Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources of Water-Carrying Lakes Affected by Retreating Polder: A Case Study of Luoma Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Evaluation Methods
2.3.1. Single Factor Pollution Index
2.3.2. Heavy Metal Pollution Index
2.3.3. Human Health Risks Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals
3.2. Heavy Metal Contamination Levels of Water-Carrying Lakes
3.3. Impact of Human Activities on Heavy Metal
3.4. Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Water-Carrying Lakes
4. Conclusions
- (a)
- Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metals
- (b)
- Heavy metal contamination levels of water-carrying lakes
- (c)
- Impact of Human Activities on Heavy Metal
- (d)
- Health Risk of Heavy Metals in water-carrying lakes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Xie, W.; Li, G.; Song, H.; Zhai, W.; Li, Y. Study on the Distribution Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Antibiotics and Resistance Genes in Water Sources of Wuhan. Toxics 2024, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K. Risk Assessment, Statistical Source Identification and Seasonal Fluctuation of Dissolved Metals in the Subarnarekha River, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Ecological and Health Risk Assessments and Water Quality Criteria of Heavy Metals in the Haihe River. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 117971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ren, B.; Luo, J.; Yuan, J.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Trends and Health Risks of Dissolved Heavy Metal Pollution in Global River and Lake Water from 1970 to 2017. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 251; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–24. ISBN 978-3-030-27149-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Yu, S. Spatio-Temporal Variational Characteristics Analysis of Heavy Metals Pollution in Water of the Typical Northern Rivers, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New Trends in Removing Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, M. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination in Sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) Using Pollution Indices and Multivariate Statistical Techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, N.A.; Dash, S.S.; Gummadi, S.N.; Deepa, V.S. Nano-Remediation of Toxic Heavy Metal Contamination: Hexavalent Chromium [Cr(VI)]. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 129204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Peng, B.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Q.; Qin, Z.; Tan, C. Distribution, Contamination and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Bed Sediments from the Lower Reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L. Ecological Risk Assessment and Heavy Metal Contamination in the Surface Sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 163, 111954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalani, N.; Riazi, B.; Karbassi, A.; Moattar, F. Measurement and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals Accumulated in Sediment and Water Collected from Gomishan International Wetland, Iran. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Azhari, A.; Rhoujjati, A.; El Hachimi, M.L.; Ambrosi, J. Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soil-Plant System and the Sediment-Water Column around a Former Pb/Zn-Mining Area in NE Morocco. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hashim, M.H.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al Qaisi, S.; Alharbi, T. Contamination and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Al-Uqair Coastal Sediments, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaoyong, Z.; Abuduwaili, J.; Fengqing, J. Heavy Metal Contamination, Sources, and Pollution Assessment of Surface Water in the Tianshan Mountains of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, B.; Zhou, Y.; Kwon, B.-O.; Choi, K.; Ryu, J.; et al. Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments and Water from the Coastal Areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, N.; Rahman, M.S.; Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Industrial Metal Pollution in Water and Probabilistic Assessment of Human Health Risk. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 185, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil for a Township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lin, M.; Peng, W.; He, C. Seasonal Changes of Heavy Metals and Health Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation in Alternate Water Sources of the Xinbian River in Suzhou City, Huaibei Plain, China. Ecotoxicol Env. Saf 2022, 236, 113445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.E.; Meek, M.E.; Boorman, G.A.; Brusick, D.J.; Cohen, S.M.; Dragan, Y.P.; Frederick, C.B.; Goodman, J.I.; Hard, G.C.; O’Flaherty, E.J.; et al. Lessons Learned in Applying the U.S. EPA Proposed Cancer Guidelines to Specific Compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 53, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.; Foret, C.; Bazin, C.; Leduc, L.; Hammada, M.; Inácio, M.; Bedell, J.P. Bioavailability and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals of Several Soils and Sediments (from Industrialized Urban Areas) for Eisenia Fetida. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Wijesiri, B.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Water-Sediment Interactions and Mobility of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z. Heavy Metal Pollution in Xinfengjiang River Sediment and the Response of Fish Species Abundance to Heavy Metal Concentrations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harguinteguy, C.A.; Cirelli, A.F.; Pignata, M.L. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Leaves of Aquatic Plant Stuckenia Filiformis and Its Relationship with Sediment and Water in the Suquía River (Argentina). Microchem. J. 2014, 114, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, R.; Juzsakova, T.; Ben Ali, M.; Rawash, M.A.; Domokos, E.; Hedfi, A.; Almalki, M.; Boufahja, F.; Shafik, H.M.; Rédey, Á. Comprehensive Environmental Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Surface Water, Sediments and Nile Tilapia in Lake Nasser, Egypt. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, N.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y. Assessment and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Contamination in Water and Surface Sediment in Dongping Lake, China. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy Metals in Drinking Water: Occurrences, Implications, and Future Needs in Developing Countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, N.; Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X. Multiple Evaluations, Risk Assessment, and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in Surface Water and Sediment of the Golmud River, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Dong, J.; Zheng, B. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediment at the Drinking Water Source of the Xiangjiang River in South China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, X. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals and Pesticides: A Case Study in the Main Drinking Water Source in Dalian, China. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.; Dongchun, S.; Seongeun, P.; Yeongwook, L.; Yoonho, C.; Seongjoon, C.; Jeeyeon, Y.; Mansik, H.; Yeosin, P.; Hyun, L. Risk Assessment and Management of Drinking Water Pollutants in Korea. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ravikumar, B.; Bai, G.; Li, X. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 626–638. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Xu, Q.; Lyu, H.; Kong, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, B.; Bi, Y. Sediment and Residual Feed from Aquaculture Water Bodies Threaten Aquatic Environmental Ecosystem: Interactions among Algae, Heavy Metals, and Nutrients. J. Environ. Manage 2023, 326, 116735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.N.; Rendina, A.E.; Orgeira, M.J. Assessment of Toxic Metal Contamination Using a Regional Lithogenic Geochemical Background, Pampean Area River Basin, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Li, H. Distribution of Heavy Metals in Soils and Vegetables and Health Risk Assessment in the Vicinity of Three Contaminated Sites in Guangdong Province, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2018, 24, 1901–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyantakyi, A.J.; Akoto, O.; Fei-Baffoe, B. Seasonal Variations in Heavy Metals in Water and Sediment Samples from River Tano in the Bono, Bono East, and Ahafo Regions, Ghana. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Comparison of Pollution Indices for the Assessment of Heavy Metal in Brisbane River Sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, C.L.; Dontu, S.I.; Levei, E.A.; Ioja, C.I.; Popa, A.-M.; Miclean, M.; Hoaghia, M.-A.; Cadar, O.; Carstea, E.M. Spatial Variation of Organochlorine Pesticides and Dissolved Organic Matter in Urban Closed Lakes. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2020, 55, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Zhu, Y.; Han, T.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Chao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Interactions of Heavy Metal Elements across Sediment-Water Interface in Lake Jiaogang. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Lu, S. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediment, and Fish from Dongting Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 34076–34090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, M.; Guo, H.; Chen, E. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Historical Evolution of Polders in the Dongting Lake Area, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1561–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L. American Public Health Association Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Reta, G.; Dong, X.; Li, Z.; Bo, H.; Yu, D.; Wan, H.; Su, B. Application of Single Factor and Multi-Factor Pollution Indices Assessment for Human-Impacted River Basins: Water Quality Classification and Pollution Indicators. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2019, 18, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Sajil Kumar, P.J.; Davis Delson, P.; Thomas Babu, P. Appraisal of Heavy Metals in Groundwater in Chennai City Using a HPI Model. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasistha, P.; Ganguly, R. Assessment of spatio-temporal variations in lake water body using indexing method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41856–41875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajar, A.B.; Malik, Z.; Ujan, J.A.; Rind, K.H.; Ullah, R.; Naz, S.; Ullah, M.; Zahid, M.; Khan, K.; Khayyam, K.; et al. Implications of Heavy Metal Accumulation in Fish Feed, Water, Sediment, and Different Fish Species in a Polyculture System. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.S.; Batool, A.I.; Rehman, M.F.U.; Naz, S. Evaluation and Association of Heavy Metals in Commonly Used Fish Feed with Metals Concentration in Some Tissues of O. Niloticus Cultured in Biofloc Technology and Earthen Pond System. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 3006–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.S.; Batool, A.I.; Rehman, M.F.U.; Naz, S. Assessment and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Fish Feeds, Water, and Some Tissues of Cyprinus Carpio Cultured in Different Environments (Biofloc Technology and Earthen Pond System). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 3474–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasistha, P.; Ganguly, R. Water quality assessment in two lakes of Panchkula, Haryana, using GIS: Case study on seasonal and depth wise variations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 43212–43236. [Google Scholar]
- Pratiwi, D.; Sumiarsa, D.; Oktavia, D.; Sunardi, S. Water Quality Influences Self-Purification in the Cihawuk and Majalaya Segments Upstream of the Citarum River, West Java, Indonesia. Water 2023, 15, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehiemere, V.C.; Ihedioha, J.N.; Ekere, N.R.; Ibeto, C.N.; Abugu, H.O. Pollution and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Water, Sediment and Fish (Clarias Gariepinus) in a Fish Farm Cluster in Niger Delta Region, Nigeria. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 927–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidery, A.; Umar, R.; Khan, I. Seasonal Variation and Spatial Distribution of Heavy Metal (Loid)s Concentration in Groundwater and Surface Water from Hard-Rock Terrain, Ranchi, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Aji, D.; Li, P.; Hu, C. Characterization of Heavy Metal Contamination in Wetland Sediments of Bosten Lake and Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pu, R.; Ma, R.; Wang, X.; Lai, X.