Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an environmental endocrine-disrupting compound that is resistant to conventional biological treatment, making it crucial to develop an oxidation process. This study introduces a novel hydrodynamic cavitation (HC) coupled with a Fenton + periodate (PI) oxidation system for the efficient degradation of BPA. By systematically examining the key parameters such as inlet pressure, Fe (II), H2O2, and PI concentration, it was found that HC performed optimally at a pressure of 0.5 MPa. A conversion of 98.14% was achieved within 60 min when the molar ratio of BPA, Fe (II), H2O2, and PI was approximately 1:1:5:1. Further analysis revealed that the gray correlation between H2O2 and PI concentrations on the degradation efficiency was 0.833 and 0.843, respectively, indicating that both of them had significant effects on the degradation process. The free radical quenching assay confirmed the hydroxyl radical (•OH) as the main active substance. Additionally, the toxicity of the degradation intermediates was evaluated using the Toxicity Estimation Software Tool (TEST). An artificial neural network (ANN)-based model was constructed to predict the BPA-degradation process, facilitating precise reagent dosing and providing robust support for the intelligent application of water-treatment technologies.
1. Introduction
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an organically synthesized compound widely utilized in polycarbonate plastics, epoxy resins, and flame retardants, with an annual global production of approximately 3.6 million tons [1]. Due to its estrogenic activity, BPA is classified as an environmental endocrine-disrupting compound (EDC) [2]. BPA is ubiquitous in the environment, including air, surface water, sludge, and tap water. According to reports published by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, over 450 tons of BPA are released into the environment annually in the US. A study on urine samples from Chinese children revealed a 100% detection rate of BPA, indicating a prevalent exposure of humans to this chemical [3]. BPA poses potential health risks to humans, particularly in relation to reproductive development and breast cancer incidence [4,5]. Consequently, wastewater containing BPA has the potential to contaminate aquatic environments. Previous studies have found the detection of BPA in different environmental media such as tap water (38.9–55.8 ng/L), wastewater treatment plant influent (193–2440 ng/L), drinking water treatment plant influent (<420 ng/L), industrial wastewater (230–149,200 ng/L), and industrial wastewater treatment plant effluent (8–370 ng/L) [6,7,8,9].
While BPA is a biodegradable organic compound, industrial wastewater containing BPA is usually accompanied by high concentrations of inorganic salts, which may pose challenges for biodegradation alone, as only a few bacteria can maintain BPA-degrading activity in this environment [10]. Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have exhibited remarkable efficacy in dealing with persistent and refractory organic pollutants. Currently, oxidation methods based on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), persulfate (PS), ozonation (O3), photocatalysis, electrochemistry, and cavitation have been proven to hold potential for BPA treatment [11,12,13,14,15]. Nevertheless, these treatment processes also have drawbacks, including high operating costs, regeneration costs, the generation of toxic by-products, low removal rates, and high energy consumption.
Hydrodynamic cavitation (HC) is a phenomenon generated by the passage of a liquid through a constriction, which is capable of generating high temperatures and pressures (hotspots) under almost natural ambient conditions, and has gained attention as a promising process for AOPs [16,17]. When a liquid passes through a hydrodynamic cavitation generator (HCR), the local pressure will be sacrificed to increase the flow rate, and when the pressure around the constriction point is lower than the cavitation threshold pressure, a cavity is generated, and downstream of the constriction region, the liquid pressure recovers, and the cavity collapses. Self-excited pulsed cavitation has higher-frequency pressure pulses, which are more conducive to the development and collapse of cavitation bubbles, resulting in better cavitation [18]. Compared to acoustic cavitation, HC has the advantage of low energy consumption and the ability to operate under ambient operating conditions, showing good potential for dissemination. Zampeta et al. used a venturi combined with an orifice plate HCR to decolorize wastewater containing five inks on a pilot scale, demonstrating an average conversion of 92.2% [19]. Agarkoti et al. assembled a novel double-slit venturi for the degradation of sulfadiazine at the pilot scale, achieving a conversion of 41.54%, which was enhanced to 96.92% when combined with the Fenton method, at a treatment cost of only 38.84% of the ultrasonic reactor at the same level [20]. The n-octanol/water partition coefficient (logP) of BPA is 3.32, which means that it tends to adhere to the surface of the cavitation vesicles, which is conducive to the treatment of BPA by hydraulic cavitation and has been reported in the literature to validate this value [21]. The reported literature verifies the feasibility of BPA degradation by HC [16,22]. However, since the slumping strength produced by HC is weaker than that of acoustic cavitation, exploring the combination of HC with other AOP processes for the removal of high concentrations of BPA in aqueous media remains to be investigated [22,23,24].
Fenton is a widely adopted advanced oxidation process that generates substantial amounts of •OH for oxidizing pollutants when H2O2 reacts with various forms of iron as transition metal catalysts under acidic conditions [25,26]. However, the inherently short lifespan of •OH poses challenges in achieving complete reactions with pollutants, inevitably leading to increased operational costs [27,28]. In contrast, periodate (PI) has garnered significant attention due to its stability, safe transportation and storage properties, as well as environmental friendliness. Existing reports demonstrate the effectiveness of PI activation in treating bisphenol A, achieving promising treatment outcomes [29]. Recent research has further revealed that the combined use of periodate and H2O2 efficiently and effectively generates a variety of radicals for treating pollutants in aqueous systems [30]. It is anticipated that the Fenton method could also exhibit synergistic effects when coupled with PI.
Considering the merits and drawbacks of individual water-treatment processes and their combined performance, this study investigates the self-excited oscillatory cavitation synergistic Fenton + PI treatment of pollutants. Utilizing BPA at a concentration of 10 mg/L as the target contaminant, we first validate the synergetic interactions within the oxidation processes of HC and Fenton, Fenton and PI, as well as HC and Fenton + PI. Secondly, we assess the influence of varying inlet pressures on the degradation process of self-induced pulsed cavitation and examine the effects of catalyst concentration, oxidant ratio, and environmental medium on the degradation process within the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system. Furthermore, the grey relational analysis method is employed to determine the correlation between the dosages of the two oxidants and the degradation efficacy. Through quenching experiments, we identify the primary active species responsible for BPA degradation. The toxicity of BPA degradation intermediates is analyzed utilizing toxicity prediction software (TEST 5.1.2.0). Lastly, the reliability of modeling this process through an artificial neural network is investigated. This research endeavors to offer a reference for the combined application of HC and AOPs, aiming to facilitate their progression toward a mature, energy-efficient, and highly effective water pollution treatment technology.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Bisphenol A (BPA, C15H16O2, purity > 99.0%), ferrous sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O, purity ≥ 99.0%), sodium periodate (NaIO4, purity ≥ 99.5%), sodium benzoate (C7H5NaO2, purity > 99%), and p-hydroxybenzoic acid (C7H6O3, purity > 99%) were purchased from the Aladdin Reagent Company (Shanghai, China) as analytical grade. Aladdin Reagent Company (Shanghai, China), and hydrogen peroxide, sulfuric acid, acetic acid, sodium hydroxide, tert-butanol (t-BuOH), and p-benzoquinone (BQ) were purchased as analytical-grade reagents from Sinopharm Group Chemical Reagent Company (Shanghai, China). Acetonitrile, methanol (MeOH), and formic acid were chromatographically pure and provided by Fisher Scientific (Hampton, NH, USA). All stock solutions were configured using ultrapure water with a resistivity of 18.25 MΩ·cm.
