Composition and Distribution of Bacteria, Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Shanghai Port, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of River Water Samples
2.2. Preparation of Water Samples
2.3. High-Throughput Metagenomic Sequencing
2.4. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. High-Throughput Sequencing Results
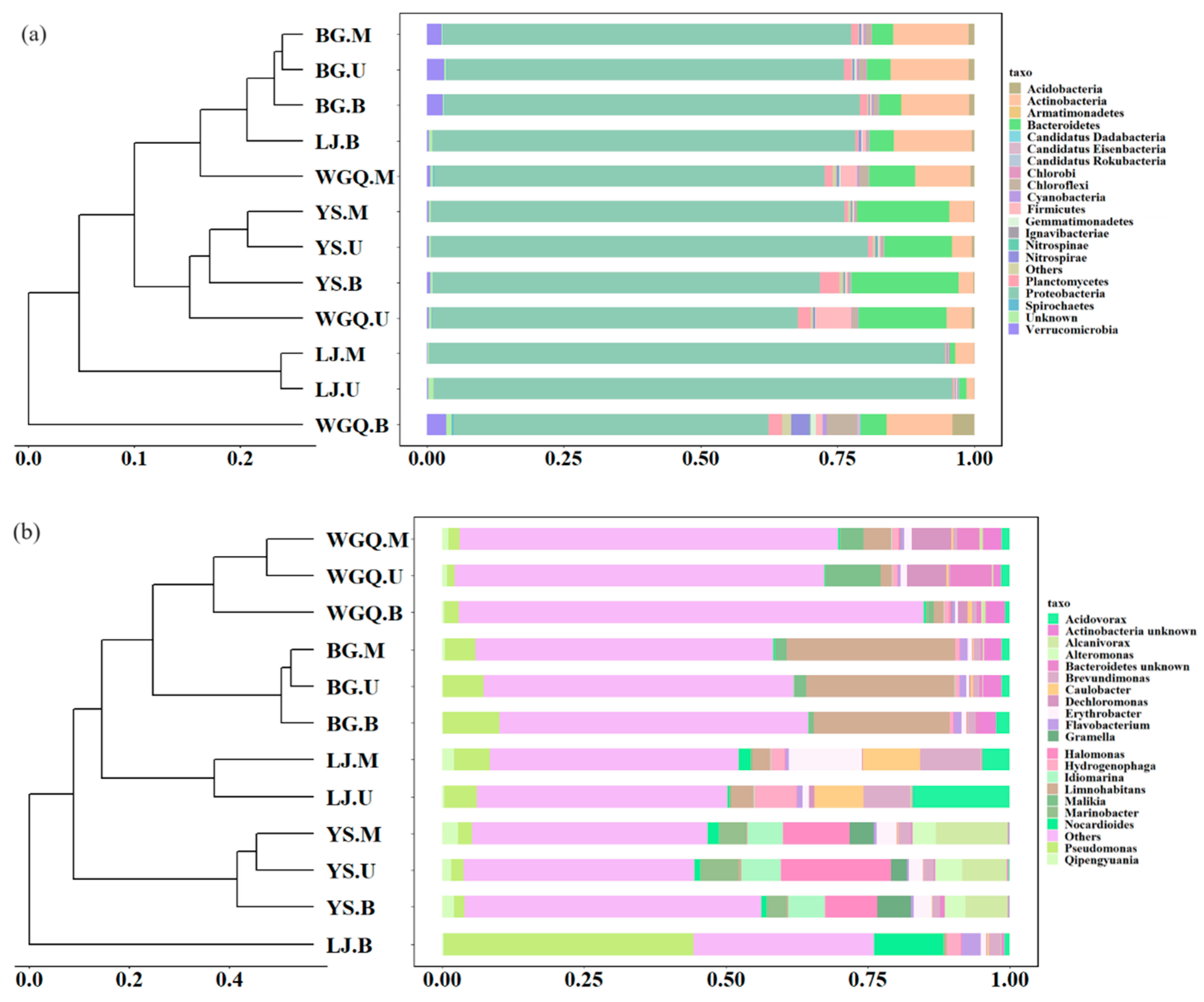
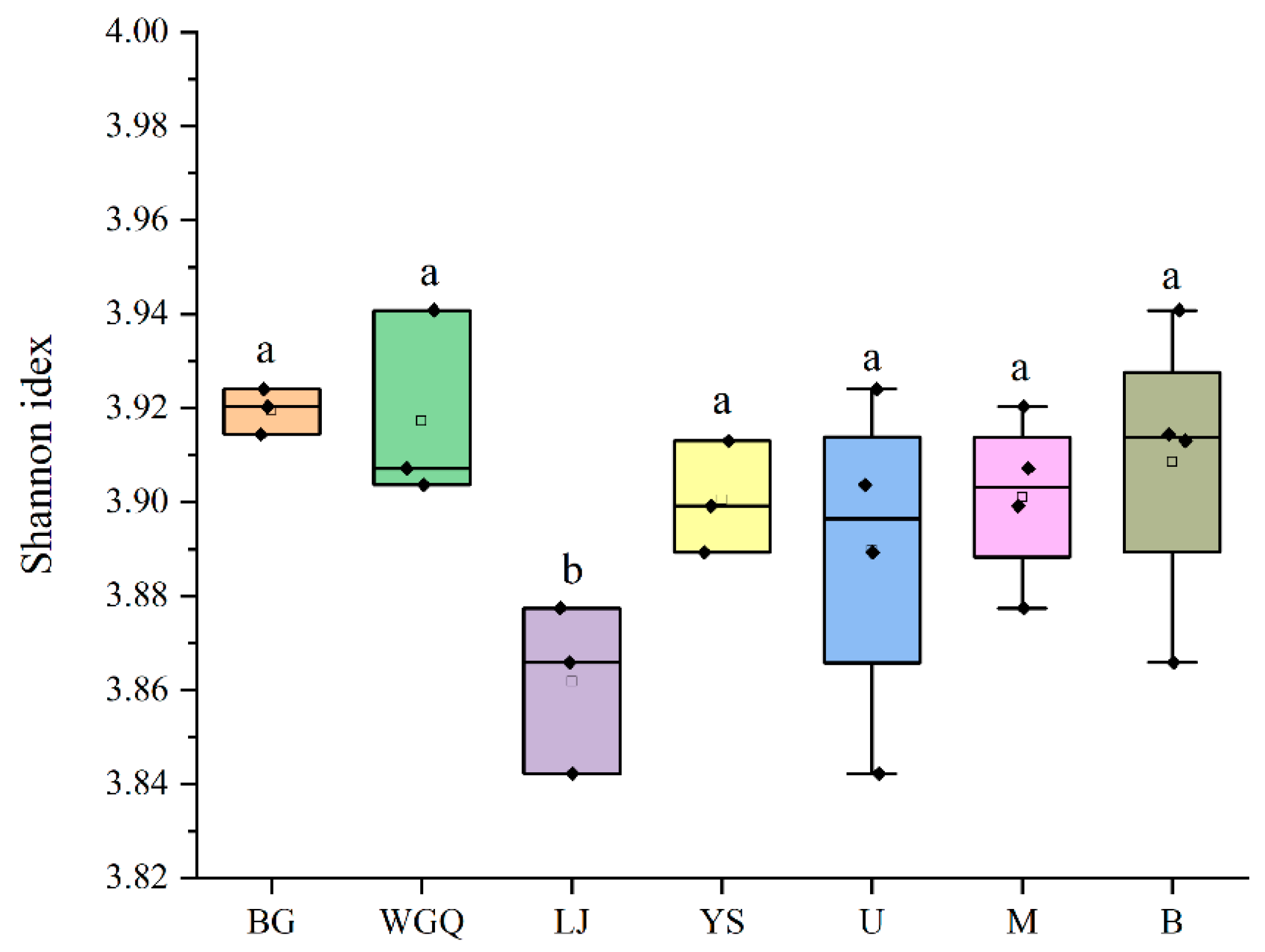
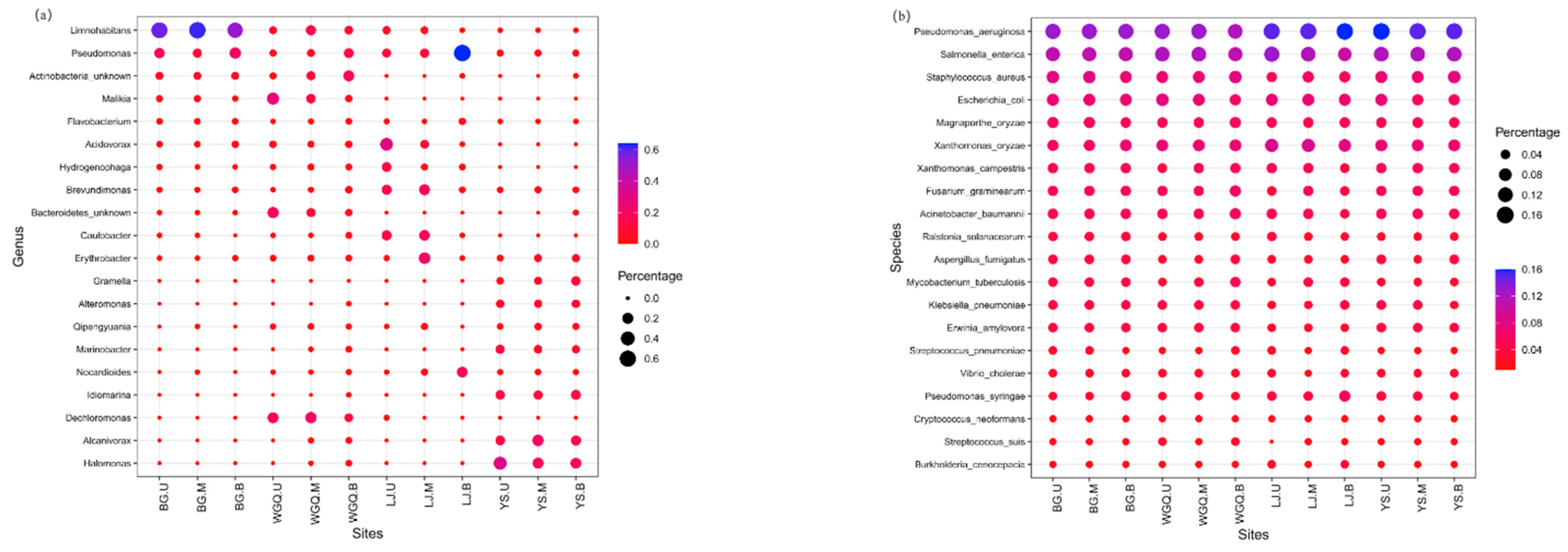
3.2. Community Structure and Distribution of Bacteria
3.3. Diversity and Composition of Pathogens
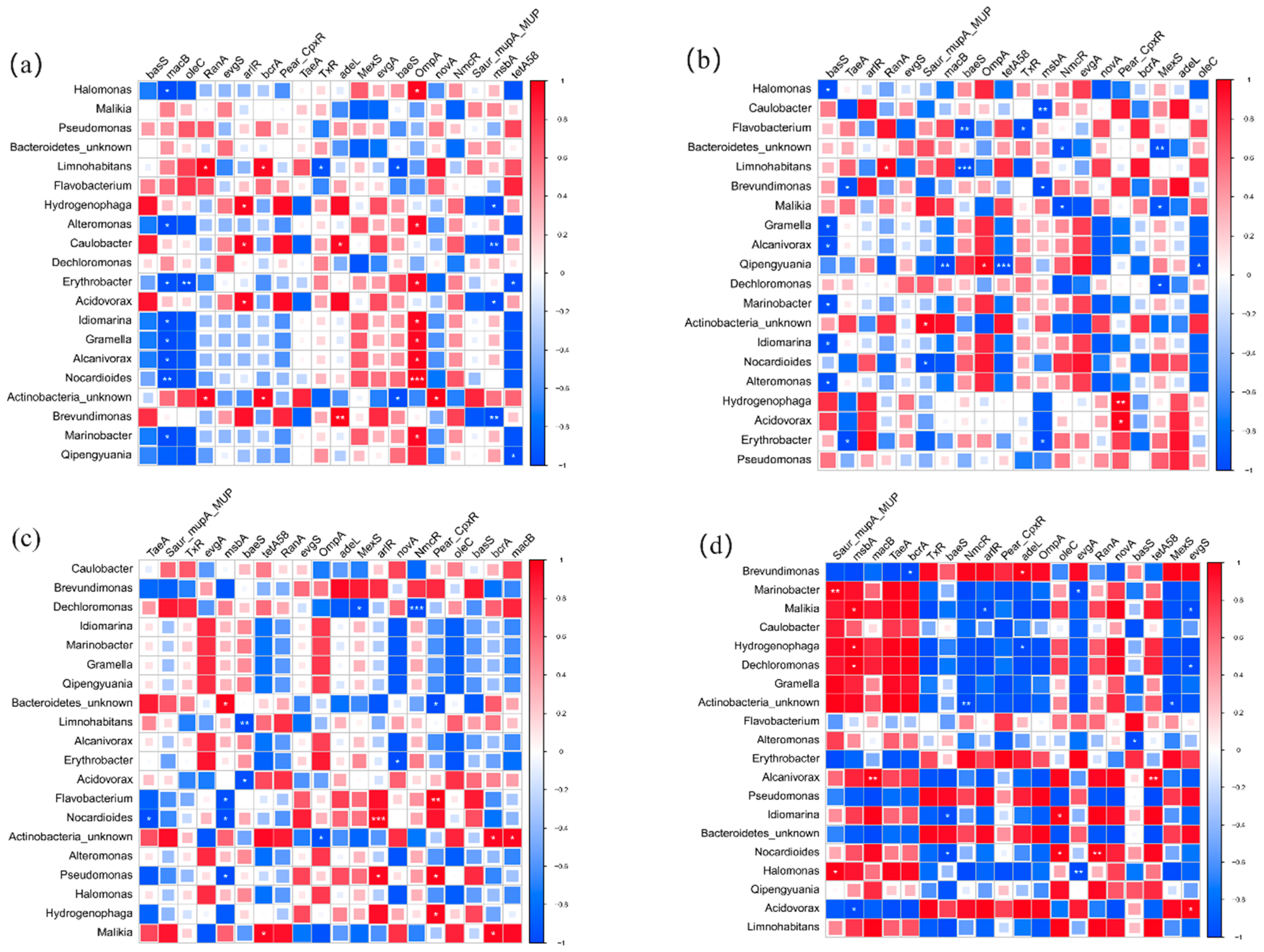
3.4. Indicator Species of Bacteria and Pathogens
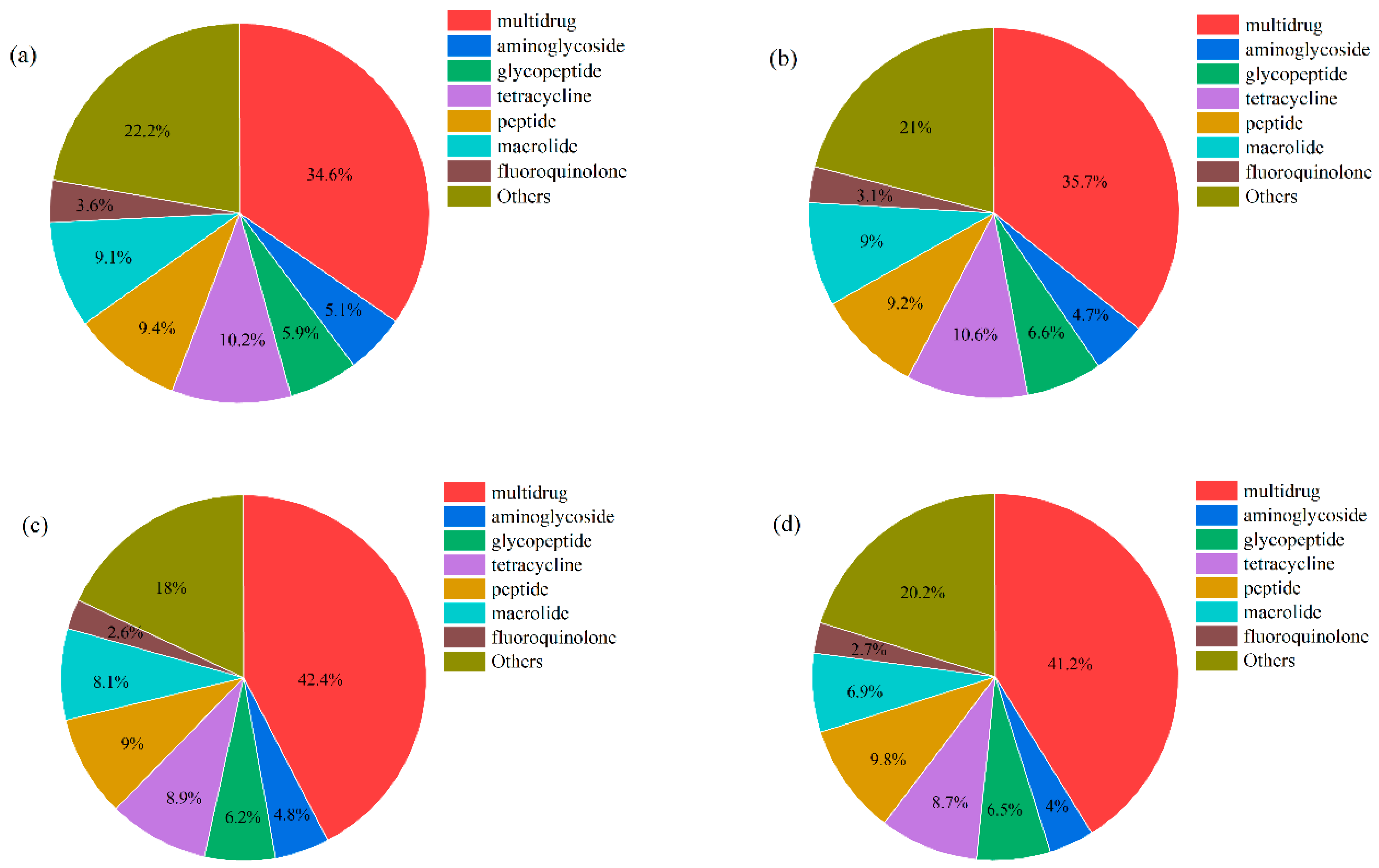
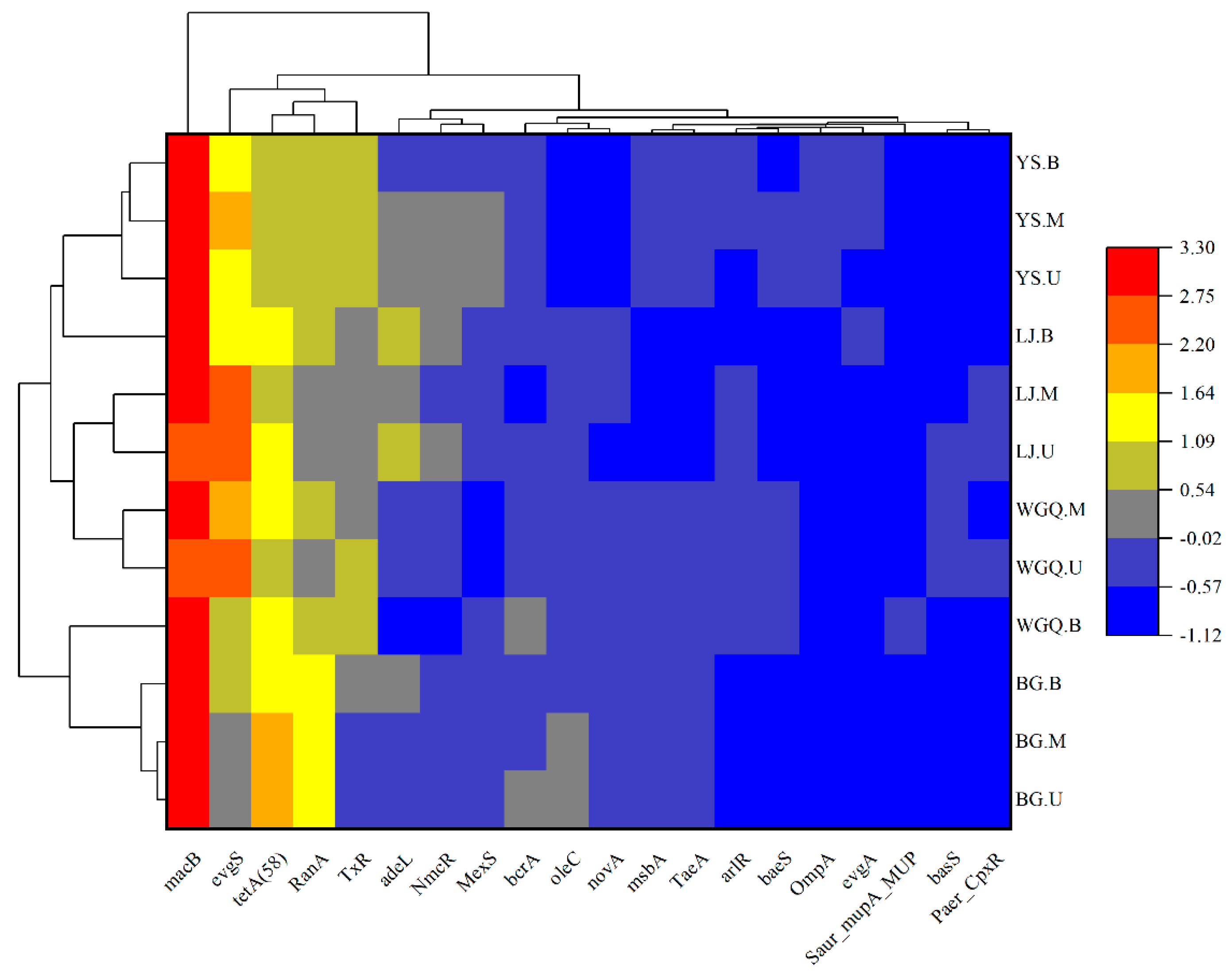
3.5. Diversity and Composition of the ARGs
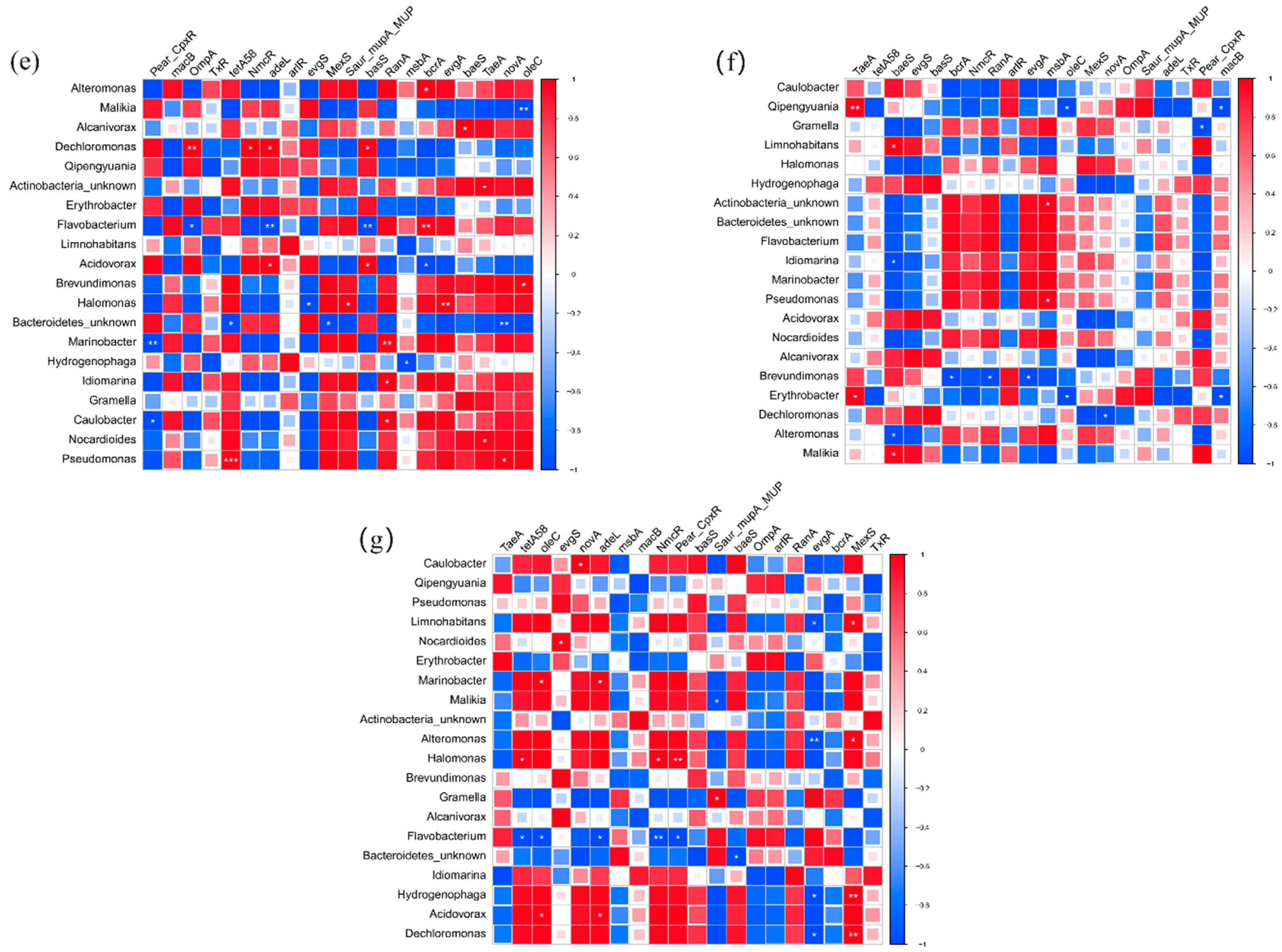
3.6. Correlation between Bacteria, Pathogens, and ARGs
4. Discussion
4.1. Occurrence and Distribution of the Bacteria
4.2. Potential Risk of Pathogens and ARGs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ward, N.D.; Megonigal, J.P.; Bond-Lamberty, B.; Bailey, V.L.; Butman, D.; Canuel, E.A.; Diefenderfer, H.; Ganju, N.K.; Goni, M.A.; Graham, E.B.; et al. Representing the function and sensitivity of coastal interfaces in Earth system models. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Munot, H.; Shouche, Y.S.; Madamwar, D. Response of bacterial community structure to seasonal fluctuation and anthropogenic pollution on coastal water of Alang-Sosiya ship breaking yard, Bhavnagar, India. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Luan, W.X.; Wang, X.T.; Wan, S.L.; Su, M.; Zhang, Z.C. Spatial expansion regular pattern and driving factors of estuarine and coastal harbors. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 216, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Wang, W.X. Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbra, R.M.; Pittam, N.; Royston, K.A.; Darbra, J.P.; Journee, H. Survey on environmental monitoring requirements of European ports. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Fenchel, T.M.; Field, J.G.; Gray, J.S.; Meyer-Reil, L.-A.; Thingstad, F.J.M.E.P.S. The Ecological Role of Water-Column Microbes in the Sea*. