Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Subtropical Urban Streams (Santo André, SP, Brazil)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Design
2.3. Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
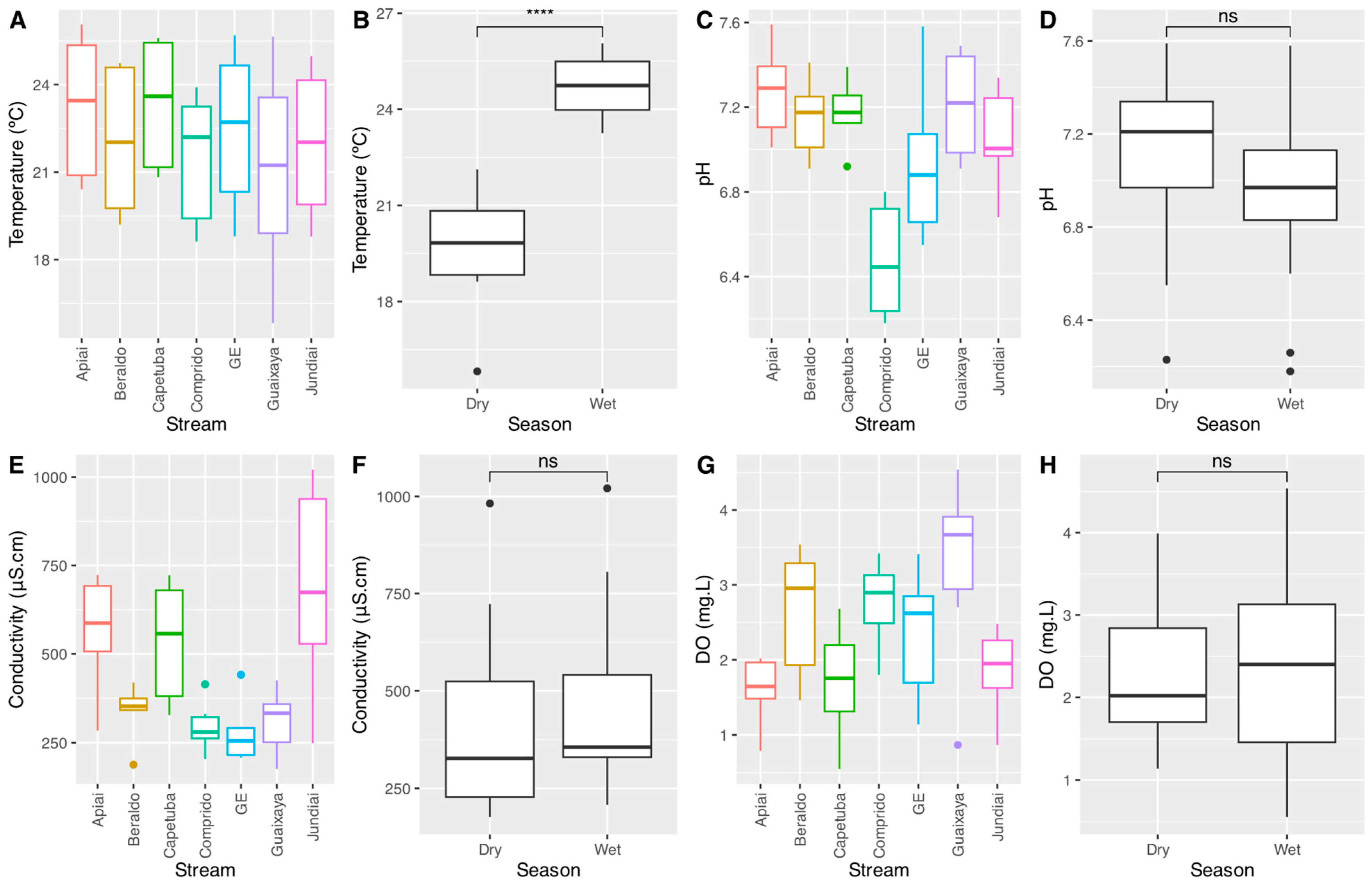
3.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of the Water
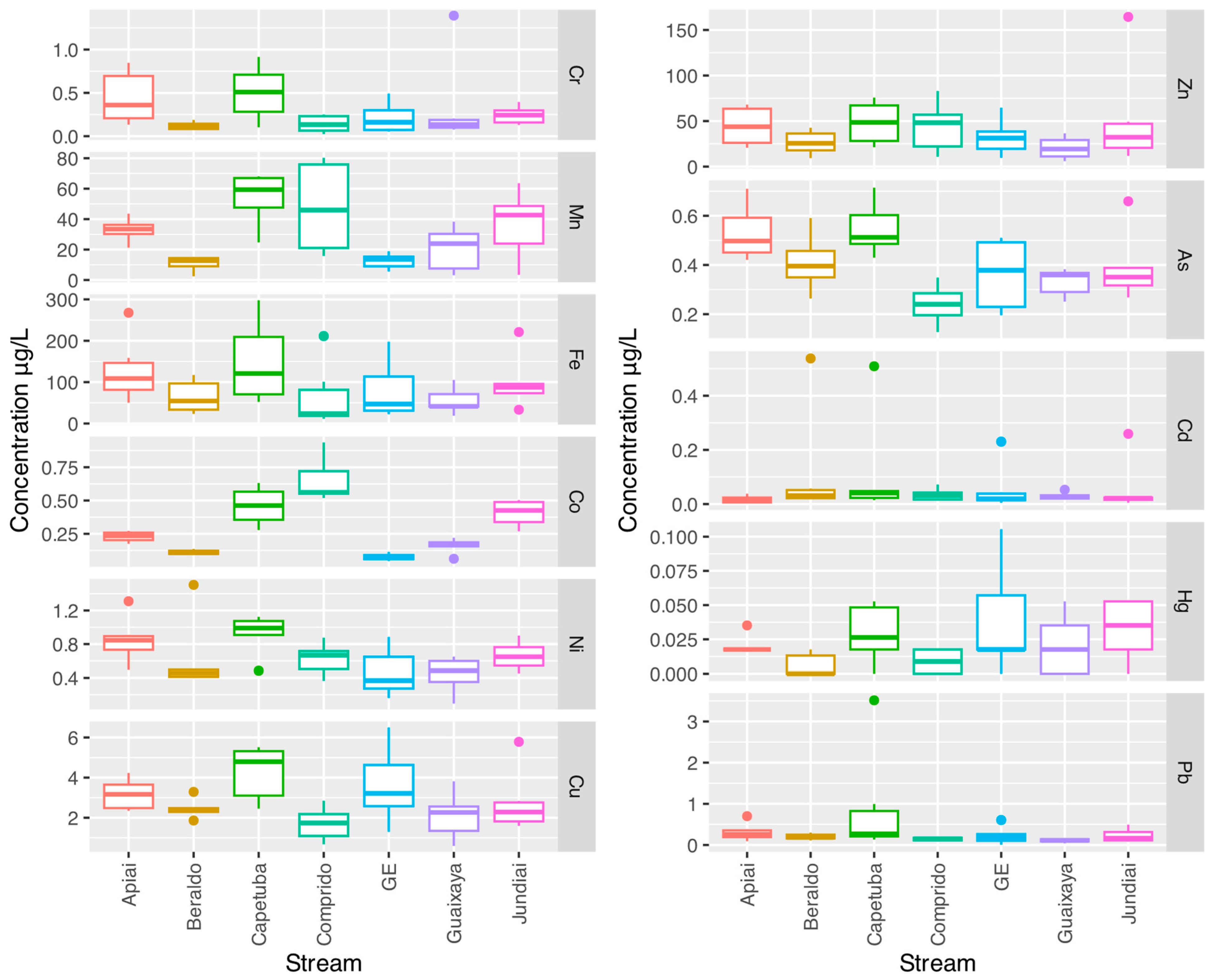
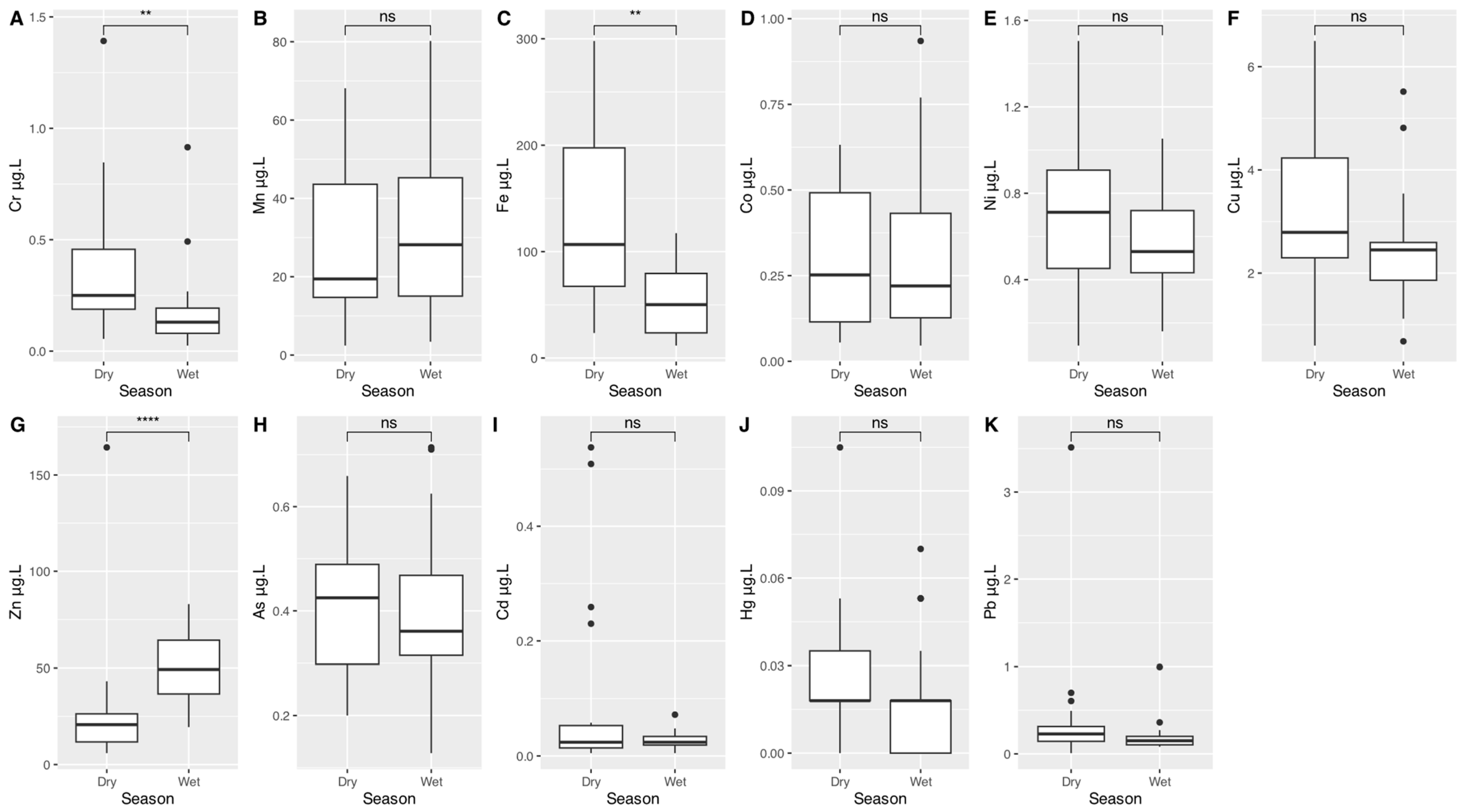
3.2. Potentially Toxic Elements
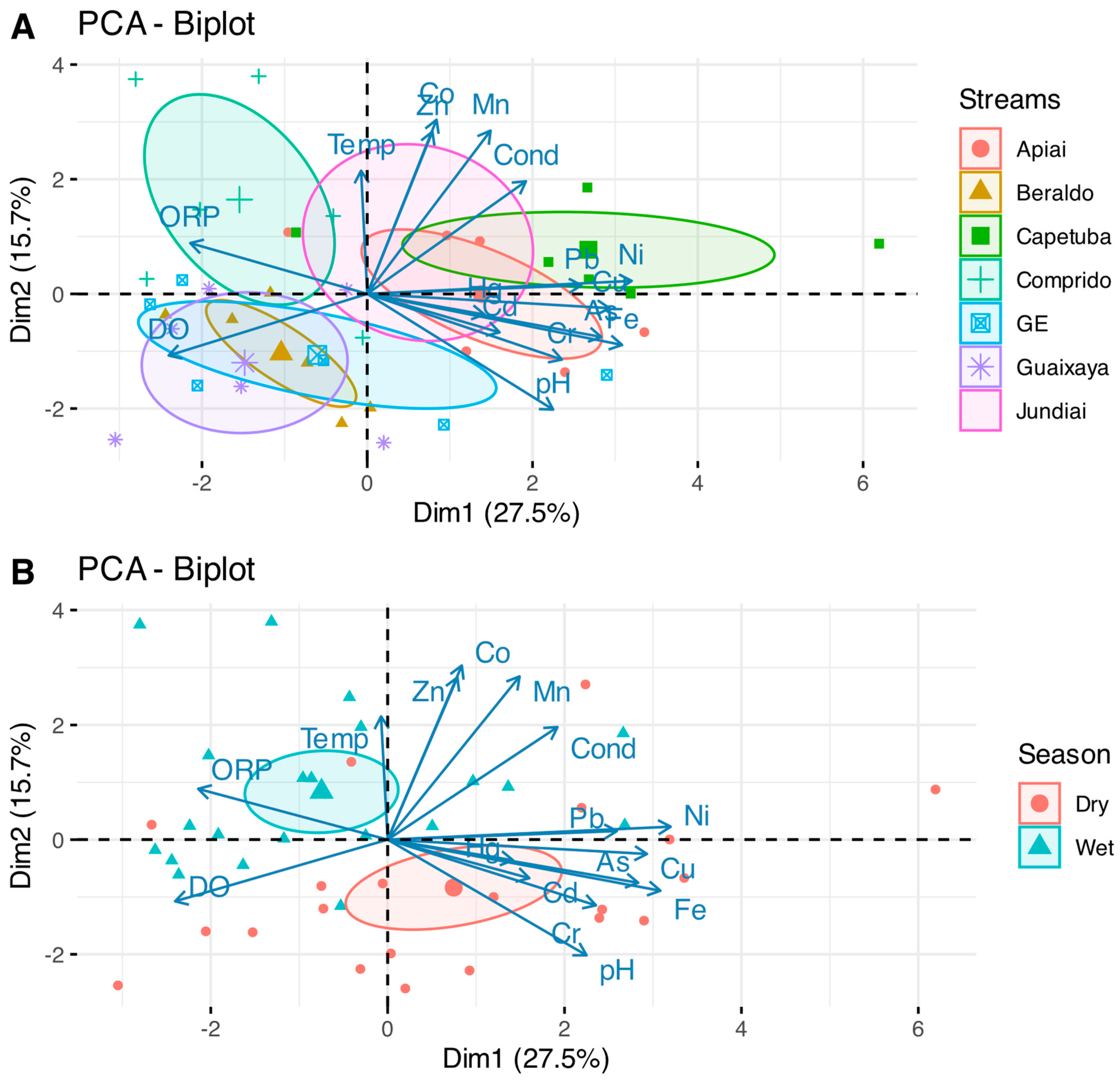
3.3. Relationships between Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) and Physical and Chemical Water Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bega, J.M.M.; de Oliveira, J.N.; Albertin, L.L.; Isique, W.D. Use of Caffeine as an Indicator of Pollution by Domestic Sewage in Urban Water Bodies. Eng. Sanit. Ambient. 2021, 26, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, K.; Taniwaki, R.H.; de Paula, F.R.; Valente, R.A.; Randhir, T.O.; Macedo, D.R.; Leal, C.G.; Rodrigues, C.B.; Hughes, R.M. Multiscale Land Use Impacts on Water Quality: Assessment, Planning, and Future Perspectives in Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascalicchio, Á.A.E. Contaminação Por Metais Pesados; Annablume Editora: São Paulo, Brazil, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Cobbina, S.J.; Mao, G.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L. A Review of Toxicity and Mechanisms of Individual and Mixtures of Heavy Metals in the Environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8244–8259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.Z.P.; Machado, A.B.; Gehlen, G. Influência