Changes in the Hydrological Characteristics of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake on the Karakoram Highway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
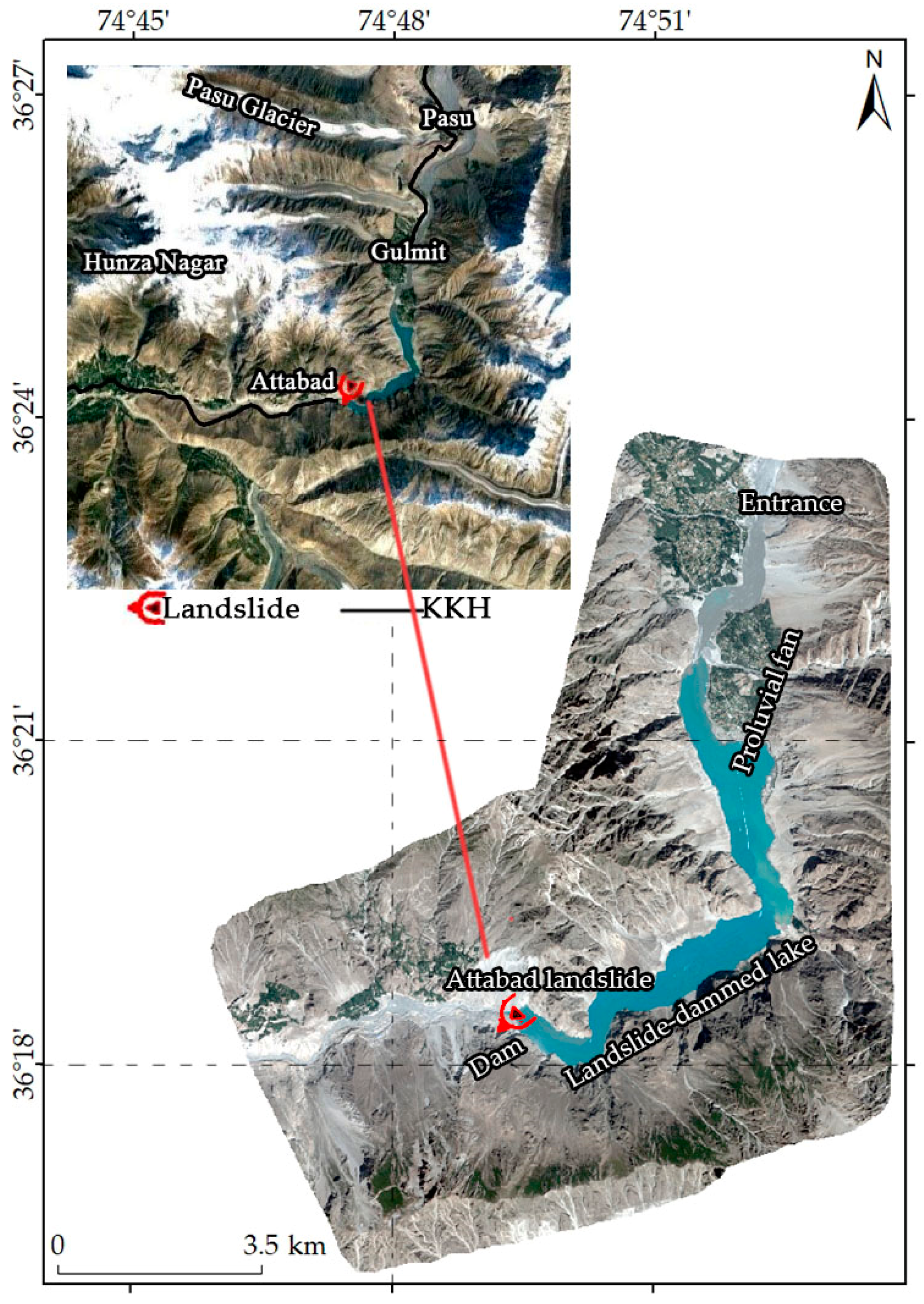
2. Overview of the Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
- (a)
- Orthorectification: High-precision control information was used to orthorectify the panchromatic and multispectral data into the CGCS2000 coordinate system;
- (b)
- Downscaling: The orthorectified results were downgraded to obtain 8-bit panchromatic and multispectral orthorectified images;
- (c)
- Image Fusion: The orthorectified panchromatic and multispectral images were fused, resulting in a combined image with both high resolution and rich color information;
- (d)
- Data Screening and Mosaic: After image fusion, data screening and image mosaic were performed to ensure seamless stitching and smooth transitions between all of the image’s edges;
- (e)
- Geometric Alignment: Due to the significant terrain deformation in the study area, remote sensing images from the seven phases exhibited differences in the same features at various times and with different sensors. To better visualize the trend of lake area change, geometric alignment was carried out, using the 2010 remote sensing images as a benchmark for absolute radiation correction and FLASH atmospheric correction was used on the other six phases of images.
