Abstract
An electrochemical floatation system (EFS)-based sewage-treatment process that applied a dimensionally stable anode (DSA) was developed to secure treated sewage water from sewage-treatment plants for reuse. The DSA was fabricated at a temperature of 673–923 K by dispersing a low quantity of activated carbon on a titanium plate coated with mixed metal oxides (Pt, Re, Pd, Re, and Ir) to a thickness of 5 μm. The average size of the bubbles generated through the DSA of the EFS was 20–40 μm, thus confirming microbubble generation. An efficiency assessment of a titanium-based DSA confirmed metal oxide activity through the removal of Escherichia coli (100%) and total organic carbon (TOC; 48.83%) at a reaction time shorter than 10 min and a low current density (19.6 A/m2). During the long-term operation of the EFS with the separation membrane process, the average removal efficiency was 94.7%, 90.0%, 96.1%, 90.9%, and 98.0% for suspended solids, biochemical oxygen demand, TOC, total nitrogen, and total phosphorous, respectively. Coliforms were not detected. Overall, our EFS coupled with the separation membrane process produced high-quality recycled water that could be used for various purposes according to the water-quality standards for different applications.
1. Introduction
Increasing industrial development and higher human living standards have led to increased use of water, causing pollution and a shortage of water resources. The World Health Organization has predicted that 40% of the global population will face water shortage over the next 50 years and regional conflicts over limited clean water resources will increase [1]. Droughts and flood events due to climate change as well as water pollution caused by increasing industrialization will aggravate the problem of a stable water supply in the future. Moreover, regional supply–demand imbalances have become an issue and the difference between the global water demand and supply is expected to increase to 40% by 2030.
To address this problem, various countries have developed technologies that can customize wastewater treatment and management according to their economic level and water-quality standards [2,3]. Specifically, the quantity of sewage and wastewater generated is increasing. As a case in point, in Korea, sewage represents 70% of the total quantity of wastewater generated, whereby it has been recognized as an important alternative water resource to address water shortage with a focus on sustainability.
Sewage reuse refers to the production of water suitable for reuse by treating sewage in sewage-treatment plants. Treatment methods for sewage reuse are relatively simple compared with seawater desalination. Moreover, sewage reuse can reduce pollutant loads released in public waters; indeed, the need for sewage reuse increases, aiming for a more efficient use of increasingly scarce water resources, as the use of clean water becomes increasingly limited [2,3].
Dissolved air flotation and fiber-type disc filters or upflow filtration/adsorption are major technologies used for sewage reuse. Furthermore, to produce recycled water, separation membrane technologies such as microfiltration (MF), ultrafiltration (UF), nanofiltration (NF), and reverse osmosis (RO) in combination with various pretreatment technologies are being utilized [4].
Most organic pollutants are efficiently treated using biological methods. However, the problem of water pollution caused by non-degradable organic pollutants, which is rapidly increasing due to the development of industrial societies, is alarmingly severe. Moreover, the associated emission allowance standards are very difficult to meet [5]. Owing to these limitations of biological treatments, various alternative physicochemical processes capable of treating non-degradable sewage and wastewater are under study.
Electrochemistry deals with the movement of electrons between substances and the various phenomena caused by such movement [6]. Electrochemical substances have been used in various water-treatment processes [7,8,9]. Particularly, the dimensionally stable anode (DSA), which is mainly used in the electro-oxidation process, has attracted attention in various water-treatment sectors such as ship ballast water treatment and sewage/wastewater treatment for reuse as a representative process to decompose non-biodegradable organic matter in water [10,11]. A DSA is manufactured by depositing an electrically conductive oxide layer on a metal support such as titanium (Ti). In applying a DSA, pollutants are oxidized by a direct electron exchange between the pollutants and electrode surfaces or through indirect oxidation by agents with a high oxidizing power such as H2O2, O3, ClO2, and Cl2 [12]. The DSA’s conductive layer is generally formed of a mixture of an active oxide and an inert metal oxide. Active oxides behave like electrocatalysts and inert metal oxides are known to control the electrochemical properties related to the catalytic activity and duration of use of active ingredients [13].
Water shortage has become a global issue of paramount importance. Sewage is an important alternative water resource to address both the demand for environmental sustainability of cities and water shortage. Although sewage discharged in large quantities is certainly an attractive water resource to cope with water shortage, and despite the efficient removal of biodegradable organic pollutants in sewage by biological means, water thus treated does not satisfy currently accepted water-quality standards for reuse.
In the separation membrane process, which is widely used in sewage-reuse systems, the quality of the treated water may vary depending on the quality of the influent water or the degree of contamination. In particular, membrane fouling is a very important factor in process operations and organic matter in sewage is a major variable in the treatment of sewage through a separation membrane. Therefore, for the stable operation of a sewage-reuse system, it is essential to use an organic matter control process that can suppress the membrane fouling phenomenon as much as possible.
Numerous studies on water treatment using DSAs have focused on high concentrations of non-degradable wastewater [14,15,16,17]. However, studies on the use of DSAs for the treatment of low-concentration sewage are scarce and, to the best of our knowledge, no study has evaluated the efficiency of DSAs on a pilot scale.
The sewage-reuse system applied in this study coupled a separation membrane process and an electrochemical floatation system (EPS). An EPS is a water-treatment system in which an electrolytic oxidation process using a DSA and a floatation separation process using microbubbles are combined. Particulate matter is removed through the decomposition of organic matter and levitation separation is caused by the oxidation reaction of the electrode.
Among the single-component electrodes, Ru/Ti and Ir/Ti electrodes coated with Ru and Ir as base metals are the most representative DSAs. These electrodes have excellent performance but have a short lifespan (Ru/Ti) or a low organic decomposition rate (Ir/Ti electrode); therefore, electrodes of two or more component systems are required for excellent performance [18,19]. The electrode in the EPS evaluated in this study has a long life and a high resolution of organic matter through the DSA produced through the synthesis of various metal oxides. This, in combination with an electrochemical process, has the ability to oxidize organic matter and remove particulate matter.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate and verify the usefulness of water produced by applying the electrochemical treatment method using a DSA, which is widely used in high-concentration wastewater to low-concentration sewage. Thus, we developed a sewage-treatment system that provided treated water for daily use. The system used a DSA coated with a mixed metal oxide after dispersing a small amount of activated carbon on a Ti plate. Dimensionally stable anodes (DSAs) in electrochemical processes show high energy efficiency. This can facilitate electrochemical reactions and increase electrical energy conversion efficiency to help minimize their impact on the environment and provide eco-friendly options that do not rely on the use of drugs and long-duration biological treatments.
The performance of the sewage-reuse system, which combined an EFS with the separation membrane (MF/RO) process using a DSA, was evaluated at various stages of the treatment process. Its field applicability was tested, based on a 73 day long-term operation period.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Influent Water-Quality Characteristics
The treatment efficiency of the EFS coupled with the membrane process was evaluated using treated water acquired from the secondary sedimentation pond of a sewage-treatment plant located in Gyeonggi-do, Korea. The sewage-treatment plant began operating in 1993. The treatment area of the plant is 33,084 m2 and the capacity is 216,000 m3/day. The sewage treatment followed the conventional active sludge process. Table 1 shows the range and average values of the different water-quality characteristics of the influent water flow (overflow from the secondary sedimentation pond of a sewage-treatment plant) used in the experiment. The average turbidity and chromaticity of the influent water flow were 13.9 NTU and 14 CU, respectively.

Table 1.
Influent water-quality characteristics.