de Metais no Comportamento Reprodutivo de Peixes, Revisão Bibliográfica. Rev. Geam. 2019, 5, 4–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sangaré, L.O.; Ba, S.; Diallo, O.; Sanogo, D.; Zheng, T. Assessment of Potential Health Risks from Heavy Metal Pollution of Surface Water for Drinking in a Multi-Industry Area in Mali Using a Multi-Indices Approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; Wang, Q.; Lv, M.; Chen, L. Microorganism Remediation Strategies towards Heavy Metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, V.M.; de Andrade, L.C.; Tiecher, T.; de Oliveira Camargo, F.A. The Urban Pressure Over the Sediment Contamination in a Southern Brazil Metropolis: The Case of Diluvio Stream. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, P.F.P.; Silva, M.H.L.; da Silva, I.S.; de Castro, A.C.L. Evaluation of Heavy Metals in Streams of the Bacanga and Cachorros Watersheds in São Luís, Brazil. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan II, R.P. The Urban Stream Syndrome: Current Knowledge and the Search for a Cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CETESB. Relatório de Qualidade Das Águas Interiores No Estado de São Paulo; CETESB: São Paulo, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, A.L.F. Hidrografia Da Cidade de São Paulo. Available online: https://www.cidadeecultura.com/hidrografia-sao-paulo/ (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Flores Salinas, V.C. Contaminação do Solo em São Paulo: O Caso da Operação Urbana Bairros do Tamanduateí. Rev. Labverde 2015, 10, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, D. Rio Tamanduateí—Nascente à Foz: Percepções Da Paisagem e Processos Participativos. Paisag. Ambiente 2007, 24, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PREFEITURA de SANTO ANDRÉ Dados Censitários. Available online: https://www2.santoandre.sp.gov.br/index.php/sabina-e-planetario/182-plano-educacao-ambiental/apresentacao (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- PREFEITURA de SANTO ANDRÉ Geografia. Available online: https://www2.santoandre.sp.gov.br/index.php/cidade-de-santo-andre/geografia (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- CLIMATE DATA Clima Em Santo André. Available online: https://pt.climate-data.org/america-do-sul/brasil/sao-paulo/santo-andre-5118/#:~:text=Clima Santo André (Brasil)&text=Em Santo André%2C o clima é quente e temperado.&text=A classificação do clima é,pluviosidade é de 1475 mm (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- INPE—Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Especiais Tutorial de Geoprocessamento. Available online: http://www.dpi.inpe.br/spring/portugues/tutorial/introducao_geo.html (accessed on 16 June 2020).
- QGIS Development Team Welcome to the QGIS Project! QGIS Geographic Information System. 2021. Available online: https://qgis.org/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- IBGE IBGE Downloads. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. 2013. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/ (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- EPA—United States Environmental Protection Agency. Determination of Trace Elements in Waters and Wastes by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry. Cincinnati, Ohio, 1998. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-06/documents/epa-200.8.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2024).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses; Package Version 1.0.7.; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Darrin, S.; Bryan, C. Data Visualization with Ggplot. In Probability, Statistics, and Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sardar, K.; Ali, S.; Hameed, S.; Afzal, S.; Fatima, S.; Shakoor, M.B.; Bharwana, S.A.; Tauqeer, H.M. Heavy Metals Contamination and What Are the Impacts on Living Organisms. Greener J. Environ. Manag. Public Saf. 2013, 2, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Yang, Y.F. Accumulation of Heavy Metals and Total Phosphorus in Intensive Aquatic Farm Sediments: Comparison of Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureu, Asian Seabass Lates calcarifer and White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei Farms. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanci, N.; Turkmen, G.; Ekingen, P.; Basoren, O. Evaluation of Plecoptera (Insecta) Community Composition Using Multivariate Technics in a Biodiversity Hotspot. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.Y.; Brandes, D.; Kney, A.D. Using Electronic Conductivity and Hardness Data for Rapid Assessment of Stream Water Quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 104, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Gonzalez, J.C.; Chavez-Parga, M.D.; Cortes, J.A.; Perez-Munguia, R.M. Photosynthesis, Respiration and Reaeration in a Stream with Complex Dissolved Oxygen Pattern and Temperature Dependence. Ecol. Modell. 