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1983, 10, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, A.; Meyer, N.; Papanikolopoulou, L.A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Pohnert, G. The Algicidal Bacterium Kordia algicida Shapes a Natural Plankton Community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02779-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, E.D. Toward a Global Classification of Coastal Anthromes. Land 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.; Suwa, Y.; Urushigawa, Y. Distribution of phospholipid ester-linked fatty acid biomarkers for bacteria in the sediment of Ise Bay, Japan. Mar. Chem. 1993, 42, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treusch, A.H.; Vergin, K.L.; Finlay, L.A.; Donatz, M.G.; Burton, R.M.; Carlson, C.A.; Giovannoni, S.J. Seasonality and vertical structure of microbial communities in an ocean gyre. ISME J. 2009, 3, 1148–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.F.; Riemann, L.; Bertilsson, S. Pyrosequencing reveals contrasting seasonal dynamics of taxa within Baltic Sea bacterioplankton communities. ISME J. 2010, 4, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, J.A.; Field, D.; Swift, P.; Newbold, L.; Oliver, A.; Smyth, T.; Somerfield, P.J.; Huse, S.; Joint, I. The seasonal structure of microbial communities in the Western English Channel. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 3132–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.C.; Silliman, B.R.; Lafferty, K.D. Marine Disease Ecology, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2020; p. ix. 269p. [Google Scholar]
- Selakovic, S.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Heesterbeek, H. Infectious disease agents mediate interaction in food webs and ecosystems. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.J.; Hopkins, S.; Bell, K.C.; Dona, J.; Godfrey, S.S.; Kwak, M.L.; Lafferty, K.D.; Moir, M.L.; Speer, K.A.; Strona, G.; et al. A global parasite conservation plan. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 250, 108596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groner, M.L.; Maynard, J.; Breyta, R.; Carnegie, R.B.; Dobson, A.; Friedman, C.S.; Froelich, B.; Garren, M.; Gulland, F.M.D.; Heron, S.F.; et al. Managing marine disease emergencies in an era of rapid change. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, J.M.; Groner, M.L.; Smith, M.W.; Vogelbein, W.K.; Taylor, D.M.; Landers, D.F.; Swenarton, J.T.; Gauthier, D.T.; Sadler, P.; Matsche, M.A.; et al. Impact of disease on the survival of three commercially fished species. Ecol. Appl. 2017, 27, 2116–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onufryk, J.I.; Ebersole, J.P.; DeFilippo, J.; Beck, G. Diadema antillarum on St. Croix, USVI: Current Status and Interactions with Herbivorous Fishes. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2018, 91, 391–397. [Google Scholar]