2.2. Characteristics and Configuration of the System
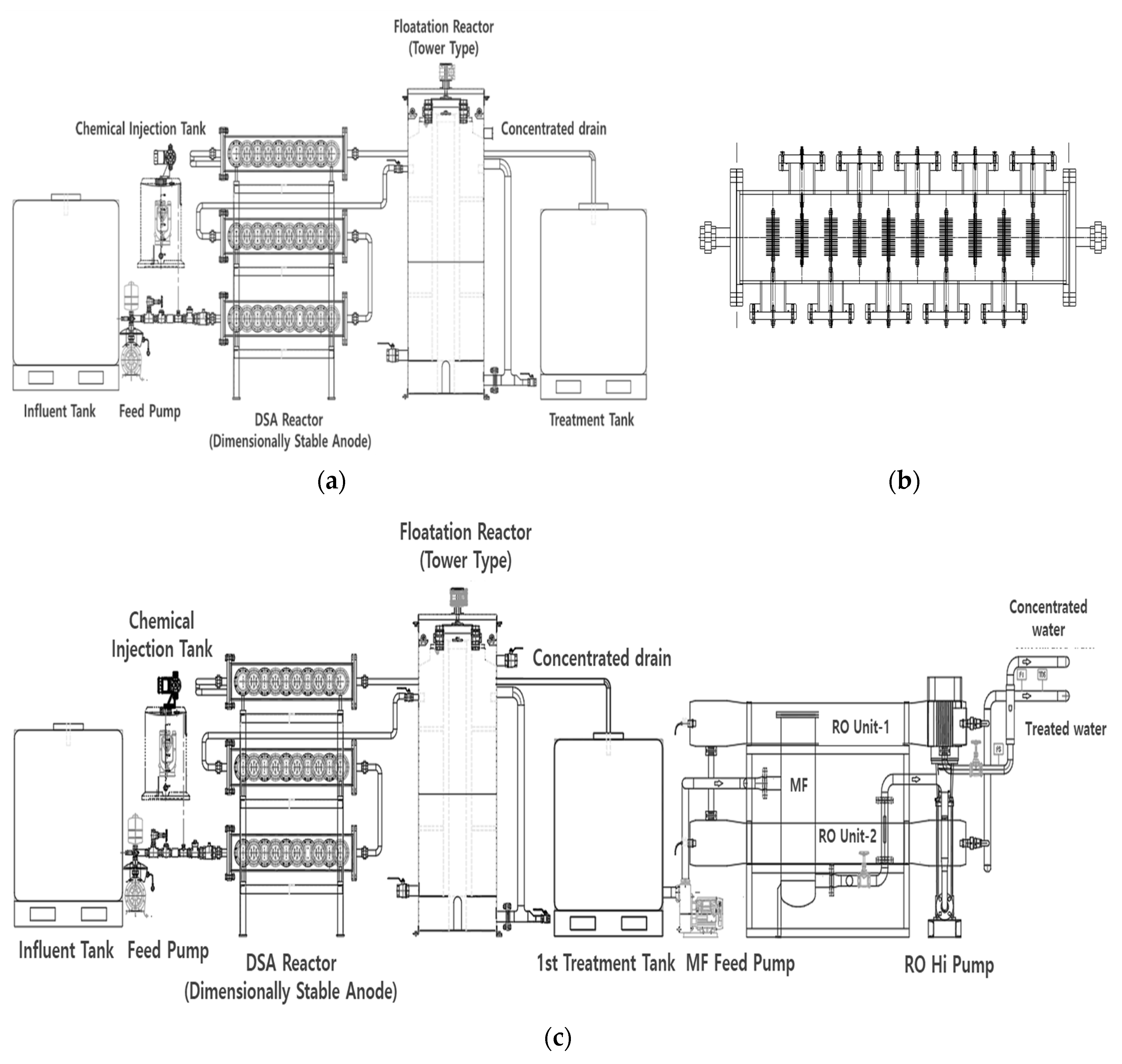
Water-treatment technology in EFSs is based on the principle of oxidation reactions and electroflotation. An EFS uses a DSA to oxidize pollutants present in sewage, thereby reducing dissolved substances such as nitrogen, phosphorus, TOC, and chromaticity. Furthermore, the system causes the floatation of suspended particulate substances upward by microbubbles generated from the electrocatalysts to separate solids and liquids from the floatation separation tank. Commonly, EFSs consist of a water-supply tank, a DSA, a flotation reactor, and a treatment water tank (Figure 1a).
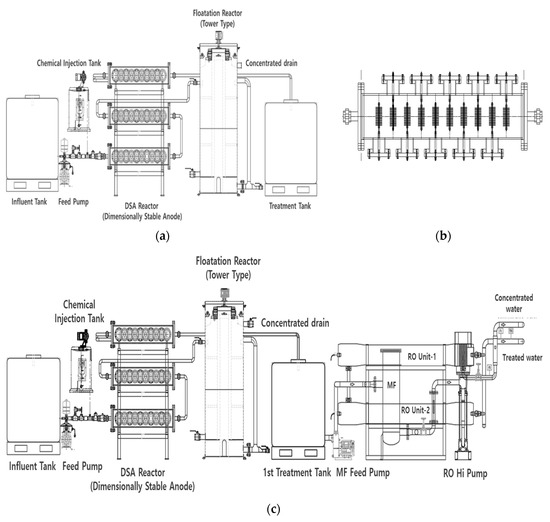
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a sewage-reuse system. (a) Electrochemical floatation system (EFS). (b) Dimensionally stable anode (DSA) module. (c) EFS coupled with the separation membrane (MF/RO) process.
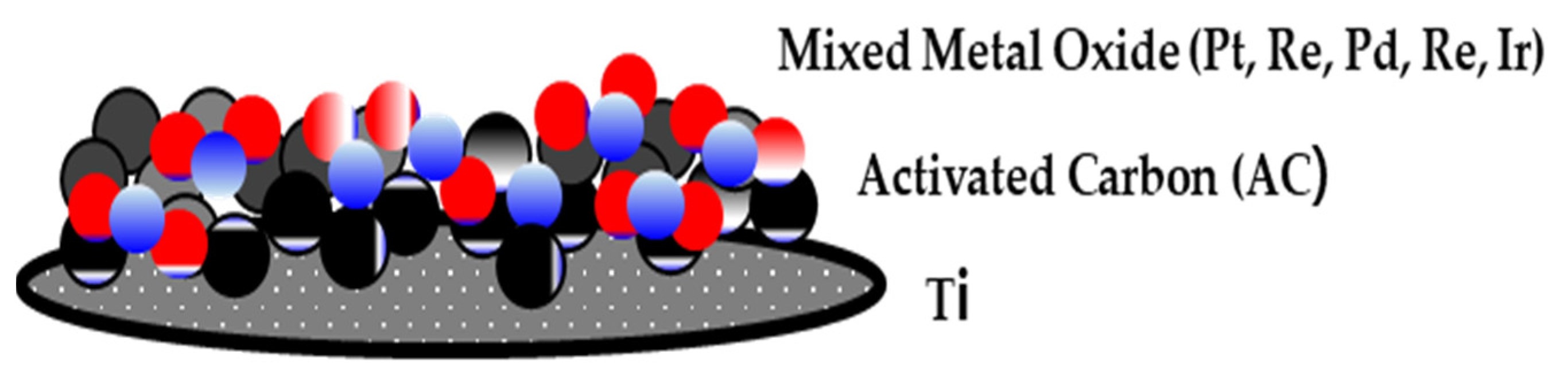
A DSA 10 cm in diameter and 1 mm thick was used as the catalytic electrode. The DSA was manufactured by dispersing a low quantity of activated carbon on a Ti plate and coating it with a mixture of metal oxides containing 50%, 15%, 15%, 10%, and 10% (mol basis) platinum (Pt), rhenium (Re), palladium (Pd), rhodium (Re), and iridium (Ir) to a thickness of 5 µm. The thickness of the electrode was 1 mm, and it was manufactured and installed in the form of a mesh to allow fluid flows (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the dimensionally stable anode (DSA) manufactured in this study.
The DSA was manufactured through pyrolysis after dispersing a transition metal precursor in ethanol and isopropyl alcohol and coating it onto a support [20,21,22]. In this study, it was manufactured at a temperature of 673–923 K to improve the conversion stability and functionality of the pole of the electrode during electrolysis.
The activated carbon of the DSA was used to activate the electrode. Activated carbon sprayed onto an electrode surface catalyzes the electrochemical reaction to improve the electrode surface and increase its electrical transfer efficiency, thereby increasing the electrochemical reaction velocity.
Figure 1b shows the arrangement of the DSA module of the EFS built in this study. The DSA module consisted of a set of 20 DSAs installed at 8 cm intervals. Ten sets of DSAs were installed in the module, five on the left side and five on the right side. The DSA module was designed in three stages and was 1.2 m in length, 0.55 m in width, and 1.6 m in height. The power of the DSA module was set at 7 V and 80 A.
The tower-type flotation reactor of the EFS had a capacity of 0.816 m3 (diameter: 0.76 m; height: 1.8 m) with an effective volume of 0.314 m3 and a residence time of approximately 2 min. The ratio of circulating water to the influent water flow was set to 50%, and the return scum ratio was adjusted to 20–50%. A scraper for sludge removal was installed as an additional feature for better work. During the operation period, the circulating water ratio was set to 80%. The return scum ratio varied between 20% and 50% according to the concentration of suspended solids (SS) in the influent water flow. The capacity of the treatment system was 50 m3/d.
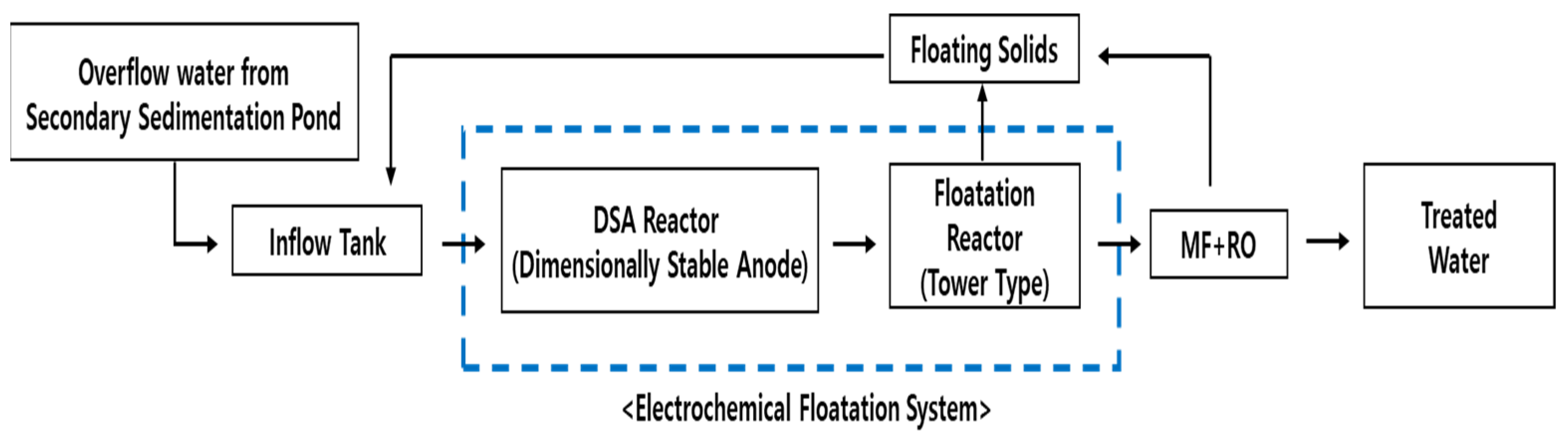
Figure 1c and Figure 3 show the flowchart and configuration of the developed sewage-reuse system combining the EFS and the separation membrane (MF/RO) process.

