Correlations Between Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Physicochemical Parameters in the Seungchon and Juksan Weirs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Physicochemical Parameter Analysis
2.3. Phytoplankton Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Characteristics
3.2. Phytoplankton Community
3.3. Multifunctional Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Environmental Trends
4.2. Algal Bloom Dynamics
4.3. Statistical Insights
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakore, B.G.; Atique, U.; An, K.G. Serial installation of massive weirs impacts the nutrients, solids, chlorophyll, and water chemistry along the river gradient. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 8261–8276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royer, T.V. Human-dominated rivers and river management in the Anthropocene. In Stream Ecosystems in a Changing Environment; Jones, J.B., Stanley, E.H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 491–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, S.; An, S.A.; Khim, J.S. Methodological advances and future directions of microalgal bioassays for evaluation of potential toxicity in environmental samples: A review. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ralston, D.K.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Fox, S.E.; Lee, K.D.; Anderson, D.M. Temperature and residence time controls on an estuarine harmful algal bloom: Modeling hydrodynamics and Alexandrium fundyense in Nauset estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 2240–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse van Vuuren, S.; Swanepoel, A. Role of the Lethabo Weir in altering the phytoplankton community structure of the Vaal River, South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci. 2023, 48, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.G.; Kwon, B.O.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Khim, J.S. Phytoplankton assemblage responses to massive freshwater inputs and anthropogenic toxic substances contamination in the Geum River Estuary, South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 199, 116020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.K.; Kang, B.G.; Hwang, S.J. Limnological study on spring-bloom of a green algae, Eudorina elegans and weirwater pulsed-flows in the Midstream (Seungchon Weir Pool) of the Yeongsan River, Korea. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 49, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.A.; Yi, H.S.; Hwang, H.S.; Kim, H.J. Modeling the flushing effect of multi-purpose weir operation on algae removal in Yeongsan River. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2015, 37, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaown, D.; Koh, D.C.; Mayer, B.; Mahlknecht, J.; Ju, Y.J.; Rhee, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, D.K.; Park, I.; Lee, H.L.; et al. Estimation of nutrient sources and fate in groundwater near a large weir-regulated river using multiple isotopes and microbial signatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, R.W.; Baumann, K.; Karl, C.; Popendorf, K.J.; Barnard, M.A.; Chang, N.Y.; Curtis, N.P.; Huang, H.; Mathieson, O.L.; et al. Harmful cyanobacterial aerosolization dynamics in the airshed of a eutrophic estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Dia, S.; Deutsch, E.S.; Alameddine, I. Analyzing eutrophication and harmful algal bloom dynamics in a deep Mediterranean hypereutrophic reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 37607–37621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiao, L.; Cheng, Q.; He, J.; Xhang, Y.; Ding, S. The evolution of a typical plateau lake from macrophyte to algae leads to the imbalance of nutrient retention. Water Res. 2023, 236, 119937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, J. The impacts of local and regional factors on the phytoplankton community dynamics in a temperate river, northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Jian, S.L.; Miao, S.Y.; Li, K.M.; Guan, H.T.; Mao, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, C.Z. Hydrodynamics regulate longitudinal plankton community structure in an alpine cascade reservoir system. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 749888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas-Parejoa, J.C.C.; Corzoa, A.; Papaspyroua, S. Seasonal cycles of phytoplankton biomass and primary production in a tropical temporarily open-closed estuarine lagoon—The effect of an extreme climatic event. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.B.; Jung, Y.H.; Sin, Y.S. Assessing nutrient limitation in Yeongsan River estuary using bioassay experiments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Wai, T.C.; Shen, P.; Lam, P.K.S. Long-term variations of phytoplankton community in relations to environmental factors in Deep Bay, China, from 1994 to 2016. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 111010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunpradid, T.; Chaimongkhon, P.; Tagun, R. Seasonal dynamics and environmental drivers of phytoplankton composition in a tropical dam over 5 years in Chiang Mai, Thailand. Trends Sci. 2024, 21, 7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Sung, J.W.; Kim, T.H.; Cho, H.M.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J. Comparative seasonality of phytoplankton community in two contrasting temperate estuaries on the western coast of Korea. Front. Marine Sci. 2023, 10, 1257904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Sin, Y.S. Response of size-fractionated phytoplankton to humic acids in the seawater of Yeongsan River Estuary. Ocean Polar Res. 2023, 45, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sin, Y.S.; Kim, S.H. Effects of humic acids on size and species composition of phytoplankton in a eutrophic temperate estuary. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.D.; Choi, J.W.; An, K.G. Chemical water quality and fish component analyses in the periods of before and after the weir constructions in Yeongsan River. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 39, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Shin, C. Algal Boom Characteristics of Yeongsan River Based on Weir and Estuary Dam Operating Conditions Using EFDC-NIER Model. Water 2021, 13, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K-Water Development of Methods for Optimal Algae Control Reflecting the Algae Growth Characteristics of Weirs in Four Major Rivers; Korea Water Resources Corporation: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2012.