- Behrens, M.D.; Lafferty, K.D. Effects of marine reserves and urchin disease on southern Californian rocky reef communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 279, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graciaa, D.S.; Cope, J.R.; Roberts, V.A.; Cikesh, B.L.; Kahler, A.M.; Vigar, M.; Hilborn, E.D.; Wade, T.J.; Backer, L.C.; Secor, E.; et al. Outbreaks Associated with Untreated Recreational Water—United States, 2000–2014. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 67, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Water Sanitation and Health [EB/OL]. 2015. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/water-sanitation-and-health (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Thompson, R.M.; Mouritsen, K.N.; Poulin, R. Importance of parasites and their life cycle characteristics in determining the structure of a large marine food web. J. Anim. Ecol. 2005, 74, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, J.D.; Leopold, D.J.; Smallidge, P.J. Pathogens, patterns, and processes in forest ecosystems. Bioscience 1995, 45, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.F.; Wang, X.C.; Han, Q.; Yu, Q.L.; Wanyan, R.J.; Li, H. Bibliometric analysis of papers on antibiotic resistance genes in aquatic environments on a global scale from 2012 to 2022: Evidence from universality, development and harmfulness. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekunberri, I.; Villagrasa, M.; Balcazar, J.L.; Borrego, C.M. Contribution of bacteriophage and plasmid DNA to the mobilization of antibiotic resistance genes in a river receiving treated wastewater discharges. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.H.; Qiao, M.; Lv, Z.E.; Guo, G.X.; Jia, Y.; Su, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.G. Impact of reclaimed water irrigation on antibiotic resistance in public parks, Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chen, Q.L.; Shen, F.X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S.Y.; Fan, H.; Da, G.; Huang, R.J.; et al. Global Survey of Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10975–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Han, M.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W. Profiles of antibiotic resistance genes in an inland salt-lake Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China: The relationship with antibiotics, environmental factors, and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.Y.; Cui, Y.X.; Tian, W.; Wei, H.W.; Chen, Q.H.; Liu, B.L.; Zhang, D.; Xie, B. Vessel transport of antibiotic resistance genes across oceans and its implications for ballast water management. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, J.P.; Yang, Y.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Chen, H.Y. Biogeography and diversity patterns of antibiotic resistome in the sediments of global lakes. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Lyons, B.; Al-Sarawi, H.A.; Behbehani, M.; Shajan, A.; Razzack, N.A.; Zakir, F.; Alam, F. Antibiotic Resistance Genes Associated with Marine Surface Sediments: A Baseline from the Shores of Kuwait. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, S.B.; Marshall, B. Antibacterial resistance worldwide: Causes, challenges and responses. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S122–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalder, T.; Barraud, O.; Casellas, M.; Dagot, C.; Ploy, M.C. Integron involvement in environmental spread of antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampani, M.; Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Chandrasekar, A.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Graham, D.W.; Gothwal, R.; Moodley, A.; Chadag, V.M.; Wiberg, D.; Langan, S. Fate and transport modelling for evaluating antibiotic resistance in aquatic environments: Current knowledge and research priorities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, F.; Shirzad-Aski, H.; Ferreira, S. Antimicrobials and Food-Related Stresses as Selective Factors for Antibiotic Resistance along the Farm to Fork Continuum. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Z.; Wang, Q.Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.X.; Lan, R.T.; He, F.L.; Yang, Q. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes within the bacterial communities in aquacultural environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, W.T.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Su, L.H.; Kong, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, J. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics, antimicrobial resistance determinants and potential human pathogens in a wastewater treatment plant and their effects on receiving waters in Nanjing, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. Clustering huge protein sequence sets in linear time. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, F.F.; Egan, S.; Kjelleberg, S. Ecology of type II secretion in marine gammaproteobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, S.B.; Sun, G.P.; Xu, Z.C.; Xu, M.Y. Phylogenetic diversity, composition and distribution of bacterioplankton community in the Dongjiang River, China. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizusawa, N.; Reza, M.S.; Oikawa, C.; Kuga, S.; Iijima, M.; Kobiyama, A.; Yamada, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Ikeda, D.; Ikeo, K.; et al. Diversity and functions of bacterial communities in water and sediment from the watershed of the Tama River flowing a highly urbanized area. Fish. Sci. 2021, 87, 697–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasalicky, V.; Zeng, Y.H.; Piwosz, K.; Simek, K.; Kratochvilová, H.; Koblízek, M. Aerobic Anoxygenic Photosynthesis Is Commonly Present within the Genus Limnohabitans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02116-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.L.; Song, Q.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.Y. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification and phosphorus removal in an aerobic granular sequencing batch reactor with mixed carbon sources: Reactor performance, extracellular polymeric substances and microbial successions. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Bi, X.J.; Peng, Y.Z.; Bai, M. Research advances of the phosphorus-accumulating organisms of Candidatus Accumulibacter, Dechloromonas and Tetrasphaera: Metabolic mechanisms, applications and influencing factors. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruprecht, J.E.; Birrer, S.C.; Dafforn, K.A.; Mitrovic, S.M.; Crane, S.L.; Johnston, E.L.; Wemheuer, F.; Navarro, A.; Harrison, A.J.; Turner, I.L.; et al. Wastewater effluents cause microbial community shifts and change trophic status. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.Y.; Luo, J.X.; Zhuang, X.L.; Zhang, D.Q.; Huang, Z.B.; Bai, Z.H. Diversity of culturable aerobic denitrifying bacteria in the sediment, water and biofilms in Liangshui River of Beijing, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xu, F.Q.; Chen, S.J.; Gou, F.; Shi, Y.C.; Xing, Z.L.; Peng, R.Q.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, T.; Xiong, J.; et al. Microecological health assessment of water environment and sediment based on metagenomics: A case study of Guixi River in Chongqing, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbeckmann, S.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Labrenz, M. Environmental Factors Support the Formation of Specific Bacterial Assemblages on Microplastics. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.X.; Li, M.T.; Tan, J.C.; He, M.