Figure 3.
Flowchart of the EFS coupled with the separation membrane process.
The post-treatment process was composed of typical MF and RO membranes. The MF membrane made of polypropylene was resistant to ultraviolet hardening, with an effective filtration area of 5 m2/10 inch and a length of 750 mm. RO is a filter for ion (heavy metal) removal. It is a separation membrane that is particularly effective for sewage treatment. Its surface, with coating layers and chemical covalent bonds, can effectively minimize surface scale and the flow rate. In this study, a RO membrane manufactured by Toray Industries, Tokyo, Japan, was used.
2.3. Experimental Methods
An evaluation of the efficiency of the sewage-reuse system was conducted for sewage in water from the secondary sedimentation pond of a sewage-treatment plant located in the city.
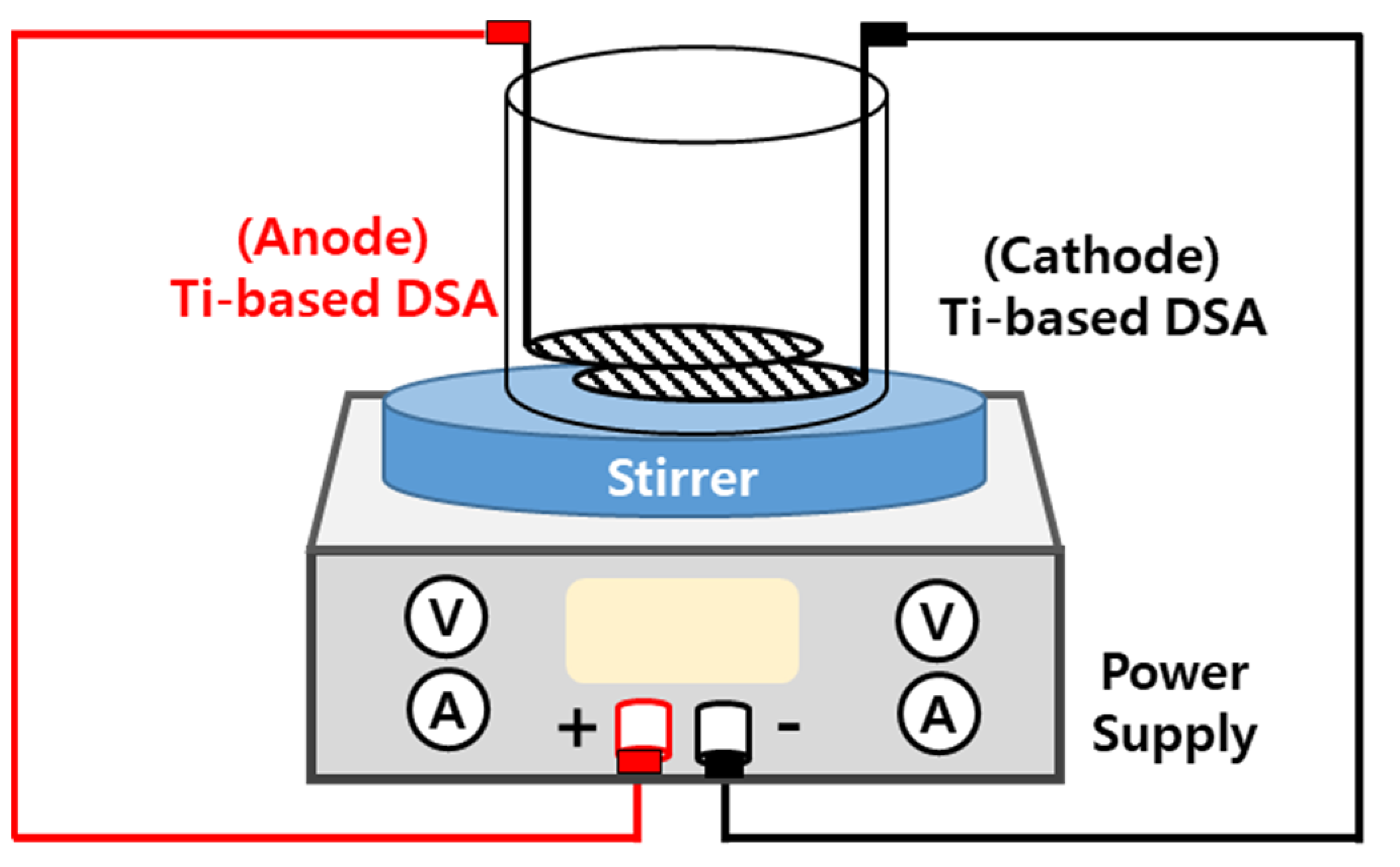
To remove pollutants from the sewage, an experiment was performed to select the optimal operating conditions for a Ti-based DSA. Table 2 and Figure 4 show the experimental conditions and the schematic diagram of the batch reactor, respectively. In sewage treatment, nitrogen is an important factor for biological treatment and is also a very important component of the water-quality index of sewage water. Accordingly, the operating parameter of the DSA was set based on the evaluation of the treatment efficiency of nitrogen present in the sewage. The experiment measured the removal of NH3-N and the change in the reaction rate with the measured current density by changing the current to 1.66, 2.50, and 3.30 A at a specific surface area of the Ti-based DSA of 84.5 cm2. NaCl was used as the electrolyte. Sampling was performed at intervals of 1, 3, 5, 10, and 15 min after the reaction with the DSA for 15 min by adding 580 mg/L NaCl. The experimental batch-type reactor featured a mesh-type DSA with a 65 mm diameter and a reactor volume of 1.0 L. The electrode was powered by a 6 to 8 V DC power supply.

Table 2.
Specific surface area and current density of DSA.

Figure 4.
Experiment apparatus for performance evaluation of the DSA.
The experiment was performed by operating the sewage-reuse system, combining the EFS at the front and the separation membrane process at the end, for approximately 73 d to evaluate the treatment efficiency of the system. Samples to analyze the quality of the treated water were collected from the inlet and outlet of each process and treatment efficiency was evaluated by assessing each water-quality parameter. The DSA module was designed to react with electrolytes in the sewage. For this purpose, the voltage, current, and operating power conditions were set to 7 to 8 V, 26 to 30 A per DSA module, and 0.196 to 0.244 Kw, respectively. For system operation, the flow rate for the sewage undergoing treatment was set to 50 m3/d. The effluent from the sewage-treatment plant was controlled by a pump. Poly aluminum chloride (15–18%; 5 mL/min) and sodium bisulfite (5 mL/min) were injected at a constant concentration using a chemical pump.
