Water Quality Analysis of a 300 Mvar Large-Scale Dual Internal Water Cooling Synchronous Condenser External Cooling System and Exploration of Optimal Water Treatment Agent Dosage at Different Temperatures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Quality Analysis
2.2. Water Treatment Agent
2.3. Static Scale Inhibition Tests
2.4. Rotating Coupon Corrosion Tests
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Analysis
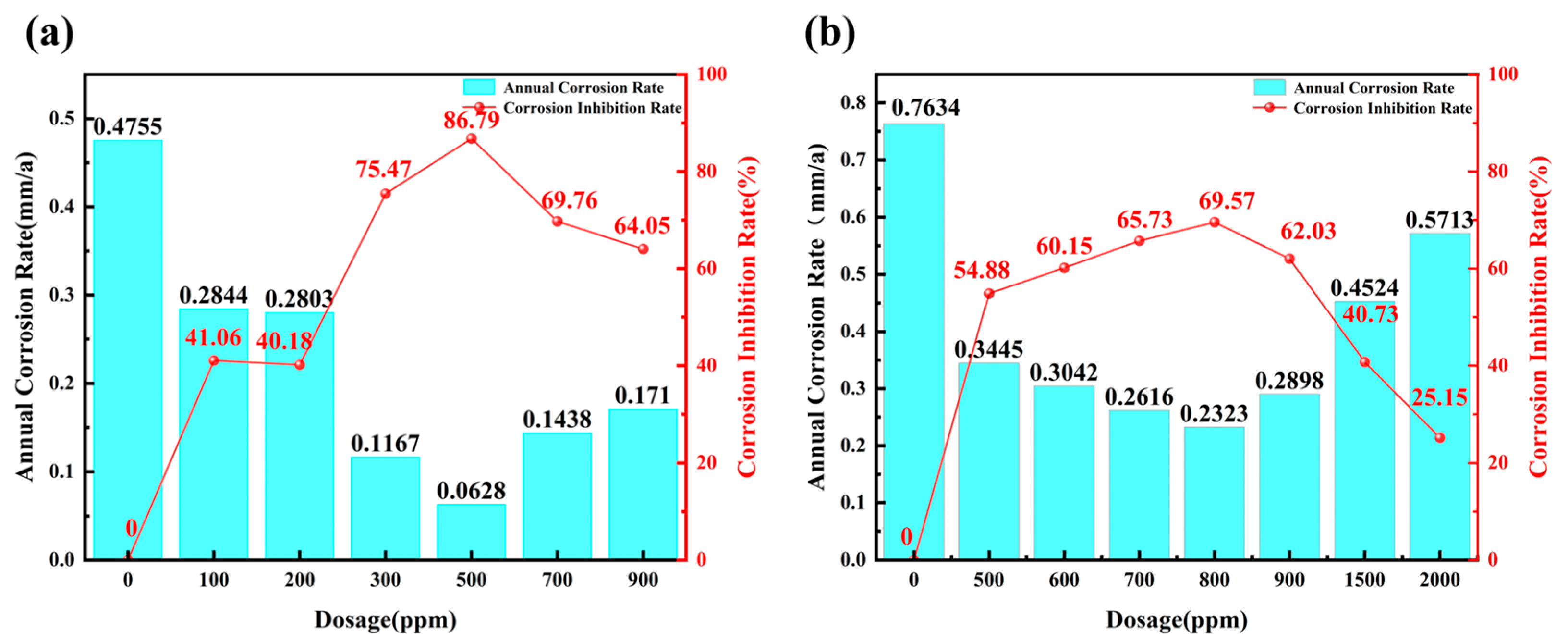
3.2. Performance Evaluation and Optimal Dosage of Corrosion and Scale Inhibitors
- (1)
- When the dosage exceeds the optimal dosage, the corrosion inhibition rate gradually decreases, showing a clear “threshold effect”. This proves that the dosage should not be arbitrarily increased, as excessive dosing not only increases the dosing cost and environmental pressure but also leads to a decrease in the corrosion inhibition effect, posing a potential risk to the stable operation of the external cooling water system.
