Abstract
This work focused on the decolorization of methyl red (MR) from an aqueous solution utilizing Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar (RAB). RAB was prepared to involve unit operations such as size reduction, drying, and carbonization. The pyrolysis of the precursor material was carried out at a temperature of 500 °C for two hours. After that, the prepared RAB was characterized by the pH point of zero charge (pHpzc), the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. On the other hand, a batch adsorption experiment of MR removal onto RAB was conducted, considering four operating parameters: pH, contact time, adsorbent dose, and initial dye concentration. The characterization of the adsorbent material revealed a porous and heterogeneous surface morphology during SEM, a specific surface area of 45.8 m2/g during the BET method, the presence of various functional groups during FTIR, and a pHpzc of 6.2. The batch adsorption experiment analysis results revealed that a maximum removal efficiency of 99.2% was attained at an optimum working condition of pH 6, contact time of 40 min, initial dye concentration of 70 mg/L and adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL. Furthermore, Freundlich isotherm (R2 = 0.99) and pseudo-second-order kinetics (R2 = 0.99) models confirmed the heterogeneous surface interaction and chemisorption nature. Generally, this study highlighted that RAB could be a potential adsorbent for the detoxification of MR-containing industrial effluents.
1. Introduction
Meeting goal 6 of the sustainable development agenda (clean, safe, sufficient, and affordable water for all of humanity) has remained challenging due to various anthropogenic and natural factors [1]. Human-induced activities, in particular, have become serious sources of water pollution, affecting the quality and quantity of freshwater [2]. According to a European investment bank report, about 380 billion cubic meters (BCM) of wastewater is generated annually worldwide, increasing alarmingly, and it is estimated to reach 470 and 574 BCM by 2030 and 2050, respectively [3]. This condition causes water quality deterioration and a reduction in its quantity, as most untreated and inadequately treated wastewater is discharged into nearby water bodies [4,5]. In line with this, industrialization has contributed profoundly to wastewater generation, and about 80% of industrial effluents are emitted into the nearby water channels [6].
Regarding wastewater generation, the textile industry is among the frontline contributors of wastewater, because about 93 BCM of fresh water is utilized in different stages of textile processing, which is estimated to be 4% of freshwater extraction globally [7]. Furthermore, industrial textile processing, such as the dyeing and finishing stages, consumes 200 L of water per kg of fabric processed, resulting in 17–20% wastewater [8]. In line with this, textile industry-based wastewater is characterized by high amounts of biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total solids and massive dyes [9], posing serious risks to human health and aquatic biota [10]. In particular, dye-saturated textile wastewater can potentially cause diseases like cancer and negatively affect aquatic biota [11].
Methyl red (MR) is a synthetic, anionic mono-azo dye with a chemical formula of C15H15N3O2 and a molecular weight of 269.30 g/mol that is almost insoluble in water, but more soluble in other solvents like glacial acetic acid, ether and methanol [12,13,14]. It is a reactive dye widely used as an acid–base indicator in laboratories [15]. Additionally, methyl red is applied in the textile dyeing and finishing processes [16] due to its high color-fixing performance and mild fading [16]. However, MR-saturated effluents raise concerns regarding human health and environment-related problems [17,18]. Long-term exposure to MR has been found to pose health risks like skin damage, and it can irritate the digestive system and eyes [19].
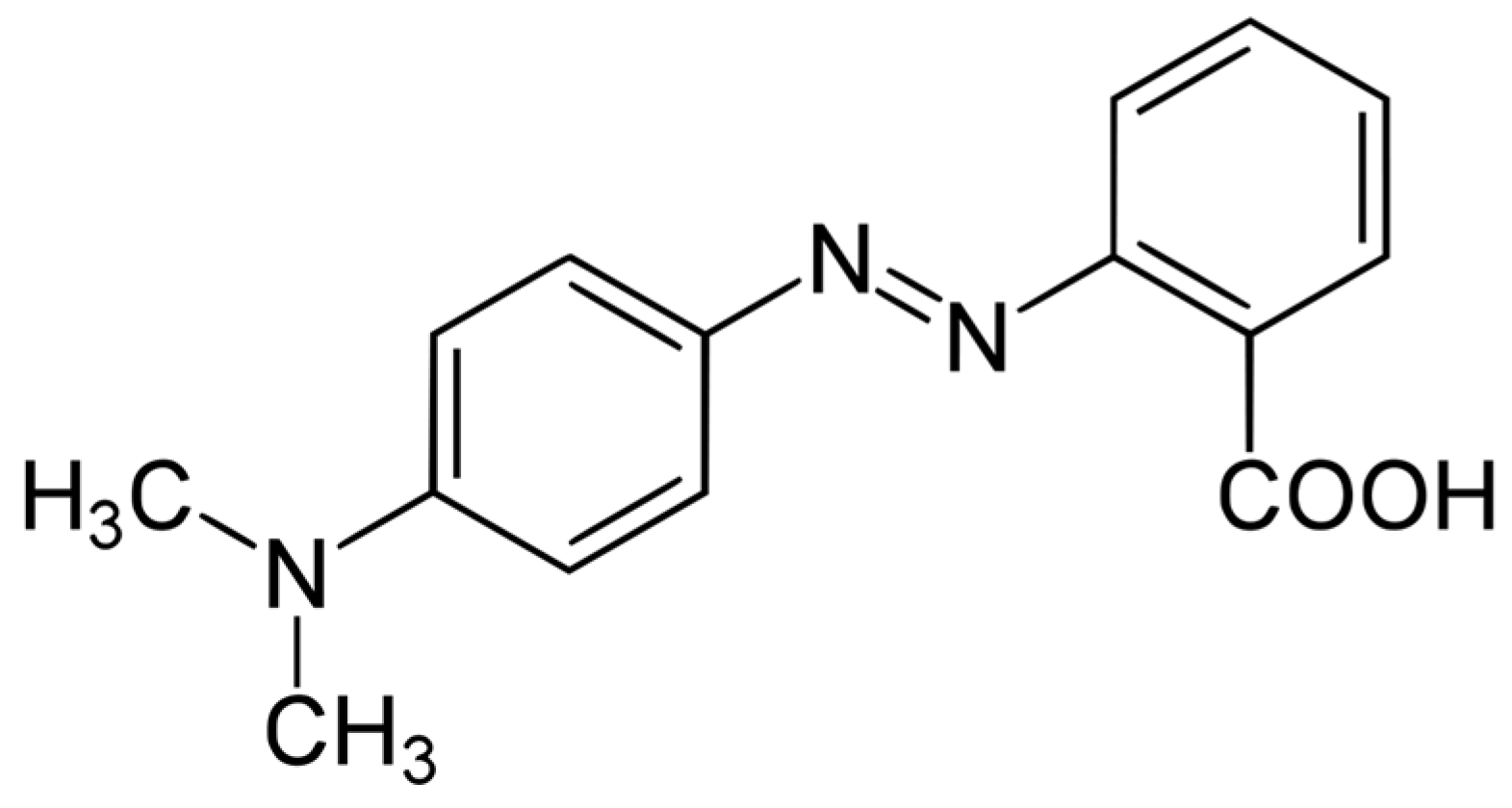
Furthermore, MR is known to be mutagenic, toxic, and carcinogenic, and its complex decomposition in water bodies makes it harmful to aquatic biota [20,21]. MR is considered mutagenic, toxic, and carcinogenic due to its complex aromatic molecular structure, which makes it more stable and difficult to biodegrade [22]. The presence of azo groups in the chemical structure of MR is responsible for its mutagenic and carcinogenic properties [23]. The azo group (–N=N–) is known to undergo reductive cleavage, leading to the formation of toxic aromatic amines [24]. The presence of these aromatic amines in MR contributes to its toxicity and potential carcinogenicity [25]. The chemical structure of MR consists of a benzoic acid moiety attached to a dimethylamino group through an azo linkage [26]. The azo linkage (–N=N–) is the functional group responsible for the color and reactivity of MR. The chemical structure of MR is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Chemical structure of methyl red.
Hence, treatment interventions are critical before discharging MR-saturated wastewater into nearby water bodies. Various MR decolorization techniques have been explored, aiming to mitigate its environmental and health impacts. These include traditional wastewater treatment techniques such as coagulation/flocculation [27], neutralization [28] and precipitation. However, these conventional methods face challenges in effectively removing MR from wastewater due to the persistent nature of the dye [29]. Hence, advanced wastewater treatment techniques such as the electrochemical process [14], photocatalytic degradation [30], membrane filtration [31], electron photo-Fenton oxidation [32], and reverse osmosis [33] are widely used for MR decontamination. These techniques effectively remove MR from aqueous or textile wastewater [34]. However, certain drawbacks such as their massive chemical consumption, high capital requirement, energy intensiveness, need for skilled human resources and formation of secondary pollutants [35] necessitate the search for environmentally benign, socially acceptable, low-cost and easily accessible treatment methods such as adsorption [36].
Adsorption, defined as the deposition of molecular species onto a solid surface [37], is regarded as a green, clean and versatile method for water and wastewater treatment [37]. Herein, the molecular species that gets adsorbed on the surface is known as the adsorbate, and the surface on which adsorption occurs is known as the adsorbent [38]. Hence, adsorption is a surface phenomenon affected by various parameters such as the temperature, concentration, contact time, pH and adsorbent dosage [39]. Adsorption techniques are classified into physisorption and chemisorption. Physisorption (physical adsorption) is reversible, does not need activation energy, is characterized by non-specificity and occurs via weak Van der Waals forces.
In contrast, chemisorption (chemical adsorption) is known for its irreversibility, specificity, formation of chemical bonds and need for activation energy [40]. Various adsorbent materials are utilized to remove contaminants from water and wastewater. These include natural minerals such as rocks and soils [41], coal-based adsorbents [42] and biomass-derived adsorbents [43]. Numerous selection criteria are considered when choosing the best-performing adsorbent materials. These include local availability, a large specific surface area, high chemical reactivity, porosity, cost-effectiveness, renewability and removal efficiency [44].
Adsorption has been extensively studied for MR removal from textile wastewater and the aqueous environment. Previous research has demonstrated the efficiency of various adsorbents, such as commercial activated carbon [45], zeolites [46], and biosorbents derived from agricultural waste [47]. Among these, commercial activated carbon has gained considerable attention due to its high surface area, pore structure, and adsorption capacity [48]. However, the sustainable development of an adsorbent is crucial to ensure its long-term viability as an effective adsorbent. The production of an adsorbent from non-renewable resources raises concerns regarding its environmental impact and long-term availability [49]. Therefore, researchers have focused on developing biobased activated carbon/biochar derived from biomass waste materials, such as agricultural residues, wood waste, and biochar. These biobased activated carbons offer a sustainable alternative and economic benefits by utilizing waste materials [50]
Various biomass-derived adsorbents have been applied for the removal of methyl red. For instance, a sorbent made of Annona squamosa leaves and barks achieved a maximum adsorption capacity of 7.2 mg/g [51]. Additionally, Bali cow bones-based hydrochar material reached a capacity of 7.2 mg/g [52]. Raphanus caudatus powdered leaves biomass exhibited a capacity of 30.86 mg/g [53]. These studies showcase the diverse adsorption capacities of different biomass-derived adsorbents for methyl red, highlighting their potential in wastewater treatment applications. However, the low adsorption capacities recorded in these studies necessitate the exploration of new locally available precursor materials, such as Rumex abyssinicus, which exhibit greater adsorption capacity.
Rumex abyssinicus, a 3–4 m tall herb found in tropical Africa, North Africa, and Ethiopia [54], is a traditional medicine used for treating diseases like sexually transmitted diseases, fungal infections, diabetes, lung tuberculosis, and leprosy [55,56]. Its roots and bark lower blood pressure, heal wounds and treat stomachaches [57]. However, the remaining parts are often discarded. This study aims to use biochar synthesized from the Rumex abyssinicus stem as an effective adsorbent for pollutant detoxification. Previous research focused on producing activated carbon from Rumex abyssinicus and its application in dye decolorization. However, preparing activated carbon from biomaterials necessitates activating agents such as chemicals and carbonization at an elevated temperature.
Furthermore, the tedious steps required to wash the acid/base used for neutralization, in addition to the massive chemical consumption and energy intensiveness, make the bio-based activated carbon preparation process uneconomical and time-consuming. Hence, this work focused on producing and applying Rumex abyssinicus-based biochar (RAB) for MR removal from aqueous solutions. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, no research has been conducted on the preparation of biochar from the Rumex abyssinicus plant. Additionally, no study has addressed the removal of MR from wastewater or aqueous solutions using RAB, which highlights the presence of a research gap. Hence, this study addresses the lack of research on the production and application of Rumex abyssinicus-based biochar for MR removal from aqueous solutions.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Biochar Preparation
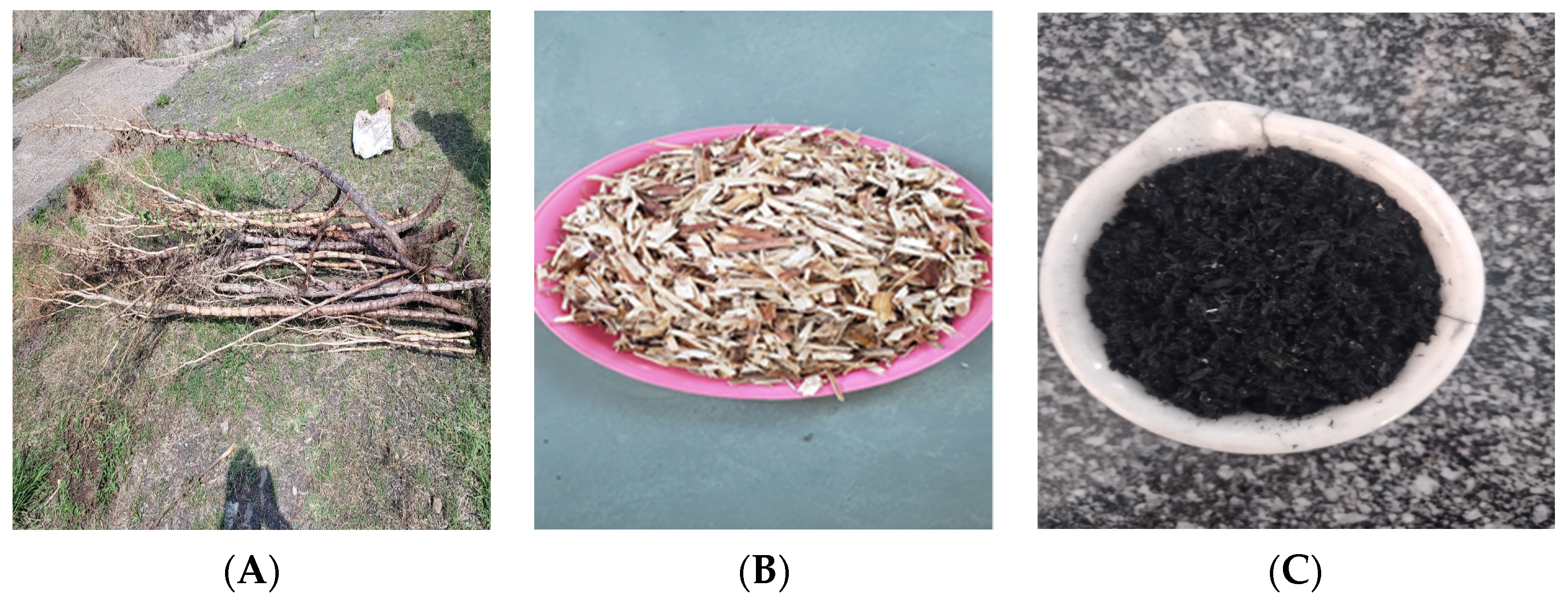
The precursor material (Rumex abyssinicus) utilized in this work was collected from Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. The sun-dried stem of Rumex abyssiniccus was thoroughly washed with tap water before being rinsed with distilled water to eliminate dirty materials that may affect the potential of the adsorbent material. After that, the dust-free sample of Rumex abyssinicus was oven-dried (model BOV-T50F, BIOBASE, China) at a temperature and time of 105 °C and 24 h, respectively. The completely dried precursor material was then pulverized into smaller pieces using a mechanical granulator (Hummer mill-008, STEDMAN, USA). The pyrolysis of the precursor material was carried out using a muffle furnace (Model Nabertherm F 330, Cole Parmer, Canada) at a carbonization temperature of 500 °C for two hours. During the carbonization process, a heating rate of 25 °C/min was used. Figure 2 depicts the major steps followed for the development of biochar from Rumex abyssinicus biomass. Finally, the prepared adsorbent material was cooled in a desiccator, reduced to a particle size of 250 μm and stored in a zip locker for subsequent batch adsorption and adsorbent characterization experiments [58,59,60].