2.4. Analytical Methods
Suspended solids (SSs) and BOD were analyzed using the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd edition. Total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorous (TP) were measured using an ultraviolet/visible spectrophotometer (DR 5000; HACH Corp., Loveland, CO, USA) according to the Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (22nd edition). In turn, pH and turbidity were measured using a pH meter (Orion Star A111; Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and a turbidimeter (2100N; HACH Corp. Loveland, CO, USA), respectively. Total organic carbon (TOC) was analyzed using a TOC analyzer from Shimadzu (H54495209104; Kyoto, Japan) and chromaticity was analyzed using an ultraviolet/visible spectrophotometer (DR 5000; HACH Corp., Loveland, CO, USA). Total coliforms (colony forming unit, or CFU) were determined using the membrane filter method. The size of fine bubbles was measured using software (Image Partner program, GTN-BT911; Korea) for bubble images captured using a CX43 Microscope (OLYMPUS, Tokyo, Japan). In Korea, TOC, which can confirm the total amount of all organic substances, including non-degradable organic substances, is used as a water-quality standard. Therefore, in this study, TOC was evaluated instead of COD.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bubble-Size Analysis
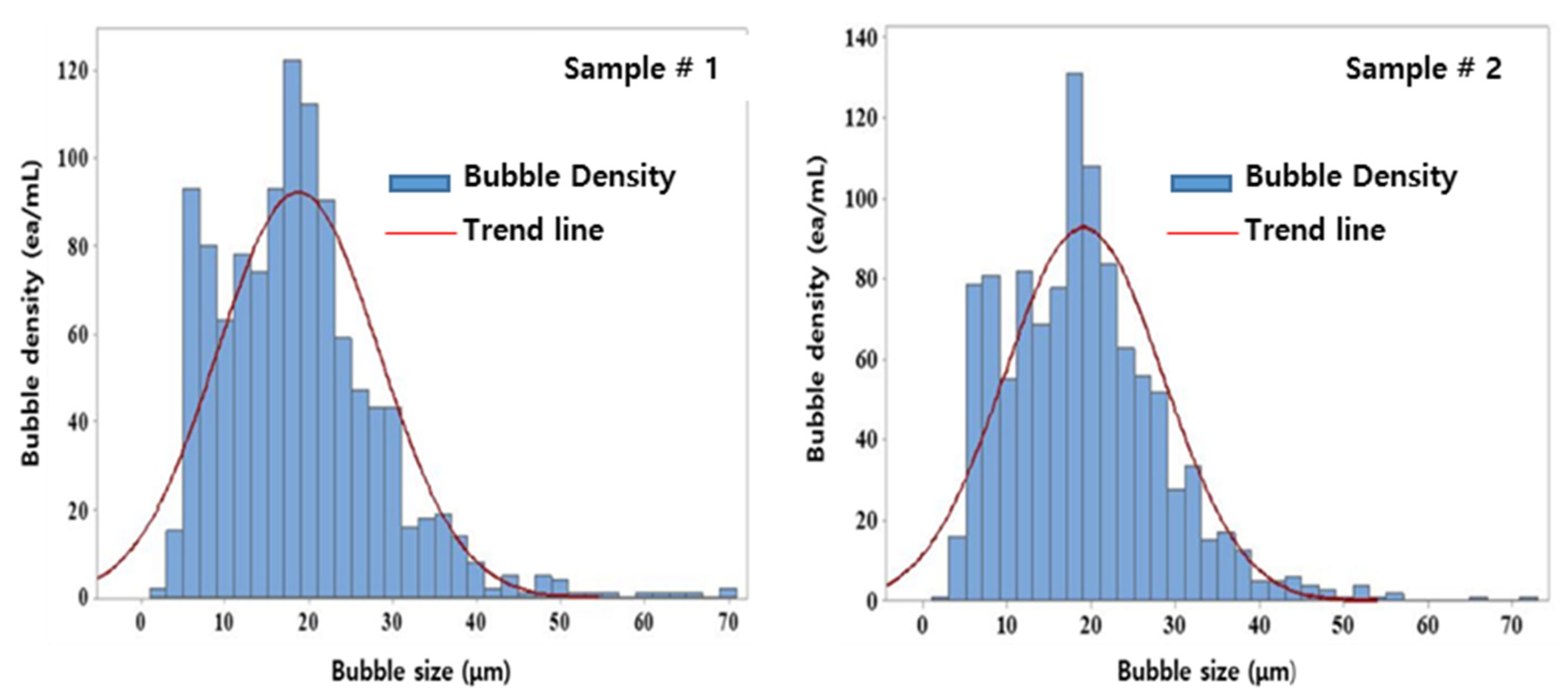
The International Organization of Standards classifies bubbles into nanobubbles with a size of <1 µm and microbubbles with larger sizes [23]. Fine bubbles of size classes 10 µm–1 nm and 500 µm–10 nm are distinguished using the dynamic light scattering method and laser diffraction method, respectively. The particle-tracking Brownian motion and resonant mass methods were used to count bubbles of sizes 1 µm–40 nm and >10 µm, respectively. The electrical sensing zone method was used to measure larger bubbles in the size range of 1 mm–500 nm and image analysis was used for bubbles >1 µm.
Table 3 and Figure 5 show the results of the measurement and distribution of the fine bubbles measured using the image analysis method. The average size of the bubbles generated by the fine-bubble generation system through catalytic electrodes ranged from 20 to 40 μm, and bubbles > 40 μm accounted for <5% of all bubbles formed. Normal bubbles, with a diameter of tens of μm, rapidly rose to the surface of the water body, ruptured there, and did not exhibit qualitative changes or an energy source. However, microbubbles generated by the catalytic electrodes slowly rose to the water surface and supplied oxygen particles in the bubble condition to water under the surface. They exhibited high air-dissolution efficiency due to the small bubble size when subjected to water treatment [24]. Therefore, a charging effect, a physical adsorption effect, and an oxidation effect for sterilization and cleaning are to be expected via generated bubbles for water treatment [25,26].

Table 3.
Bubble-size analysis.
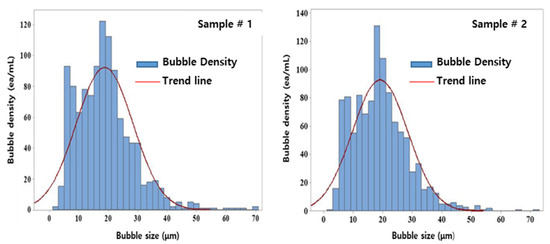
Figure 5.
Bubble-size distribution.
In general, microbubbles are produced in a mechanical manner such as setting the pressure of a pump and the quantity of air intake. This process has the disadvantage of the size of the air bubbles being dependent on the pressure of the pump and the size of the nozzle used. However, microbubbles produced in EFSs are produced by a series of reactions on the electrodes that enable stable bubble production without pressure or mechanical manipulation.
3.2. Evaluation of Treatment Efficiency According to Current Density of the DSA
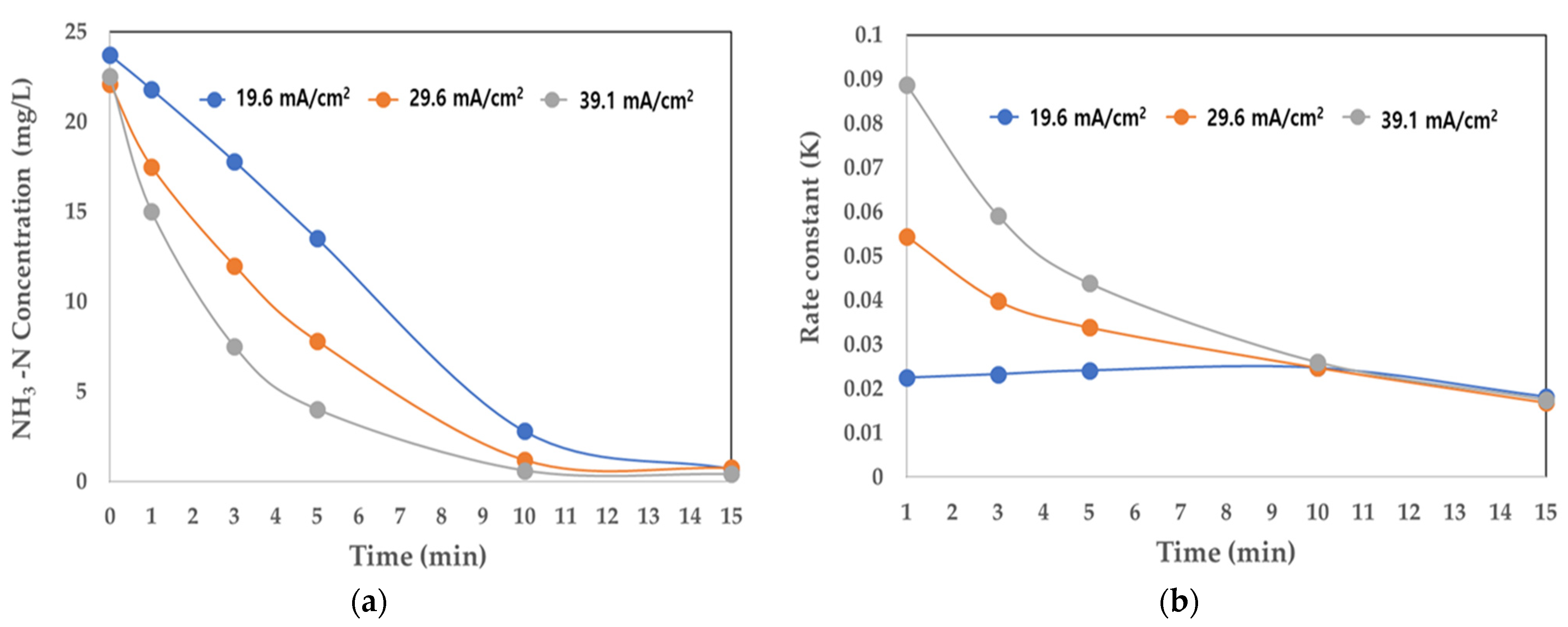
Table 4 and Figure 6a shows the change in NH3-N concentration by reaction time according to the change in current density. At a current density of 39.1 mA/cm2, 82.2 and 97.3% of NH3-N were removed after 5 and 10 min of reaction time, respectively. At a relatively low current density of 19.6 mA/cm2, 43.0 and 88.1% of NH3-N were removed after 5 and 10 min of reaction time, respectively.

Table 4.
Specific surface area and current density of DSA.