2.2. Experimental Procedure
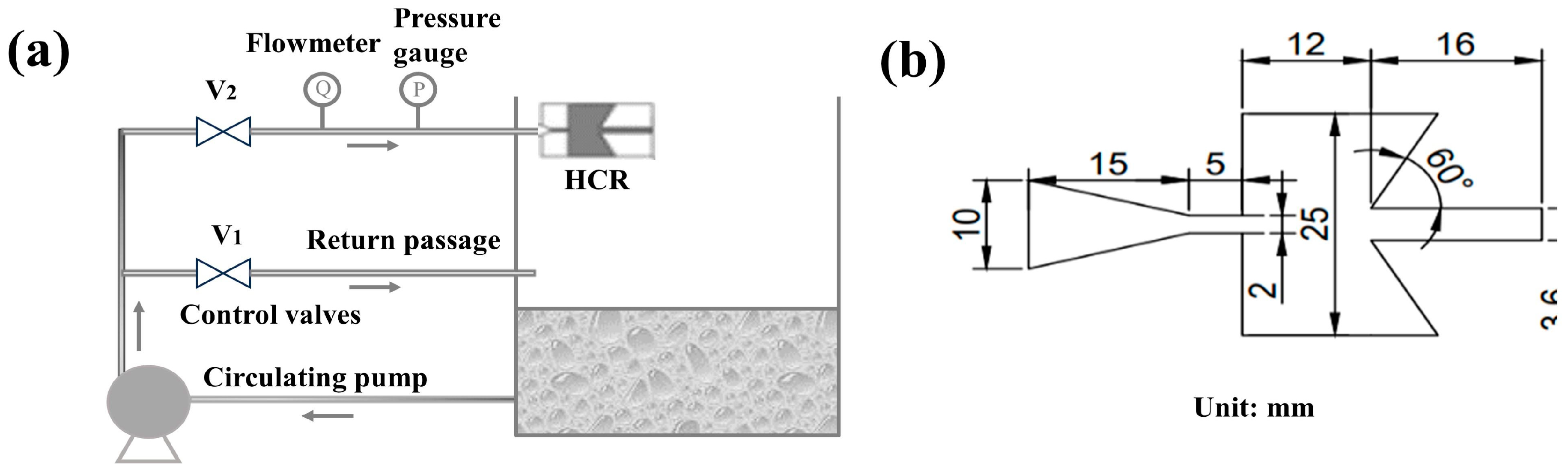
The HC reactor setup used in this study is shown schematically in Figure 1a. Specifically, this consists of a collection tank with a capacity of 36 L, an HCR, and an interconnecting pipe, where the inner wall surface of the collection tank is the jet target surface. A pump rated at 1.5 kW is connected to the collection tank, and the piping on the pressure pipe side of the pump branches through a tee to the pressure piping and return piping and terminates in the tank above the liquid level. The pressure piping is equipped with a flow meter, a pressure gauge, and a self-excited oscillatory cavitation generator (structure is shown in Figure 1b). Both the pressure pipeline and the return pipeline were equipped with throttling valves to regulate the inlet pressure of the hydrodynamic cavitation reactor. The experimental temperature was set at 25 °C, 4 L of BPA-simulated wastewater with a concentration of 10 mg/L was injected into the tank, and the initial pH was adjusted to 3 with H2SO4 for each group of experiments. A total of 3 mL of each group of experiments was sampled at 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 min, and the concentration of BPA was determined after quenching with the addition of 200 µL of methanol.
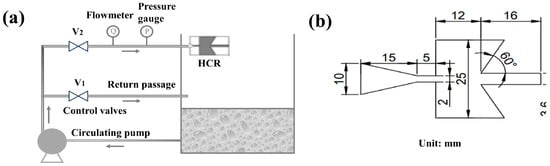
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the setup used for the experiment (a) and structure of the HCR (b).
2.3. Analysis
H2O2 measurements were carried out by a colorimetric method using UV-Vis spectrophotometry (AOE UV-1800, Shanghai Aoyi Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) at 400 nm to monitor the yellow complex produced by the oxidation of titanium sulfate by H2O2. A high-performance liquid chromatograph (LC5090, Zhejiang Fuli Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd., Wenling, China) equipped with a C18 column (4.6 mm × 150 mm × 5 µm, Shimadzu Corporation., Kyoto, Japan) was used to monitor the BPA concentration. The isocratic elution was used, and the mobile phase consisted of a binary compound of 70% methanol and 30% ultrapure water at a flow rate of 1 mL/min with an injection volume of 20 µL and a detection wavelength of 278 nm. The maximum value of relative experimental error is 10.24%.
The BPA conversion was calculated using Equation (1):
where C0 and Ct are the initial and instantaneous concentration of BPA (mg/L), respectively.
The degradation reactions follow a kinetic model of pseudo-first order reaction for the first 30 min, with the kinetic constant (k, min−1) calculated using Equation (2):
where C denotes the concentration of BPA, t denotes time, and k denotes the degradation kinetic constant of the reaction system.
The half-life equation for the pseudo-first order reaction was calculated from Equation (3):
The synergy index (SI) calculation was calculated from Equation (4):
where k(combined process) and k(single process) are the kinetic constants of the combined process and the kinetic constants of the single process, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of the HC + Fenton + PI Oxidation System
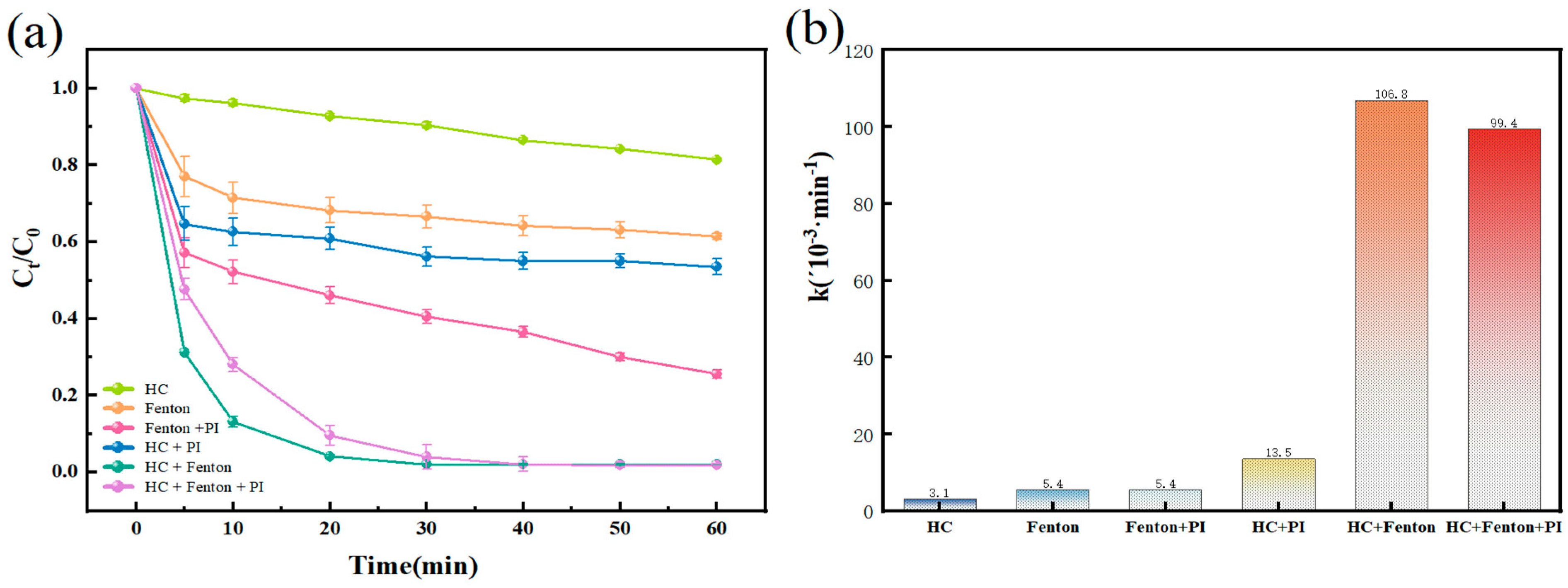
Without activation conditions, both H2O2 and PI alone exhibit minimal degradation effects on BPA, with their oxidizing abilities being negligible. We conducted tests to assess the effects of six oxidation systems—HC, Fenton, Fenton + PI, HC + PI, HC + Fenton, and HC + Fenton + PI—on BPA. The process is shown in Figure 2a. After 60 min, the conversion of each oxidation system was 18.64 ± 0.28%, 38.58 ± 0.86%, 74.43% ± 1.02%, 43.62 ± 2.14%, 95.14 ± 1.51%, and 98.14 ± 0.97%, respectively. The kinetic constants were 3.1 × 10−3, 5.4 × 10−3, 5.4 × 10−3, 13.5 × 10−3, 107 × 10−3, and 99.4 × 10−3 min−1, respectively. The synergy indices SI of HC with Fenton and Fenton + PI were 12.57 and 6.01, respectively. The introduction of PI notably enhanced the conversion of BPA in the Fenton process. This enhancement can be attributed to the fact that the regeneration rate of Fe (II) in the conventional Fenton oxidation system is significantly lower than the oxidation rate. Consequently, a large amount of Fe (II) is oxidized in the early stages of the reaction, generating a substantial number of •OH radicals. Nevertheless, these free radicals possess a limited lifespan, which hinders their ability to adequately break down organic substances within a little period of time, ultimately leading to an unsatisfactory degradation outcome. The introduction of periodate opens up a new pathway for the generation of •OH and various free radicals. It slows down the oxidation of Fe (II) by consuming H2O2, thereby allowing the reaction to proceed (Equations (5)–(10)). Therefore, despite the HC + Fenton oxidation system demonstrating favorable outcomes in treating bisphenol A wastewater, the exploration of the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system is necessary due to its potential for long-term effectiveness in adapting to complex and variable water environments. This investigation also aids in comprehending the mechanism of synergistic effects among multiple oxidants.