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. The Methods for Extracting Lake Water Bodies and Studying Lake Geometric Features
The Methods for Lake Water Body Extraction
The Methods for Studying the Geometric Characteristics of the Lake
- (1)
- Rate of change of lake area
- (2)
- Lake landscape Shape Index
- (3)
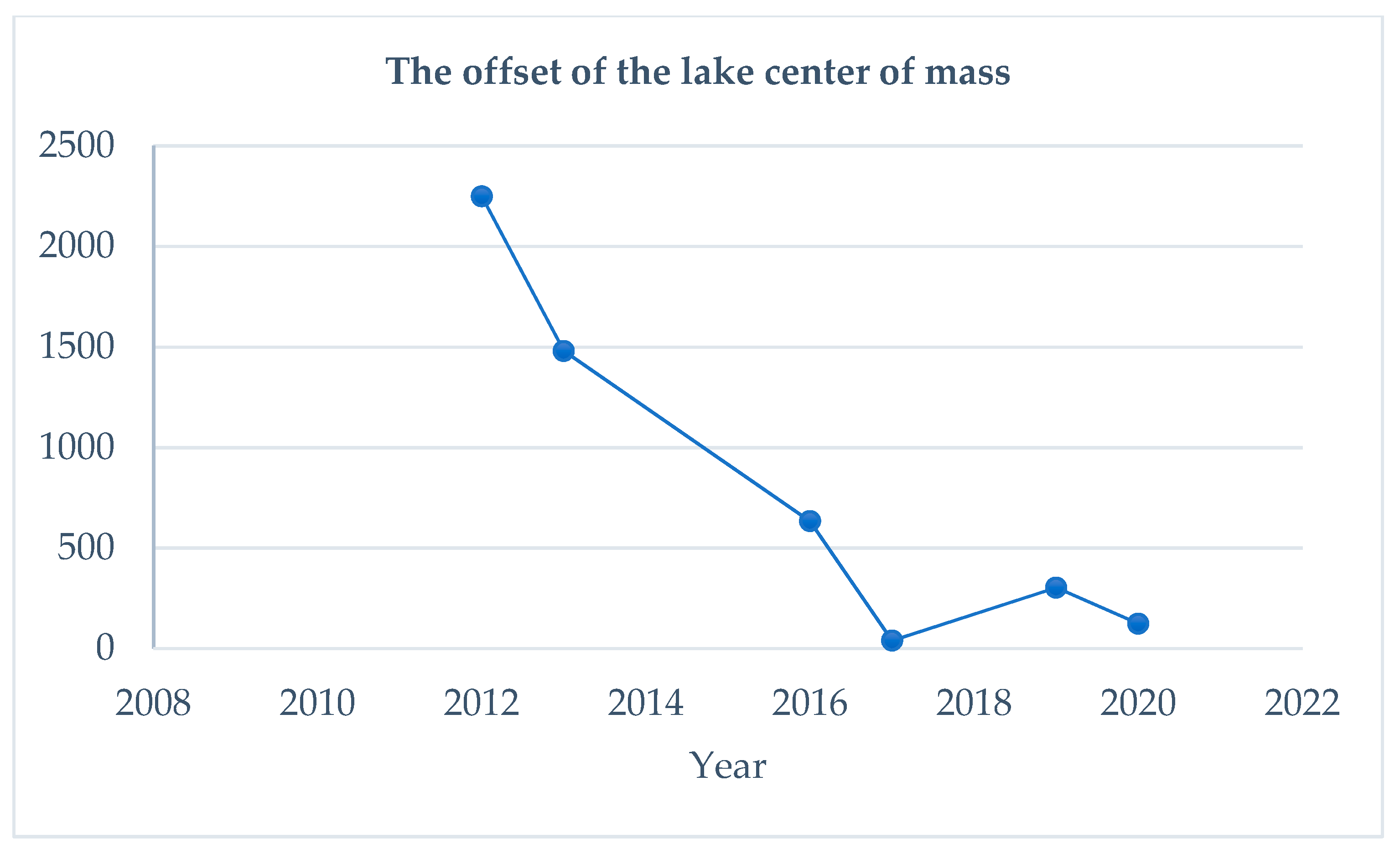
- Offset of the lake center of mass
3.2.2. The Methods for the SSC of the Attabad Landslide Dammed Lake
4. Results and Discussion
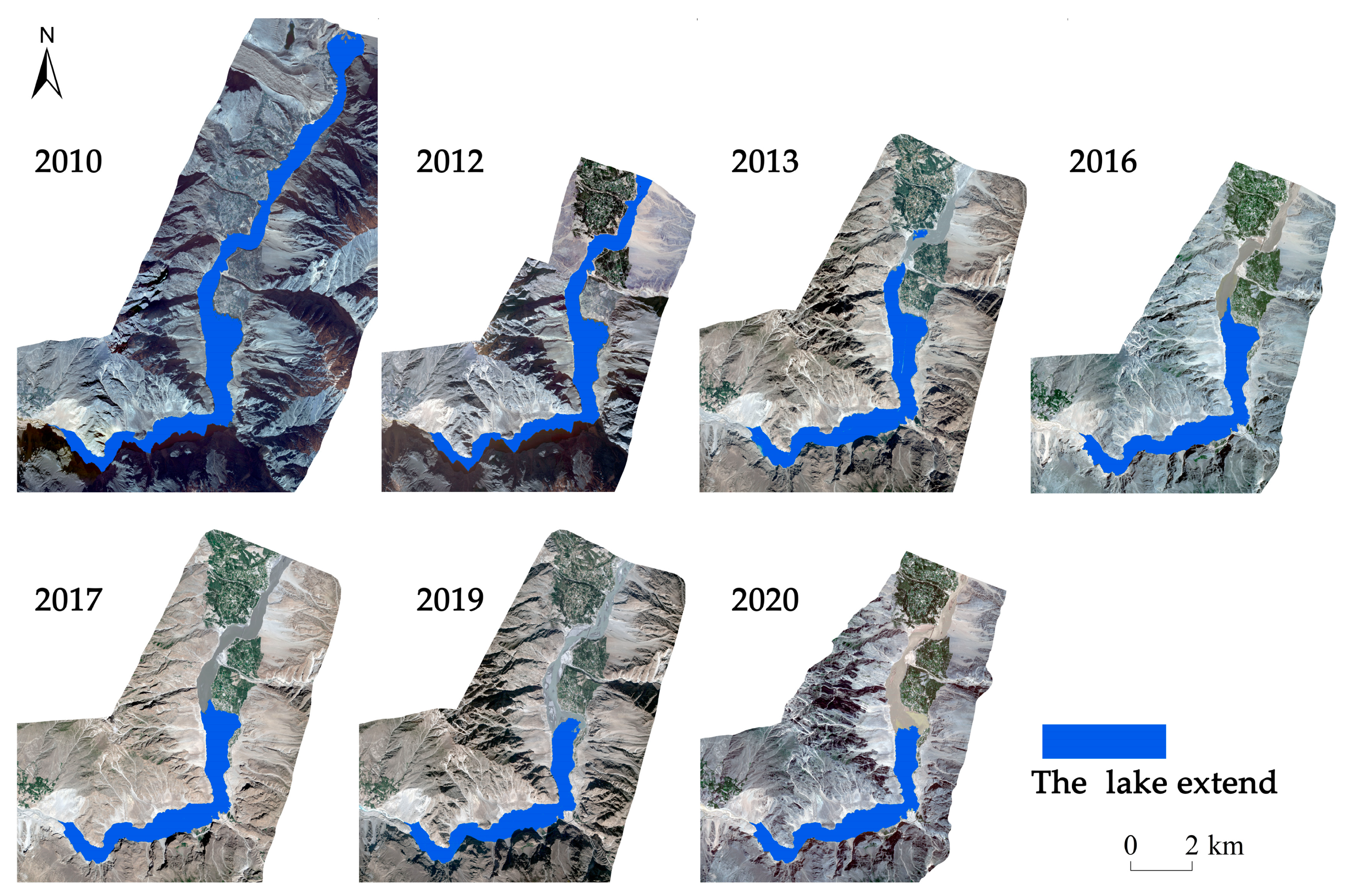
4.1. Change of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake Area
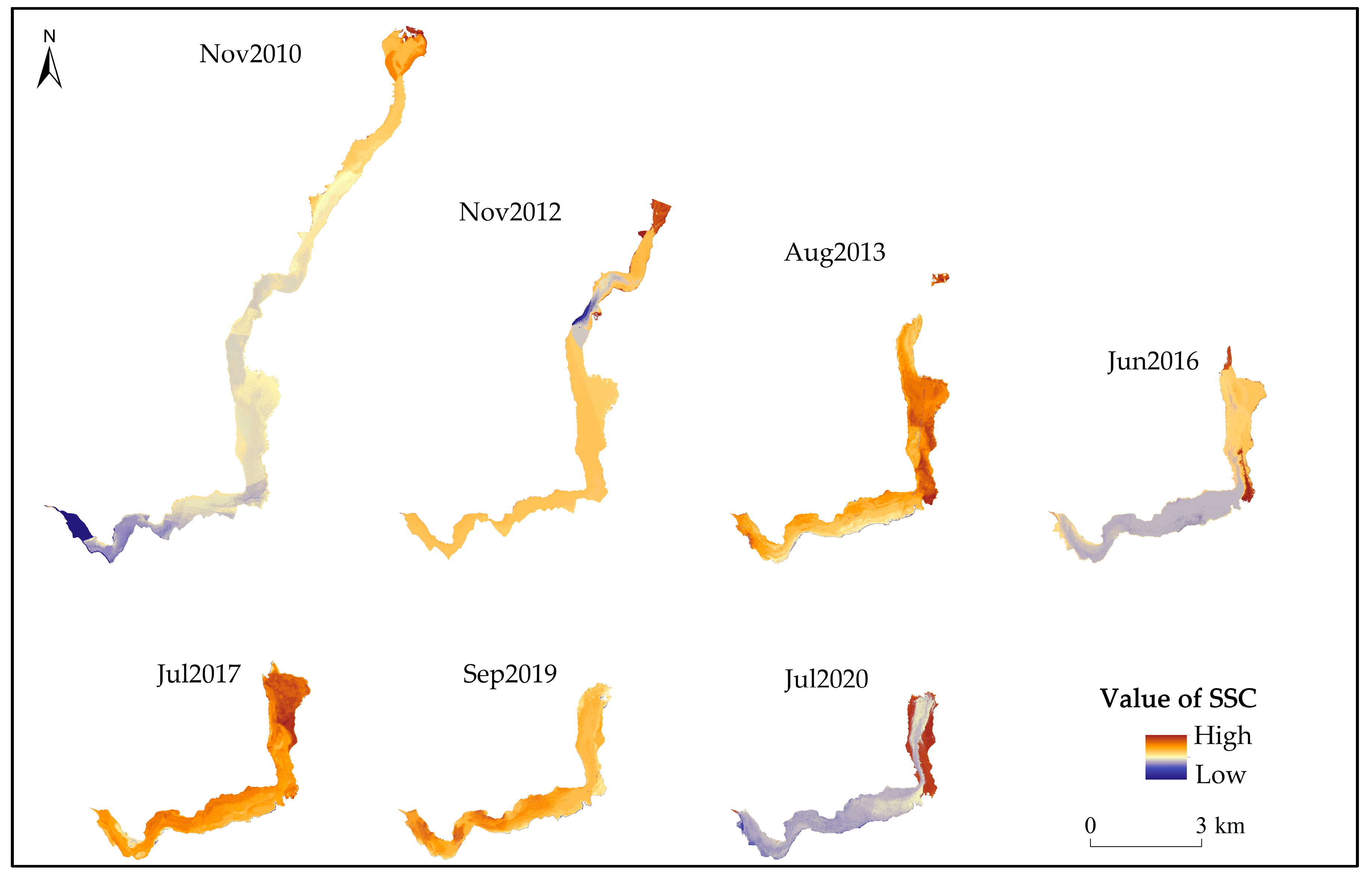
4.2. Changes in SSC of Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake
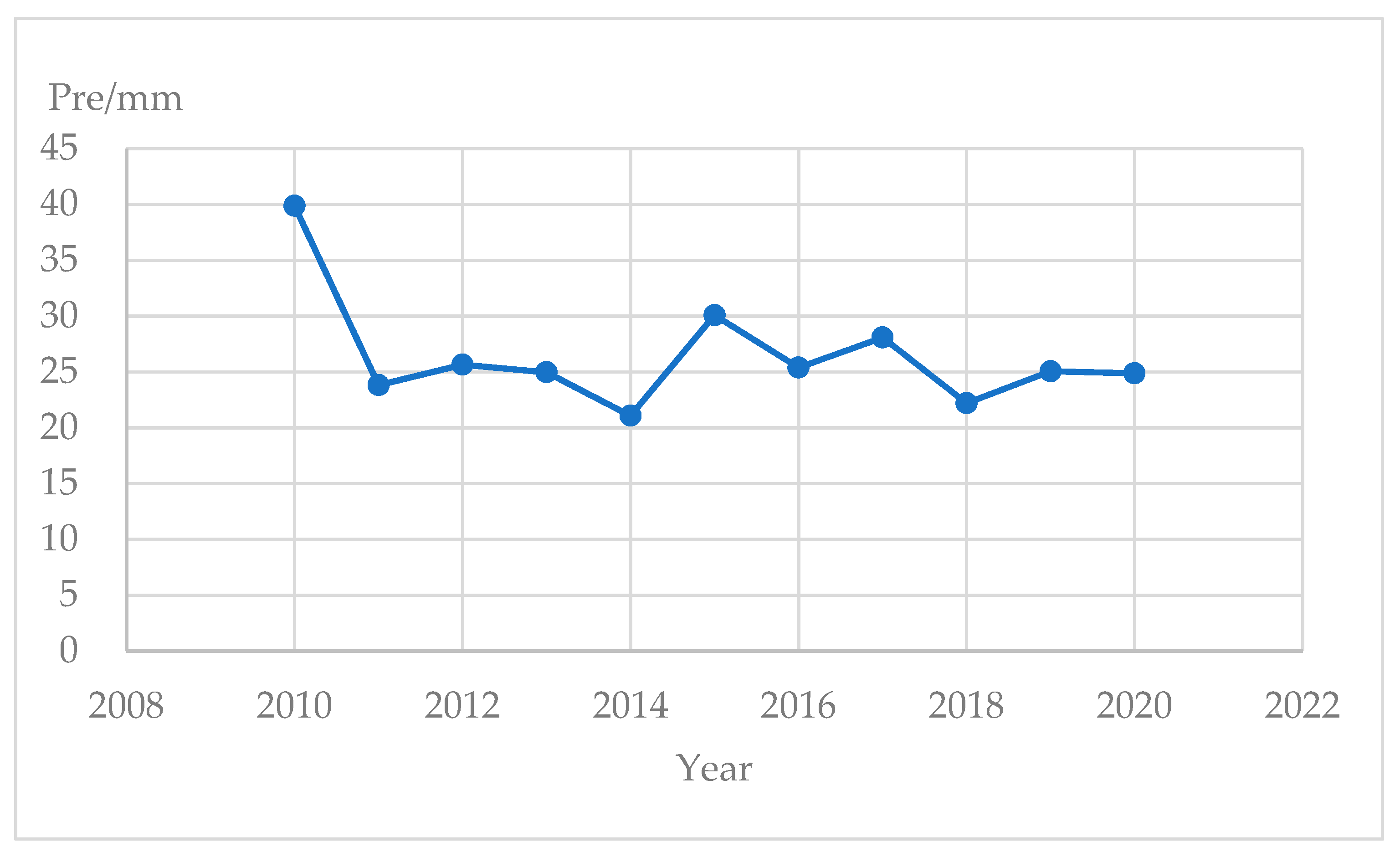
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Butt, M.J.; Umar, M.; Qamar, R. Landslide dam and subsequent dam-break flood estimation using HEC-RAS model in Northern Pakistan. Nat. Hazards 2012, 65, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.-M.; Yue, D.-X.; Ma, J.-H.; Guo, F.