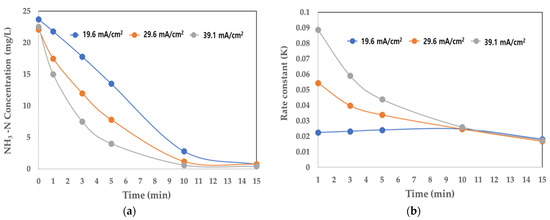
Figure 6.
Changes in NH3-N and rate constant (K) according to current density. (a) Concentration of NH3-N (mg/L); (b) rate constant (K).
Table 4 and Figure 6b shows the change in the rate constant (K) with respect to the change in current density. At 39.1 mA/cm2, K was very high (at 0.088 at the initial reaction) but after 10 min, it reduced sharply to 0.0259. At 19.6 mA/cm2, K was 0.0225 at the initial reaction and even after 10 min it remained stable. Therefore, continuous electrolysis was possible, even at a low current density. Despite variations in current density, the NH3-N removal rate and K exhibited similar results even after 15 min of reaction time.
This study established operational parameters for Ti-based DSA operation in a sewage utilization system by considering recommended water quality and system power consumption. After assessing removal efficiency and reaction rate variations with different current densities, this study determined optimal conditions at a current density of 19.6 mA/cm2 and a reaction time of 10 min. These parameters were used as design factors to evaluate the field application of a pilot-scale system on a real scale.
3.3. Evaluation of the Treatment Efficiency of the EFS
Our EFS was a Ti-based DSA that consumed 7 V and 80 A, and had a current density of 19.6 A/m2. The water-treatment reaction time was set to approximately 10 min. The reaction process generated microbubbles (20–40 μm) by inducing an oxidation reaction at cation catalytic electrodes. This process instantly performed solid–liquid separation for suspended matter in water by inducing the cohesion and adsorption of colloids with aluminum coagulants, and eliminated harmful bacteria and oxidize pollutants.
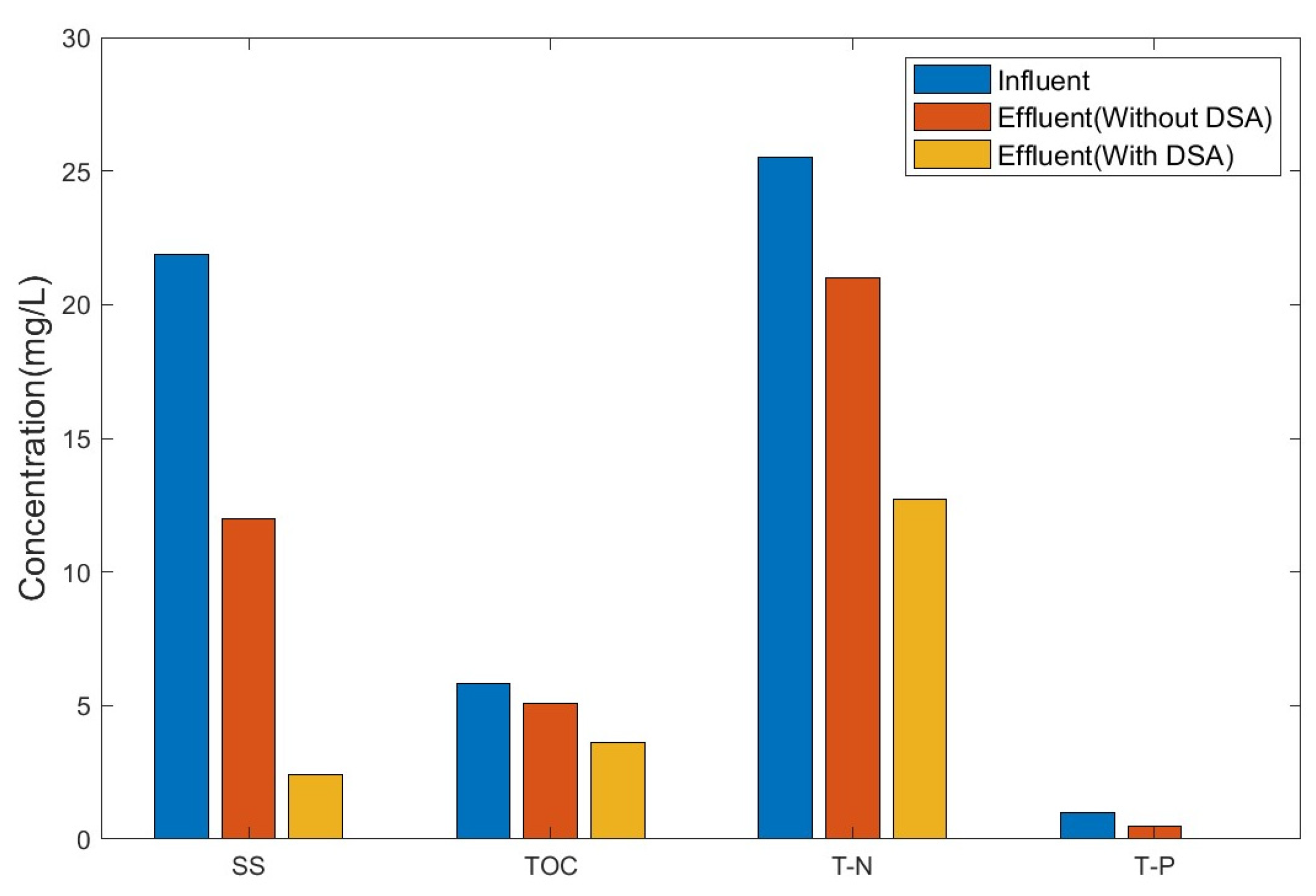
Table 5 and Figure 7 show the experimental results of the evaluation of the treatment efficiency of our DSA-dependent EFS. The removal efficiency evaluation of this study was measured for the water-quality standard items of SS, BOD, TOC, TN, TP, and total coliforms of sewage-reused water. Cations and heavy metals were excluded from the removal efficiency evaluation.

Table 5.
Comparison of treatment efficiency depending on the use of DSA.

Figure 7.
Comparison of treatment efficiency with and without the intervention of a DSA.
In general, treatment for sewage reuse is based on a coagulation and settlement process, floatation, sand filtration, and chlorination and is usually applied in combination with ozone treatment, activated carbon adsorption, and membrane separation processes. The treatment efficiency of our EFS was evaluated through a comparison with levitation separation systems commonly used for the treatment of sewage for reuse.
Without a DSA, sewage water was treated using a typical flotation separation system and the treatment efficiency corresponded with that of simple cohesion and flotation separation. In this case, the removal efficiencies for SS, TP, TOC, and TN were 45.2%, 50.5%, 10.3%, and 17.6%, respectively. The treatment efficiency of the DSA-based EFS was more than twice as high as that without using a DSA. Particularly, the treatment efficiency increased 3.7- and 2.8-fold for TOC and TN (SS: 2.4 mg/L, TOC: 3.6 mg/L, TN: 12.7 mg/L, and TP: 0.04 mg/L), respectively. Total coliforms are rarely treated under the operation of a typical flotation separation system, but they were completely removed (100%) when a DSA was used (total coliforms are not shown in Figure 7).
As for particulate matter, the introduced pollutants were turned into flocs through the cohesion reaction of the oxygen and hydrogen bubbles generated during water electrolysis using insoluble electrodes such as the DSA. Bubbles rapidly rose to the water surface by combining with small bubbles to be rapidly removed through solid separation from water [27,28].
Additionally, the DSA induced the reaction of soluble cations such as Mg2+, Ca2+, total dissolved solids, and heavy metals with the hydroxyl group. The DSA increased the treatment efficiency in terms of the quality of treated water through the reduction, adsorption, and cohesion reactions of suspended and ionic substances (Equations (1)–(5)) as well as through sterilization, organic matter oxidation, and decomposition processes [12].