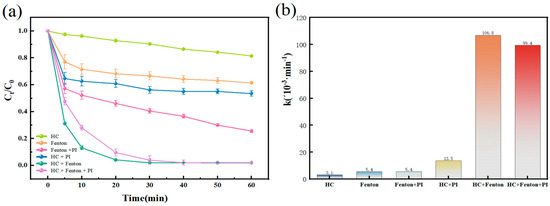
Figure 2.
(a) Degradation process of BPA under different oxidizing systems and (b) corresponding kinetic constants. Experimental conditions: optimal operating conditions: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.25 mM, inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures.
In addition, the turbulent conditions in the HCR eliminate the mass transfer resistance with the Fenton and its related processes [31]. Meanwhile, the H2O2 and solid particles in the Fenton process act as additional nuclei, allowing more cavitation to occur in the reactor, thus enhancing the overall degradation [32]. At the same time, the heat released from the collapse of cavitation bubbles provides favorable conditions for PI activation (Equation (11)) [33].
3.2. Review and Comparison of Similar Processes
Lu et al. performed a study to assess how the shape of a well plate and several operational parameters impact the removal of BPA by HC. Under optimal circumstances, they attained a conversion of 27.58% within 3 h [16]. Furthermore, Chinthala et al. discovered that the utilization of well plates in conjunction with H2O2 and Fenton’s reagent resulted in a significant enhancement in the transformation of bisphenol A. This transformation reached a remarkable 75.32% during 60 min [34]. The study’s discussion on reagent dosage is insufficient and requires further elaboration to enhance its practical utility. Choi et al. found that hot spots generated by HC at elevated temperatures activate persulfate, which effectively destroys BPA [22]. However, their study showed that for this oxidation system to work properly, a water temperature of 50 °C must be maintained. This requirement makes it difficult to be used in a wide range of applications. Asadi et al. introduced a novel approach for integrating HC with CoFeO photocatalysts [35]. This approach harnesses the powerful turbulence and pressure waves produced by the collapse of a cavity to enhance the active sites of the catalyst, resulting in the synergistic activation of peroxyacetic acid and degradation of BPA. Achieving a conversion of 97.29% and a mineralization rate of 73.04% was the outcome. This indicates that the comprehensive impact of HC in conjunction with various AOPs has not been extensively examined. The objective of our work is to enhance the combined effect of HC with AOPs by investigating the impact of catalyst and oxidant dosage on the treatment efficiency of the system. To achieve this objective, we integrated a self-excited oscillatory jet with a Fenton and a PI. The advanced HCR structure was employed to maximize the utilization of turbulence and shear forces resulting from cavity collapse, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of HC in the removal of BPA.
3.3. Effect of Initial Bisphenol A Concentration
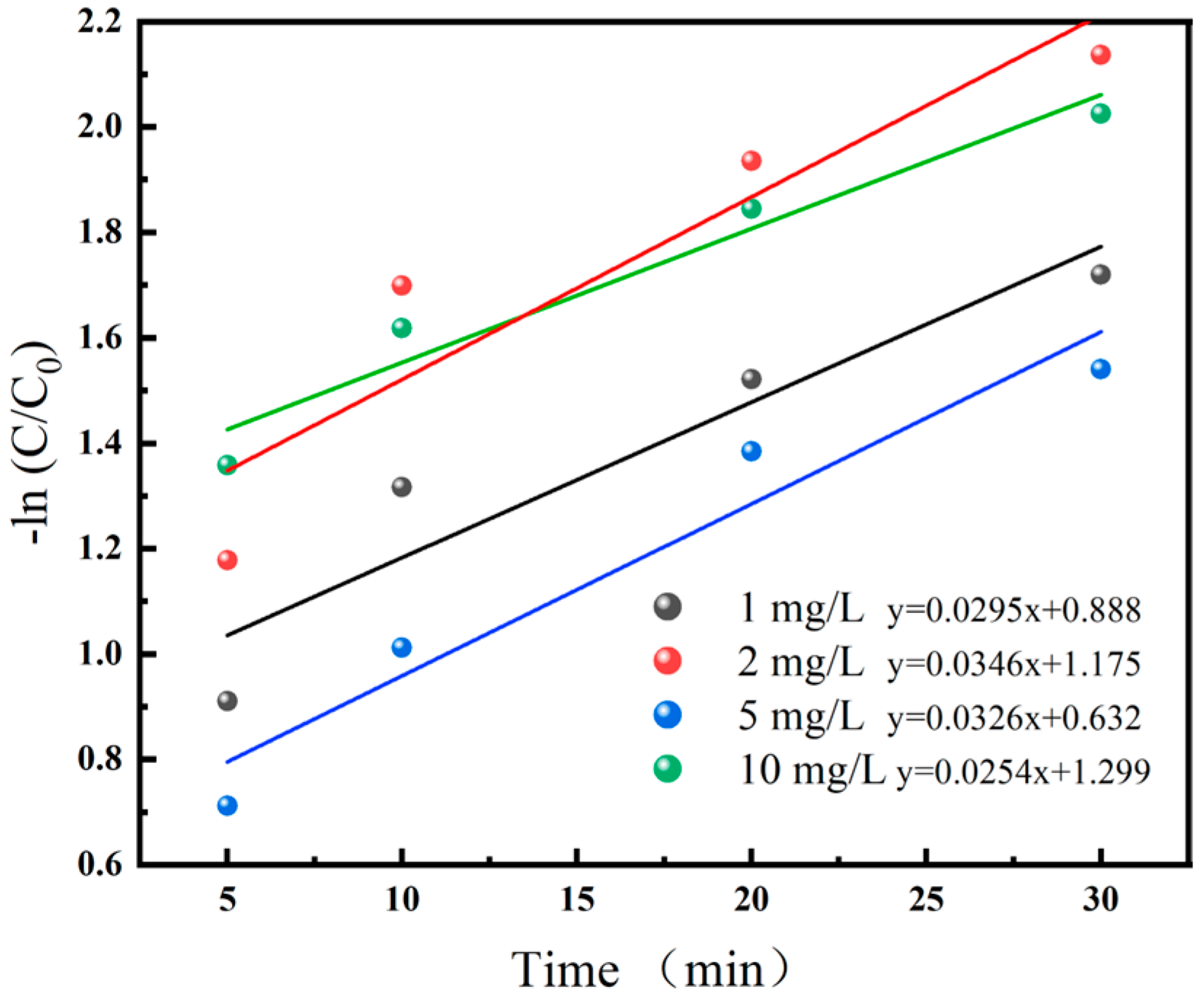
Figure 3 illustrates the fitting of pseudo-first-order reaction kinetics under different initial BPA concentrations, where the slope of the formula represents the kinetic constant. As observed from the results, variations in the substrate concentration of BPA have a negligible impact on the reaction kinetic constant, indicating that the oxidation rate of BPA serves as the limiting stage of the entire reaction within the acceptable experimental error range. Therefore, despite the coexistence of multiple reactants involved in this work, the pseudo-first-order reaction kinetics model can still be applied for fitting purposes.
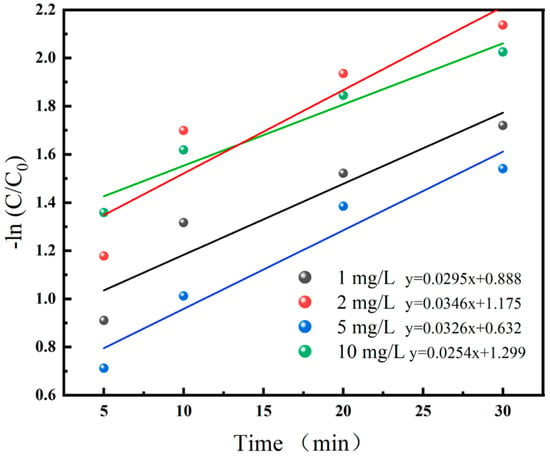
Figure 3.