- ME Standard Method for Water and Wastewater; Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2017.
- MOE. Standard Method for the Examination of Water Pollution; Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Süsβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Band 2/1: Bacillariophyceae 1. Teil: Naviculaceae; Ettl, H., Gerloff, J., Heying, H., Mollenhauer, D., Eds.; Elsevier Book Co.: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Masaru, A.; Teru, I.; Kozo, I.; Hideo, K.; Shigeru, K.; Hiromu, K.; Eigi, T.; Kohei, T.; Minoru, H.; Takaaki, Y. Illustration of the Japanese Fresh-water Algae; Uchidarokakuho Publishing Company: Tokyo, Japan, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen, R. The diatom system: Ideas on phylogeny. Bacillaria 1979, 2, 9–71. [Google Scholar]
- Soltani, N.; Khodaei, K.; Alnajar, N.; Shahsavari, A.; Ashja Ardalan, A. Cyanobacterial community patterns as water quality bioindicators. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2012, 11, 876–891. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Ma, C. Phytoplankton community structure in relation to environmental factors and ecological assessment of water quality in the upper reaches of the Genhe River in the Greater Hinggan Mountains. 2019. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 17512–17519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.J.; Na, J.E.; Kim, G.M.; Shim, S.S.; Lee, H.Y. Water temperature and community of phytoplankton in Youngsan River, Korea. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2010, 28, 56–63. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y. Analysis of water quality and the response of phytoplankton in the low-temperature environment of Majiagou Urban River, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.S.; Son, M.S.; Ryu, H.S.; Park, C.H.; Lee, R.R.; Cho, M.S.; Lim, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, K.H. Variation of cyanobacteria occurrence pattern and environmental factors in Lake Juam. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2019, 37, 640–651. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.A.; Na, J.E.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, K.H. Characteristics of nitro-nutrients and phytoplankton dynamics in the Yeongsan River after weir construction. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 423–430. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.S.; Chung, H.S.; Park, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Lim, C.H.; Kim, K.H. The change of phytoplankton community structure and water quality in the Juksan Weir of the Yeongsan River watershed. Korean J. Environ. Biol. 2018, 36, 591–600. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, J.P.; Chrzanowski, T.H. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton in two warm temperate reservoirs: Association of taxonomic composition with temperature. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.S.; Park, H.K.; Lee, H.J.; Shin, R.Y.; Cheon, C.U. Occurrence and succession pattern of cyanobacteria in the upper region of the Nakdong River: Factors influencing Aphanizomenon bloom. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2016, 32, 52–59. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, E.A.; Han, B.H.; Kim, B.H. Assessing the impact of weirs on water quality and phytoplankton dynamics in the south Han River: A two-year study. Water 2024, 16, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, C.Y.; Yun, S.L.; Kim, S.; Lee, W. Occurrence of harmful blue-green algae at the algae alert system and water quality forecast system sites in Daegu and Gyeongsangbuk-do between 2012 and 2019. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2020, 42, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.; Xu, D. Survival strategies of phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in a drinking water reservoir, central China. Intl. J. Limnol. 2021, 57, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Seo, D. Effect of major pollution sources on algal blooms in the seungchon weir in the Yeongsan River using EFDC. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2020, 5, 369–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, D.; Westerhoff, P. Wastewater discharge impact on drinking water sources along the Yangtze River (China). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1399–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Environment Information System (WEIS). 2024. Available online: http://water.nier.go.kr/ (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, N.; Tian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Nam, W.H. A systematic review and quantitative meta-analysis of the relationships between driving forces and cyanobacterial blooms at global scale. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Peng, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, J.; Xi, S.; Lue, T. Research on the relationship between eukaryotic phytoplankton community structure and key physiochemical properties of water in the western half of the Chaohu Lake using high-throughput sequencing. Water 2024, 16, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gonzalez, R.; Soria-Perpinya, X.; Soria, J.; Sendra, M.D.; Vicente, E. Relationship between cyanobacterial abundance and physicochemical variables in the Ebro Basin Reservoirs (Spain). Water 2023, 15, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.K.; Sim, Y.B.; Hwang, S.J.; Byeon, M.S.; Kang, T.G. Temporal and seasonal variations in a phytoplankton community structure in artificial Lake Uiam, South