Determination and Optimization of Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition of Paper Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
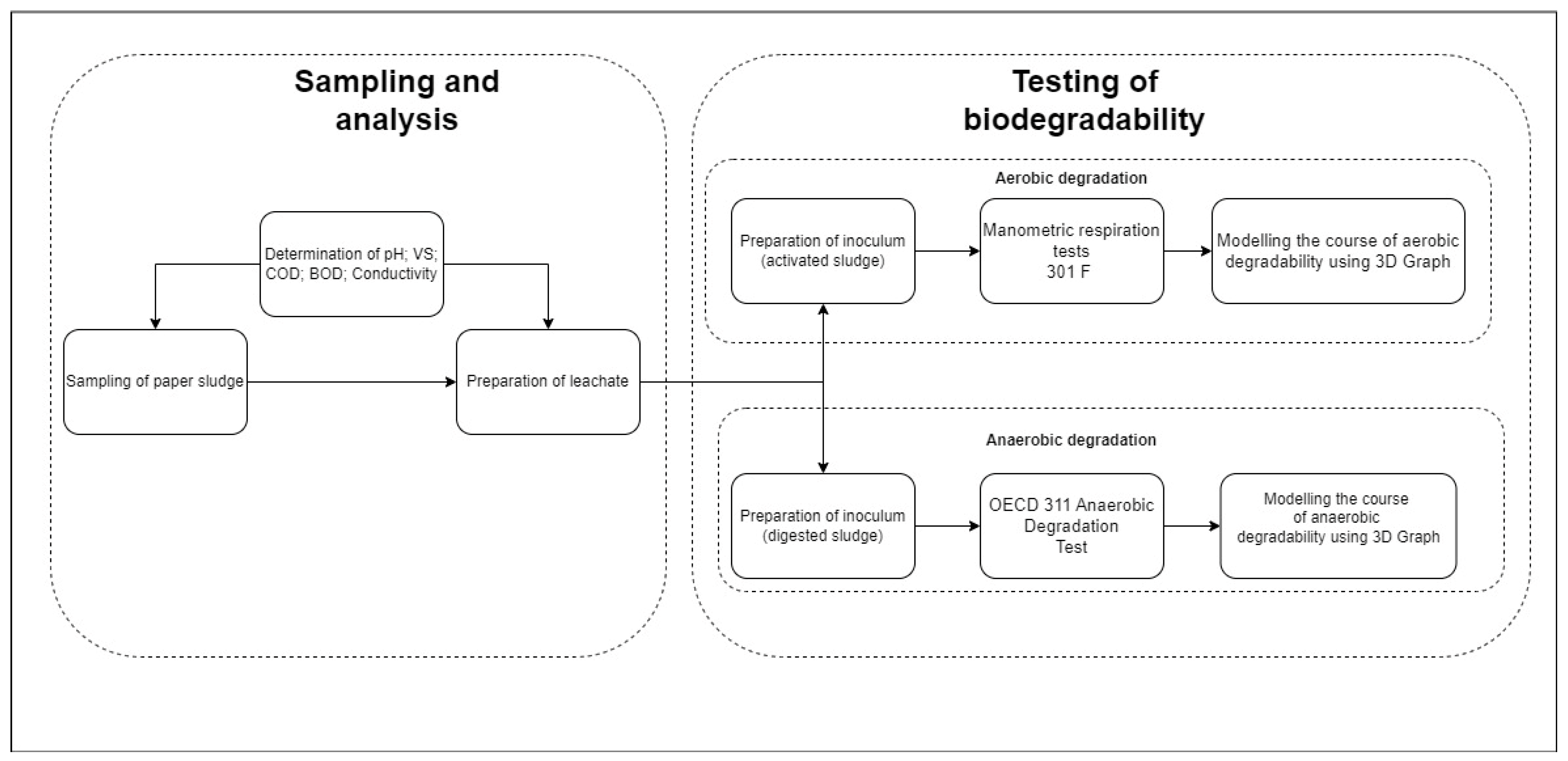
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Used Inoculum
2.2. Description of Paper Sludge
2.3. Adjust Samples
Preparation of Leachate
2.4. Aerobic Decomposition
2.4.1. Preparation of Inoculum
2.4.2. Manometric Respiration Tests 301 F
2.4.3. Preparation of Activated Sludge
2.5. Anaerobic Decomposition
2.5.1. Preparation of Inoculum
2.5.2. OECD 311 Anaerobic Degradation Test
2.5.3. Measurement of Pressure Difference
2.5.4. Measurement of Biogas Production
2.6. Used Analytical Methods
2.6.1. Determination of pH
2.6.2. Determination of the Dry Matter Content
2.6.3. Determination of VS
2.6.4. Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand
2.6.5. Determination of Biological Oxygen Demand
2.6.6. Determination of Electrical Conductivity
2.6.7. Description of MATLAB Software
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Physical and Chemical Analysis in the Sample
3.2. Evaluation of Biodegradability Tests
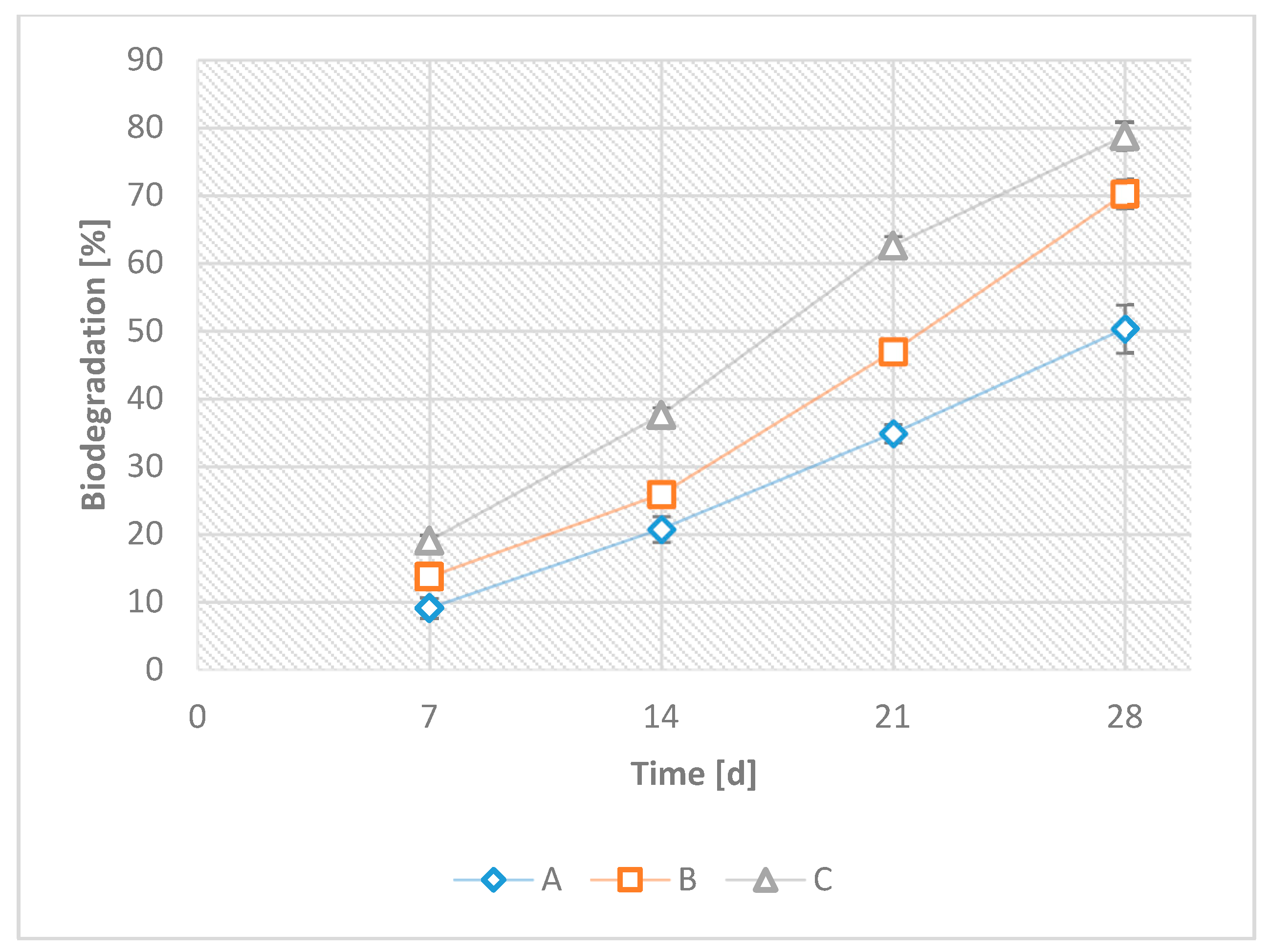
3.2.1. Aerobic Biodegradability
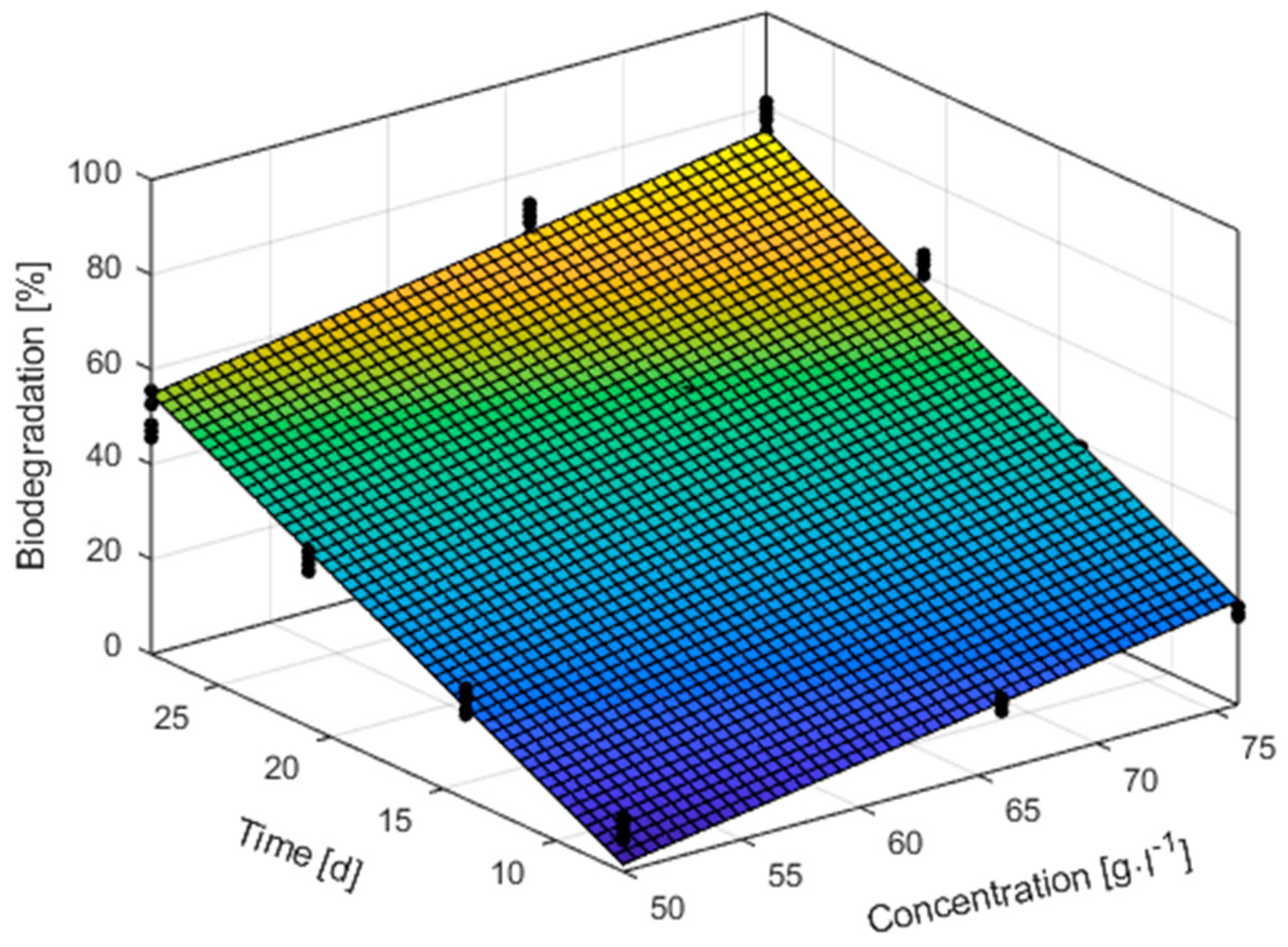
3.2.2. Modelling the Course of Aerobic Degradability Using 3D Graph
3.2.3. Anaerobic Degradability
3.2.4. Modelling the Course of Anaerobic Degradability Using 3D Graph
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Paper and Paperboard Production 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/270314/global-paper-and-cardboard-production/ (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Veluchamy, C.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Influence of Pretreatment Techniques on Anaerobic Digestion of Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1206–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubert, P.; Barnabé, S.; Bouchard, S.; Côté, R.; Villeneuve, C. Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge Management Practices: What Are the Challenges to Assess the Impacts on Greenhouse Gas Emissions? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 108, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, C.J.; Chen, J.C.; Yang, G.H. Some Properties and Disposal Process of Paper Sludge. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 550–553, 3262–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibril, M.E.; Lekha, P.; Andrew, J.; Sithole, B.; Tesfaye, T.; Ramjugernath, D. Beneficiation of Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge: Production and Characterisation of Functionalised Crystalline Nanocellulose. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekha, P.; Andrew, J.; Gibril, M.; Sithole, B. Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge: A Potential Resource for Producing High-Value Products. J. Tech. Assoc. Pulp Pap. Ind. S. Afr. 2017, 1, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Bremer, J.R.A. Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation. J. Ecosyst. Ecography 2022, 12, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, T.; Wheeler, R.; Oliver, I.W. Evaluating Land Application of Pulp and Paper Mill Sludge: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali, M.; Gameiro, T.; Costa, M.E.V.; Capela, I. Anaerobic Digestion of Pulp and Paper Mill Wastes—An Overview of the Developments and Improvement Opportunities. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 298, 162–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goycoechea, N.; Borges, I.; Castello, E.; Borzacconi, L. Improvements in the Anaerobic Digestion of Biological Sludge from Pulp and Paper Mills Using Thermal Pretreatment. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zule, J.; Černec, F.; Likon, M. Chemical Properties and Biodegradability of Waste Paper Mill Sludges to Be Used for Landfill Covering. Waste Manag. Res. 2007, 25, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, G.