coelho, E.F. Irrigation Systems, Fertigation and Mulch: Effects on the Physical, Chemical and Biological Attributes of the Soil with Banana Crop in Northeastern Brazil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2592–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Tian, C. Growing Season Carbon Dioxide Exchange in Flooded Non-Mulching and Non-Flooded Mulching Cotton. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryor, S.W.; Smithers, J.; Lyne, P.; van Antwerpen, R. Impact of Agricultural Practices on Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions for South African Sugarcane Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Qi, Y.; Peng, Q.; Dong, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, L. Influences of Drip and Flood Irrigation on Soil Carbon Dioxide Emission and Soil Carbon Sequestration of Maize Cropland in the North China Plain. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, C.; Burger, M.; Horwath, W.R.; Smart, D.; Six, J.; Guo, L.; Salas, W.; Frolking, S. Assessing Short-Term Impacts of Management Practices on N2O Emissions from Diverse Mediterranean Agricultural Ecosystems Using a Biogeochemical Model. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018, 123, 1557–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Cobena, A.; Lassaletta, L.; Aguilera, E.; del Prado, A.; Garnier, J.; Billen, G.; Iglesias, A.; Sánchez, B.; Guardia, G.; Abalos, D.; et al. Strategies for Greenhouse Gas Emissions Mitigation in Mediterranean Agriculture: A Review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 238, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ren, S.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Xu, Z.; Wei, R.; Wang, S.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, M. Effects of Irrigation Methods and Salinity on CO2 Emissions from Farmland Soil during Growth and Fallow Periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, W. Water Sustainability for China and Beyond. Science 2012, 337, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, Z.; Zhi, J.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; Xia, W. Effects of Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil Carbon Leaching in Cotton Fields in Arid Areas. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G. Increasing Net Ecosystem Carbon Budget and Mitigating Global Warming Potential with Improved Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization Management of a Spring Wheat Farmland System in Arid Northwest China. Plant Soil 2023, 489, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, T.; Niu, X.; Hou, Z.; Ma, X. Sound Water and Nitrogen Management Decreases Nitrogen Losses from a Drip-Fertigated Cotton Field in Northwestern China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entz, M.H.; Gross, K.G.; Fowler, D.B. Root Growth and Soil-Water Extraction by Winter and Spring Wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1992, 72, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Ge, Z. Effects of different furrow irrigation patterns, water and nitrogen supply levels on hydraulic conductivity and yield of maize. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, F. Effect of root zone water and nitrogen regulation on cotton population physiological indices under different furrow irrigation patterns. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2011, 27, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liang, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y.; Jia, H. Enhancement Growth, Water Use Efficiency and Economic Benefit for Maize by Drip Irrigation in Northwest China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Y.; Han, Q.; Ma, S. Drip Fertilization Improve Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiency by Optimizing Root and Shoot Traits of Winter Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1201966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Niu, J.; Wang, C.; Fu, Q.; Yang, G.; Liang, F.; Wang, Y. Effects of Different Irrigation Modes on the Growth, Physiology, Farmland Microclimate Characteristics, and Yield of Cotton in an Oasis. Water 2022, 14, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-L.; Dai, T.-F.; Jia, L.-M. Evaluation of the Cumulative Effect of Drip Irrigation and Fertigation on Productivity in a Poplar Plantation. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J.D.; Gong, S.H.; Xu, D.; Sui, J.; Wu, Z. Analysis of water saving and yield increasing mechanism in maize field with drip irrigation under film mulching based on transpiration estimated by sap flow meter. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.J.; Yang, J.J.; Fan, F.F.; Hou, Y.P.; Xie, J.G. Effect of plastic film mulching on dry mass accumulation and phosphorus uptake of corn receiving different fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2011, 17, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Du, G.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W. Effect of Irrigation Methods on Root Growth, Root-Shoot Ratio and Yield Components of Cotton by Regulating the Growth Redundancy of Root and Shoot. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 234, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, O.S.; Gupta, R.K.; Thind, H.S.; Jat, M.L.; Sidhu, H.S. Yadvinder-Singh Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Management for Improving Crop Yields, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Water Productivity of Maize-Wheat System on Permanent Beds in North-West India. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 219, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wei, Y.; Laghari, A.H.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, S.; Wei, Y.; Laghari, A.H.; Yang, X.; Wang, T. Modelling Effect of Different Irrigation Methods on Spring Maize Yield, Water and Nitrogen Use Efficiencies in the North China Plain. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 9651–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assefa, T.; Jha, M.; Reyes, M.; Worqlul, A.W.; Doro, L.; Tilahun, S. Conservation Agriculture with Drip Irrigation: Effects on Soil Quality and Crop Yield in Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J. The Effect of Drip Irrigation and Drip Fertigation on N2O and NO Emissions, Water Saving and Grain Yields in a Maize Field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, A.; Gao, Y.; Duan, A.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z. Interactive Effects of Irrigation System and Level on Grain Yield, Crop Water Use, and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Summer Maize in North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Liu, J.; He, K. Effect of N Fertilizer Types on N2O and NO Emissions under Drip Fertigation from an Agricultural Field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.; Chen, C.; Zhou, B.; Ma, D.; Batchelor, W.D.; Han, X.; Ding, Z.; Du, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; et al. Drip Fertigation with Relatively Low Water and N Input Achieved Higher Grain Yield of Maize by Improving Pre- and Post-Silking Dry Matter Accumulation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Multisplit Nitrogen Application via Drip Irrigation Improves Maize Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Hu, T. Sustainable High Grain Yield, Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Water Productivity Can Be Achieved in Wheat-Maize Rotation System by Changing Irrigation and Fertilization Strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, Q.; Liu, F. Effects of Drip Irrigation Nitrogen Coupling on Dry Matter Accumulation and Yield of Summer Maize in Arid Areas of China. Field Crops Res. 2021, 274, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; El-Baroudy, A.A.; Taha, A.M. Irrigation and Fertigation Scheduling under Drip Irrigation for Maize Crop in Sandy Soil. Int. Agrophysics 2016, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Bian, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, Y. Drip Irrigation Incorporating Water Conservation Measures: Effects on Soil Water–Nitrogen Utilization, Root Traits and Grain Production of Spring Maize in Semi-Arid Areas. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3127–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Ullah, I.; Chen, S. Effect of Two Types of Irrigation on Growth, Yield and Water Productivity of Maize under Different Irrigation Treatments in an Arid Environment. Irrig. Drain. 2020, 69, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanli, A.M.; Ebrahimizadeh, M.A.; Beecham, S. The Effects of Irrigation Methods with Effluent and Irrigation Scheduling on Water Use Efficiency and Corn Yields in an Arid Region. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, T.; Pandian, B.J.; Ranghaswamy, M.V.; Manickasundaram, P. Yield and Water Relations of Cotton–Maize Cropping Sequence Under Deficit Irrigation Using Drip System. Irrig. Drain. 2012, 61, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrada, A.F.; Halvorson, A.D. Manure and Nitrogen Fertilizer Effects on Corn Productivity and Soil Fertility under Drip and Furrow Irrigation. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2012, 58, 1329–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmakci, T.; Sahin, U. Improving Silage Maize Productivity Using Recycled Wastewater under Different Irrigation Methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilundo, M.; Joel, A.; Wesström, I.; Brito, R.; Messing, I. Response of Maize Root Growth to Irrigation and Nitrogen Management Strategies in Semi-Arid Loamy Sandy Soil. Field Crops Res. 2017, 200, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, H.S.; Vashist, K.K. Drip Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization Alter Phenological Development and Yield of Spring Maize (Zea Mays L.) under Semi-Arid Conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.T.; Irmak, S. Maize Response to Coupled Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization under Center Pivot, Subsurface Drip and Surface (Furrow) Irrigation: Soil-Water Dynamics and Crop Evapotranspiration. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.; Cui, Z.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Han, W.; Huang, G. Effect of Irrigation and Fertilization Regimes on Grain Yield, Water and Nitrogen Productivity of Mulching Cultivated Maize (Zea Mays L.) in the Hetao Irrigation District of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 232, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Feng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, T.; Si, B. Root-Shoot Regulation and Yield of Mulched Drip Irrigated Maize on Sandy Soil. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2017, 11, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Ruiz Padín, A.; Reinoso, B. Comparative Yield and Water Use Efficiency of Two Maize Hybrids Differing in Maturity under Solid Set Sprinkler and Two Different Lateral Spacing Drip Irrigation Systems in León, Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 124, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Shao, H.; Sokolowski, E.; Mi, G. Effect of Different Drip Fertigation Methods on Maize Yield, Nutrient and Water Productivity in Two-Soils in Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Geng, C.; Cui, X.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Hu, T. Response of Drip Fertigated Wheat-Maize Rotation System on Grain Yield, Water Productivity and Economic Benefits Using Different Water and Nitrogen Amounts. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 258, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, J.; García, S.M.; Molle, B.; Bendoula, R.; Ait-Mouheb, N. Methods for Drip Irrigation Clogging Detection, Analysis and Understanding: State of the Art and Perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W. Drip Irrigation in Agricultural Saline-Alkali Land Controls Soil Salinity and Improves Crop Yield: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Chen, F. Effects of Soil Water Content on Cotton Root Growth and Distribution Under Mulched Drip Irrigation. Agric. Sci. China 2009, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamba, D.; Zubelzu, S.; Juana, L. Energy, Cost and Uniformity in the Design of Drip Irrigation Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 178, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, D.; Makadia, J.J.; Rudrapur, S. Economic Impact and Decomposition Analysis of Income Change Vis-a-Vis Drip and Conventional Irrigation Technology in Bananas: A Case Study of the South Gujarat Region in India. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng-ASCE 2023, 149, 04023029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, L.; Lin, C.-Y.C. Does Efficient Irrigation Technology Lead to Reduced Groundwater Extraction? Empirical Evidence. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2014, 67, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, F.A.; Pulido-Velazquez, M. Water Conservation in Irrigation Can Increase Water Use. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18215–18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Williams, J.; Perry, C.J.; Molle, F.; Ringler, C.; Steduto, P.; Udall, B.; Wheeler, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Garrick, D.; et al. The Paradox of Irrigation Efficiency. Science 2018, 361, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Vicuña, S.; Blanco-Gutiérrez, I.; Meza, F.; Varela-Ortega, C. Irrigation Efficiency and Water-Policy Implications for River Basin Resilience. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, S.; Francés, F.; Garcia-Prats, A.; Puertes, C.; Pulido-Velazquez, M.; Sanchis-Ibor, C.; Schirmer, M.; Yang, H.; Jiménez-Martínez, J. Hydrological Modeling of the Effect of the Transition from Flood to Drip Irrigation on Groundwater Recharge Using Multi-Objective Calibration. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR029677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Abadía, R.; Camacho, E.; Rocamora, C.; Moreno, M.A. Efficient Water and Energy Use in Irrigation Modernization: Lessons from Spanish Case Studies. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 162, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Duan, W.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; Rosa, L. Global Energy Use and Carbon Emissions from Irrigated Agriculture. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Site | Latitude and Longitude | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Crop | Irrigation Method | Control Group | Irrigation (Drip Irrigation) (mm) | Irrigation (Control) (mm) | ET (Drip Irrigation) (mm) | ET (Control) (mm) | Irrigation Amount Variation (%) | ET Variation (%) | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei, China | - | - | Winter wheat | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 148 | 188 | 260 | 300 | −21.28 | −13.55 | [33] |
| Henan, China | 35°08′ N, 113°45′ E | Wheat | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 210 | 300 | 299 | 341 | −30.00 | −12.32 | [34] | |
| Henan, China | 35°08′ N, 113°45′ E | Wheat | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 180 | 240 | 310 | 319 | −25.00 | −2.82 | [34] | |
| Hebei, China | 37.90° N, 115.70° E | 555.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 146 | 205 | 400 | 429 | −28.78 | −6.76 | [35] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | Maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 3600 | 5300 | - | - | −32.08 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | Cabbage | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 3900 | 5950 | - | - | −34.45 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | Sunflower | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 2700 | 4000 | - | - | −32.50 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | sugar beet | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 3500 | 4900 | - | - | −28.57 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | Garlic | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 2200 | 4000 | - | - | −45.00 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | Barley | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 1800 | 2800 | - | - | −35.71 | - | [36] |
| Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt | 31°6′ N, 30°56′ E | - | onion | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 2000 | 4300 | - | - | −53.49 | - | [36] |
| Maharashtra, India | 19°57′ N, 74°42′ E | 450.0 | Cabbage | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 319 | 600 | - | - | −46.83 | - | [37] |
| Kayeshpur, India | 23°5.4′ N, 83°5.4’ E | 1600.0 | Strawberry | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 160 | 233 | 169 | 247 | −31.33 | −31.78 | [38] |
| Qinghai, China | 36°22′ N, 96°27′ E | 57.1 | Barley | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 573 | 584 | 474 | 501 | −1.88 | −5.39 | [39] |
| Qinghai, China | 36°22′ N, 96°27′ E | 57.1 | Barley | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 534 | 554 | 432 | 480 | −3.61 | −10.00 | [39] |
| Qinghai, China | 36°22′ N, 96°27′ E | 57.1 | Barley | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 404 | 453 | 276 | 361 | −10.82 | −23.55 | [39] |
| Qinghai, China | 36°22′ N, 96°27′ E | 57.1 | Barley | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 361 | 405 | 241 | 281 | −10.86 | −14.23 | [39] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 340 | 525 | 332 | 553 | −35.24 | −39.89 | [40] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 340 | 525 | 361 | 526 | −35.24 | −31.33 | [40] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 340 | 525 | 421 | 533 | −35.24 | −21.09 | [40] |
| Ludhiana | 30°56′ N, 75°48′ E | 600.0 | Sunflower | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | - | - | 504 | 567 | - | −11.11 | [41] |
| Shandong, China | 36°50′ N, 118°52′ E | 550.0 | Tomato | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 364 | 535 | 185 | 199 | −31.96 | −7.04 | [42] |
| Shandong, China | 36°50′ N, 118°52′ E | 550.0 | Tomato | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 296 | 581 | 234 | 234 | −49.05 | 0.00 | [42] |
| Shibin El-Kom, Egypt | 30°30′ N, 31°18′ E | - | tomato | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | - | - | 314 | 600 | - | −47.67 | [43] |
| Henan, China | 34°27′ N, 113°31′ E | 542.0 | Cucumber | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 468 | 909 | - | - | −48.58 | - | [44] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 340 | 450 | 332 | 464 | −24.44 | −28.36 | [40] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 340 | 450 | 361 | 437 | −24.44 | −17.35 | [40] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135.0 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 340 | 450 | 421 | 439 | −24.44 | −4.19 | [40] |