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Kang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.Z. Distribution, sources, ecological risk and microbial response of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Qingdao bays, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, N.L.; Nievas, M.L.; Lozada, M.; del Prado, G.; Dionisi, H.M.; Siñeriz, F. Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant-producing Alcanivorax strains: Hydrocarbon accession strategies and alkane hydroxylase gene analysis. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Lai, Q.L.; Zhou, Z.W.; Qiao, N.; Liu, C.L.; Shao, Z.Z. Alcanivorax hongdengensis sp. nov., an alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from surface seawater of the straits of Malacca and Singapore, producing a lipopeptide as its biosurfactant. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadjelovic, V.; Gibson, M.I.; Dorador, C.; Christie-Oleza, J.A. Genome of Alcanivorax sp. 24: A hydrocarbon degrading bacterium isolated from marine plastic debris. Mar. Genom. 2020, 49, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusupova, A.A.; Giruts, M.V.; Vylekzhanina, D.S.; Semenova, E.M.; Gordadze, G.N. Formation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons from Prokaryote Biomass: 4. Formation of Petroleum Biomarker Hydrocarbons from the Biomass of Halomonas titanicae Bacteria Isolated from Romashkino Crude Oil. Pet. Chem. 2022, 62, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Kou, Z.G.; Teng, X.; Cai, W.; Hu, J. Shift of Sediments Bacterial Community in the Black-Odor Urban River during In Situ Remediation by Comprehensive Measures. Water 2019, 11, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.C.M.; Manco, S.C.; Pires, A.C.C.; Gonçalves, S.F.; Calado, R.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Loureiro, S. Richness and composition of sediment bacterial assemblages in an Atlantic port environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.C.; Sheng, D.; Yin, D.Q. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics in the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.P.; Yang, Y.; Lu, D.P.; Niu, Z.S.; Feng, J.N.; Chen, Y.R.; Tou, F.Y.; Garner, E.