-S.; Jo, H.-S.; Nam, H.-G.; Park, H.-H.; Moon, S.-O. Physico-chemical Characteristics of Biodegradable Seedling Pots Made of Paper Mill Sludges. J. Korea Tech. Assoc. Pulp Pap. Ind. 2014, 46, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, M.; Rodríguez, O.; Sánchez de Rojas, M.I. Paper Sludge, an Environmentally Sound Alternative Source of MK-Based Cementitious Materials. A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strezov, V.; Evans, T.J. Thermal Processing of Paper Sludge and Characterisation of Its Pyrolysis Products. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, G.; Kalamdhad, A.S. An Investigation on Use of Paper Mill Sludge in Brick Manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D.; Zheng, H. Adsorption Behaviors of Paper Mill Sludge Biochar to Remove Cu, Zn and As in Wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzin, F.; Bahri Rasht Abadi, M. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Adsorbent Prepared from Paper Mill Sludge: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Kato, M.; Lettinga, G. The Anaerobic Biodegradability of Paper Mill Wastewater Constituents. Environ. Technol. 1990, 11, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Qin, Y.; Wu, J.; Ye, M.; Li, Y.-Y. Characterization of Biogas Production and Microbial Community in Thermophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Paper Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 337, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Alvarez, J.; Cecchi, F.; Pavan, P.; Llabres, P. The Performances of Digesters Treating the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Wastes Differently Sorted. Biol. Wastes 1990, 33, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chynoweth, D.P.; Turick, C.E.; Owens, J.M.; Jerger, D.E.; Peck, M.W. Biochemical Methane Potential of Biomass and Waste Feedstocks. Biomass Bioenergy 