- (2)
- As the test temperature increases from 25 to 40 °C, the annual corrosion rate increases significantly, and the commercial corrosion and scale inhibitor AS-582 not only has a change in the optimal dosage but also a significant decrease in the corrosion inhibition effect, requiring the use of additional corrosion inhibitors.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chubraeva, L.; Timofeev, S. Modern Reactive Power Generators. In Proceedings of the Actual Problem of Electromechanics and Electrotechnology, Yekaterinburg, Russia, 13–16 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Igbinovia, F.O.; Fandi, G.; Muller, Z.; Tlusty, J. Reputation of the Synchronous Condenser Technology in Modern Power Grid. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Power System Technology (POWERCON), Guangzhou, China, 6–8 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Yan, Y.; Yan, G.; Xu, B.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, T. Research on the Function and Key Technology of the Large-capacity Dual Internal Water Cooled Synchronous Condenser in UHVDC System. High Volt. Eng. 2019, 45, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Sun, F. Faults Analysis of Double Water Inner Cooled Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management (ICPHM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, H. Design and application of water-saving devices for external cooling water in DC converter stations. China Water Wastewater 2010, 26, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X. Retrofit and application of dosing systems in circulating water pump rooms for waste heat and energy recovery power generation units in steel enterprises. Water Wastewater Eng. 2018, 54, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Niu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zheng, J.