Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
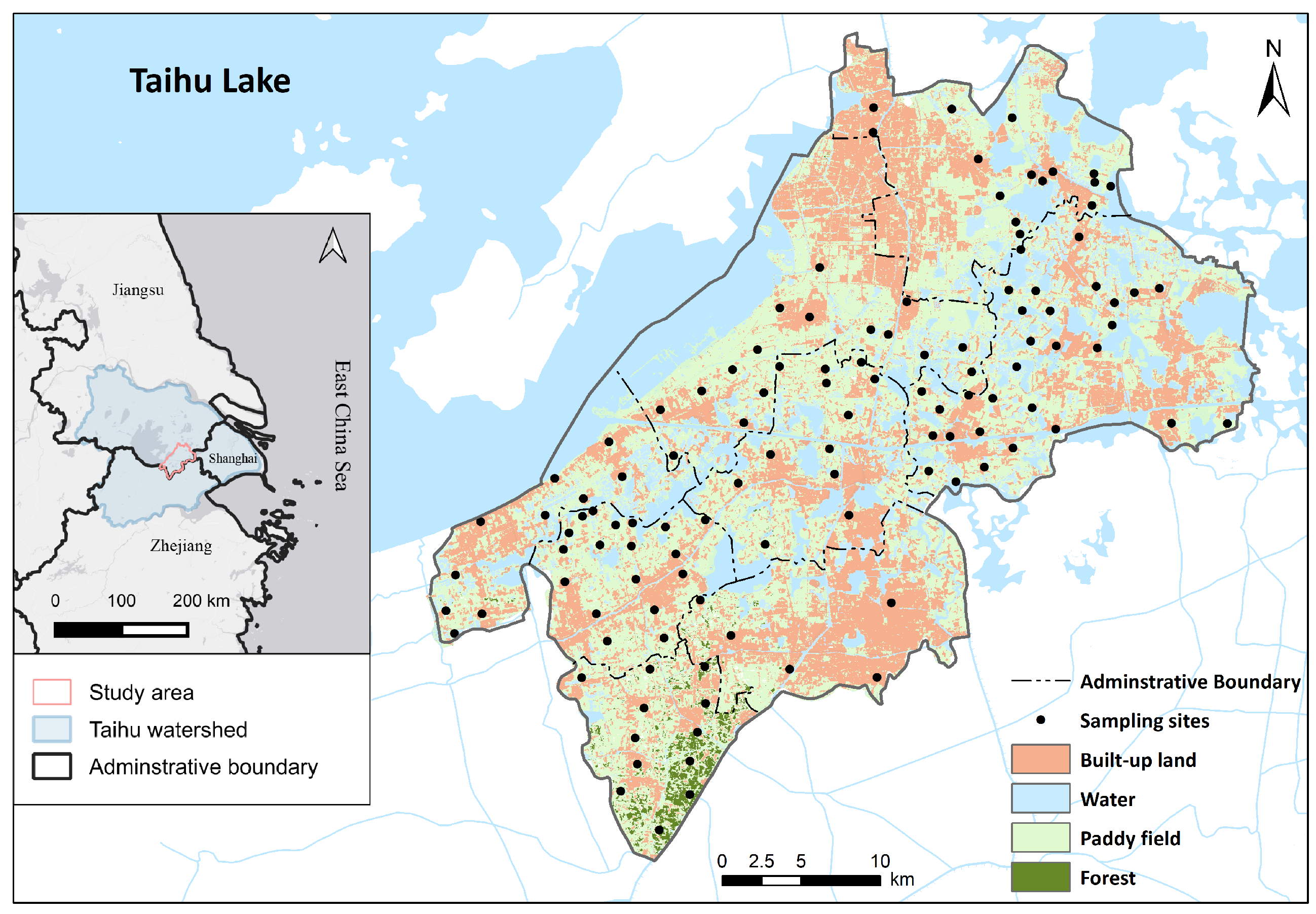
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling Collection and Analysis
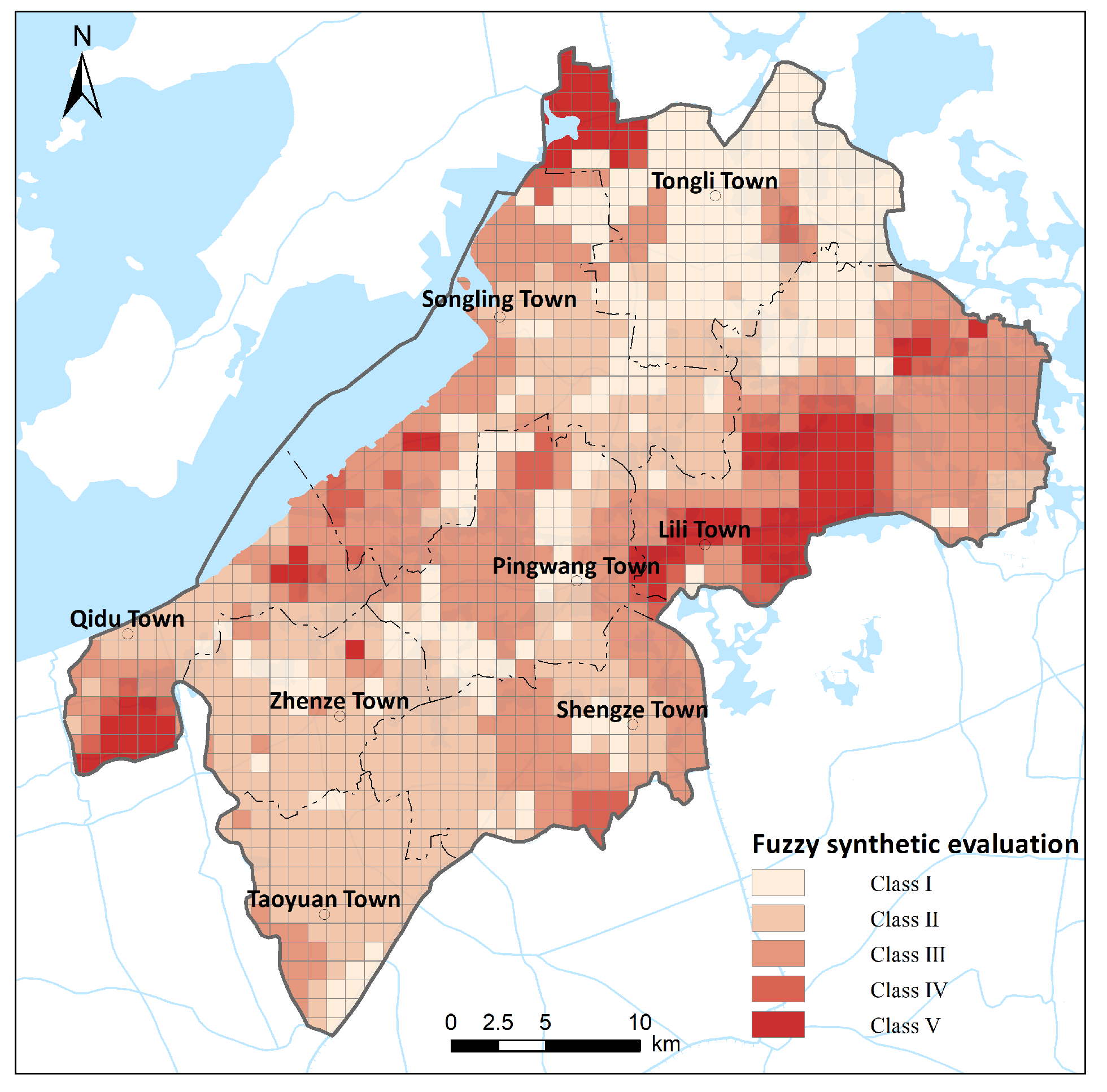
2.3. Fuzzy Synthetic Evaluation
2.4. Principal Component Analysis
2.5. APCS-MLR Model
3. Results
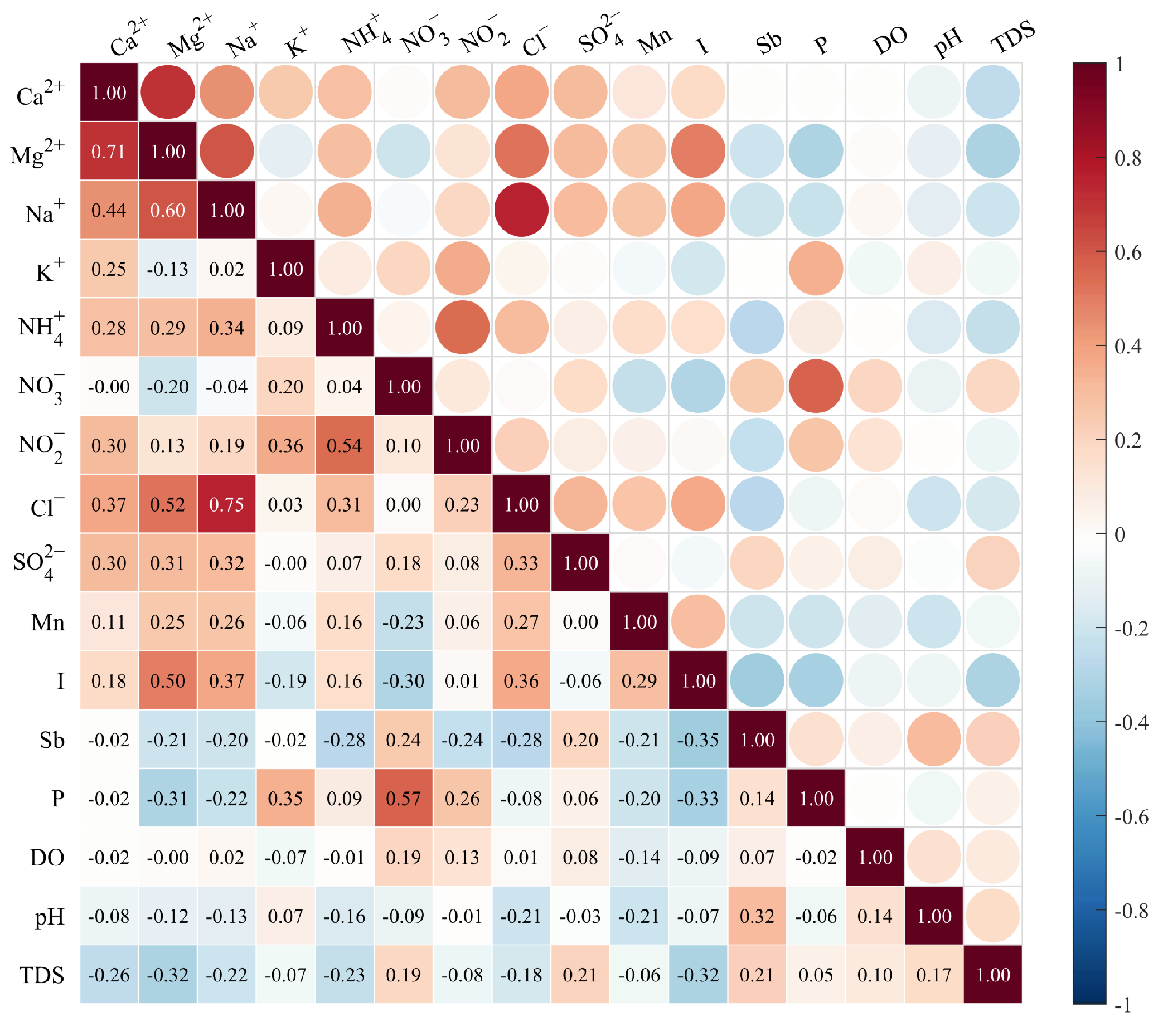
3.1. Hydrochemical Characteristics
3.2. Source Identification
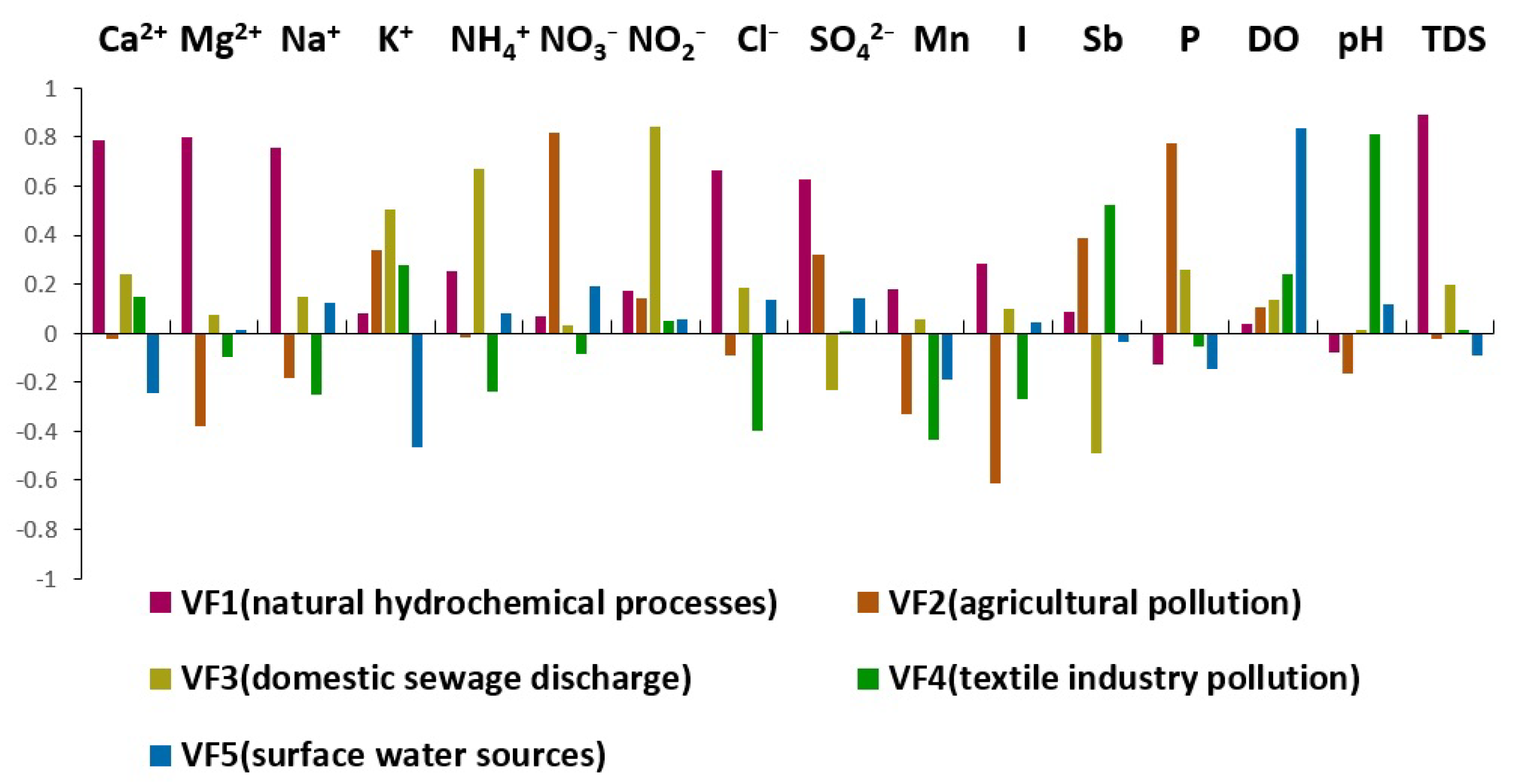
3.2.1. PCA
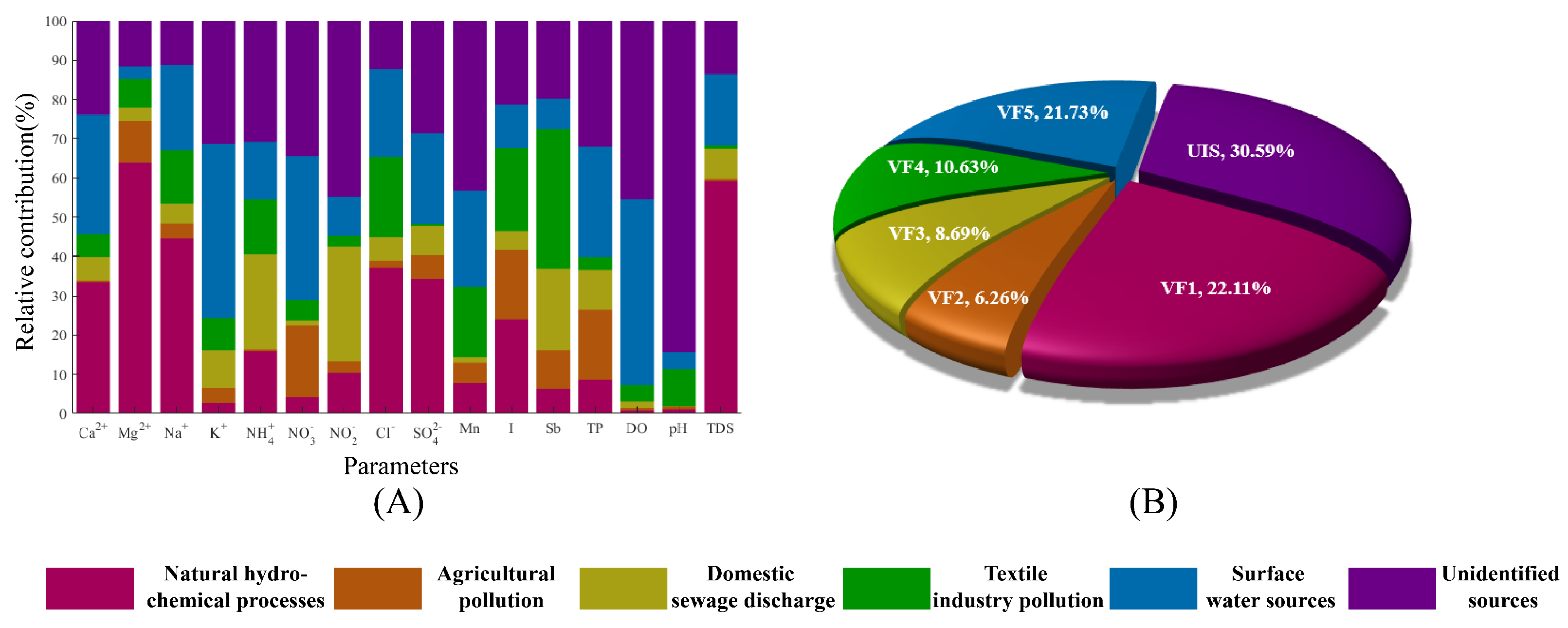
3.2.2. APCS-MLR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Huan, H.; Li, M.; Xi, B.; Lv, N.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Method for screening prevention and control measures and technologies based on groundwater pollution intensity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegahita, N.K.; Ma, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, T.; Luo, Q.; Qian, J. Spatial Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Health Risk of Nitrogen Pollution for Shallow Groundwater Aquifer around Fuyang City, China. Water 2020, 12, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, B.X.; Davis, H.; Cao, J. Simulating long term nitrate-N contamination processes in the Woodville Karst Plain using CFPv2 with UMT3D. J. Hydrol. 2015, 524, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X. Critical review of measures and decision support tools for groundwater nitrate management: A surface-to-groundwater profile perspective. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, F. Impact of anthropogenic and natural processes on the evolution of groundwater chemistry in a rapidly urbanized coastal area, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, T.K.; Opoku, F.; Acquaah, S.O.; Akoto, O. Groundwater quality assessment using statistical approach and water quality index in Ejisu-Juaben Municipality, Ghana. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouderbala, A.; Gharbi, B.Y. Hydrogeochemical characterization and groundwater quality assessment in the intensive agricultural zone of the Upper Cheliff plain, Algeria. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugga, P.; Pervez, S.; Tripathi, M.; Siddiqui, M.N. Spatiotemporal variability and source apportionment of the ionic components of groundwater of a mineral-rich tribal belt in Bastar, India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, E.; Wang, C.; Han, S.; Zheng, Y. Arsenic, fluoride and iodine in groundwater of China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, P.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Elumalai, V. Groundwater Arsenic and Fluoride and Associated Arsenicosis and Fluorosis in China: Occurrence, Distribution and Management. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorski, J.; Berg, M. Global threat of arsenic in groundwater. Science 2020, 368, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushotham, D.; Prakash, M.R.; Rao, A.N. Groundwater depletion and quality deterioration due to environmental impacts in Maheshwaram watershed of R.R. district, AP (India). Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurunc, A.; Ersahin, S.; Sonmez, N.K.; Kaman, H.; Uz, I.; Uz, B.Y.; Aslan, G.E. Seasonal changes of spatial variation of some groundwater quality variables in a large irrigated coastal Mediterranean region of Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 554–555, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCance, W.; Jones, O.A.; Edwards, M.; Surapaneni, A.; Chadalavada, S.; Currell, M. Contaminants of Emerging Concern as novel groundwater tracers for delineating wastewater impacts in urban and peri-urban areas. Water Res. 2018, 146, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, P.S.; Deb, D.L.; Tyagi, S.K. Assessment of groundwater contamination from fertilizers in the Delhi area based on 18O, NO3/- and K+ composition. J. Contam. Hydrol. 1997, 27, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Ge, Y.; Chang, S.X.; Luo, W.; Chang, J. Nitrate in groundwater of China: Sources and driving forces. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Du, Y.; Xu, Y.; Leng, Z.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y. Sources and enrichment of phosphorus in groundwater of the Central Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagure, G.R.; Mirgane, S.R. Heavy metal concentrations in groundwaters and soils of Thane Region of Maharashtra, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutiani, R.; Kulkarni, D.B.; Khanna, D.R.; Gautam, A. Water Quality, Pollution Source Apportionment and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Groundwater of an Industrial Area in North India. Expo. Health 2016, 8, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.K.; Kumar, M. Sulphate contamination in groundwater and its remediation: An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Currell, M.J.; Cao, G. Deep challenges for China’s war on water pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Hernández, J.J.; Xu, T. Contaminant Source Identification in Aquifers: A Critical View. Math. Geosci. 2021, 54, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate and occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.A.; Yaftian, M.R.; Parizanganeh, A. Multivariate statistical assessment of heavy metal pollution sources of groundwater around a lead and zinc plant. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, I.; Schmidt, M.; Pellegatti, E.; Paramatti, E.; Richnow, H.H.; Gargini, A. A stable isotope approach for source apportionment of chlorinated ethene plumes at a complex multi-contamination events urban site. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2013, 153, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gómez-Hernández, J.J.; Li, L. Inverse methods in hydrogeology: Evolution and recent trends. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 63, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, F.; Gao, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, K.; Leng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Yang, F.; et al. A comparison of various approaches used in source apportionments for precipitation nitrogen in a mountain region of southwest China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhang, W.; Gómez-Hernández, J.J.; Xie, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lu, C. Non-point contaminant source identification in an aquifer using the ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, T.; Gómez-hernández, J.J.; Zanini, A.; Zhou, Q. Reconstructing the release history of a contaminant source with different precision via the ensemble smoother with multiple data assimilation. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 252, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zong, L.; Gómez-Hernández, J.J.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Jia, Z.; Mei, S. Contaminant source and aquifer characterization: An application of ES-MDA demonstrating the assimilation of geophysical data. Adv. Water Resour. 2023, 181, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, V.; Lefebvre, R.; Therrien, R.; Savard, M.M. Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J. Hydrol. 2008, 353, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Tian, R.; Liu, R. Solute Geochemistry and Multivariate Analysis of Water Quality in the Guohua Phosphorite Mine, Guizhou Province, China. Expo. Health 2019, 11, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, P.; Somashekar, R.K. Principal component analysis and hydrochemical facies characterization to evaluate groundwater quality in Varahi river basin, Karnataka state, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulgundi, M.S.; Shetty, A. Groundwater quality assessment of urban Bengaluru using multivariate statistical techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Qian, H.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, X. Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: A case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 3973–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wang, D.; Ren, X.; Wei, M. Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2020, 26, 1603–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ielpo, P.; Cassano, D.; Lopez, A.; Pappagallo, G.; Uricchio, V.F.; De Napoli, P.A. Source apportionment of groundwater pollutants in Apulian agricultural sites using multivariate statistical analyses: Case study of Foggia province. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Jing, J.; Li, L. A regional scale investigation on factors controlling the groundwater chemistry of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized area: A case study of the Pearl River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Spengler, J.D. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; An, J.; Cheng, M.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Sullivan, A.; Xia, L. One year online measurements of water-soluble ions at the industrially polluted town of Nanjing, China: Sources, seasonal and diurnal variations. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Bhuiyan, S.S.; Ahmed, Z.; Saha, N.; Begum, B.A. Characterization and source apportionment of elemental species in PM2.5 with especial emphasis on seasonal variation in the capital city “Dhaka”, Bangladesh. Urban Clim. 2021, 36, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Im, J.K. Water Quality Assessment and Potential Source Contribution Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques in Jinwi River Watershed, South Korea. Water 2021, 13, 2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.c.; Choi, H.; Lee, M.G.; Kim, S.-H.; Im, J.-K. Identification and Apportionment of Potential Pollution Sources Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and APCS-MLR Model to Assess Surface Water Quality in Imjin River Watershed, South Korea. Water 2022, 14, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proshad, R.; Kormoker, T.; Al, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Khadka, S.; Idris, A.M. Receptor model-based source apportionment and ecological risk of metals in sediments of an urban river in Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. The source apportionment of N and P pollution in the surface waters of lowland urban area based on EEM-PARAFAC and PCA-APCS-MLR. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, H. Application of the dual-isotope approach and Bayesian isotope mixing model to identify nitrate in groundwater of a multiple land-use area in Chengdu Plain, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Mei, S.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Y.; et al. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Using APCS-MLR Model: A Case Study in the Pilot Promoter Region of Yangtze River Delta Integration Demonstration Zone, China. Water 2023, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhu, L. Groundwater quality assessment and pollution source apportionment in an intensely exploited region of northern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16639–16650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zuo, R.; Wang, J.-s.; Yang, J.; Teng, Y.-g.; Shi, R.-t.; Zhai, Y.-z. Apportionment and evolution of pollution sources in a typical riverside groundwater resource area using PCA-APCS-MLR model. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2018, 218, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zheng, T.; Yuan, R.; Zheng, X. APCS-MLR model: A convenient and fast method for quantitative identification of nitrate pollution sources in groundwater. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Meng, X.; Wen, X.; Wu, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, M. Contamination characteristics, source identification, and source-specific health risks of heavy metal(loid)s in groundwater of an arid oasis region in Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haji Gholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566-567, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Source apportionment of water pollutants in the upstream of Yangtze River using APCS-MLR. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 3795–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.; Li, H.; Fu, K.; Xu, Y. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Teng, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, B.; Yue, W. Groundwater pollution and risk assessment based on source apportionment in a typical cold agricultural region in Northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Cao, Y.; Shi, S.; Sun, G.; Du, L.; Zhu, J. N pollution sources and denitrification in waterbodies in Taihu Lake region. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2001, 44, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zheng, B. Effect of sewage and industrial effluents on bacterial and archaeal communities of creek sediments in the Taihu Basin. Water 2017, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Jiang, B.; Feng, Z.; Yao, B.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J. Comprehensive evaluation of shallow groundwater quality in Central and Southern Jiangsu Province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ni, H.; Zhou, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, J.; Ren, H.; Fan, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Key technology of ecological restoration demonstration in the Yangtze River Economic Zone and its application. Geol. China 2021, 48, 1305–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Mujumdar, P.P.; Sasikumar, K. A fuzzy risk approach for seasonal water quality management of a river system. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 3653–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, D.; Tang, C.; Yu, Y.; Ma, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of surface water and groundwater in Songnen plain, Northeast China. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2737–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahiya, S.; Singh, B.; Gaur, S.; Garg, V.K.; Kushwaha, H.S. Analysis of groundwater quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.B.; Chen, H.W.; Ning, S.K. Identification of river water quality using the fuzzy synthetic evaluation approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 63, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 14848-2017; Standard for Groundwater Quality. National Resources and Territory Spatial Planning Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 93). General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena, B.; Pardo, R.; Vega, M.; Barrado, E.; Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez, L. Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Res. 2000, 34, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, Z.; Kong, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Huang, K.; Wang, Z. Tracing the potential pollution sources of the coastal water in Hong Kong with statistical models combining APCS-MLR. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 245, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Nsabimana, A. Groundwater Pollution Source Identification and Apportionment Using PMF and PCA-APCS-MLR Receptor Models in Tongchuan City, China. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 81, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Guo, S.; Fu, K.; Liao, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, S. Groundwater pollution source apportionment using principal component analysis in a multiple land-use area in southwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9000–9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Cheng, S. Water quality assessment and pollution source apportionment using multi-statistic and APCS-MLR modeling techniques in Min River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 41987–42000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Abbreviation | Unit | Analytical Equipment | Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | mg/L | ICAP 6300Duo | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | |
| Magnesium | mg/L | ICAP 6300Duo | / | |
| Sodium | mg/L | ICAP 6300Duo | / | |
| Potassium | mg/L | ICAP 6300Duo | / | |
| Ammonical nitrogen | mg/L | AutoAnalyzer3 | Seal Analytical, USA | |