| Southeast Spain | 39°03′ N, 2°05′ W, | 314.0 | Maize | drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 703 | 743 | 510 | 590 | −5.38 | −13.56 | [45] |
| Southeast Spain | 39°03′ N, 2°05′ W, | 314.0 | Maize | drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 642 | 722 | 480 | 620 | −11.08 | −22.58 | [45] |
| Henan, China | 35°08′ N, 113°45′ E | - | Wheat | Drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 210 | 240 | 299 | 302 | −12.50 | −0.99 | [34] |
| Henan, China | 35°08′ N, 113°45′ E | - | Wheat | Drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 180 | 210 | 310 | 307 | −14.29 | 0.98 | [34] |
| Maharashtra, India | - | Cabbage | Drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 319 | 471 | - | - | −32.27 | - | [37] | |
| Heilongjiang, China | 45°22′ N, 125°45′ E | - | Maize | Drip irrigation | Rainfed | - | - | 519 | 521 | - | −0.38 | [46] |
| Site | Latitude and Longitude | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Crop | Irrigation Method | Control Group | Pn Variation | NPP | NEE | Rs | DOC | SOC | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei, China | - | - | Winter Wheat | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 15% | - | - | - | - | - | [33] |
| Liaoning, China | - | - | Tomato | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | - | - | - | - | −7% | - | [72] |
| Southern Arizona, USA | - | 230 | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | - | - | + | [73] | |
| Inner Mongolia, China | 41°05′ N, 108°03′ E | Maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | + | + | + | - | - | [61] | |
| Bhubaneswar | 20° N, 85°38′ E | Capsicum | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 24% | - | - | - | - | - | [55] | |
| HID, China | 41°09′ N, 107°39′ E | 180 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | - | - | - | 17% | - | - | [74] |
| Heilongjiang, China | 45°22′ N, 125°45′ E | 600 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Rainfed | 13% | - | - | - | - | - | [56] |
| Heilongjiang, China | 45°22′ N, 125°45′ E | 600 | Maize | Drip irrigation | Rainfed | 42% | - | - | - | - | - | [56] |
| Imperial County, CA | - | - | Sudangrass | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | 1% | - | - | [66] |
| Imperial County, CA | - | - | Alfalfa | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | −50% | - | - | [66] |
| Xinjiang, China | 44°17′ N, 85°49′ E | 211 | Cotton | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | 5% | - | 0.40% | [75] |
| Xinjiang, China | 44°17′ N, 85°49′ E | 211 | Cotton | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | - | - | −2% | [75] |
| Hebei, China | 37°41′ N, 116°38′ E | - | Maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | - | - | 10% | - | - | [76] |
| Hebei, China | 37°41′ N, 116°38′ E | - | Maize | Drip irrigatHion | Rainfed | - | - | - | 25% | - | - | [76] |
| Bahia, Brazil | 12°40′ S, 39°06′ W | 1143 | Banana | Drip irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation | - | - | - | - | - | −21% | [77] |
| Xinjing, China | 87°56′ E, 44°17′ N | - | Cotton | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | - | 65% | - | 34% | - | - | [63] |
| Site | Latitude and Longitude | Annual Rainfall (mm) | Soil Type | Crop | Irrigation Method | Control Group | Yield (t ha−1) (Drip Irrigation) | Yield (t ha−1) (Control) | Amplitude of Variation | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan province, China | 38°1′ N, 115°5′ E | 555 | Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 11.32 | 8.84 | 28% | [93] |
| Hebei province, China | 37°41′ N, 116°38′ E | 600 | Silt loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 11.25 | 10.12 | 11% | [77] |
| Henan province, China | 35°18′ N, 113°54′ E, | 555 | Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 8.69 | 7.50 | 16% | [94] |
| Hebie province, China | 38°1′ N, 115°5′ E | 519 | Sandy Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 8.03 | 7.22 | 11% | [95] |
| Henan province, China | 35°11′30″ N, 113°48′ E | - | Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 8.40 | 7.48 | 12% | [96] |
| Henan province, China | 35°11′30″ N, 113°48′ E | 573 | Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 9.00 | 7.88 | 14% | [97] |
| Henan province, China | 34°47′ N, 113°38′ E | 480 | Sandy loam | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 22.45 | 20.43 | 10% | [60] |
| Shaanxi Province, China | 34°17′ N, 108°4′ E | 560 | Silty clay loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 11.05 | 8.45 | 31% | [98] |
| Xinjiang, China | 80°14′ E, 41°16′ N | 42.4–94.4 | Loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 12.63 | 11.50 | 10% | [99] |