Pseudo-first-order reaction kinetics at different initial BPA concentrations. Experimental conditions: [BPA]0 = 1−10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = 0.05 mM, [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.1 mM, inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C.
3.4. Effect of Inlet Pressure
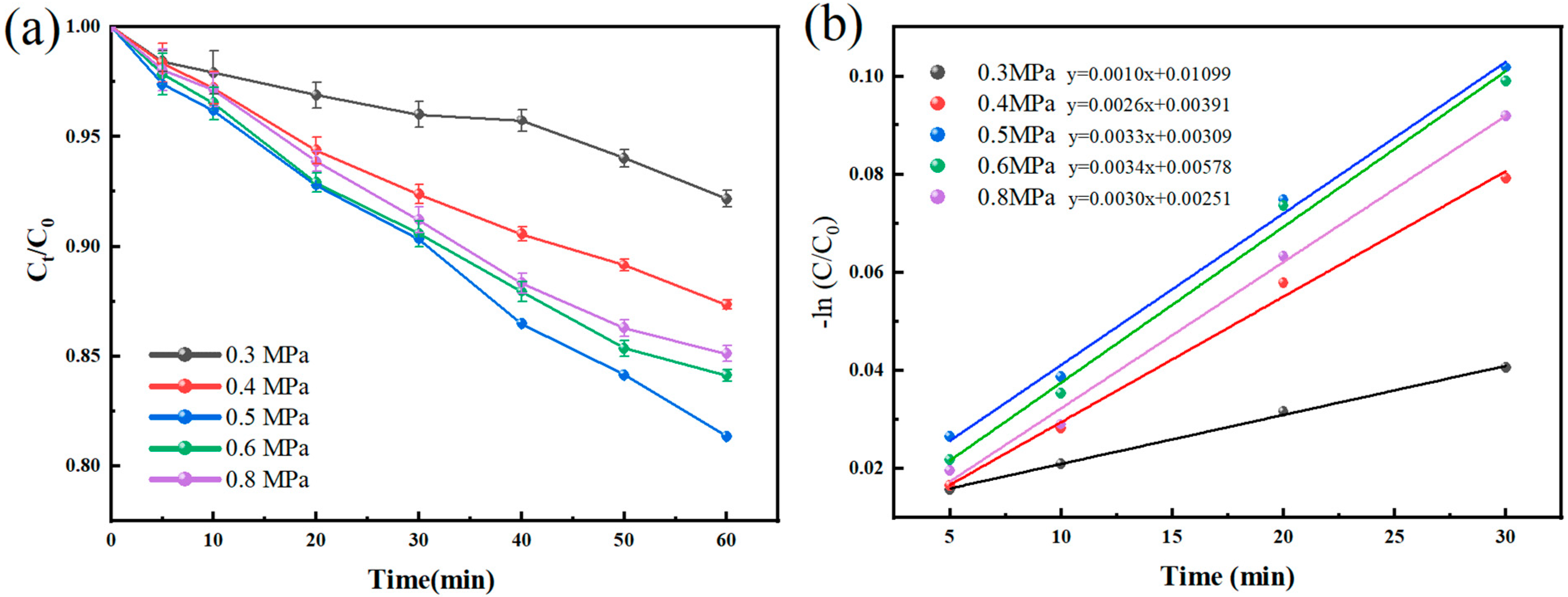
The inlet pressure is an important parameter affecting the performance of the hydrodynamic cavitation generator, which can act on the occurrence and collapse process of cavitation bubbles. Also, it has a significant effect on the oscillation frequency and oscillation peak value of the resonant cavity in this study. To study the effect of the inlet pressure on the degradation of BPA using self-excited pulsed cavitation, the experiments were carried out under the inlet pressures of 0.3 MPa, 0.4 MPa, 0.5 MPa, 0.6 MPa, and 0.8 MPa, respectively, and the results obtained are shown in Figure 4.
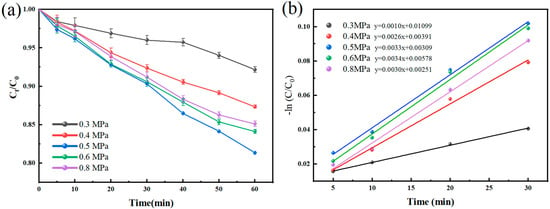
Figure 4.
(a) Degradation of BPA by HC at different inlet pressures. Experimental conditions: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures. (b) Pseudo first-order reaction kinetics.
The increase in inlet pressure plays a bidirectional effect on the removal effect of BPA, from 0.3 MPa to 0.8 MPa; after 60 min, the conversion of each inlet pressure was 7.83 ± 0.48%, 12.65 ± 0.33%, 18.46% ± 0.28%, 15.87 ± 0.37%, and 98.14 ± 0.47%, respectively. The kinetic constants were 1.0 × 10−3, 2.6 × 10−3, 3.3 × 10−3, 3.4 × 10−3, and 3.0 × 10−3 min−1, respectively. Both the conversion and the kinetic constant showed an increase and then a decrease with increasing pressure. This may be because the pulse frequency is closer to the intrinsic frequency of the cavity when the inlet pressure is 0.5 MPa, and thus resonance occurs. Currently, the pulsed jet is more stable and has higher pressure peaks, resulting in a stronger cavitation effect. In addition, as the inlet pressure increases, the inlet velocity also rises accordingly. Due to the fixed structure of the nozzle, the frequency of the exit velocity pulsation also increases, resulting in a shorter cavitation development time. When the inlet pressure exceeds 0.3 MPa, the shorter cavitation development time results in an increased cavitation frequency and a better cavitation effect. However, when the cavitation development time is shortened to the optimum point, by further shortening, the growth time of the cavitation bubbles is compressed, resulting in a decrease in the number of cavitation bubbles that reach the collapse state and ultimately lessening the cavitation effect [36]. Table 1 compares the effect of the venturi, orifice plate, and self-excited oscillatory cavitation generator on BPA after 60 min under optimal structural parameters, respectively. Self-excited pulsed cavitation achieves the highest conversion and kinetic constant at the lowest reaction temperature for the same reaction time.

Table 1.
Removal of BPA by different HCRs.
3.5. Effect of Initial Fe (II) Concentration
Fe (II), serving as a catalyst for both H2O2 and PI, exerts an influence on the generation rate and yield of active radicals (as shown in Equations (12)–(14)). To assess its concentration-dependent effects on the reaction system, we varied the initial Fe (II) concentrations. The results are depicted in Figure 5. In all experimental sets, BPA underwent rapid degradation within the initial five minutes, followed by a gradual deceleration. This phenomenon can be rationalized by the rapid consumption of Fe (II) within the first five minutes, which vigorously reacted with H2O2 and PI to yield a copious amount of radicals. Subsequently, as Fe (II) decreased and Fe (III) exhibited inferior activation efficiency for H2O2 and PI, the reduced radical formation led to a decrease in the degradation rate. This observation aligns with the findings of Grčić and Xiong et al. [37,38]. Despite reports suggesting that excessive Fe (II) may diminish degradation rates by reacting with radicals, we refrained from investigating the inhibitory effects of higher ferrous sulfate doses, given the already satisfactory degradation achieved in this study [39]. Remarkably, the initial Fe (II) concentrations did not significantly alter the ultimate degradation efficiency, indicating that hydraulic cavitation sustains a moderate level of free Fe (II) in the reaction system. The possible reason for this phenomenon is the unavoidable erosion of the water pump impeller; in the blank control group, the concentration of total iron in the 60 min water samples was 2.38 × 10−2 (±0.02 × 10−2) mM, and the concentration of Fe (II) was 1.2 × 10−2 (±0.04 × 10−2) mM. Considering that Fenton and Fenton-like processes necessitate iron sludge treatment, the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system, even with low catalyst usage, demonstrates practical significance through its commendable treatment outcomes.