H+ + H2O → ⦁OH + H2 (gas) → sterilization
H+ + H2O + Cl− → HCl + H2O
H3O+ + Cl− → 2(H3O)+ + Cl2 → 2(H2O) + H2 (gas), Cl2 (gas)
HClO + H2 (gas) → HCl (soluble) + O + (C5H10O4) → CO2, H2O
OH− (aq) + ionized metal ions (Mg2+, Ca2+, etc.) (aq) → Mg(OH)2(s) → total dissolved
solid reduction, adsorption, flocculation
solid reduction, adsorption, flocculation
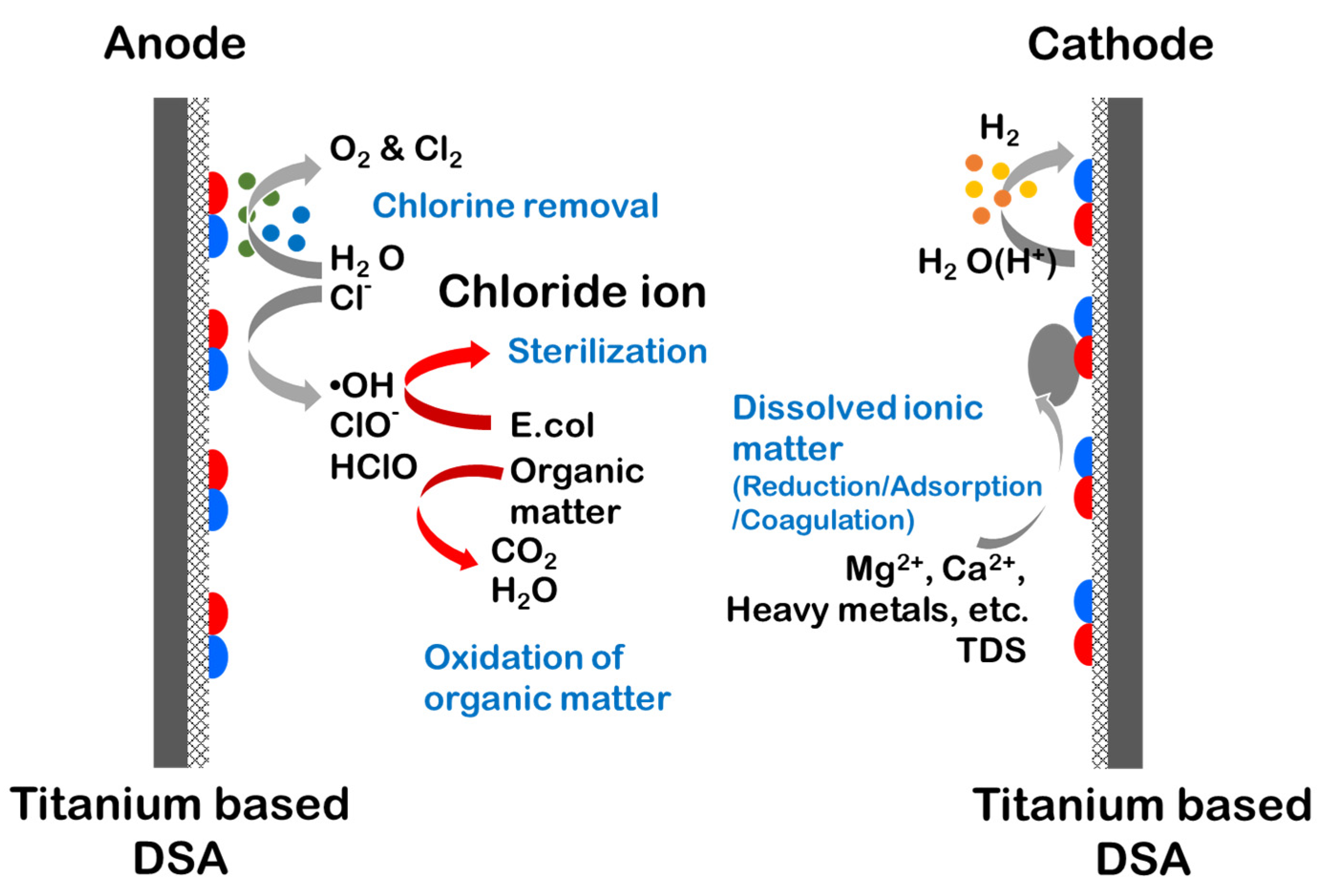
Figure 8 shows the schematic representation of electrochemical activity on the DSA. The Ti-based DSA enabled the direct or indirect electrochemical decomposition of organic pollutants through Cl2, O2, and ⦁OH due to the activation of metal oxides. At the anode, the generated Cl− reacted with NH3-N in the sewage to oxidize it to N2, thereby removing nitrogen. Further, we confirmed that ⦁OH removed the chromaticity and E. coli of sewage. In addition, O2 at the cathode and H2 at the anode were generated to remove the particulate material after oxidizing the soluble material in water to change it into a particulate material.

Figure 8.
Schematic representation of the electrochemical decomposition activity occurring on the DSA [12].
When the DSA in the EFS was used, the treated water met the water-quality standards for recycled water that can be used for cleaning and landscaping. Lastly, based on its total coliform content, this treated water also met the quality standards for river maintenance and agricultural use.
In general, owing to their excellent physical properties, chemical treatment systems provided with a DSA are used in various fields such as chlor-alkali processes, electrochemical water treatment, and water electrolysis [29]. Additionally, they have been applied to treat wastewater containing high concentrations of non-degradable contaminants (Table 6).

Table 6.
Comparison of electrochemical effective processing of pollutants using DSA.
Goya et al. reported the application of a Ti/RuO2-based DSA electrode to treat wastewater with a COD of 643,000 ± 50,000 mg/L and pH of 0.4 ± 0.1; their results showed considerably high activity, with a COD removal of 48.83% at a high current density of 720 A/m2 [30]. Similarly, Markou et al. reported 96.70% of COD removal from dairy wastewater (COD of 4000 mg/L) using a Ti/IrO2-based DSA at a current density of 200 mA/cm2 [31]. In turn, Cotillas et al. studied the removal of Escherichia coli from secondary septic tank effluent using a Ti/RuO2-based DSA; they confirmed 100% E. coli removal at a current density of 11.46 mA/cm2 [30]. In this study, metal oxide activity using a Ti-based DSA at a current density of 19.6 mA/cm2 effectively removed 100% of E. coli and 48.83% of TOC.
Previous studies have shown that the treatment of highly contaminated water requires high metal oxide activity at a high current density, while water with a low level of contamination requires a low current density.
Current density refers to the electric current flowing per unit area in the cross-section of a conductor. If the current density is high, the processing speed may be accelerated but this may cause chemical changes in the electrolyte and an increase in energy consumption. Hence, for efficient water treatment, it is important not only to control the current density but also to maintain balanced chemical characteristics and treatment conditions of the electrolyte.
This study on sewage showed that water treated at a low current density (19.6 mA/cm2) and high treatment speed (10 min) met the water-quality standards of sewage for reuse.
3.4. Pressure Change in the Separation Membrane Process Depending on the Input of Anti-Scalants
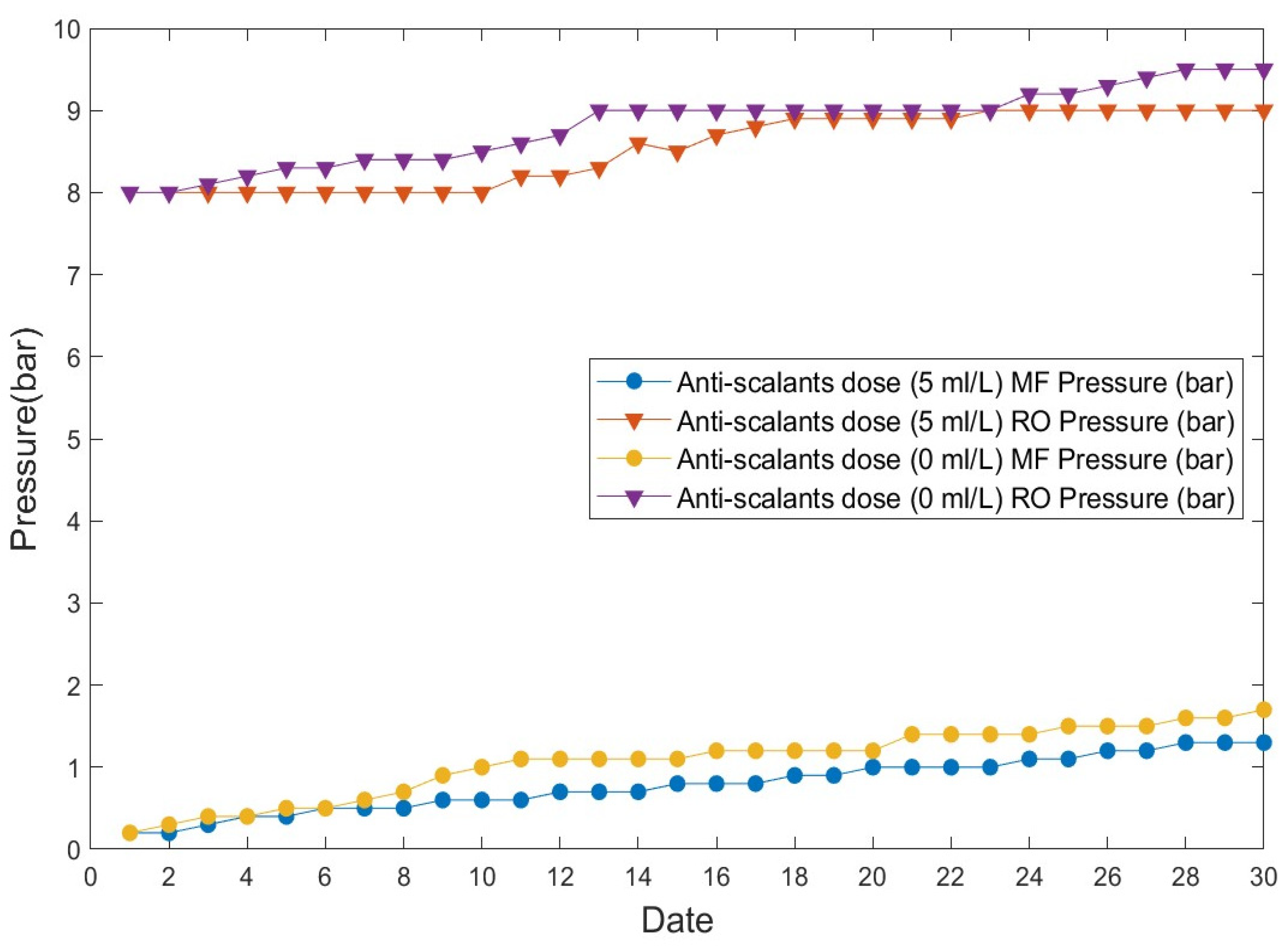
A pressure-change experiment of the separation membrane process was performed to evaluate its effect on the final treatment of the sewage by the EFS.