1993, 5, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Huang, L. Kinetic Study of Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Pulp & Paper Sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 4862–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Brar, S.K.; Riopel, A.R.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Pre-Treatment of Wastewater Sludge—Biodegradability and Rheology Study. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrère, H.; Bougrier, C.; Castets, D.; Delgenès, J.P. Impact of Initial Biodegradability on Sludge Anaerobic Digestion Enhancement by Thermal Pretreatment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2008, 43, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Pérez-Elvira, S.; Aymerich, E.; Fdz-Polanco, F. Assessment of the Influence of Thermal Pre-Treatment Time on the Macromolecular Composition and Anaerobic Biodegradability of Sewage Sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ďuricová, A. Výskum Nakladania s Odpadovým Kalom z ČOV a Sledovanie Distribúcie Ťažkých Kovov v Kale: [Vedecká Štúdia], 1st ed.; Technická Univerzita vo Zvolene: Zvolen, Slovakia, 2015; ISBN 978-80-228-2827-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hybská, H.; Ďuricová, A. Treatment Sewage Sludge with the Addition of Charcoal. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1001, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ďuricová, A. Influence the Properties of Sewage Sludge Creating Mixtures with Biochar. In Proceedings of the 14th International Multidisciplinary Scientific Geoconference SGEM 2014, Albena, Bulgaria, 29 June–8 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- STN EN 12457-4 (83 8231); Charakterizácia Odpadov: Vylúhovanie: Overovacia Skúška Na Vylúhovanie Zrnitých Odpadových Materiálov a Kalov. Časť 4., Jednostupňová Dávková Skúška Pri Pomere Kvapaliny a Tuhej Látky 10 l/Kg Materiálov s Veľkosťou Častíc Menšou Ako 10 Mm (Bez Zmenšovania Alebo Zmenšovaním Veľkosti). Slovenský Ústav Technickej Normalizácie: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2006.