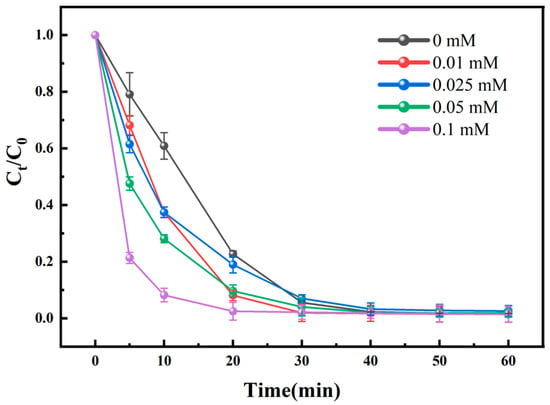
Figure 5.
Degradation of BPA by HC + Fenton + PI at different initial Fe (II) concentrations. Experimental conditions: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = 0−0.10 mM, [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.25 mM, inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures.
3.6. Effect of Initial H2O2 and PI Concentration
Figure 6a depicts the effect of the initial H2O2 concentration in the range of 0–1 mM of HC + Fenton + PI on the removal of BPA, and we can observe that the removal of BPA increases with the increase in the amount of oxidant H2O2. A higher initial H2O2 concentration will increase the yield of active radicals within the reaction system. The reactive radicals dominate the treatment of pollutants in this reaction system. When the initial H2O2 concentration was gradually increased from 0 mM to 0.25 mM, the removal rate of BPA was correspondingly increased from 46.48 ± 2.68% to 98.14 ± 0.97% with the pseudo-primary reaction half-lives of 129.08, 31.99, 13.73, and 6.97 min, respectively. Furthermore, an increase in the H2O2 concentration resulted in a significant increase in the rate of degradation of BPA within 5 min. This result is in agreement with the findings of Chadi et al. [30]. Specifically, the extreme conditions created by hydrodynamic cavitation and the catalysis by Fe (II) are available for the generation of •OH from H2O2, and the increase in the H2O2 concentration can accelerate the generation of •OH and singlet oxygen (as shown in Equations (5) and (6)) and inhibit the conversion of •OH to H2O2. Furthermore, the presence of large amounts of H2O2 promotes the regeneration reaction of Fe (III) reduction to Fe (II) (as shown in Equations (15)–(17)). This series of effects slowed down the competition between H2O2 and PI for Fe (II), which resulted in more significant degradation of BPA.
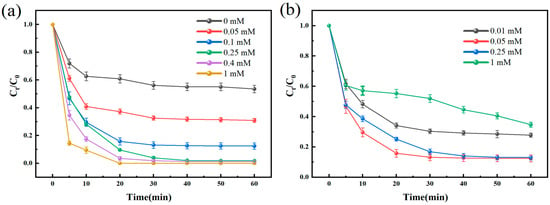
Figure 6.
Effect of (a) initial H2O2 concentration and (b) initial PI concentration on BPA removal in the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system. Experimental conditions: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = 0.05 mM, [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0−1 mM for (a), [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.1 mM, [PI]0 = 0.01−1 mM for (b), inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures.
The effect of periodate on the removal of BPA by the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system was tested at five different concentrations: 0.01, 0.05, 0.25, 0.40, and 1.00 mM, respectively. The results obtained are shown in Figure 6b. With the increase in the initial PI concentration, the degradation effect of BPA exhibited a trend of increasing followed by a decrease. When the initial PI concentration was increased from 0.01 mM to 0.05 mM, the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system effectively increased the BPA conversion from 72.24 ± 1.39% to 87.56 ± 2.24%, and the reaction rate constant increased from 28.3 × 10−3 min−1 to 41.8 × 10−3 min−1. However, when the initial concentration of PI was increased to 1 mM, the reaction process presented two phases. In the first phase, the excess PI acted as a free radical scavenger (as in Equation (10)), exerting a negative influence on the chemical activity of the system. The self-quenching of the reactive species led to a decrease in the rate constant. The reaction was only 5.7 × 10−3 min−1. As the reaction time continued to 30 min, the concentration of PI decreased, and its activation by HC and Fe (II) was manifested in the second stage, forming active substances as described before, which continued to react with BPA molecules and eventually improved the degradation effect. This process was confirmed by Chadi et al., who reported that the over-dosing of periodate rapidly consumed •OH and IO3• [30].
Gray correlation analysis is a method used for assessing the degree of association between factors in a system by comparing the degree of similarity or dissimilarity of trends between factors, and it is widely used in the fields of economics, engineering, environment, and health care. In this work, we used gray correlation analysis to evaluate the effects of the initial H2O2 concentration and PI concentration on the degradation of BPA. First, the convection of BPA was used as a reference series and each influence factor as a comparison series, and the experimental data were dimensionless using the mean value method. Subsequently, we calculated the correlation coefficient and correlation (ri) between the reference series and each comparison series, as shown in Equations (18) and (19).
The resolution coefficient ρ is 0.5, the minimum difference between the reference series and the comparison series is Δ(min), the maximum difference between the reference series and the comparison series is Δ(max), and the absolute difference between the comparison series and the reference series at each point is Δ0i(k).
The closer the correlation coefficient approaches 1, the higher the correlation. The correlation between the initial H2O2 concentration, PI concentration, and BPA convection were found to be 0.833 and 0.843, respectively, which revealed that the initial hydrogen peroxide concentration and periodate concentration would greatly affect the treatment of BPA by the HC + Fenton + PI method, with the periodate concentration having a slightly more prominent effect on it. Since the amount of periodate will have a bi-directional effect on the degradation of the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system, this seems to create resistance to the dissemination of the process. This phenomenon is prevalent in Fenton-like oxidation systems [40,41]. With the development of mechanistic learning, precise modulation of oxidant dosage has become possible, and we will present this approach in a later section with a view to overcoming this shortcoming.
3.7. Identification of the Radicals
Based on published reports, it is hypothesized that the reactive substances produced by the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system are mainly ROS (•OH, O2•−, and 1O2) and RIS (IO3• and IO4•) [13,30]. To explore the major radicals in the reaction, quenching experiments were performed by adding 5 mM of methanol (MeOH), tert-butanol (t-BuOH), and p-benzoquinone (BQ) as •OH, O2•− quenchers, respectively. The experimental results are shown in Figure 7. It can be observed that the degradation effect of BPA was significantly reduced after the addition of various quenching agents, which indicated that •OH and O2•− were the main active substances affecting the reaction system. The inhibitory effect of alcohols on the system was more pronounced than that of BQ, with the introduction of MeOH and t-BuOH leading to a 79.58 ± 4.07% and 76.52 ± 3.92% reduction in the convection of BPA, respectively, and the introduction of BQ leading to a 69.42 ± 3.56% reduction when compared with the blank group. Many studies have found that O2•− is not directly involved in oxidative reactions with organic matter, but rather as a precursor for the formation of •OH and 1O2 [13,30,42]. This also explains the more pronounced inhibition shown by alcohols. In conclusion, the degradation of BPA in the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system proceeds mainly via •OH oxidation, with O2•−, 1O2, IO3•, and IO4• participating as reactive species, while pyrolysis due to HC also provides some contribution.
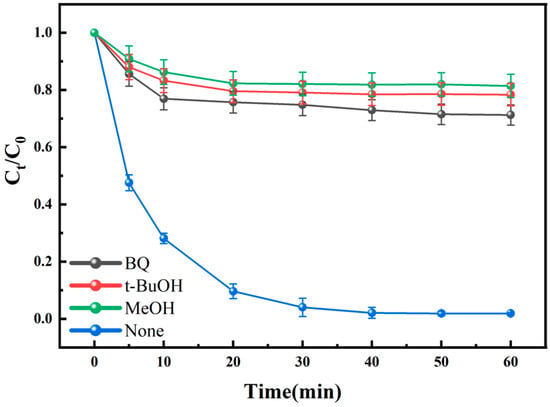
Figure 7.
Effect of MeOH, t-BuOH, and BQ on BPA removal by the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system. Condition: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.25 mM, inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures.