Figure 2.
RAB preparation stages: (A) stem of Rumex abyssinicus, (B) partially size-reduced sample and (C) ready-made adsorbent.
2.2. Adsorbent Characterization
2.2.1. pH Point of Zero Charge
Techniques such as acid titration and salt addition are widely used to determine the pH point of zero charges (pHpzc), so the mass addition method for pHpzc determination was used in this study. Precisely, six 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks were used to prepare 50 mL of 0.1 M NaCl, and the pH variation between 2 and 12 was adjusted using 0.1 M HCl or 0.1 M NaOH. After adjusting the pH, 1 g of the sample was added to each of the flasks and the sample was shaken at 125 rpm for 48 h. In the end, the pHpzc for the sample was determined by drawing curves relating to the initial pH and pH (pH initial–pH final) [61].
2.2.2. The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller Surface Area Analysis
The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was employed in order to ascertain the specific surface area of the adsorbent material. Within this methodology, a BET sampler was utilized to prepare 0.4 g of the adsorbent, which was subsequently degassed under vacuum conditions at a temperature of 200 °C for a duration of 1 h. The adsorption–desorption isotherm of nitrogen at an atmospheric pressure of 700 mm was employed to determine the specific surface area of the adsorbent. The adsorption of nitrogen on the adsorbent’s surface was intensified through the utilization of liquid nitrogen at a temperature of −196.5 °C. Ultimately, the BET-specific surface area of the biochar was assessed on the basis of the partial pressure to saturated vapor pressure ratio [62].
2.2.3. Surface Morphology Analysis
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) analysis was performed in order to examine the various surface morphologies and porosity formation that characterized the adsorbent. The operating procedures outlined in the SEM machine manual were utilized to prepare the samples and conduct the scanning. In this study, RAB powder was attached to aluminum specimen stubs that had double-sided SEM functionality. These stubs were sputter-coated with a thin layer of gold. Imaging was carried out using a resolution of 10 μm and a guaranteed capacity of 10 kV, using the JCM-6000PLUS BENCHTOP SEM (JOEL), a model from Japan [63,64].
2.2.4. Functional Group Analysis
Functional group analysis was carried out using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR, (FT-IR spectroscopy, Perkin Elmer, USA)). Recording of the FTIR spectrum was performed in the region of 4000 to 400 cm−1. In this process, the adsorbent was mixed thoroughly with dry KBr at the ratio of 2:200. Formerly, the mixture of the adsorbent and dry KBr was crushed in a mortar to yield a homogenous powder combination. Then, the powder was injected into a molder to produce a very fine plate. Finally, FTIR data graphs were presented using Origin Pro version 22.
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
The stock solution of the target pollutant (MR) was prepared by dissolving 1 g of MR in 1 L of distilled water, giving a dye concentration of 1000 mg/L. Then, serial dilution was thoroughly performed to obtain the intended concentration of MR. The optimization of MR removal was carried out considering the four operating parameters affecting the batch adsorption efficiency. Accordingly, the pH, adsorbent dosage, contact time and initial MR dye concentration were optimized using the one variable at a time (OVAT) approach. Normally, in OVAT, changing one variable is accompanied by fixing other variables at their specified values. Therefore, the effects of the operating parameters were investigated by varying the pH (3–9), contact time (20–60 min), adsorbent dosage (0.1–0.3 g/100 mL) and MR concentration of 50–100 mg/L. The temperature was maintained at 25 °C for all batch adsorption experiments whereas a shaking speed of 250 rpm was used. The residual MR left unadsorbed was quantified using UV–Vis spectroscopy (JASCO V-770, JASCO, and Oceania) at a maximum wavelength of 520 nm. Precisely, 100 mL of the target pollutant solution was transferred into an Erlenmeyer flask, whose pH was adjusted using 0.1 M NaOH and HCl, depending on the required pH value. A known amount of the adsorbent material was added to the pH-adjusted solution. The adsorption process was then initiated by placing the target pollutant and adsorbent material mixture in an orbital shaker (70–400 LCD Digital Orbital Shaker) at 250 rpm. As the contact time expired, the solution was filtered out using Whatman filter paper and the filtrates were collected using various sampling bottles. Then, the dye-containing solution was transferred into a cuvette, and the absorbance reading was carried out by inserting the residual dye-containing cuvette into the UV–Vis spectroscope (JASCO V-770, JASCO, Oceania). The absorbance read was then used to calculate the final MR concentration. Finally, the adsorption capacity (QE) in mg/g and the removal efficiency (RE) in % were calculated using Equations (1) and (2), respectively.
where and both in mg/L, denote the initial and final dye concentration, respectively, and m and V are the mass of Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar (g) and the volume of the solution (L), respectively [52].
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
Langmuir and Freundlich are the most popular adsorption isotherm models used to investigate the nature of the adsorption at equilibrium [65,66]. Fundamentally, these two isotherm models differ because the Langmuir isotherm is assumed to indicate monolayer and homogenous surface interaction. In contrast, the heterogeneous and multilayered interaction was observed when the Freundlich isotherm model was found to fit data better [67,68]. The equations for the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models.
Varied initial dye concentrations (50, 60, 70, 80, 90 and 100 mg/L) at the constant operating conditions of pH 6, a contact time of 40 min and an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL were used while investigating the adsorption isotherm.
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
The rate of the target pollutant uptake and the adsorption mechanism were investigated using various kinetics models [69,70]. The pseudo-first-order (PFO), pseudo-second-order (PSO) and intraparticle diffusion (IPD) models are the most widely used kinetic models. During the kinetic study of MR adsorption onto RAB, the contact time was varied from 20 to 60 min while maintaining the other independent variables at their respective values of pH 6, an MR concentration of 70 mg/L and an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL. Finally, the equations for the PFO, PSO, and IPD models are presented in Table 2 [61].

Table 2.
Adsorption kinetics models.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Adsorbent Characteristics
3.1.1. pH Point of Zero Charge
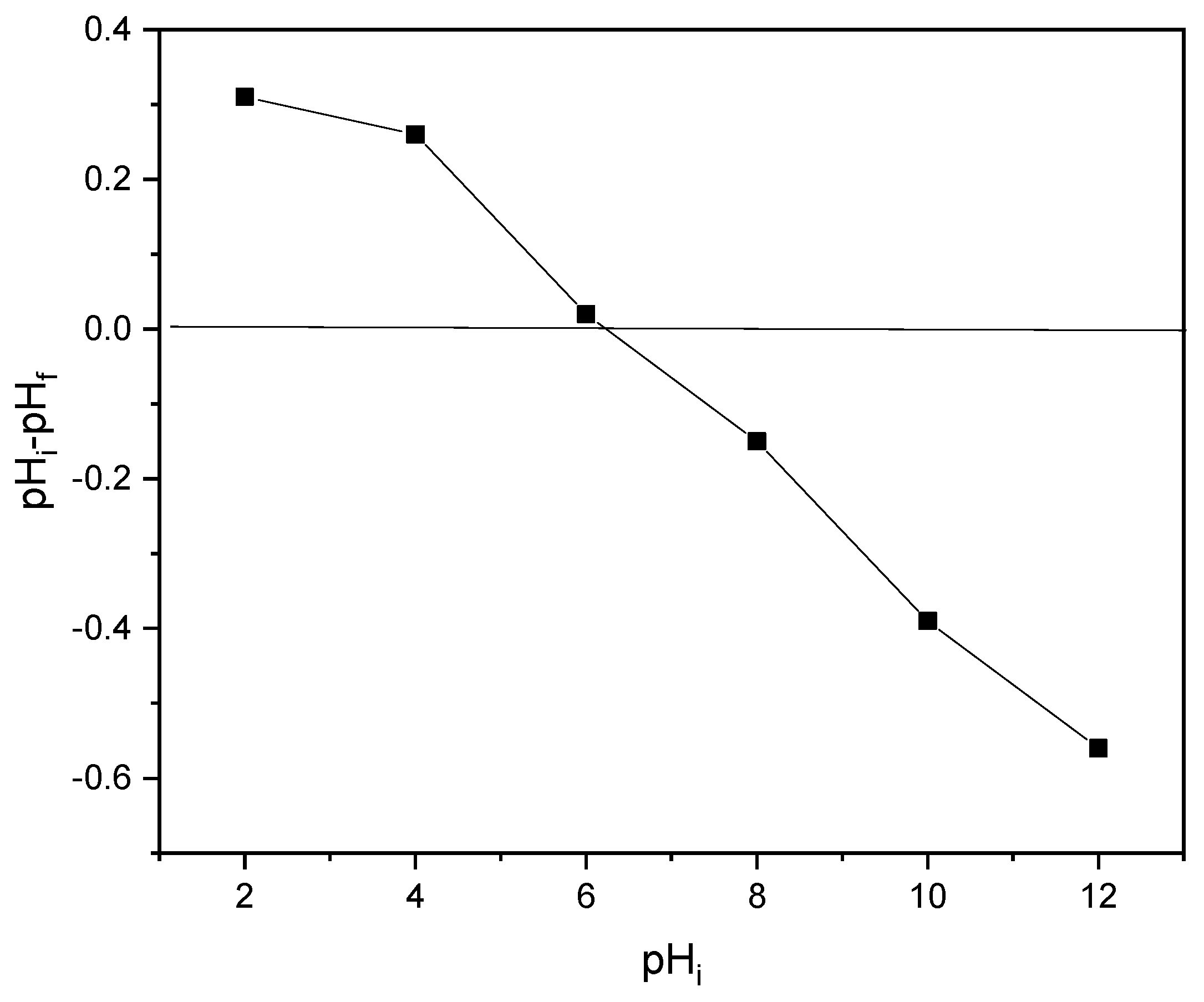
The pH of zero charges (pHpzc) is the pH value at which the surface density of cations, or positive charges, equals the surface density of anions or negative charges. Its value is paramount since many adsorption processes depend highly on pH. As a result, the pHpzc of the RAB was determined to be 6.2, as shown in Figure 3. This indicated that the surface density of the adsorbent material is negatively and positively charged, above and below the pH value of 6.2, respectively. Hence, anionic dyes like MR are significantly adsorbed when the pH of the solution is less than 6.2. This pHpzc value is comparable with the values reported by the same researchers for Rumex abyssinicus-based adsorbents, such as pHpzc values of 7.9 [71], 5.03 [72], 6.9 [73], 5.1 [74] and 7.2 [75].