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-Q.; Rehman, M.U.; Khalid, Z.; Chen, G.; et al. Landslide mapping and analysis along the China-Pakistan Karakoram Highway based on SBAS-InSAR detection in 2017. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 2540–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Huai, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T. Surge-type glaciers in Karakoram Mountain and possible catastrophes alongside a portion of the Karakoram Highway. Nat. Hazards 2017, 90, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, P.; You, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Khan, A.; Ye, C.; Zhang, S. Dam-break risk analysis of the Attabad landslide dam in Pakistan and emergency countermeasures. Landslides 2016, 14, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Zhong, Y.G.; Reng, Y. Analyses and prevention and treatment measures of water-distroyed highway along rivers in Karakorum range area in Pakistan. Highway 2013, 4, 182–186. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Shafique, M.; Khan, M.A.; Bacha, M.A.; Shah, S.U.; Calligaris, C. Landslide susceptibility assessment using Frequency Ratio, a case study of northern Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Rogers, J.D.; Abu Bakar, M.Z. Hunza river watershed landslide and related features inventory mapping. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, A.S.; Shafique, M.; van der Werff, H. Landslide inventory and susceptibility modelling using geospatial tools, in Hunza-Nagar valley, northern Pakistan. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 1354–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brideau, M.-A.; Shugar, D.H.; Bevington, A.R.; Willis, M.J.; Wong, C. Evolution of the 2014 Vulcan Creek landslide-dammed lake, Yukon, Canada, using field and remote survey techniques. Landslides 2019, 16, 1823–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Cheng, Z.L.; Cui, P.; Chen, N.S. Dammed Lake and Risk Management; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vergara, I.; Garreaud, R.; Moreiras, S.; Araneo, D.; Beigt, D. Exploring the