Figure 9 shows the changes in pressure in post-treatment MF/RO membranes caused by microbial fouling during the operation of the RO membrane that was used as an alternative to the input of anti-scalants to suppress organic matter in the EFS process. Changes in pressure in the MF and RO processes caused by membrane fouling were observed, depending on the input of anti-scalants.
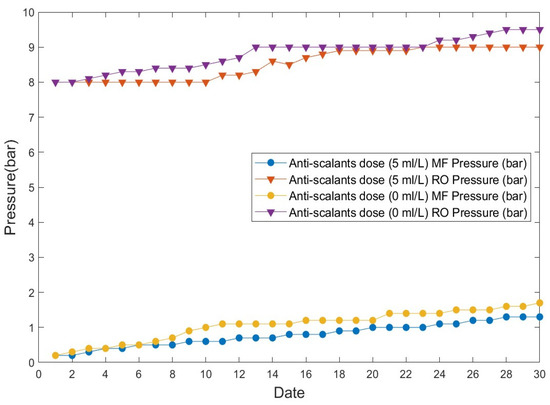
Figure 9.
Anti-scalant-dependent pressure changes occurring in the separation membrane (MF/RO) process.
The results of the 30 d operation with (5 mL/min) and without anti-scalants for sewage treatment using a typical fine-bubble flotation separation system and the EFS process are shown in Figure 9.
In the case of sewage effluent treatment, the initial operating pressures were 0.2 bar for MF and 8 bar for RO at the time the operation of the MF and RO processes began. When anti-scalants (5 mL/min) were added to the water treated using the typical flotation separation system process, the pressure increased to 1.3 bar for MF and to 9 bar for RO. When anti-scalants were not added to the water treated using the EFS, the pressure increased to 1.7 bar for MF and 9.5 bar for RO. Generally, anti-scalants are used to suppress organic matter when an RO membrane is used for water reuse. A certain amount of sodium bisulfite is also used to remove NaOCl. Our results showed that there were no pressure changes over operation time, even in the absence of anti-scalants. Similarly, the comparison of this outcome with that observed when anti-scalants were added showed that there were no sudden pressure changes, despite a slightly high pressure on the membrane.
The membrane process enables treatment according to the characteristics of influent water along with water-quality control according to the use of recycled water. The application of the membrane filtration process to treated sewage water, however, showed the disadvantage of membrane fouling [33]. The occurrence of rapid membrane fouling has previously been reported in cases in which treated sewage water was reused using MF or RO membranes [34].
However, there was no membrane fouling during the operation of the membrane separation process during the treatment of sewage water by the EFS process tested in this study. This was presumably due to the reduction in fouling substances such as dissolved substances, coliforms, and other microorganisms by the EFS process. In addition, as anti-scalants, which have been used for several years, were not used during the treatment, the service life of the MF and RO should be extended while maintenance costs should be minimized by the reduction in chemical costs.
3.5. Performance of the Sewage-Reuse System (EFS + MF/RO)
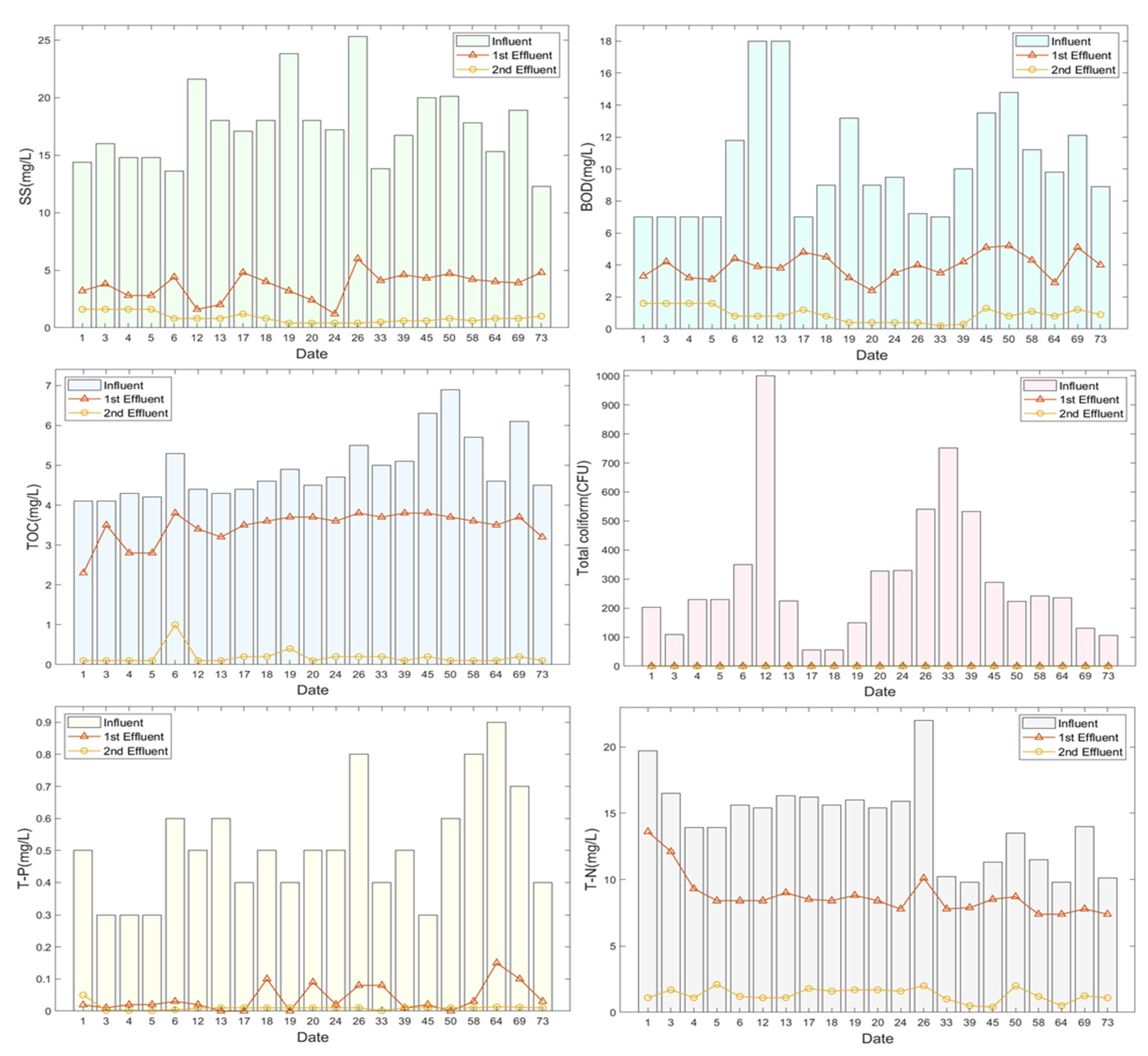
Table 7 and Figure 10 show the changes in treatment efficiency for the 73 d continuous operation of the EFS coupled with the separation membrane (MF/RO) process. For the operating conditions of the entire process used herein, the flow rate of the influent was designed to be 50 m3/d. The pH for the entire process ranged from 6.0 to 8.5 and the treatment resulted in treated water with a pleasant odor and chromaticity.

Table 7.
Removal efficiency change of the sewage-reuse system (EFS + MF/RO).

Figure 10.
Changes in the efficiency for removal of various contents by the sewage-reuse system (EFS + MF/RO).
SS ranged from 2.0 to 4.8 mg/L for the water treated using the EFS process (first step) and from 0.40 to 1.6 mg/L for the water finally treated using the MF/RO system (second step). In turn, BOD ranged from 2.4 to 5.2 mg/L for the water treated using the EFS and from 0.2 to 1.22 mg/L for the water finally treated using the MF/RO system. Meanwhile, the treatment efficiency for TOC removal was as low as 38.8% for the EFS process but it increased to 96.1% using the MF/RO system. Meanwhile, that for TN removal ranged from 7.4 to 13.6 mg/L for the water treated using the EFS and from 0.5 to 1.7 mg/L (average: 1.3 mg/L) for the water finally treated using the MF/RO system. As for TP, the removal efficiency using the EFS was 92.8%, which increased to 98.0% when using the MF/RO system as the TP concentration of the finally treated water was 0.01 mg/L. Furthermore, 100% of total coliforms were treated in the EFS process, whereby turbidity decreased from 13.9 NTU (influent) to 0.04 NTU and the chromaticity decreased from 14 CU to 1 CU.