Korea. Water 2023, 15, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhi, P.; Pranab, G.; Lianthuamluaia, L.; Chayna, J.; Tasso, T.; Suman, K.; Uttam, K.S.; Basanta, K.D. Assessing spatiotemporal dynamics of phytoplankton assemblage and ecohydrological interaction in a community managed reservoir using GIS for sustainable fisheries management. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2023, 23, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitois, F.; Thoraval, I.; Baures, E.; Thomas, O. Geographical patterns in cyanobacteria distribution: Climate influence at regional scale. Toxins 2014, 6, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.T.; Jakobi, A.J. Structural biology of microbial gas vesicles: Historical milestones and current knowledge. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parakkandi, J.; Saha, A.; Sarkar, U.K.; Das, B.K.; Puthiyottil, M.; Muhammadali, S.A.; Ramteke, M.; Johnson, C.; Kumari, S. Spatial and temporal dynamics of phytoplankton in association with habitat parameters in a tropical reservoir, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshith, C.M.; Meena, D.K.; Manna, R.K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Swain, H.S.; Raman, R.K.; Sengupta, A.; Das, B.K. Phytoplankton community structure of the Gangetic (Hooghly-Matla) estuary: Status and ecological implications in relation to eco-climatic variability. Flora 2018, 240, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Duda, M.P.; Antoniades, D.; Smol, J.P.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Diatom species responses along gradients of dissolved inorganic carbon, total phosphorus, and lake depth from lakes across Canada. J. Phycol. 2024, 60, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Seewald, M.; Dadi, T.; Friese, K.; Mi, C.; Boehrer, B.; Schultze, M.; Rinke, K.; Shatwell, T. Unravelling winter diatom blooms in temperate lakes using high frequency data and ecological modeling. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.A.; Rachid, C.T.; Rangel, L.M.; Silva, L.H.; Bisch, P.M.; Azevedo, S.M.; Pacheco, A.B. Close link between harmful cyanobacterial dominance and associated bacterioplankton in a tropical eutrophic reservoir. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Wu, H.; Lin, L.; Li, M. Seasonal succession of phytoplankton in two temperate artificial lakes with different water sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 42324–42334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, A.S.; Chia, M.A.; Lopes, F.A.C.; Silva, G.G.Z.; Edwards, R.A.; do Carmo Bittencourt-Oliveira, M. Cyanobacterial biodiversity of semiarid public drinking water supply reservoirs assessed via next-generation DNA sequencing technology. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reavie, E.D.; Cai, M.; Twiss, M.R.; Carrick, H.J.; Davis, T.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Gossiaux, D.; Smith, D.E.; Palladino, D.; Burtner, A.; et al. Winter-spring diatom production in Lake Erie is an important driver of summer hypoxia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, M.A.; Ameh, I.; George, K.C.; Balogun, E.O.; Akinyemi, S.A.; Lorenzi, A.S. Genetic diversity of microcystin producers (cyanobacteria) and microcystin congeners in aquatic resources across Africa: A review paper. Toxics 2022, 10, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraker, M.E.; Aloysius, N.R.; Martin, J.F.; Keitzer, S.C.; Dippold, D.A.; Yen, H.; Arnold, J.; Daggupati, P.; Johnson, M.; Robertson, D.; et al. Agricultural conservation practices could help offset climate change impacts on cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2023, 49, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Feng, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics of Phytoplankton Community Structure and Indication to Water Quality in the Lake in Agricultural Areas. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 833409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