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Biofilms as a sink for antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the Yangtze Estuary. Water Res. 2018, 129, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, C.E.; Odume, O.N. Freshwater environments as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and their role in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerde, C.L.; Olds, B.P.; Shogren, A.J.; Andruszkiewicz, E.A.; Mahon, A.R.; Bolster, D.; Tank, J.L. Influence of Stream Bottom Substrate on Retention and Transport of Vertebrate Environmental DNA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8770–8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Li, B.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J. Distribution and co-occurrence of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial pathogens in the effluent of decentralized sewage treatment systems in China. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2023, 180, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harakeh, S.; Yassine, H.; El-Fadel, M. Antimicrobial-resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from the lebanese environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Torres-Viera, C.; Venkataraman, L.; DeGirolami, P.; Samore, M.; Carmeli, Y. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of patients with multiresistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1999, 28, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.L.; Li, J.; Wang, S.Y.; Fan, F.; McLaughlin, R.W.; Wang, K.X.; Wang, D.; Zheng, J.S. Biogeographic patterns of potential pathogenic bacteria in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River as well as its two adjoining lakes, China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 972243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reem, A.; Almansoob, S.; Senan, A.M.; Raj, A.K.; Shah, R.J.; Shrewastwa, M.K.; Kumal, J.P.P. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and related antibiotic resistance genes as indicators for wastewater treatment. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqee, M.H.; Henry, R.; Coulthard, R.; Schang, C.; Williamson, R.; Coleman, R.; Rooney, G.; Deletic, A.; McCarthy, D. Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium and Escherichia coli Survival in Estuarine Bank Sediments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.R.; Gast, R.J.; Fujioka, R.S.; Solo-Gabriele, H.M.; Meschke, J.S.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A.; del Castillo, E.; Polz, M.F.; Collier, T.K.; Strom, M.S.; et al. The coastal environment and human health: Microbial indicators, pathogens, sentinels and reservoirs. Environ. Health 2008, 7, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.A.; Khambaty, F.M. International dissemination of epidemic Vibrio cholerae by cargo ship ballast and other nonpotable waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 2597–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J.Z.; Xiao, N.Y.; Lv, B.Y.; Wu, H.X. Effects of holding time on the diversity and composition of potential pathogenic bacteria in ship ballast water. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 160, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