Figure 3.
pH point of zero charge for RAB0.
3.1.2. SEM Analysis
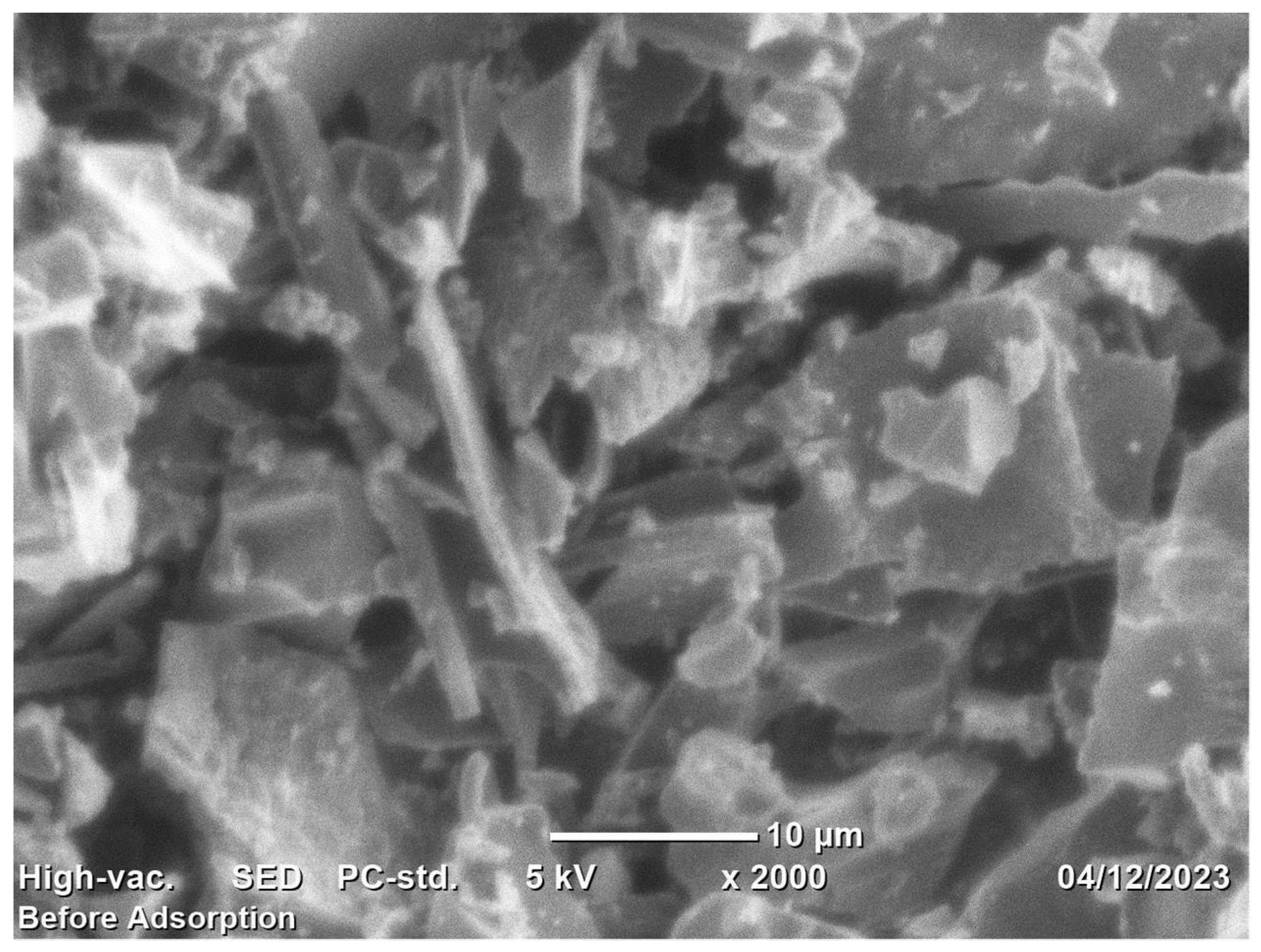
Figure 4 displays the RAB SEM image magnified 2000 times at a resolution of . The RAB appears in dark and bright colors, as shown in Figure 1. Throughout the carbonization process, Rumex abyssinicus undergoes breakdown, polycondensation, and cyclization, which turn it into a material with a high carbon content. The SEM micrograph shows that surface porosity and roughness developed on the char’s smooth surface. This was explained by the carbon structure breaking down during pyrolysis at 500 °C. Fundamentally, biochar with holes, cavities, morphological cracks, pores and rough surfaces is suitable for surface adsorption. As a result, the adsorption capacity and removal efficiency of the target pollutant tend to increase [76,77,78].
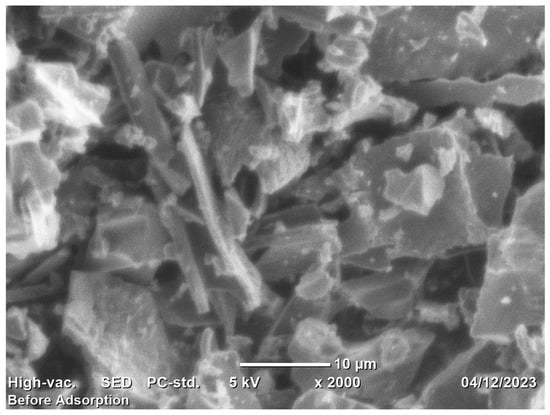

Figure 4.
SEM micrograph of Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar.
3.1.3. FTIR Analysis
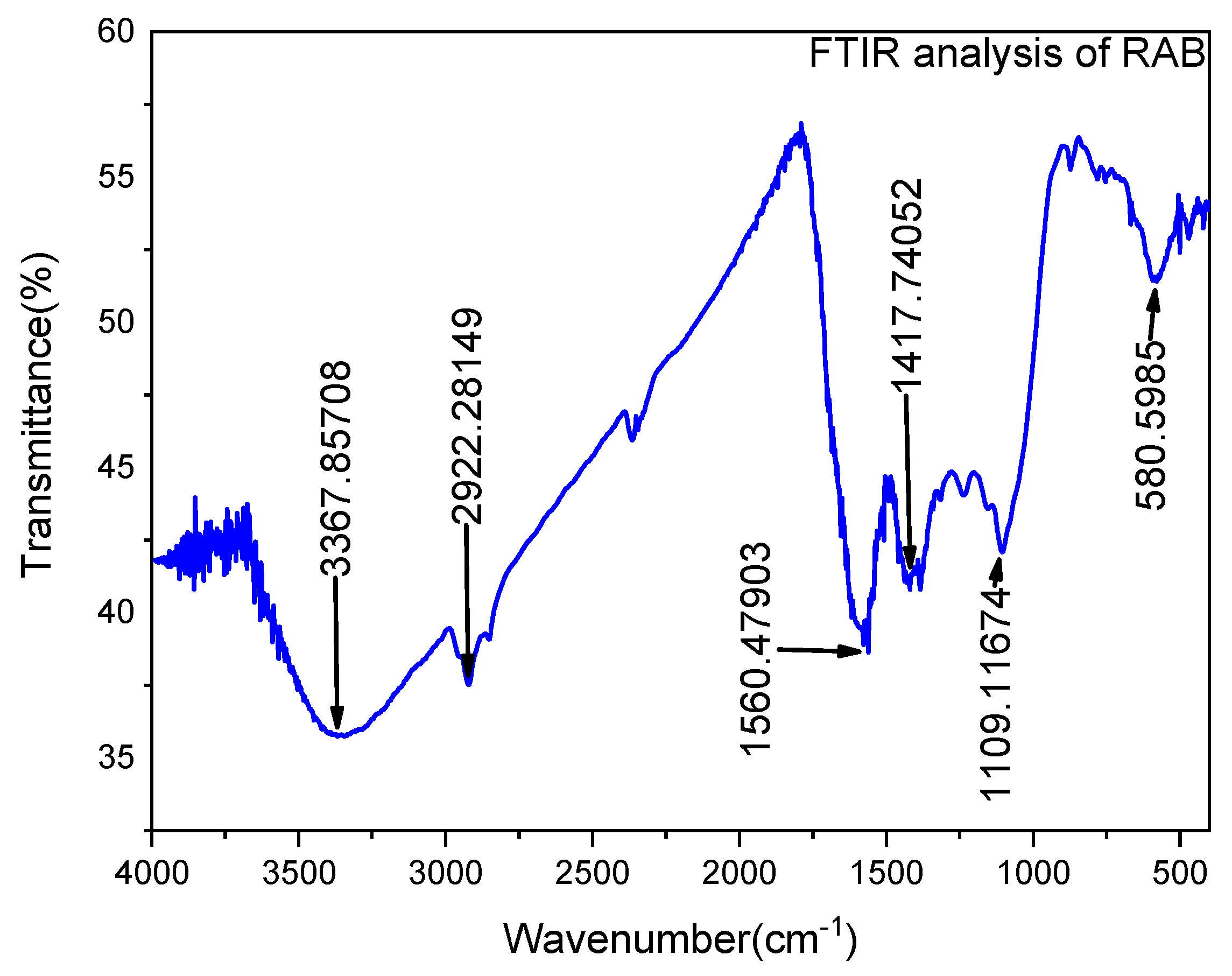
The functional group composition of the adsorbent material was investigated using FTIR along a wavelength range of 4000–400 cm−1, as shown in Figure 5. The FTIR spectrum of Rumex abyssinicus-based biochar reveals several prominent peaks corresponding to specific functional groups. The peak at 3367 cm−1 indicates the presence of hydroxyl (OH) groups, possibly associated with surface hydroxyls or hydroxylated aromatic structures. Aliphatic C–H stretching vibrations are observed at 2922 cm−1, suggesting the presence of aliphatic hydrocarbons. Carboxylic acid (COOH) functional groups are evident at 1190 cm−1, while the peak at 1417 cm−1 signifies aromatic C=C stretching vibrations, indicative of aromatic structures within the biochar. Additionally, the presence of C–O stretching vibrations at 1560 cm−1 suggests the presence of ether or ester functional groups, while the peak at 580 cm−1 corresponds to alkene (C=C) stretching vibrations, indicating the presence of unsaturated hydrocarbons. Together, these functional groups contribute to the diverse chemical properties of the biochar, potentially influencing its applications in various fields [79].
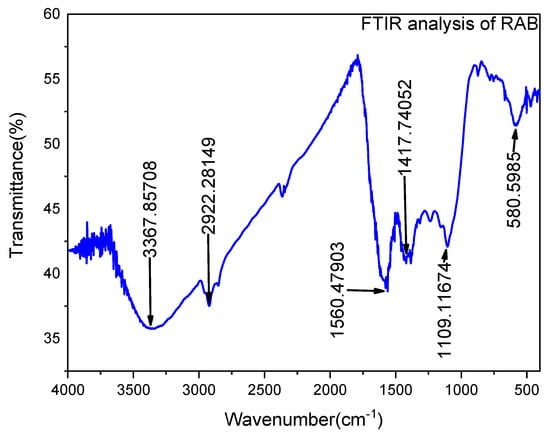
Figure 5.
FTIR peaks for Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar.
3.1.4. BET Analysis
The BET surface area of the adsorbent material was determined to be 45.8 m2/g. This surface area is lower than that reported for the same precursor material-based activated carbons. Precisely, BET-specific surface areas of 2522 m2/g [72], 524 m2/g [73], 962.3 m2/g [74] and 3619.7 m2/g [75] were reported in previous research. The significant decrease in the surface area of the biochar compared to the activated carbons of the same material is attributed to the absence of chemical activation. Normally, activated carbons have higher surface areas than biochar because activated carbons are produced at elevated temperatures and necessitate chemical treatments. However, a higher specific surface area alone does not determine the quality of the adsorbent material since the surface morphologies and composition of functional groups are vital for adsorbent development. The specific surface area of this adsorbent material is still higher than that of many unmodified biochars prepared from biomass residue and lignocellulosic materials, with surface areas like 1.71 m2/g [80], 44.38 m2/g [81], 17.65 m2/g, 20.9 m2/g [82], 9 m2/g [83] and 17.65 m2/g [84].
3.2. Effect of Operating Parameters
3.2.1. Effect of Contact Time
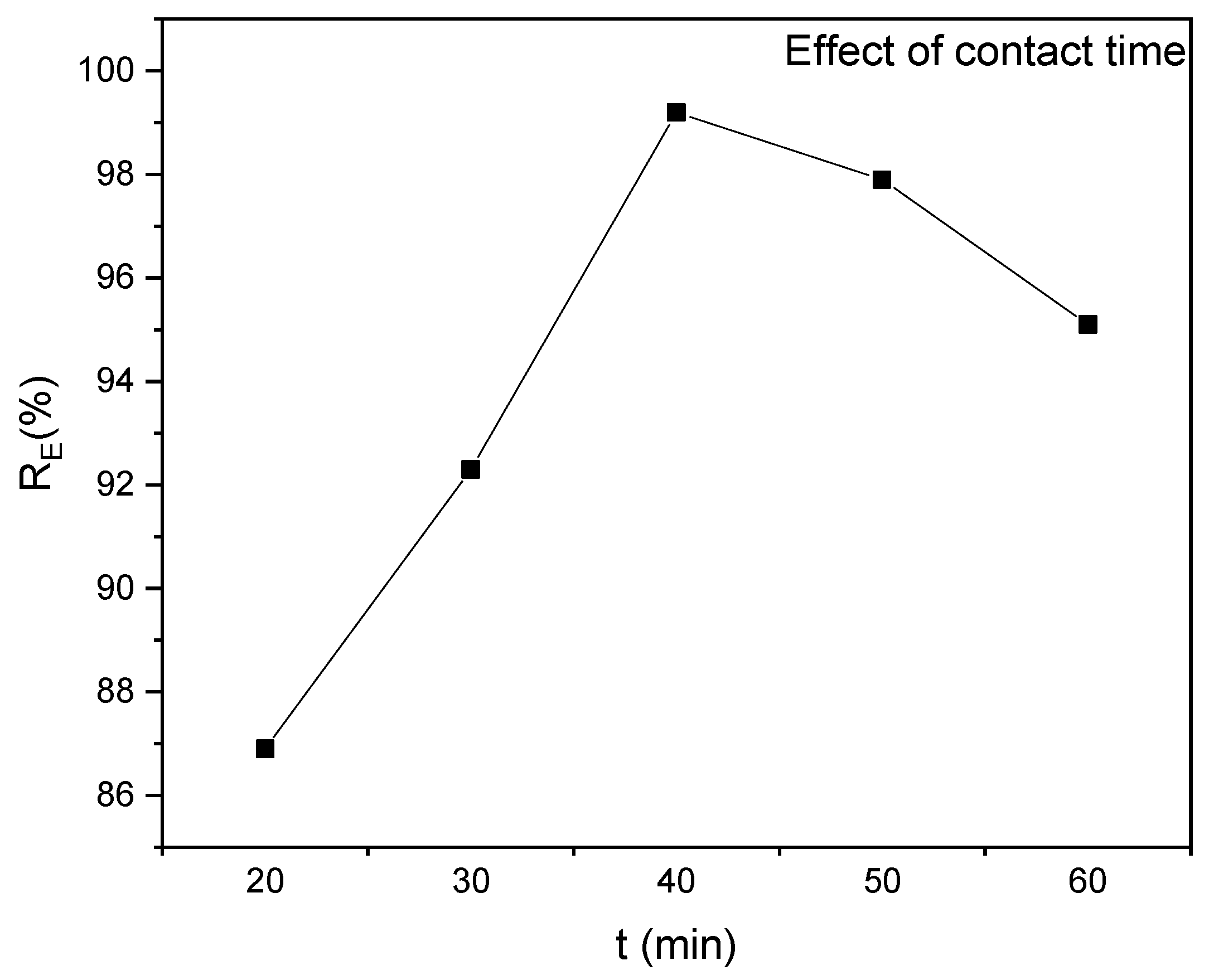
The contact time impacts the removal efficiency and capacity of pollutants to be adsorbed onto the adsorbent materials. This study evaluates the impact of contact time on the adsorption capacity and removal percentage when removing methyl red from an aqueous solution using RAB. Different contact times were used, with a constant pH of 6, adsorbent dose of 0.2 g/100 mL, and initial methyl red concentration of 70 mg/L. The removal process occurs in three stages: initial, intermediate, and equilibrium. The initial stage involves rapid uptake due to a higher concentration gradient and increased adsorption capacity. As the contact time increases, the concentration gradient driving force and available active sites decrease, decreasing the adsorption rate and removal percentage [85]. As shown in Figure 6, the equilibrium stage occurs at 40 min, with a maximum removal percentage of 99%.