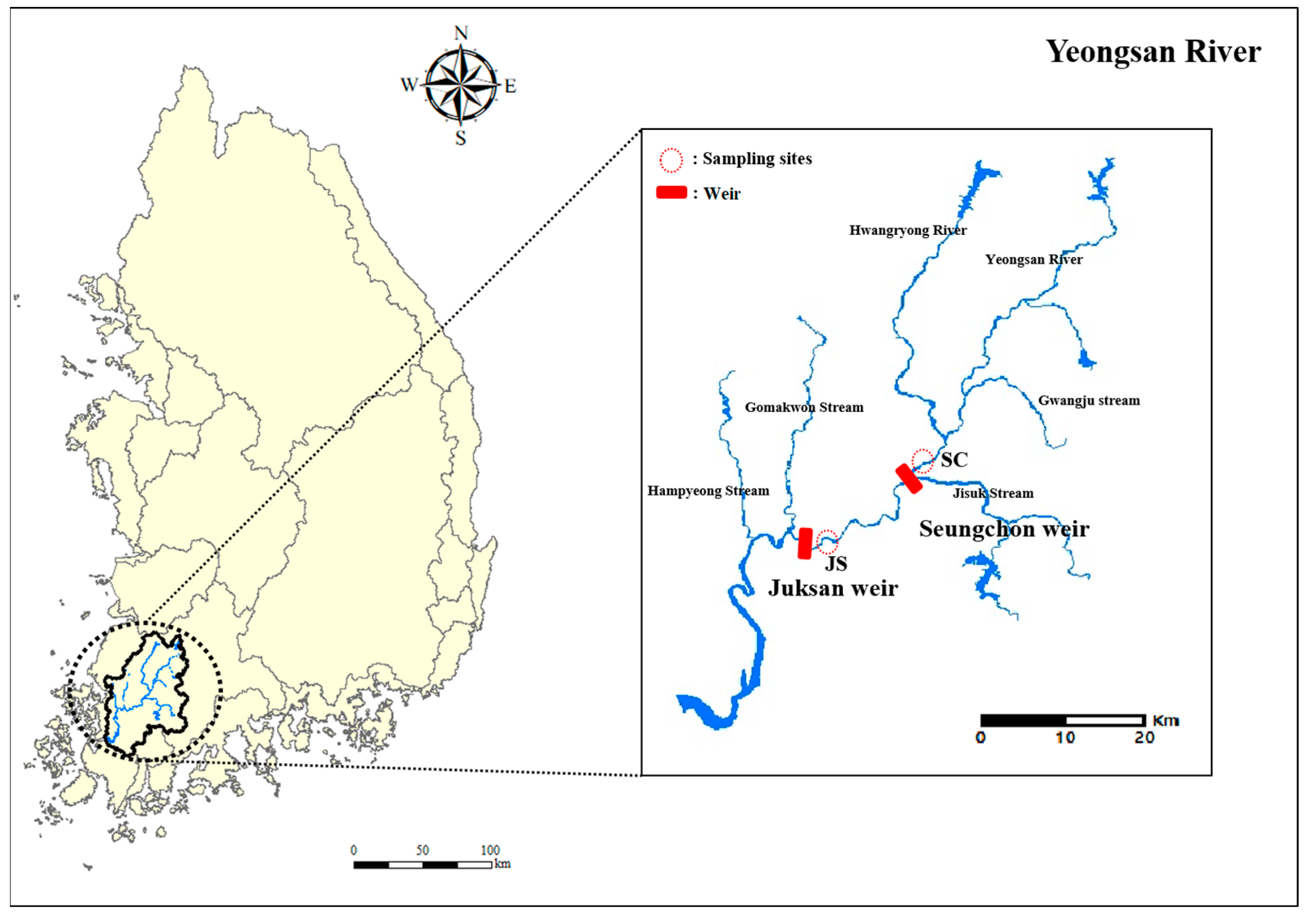
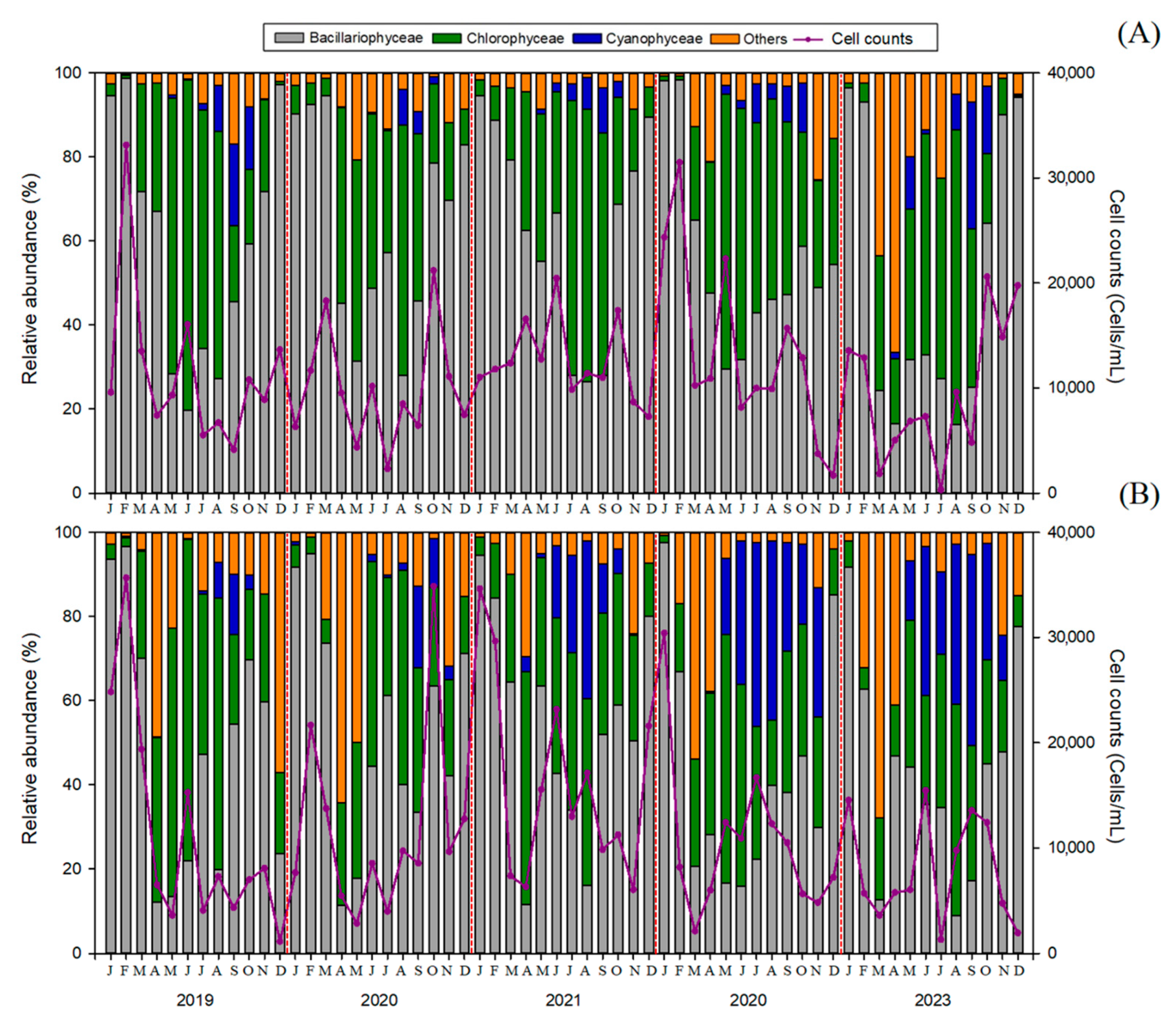
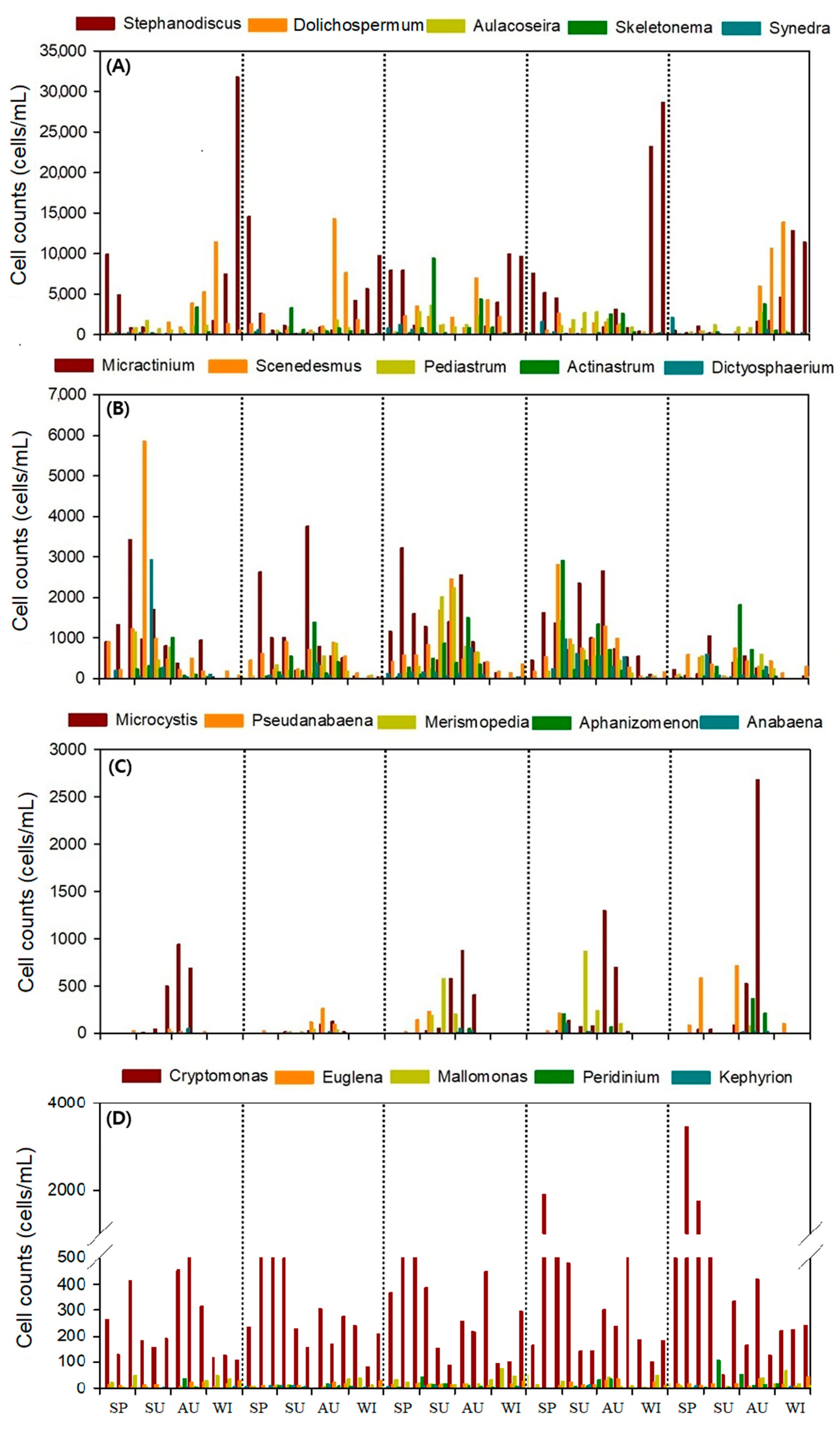



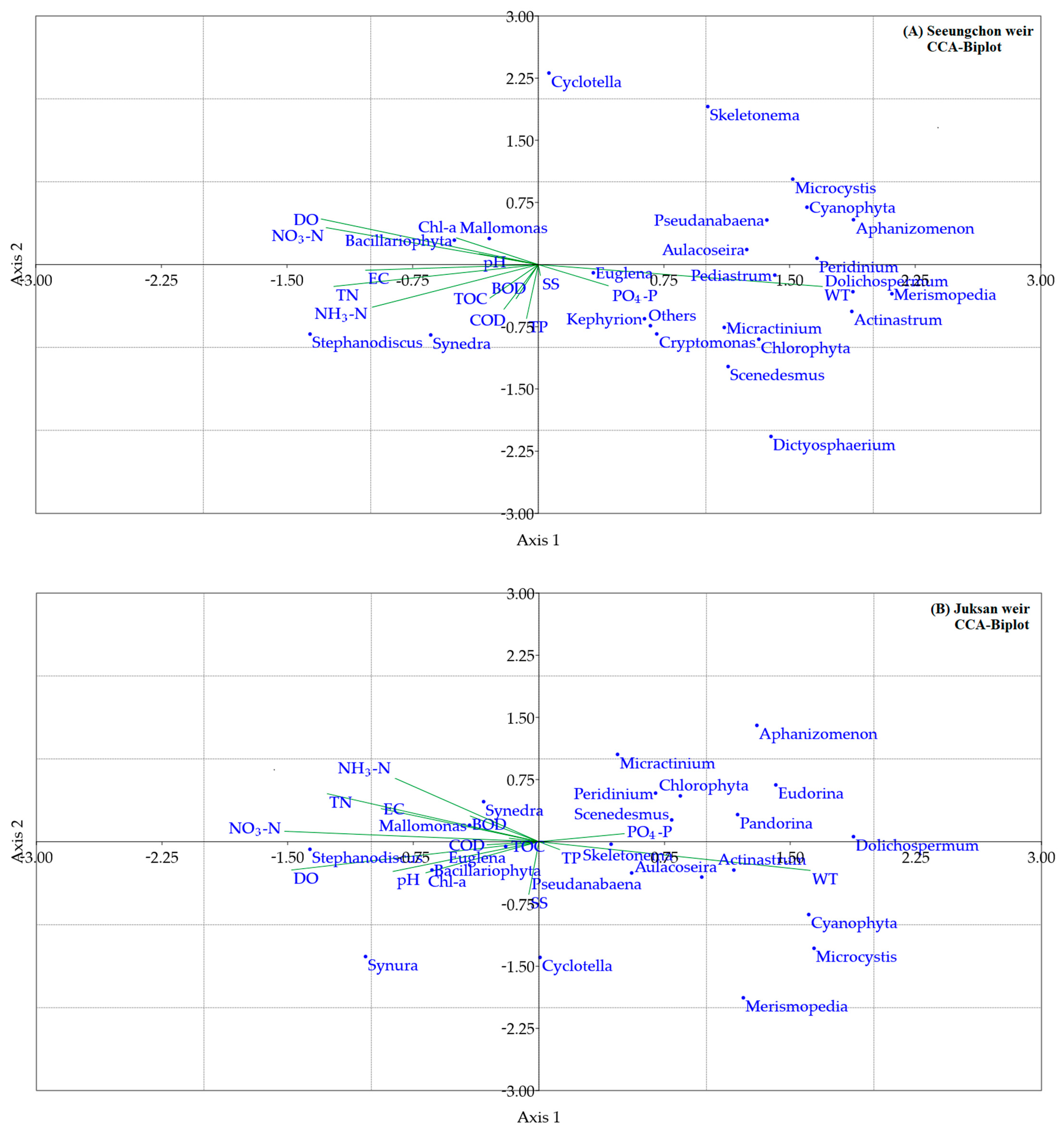
| Site | Elevation (m) | Capacity (106 m3) | Drainage Area (km2) | Average Depth (m) | Geographic Coordinates (Latitude/Longitude) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 7.5 | 9.0 | 1327.0 | 7.5 | 35°04′13.90″ N/126°46′34.09″ E |
| JS | 3.5 | 25.7 | 2359.0 | 7.1 | 34.976675° N/126.632778° E |
| Site | Season | WT (°C) | pH | DO (mg/L) | TN (mg/L) | NO3-N (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | PO4-P (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | Spring | 16.5 (10.2–26.8) | 7.4 (6.6–9.0) | 9.5 (1.6–16.3) | 6.54 (2.74–12.95) | 2.03 (0.75–3.18) | 3.43 (0.74–9.23) | 0.19 (0.09–0.58) | 0.04 (0.01–0.27) |
| Summer | 26.4 (20.6–30.9) | 7.2 (6.2–8.7) | 6.7 (1.5–12.4) | 3.66 (2.01–6.42) | 1.44 (0.76–2.41) | 1.42 (0.21–4.24) | 0.17 (0.08–0.38) | 0.06 (0.00–0.23) | |
| Autumn | 19.7 (10.7–28.3) | 7.2 (6.2–8.9) | 9.1 (4.0–16.5) | 4.41 (2.22–6.99) | 2.11 (0.76–3.35) | 1.47 (0.17–3.49) | 0.13 (0.05–0.28) | 0.04 (0.00–0.20) | |
| Winter | 7.8 (5.2–12.7) | 7.3 (6.7–8.2) | 12.4 (8.9–15.6) | 8.14 (3.63–11.81) | 2.96 (2.04–3.96) | 4.12 (0.70–7.13) | 0.16 (0.06–0.31) | 0.03 (0.00–0.16) | |
| Total | 17.7 (5.2–30.9) | 7.3 (6.2–9.0) | 9.4 (1.5–16.5) | 5.65 (2.01–12.95) | 2.12 (0.75–3.96) | 2.59 (0.17–9.23) | 0.16 (0.05–0.58) | 0.05 (0.00–0.27) | |
| JS | Spring | 15.8 (8.0–23.9) | 7.7 (6.9–9.0) | 9.1 (4.4–15.5) | 5.08 (2.77–9.22) | 2.08 (0.83–3.22) | 1.99 (0.08–5.23) | 0.13 (0.06–0.24) | 0.03 (0.00–0.13) |