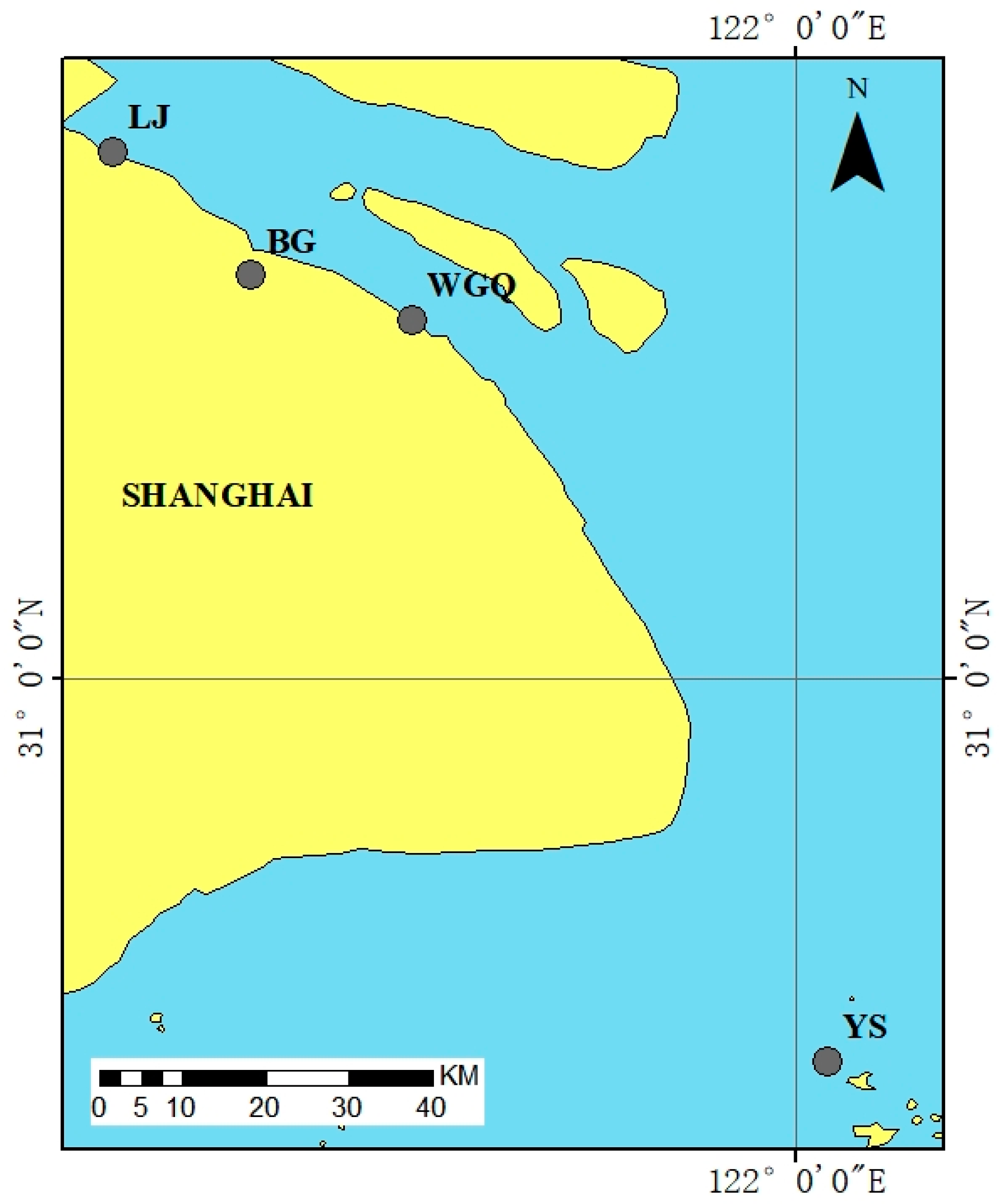
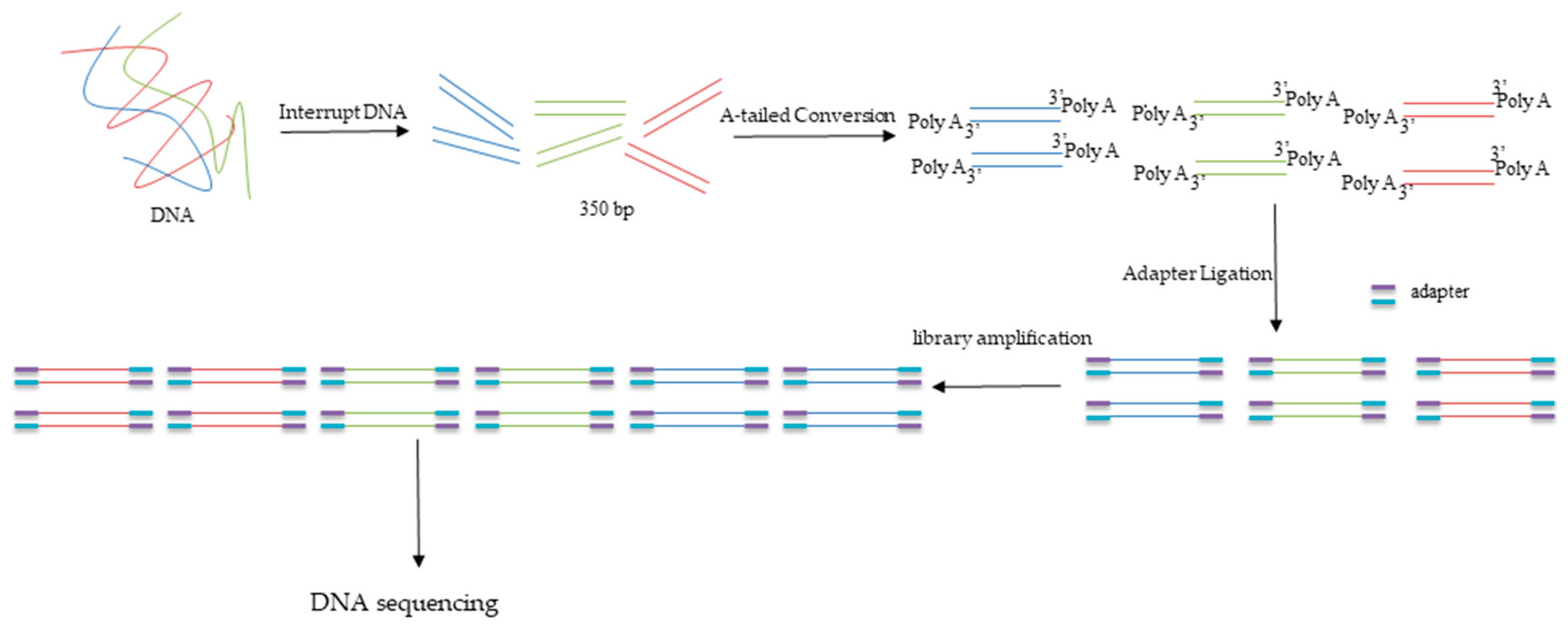

| Positional Name | Positional Information | North Latitude | East Longitude | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | Baoshan Port | 31°27′27.91″ | 121°26′46.84″ | 15.6 m |
| WGQ | Waigaoqiao Phase 6 Port | 31°22′27.43″ | 121°35′59.56″ | 15.5 m |
| LJ | Luojing Port | 31°29′22.48″ | 121°23′51.46″ | 16 m |
| YS | Yanshan Port | 30°37′25.37″ | 122°4′29.59″ | 18.9 m |
| Groups | Raw Data (Gbp) | Clean Data (Gbp) | Effective (%) | Scatigs’ Total Number | Scatigs’ Max Len. (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BG | 15.88 ± 0.77 | 11.96 ± 2.39 | 69.25 ± 17.80 | 670,918 ± 151,331 | 184,714 |
| WGQ | 20.62 ± 6.71 | 14.31 ± 2.94 | 67.91 ± 1.85 | 624,703 ± 144,363 | 687,021 |
| LJ | 21.12 ± 3.92 | 14.62 ± 2.85 | 71.57 ± 16.80 | 306,665 ± 38,778 | 402,585 |
| YS | 17.29 ± 3.21 | 13.21 ± 1.13 | 74.13 ± 14.33 | 422,707.5 ± 46,925.5 | 943,574 |
| U | 20.15 ± 3.50 | 12.59 ± 2.92 | 64.21 ± 6.14 | 430,114 ± 98,023 | 943,574 |
| M | 21.22 ± 6.11 | 13.41 ± 3.84 | 64.71 ± 3.68 | 557,254.5 ± 211,811.5 | 598,874 |
| B | 19.48 ± 5.56 | 14.88 ± 2.59 | 83.23 ± 13.47 | 545,068 ± 277,181 | 622,968 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, L.; Xue, J.; Wu, H. Composition and Distribution of Bacteria, Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Shanghai Port, China. Water 2024, 16, 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182569
Hu L, Xue J, Wu H. Composition and Distribution of Bacteria, Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Shanghai Port, China. Water. 2024; 16(18):2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182569
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Lei, Junzeng Xue, and Huixian Wu. 2024. "Composition and Distribution of Bacteria, Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Shanghai Port, China" Water 16, no. 18: 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182569
APA StyleHu, L., Xue, J., & Wu, H. (2024). Composition and Distribution of Bacteria, Pathogens, and Antibiotic Resistance Genes at Shanghai Port, China. Water, 16(18), 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182569