Figure 6.
Effect of contact time on MR removal efficiency at pH 6, an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL and an initial dye concentration of 70 mg/L.
3.2.2. Impact of Initial MR Concentration
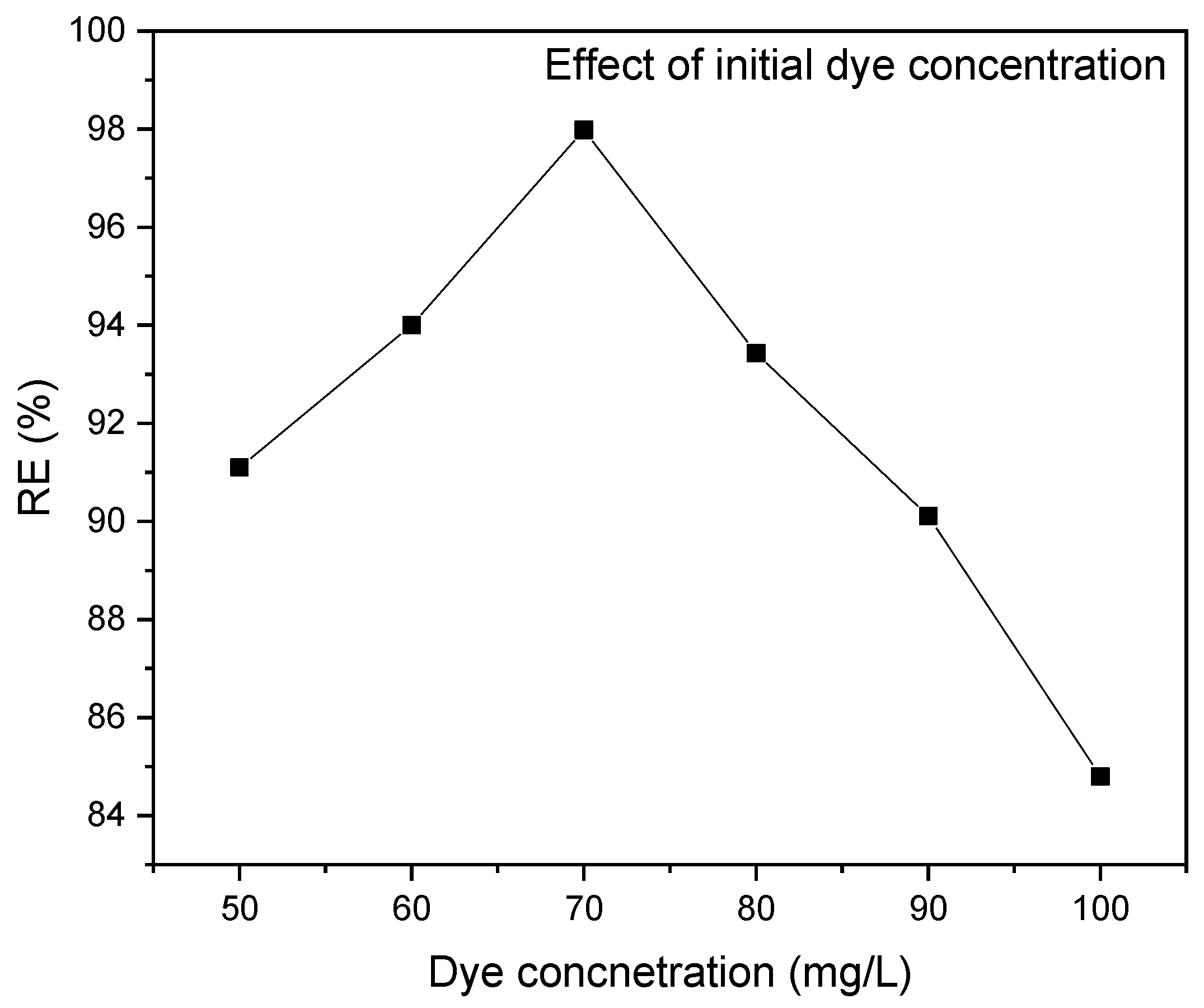
This study investigated the influence of the initial solution concentration on the uptake of MR on RAB. The results showed a reduction in the MR percentage removal from 91.1 to 82.62% when the concentration of MR was increased from 50 to 100 mg/L, as depicted in Figure 7. This is due to the high surface area and more unoccupied adsorption active sites at the lowest solution concentration. However, there are limited active sites at higher initial concentrations, resulting in a reduction in MR ion removal [86]. The study also found that increasing the solution concentration increases the number of solute molecules dispersed in the solution, allowing for toxic MR uptake onto the RAB surface.

Figure 7.
Effect of initial MR concentration on the dye removal efficiency at pH 6, a contact time of 40 min and an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL.
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
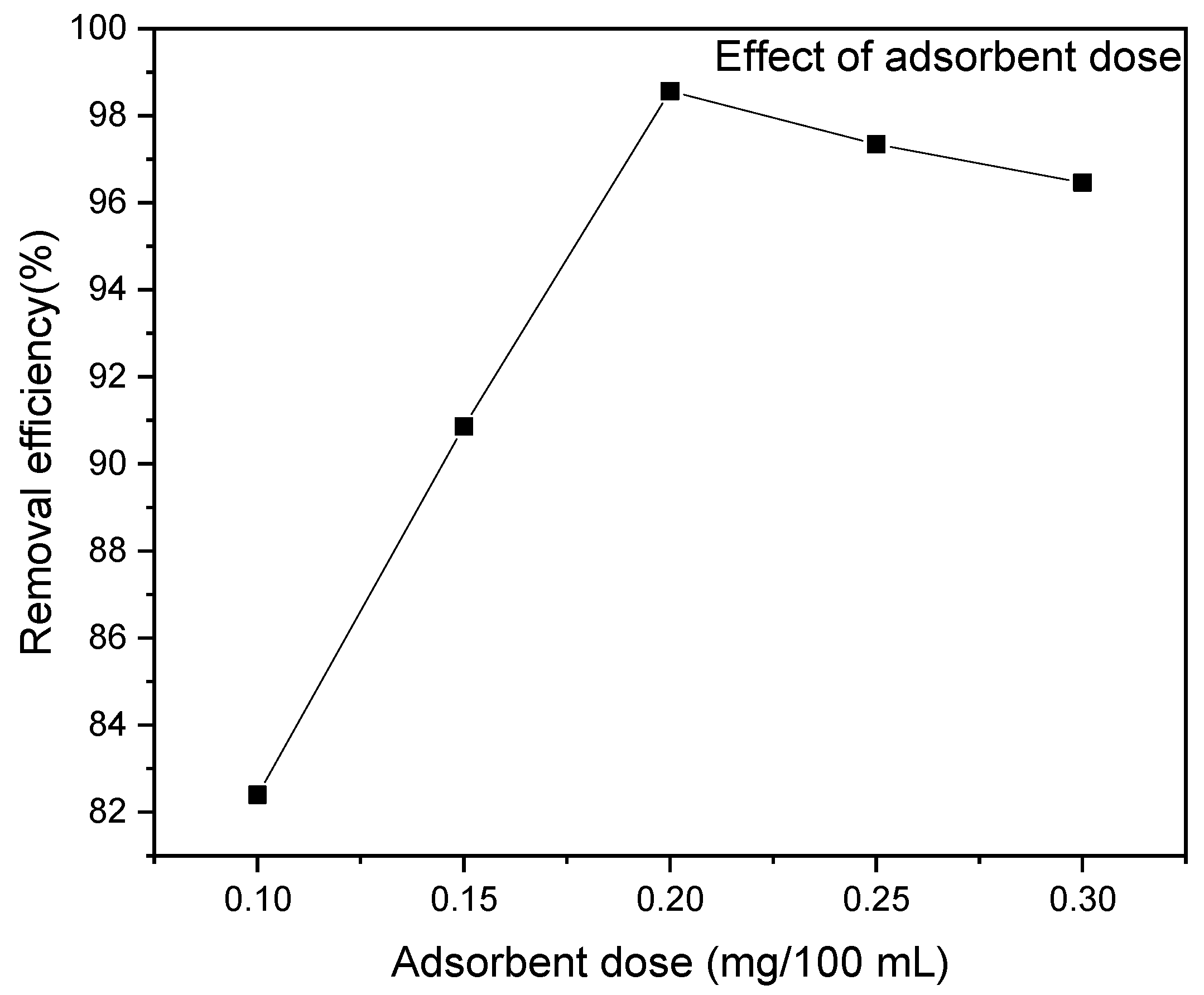
The adsorbent dose is crucial in adsorption studies as it affects the adsorbent–adsorbate equilibrium. This study investigated the effect of the RAB dose on MR adsorption at pH 6, a concentration of 70 mg/L, and a contact time of 40 min, as shown in Figure 8. The results showed that increasing the RAB dose from 0.1 to 0.3 g/100 mL increased the MR adsorption capacity from 28.3 to 33.79 mg/g. Under the same condition, the MR molecule percentage removal increased with increasing the adsorbent dose from 82.4 to 96.46%. A maximum MR adsorption removal of 98.56% and an adsorption capacity Qe of 34.5 mg/g were achieved at an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL. The higher uptake at a low pH is attributed to the strong attraction between the protonated surface of the RAB and the species of MR in the solution. The optimum adsorbent dosage was 0.2 g; when the biosorbent dosage is increased beyond this point, the adsorption capability decreases because fewer MR ions occupy the active sites [87]. Additionally, the slight decrease in the removal efficiency observed after a 0.20 mg/100 mL adsorbent dosage is likely due to the agglomeration of adsorbent particles at higher dosages, which can block active sites and hinder mass transfer rates. The dense packing of adsorbents on the surface of the adsorption medium also leads to longer diffusion distances and reduced mass transfer rates, resulting in a decrease in the removal efficiency [88].