- ISO 11734; Water Quality—Evaluation of the “Ultimate” Anaerobic Biodegradability of Organic Compounds in Digested Sludge—Method by Measurement of the Biogas Production Multiple. Distributed through American National Standards Institute (ANSI): Geneve, Switzerland, 1995.
- OECD Test No. 311; Anaerobic Biodegradability of Organic Compounds in Digested Sludge: By Measurement of Gas Production. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 2006.
- Gartiser, S.; Hydrotox GmbH. Manometric Respiration Tests According to OECD 301F with the OxiTop® Control Measuring System under GLP Conditions; Xylem: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- STN ISO 10390. Available online: https://cdn.standards.iteh.ai/samples/75243/799ee470118f4d3a9078129d9937be56/ISO-10390-2021.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- EN 14346:2006. Characterization of Waste—Calculation of Dry Matter by Determination of Dry Residue or Water Content. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/cen/c345ad72-3222-4b57-920b-29865d273a3c/en-14346-2006 (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- UNE EN 15169:2007. Characterization of Waste—Determination of Loss on Ignition in Waste, Sludge and Sediments. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/une-en-15169-2007-characterization-of-waste-determination-of-loss-on-ignition-in-waste-sludge-and-sediments/ (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- ISO 6060:1989. Available online: https://www.iso.org/cms/render/live/en/sites/isoorg/contents/data/standard/01/22/12260.html (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- STN EN 1899-2; Stanovenie Biochemickej Spotreby Kyslííka po n Dňoch (BSKn). Časť 2: Metóda pre Neriedené Vzorky. Slovenský Ústav Technickej Normalizácie: Bratislava, Slovensko, 2011.