The continuous operation of our EFS system coupled with the separation membrane process for a 73 d period confirmed that high-quality recycled water that can be used for various purposes could be produced through the separation and combination of treatment processes according to the water-quality standards for each use.
Sewage-reuse water may serve a range of purposes and the required water-quality standards vary depending on each specific intended use. Conventional methods using biological treatments exhibit limitations to comply with diverse water-quality standards due to constrained technical applications and intractable non-biodegradable substances. Therefore, various physicochemical processes have been investigated. Specifically, the DSA-based EFS sewage-reuse system applied in this study demonstrated technical efficacy for the electrocoagulation and electroflocculation processes that led to the oxidation of organic compounds through direct/indirect treatments. An EFS can be altered, depending on the use of water-quality standards for various technical applications, thus allowing for a selective water supply for various end uses. Ongoing and future research in our laboratory aims to focus on the technical evaluation and validation of the system presented herein to secure treatment methods to obtain reuse water from industrial effluents and other sources.
4. Conclusions
The sewage-reuse system applied in this study was a combination of an EFS and a separation membrane system. The combined system could be individually used for each throughput, implying that it could flexibly respond to the water-quality standards of the water to be used. A DSA within an EFS has typically been widely used for high concentrations of wastewater [10,11]. This study was able to achieve the recommended water-quality concentration of sewage-reused water even at a low current density and short reaction time for a low concentration of sewage. It can be stated that the developed sewage-reuse system has a wide range of applications in the treatment of various concentrations of contaminated water. It was judged that the application of a high concentration of wastewater other than sewage could be treated by increasing the current density. This could be indirectly predicted from the results of other studies on the treatment of contaminated water containing high concentrations of pollutants [30,31].
In the reuse of sewage-treatment water, the focus may be on determining the level of sewage treatment required for specific reuse purposes. The configuration and process of the treatment system can be determined according to the target water quality for each reuse purpose, which is directly related to its economic feasibility. The treatment of sewage water should be to an extent that potential users are not esthetically offended and their health is not affected. In addition, the surrounding environment, animals, and plants should not be affected by the treated sewage water and it should not have deleterious effects on machinery and equipment that it comes into contact with. The purpose of this study was to establish a sewage-treatment system that could be used in various ways.
The evaluation of the performance of the electrofloatation technology over a long-term operation confirmed that the EFS coupled with the separation membrane process could provide high-quality recycled water from sewage. Therefore, this method is expected to enhance the economic feasibility of sewage-water utilization by varying the treatment process conditions according to the water-quality standards for different applications, including agricultural, industrial, instream, flushing, cleaning, sprinkling, and car-wash water.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.-L.Y. and M.H.; data curation, M.H. and H.-C.O.; formal analysis, S.-L.Y. and M.H.; methodology, S.-L.Y. and M.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.-L.Y.; writing—review and editing, S.-L.Y.; visualization, S.-L.Y. and H.-C.O.; supervision, S.-L.Y. and S.K.; project administration, H.-C.O.; funding acquisition, S.-L.Y. and S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) (Research on next generation Environmental Technology for Carbon Neutrality (3/3) (Project #20230160-001)), and the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) (Research on next generation Environmental Technology for Carbon Neutrality (4/4) (Project #2024)).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- WHO. Guideline for the Safe Use of Wastewaters, Excreta and Greywater; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrat, R.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T.; Jeffrey, P. Assessing the European wastewater reclamation and reuse potential—A scenario analysis. Desalination 2006, 188, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togna, A.P.; Bohner, A.; Webster, T.; Guarini, W.; Sutton, P.M.; Murray, M.; Robinson, S.; Presgrave, C. Membrane biological reactor system development for treatment of high-strength industrial wastewater. In Proceedings of the WEFTEC, Annual Technical Exhibition & Conference 75th, Chicago, IL, USA, 26–30 September 2002; Volume 108. [Google Scholar]
- Sadr Ghayeni, S.B.; Beatson, P.J.; Schneider, R.P.; Fane, A.G. Water reclamation from municipal wastewater using combined microfiltration-reverse osmosis (ME-RO): Preliminary performance data and microbiological aspects of system operation. Desalination 1998, 116, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.K. A study on the interrelation among organic pollutant indices of non-biodegradable paper wastewater. J. Korean Soc. Wat. Sci. Tech. 2008, 16, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, A.T.; Sunde, S.; Tsypkin, M.; Tunold, R. Performance of a PEM water Electrolysis Cell Using IrxRuyTazO2 electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution Electrode. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 2320–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, Y.; Sugimoto, W.; Nishiki, Y.; Nakamatsu, S. Structural analyses of RuO2-TiO2/Ti and IrO2-RuO2/Ti anodes used in industrial chlor-alkali membrane processes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moats, M.; Hardee, K.; Brown, C. Mesh-on-lead anodes for copper electrowinning. JOM 2003, 55, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.R.; Botta, C.M.R.; Espindola, E.L.G.; Olivi, P. Electrochemical treatment of tannery wastewater using DSA electrodes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, E.H.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, K.H.; Jung, B.I.; Kim, K.H. Performance improvement of Ir oxide electrode for organic destruction. Korean Chem. Eng. Res. 2002, 40, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Bertazzoli, L.; Pelegrini, R. Photoelectrochemical discoloration and degradation of organic pollutants in aqueous solutions. Quim. Nova 2002, 25, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Profeti, D.; Lassali, T.A.F.; Olivi, P. Preparation of Ir0.3Sn(0.7−x)TixO2 electrodes by the polymeric precursor method: Characterization and lifetime study. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2006, 36, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.É.S.; Silva, R.S.; Eguiluz, K.I.B.; Salazar-Banda, G.R. Development of Ti/(RuO2)0.8(Mo2)0.2 (M= Ce, Sn, or Ir) Anodes for atrazine Electro-Oxidation: Influence of the Synthesis method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 146, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, B.; Wang, L. Effect of calcination temperature and molar ratio of tin and manganese on capacitance of Ti/SnO2-Sb-Mn/β-PbO2 electrode during phenol electro-oxidation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 747, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dbira, S.; Bensalah, N.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Bedoui, A. The Electrolytic treatment of synthetic urine Using DSA Electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 744, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddouh, A.; Bessegato, G.G.; Rguiti, M.M.; El Ibrahimi, B.E.; Bazzi, L.; Hilali, M.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Electrochemical decolorization of rhodamine b dye: Influence of anode material, chloride concentration and current density. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.C.; Park, S.C. Electrochemical treatment of wastewater containing Fluoride. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2007, 15, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.J.; Min, K.S.; Park, J.M. Treatment characteristics of refractory compounds in dying wastewater by electrocatalytic electrode. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2003, 25, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Feng, Z.; Tang, M.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, R.; et al. A Study on the Performance of IrO2-Ta2O5 Coated anodes with Surface Treated Ti Substrates. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 157, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Tang, M.; Zhang, R. Electro-catalytic study of IrO2Ta2O5 coated anodes with pretreated titanium substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 680, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Morimitsu, M. Effects of Oxide Composition on Structure, Surface Morphology, and Oxygen Evolution Behaviors of IrO2-Ta2O5/Ti Anodes Prepared at a High Temperature. Electrochemistry 2015, 83, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 20298-1; Fine Bubble Technology—Sampling and Sample Preparation for Measurement—Part 1: Ultrafine Bubble Dispersion in Water. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Zhou, Z.A.; Xu, Z.; Finch, J.A.; Masliyah, J.H.; Chow, R.S. On the role of cavitation in particle collection in flotation—A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Poele, S.T.; Van Der Graaf, J. Enzymatic cleaning in ultrafiltration of wastewater treatment plant effluent. Desalination 2005, 179, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laabs, C.N.; Amy, G.L.; Jekel, M. Understanding the size and character of fouling-causing substances from effluent organic matter (EfOM) in low-pressure membrane filtration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüttner, K.; Galla, U.; Schmieder, H. Electrochemical approaches to environmental problems in the process industry. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2575–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Park, Y.S. A study on the preparation of the dimensionally stable anode (DSA) with high generation rate of oxidants (I). J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2009, 18, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.R.; Park, J.S. An Updated Review of Recent Studies on Dimensionally Stable Anodes (DSA). J. Korean Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, A.; Srivastava, V.C. Treatment of highly acidic wastewater containing high energetic compounds using dimensionally stable anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markou, V.; Kontogianni, M.C.; Frontistis, Z.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Katsaounis, A.; Vayenas, D. Electrochemical treatment of biologically pretreated dairy wastewater using dimensionally stable anodes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillas, S.; Llanos, J.; Castro-Ríos, K.; Taborda-Ocampo, G.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Cañizares, P. Synergistic integration of sonochemical and electrochemical disinfection with DSA anodes. Chemosphere 2016, 163, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, K.-I. Applicability evaluation of microbubble for membrane fouling reduction in wastewater reuse membrane process. J. Korean Soc. Water Wastewater 2017, 31, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roorda, J.H.; Wortel, N.C.; van Dalen, R. New process for treatment of organically fouled water: Experiences with WWTP effluent. Desalination 2005, 178, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).