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Z. Mapping Long-Term Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Pen Aquaculture in a Shallow Lake: Less Aquaculture Coming along Better Water Quality. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E. Trophic Transfer, Bioaccumulation, and Biomagnification of Non-Essential Hazardous Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Food Chains/Webs—Concepts and Implications for Wildlife and Human Health. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 1353–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, W.J.; Ghaffar, M.A.; Noor, M.I.; Lananan, F.; Azra, M.N. Understanding Climate Change and Heavy Metals in Coastal Areas: A Macroanalysis Assessment. Water 2023, 15, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.B.; Goran, S.M.A.; Tarafdar, A. Profiling of Seasonal Variation in and Cancer Risk Assessment of Benzo(a)Pyrene and Heavy Metals in Drinking Water from Kirkuk City, Iraq. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 22203–22222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, P.; Agrawal, M.; Sagar, R. Assessment of Potential Health Risks Due to Heavy Metals through Vegetable Consumption in a Tropical Area Irrigated by Treated Wastewater. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2015, 35, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Guo, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Associations between Patterns of Blood Heavy Metal Exposure and Health Outcomes: Insights from NHANES 2011–2016. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletić, A.; Lučić, M.; Onjia, A. Exposure Factors in Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Sediment. Metals 2023, 13, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagliasindi, F.G.A.; Benjami, M.M. Arsenic removal in fresh and nom-pre-loaded ion exchange packed bed adsorption reactors. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwirka, J.D.; Colvin, C.; Gomez, J.D.; Mueller, P.A. Arsenic removal from drinking water using the coagulation/microfiltration process. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2004, 96, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianisa, H.A.; Ito, A.; Sasaki, A.; Aizawa, J.; Umitaet, T. Biotransformation of arsenic species by activated sludge and removal of bio-oxidised arsenate from wastewater by coagulation with ferric chloride. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4809–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.F.; Di, P.K. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by adsorbing colloid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1994, 33, 922–928. [Google Scholar]
- Bissen, M.; Vieillard-Baron, M.M.; Schindelin, A.J.; Frimmel, F.H. TiO2-cata-lyzed photooxidation of arsenite to arsenate in aqueous samples. Chemosphere 2001, 44, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, J.; Jiang, F.; et al. Arsenic pollution and its treatment in Yangzonghai lake in China: In situ remediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 122, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Z.; Zhang, C. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of surface water in the Guanzhong section of the Weihe River Basin. J. Ecol. Environ. 2022, 31, 131–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