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lang, B.; Luo, H.; Ma, S. Analysis of scaling causes and anti-scaling strategies for the external cooling system of a large synchronous condenser in Northwest China. Therm. Power Gener. 2024, 53, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Scale Inhibitors for Industrial Circulating Water Systems: A Review. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2022, 43, 517–525. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, K.; Jadidian, R.; Haghtalab, S. Evaluation of inhibitors and biocides on the corrosion, scaling and biofouling control of carbon steel and copper-nickel alloys in a power plant cooling water system. Desalination 2016, 393, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Zheng, X. Inter-component synergetic corrosion inhibition mechanism of Passiflora edulia Sims shell extract for mild steel in pickling solution: Experimental, DFT and reactive dynamics investigations. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, H. Effects of chemical inhibitors on the scaling behaviors of calcite and the associated surface interaction mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 618, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Tan, X.; Qi, S. High-Temperature-Resistant Scale Inhibitor Polyaspartic Acid-Prolineamide for Inhibiting CaCO3 Scale in Geothermal Water and Speculation of Scale Inhibition Mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Eljack, F.; Kazi, M.K.; Almomani, F.; Ahmed, E.; El Jack, Z. Treatment Technologies for Cooling Water Blowdown: A Critical Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, G.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R. An investigation on scaling failure of heat exchanger in cooling water system of natural gas purification plant. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 17, e2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, P.; Swaminathan, G.; Anoop, B.; Prasad, G.; Nagarajan, J. Assessing the factors affecting the water chemistry parameters in the auxiliary water system of a nuclear power plant. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, H.; Pei, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D. Cooling recirculating water system and water quality control technology in polysilicon production. China Nonferrous Met. 2021, 50, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xu, Y. Nanosilica modified with polyaspartic acid as an industrial circulating water scale inhibitor. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Qin, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L.; Yang, N. Probing pipe flow impact corrosion monitoring effectiveness under corrosion monitor coupons conditions. Fuel 2023, 353, 129288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Ma, D.; Rong, H.; Zhao, P.; Teng, P. Effect of six kinds of scale inhibitors on calcium carbonate precipitation in high salinity wastewater at high temperatures. J. Environ. Sci. 2015, 29, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Ge, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, S.; Sheng, K.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Y. Influence of pH on corrosion behavior of carbon steel in simulated cooling water containing scale and corrosion inhibitors. Mater. Corros. Werkst. Korros. 2020, 71, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, M.; Tian, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Xia, L.; He, S.; Zhou, Y.; et al. The role of corrosion inhibition in the mitigation of CaCO3 scaling on steel surface. Corros. Sci. 2018, 140, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajala, P.; Bomberg, M.; Huttunen-Saarivirta, E.; Priha, O.; Tausa, M.; Carpén, L. Influence of Chlorination and Choice of Materials on Fouling in Cooling Water System under Brackish Seawater Conditions. Materials 2016, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, P. Preparation of fluorescent polyaspartic acid and evaluation of its scale inhibition for CaCO3 and CaSO4. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 28, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Theregowda, R.B.; Small, M. Statistical Model for Scaling and Corrosion Potentials of Cooling-System Source Waters. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, S.; Trukhina, M.; Ryabova, A.; Oshchepkov, M.; Kamagurov, S.; Popov, K. Fluorescent-Tagged Antiscalants—The New Materials for Scale Inhibition Mechanism Studies, Antiscalant Traceability and Antiscaling Efficacy Optimization during CaCO3 and CaSO4·2H2O Scale Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketrane, R.; Saidani, B.; Gil, O.; Leleyter, L.; Baraud, F. Efficiency of five scale inhibitors on calcium carbonate precipitation from hard water: Effect of temperature and concentration. Desalination 2009, 249, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
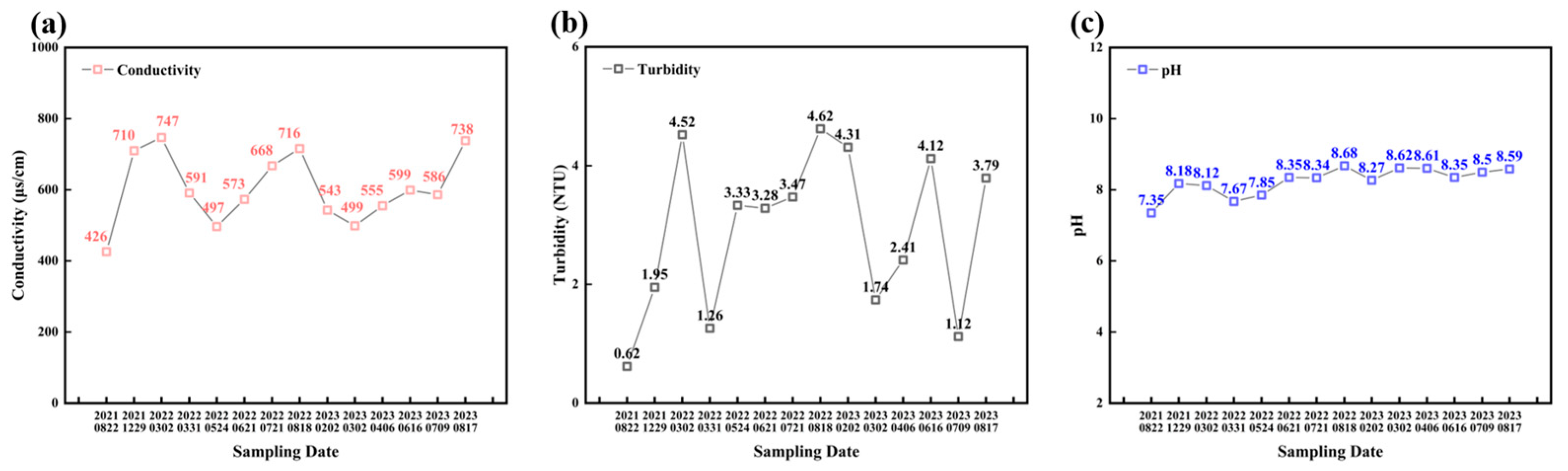
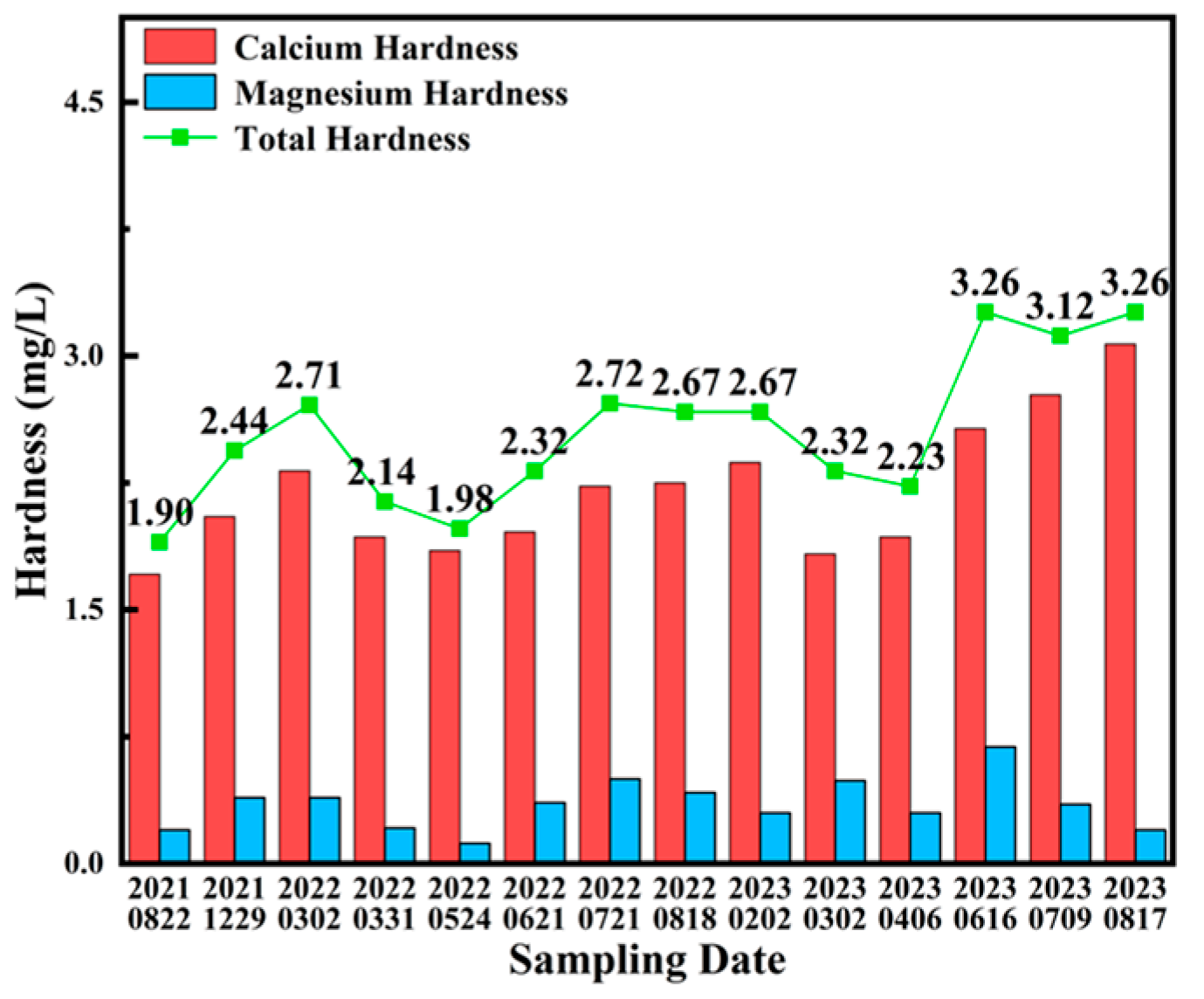
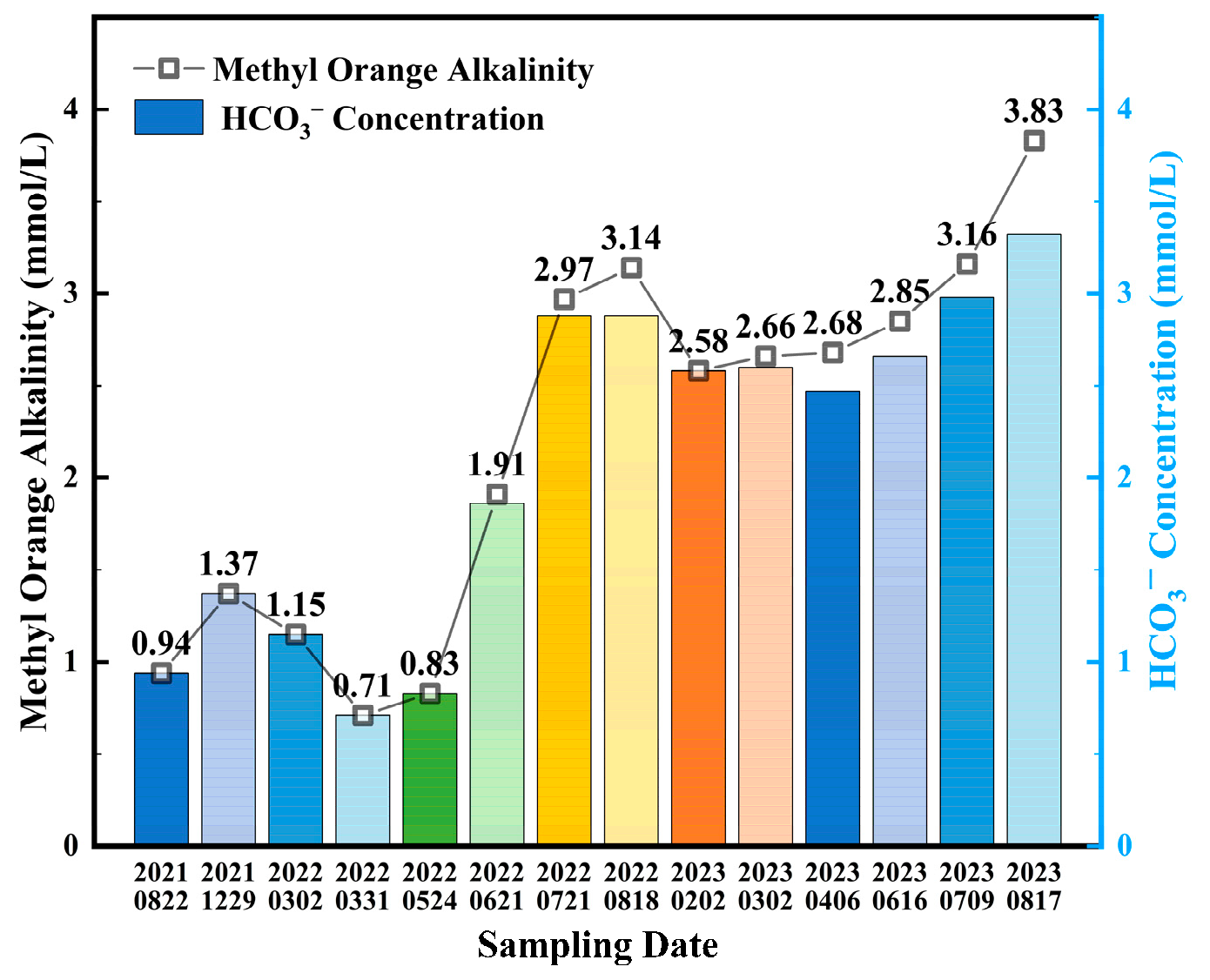
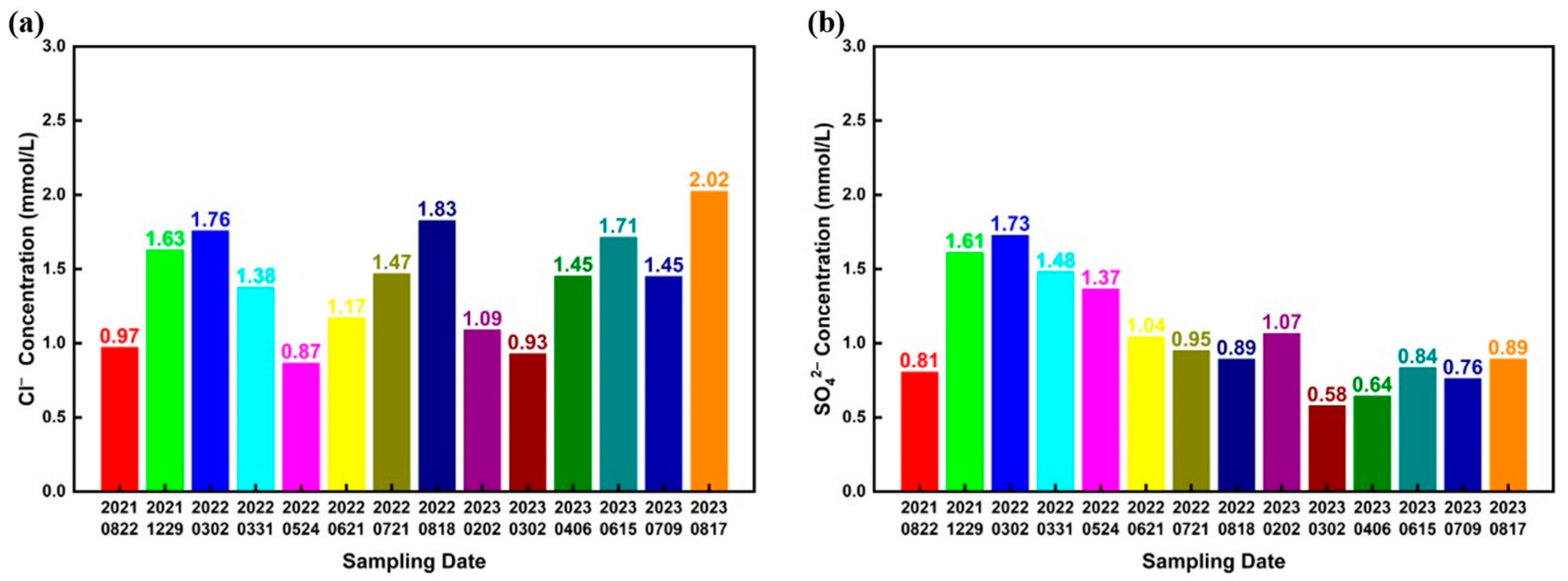

| Parameter | pH | Conductivity (μS/cm) | Alkalinity (mg/L) | Calcium Hardness (mg/L) | Total Hardness (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External cooling water | 8.10 | 600 | 45 | 225 | 262.5 |
| Temperature (°C) | LSI | LSI Analysis | RSI | RSI Analysis | PSI | PSI Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | −0.18 | Prone to corrosion | 8.46 | Severe corrosion | 9.60 | Prone to corrosion |