| Summer | 26.3 (20.9–31.4) | 7.4 (6.6–8.9) | 7.1 (4.1–11.4) | 2.68 (1.51–4.03) | 1.36 (0.83–2.03) | 0.57 (0.04–1.73) | 0.13 (0.07–0.23) | 0.05 (0.00–0.13) | |
| Autumn | 19.5 (9.6–28.2) | 7.7 (6.5–9.2) | 9.8 (6.2–14.2) | 3.31 (1.64–5.57) | 2.02 (1.04–2.01) | 0.48 (0.02–2.01) | 0.11 (0.04–0.26) | 0.04 (0.00–0.14) | |
| Winter | 6.3 (3.3–9.9) | 8.1 (7.0–9.2) | 14.2 (9.4–18.0) | 6.41 (3.21–9.19) | 3.26 (2.14–4.75) | 2.15 (0.49–4.29) | 0.12 (0.04–0.24) | 0.02 (0.00–0.19) | |
| Total | 17.1 (3.3–31.4) | 7.7 (6.5–9.2) | 10.0 (4.1–18.0) | 4.33 (1.51–9.22) | 2.16 (0.83–4.75) | 1.28 (0.02–5.23) | 0.12 (0.04–0.26) | 0.03 (0.00–0.19) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, H.; Son, M.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Lee, W.-S. Correlations Between Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Physicochemical Parameters in the Seungchon and Juksan Weirs. Water 2024, 16, 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202976
Chung H, Son M, Kim T, Park J, Lee W-S. Correlations Between Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Physicochemical Parameters in the Seungchon and Juksan Weirs. Water. 2024; 16(20):2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202976
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Hyeonsu, Misun Son, Taesung Kim, Jonghwan Park, and Won-Seok Lee. 2024. "Correlations Between Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Physicochemical Parameters in the Seungchon and Juksan Weirs" Water 16, no. 20: 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202976
APA StyleChung, H., Son, M., Kim, T., Park, J., & Lee, W.-S. (2024). Correlations Between Spatiotemporal Variations in Phytoplankton Community Structure and Physicochemical Parameters in the Seungchon and Juksan Weirs. Water, 16(20), 2976. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202976