3.8. Degradation Pathway Prediction and Toxicity Assessment of BPA
The predicted degradation pathway of BPA is shown in Figure 8. The degradation of the BPA molecule occurs mainly through two pathways: pyrolysis and free radical degradation. In the environment of high temperature and high pressure generated by cavity collapse, the C–C bonds attached to the isopropyl and aromatic rings of BPA are homolyzed to form phenol (PhOH) and p-isopropylphenol (IPP) [43,44]. In general, •OH is mainly involved in hydrogen capture or electrophilic addition reactions. Combined with the pathway detection and the type of substances obtained in the available literature, it is hypothesized that the possible degradation pathway of BPA is the attack of hydroxyl radicals on the structure of the aromatic ring of BPA, joining the neighboring positions of the aromatic ring to form the monohydroxylated product Monohydroxylated bisphenol A (C15H16O3) and further to form the dihydroxylated product Dihydroxylated bisphenol A (C15H16O4) [45]. With the breaking of the C–C bond between the isopropyl group and the aromatic ring structure, 4-isopropenylphenol (C9H10O) and 4-hydroxyacetophenone (C8H8O2) were formed, and finally, carbon dioxide and water were formed by a ring-opening reaction and mineralization. This is in agreement with the findings of Torres et al. [44]. Tugba et al. studied the degradation of Bisphenol A via the hydroxyl radical pathway and similarly concluded that BPA is degraded through a process of monohydroxylation and dihydroxylation, which is facilitated by the coupling reaction of stabilizing organic radicals [46].
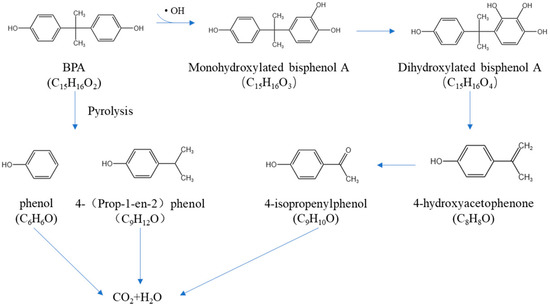
Figure 8.
BPA-degradation pathway prediction.
Table 2 shows the toxicity of BPA and intermediates, which were obtained using the chemical toxicity prediction software T.E.S.T. This software is developed to allow users to easily estimate the toxicity of chemicals using Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships (QSARs) methodologies. The physical properties (molecular descriptors) possessed by the structure of the chemical are used to construct mathematical models that predict toxicity measurements.

Table 2.
Predicted toxicity of BPA and intermediates.
The acute toxicity indicator LC50 is the concentration of the chemical tested in water that resulted in the deaths of half of the blackhead minnow (Fathead minnow) after an exposure period of 96 h. The information presented here is obtained from the ECOTOX aquatic toxicity database. When the LC50 value is below 1 mg/L, the toxicity is categorized as highly toxic. If the value falls between 1 and 10 mg/L, it is classified as toxic. Similarly, if the value ranges from 10 to 100 mg/L, the substance is considered toxic. The developmental toxicity values are derived from the binary toxicity revision values that were established for the CAESAR study. Mutagenicity is evaluated by analyzing data obtained from the Ames test. The criteria for assessing developmental toxicity and mutagenicity are comparable: a data value above 0.5 indicates a significant impact on biological development or mutagenicity, while a value equal to or below 0.5 suggests a lesser impact on biological development or mutagenicity.
This is a good example of the toxicity of BPA and intermediates, and it is not surprising to see that this is the case for BPA. It can be seen that some of the by-products from the degradation process show an increasing trend of toxicity. Therefore, further treatment techniques are needed to ultimately achieve complete oxidation.
3.9. Effects of Different Water Sources
To investigate the influence of the water matrix on the effect of HC + Fenton + PI and HC + Fenton combination processes on the treatment of BPA, its treatment effect was compared in three aqueous environments, namely, ultrapure water, tap water, and lake water (longitude: 114.270, latitude: 30.455). The main water quality parameters of lake water and tap water are shown in Table 3. The degradation process is shown in Figure 9a and Figure 9b, respectively. The conversion after 60 min was 98.14 ± 0.97%, 98.50 ± 0.83%, and 42.56 ± 3.78%, respectively. The conversion increased by 3.00 ± 0.24%, 6.83 ± 0.04%, and 10.24 ± 2.00%, respectively, compared to the HC + Fenton oxidation system.

Table 3.
Main water quality parameters of lake water and tap water (mean ± absolute deviation).
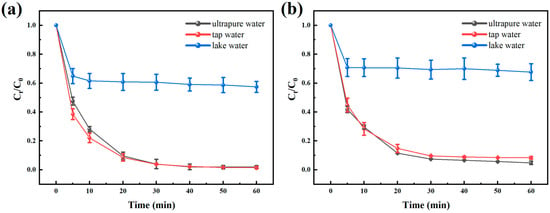
Figure 9.
Effects of different water sources on BPA removal by (a) the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system and (b) the HC + Fenton oxidation system. Experimental conditions: [BPA]0 = 10 mg/L, [Fe (II)]0 = [PI]0 = 0.05 mM, [H2O2]0 = 0.25 mM, inlet pressure = 0.5 MPa, pH = 3 ± 0.2, temperature = 25 °C. The error bars represent the standard deviation of duplicated measures.
The degradation rate decreased sharply after 10 min in lake water. This was attributed to the high content of dissolved organic matter (DOM) that competed with BPA for active free radicals and surface active sites available for pyrolysis on the surface of the cavitation vesicles [47,48]. Meanwhile, the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the lake water may evaporate into the gas phase of the cavitation bubbles, and the process of their thermolysis and dissociation will consume the energy generated in the process of the collapse of the cavitation bubbles, affecting the synergistic effect of the system [49,50].
3.10. Surrogate Model and Projection
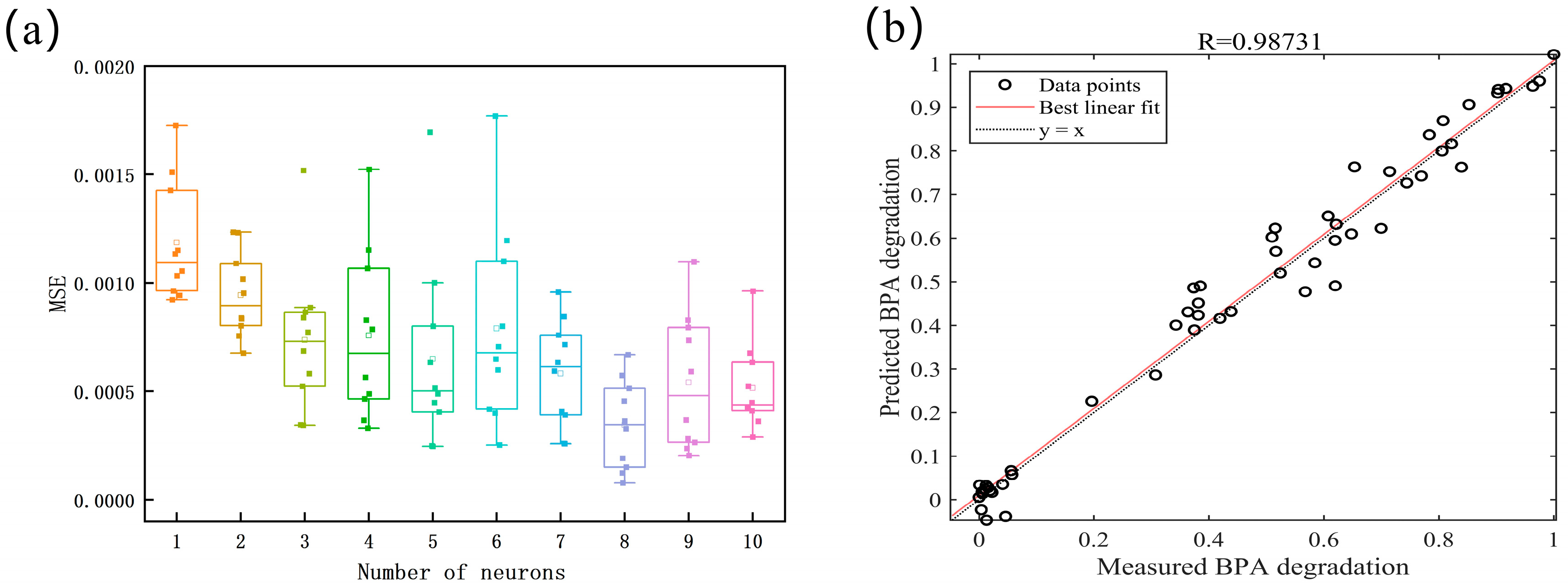
This section aims to provide an accurate simulation and prediction tool for the oxidative degradation of BPA within a combined HC + Fenton + PI process, leveraging artificial neural network (ANN) technology to enhance automation and intelligence in the realm of chemical oxidation processes. In this work, the neural network comprises a three-layer back-propagation ANN, including an input layer (independent variable), an output layer (dependent variable), and a hidden layer, with the Levenberg–Marquardt back-propagation algorithm employed for optimization. After debugging, appropriate mean square error parameters and radial basis function distribution parameters were selected, and the network was subsequently constructed and trained while utilizing the neural network toolbox in MATLAB R2017 software. In turn, the fitting and extension of the performance curve of the combined process was accomplished.