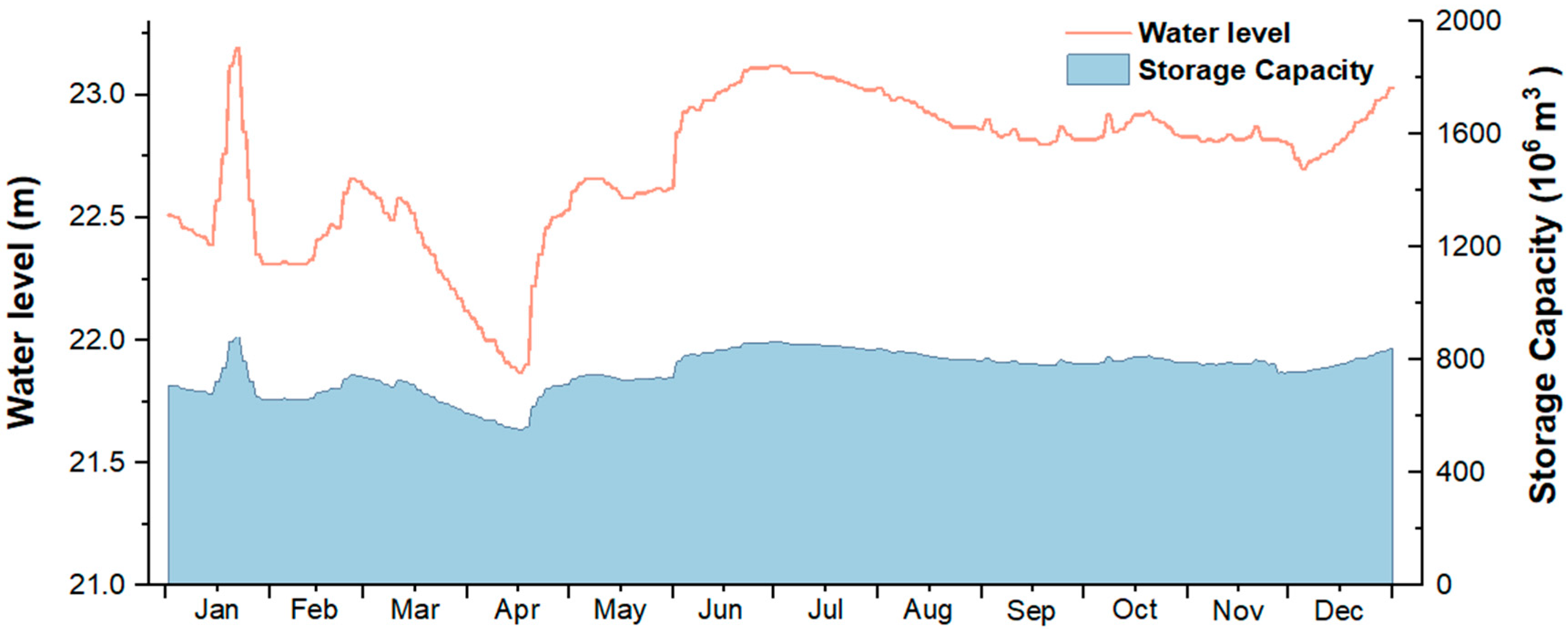
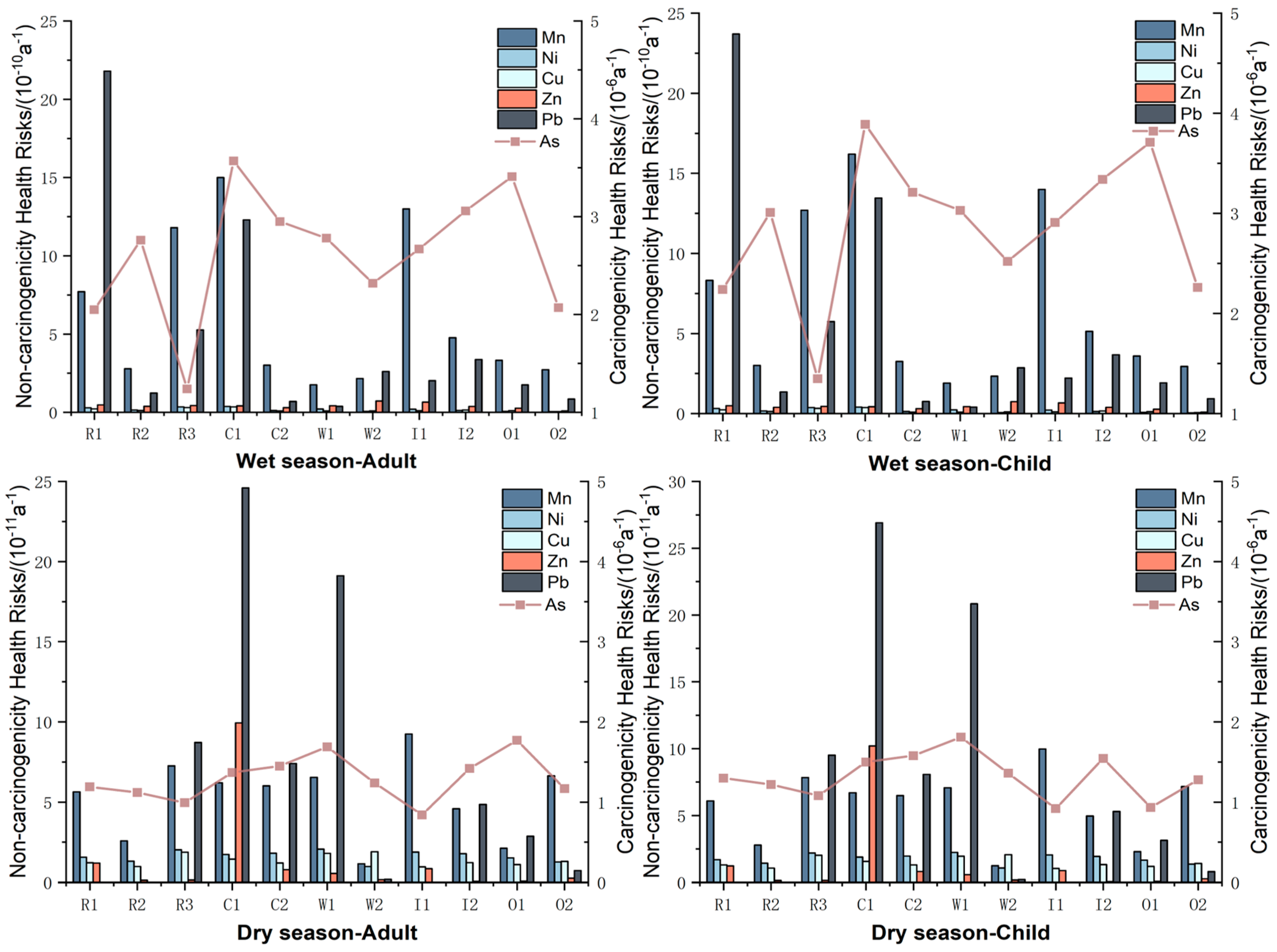
| Regional | Mn | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Pb | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jul. | Dec. | Jul. | Dec. | Jul. | Dec. | Jul. | Dec. | Jul. | Dec. | Jul. | Dec. | ||
| Retreating polder Area | Mean | 70.78 | 4.92 | 1.13 | 0.69 | 1.81 | 1.13 | 23.36 | 2.66 | 2.87 | 1.56 | 2.81 | 0.09 |
| Max | 112.4 | 6.92 | 1.48 | 0.85 | 2.56 | 1.56 | 25.71 | 6.43 | 3.92 | 1.69 | 6.49 | 0.26 | |
| Min | 26.55 | 2.46 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 1.01 | 0.82 | 20.79 | 0.74 | 1.76 | 1.41 | 0.37 | 0.00 | |
| SD | 42.98 | 2.24 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.78 | 0.37 | 2.47 | 2.65 | 1.08 | 0.14 | 3.24 | 0.15 | |
| CV | 0.61 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.38 | 0.09 | 1.15 | 1.67 | |
| Control Area | Mean | 85.76 | 5.82 | 1.06 | 0.75 | 1.86 | 1.11 | 19.36 | 28.74 | 4.62 | 2.00 | 1.94 | 0.48 |
| Max | 142.72 | 5.91 | 1.60 | 0.77 | 2.94 | 1.21 | 22.4 | 53.24 | 5.06 | 2.05 | 3.68 | 0.74 | |
| Min | 28.8 | 5.73 | 0.52 | 0.73 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 16.32 | 4.23 | 4.19 | 1.95 | 0.21 | 0.22 | |
| SD | 80.55 | 0.11 | 0.76 | 0.03 | 1.53 | 0.15 | 4.30 | 34.8 | 0.62 | 0.07 | 2.45 | 0.36 | |
| CV | 0.94 | 0.02 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.82 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 1.21 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 1.26 | 0.75 | |
| Water Source Area | Mean | 18.72 | 3.67 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.77 | 1.55 | 30.83 | 1.96 | 3.62 | 2.06 | 0.45 | 0.29 |
| Max | 20.61 | 6.24 | 0.93 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 1.59 | 38.93 | 3.00 | 3.95 | 2.36 | 0.78 | 0.57 | |
| Min | 16.84 | 1.10 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.73 | 1.5 | 22.73 | 0.91 | 3.29 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.01 | |
| SD | 2.67 | 2.72 | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 11.45 | 1.48 | 0.47 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 0.28 | |
| CV | 0.14 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.50 | 0.07 | 0.19 | 0.37 | 0.76 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 1.06 | 0.97 | |
| Inlet/Outlet | Mean | 56.15 | 5.38 | 0.48 | 0.68 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 18.85 | 1.70 | 3.98 | 1.85 | 0.60 | 0.06 |
| Max | 123.47 | 8.81 | 0.88 | 0.79 | 1.29 | 1.09 | 35.04 | 4.6 | 4.84 | 2.52 | 1.01 | 0.15 | |
| Min | 25.98 | 2.03 | 0.22 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.8 | 5.29 | 0.33 | 2.94 | 1.2 | 0.26 | 0.00 | |
| SD | 45.85 | 2.81 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 13.34 | 1.84 | 0.86 | 0.61 | 0.33 | 0.07 | |
| CV | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.20 | 0.71 | 1.08 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 1.17 | |
| Regional | Elements | Wet Season | Dry Season | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pi | HPI | Description | Pi | HPI | Description | ||
| Retreated Area | Mn | 0.708 | 25.47 | Medium | 0.049 | 7.15 | Low |
| Ni | 0.057 | 0.035 | |||||
| Cu | 0.002 | 0.001 | |||||
| Zn | 0.023 | 0.003 | |||||
| As | 0.287 | 0.156 | |||||
| Pb | 0.281 | 0.009 | |||||