- ISO 7888:1985. Available online: https://www.iso.org/cms/render/live/en/sites/isoorg/contents/data/standard/01/48/14838.html (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Jalalvand, A.R.; Roushani, M.; Goicoechea, H.C.; Rutledge, D.N.; Gu, H.-W. MATLAB in Electrochemistry: A Review. Talanta 2019, 194, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Lü, F.; He, P. Comparison of Sludge Digestion under Aerobic and Anaerobic Conditions with a Focus on the Degradation of Proteins at Mesophilic Temperature. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbeck, N.; Erley, R.; Mc Swain, B.S.; Wilderer, P.A.; Irvine, R.L. Treatment of Malting Wastewater in a Granular Sludge Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR). Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2004, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, G.D.; Roš, M. Aerobic and Two-Stage Anaerobic–Aerobic Sludge Digestion with Pure Oxygen and Air Aeration. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Xuan, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, J. Stability of Aerobic Granular Sludge in a Pilot Scale Sequencing Batch Reactor Enhanced by Granular Particle Size Control. Chemosphere 2019, 225, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, D.; Viraraghavan, T. Treatment of Pulp and Paper Mill Wastewater—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 333, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.J.; Hobbs, P.J.; Holliman, P.J.; Jones, D.L. Optimisation of the Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7928–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.-H.; Yu, H.-Q.; Zhu, R.-F. Influence of Particle Size and pH on Anaerobic Degradation of Cellulose by Ruminal Microbes. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2005, 55, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Test Name | Value | Unit | Uncertainty U [%] | Used Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash content | 61.43 | % | 5 | PP-DCH-78 |
| DM * 105 °C | 47.89 | % | 5 | PP-DCH-66 |
| Volatile solids | 99.62 | % [DM] | ||
| Organic proportion | 38.57 | % | - | PP-DCH-78 |
| TOC * | 222,000 | mg/kgDM | 20 | PP-DCH-93 |
| COD * | 10,403.4 | mg/L | - | STN No. 6060 |
| Conductivity | 5550 | mS/cm | - | ISO 7888:1985 |
| pH | 7.08 | - | - | ISO No. 10390 |
| Sample | COD [mg/L] | Volatile Solids [% DM] | Conductivity [mS/cm] | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated sludge | 10,763–11,000 | 99.783 | 0.57 | 7.83 |
| A | 847.8 | 99.92 | 735 | 8.00 |
| B | 960.84 | 99.92 | 746 | 8.3 |
| C | 1073.88 | 99.93 | 751 | 7.3 |
| Sample | COD [mg/L] | Volatile Solids [% DM] | Conductivity (mS/cm) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digested sludge | 396.32 | 99.93 | 896 | 6.88 |
| A | 401.27 | 99.92 | 735 | 9.3 |
| B | 421.09 | 99.92 | 746 | 9.00 |
| C | 416.48 | 99.93 | 751 | 9.3 |
| Conditions | Biogas Value [m3/tVS] | Reference Study of Anaerobic Degradability | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Our results | initial concentration of 61 g/L, duration of the test: 28 days | 149.06 | - |
| initial concentration of 54 g/L, duration of the test: 28 days | 102.66 | - | |
| initial concentration of 50 g/L, duration of the test: 28 days | 61.20 | - | |
| Other studies | ratio cleaning sludge: paper sludge 4:0 | 438 ± 53 | [19] |
| ratio cleaning sludge: paper sludge 4:2 | 458 ± 73 | [19] | |
| ratio cleaning sludge: paper sludge 4:4 | 539 ± 81 | [19] | |
| ratio cleaning sludge: paper sludge 4:6 | 594 ± 72 | [19] | |
| ratio cleaning sludge: paper sludge 4:8 | 569 ± 78 | [19] | |
| during mechanical sorting of waste | 225 | [20] | |
| when sorting the material at the source | 637 | [20] | |
| waste streams fractions 0.8 | 220 | [21] | |
| waste streams fractions 1.6 | 220 | [21] | |
| waste streams fractions 3.2 | 540 | [21] | |
| waste streams fractions 12.7 | 230 | [21] | |
| cellulosic and paper sludge | 733 | [22] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samešová, D.; Poništ, J.; Pochyba, A.; Hýrošová, T.; Schwarz, M.; Veverková, D. Determination and Optimization of Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition of Paper Sludge. Water 2024, 16, 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223209
Samešová D, Poništ J, Pochyba A, Hýrošová T, Schwarz M, Veverková D. Determination and Optimization of Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition of Paper Sludge. Water. 2024; 16(22):3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223209
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamešová, Dagmar, Juraj Poništ, Adam Pochyba, Tatiana Hýrošová, Marián Schwarz, and Darina Veverková. 2024. "Determination and Optimization of Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition of Paper Sludge" Water 16, no. 22: 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223209
APA StyleSamešová, D., Poništ, J., Pochyba, A., Hýrošová, T., Schwarz, M., & Veverková, D. (2024). Determination and Optimization of Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition of Paper Sludge. Water, 16(22), 3209. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16223209