Figure 8.
Effect of adsorbent dosage on MR removal efficiency at pH 6, a dye concentration of 70 mg/L, a contact time of 40 min and a temperature of 25 °C
3.2.4. Effect of pH
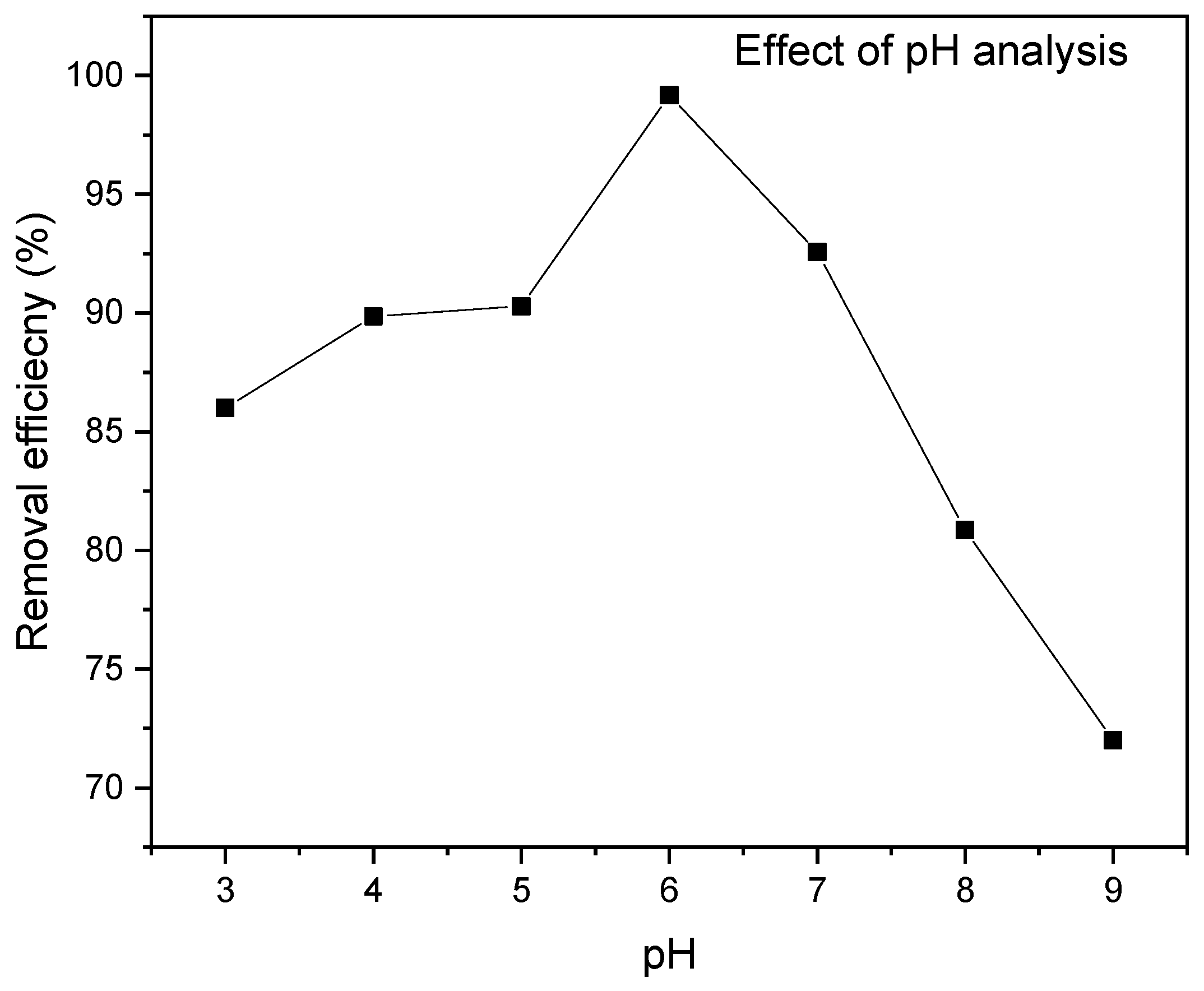
This study investigated the effect of the initial solution pH on the adsorption of MR ions onto RAB, as shown in Figure 9. The results show that the adsorption capacity and percentage removal increase with increasing the pH from 3 to 6. However, a further increase in pH from 6 to 9 decreased the removal efficiency and adsorption capacity. This is probably due to the interaction effect among the operating parameters. A maximum MR adsorption removal of 99.17% and adsorption capacity Qe of 40.9 mg/g were achieved at pH 6. The MR uptake became high at a lower solution pH and decreased as the solution pH increased. This is due to the strong attraction between the RAB adsorbent material’s protonated surface and the MR species in the solution [87]. This study selected pH six as the optimum MR uptake due to its highest removal efficiency. The removal efficiency of MR onto RAB decreases at near-neutral and alkaline pH conditions due to the enhanced deprotonation of acid functional groups (AFGs) on the biochar surface. This results in a greater negative surface charge density (SCD), which repulses the methyl red molecules and reduces their sorption onto the biochar. The decrease in sorption is attributed to the repulsive forces between the negatively charged biochar surface and the negatively charged methyl red molecules at higher pH values. Furthermore, the pHpzc of RAB was determined to be 6.2, indicating that the surface charge of the adsorbent is dominated by negative charges above a pH of 6.2. Hence, repulsive forces between negatively charged MR molecules and negatively charged RAB above a pH of 6.2 resulted in a decrease in the removal efficiency at near-neutral and alkaline pH conditions.

Figure 9.
Effect of pH on the MR removal efficiency at a contact time of 40 min, initial dye concentration of 70 mg/L, adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL and temperature of 25 °C
3.3. Adsorption Isotherm
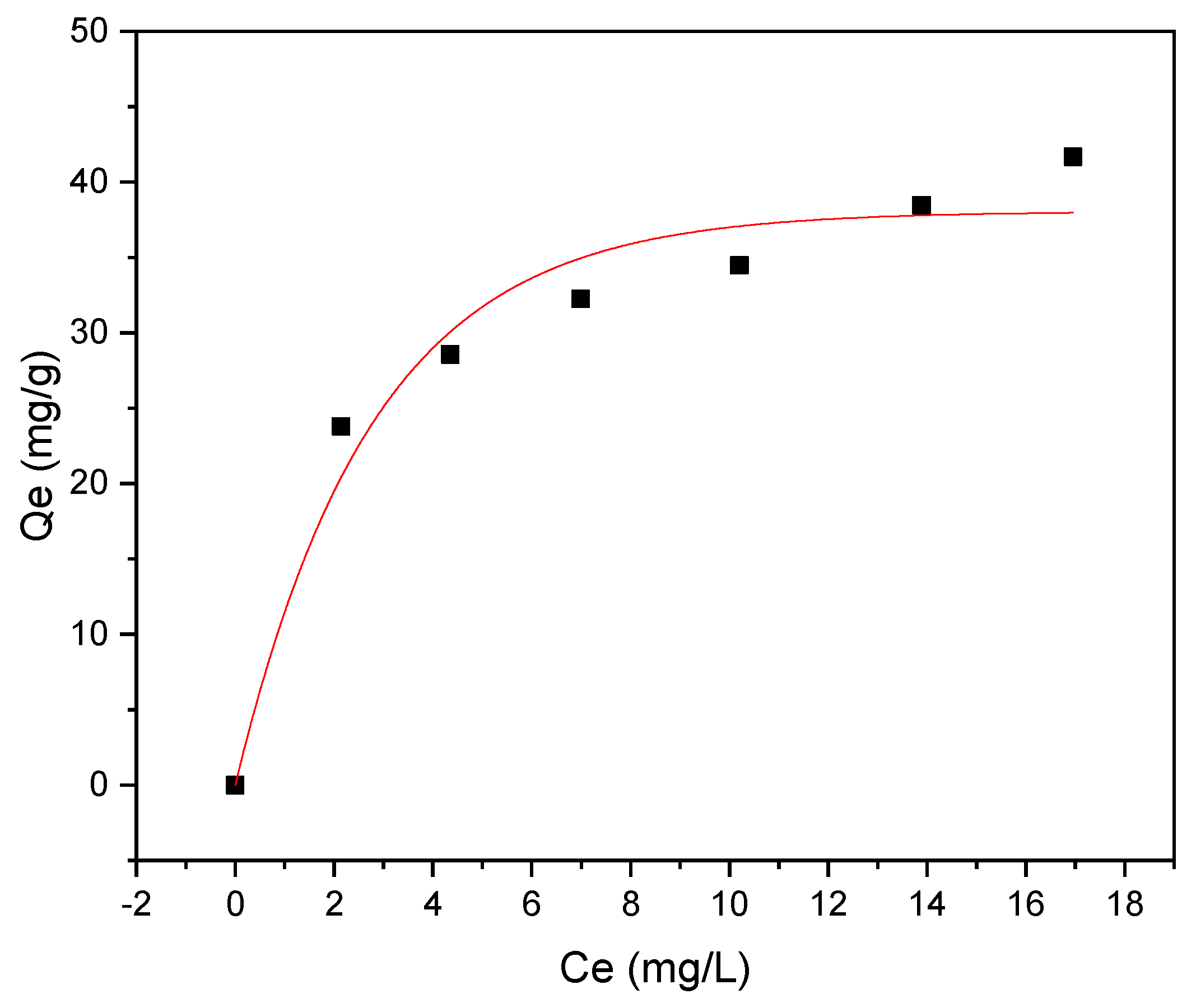
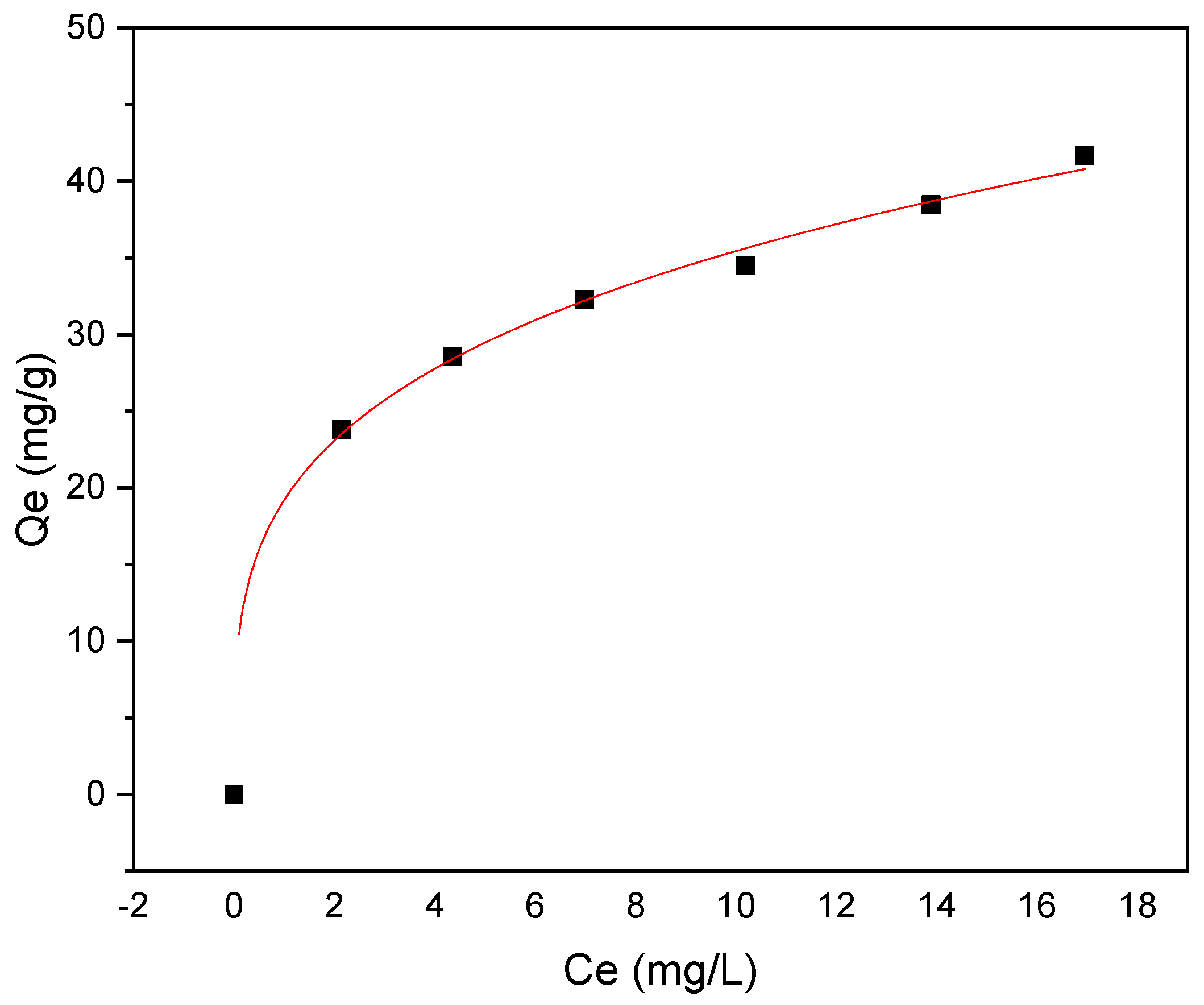
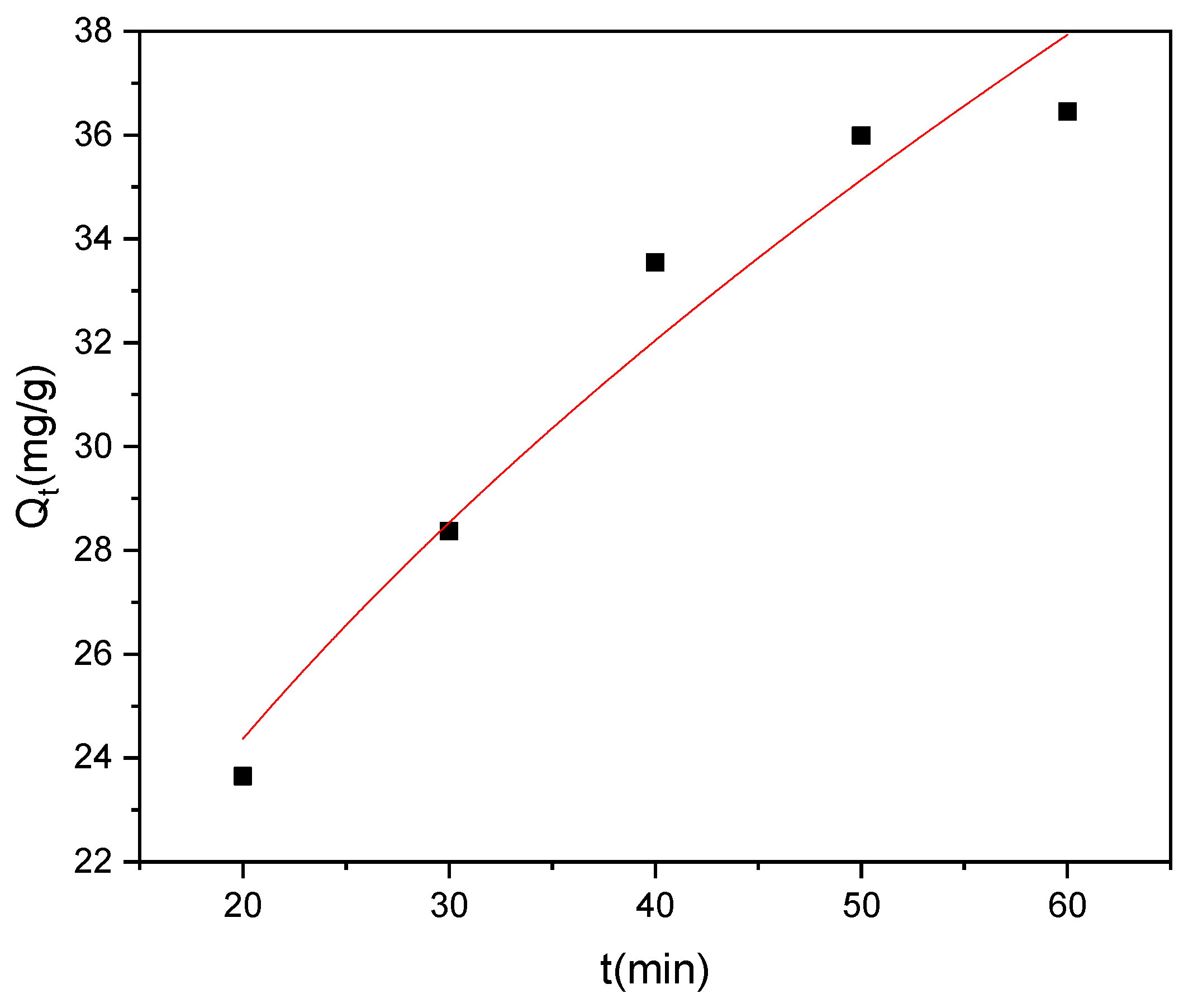
The adsorption isotherm was investigated using Langmuir and Freundlich models, as shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11, respectively. The investigation of methyl red adsorption onto Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar using Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models reveals important insights. The Langmuir model suggests a maximum adsorption capacity (Qmax) of 42.34 mg/g, favorable adsorption (RL < 1) and a good fit to the experimental data (R2 = 0.96), as shown in Table 3. Meanwhile, the Freundlich model also fits well (R2 = 0.99) and suggests a higher adsorption capacity (KF) = 19.19 (mg/g)(mg/L)n and a more heterogeneous adsorption surface (1/n = 0.266). However, the lower Reduced Chi-Square value for the Freundlich model implies a better fit to the data compared to the Langmuir model. Overall, both models provide valuable insights into the adsorption process, with the Freundlich model potentially better capturing the complexities of the system due to its lower Reduced Chi-Square value [89,90].