| Egypt | 31°02′ N,30°28′ E | - | Sandy | - | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 7.98 | 7.49 | 7% | [100] |
| Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46′ N, 107°24′ E | 105 | Silty loam | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Flood irrigation | 16.06 | 14.25 | 13% | [70] |
| Jilin province, China | 45°33’ N, 122°78’ E | 419.7 | Clay | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 12.90 | 9.39 | 37% | [101] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135 | Sandy loam | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 16.00 | 13.00 | 23% | [41] |
| Faisalabad, Pakistan | 31.25° N, 73.09° E | - | Clay loam | - | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 10.02 | 4.58 | 119% | [102] |
| Marvdasht, Iran | 29°47′ N, 52°42′ E | 340 | Clay loam | - | Subsurface drip | Furrow irrigation | 11.91 | 10.02 | 19% | [103] |
| Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 11.49 | 10.02 | 15% | ||||||
| Coimbatore, India | 11°8′ N, 77°8′ E | 648 | Sandy Clay | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 7.57 | 5.31 | 43% | [104] |
| Guanajuato, Mexico | 20°45 ′ N, 101°20′ W | 700 | - | - | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 13.15 | 12.45 | 6% | [25] |
| Colorado State, USA | 38°2′23″ N, 103°41′43″ W | - | Clay loam | - | Subsurface drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 13.20 | 12.70 | 4% | [105] |
| Van, Turkey | 38.576° N, 43.29° E | 393.8 | Sandy clay loam | - | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 13.92 | 12.71 | 10% | [106] |
| Southern Mozambique | 25°19′13″ S; 32°15′53″ E, | 580 | Sandy laom | - | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 5.81 | 5.50 | 6% | [107] |
| Ludhiana, India | 30°54′ N; 75°48′ E | - | Sandy loam | - | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 8.00 | 6.62 | 21% | [108] |
| Nebraska, USA | 44.6° N, 98.1° W; | 680 | Silt loam | - | Subsurface drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 16.25 | 14.45 | 12% | [109] |
| Ladhowal, India | 30.99° N, 75.44° E | 680 | Sandy loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Furrow irrigation | 5.18 | 4.63 | 12% | [90] |
| Bayannur of Inner Mongolia, China | 40°46″ N, 107°24″ E | 135 | Sandy loam | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 16.00 | 13.20 | 21% | [41] |
| Inner Mongolia, China | 41°09′ N, 107°39′ E | 160 | Loam | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 14.25 | 13.70 | 4% | [110] |
| Inner Mongolia, China | 40°43 ′ N, 107°13′ E | 135 | Silty loam | Spring maize | Fully mulched drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 14.41 | 10.28 | 40% | [111] |
| Inner Mongolia, China | 40°43 ′ N, 107°13 ′ E | 135 | Silty loam | Spring maize | Partially mulched drip irrigation | Border irrigation | 11.36 | 10.28 | 11% | [111] |
| León, Spain | 5°31′18″ W, 42°19′9″ N, | - | Sandy loam | - | Drip irrigation | Sprinkler irrigation | 17.68 | 17.01 | 4% | [112] |
| Heilongjiang province, China | 45°22′ N, 125°45′ E | 400–650 | Silty loam | Spring maize | Mulched drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 12.48 | 10.16 | 23% | [58] |
| Non-mulched drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 11.66 | 10.16 | 15% | ||||||
| Jilin province, China | 43°21′ N, 124°05′ E | 540 | Loam sandy | Spring maize | Drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 13.45 | 11.34 | 19% | [113] |
| Heilongjiang province, China | 45°22′ N, 125°45′ E | 400–650 | - | Spring maize | Mulched drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 11.50 | 9.45 | 22% | [57] |
| Non-mulched drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 11.00 | 9.45 | 16% | ||||||
| Shaanxi Province, China | 34°17′ N, 108°4′ E | 560 | Silty clay loam | Summer maize | Drip irrigation | Rain-fed | 11.10 | 10.20 | 9% | [114] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Li, S. A Review of Drip Irrigation’s Effect on Water, Carbon Fluxes, and Crop Growth in Farmland. Water 2024, 16, 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152206
Guo H, Li S. A Review of Drip Irrigation’s Effect on Water, Carbon Fluxes, and Crop Growth in Farmland. Water. 2024; 16(15):2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152206
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hui, and Sien Li. 2024. "A Review of Drip Irrigation’s Effect on Water, Carbon Fluxes, and Crop Growth in Farmland" Water 16, no. 15: 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152206
APA StyleGuo, H., & Li, S. (2024). A Review of Drip Irrigation’s Effect on Water, Carbon Fluxes, and Crop Growth in Farmland. Water, 16(15), 2206. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152206





