Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Stream Sediments from Coastal Oecusse (Timor)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
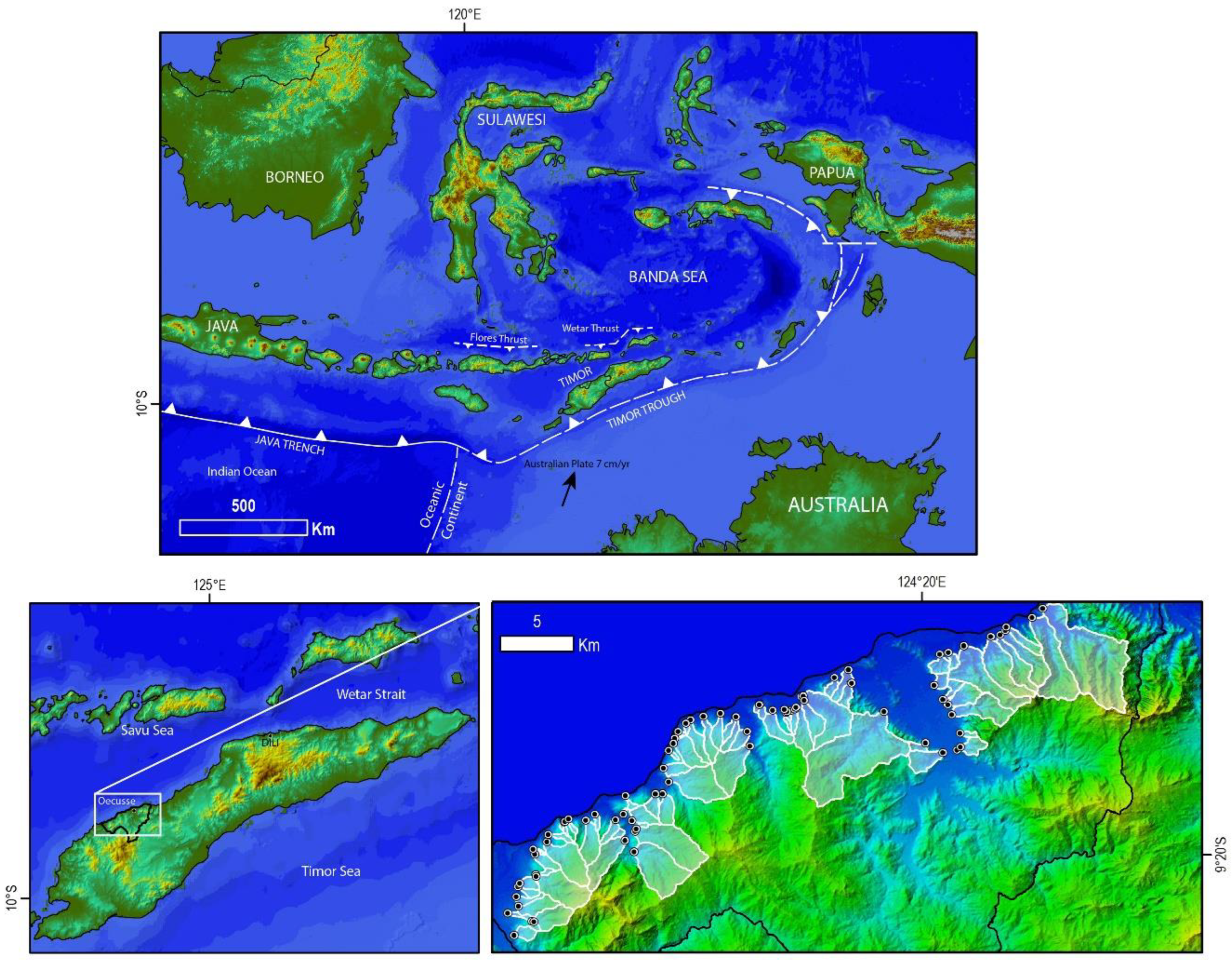
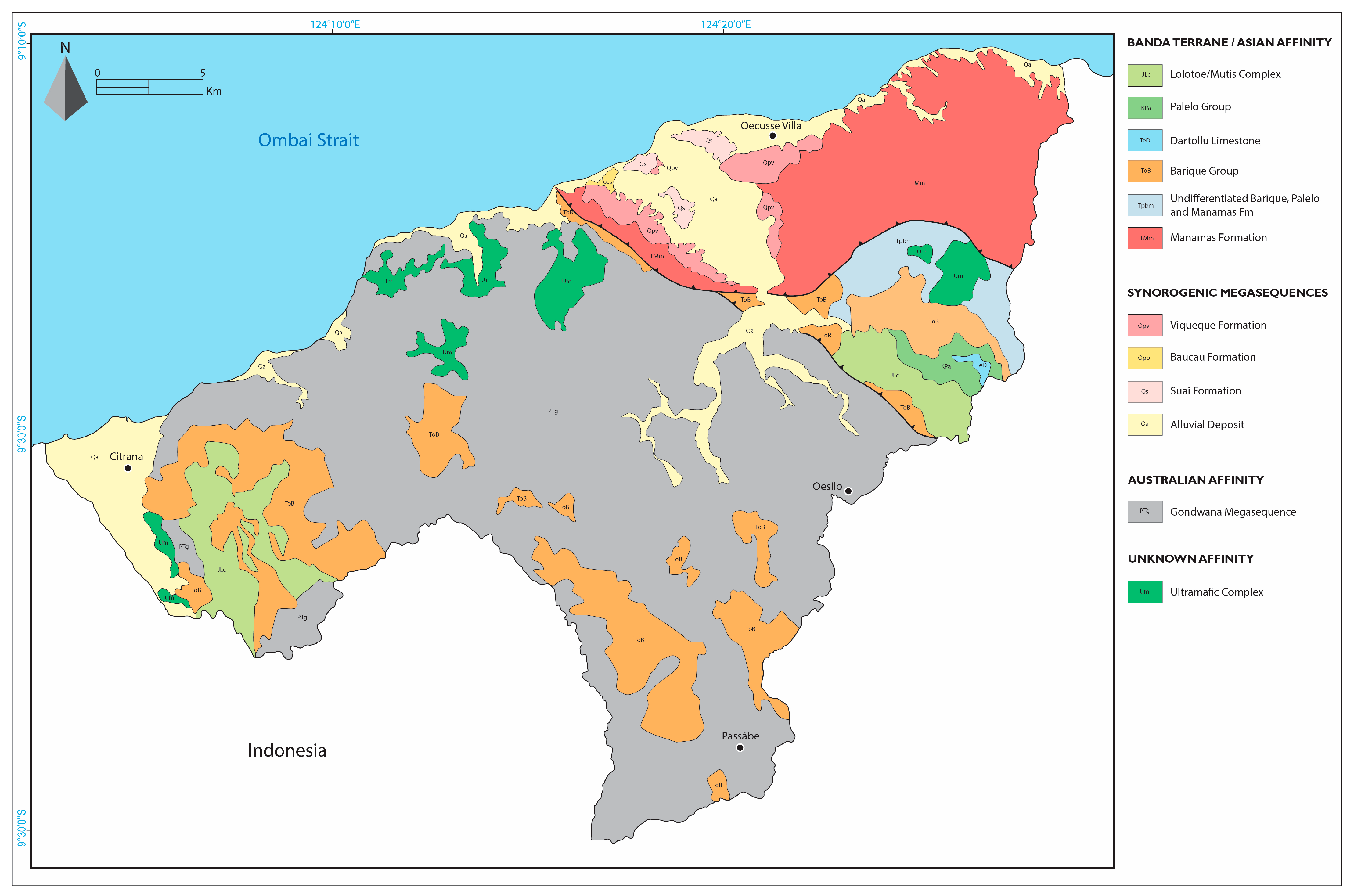
2. Natural Setting
3. Methodology
3.1. Sampling
3.2. Chemical Analysis and Data Treatment
4. Results and Discussion
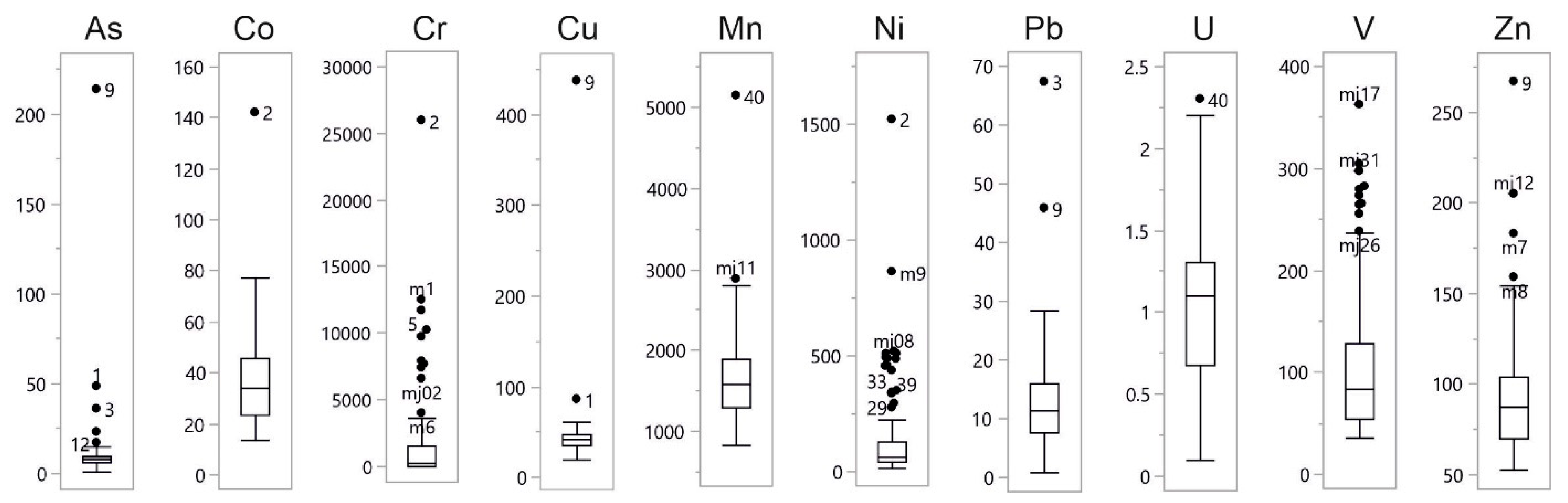
4.1. Univariate and Multivariate Statistics
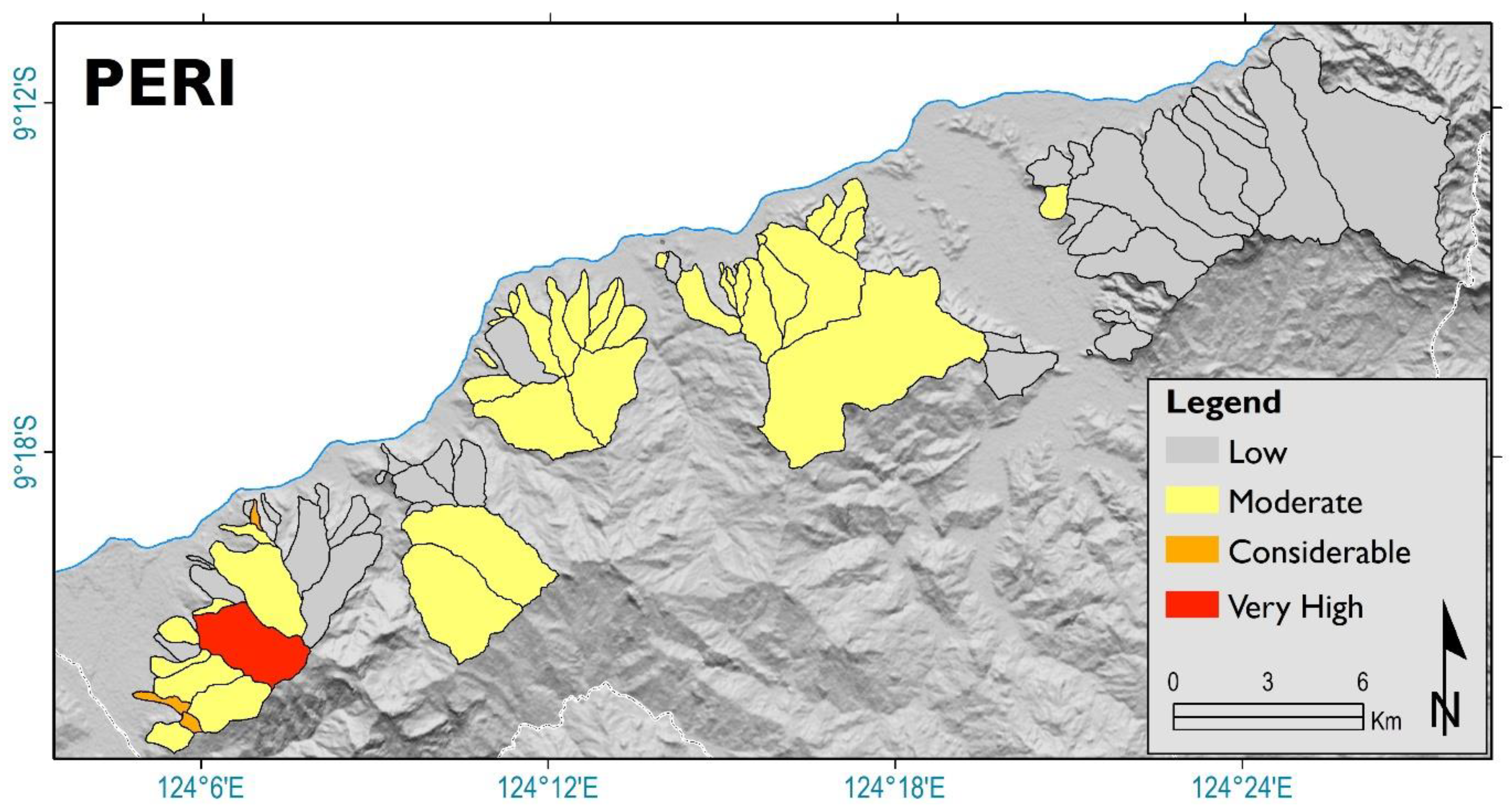
4.2. Ecologic Risks
4.3. Assessment of Health Risks Associated with Exposure PTEs
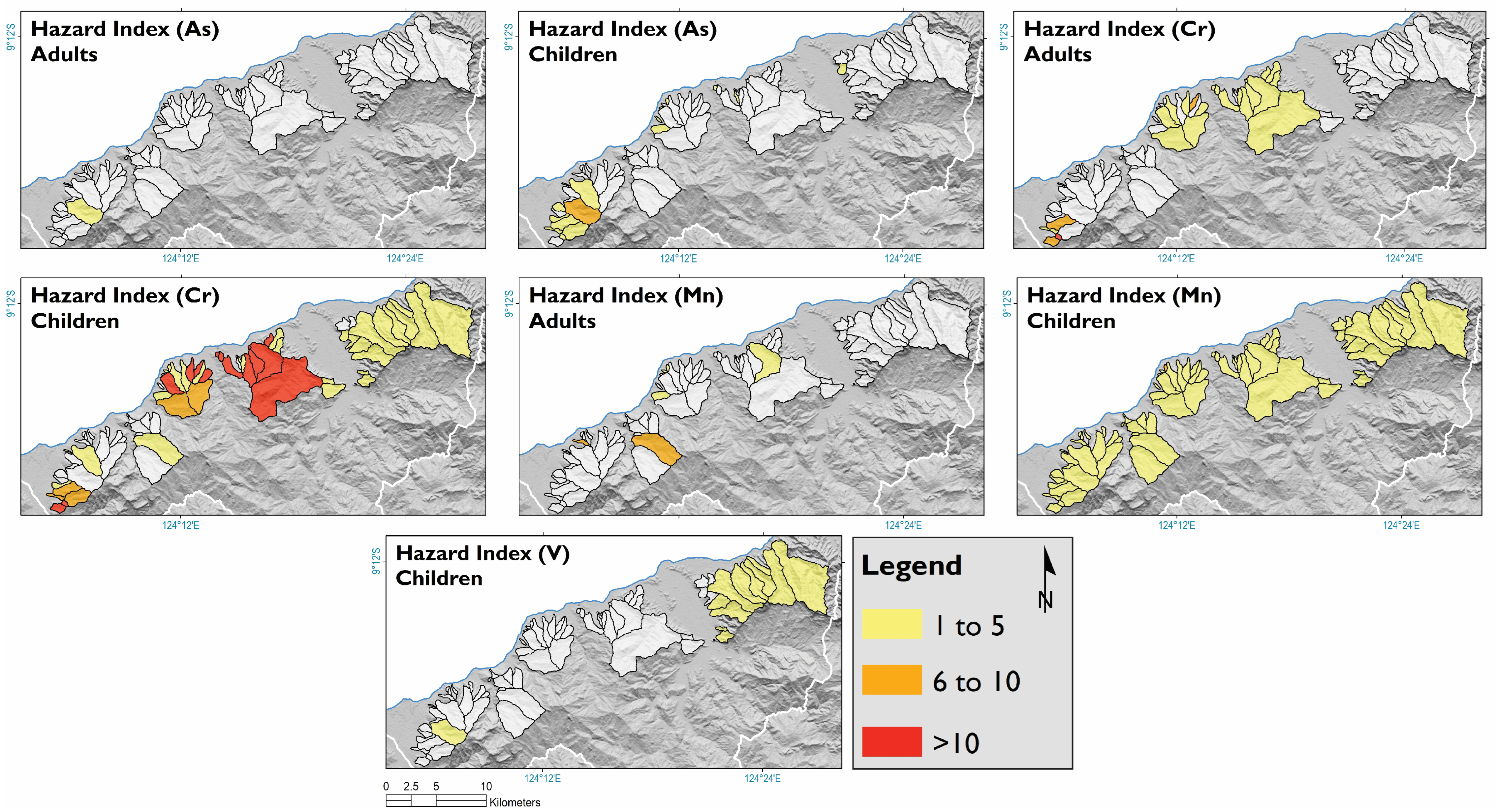
4.3.1. Non-Carcinogenic Risk
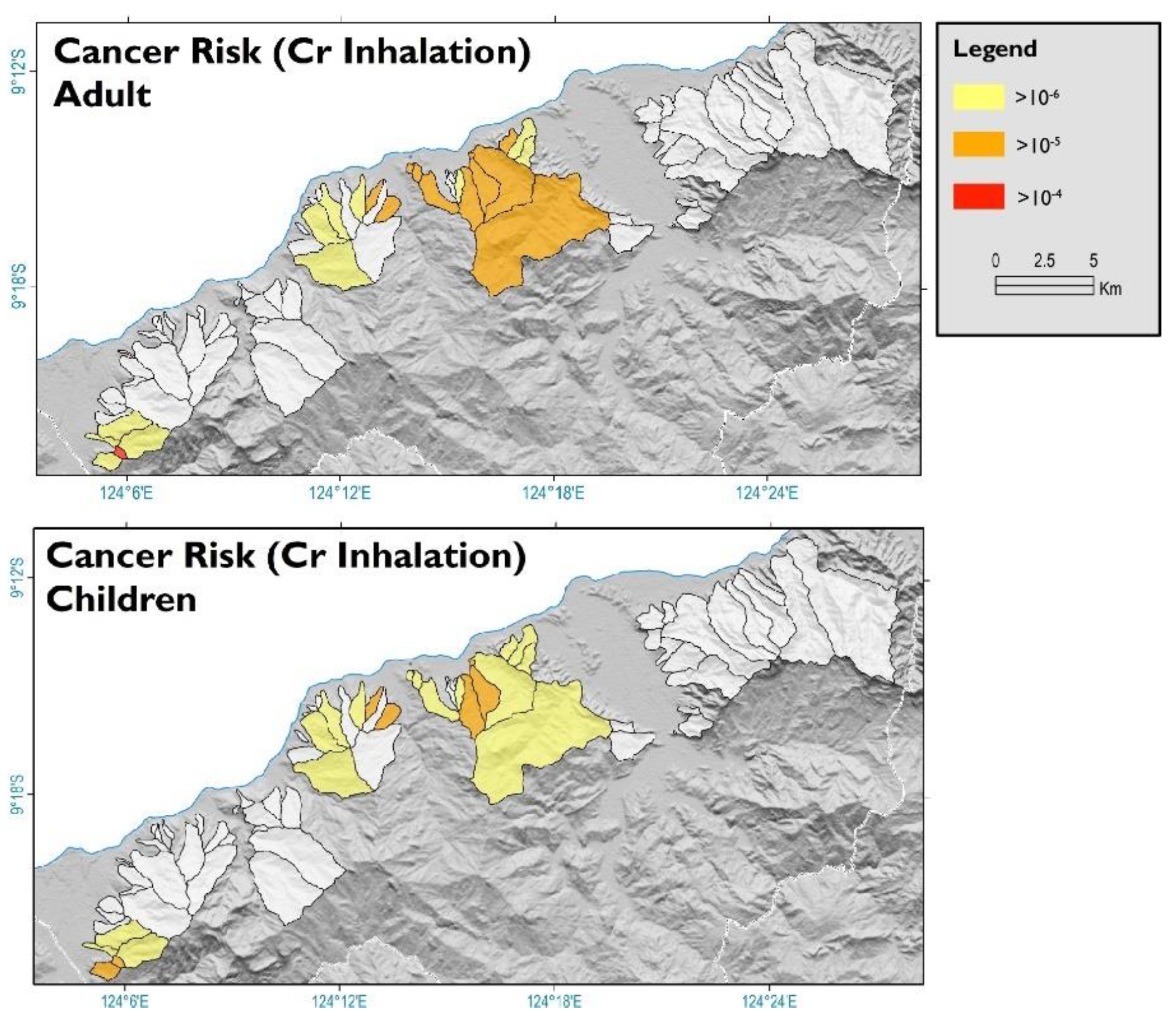
4.3.2. Carcinogenic Risks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horton, R.; Beaglehole, R.; Bonita, R.; Raeburn, J.; McKee, M.; Wall, S. From public to planetary health: A manifesto. Lancet 2014, 383, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.L.; Maslin, M.A. Defining the anthropocene. Nature 2015, 519, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347, 1259855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, W.; Grinevald, J.; Crutzen, P.; McNeill, J. The Anthropocene: Conceptual and historical perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 842–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Inácio, M.; Neves, O.; Almeida, A.A.; Pinto, E.; Oliveiros, B.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Human health risk assessment due to agricultural activities and crop consumption in the surroundings of an industrial area. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, R.; Chekushin, V.; Tenhola, M.; Bogatyrev, I.; Gregorauskiene, V.; Fedotova, E.; Gregorauskiene, V.; Kashulina, G.; Niskavaara, H.; Polischuok, A.; et al. Geochemical Atlas of Eastern Barents Region; Gulf Professional Publishing: Houston, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Vivo, B.; Lima, A.; Bove, M.A.; Albanese, S.; Cicchella, D.; Sabatini, G.; Di Lella, L.A.; Protano, G.; Riccobono, F.; Frizzo, P.; et al. Environmental geochemical maps of Italy from the FOREGS database. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2008, 8, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, L.R.; Hengl, T.; Reuter, H.I. Heavy metals in European soils: A geostatistical analysis of the FOREGS Geochemical database. Geoderma 2008, 148, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBravo, S.; García-Ordiales, E.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Amorós, J.; Pérez-De-Los-Reyes, C.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; Esbrí, J.M.; García-Noguero, E.M.; Higueras, P. Geochemical distribution of major and trace elements in agricultural soils of Castilla-La Mancha (central Spain): Finding criteria for baselines and delimiting regional anomalies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3100–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinelli, G.; Tollefsen, T.; Bossew, P.; Gruber, V.; Bogucarskis, K.; De Felice, L.; De Cort, M. Digital version of the European Atlas of natural radiation. J. Environ. Radioact. 2019, 196, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Caritat, P.; Cooper, M. A Continental-Scale Geochemical Atlas for Resource Exploration and Environmental Management: The National Geochemical Survey of Australia; The Geological Society of London: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove, M. The occurrence and distribution of strontium in US groundwater. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 126, 104867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Wang, X.; Reeder, S.; Demetriades, A. The IUGS/IAGC task group on global geochemical baselines. Earth Sci. Front. 2012, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Team, T.C.S. Reprint of “China geochemical baselines: Sampling methodology”. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 154, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzolo, D.; Cicchella, D.; Demetriades, A.; Birke, M.; Albanese, S.; Dinelli, E.; Lima, A.; Valera, P.; De Vivo, B. Arsenic: Geochemical distribution and age-related health risk in Italy. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desenfant, F.; Petrovský, E.; Rochette, P. Magnetic signature of industrial pollution of stream sediments and correlation with heavy metals: Case study from South France. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 152, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, R.G.; Reimann, C.; Smith, D.B.; Xie, X. From geochemical prospecting to international geochemical mapping: A historical overview. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2008, 8, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Smith, S.M.; Horton, J.D. History and evaluation of national-scale geochemical data sets for the United States. Geosci. Front. 2013, 4, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatina, M. Medical Geology: Effects of Geological Environments on Human Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Panaullah, G.M.; Alam, T.; Hossain, M.B.; Loeppert, R.H.; Lauren, J.G.; Meisner, C.A.; Ahmed, Z.U.; Duxbury, J.M. Arsenic toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Bangladesh. Plant Soil 2009, 317, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Shui, B. Spatial variations and potential risks of heavy metals in sediments of Yueqing Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 173, 112983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Chromium, nickel and welding. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 1990, 49, 1–648. [Google Scholar]
- Klotz, K.; Weistenhöfer, W.; Neff, F.; Hartwig, A.; van Thriel, C.; Drexler, H. The health effects of aluminum exposure. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2017, 114, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Ikram, M.; Park, J.S.; Park, T.J.; Kim, M.O. Gut microbiota, its role in induction of Alzheimer’s disease pathology, and possible therapeutic interventions: Special focus on anthocyanins. Cells 2020, 9, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfiglio, R.; Scimeca, M.; Mauriello, A. Addressing environmental pollution and cancer: The imperative of the 2030 agenda. Future Oncol. 2023, 19, 2273–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djouina, M.; Esquerre, N.; Desreumaux, P.; Vignal, C.; Body-Malapel, M. Toxicological consequences of experimental exposure to aluminum in human intestinal epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 91, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miah, M.R.; Ijomone, O.M.; Okoh, C.O.; Ijomone, O.K.; Akingbade, G.T.; Ke, T.; Krum, B.; Martins, A.d.C.; Akinyemi, A.; Aranoff, N.; et al. The effects of manganese overexposure on brain health. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 135, 104688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Hassloff, H.; Straube, B.; Nuscheler, B.; Wemken, G.; Kircher, T. Adult attachment style modulates neural responses in a mentalizing task. Neuroscience 2015, 303, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, A.B.; Cushing, C.A.; Antonini, J.M.; Finley, B.L.; Mowat, F.S. State-of-the-science review: Does manganese exposure during welding pose a neurological risk? J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2007, 10, 417–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, M.R.; Susi, P. Neurological risks associated with manganese exposure from welding operations—A literature review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2009, 212, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Li, G.J.; Guo, W.; Liang, W.; Zheng, W. Alteration of serum concentrations of manganese, iron, ferritin, and transferrin receptor following exposure to welding fumes among career welders. Neurotoxicology 2005, 26, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, M.; Santinelli, F.B.; Lisboa-Filho, P.N.; Barbieri, F.A. The blood concentration of metallic nanoparticles is related to cognitive performance in people with multiple sclerosis: An exploratory analysis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Ma, J.J.; Yu, R.L.; Hu, G.R.; Yan, Y. Bioaccessibility of microplastic-associated heavy metals using an in vitro digestion model and its implications for human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 76983–76991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzan, S.F.; Eunus, H.M.; Haque, S.E.; Sarwar, G.; Hasan, A.R.; Wu, F.; Islam, T.; Ahmed, A.; Shahriar, M.; Jasmine, F.; et al. Arsenic exposure from drinking water and endothelial dysfunction in Bangladeshi adolescents. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DesMarias, T.L.; Costa, M. Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahane, S.P.; Kumar, A. Estimation of health risks due to copper-based nanoagrochemicals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25046–25059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, X.S.; Ren, K.D.; Peng, J.; Luo, X.J. Restoration of metal homeostasis: A potential strategy against neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Alam, M.; Kumar, S.; Prasad, S. Appraisal of contamination of heavy metals and health risk in agricultural soil of Jhansi city, India. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 103740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pinto, M.C.; Candeias, C.; Dinis, P.A. Baseline maps of potentially toxic elements in the soils of Garhwal Himalayas, India: Assessment of their eco-environmental and human health risks. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3856–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.M.S.C.; Marinho-Reis, A.P.; Almeida, A.; Freitas, S.; Simões, M.R.; Diniz, M.L.; Pinto, E.; Ramos, P.; da Silva, E.F.; Moreira, P.I. Fingernail trace element content in environmentally exposed individuals and its influence on their cognitive status in ageing. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, I.A.; Abdurrachman, M.; Sakakibara, M.; Xiaoxu, K.; Meilano, I.; Basuki, N.I.; Sucipta, I.G.B.E.; Arifa, A.N. Mercury Exposure from Artisanal Small-Scale Gold Mining in Bunikasih, West Java, Indonesia. In Selected Studies in Environmental Geosciences and Hydrogeosciences; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Alodia, G.; Dyan, P.; Sobarudin, N.; Adrianto, D.; Dwinovantyo, A.; Solikin, S.; Hanafi, M.; Pamumpuni, A.; Kurniawan, I.A.; Poerbandono; et al. Discovery of a conical feature in Halmahera waters, Indonesia: Traces of a late-stage hydrothermal activity. Geosci. Lett. 2023, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.; Marinho-Reis, A.P.; Almeida, A.; Ordens, C.M.; Silva, M.M.; Freitas, S.; Simões, M.R.; Moreira, P.I.; Dinis, P.A.; Diniz, M.L.; et al. Human predisposition to cognitive impairment and its relation with environmental exposure to potentially toxic elements. Environ. Geochem. Health 2018, 40, 1767–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.A. Cadmium, chromium, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation 1967, 35, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.; Ordens, C.M.; Condesso de Melo, M.T.; Inácio, M.; Almeida, A.; Pinto, E.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. An inter-disciplinary approach to evaluate human health risks due to long-term exposure to contaminated groundwater near a chemical complex. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handoko, A.D.; Sapiie, B.; Rudyawan, A. Geochemical and geological properties of tin related to ore deposits: A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1245, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, B.; Nogueira, J.; Pinto, M.C.; Almeida, A.; Simões, M.R.; Freitas, S. Trace Elements and Cognitive Function in Adults and Older Adults: A Comprehensive Systematic Review. Expo. Health 2024, 1–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré-Huguet, N.; Martí-Cid, R.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Risk assessment of metals from consuming vegetables, fruits and rice grown on soils irrigated with waters of the Ebro River in Catalonia, Spain. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2008, 123, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Saha, N.; Ordens, C.M.; Pitta-Grós, D.; Carlos, G.; Dinis, P.; Marques, R.; Prudêncio, I.; Rocha, F.; Silva, E.A.F.d. Integrated Geochemical and Mineralogical Investigation of Soil from the Volcanic Fogo Island (Cape Verde): Implications for Ecological and Probabilistic Human Health Risks. Expo. Health 2023, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, T.O.; Ajibade, O.M.; Olajide-Kayode, J.O.; Fomba, K.W. Level, distribution, ecological, and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and stream sediments around a used-automobile spare part market in Nigeria. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 1573–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhungu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y. Estimation of the cumulative risks from dietary exposure to cadmium, arsenic, nickel, lead and chromium Guangzhou, China. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 178, 113887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, Q.; Meng, X. Combined effects of lead and manganese on locomotor activity and microbiota in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.A. Trace elements and cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1986, 59, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Filippini, T.; Ajsuvakova, O.P.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Aaseth, J.; Bjørklund, G.; Gatiatulina, E.R.; Popova, E.V.; Nemereshina, O.N.; Huang, P.-T.; et al. Cadmium and atherosclerosis: A review of toxicological mechanisms and a meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 240–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C.; Phelps, K.R. Estimation of health risks associated with dietary cadmium exposure. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, V.; Prasad, S.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.; Jeon, B.H.; Kumar, S.; Abdellattif, M.H.; Alsukaibia, A.K. Investigation of heavy metal accumulation in vegetables and health risk to humans from their consumption. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 791052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergi, C.M. Nickel’s carcinogenicity: The need of more studies to progress. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Flynn, M.R.; Lewis, M.M.; Mailman, R.B.; Huang, X. Welding-related brain and functional changes in welders with chronic and low-level exposure. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesch, B.; Weiss, T.; Kendzia, B.; Henry, J.; Lehnert, M.; Lotz, A.; Berges, M.; Hahn, J.; Mattenklott, M.; Punkeenburg, E.; et al. Levels and predictors of airborne and internal exposure to manganese and iron among welders. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, M.R.; Susi, P. Manganese, iron, and total particulate exposures to welders. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 7, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Bornhorst, J.; Aschner, M.A. Manganese metabolism in humans. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1655–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral Pinto, M.M.; Ferreira da Silva, E.A. Heavy Metals of Santiago Island (Cape Verde) alluvial deposits: Baseline value maps and human health risk assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.M.C.; Silva, M.M.; da Silva, E.A.F.; Dinis, P.A.; Rocha, F. Transfer processes of potentially toxic elements (PTE) from rocks to soils and the origin of PTE in soils: A case study on the island of Santiago (Cape Verde). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 183, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Pandey, R.; ZhiGuo, Y.; Cabral-Pinto, M. Forest soil nutrient stocks along altitudinal range of Uttarakhand Himalayas: An aid to Nature Based Climate Solutions. Catena 2021, 207, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosbois, C.; Meybeck, M.; Lestel, L.; Lefèvre, I.; Moatar, F. Severe and contrasted polymetallic contamination patterns (1900–2009) in the Loire River sediments (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 435, 290–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B. Cadmium concentration limits in agricultural soils: Weaknesses in USEPA’s risk assessment and the 503 rule. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2003, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.H.; Wang, G.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L. Physiological response of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus experimentally exposed to cadmium. Aquac. Aquar. Conserv. Legis. 2011, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Barletta, M.; Lima, A.R.; Costa, M.F. Distribution, sources and consequences of nutrients, persistent organic pollutants, metals and microplastics in South American estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 1199–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, V.A.; Pratas, J.A.; Santos, F.C.; Silva, M.M.; Favas, P.J.; Conde, L.E. Geochemical anomalies from a survey of stream sediments in the Maquelab area (Oecusse, Timor-Leste) and their bearing on the identification of mafic-ultramafic chromite rich complex. Appl. Geochem. 2021, 126, 104868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.L. Mineral–Hydrocarbon Database and Bibliography of the Geology of East Timor; United Nations Development Programme: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, R.; Ling, H.; Natonis, R.; Hobgen, S.; Kaho, N.R.; Mudita, W.; Markus, J.; Bunga, W.; Nampa, W. Artisanal and small-scale mining and rural livelihood diversification: The case of manganese extraction in West Timor, Indonesia. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Ptak, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Krasniqi, V. Ecological and health risk assessments of heavy metals contained in sediments of Polish dam reservoirs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbonegoro, T.; Damar, A.; Riani, E.; Butet, N.A.; Cordova, M.R. Accumulation of Cd and Pb in sediments and Asian swamp eels (Monopterus albus) from downstream area of Cisadane River, Indonesia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geen, A.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; He, Y.; Dhar, R.K.; Garnier, J.M.; Rose, J.; Seddique, A.; Hoque, M.A.; Ahmed, K.M. Impact of irrigating rice paddies with groundwater containing arsenic in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brammer, H.; Ravenscroft, P. Arsenic in groundwater: A threat to sustainable agriculture in South and South-east Asia. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Bi, J.; Zhao, J.; Bu, R. Spatial distribution and ecotoxicological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the southern Bohai Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasfar, R.H.; Isaifan, R.J. Aluminum environmental pollution: The silent killer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44587–44597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabbir, U.; Tyagi, A.; Elahi, F.; Aloo, S.O.; Oh, D.H. The potential role of polyphenols in oxidative stress and inflammation induced by gut microbiota in alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, D.; Marquès, M.; Torrente, M. Metals linked with the most prevalent primary neurodegenerative dementias in the elderly: A narrative review. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellström, H.O.; Michaëlsson, K.; Mallmin, H.; Mjöberg, B. The aluminium content of bone, and mortality risk. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, R.; Sisto, R.; Casciardi, S.; Palumbo, V.; Scioli, M.P.; Palumbo, A.; Trivigno, D.; Giacobbi, E.; Servadei, F.; Melino, G.; et al. The impact of toxic metal bioaccumulation on colorectal cancer: Unravelling the unexplored connection. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 906, 167667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, A.T.G.; de Castro Silva, A.; Tinkov, A.A.; Khan, H.; Santamaría, A.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Skalny, A.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschener, A.; et al. The impact of manganese on neurotransmitter systems. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 61, 126554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrtička, P.; Bondolfi, G.; Sander, D.; Vuilleumier, P. The neural substrates of social emotion perception and regulation are modulated by adult attachment style. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 7, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, N.; Wu, G.; Luo, L.; Wang, D.; Cheng, Q. Mineral prospectivity mapping based on wavelet neural network and Monte Carlo simulations in the Nanling W-Sn metallogenic province. Ore Geol. Rev. 2022, 143, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Khalid, J.; Qaiser, Z.; Sarfraz, W.; Ejaz, U.; Naeem, N.; Masood, A.; Tufail, A.; Arshad, K.; Zaka, S.; et al. Nickel contamination, toxicity, tolerance, and remediation approaches in terrestrial biota. In Bio-Organic Amendments for Heavy Metal Remediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 479–497. [Google Scholar]
- Hossini, H.; Shafie, B.; Niri, A.D.; Nazari, M.; Esfahlan, A.J.; Ahmadpour, M.; Nazmara, Z.; Ahmadimanesh, M.; Makhdoumi, P.; Mirzaei, N.; et al. A comprehensive review on human health effects of chromium: Insights on induced toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 70686–70705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audley-Charles, M.G. Ocean trench blocked and obliterated by Banda forearc collision with Australian proximal continental slope. Tectonophysics 2004, 389, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, A.J.; Audley-Charles, M.G.; Carter, D.J. Thrust tectonics in Timor. J. Geol. Soc. Aust. 1977, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, T.R.; Barber, A.J.; Barkham, S.T. The structural evolution of the Timor collision complex, eastern Indonesia. J. Struct. Geol. 1991, 13, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, J. Victors, Villains, and Victims: Capitalizing on Memory in Timor-Leste. Ethnopolitics 2012, 12, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Vietz, G.; Walsh, C.J. Protection of stream ecosystems from urban stormwater runoff: The multiple benefits of an ecohydrological approach. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 38, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Traver, R.G.; Hunt, W.F.; Lee, R.; Brown, R.; Olszewski, J. Hydrologic performance of bioretention storm-water control measures. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Q.Y.; Cui, Y.; Liu, X. Instances of soil and crop heavy metal contamination in China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2001, 10, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Legislation: Ministry of the Environment. Soil, Ground Water and Sediment Standards for Use Under Part XV.1 of the Environmental Protection Act; Canadian Legislation/Ministry of the Environment: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and the Environment (VROM). Circular on Target Values and Intervention Values for Soil Remediation. The Netherlands Government Gazette, No. 39, Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment, Directorate General for Environmental Protection, Department of Soil Protection. Available online: http://www.esdat.net/Environmental%20Standards/Dutch/annexS_I2000Dutch%20Environmental%20Standards.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Environmental Affairs Republic of South Africa, DEA. Framework for the Management of Contaminated Land of South Africa; Environmental Affairs Republic of South Africa, DEA: Pretoria, South Africa, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Portuguese Agency for Environment (APA). Amadora, Lisbon, January of 2019 (Revision 3—September 2022); Portuguese Agency for Environment (APA): Amadora, Portugal, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentol. Approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Ye, S.; Yuan, H.; Krauss, K.W. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in coastal surface sediments in the Hebei Province offshore area, Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Ahmed, K.; Al-Mamun, H. Distribution of trace elements in different soils and risk assessment: A case study for the urbanized area in Bangladesh. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 158, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moni, F.N.; Miazi, M.S.A.; Kabir, M.H.; Shammi, R.S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, M.S.; Sarke, M.; Khan, M.; Ahammed, S.; Siddique, A.; et al. Enrichment, sources, and distributions of toxic elements in the farming land’s topsoil near a heavily industrialized area of central Bangladesh, and associated risks assessment. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diniz, L.; Carlos, G.; Miranda, C.; Dinis, P.; Marques, R.; Rocha, F.T.; da Silva, E.F.; Almeida, A.; Pinto, M.C. Soil Geochemical Mapping of the Sal Island (Cape Verde): Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment. Land 2024, 13, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Li, L.; Min, X.; Luo, Y. Pollution, ecological-health risks, and sources of heavy metals in soil of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Suryadevara, N.; Hill, T.M.; Bezbradica, J.S.; Van Kaer, L.; Joyce, S. Natural killer T cells: An ecological evolutionary developmental biology perspective. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležalová Weissmannová, H.; Mihočová, S.; Chovanec, P.; Pavlovský, J. Potential ecological risk and human health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in industrial affected soils by coal mining and metallurgy in Ostrava, Czech Republic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III—Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; [EPA 540-R-02-002]; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency); Science Policy Council. Guidance on Cumulative Risk Assessment. Part 1; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Guidelines for Exposure Assessment, Risk Assessment Forum; [EPA/600/Z-92/001]; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). Toxicological Review of Inorganic Arsenic; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rim, K.T. Evaluations of carcinogens from comparison of cancer slope factors: Meta-analysis and systemic literature reviews. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 635–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| mg/kg | As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Hg | Mn | Ni | Pb | U | V | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 0.25 | 0.05 | 14 | 28 | 19 | 0.005 | 823 | 11.2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 36 | 52.2 |