Figure 10.
Langmuir isotherm model for MR adsorption onto RAB at pH 6, a contact time of 60 min, an adsorbent dosage of 0.4 g/100 mL and a temperature of 25 °C
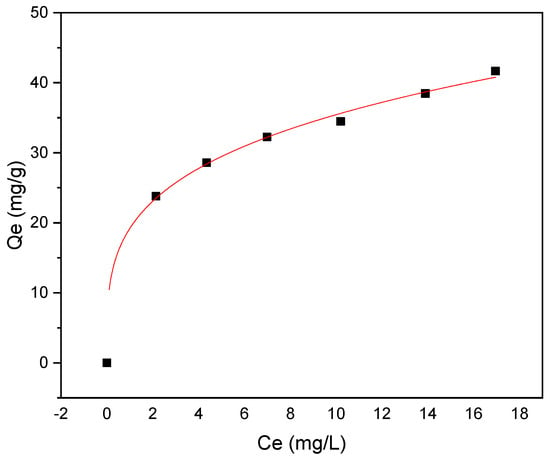
Figure 11.
Freundlich isotherm model for MR adsorption onto RAB at pH 6, a temperature of 25 °C, an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL and a contact time of 60 min.

Table 3.
Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherm parameters.
3.4. Adsorption Kinetics
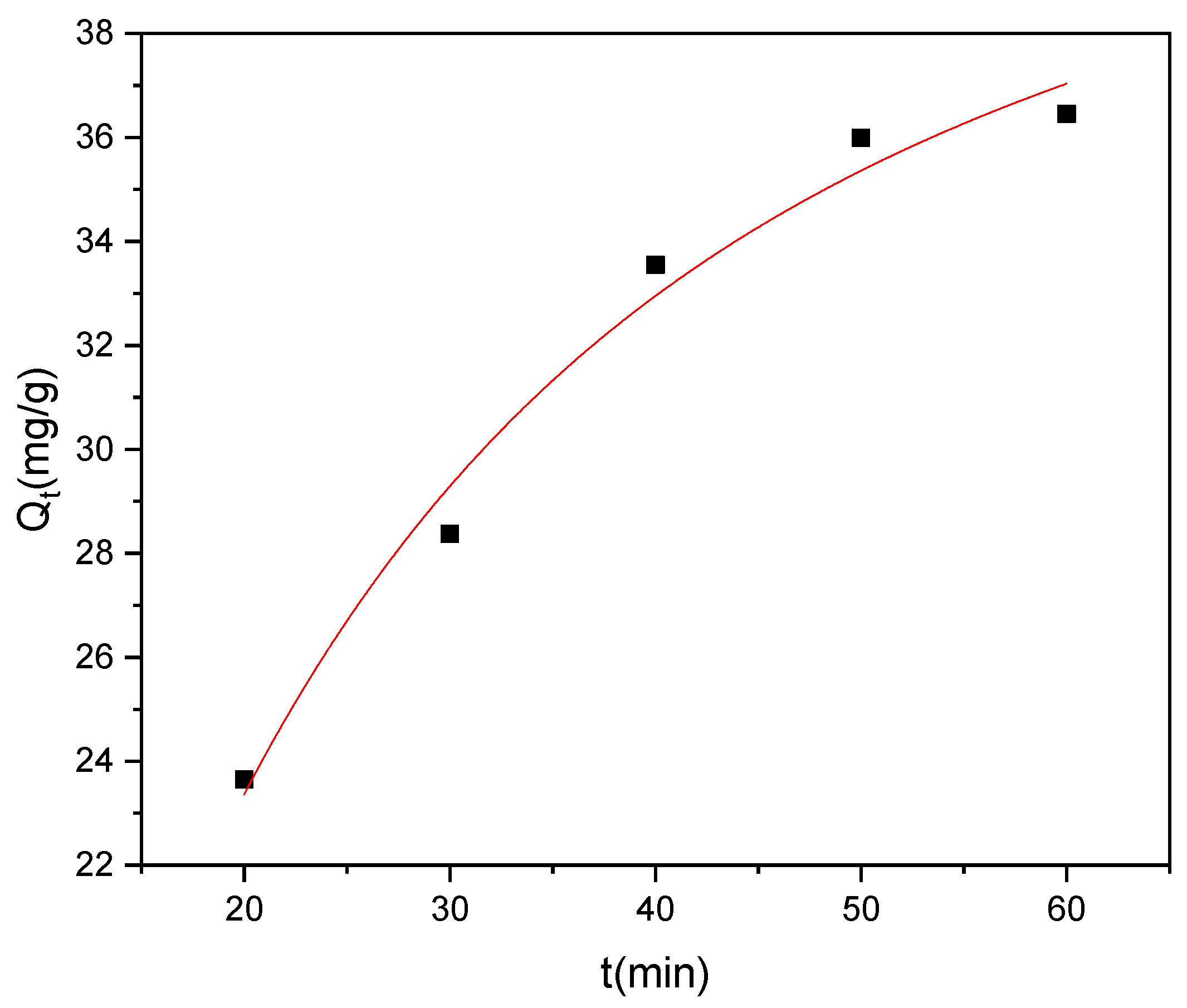
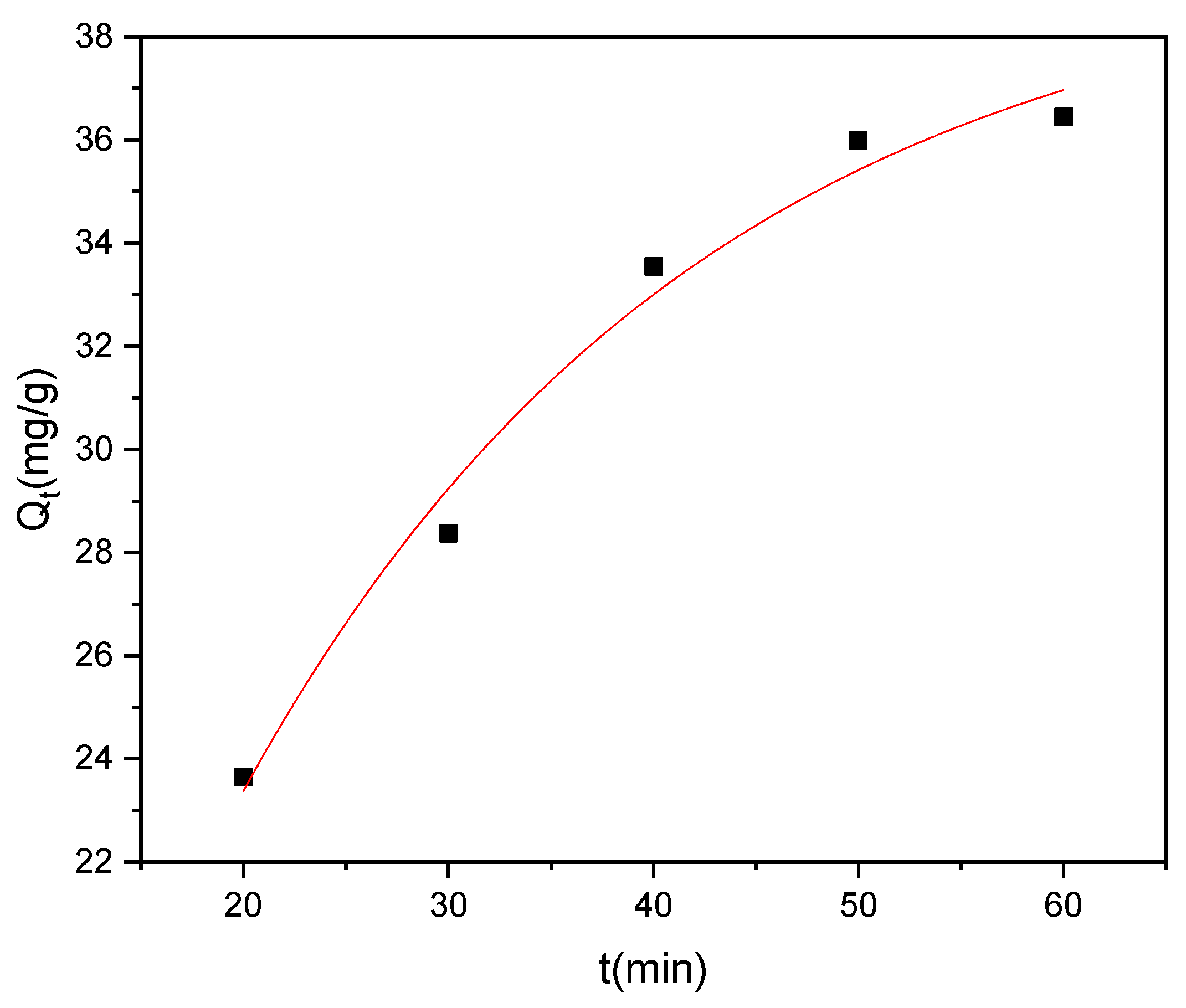
The investigation of methyl red adsorption kinetics onto Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar reveals significant insights across multiple kinetic models. The kinetic parameters associated with PFO, PSO, and IPD were determined from nonlinear plots of their respective models, as shown in Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14, respectively. The pseudo-first-order model yielded a rate constant (K₁) of 0.018 min⁻1 and an equilibrium adsorption capacity (Qe) of 39.74 mg/g, exhibiting a good fit to the experimental data with an R2 of 0.98 and a Reduced Chi-Square value of 1.01. Meanwhile, the pseudo-second-order model demonstrated a higher rate constant (K₂) of 1.34 g/mg min and a slightly higher equilibrium adsorption capacity (Qe = 41.86 mg/g), with a superior goodness of fit (R2 = 0.99) and a lower Reduced Chi-Square value of 0.57, as shown in Table 4. Additionally, the intraparticle diffusion model revealed a diffusion rate constant (Kp) of 4.14 mg/g min0.5 and a constant intercept (C) of 5.84 mg/g, indicating that while intraparticle diffusion contributes to the overall adsorption process, it might not be the sole controlling mechanism. Overall, the pseudo-second-order model seems to best describe the experimental data, suggesting that the adsorption of methyl red onto Rumex abyssinicus-derived biochar involves chemisorption and further indicating the complexity of the adsorption kinetics, which are potentially influenced by multiple mechanisms [72,91].

Figure 12.
PFO kinetic model for the adsorption of MR onto RAB at pH 6, an adsorbent dosage of 0.4 g/100 mL, a temperature of 25 °C and an initial MR concentration of 70 mg/L.

Figure 13.
PSO kinetics plot at an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL, dye concentration of 70 mg/L, pH of 6 and temperature of 25 °C.

Figure 14.
IPD model for adsorption of MR from aqueous solution at pH 6, a dye concentration of 70 mg/L, an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g/100 mL and a temperature of 25 °C.