2014, 273, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.A.; Matson, P.A.; Fendorf, S.E. Effects of a Diel Oxygen Cycle on Nitrogen Transformations and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in a Eutrophied Subtropical Stream. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 67, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, A.R.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Fontainhas-Fernandes, A.; Monteiro, S.M.; Pacheco, F.A.L. The Impact of Freshwater Metal Concentrations on the Severity of Histopathological Changes in Fish Gills: A Statistical Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 217–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Tang, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, R.; Qin, B.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Long-Term Manganese Exposure-Mediated Benthic Diatom Assemblage in a Subtropical Stream: Distribution, Substrate Preferences and Mn-Tolerance. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.S.; Kiffney, P.M. Responses of a Macroinvertebrate Community from a Pristine, Southern British Columbia, Canada, Stream to Metals in Experimental Mesocosms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Dhote, S. Evaluation of Uptake Rate of Heavy Metals by Eichhornia Crassipes and Hydrilla Verticillata. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 169, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saalidong, B.M.; Aram, S.A.; Otu, S.; Lartey, P.O. Examining the Dynamics of the Relationship between Water PH and Other Water Quality Parameters in Ground and Surface Water Systems. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plette, A.C.C.; Nederlof, M.M.; Temminghoff, E.J.M.; Van Riemsdijk, W.H. Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Terrestrial and Aquatic Systems: A Quantitative Approach. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1999, 18, 1882–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, L.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Sousa, D.Z. Methanogens, Sulphate and Heavy Metals: A Complex System. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.M.; Valle, L.; Rodriguez, F.; Moriñigo, M.A.; Borrego, J.J. Inhibition of Methanogenesis by Several Heavy Metals Using Pure Cultures. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1996, 23, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
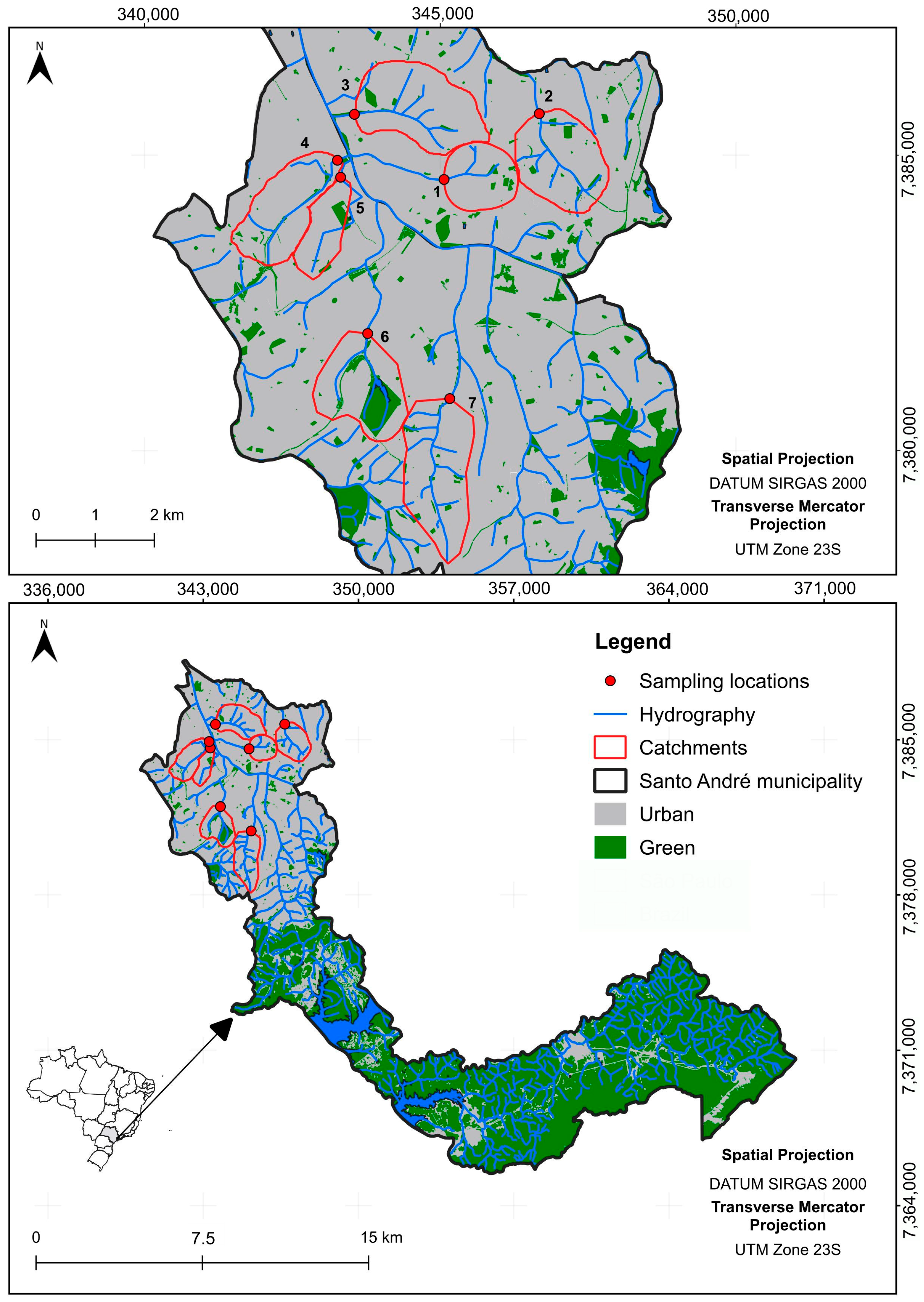
| Catchment Number | Catchment Name | Coordinates | Ind (%) | Urb (%) | Gre (%) | Total Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Comprido | 23°38′29.7″ S 46°31′18.3″ W | 0.00 | 98.06 | 1.94 | 2.47 |
| 2 | Guaixaya | 23°37′53.5″ S 46°30′11.5″ W | 0.00 | 96.68 | 3.32 | 2.67 |
| 3 | Jundiaí | 23°37′52.7″ S 46°31′45.1″ W | 0.16 | 99.03 | 0.81 | 2.87 |
| 4 | Beraldo | 23°38′28.6″ S 46°32′16.2″ W | 0.76 | 96.39 | 2.85 | 1.93 |
| 5 | G.E. | 23°38′44.1″ S 46°32′07.0″ W | 1.08 | 90.32 | 8.60 | 0.99 |