| Nitrate nitrogen | mg/L | Dionex-2500 | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | |
| Nitrite nitrogen | mg/L | TU-1950 | PERSEE, China | |
| Chloride | mg/L | Dionex-2500 | / | |
| Sulfate | mg/L | Dionex-2500 | / | |
| Manganese | g/L | ICAP Q | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA | |
| Iodine | I | g/L | ICAP Q | / |
| Antimony | g/L | ICAP Q | / | |
| Total phosphorus | g/L | ICAP 6300Duo | / | |
| Dissolved oxygen | DO | mg/L | SX-630 ORP Testor | Apera Instruments, German |
| Pondus Hydrogenii | pH | pH unit | SX-620 pH Testor | Apera Instruments, German |
| Total dissolved solids | TDS | mg/L | Hanna DiST | Hanna Instruments, USA |
| Parameter | Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation | Coefficients of Variation (%) | National Standard, Class III | Exceeding Standard Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.60 | 158.50 | 70.08 | 27.56 | 39 | / | / | |
| 0.83 | 75.20 | 17.75 | 12.41 | 70 | / | / | |
| 2.57 | 139.40 | 49.55 | 24.31 | 49 | 200 | 0 | |
| 0.42 | 90.30 | 17.71 | 18.05 | 102 | / | / | |
| / | 6.62 | 0.50 | 1.14 | 228 | 0.50 | 18 | |
| / | 23.26 | 4.89 | 5.44 | 111 | 20 | 3 | |
| / | 2.98 | 0.25 | 0.52 | 207 | 1 | 8 | |
| 2.14 | 138.60 | 46.29 | 29.44 | 64 | 250 | 0 | |
| 3.00 | 171.10 | 46.28 | 32.31 | 70 | 250 | 0 | |
| 0.10 | 2050.00 | 117.21 | 368.12 | 314 | 100 | 14 | |
| I | 1.81 | 605.00 | 82.42 | 110.55 | 134 | 80 | 28 |
| / | 5.89 | 2.31 | 1.40 | 61 | 5 | 4 | |
| P | 6.37 | 3740.00 | 530.38 | 625.94 | 118 | / | / |
| 0.2 | 21.0 | 3.1 | 2.3 | 75 | / | / | |
| 6.57 | 8.67 | 7.19 | 0.33 | 5 | 6.5–8.5 | 1 | |
| 40 | 801 | 406 | 153 | 38 | 1000 | 0 |
| Parameters | VF1 | VF2 | VF3 | VF4 | VF5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.79 | −0.03 | 0.24 | 0.15 | −0.24 | |
| 0.80 | −0.38 | 0.07 | −0.10 | 0.01 | |
| 0.76 | −0.19 | 0.15 | −0.25 | 0.12 | |
| 0.08 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.28 | −0.47 | |
| 0.25 | −0.02 | 0.67 | −0.24 | 0.08 | |
| 0.07 | 0.82 | 0.03 | −0.09 | 0.19 | |
| 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.84 | 0.05 | 0.06 | |
| 0.67 | −0.09 | 0.19 | −0.40 | 0.14 | |
| 0.63 | 0.32 | −0.23 | 0.01 | 0.14 | |
| 0.18 | −0.33 | 0.06 | −0.44 | −0.19 | |
| I | 0.29 | −0.61 | 0.10 | −0.27 | 0.05 |
| 0.09 | 0.39 | −0.49 | 0.53 | −0.04 | |
| P | −0.13 | 0.78 | 0.26 | −0.05 | −0.14 |
| 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.84 | |
| −0.08 | −0.17 | 0.01 | 0.81 | 0.12 | |
| 0.89 | −0.02 | 0.20 | 0.01 | −0.09 | |
| Eigenvalues | 4.40 | 2.43 | 1.69 | 1.21 | 1.12 |
| % of Variance | 27.47 | 15.23 | 10.57 | 7.59 | 7.02 |
| Cumulative % | 27.47 | 42.70 | 53.27 | 60.86 | 67.88 |