Table 4.
Values of parameters for PFO, PSO and IPD adsorption kinetics models.
3.5. Comparative Analysis
The maximum adsorption capacity (42.34 mg/g) for MR adsorption from aqueous solution obtained using RAB is compared with other biosorbents derived from lignocellulosic, agricultural leftovers and woody materials. As a result, the findings of the comparison with recent works in the literature indicated that RAB is superior in removing MR from aqueous solution. This is probably due to the nature of the precursor material and the affinity of the target pollutant towards forming an interaction with the adsorbent materials. Hence, the prepared biochar can be taken as an alternative adsorbent for the removal of reactive and persistent dyes like MR. Table 5 presents the findings of a literature search where biosorbents prepared from different materials used to remove MR are compared with this research.

Table 5.
Comparative analysis of methyl red adsorption using biobased adsorbents.
3.6. Proposed Adsorption Mechanism
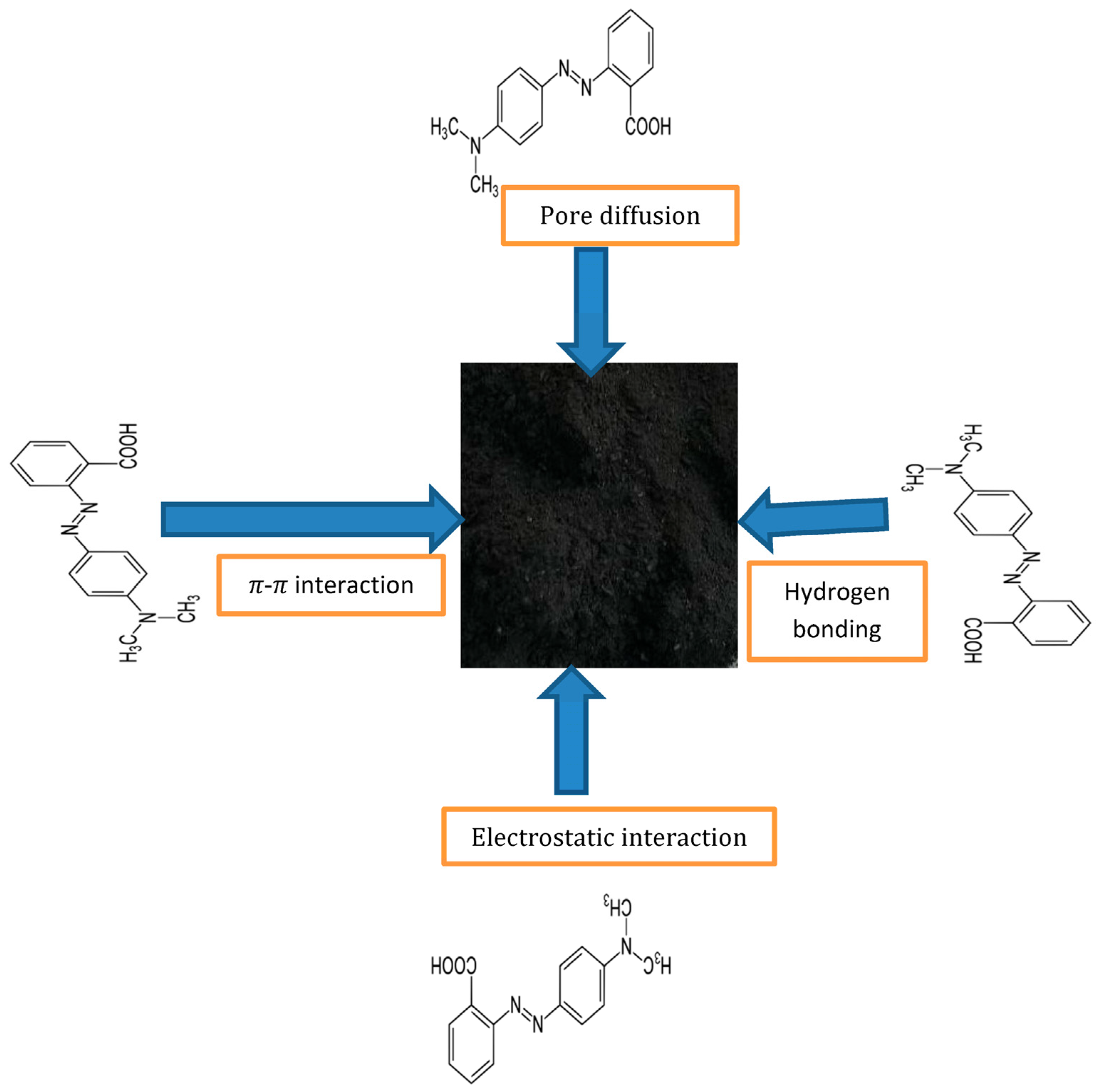
The conceptual illustration of the interaction between methyl red (MR) and the proposed sorbent, based on the characterization and adsorption performance results, reveals several key points, as shown in Figure 15. Firstly, the porous surface morphology of the biochar provides ample surface area, enhancing the contact between dye molecules and the sorbent, supported by a high BET surface area (45.8 m2/g). Secondly, various functional groups on the biochar surface facilitate interaction between the adsorbent and the adsorbate. Hydroxyl groups (–OH) can participate in hydrogen bonding with the functional groups of methyl red molecules. Aliphatic hydrocarbons can contribute to hydrophobic interactions with the hydrophobic regions of methyl red molecules. Carboxylic acid groups (–COOH) can undergo ion–dipole interactions with the charged regions of methyl red molecules. Aromatic carbon–carbon double bonds can engage in π-π interactions with the aromatic rings of methyl red molecules. Additionally, the C–O groups may participate in hydrogen bonding or other polar interactions with functional groups of methyl red. On the other hand, alkene groups can contribute to hydrophobic interactions with the hydrophobic regions of methyl red molecules. These functional groups collectively play a pivotal role in the adsorption process of methyl red onto Rumex abyssinicus-based biochar, highlighting the diverse chemical interactions involved in this adsorption mechanism. Finally, at pH 6, the maximum removal efficiency of 99.2% suggests the significance of surface charge interactions in the adsorption process [95]. Overall, the interaction between methyl red and the proposed sorbent involves a combination of physical and chemical mechanisms, facilitated by the surface morphology and functional groups of the biochar.