| 6 | Carapetuba | 23°39′59.4″ S 46°31′55.6″ W | 0.03 | 84.03 | 15.94 | 2.83 |
| 7 | Apiaí | 23°40′35.0″ S 46°31′10.1″ W | 0.00 | 97.75 | 2.25 | 2.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Espeçoto, R.M.T.; Luciano, M.M.; Batista, B.L.; Lange, C.N.; Maltez, H.F.; Schiesari, L.C.; França, M.V.; Fushita, Â.T.; Coelho, L.H.G.; Taniwaki, R.H. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Subtropical Urban Streams (Santo André, SP, Brazil). Water 2024, 16, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182681
Espeçoto RMT, Luciano MM, Batista BL, Lange CN, Maltez HF, Schiesari LC, França MV, Fushita ÂT, Coelho LHG, Taniwaki RH. Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Subtropical Urban Streams (Santo André, SP, Brazil). Water. 2024; 16(18):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182681
Chicago/Turabian StyleEspeçoto, Rafaella M. T., Marilena M. Luciano, Bruno L. Batista, Camila N. Lange, Heloísa F. Maltez, Luís C. Schiesari, Marcus V. França, Ângela T. Fushita, Lúcia H. G. Coelho, and Ricardo H. Taniwaki. 2024. "Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Subtropical Urban Streams (Santo André, SP, Brazil)" Water 16, no. 18: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182681
APA StyleEspeçoto, R. M. T., Luciano, M. M., Batista, B. L., Lange, C. N., Maltez, H. F., Schiesari, L. C., França, M. V., Fushita, Â. T., Coelho, L. H. G., & Taniwaki, R. H. (2024). Assessment of Potentially Toxic Elements in Subtropical Urban Streams (Santo André, SP, Brazil). Water, 16(18), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182681