| Parameters | Measured Mean | Predicted Mean | Source Contribution | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VF1 | VF2 | VF3 | VF4 | VF5 | UIS | ||||
| 70.08 | 70.07 | 0.76 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.30 | 0.24 | |
| 17.75 | 17.75 | 0.79 | 0.64 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.12 | |
| 49.55 | 49.55 | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.11 | |
| 17.71 | 17.71 | 0.67 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.44 | 0.31 | |
| 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.15 | 0.31 | |
| 4.89 | 4.89 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.35 | |
| 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.76 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.03 | 0.10 | 0.45 | |
| 46.29 | 46.29 | 0.66 | 0.37 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.12 | |
| 46.28 | 46.28 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.23 | 0.29 | |
| 117.21 | 117.21 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.43 | |
| I | 82.42 | 82.42 | 0.54 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.21 |
| 2.31 | 2.25 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.08 | 0.20 | |
| P | 530.38 | 530.37 | 0.71 | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 0.28 | 0.32 |
| 3.1 | 3.10 | 0.79 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.47 | 0.45 | |
| 7.19 | 7.19 | 0.71 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.84 | |
| 406 | 406.00 | 0.84 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.18 | 0.14 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, L.; Qi, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Lv, J.; Zong, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, H.; Jia, Z.; Mei, S.; et al. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City. Water 2024, 16, 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213139
Hou L, Qi Q, Zhou Q, Lv J, Zong L, Chen Z, Jiang Y, Yang H, Jia Z, Mei S, et al. Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City. Water. 2024; 16(21):3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213139
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Lili, Qiuju Qi, Quanping Zhou, Jinsong Lv, Leli Zong, Zi Chen, Yuehua Jiang, Hai Yang, Zhengyang Jia, Shijia Mei, and et al. 2024. "Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City" Water 16, no. 21: 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213139
APA StyleHou, L., Qi, Q., Zhou, Q., Lv, J., Zong, L., Chen, Z., Jiang, Y., Yang, H., Jia, Z., Mei, S., Jin, Y., Zhang, H., Li, J., & Xu, F. (2024). Shallow Groundwater Quality Assessment and Pollution Source Apportionment: Case Study in Wujiang District, Suzhou City. Water, 16(21), 3139. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16213139