| Control Area | Mn | 0.858 | 29.33 | Medium | 0.058 | 10.41 | Low |
| Ni | 0.053 | 0.038 | |||||
| Cu | 0.002 | 0.001 | |||||
| Zn | 0.019 | 0.029 | |||||
| As | 0.462 | 0.200 | |||||
| Pb | 0.194 | 0.048 | |||||
| Water Source Area | Mn | 0.187 | 16.84 | Low | 0.037 | 9.72 | Low |
| Ni | 0.031 | 0.032 | |||||
| Cu | 0.001 | 0.002 | |||||
| Zn | 0.031 | 0.002 | |||||
| As | 0.362 | 0.206 | |||||
| Pb | 0.045 | 0.029 | |||||
| Inlet/Outlet | Mn | 0.562 | 18.06 | Low | 0.054 | 8.15 | Low |
| Ni | 0.024 | 0.034 | |||||
| Cu | 0.001 | 0.001 | |||||
| Zn | 0.019 | 0.002 | |||||
| As | 0.398 | 0.185 | |||||
| Pb | 0.060 | 0.006 | |||||
| Elements | Adult/a−1 | Child/a−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet season | Drinking pathway | Carcinogenicity | As | 2.88 ×10−5 | 3.15 × 10−5 |
| Non-carcinogenicity | Mn | 6.61 × 10−9 | 7.21 × 10−9 | ||
| Ni | 2.02 × 10−10 | 2.20 × 10−10 | |||
| Cu | 1.67 × 10−10 | 1.83 × 10−10 | |||
| Zn | 3.84 × 10−10 | 4.19 × 10−10 | |||
| Pb | 5.23 × 10−9 | 5.70 × 10−9 | |||
| Dermal pathway | Carcinogenicity | As | 3.65 × 10−8 | 2.56 × 10−8 | |
| Non-carcinogenicity | Mn | 1.97 × 10−10 | 1.38 × 10−10 | ||
| Ni | 2.62 × 10−12 | 1.84 × 10−12 | |||
| Cu | 4.34 × 10−12 | 3.04 × 10−12 | |||
| Zn | 7.47 × 10−11 | 5.24 × 10−11 | |||
| Pb | 4.74 × 10−12 | 3.33 × 10−12 | |||
| Dry season | Drinking pathway | Carcinogenicity | As | 1.42 × 10−5 | 1.55 × 10−5 |
| Non-carcinogenicity | Mn | 5.64 × 10−10 | 6.15 × 10−10 | ||
| Ni | 1.78 × 10−10 | 1.94 × 10−10 | |||
| Cu | 1.47 × 10−10 | 1.60 × 10−10 | |||
| Zn | 1.19 × 10−10 | 1.30 × 10−10 | |||
| Pb | 6.85 × 10−10 | 7.47 × 10−10 | |||
| Dermal pathway | Carcinogenicity | As | 1.80 × 10−8 | 1.26 × 10−8 | |
| Non-carcinogenicity | Mn | 1.68 × 10−11 | 1.18 × 10−11 | ||
| Ni | 2.30 × 10−12 | 1.62 × 10−12 | |||
| Cu | 3.81 × 10−12 | 2.67 × 10−12 | |||
| Zn | 2.31 × 10−11 | 1.62 × 10−11 | |||
| Pb | 6.21 × 10−13 | 4.36 × 10−13 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Han, Y.; Liang, W.; Shi, Y.; Song, F.; Yao, L.; et al. Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources of Water-Carrying Lakes Affected by Retreating Polder: A Case Study of Luoma Lake. Water 2024, 16, 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182699
Wang J, Zhu X, Dai Y, Xu M, Wang D, Han Y, Liang W, Shi Y, Song F, Yao L, et al. Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources of Water-Carrying Lakes Affected by Retreating Polder: A Case Study of Luoma Lake. Water. 2024; 16(18):2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182699
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jindong, Xiaolong Zhu, Yicong Dai, Minyue Xu, Dongmei Wang, Yingcai Han, Wenguang Liang, Yifan Shi, Fanhao Song, Li Yao, and et al. 2024. "Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources of Water-Carrying Lakes Affected by Retreating Polder: A Case Study of Luoma Lake" Water 16, no. 18: 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182699
APA StyleWang, J., Zhu, X., Dai, Y., Xu, M., Wang, D., Han, Y., Liang, W., Shi, Y., Song, F., Yao, L., Zhen, Y., & Zhu, Q. (2024). Health Risk of Heavy Metals in Drinking Water Sources of Water-Carrying Lakes Affected by Retreating Polder: A Case Study of Luoma Lake. Water, 16(18), 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182699