The neural network architecture is depicted in Figure 10, featuring an input layer comprising five variables: the inlet pressure, reaction time, Fe (II) concentration, H2O2 concentration, and PI concentration. The output layer, meanwhile, encompasses the dependent variable, which is the average convection of BPA. A total of 60 experimental data points, spanning 5, 10, and 20 min, were selected for modeling purposes, aimed at mitigating overfitting issues that could arise due to the proximity of multiple experimental data sets at the later stages of the reaction. Here, the data are dimensionless and subsequently normalized to mitigate the instability that arises from varying magnitudes and value ranges. This normalization facilitates faster convergence of the neural network and enhances its model performance. The entire data set is partitioned into a training set (70%, 42 data points), a validation set (15%, 9 data points), and a test set (15%, 9 data points). This division ensures a more comprehensive and objective assessment of the performance and generalization capabilities of the ANN model. The optimal number of neurons in the hidden layer is determined through the trial-and-error method, where the number of hidden layers is varied from 1 to 10 during training. Each configuration is trained 10 times to account for variations in initial weights, biases, and other training parameters, which can lead to different training outcomes. Additionally, this approach facilitates the evaluation of the model’s stability. The mean square error (MSE) is used as a comparison condition, and its calculation process is shown in Equation (20):
where Yi.pred and Yi.exp are the experimental and predicted values of the i-th dependent variable, respectively, and n is the number of data points.
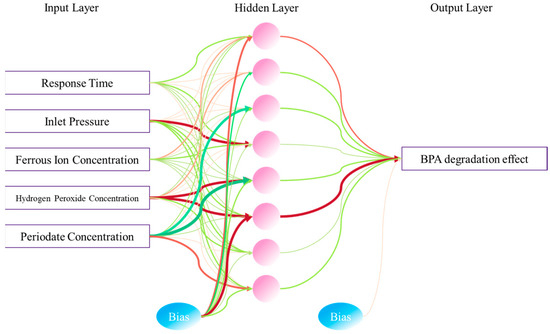
Figure 10.
Neural network topology (the thickness of the line indicates the magnitude of the weights, and the green line indicates signal enhancement, the red line indicates signal weakening).
Figure 11a illustrates the optimization process for the number of neurons in the hidden layer. It is evident that when the number of neurons is set to 8, the model attains the smallest MSE mean value alongside improved stability, thus establishing the neural network structure with this optimal number. Figure 11b presents a comparison between the predicted and experimental values of the neural network, trained with the optimized structure, for the BPA-degradation process. The y = x line signifies a perfect alignment between the experimental and predicted values, and the high degree of agreement is further corroborated by the regression coefficient of R² = 0.98731, thereby validating the ANN model’s high accuracy in simulating the BPA-removal process via the HC + Fenton + PI method [51,52]. Liu et al. reviewed 155 articles on the application of AI techniques in textile coloring-related fields, and they found that 90.9% of these articles focused on textile wastewater treatment. This shows that the application of AI in water environment management still needs to be explored, and future research should more extensively expand the effects of different environmental factors and dynamic process optimization to promote the improvement in water environment management capability [53].
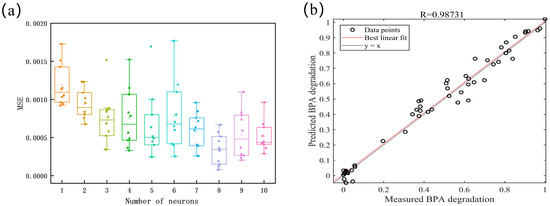
Figure 11.
(a) Relationship between the number of neurons in the hidden layer and MSE; (b) Comparison between predicted and experimental values.
4. Conclusions
This study examined the effectiveness of the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation method in treating BPA. At an inlet pressure of 0.5 MPa and a molar ratio of BPA, Fe (II), H2O2, and PI of 1:1:5:1, the average conversion rates of BPA in ultrapure water, tap water, and lake water within 60 min were 98.14%, 98.50%, and 42.56%, respectively. When compared to the HC + Fenton oxidation system, the rates exhibited enhancements of 3.00%, 6.83%, and 10.24%, respectively. The boost is due to the introduction of PI, which has extended the range of reactive radicals and improved resistance to complicated water conditions. The quenching studies provided evidence that the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system is resistant to failure caused by a single quenching agent. Furthermore, the predominant reactive species was determined to be •OH. The toxicological research results showed a decrease in the toxicity of BPA as it underwent degradation. The ANN model demonstrated exceptional accuracy in simulating and predicting the process of BPA elimination by the HC + Fenton + PI oxidation system. In summary, this work broadens the potential for combining HC with AOPs, which helps improve the effectiveness of treating contaminated water.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.W.; Investigation, B.L.; Writing—review and editing, J.W.; Visualization, B.L.; Formal analysis, S.X.; Supervision, S.X.; Funding acquisition, J.W.; Resources B.J.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2021CFB495) and the Hubei Provincial Construction Science and Technology Research Plan (2023-1656-177).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Wang, P.W.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, C.H.; Fang, L.J.; Chen, M.L. Prenatal to Preschool Exposure of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A Exposure and Neurodevelopment in Young Children. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2024, 65, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, S.; Mizutare, T.; Makishima, M.; Suzuki, N.; Fujimoto, N.; Igarashi, K.; Ohta, S. Potent Estrogenic Metabolites of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B Formed by Rat Liver S9 Fraction: Their Structures and Estrogenic Potency. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 78, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ying, G.G.; Zhao, J.L.; Chen, Z.F.; Lai, H.J.; Su, H.C. 4-Nonylphenol, Bisphenol-A and Triclosan Levels in Human Urine of Children and Students in China, and the Effects of Drinking These Bottled Materials on the Levels. Environ. Int. 2013, 52, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montévil, M.; Acevedo, N.; Schaeberle, C.M.; Bharadwaj, M.; Fenton, S.E.; Soto, A.M. A Combined Morphometric and Statistical Approach to Assess Nonmonotonicity in the Developing Mammary Gland of Rats in the Clarity-BPA Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 057001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Davis, B.; Schaeberle, C.M.; Sonnenschein, C.; Soto, A.M. Perinatally Administered Bisphenol A as a Potential Mammary Gland Carcinogen in Rats. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarny-Krzymińska, K.; Krawczyk, B.; Szczukocki, D. Toxicity of Bisphenol A and Its Structural Congeners to Microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Desmodesmus armatus. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukazawa, H.; Hoshino, K.; Shiozawa, T.; Matsushita, H.; Terao, Y. Identification and Quantification of Chlorinated Bisphenol A in Wastewater from Wastepaper Recycling Plants. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.C.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlström, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A Review of Sources, Environmental Levels, and Potential Human Health Impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.B.; Peart, T.E. Determination of Bisphenol A in Sewage Effluent and Sludge by Solid-Phase and Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2000, 83, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahanshahi, S.; Badiefar, L.; Khodabandeh, M.; Heidarnia, M.A.; Yakhchali, B. Bioremediation of a Salty Petrochemical Wastewater Containing Bisphenol A by a Novel Indigenous Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. RSC Adv. 2022, 13, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takdastan, A.; Kakavandi, B.; Azizi, M.; Golshan, M. Efficient Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Using Ferroferric Oxide Supported on Carbon/UV/US System: A New Approach into Catalytic Degradation of Bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wei, X.J.; Shang, Y.B.; Qi, Y.T.; Shi, J.; Li, K.Q.; Jin, X.; Bai, X.; Shi, X.; Jin, P.K. Ti3+ Self-Doped TiO2 Anchored with Iron Oxide Quantum Dots as an Efficient Persulfate Catalyst for the Enhanced Removal of Typical Phenolic Pollutants from Water under Visible Light. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, H.; Oh, H.; Haider, Z.; Choi, J.; Shin, Y.U.; Kim, H.I.; Lee, J. Revisiting the Oxidizing Capacity of the Periodate-H Mixture: Identification of the Primary Oxidants and Their Formation Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5763–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, B.-M.; Nam, S.-N.; Jung, B.; Choi, J.S.; Park, C.M.; Choong, C.E.; Jang, M.; Jho, E.H.; Son, A.; Yoon, Y. Photocatalytic and Electrocatalytic Degradation of Bisphenol A in the Presence of Graphene/Graphene Oxide-Based Nanocatalysts: A Review. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, F.S.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Cui, M.C.; Ma, J.J.; Han, Z.C.; Khim, J. Comparison of Effects of Multiple Oxidants with an Ultrasonic System under Unified System Conditions for Bisphenol A Degradation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2023, 329, 138526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.L.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, M.F.; Deng, C.; Liu, H.B.; Ma, J.; Li, Y. Effect of Cavitation Hydrodynamic Parameters on Bisphenol A Removal. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Ji, L.; Wang, G.; Zhao, S.; Yoon, J.Y.; Chen, S. A Review on Hydrodynamic Cavitation Disinfection: The Current State of Knowledge. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moholkar, V.S.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Pandit, A.B. Hydrodynamic Cavitation for Sonochemical Effects. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 1999, 6, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampeta, C.; Bertaki, K.; Triantaphyllidou, I.-E.; Frontistis, Z.; Koutsoukos, P.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Pilot-Scale Hybrid System Combining Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Sedimentation for the Decolorization of Industrial Inks and Printing ink Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 114108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarkoti, C.; Gujar, S.K.; Gogate, P.R.; Pandit, A.B. Pilot Scale Degradation of Sulfamerazine Using Different Venturi Based Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Ultrasound Reactors in Combination with Oxidation Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. Pubchem Compound Summary for CID 6623, Bisphenol A. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Bisphenol-A (accessed on 7 August 2024).