Figure 15.
Methyl red adsorption mechanism onto Rumex abyssinicus biochar.
3.7. Scale-Up and Cost Implications, and Environmental Impact Assessment
Scaling up the production of biochar derived from Rumex abyssinicus stems for the removal of methyl red from aqueous solutions needs a comprehensive analysis with significant implications. For adsorbent preparation from Rumex abyssinicus biochar, only 4.64 Ethiopian birr (ETB) was utilized per 1 kg of the product. The total cost includes the estimated costs for size reduction (2.29 ETB/kg) and thermal activation (2.65 ETB/kg). Hence, leveraging the underutilized stems of Rumex abyssinicus as a raw material could potentially provide a cost-effective and sustainable source for the adsorbent. However, the scale-up process necessitates the careful consideration of factors such as an increased production capacity, the efficient collection and processing of raw materials, and market demand. The estimated costs for size reduction and thermal activation are critical components, with opportunities for cost optimization through process efficiency improvements. Moreover, the environmental impacts, including resource utilization, energy consumption, and waste generation, require a thorough assessment to ensure sustainability. Overall, a comprehensive approach that integrates considerations of cost, scalability, and environmental sustainability is essential for realizing the full potential of biochar made from Rumex abyssinicus as an effective adsorbent for methyl red removal on a larger scale.
4. Conclusions
This study investigated the removal of methyl red from an aqueous solution using biochar prepared from Rumex abyssinicus stem. Accordingly, the prepared adsorbent was found to reveal characteristics of a 45.8 m2/g BET surface area composed of various functional groups. Additionally, morphological studies showed irregular and heterogeneous surfaces. The effects of various operating parameters such as the contact time, initial methyl red concentration, biochar dosage and pH were investigated by varying the respective parameters while holding the other parameters at constant values. As a result, a maximum methyl red removal efficiency of 99.2% was attained at optimum treatment conditions of pH 6, a contact time of 40 min, an initial dye concentration of 70 mg/L and an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 mg/100 mL. The adsorption isotherm was investigated using Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models, in which the Freundlich isotherm with a maximum R2 of 0.99 was determined to give a suitable description of the adsorption process. Additionally, a pseudo-second-order kinetics model was found to express adsorption with an R2 . In conclusion, it could be shown that Rumex abyssinicus-based biochar has the potential to effectively remove persistent dyes like methyl red from wastewater.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.T. methodology, M.D.T.; software, M.D.T.; validation, M.D.T. and M.O.D.; formal analysis, M.D.T.; investigation, M.D.T.; resources, M.D.T.; data curation, M.D.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.T.; writing—review and editing, M.D.T.; supervision, M.O.D.; project administration, M.D.T.; funding acquisition, M.D.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated is included in the main body of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We want to express our sincere gratitude to the University of Johannesburg for its dedication to creating a lively and supportive research environment, as their support has given us an invaluable opportunity to delve deeply into the research. We have succeeded in my research endeavors because of its state-of-the-art facilities, access to cutting-edge resources, and collaborative atmosphere. In addition, We would like to express our gratitude to Adama and Addis Ababa Science and Technology Universities for their support in our laboratory facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Roy, A.; Pramanick, K. Analysing progress of sustainable development goal 6 in India: Past, present, and future. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 1049–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Natural Resources Department. Wastewater as Resources: May 2022; European Investment Bank: Athens, Greece, 2022; ISBN 9789286153358. [Google Scholar]
- Tariq, A.; Mushtaq, A. Untreated Wastewater Reasons and Causes: A Review of Most Affected Areas and Cities. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Bisimwa, A.M.; Amisi, F.M.; Bamawa, C.M.; Muhaya, B.B.; Kankonda, A.B. Water quality assessment and pollution source analysis in Bukavu urban rivers of the Lake Kivu basin (Eastern Democratic Republic of Congo). Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 14, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, C.C.; Madu, C.N.; Ajaero, C.C.; Ibekwe, J.C. Sustainable management of textile and clothing. Clean Technol. Recycl 2021, 1, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, D.; Gaekwad, A.; Dani, H.; Shabiimam, M.A.; Kandya, A. Recent techniques of textile industrial wastewater treatment: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 77, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidu, J.M.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Rwiza, M.J.; Njau, K.N. Current status of textile wastewater management practices and effluent characteristics in Tanzania. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Ahmed, S.; Dhoble, Y.; Madhav, S. A critical review of hazardous waste generation from textile industries and associated ecological impacts. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Repon, M.R.; Islam, T.; Sarwar, Z.; Rahman, M.M. Impact of textile dyes on health and ecosystem: A review of structure, causes, and potential solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 9207–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus, S.S.; Ferreira, G.F.; Moreira, L.S.; Maciel Filho, R. Biodiesel production from microalgae by direct transesterification using green solvents. Renew. Energy 2020, 160, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, S.M.; Al-Mashhadani, M.K.H.; Eisa, M.Y. Optimization of dye adsorption process for Albizia lebbeck pods as a biomass using central composite rotatable design model. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2019, 25, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Pandit, S.; Mathuriya, A.S.; Gupta, P.K.; Pant, K.; Jadhav, D.A. Microbial Electrochemical Treatment of Methyl Red Dye Degradation Using Co-Culture Method. Water 2022, 15, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Naeem, M.; Zahoor, M.; Rahim, A.; Hanafiah, M.M.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Shah, A.B.; Mahnashi, M.H.; Al Ali, A.; Jalal, N.A. Biodegradation of Azo Dye Methyl Red by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Optimization of Process Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Ji, B.; Xu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z. Customizable High-Contrast Optical Responses: Dual Photosensitive Colors for Smart Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 54085–54097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, P.; Kaushal, J. Phytoremediation of azo dye methyl red by macroalgae Chara vulgaris L.: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 26406–26418. [Google Scholar]
- Adusei, J.K.; Agorku, E.S.; Voegborlo, R.B.; Ampong, F.K.; Danu, B.Y.; Amarh, F.A. Removal of Methyl red in aqueous systems using synthesized NaAlg-g-CHIT/nZVI adsorbent. Sci. Afr. 2022, 17, e01273. [Google Scholar]
- Waghchaure, R.H.; Adole, V.A.; Jagdale, B.S. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue, rhodamine B, methyl orange and Eriochrome black T dyes by modified ZnO nanocatalysts: A concise review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109764. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. A review on the water problem associate with organic pollutants derived from phenol, methyl orange, and remazol brilliant blue dyes. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, A141–A150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Gupta, S. Toxicological Impact of Azo Dyes Azo dyes and Their Microbial Degraded Byproducts on Flora and Fauna. In Innovations in Environmental Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 319–343. [Google Scholar]
- Olawale, M.D.; Akintemi, E.O.; Agbaffa, B.E.; Obaleye, J.A. Synthesis, characterization, adsorption study, quantum mechanics, monte carlo and molecular dynamics of lead based polymeric compound towards mopping of aqueous methyl red dye. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takkar, S.; Tyagi, B.; Kumar, N.; Kumari, T.; Iqbal, K.; Varma, A.; Thakur, I.S.; Mishra, A. Biodegradation of methyl red dye by a novel actinobacterium Zhihengliuella sp. ISTPL4: Kinetic studies, isotherm and biodegradation pathway. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 26, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K.; Goswami, P.; Barman, C.; Das, B. Methyl red: A fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ over Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, and Cd2+. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 17, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Manjunatha, A.S.; Sukhdev, A. Puttaswamy spectrophotometric oxidative decolorization of methyl red with chloramine-T and bromamine-T: Comparative kinetic modeling and mechanistic study. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 92, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, S.J.; Abdel-Rahim, I.A.; Alshamaileh, E.M.; Altwaiq, A.M. Equilibrium and structural study of m-methyl red in aqueous solutions: Distribution diagram construction. J. Solut. Chem. 2013, 42, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Webster, A.; Ntwampe, I.O.; Waanders, F.B. Coagulation/flocculation potential of polyaluminium chloride and bentonite clay tested in the removal of methyl red and crystal violet. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2017, 42, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Goyal, N.; Gupta, A. Degradation of azo dye methyl red by alkaliphilic, halotolerant Nesterenkonia lacusekhoensis EMLA3: Application in alkaline and salt-rich dyeing effluent treatment. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkiligadda, V.R.; Pokala, R.K.V.; Karumuri, A.; Bollikola, H.B. Adsorption Potentialities of Bio-Sorbents Derived from Pomegranate in the Removal of Methyl Red Dye from Polluted Waters. Caribb. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, Y.C.; Kaundal, J.B.; Begzaad, S.; Tiwari, R.K. Photocatalytic degradation of Methyl Red dye using highly efficient ZnO/CdS hierarchical heterostructures under white LED. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2023, 20, 1681–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Guo, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.-F.; Feng, Y.; He, M.; Yao, J. Glutaraldehyde and polyvinyl alcohol crosslinked cellulose membranes for efficient methyl orange and Congo red removal. Cellulose 2019, 26, 5065–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebratkhahan, M.; Naghash Hamed, S.; Zarei, M.; Jafarizad, A.; Rostamizadeh, M. Removal of neutral red dye via electro-fenton process: A response surface methodology modeling. Electrocatalysis 2021, 12, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Huang, W.; Liu, C. Double-barrier forward osmosis membrane for rejection and destruction of bacteria and removal of dyes. Desalination 2022, 529, 115609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, S.; Nosheen, S.; Abrar, S.; Anjum, F.; Gulzar, T.; Naz, S. Advanced approaches for remediation of textile wastewater: A comparative study. In Advanced Functional Textiles and Polymers: Fabrication, Processing and Applications; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 201–264. [Google Scholar]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Ravindran, V.; Gopinath, A.; Kumar, M.S. Emerging technologies for mixed industrial wastewater treatment in developing countries: An overview. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2022, 31, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A review on heavy metal ions and containing dyes removal through graphene oxide-based adsorption strategies for textile wastewater treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Tu, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, J. Adsorption and reaction of an alkyne molecule on diverse oxygen-reconstructed Cu (110) surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2022, 719, 122039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellenz, L.; de Oliveira, C.R.S.; da Silva Júnior, A.H.; da Silva, L.J.S.; da Silva, L.; de Souza, A.A.U.; Ulson, S.M.; Borba, F.H.; da Silva, A. A comprehensive guide for characterization of adsorbent materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Farias Silva, C.E.; da Gama, B.M.V.; da Silva Gonçalves, A.H.; Medeiros, J.A.; de Souza Abud, A.K. Basic-dye adsorption in albedo residue: Effect of pH, contact time, temperature, dye concentration, biomass dosage, rotation and ionic strength. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Akperov, E.O.; Akperov, O.H. Removal of the basic green 5 dye from aqueous solutions by grape (Vitis vinifera L.) bushes wastes. New Mater. Compd. Appl. 2019, 3, 171. [Google Scholar]
- An, N.; Zagorščak, R.; Thomas, H.R. Adsorption characteristics of rocks and soils, and their potential for mitigating the environmental impact of underground coal gasification technology: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaida, M.A.; Dutta, R.K.; Sen, A.K.; Ram, S.S.; Sudarshan, M.; Naushad, M.; Boczkaj, G.; Nawab, M.S. Chemical analysis of low carbon content coals and their applications as dye adsorbent. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, Z.; Jatoi, A.S.; Nadeem, S.; Anjum, A.; Imam, S.M.; Jangda, H. Comparative analysis of conventional to biomass-derived adsorbent for wastewater treatment: A review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 45–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nasseri, S. Integrated Fuzzy AHP-TOPSIS for selecting the best color removal process using carbon-based adsorbent materials: Multi-criteria decision making vs. systematic review approaches and modeling of textile wastewater treatment in real conditions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 7329–7344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, T.; Grich, A.; Naboulsi, A.; Regti, A.; Tahiri, A.A.; El Himri, M.; El Haddad, M. Adsorption of Methyl Red on porous activated carbon from agriculture waste: Characterization and response surface methodology optimization. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 158, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Jayakumar, A.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Efficient removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using mesoporous ZSM-5 zeolite: Synthesis, kinetics and isotherm studies. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 611, 125852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolski, R.; Bazan-Wozniak, A.; Pietrzak, R. Adsorption of methyl red and methylene blue on carbon bioadsorbents obtained from biogas plant waste materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, J.; Lei, E.; Ma, C.; Luo, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, S. Effects of the pore structure of commercial activated carbon on the electrochemical performance of supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2022, 45, 103457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamat, N.A.; Abd Halim Md Ali, M.R.; Yusof, M.; Che, N.W.; Jusoh, N.R.J.; Mail, K.M.P. Development of carbon dioxide adsorbents from renewable and non-renewable sources: A review. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2020, 16, 544–556. [Google Scholar]
- Adeleye, A.T.; Akande, A.A.; Odoh, C.K.; Philip, M.; Fidelis, T.T.; Amos, P.I.; Banjoko, O.O. Efficient synthesis of bio-based activated carbon (AC) for catalytic systems: A green and sustainable approach. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, K.V.; Mohan, K.C.; Ravindhranath, K.; Babu, B.H. Bio-Sorbent Derived from Annona Squamosa for the Removal of Methyl Red Dye in Polluted Waters: A Study on Adsorption Potential. Chem. Chem. Technol 2020, 14, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neolaka, Y.A.B.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.; Lalang, A.C.; Widyaningrum, B.A.; Ngasu, G.F.; Niga, K.A.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Iqbal, M.; Kusuma, H.S. Adsorption of methyl red from aqueous solution using Bali cow bones (Bos javanicus domesticus) hydrochar powder. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balu, P.; Asharani, I.V.; Thirumalai, D. Catalytic degradation of hazardous textile dyes by iron oxide nanoparticles prepared from Raphanus sativus leaves’ extract: A greener approach. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 10669–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguale, T.; Tadesse, D.; Giday, M. In vitro anthelmintic activity of crude extracts of five medicinal plants against egg-hatching and larval development of Haemonchus contortus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iriti, M.; Date, P. Bioactive compounds and health benefits of edible Rumex species—A review. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, T.; Urga, K.; Engidawork, E. Evaluation of the diuretic and analgesic activities of the rhizomes of Rumex abyssinicus Jacq in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Panda, R.C.; Madhan, B. Extraction of bio-active compounds from Ethiopian plant material Rumex abyssinicus (mekmeko) root—A study on kinetics, optimization, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 75, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yan, Y.; Hsu, C.; Lin, H. Waste bamboo-derived biochar and multiporous carbon as adsorbents for methyl orange removal. J. Chinese Chem. Soc. 2023, 70, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Uribe, C.; Ortiz, J.; Duran, F.; Vallejo, W.; Fals, J. Methyl Orange Adsorption on Biochar Obtained from Prosopis juliflora Waste: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Study. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, H.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J. Facile preparation of multi-porous biochar from lotus biomass for methyl orange removal: Kinetics, isotherms, and regeneration studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifetew, M.; Prabhu, V.; Worku, Z.; Fito, J.; Alemayehu, E. Adsorptive removal of reactive yellow 145 dye from textile industry effluents using teff straw-activated carbon: RSM-based process optimization. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 362–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takele, T.; Angassa, K.; Abewaa, M.; Kebede, A.M.; Tessema, I. Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater using activated carbon developed from H3PO4-activated khat stem waste. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abewaa, M.; Arka, A.; Haddis, T.; Mengistu, A.; Takele, T.; Adino, E.; Abay, Y.; Bekele, N.; Andualem, G.; Girmay, H. Results in Engineering Hexavalent chromium adsorption from aqueous solution utilizing activated carbon developed from Rumex abyssinicus. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimbo, D.; Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Mengistu, A.; Takele, T.; Oro, A.; Rangaraju, M. Methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution using activated carbon of spathodea campanulata. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuza, M.; Premlall, K.; Daramola, M.O. Modelling and thermodynamic properties of pure CO2 and flue gas sorption data on South African coals using Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, and extended Langmuir isotherm models. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2022, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.K.; Kini, S.; Prabhu, B.; Jeppu, G.P. A simplified modeling procedure for adsorption at varying pH conditions using the modified Langmuir–Freundlich isotherm. Appl. Water Sci. 2023, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S.; Eris, S. Adsorption isotherms and kinetics. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 33, pp. 445–509. ISBN 1573-4285. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, G.; Naushad, M. Adsorptive removal of noxious cadmium ions from aqueous medium using activated carbon/zirconium oxide composite: Isotherm and kinetic modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Nazal, M.K.; Angove, M.J.; Morton, D.W.; Hoque, K.A.; Reaz, A.H.; Islam, M.T.; Karim, S.M.A.; Chowdhury, A.-N. Emerging iron-based mesoporous materials for adsorptive removal of pollutants: Mechanism, optimization, challenges, and future perspective. Chemosphere 2023, 349, 140846. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Mengistu, A. Heliyon Preparation of Rumex abyssinicus based biosorbent for the removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fito, J.; Abewaa, M.; Mengistu, A.; Angassa, K.; Ambaye, A.D.; Moyo, W.; Nkambule, T. Adsorption of methylene blue from textile industrial wastewater using activated carbon developed from Rumex abyssinicus plant. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.; Abewaa, M.; Adino, E.; Gizachew, E.; Abdu, J. The application of Rumex abyssinicus based activated carbon for Brilliant Blue Reactive dye adsorption from aqueous solution. BMC Chem. 2023, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abewaa, M.; Mengistu, A.; Takele, T.; Fito, J.; Nkambule, T. Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution using Rumex abyssinicus derived activated carbon. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fito, J.; Mengistu, A.; Abewaa, M.; Angassa, K.; Moyo, W.; Phiri, Z.; Mafa, P.J.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Nkambule, T.T.I. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers Adsorption of Black MNN reactive dye from tannery wastewater using activated carbon of Rumex Abysinicus. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Tai, D.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A. A comprehensive review on the adsorption of heavy metals by zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) based nanocomposite in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, X. Aromatic polymer dual-confined magnetic metal-organic framework microspheres enable highly efficient removal of dyes, heavy metals, and antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 472, 145159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of adsorption process for effective removal of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demiral, İ.; Samdan, C.; Demiral, H. Enrichment of the surface functional groups of activated carbon by modification method. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 22, 100873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švábová, M.; Bičáková, O.; Vorokhta, M. Biochar as an effective material for acetone sorption and the effect of surface area on the mechanism of sorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, S.A.; Yunus, R.; Samsuri, A.W.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Asady, B. Removal of Zinc from Aqueous Solution by Optimized Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches Biochar as Low Cost Adsorbent. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2017, 2017, 7914714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Price, G.W.; Burton, D.; Wang, Y. Removal of Cadmium (II) using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) biochar alginate beads in aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, B.M.; Morales-Torres, S.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Madeira, L.M. Fitting biochars and activated carbons from residues of the olive oil industry as supports of fe-catalysts for the heterogeneous fenton-like treatment of simulated olive mill wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahi, R.; Zuhaidi, N.F.Q.A.; Yusof, Y.; Jamel, J.; Kanakaraju, D.; Ngaini, Z. Chemically treated microwave-derived biochar: An overview. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 107, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villabona-Ortíz, Á.; Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Ortega-Toro, R. Kinetics and adsorption equilibrium in the removal of azo-anionic dyes by modified cellulose. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuku, M.; Nure, J.F.; Atagana, H.I.; Hlongwa, N.; Nkambule, T.T.I. Advancing the development of nanocomposite adsorbent through zinc-doped nickel ferrite-pinecone biochar for removal of chromium (VI) from wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fa Soliman, M.; Mahrous, M.; Gad, A.; Ali, I. Optimization of total hardness removal efficiency of industrial wastewater using novel adsorbing materials. Aswan Univ. J. Environ. Stud. 2023, 4, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmier, M.; Norhidayah, A. Modified durian seed as adsorbent for the removal of methyl red dye from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solution, A.; White, U.; Peel, P.; Enenebeaku, C.K.; Okorocha, N.J. Adsorption and Equilibrium Studies on the Removal of Methyl Red from Adsorption and Equilibrium Studies on the Removal of Methyl Red from Aqueous Solution Using White Potato Peel Powder. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2017, 72, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomeyrani, S.F.N.; Azqhandi, M.H.A.; Ghalami-Choobar, B. Rapid and efficient ultrasonic assisted adsorption of PNP onto LDH-GO-CNTs: ANFIS, GRNN and RSM modeling, optimization, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 333, 115917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, D.; Bazan-Wozniak, A.; Wolski, R.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Pietrzak, R. Removal of Methyl Red from Aqueous Solution Using Biochar Derived from Fennel Seeds. Molecules 2023, 28, 7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, D.; Bazan-Wozniak, A.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Pietrzak, R. Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Red from Aqueous Solutions Using Activated Carbons Obtained by Chemical Activation of Caraway Seed. Molecules 2023, 28, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, A.; Bouchareb, E.M.; Derbal, K.; Boukhaloua, S.; Chahbouni, B.; Bouchareb, R. Uptake of Methyl Red dye from aqueous solution using activated carbons prepared from Moringa Oleifera shells. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 4, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Yadav, V.K.; Pathan, S.K.; Singh, B.; Osman, H.; Choudhary, N.; Khedher, K.M.; Basnet, A. Remediation of Methyl Red Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Using Biosorbents Developed from Floral Waste. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2023, 2023, 1532660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).