| 40 | 0.09 | Prone to scaling | 7.92 | Severe corrosion | 9.06 | Prone to corrosion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, P.; Gao, Y.; Ji, Q.; et al. Water Quality Analysis of a 300 Mvar Large-Scale Dual Internal Water Cooling Synchronous Condenser External Cooling System and Exploration of Optimal Water Treatment Agent Dosage at Different Temperatures. Water 2024, 16, 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223158
Gu X, Xu Y, Wu Y, Yang L, Zhang J, Chen X, Zhou Z, Fan P, Gao Y, Ji Q, et al. Water Quality Analysis of a 300 Mvar Large-Scale Dual Internal Water Cooling Synchronous Condenser External Cooling System and Exploration of Optimal Water Treatment Agent Dosage at Different Temperatures. Water. 2024; 16(22):3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223158
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Xiantao, Yunqing Xu, Yuquan Wu, Lin Yang, Junjie Zhang, Xiaochun Chen, Zhongkang Zhou, Peipei Fan, Yuxiang Gao, Qiaozhen Ji, and et al. 2024. "Water Quality Analysis of a 300 Mvar Large-Scale Dual Internal Water Cooling Synchronous Condenser External Cooling System and Exploration of Optimal Water Treatment Agent Dosage at Different Temperatures" Water 16, no. 22: 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223158
APA StyleGu, X., Xu, Y., Wu, Y., Yang, L., Zhang, J., Chen, X., Zhou, Z., Fan, P., Gao, Y., Ji, Q., Wu, Y., Dong, H., Ma, X., Liu, Z., & Guo, X. (2024). Water Quality Analysis of a 300 Mvar Large-Scale Dual Internal Water Cooling Synchronous Condenser External Cooling System and Exploration of Optimal Water Treatment Agent Dosage at Different Temperatures. Water, 16(22), 3158. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223158