- Choi, J.; Cui, M.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Son, Y.; Khim, J. Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Activated Persulfate Oxidation for Degradation of Bisphenol A: Kinetics and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagol, M.; Przyjazny, A.; Boczkaj, G. Wastewater Treatment by Means of Advanced Oxidation Processes Based on Cavitation—A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 599–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Cui, M.; Lee, Y.; Ma, J.; Kim, J.; Son, Y.; Khim, J. Hybrid Reactor Based on Hydrodynamic Cavitation, Ozonation, and Persulfate Oxidation for Oxalic Acid Decomposition during Rare-Earth Extraction Processes. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 52, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioan, I.; Wilson, S.; Lundanes, E.; Neculai, A. Comparison of Fenton and Sono-Fenton Bisphenol A Degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignatello, J.J.; Oliveros, E.; MacKay, A. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Organic Contaminant Destruction Based on the Fenton Reaction and Related Chemistry. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 36, 1–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J. A Review of Classic Fenton’s Peroxidation as an Advanced Oxidation Technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleveland, V.; Bingham, J.P.; Kan, E. Heterogeneous Fenton Degradation of Bisphenol A by Carbon Nanotube-Supported Fe3O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadi, N.E.; Merouani, S.; Hamdaoui, O.; Bouhelassa, M.; Ashokkumar, M. H2O2/Periodate (IO4−): A Novel Advanced Oxidation Technology for the Degradation of Refractory Organic Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Moholkar, V.S. Carbamazepine Degradation Using Ternary Hybrid Advanced Oxidation Process of Hydrodynamic Cavitation + Photocatalysis (UV/ZnO/ZnFe2O4) + persulfate: Kinetic Investigations. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarniya, Z.; Sadeghi, M.-T.; Baradaran, S. Decolorization of Congo Red via Hydrodynamic Cavitation in Combination with Fenton’s Reagent. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 150, 107874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Chen, M.-J.; Huang, C.-P.; Kuo, J.; Lo, S.-L. Efficient Sonochemical Degradation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Using Periodate. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 31, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinthala, M.; Ashwathanarayanaiah, B.K.; Kulkarni, S.; Udayakishore, Y.; Halyal, A.; Chavan, A. Intensification of Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) for the Degradation of Bisphenol-A. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2021, 19, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Beigrezaee, S.; Daglioglu, N.; Guzel, E.Y.; Heydari, M.; Ravankhah, N. Combination of Hydrodynamic Cavitation with CoFe2O4 Photocatalyst for Activation of Peracetic Acid under UVC Irradiation in Synergistic Degradation of Bisphenol A. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogate, P.R.; Patil, P.N. Combined Treatment Technology Based on Synergism between Hydrodynamic Cavitation and Advanced Oxidation Processes. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2015, 25, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grčić, I.; Vujević, D.; Koprivanac, N. Modeling the Mineralization and Discoloration in Colored Systems by (US)Fe2+/H2O2/S2O82− Processes: A Proposed Degradation Pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 157, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.H.; Zhou, T.; Bao, J.G.; Du, J.K.; Faheem, M.; Luo, L.T. Degradation Mechanism of Bisphenol S via Hydrogen Peroxide/Persulfate Activated by Sulfidated Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 83545–83557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Suo, N.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y. Removal of Diclofenac by Three-Dimensional Electro-Fenton-persulfate (3D Electro-Fenton-PS). Chemosphere 2019, 219, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epold, I.; Trapido, M.; Dulova, N. Degradation of Levofloxacin in Aqueous Solutions by Fenton, Ferrous Ion-Activated Persulfate and Combined Fenton/Persulfate Systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Ayaz, T.; Ali, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Sheng, X.; Fu, R.; Ullah, S.; Lyu, S. Innovative Strategy for the Effective Utilization of Coal Waste Slag in the Fenton-like Process for the Degradation of Trichloroethylene. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.N.A.; Li, H.F.; Lin, J.M. Enhancement of Periodate-Hydrogen Peroxide Chemiluminescence by Nitrogen Doped Carbon Dots and Its Application for the Determination of Pyrogallol and Gallic Acid. Talanta 2016, 153, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, S.; Ono, S.; Yokoyama, S.; Kameda, T.; Yoshioka, T. Fate of Bisphenol A Pyrolysates at Low Pyrolytic Temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 125, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.A.; Abdelmalek, F.; Combet, E.; Pétrier, C.; Pulgarin, C. A Comparative Study of Ultrasonic Cavitation and Fenton’s Reagent for Bisphenol A Degradation in Deionised and Natural Waters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 146, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, J.C.C.; Teodoro, J.A.R.; Afonso, R.; Aquino, S.F.; Augusti, R. Photodegradation of Bisphenol A in Aqueous Medium: Monitoring and Identification of by-Products by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I.; Genc, B. Bisphenol A Treatment by the Hot Persulfate Process: Oxidation Products and Acute Toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sonochemical Degradation of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in Landfill Groundwater: Environmental Matrix Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8057–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, A.; Baradaran, S.; Movahedirad, S. Synergistic Degradation of Congo Red by Hybrid Advanced Oxidation via Ultraviolet Light, Persulfate, and Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 272, 116042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferkous, H.; Hamdaoui, O.; Merouani, S. Sonochemical Degradation of Naphthol Blue Black in Water: Effect of Operating Parameters. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2015, 26, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpe, S.; Rao, P.V. Application of Advanced Oxidation Processes and Cavitation Techniques for Treatment of Tannery Wastewater—A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontistis, Z.; Hapeshi, E.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Mantzavinos, D. Ultraviolet-Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Methyl Orange: A Comparison between Artificial Neural Networks and Factorial Design for Process Modelling. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Maurya, A.K.; Narayana, P.L.; Pasha, S.K.K.; Reddy, M.R.; Hatshan, M.R.; Darwish, N.M.; Kori, S.A.; Cho, K.-K.; Reddy, N.S. Knowledge Extraction of Sonophotocatalytic Treatment for Acid Blue 113 Dye Removal by Artificial Neural Networks. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.B.; Lo, C.K.Y.; Kan, C.W. Application of Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Textile Wastewater Decolorisation Fields: A Systematic and Citation Network Analysis Review. Color. Technol. 2022, 138, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, L.; Bi, X.; Khanal, S.K.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Guo, G. Optimization of a Novel Engineered Ecosystem Integrating Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur Biotransformation for Saline Wastewater Treatment Using an Interpretable Machine Learning Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12989–12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).