| Median | 7.7 | 0.05 | 33.9 | 270.5 | 41.45 | 0.04 | 1580 | 64.3 | 11.35 | 1.1 | 84 | 87.1 |
| Mean | 10.79 | 0.085 | 36.7 | 1776.5 | 46.03 | 0.04 | 1660.8 | 154.7 | 12.23 | 1.01 | 111.8 | 94.1 |
| maximum | 214 | 0.4 | 142 | 25940 | 437 | 0.08 | 5140 | 1520.0 | 67.3 | 2.3 | 362 | 267 |
| DP | 23.74 | 0.071 | 18.4 | 3880.0 | 44.7 | 0.014 | 582.4 | 225.5 | 9.3 | 0.55 | 77.9 | 34.0 |
| Median | Canadian Guidelines | Dutch Guidelines | South Africa Guidelines | Portugal Guidelines | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 8 | 6 | 29 | 5.8 7.5 | 18 |
| Cd | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 7.5 | 1.2 |
| Co | 33 | 50 | 9 | 18 | 21 |
| Cr | 324 | 26 | 100 | 46 | 69 |
| Cu | 42 | 16 | 36 | 16 | 92 |
| Mn | 1630 | - | - | 740 | - |
| Ni | 63 | 16 | 36 | 9.1 | 37 |
| Pb | 12 | 31 | 85 | 20 | 120 |
| U | 1.1 | 86 | 80 | 1.9 | 2.5 - |
| V | 84 | 86 | - | 155 | 21 |
| Zn | 90 | 120 | 140 | 240 | 290 |
| Parameter | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Pn: potential ecological risk factor of individual PTE. PERI < 95: low potential ecological risk; 95 ≤ PERI < 190: moderate ecological risk; 190 ≤ PERI < 380: considerable ecological risk and PERI ≥ 3.5. | |
| Tn (toxic response factor), which expresses the toxic response of individual metals. Tn for As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Hg, Mn, Ni, V, Pb, and Zn are 30, 30, 2, 2, 5, 40, 10, 5, 1, 5, 1, respectively [101,105,106]. Pn classified as: Pn < 40: low potential ecological risk; 40 ≤ Pn < 80: reasonable ecological risk; 80 < Pn < 160: considerable ecological risk; 160 ≤ Pn < 320: high ecological risk and Pn ≥ 320: very high ecological risk | |
| CFi = Csample/Median | C: element (i) concentration |
| Parameter | Unit | Adult Value | Children Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IR | mg/day | 100 | 200 |
| EF | Days/Year | 312 | 312 |
| ED | Years | 35 | 6 |
| BW | Kg | 70 | 15 |
| ATnc | Days | 375 × 35 | 365 × 6 |
| ATc | Days | 365 × 70 | 365 × 70 |
| CF | mg/day | 10−6 | 10−6 |
| SA | cm2 | 6032 | 2373 |
| AF | mg/cm2 | 0.07 | 0.2 |
| ABS | Unitless | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| InhR | m3/h | 1.56 | 1.2 |
| ET | h/day | 8 | 4 |
| PEF | m3/day | 1.36 × 109 | 1.36 × 109 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vicente, V.A.S.; Cabral Pinto, M.; Dinis, P.; Pratas, J.A.M.S. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Stream Sediments from Coastal Oecusse (Timor). Water 2024, 16, 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213020
Vicente VAS, Cabral Pinto M, Dinis P, Pratas JAMS. Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Stream Sediments from Coastal Oecusse (Timor). Water. 2024; 16(21):3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213020
Chicago/Turabian StyleVicente, Victor A. S., Marina Cabral Pinto, Pedro Dinis, and João A. M. S. Pratas. 2024. "Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Stream Sediments from Coastal Oecusse (Timor)" Water 16, no. 21: 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213020
APA StyleVicente, V. A. S., Cabral Pinto, M., Dinis, P., & Pratas, J. A. M. S. (2024). Ecological and Human Health Risk Assessment Based on Stream Sediments from Coastal Oecusse (Timor). Water, 16(21), 3020. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213020