association between landslides and fluvial suspended sediment in a semi-arid basin in central Chile. Geomorphology 2022, 402, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Shi, Z.; Peng, M.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, M. Longevity analysis of landslide dams. Landslides 2020, 17, 1797–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gupta, V.; Jamir, I.; Chattoraj, S.L. Evaluation of potential landslide damming: Case study of Urni landslide, Kinnaur, Satluj valley, India. Geosci. Front. 2018, 10, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, T.K.; Wu, H.; Chen, G.Q.; Zheng, D.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Li, D.Y. Research progress on stability evaluation method and disaster chain effect of landslide dam. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Yan, K. A destructive mudstone landslide hit a high-speed railway on 15 September 2022 in Xining city, Qinghai province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 871–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Yang, S.; Ye, S. Integrated Application of Remote Sensing, GIS and Hydrological Modeling to Estimate the Potential Impact Area of Earthquake-Induced Dammed Lakes. Water 2017, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-W.; Cui, P.; Fang, H. Dynamic process analysis for the formation of Yangjiagou landslide-dammed lake triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake, China. Landslides 2013, 10, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Huang, C.Z.; Zhou, Y.L.; Pang, J.L.; Zha, X.C.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Zheng, Z.X.; Hu, Y.; et al. Formation and development of the prehistorical landslide dammed-lake in the Jishixia gorge along the upper Yellow River. Sci. Sin. Terrae 2017, 47, 1357–1370. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.M.; Xiao, T.; He, J.; Chen, C. Erosion-based analysis of breaching of Baige landslide dams on the Jinsha River, China, in 2018. Landslides 2019, 16, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argentin, A.-L.; Hauthaler, T.; Liebl, M.; Robl, J.; Hergarten, S.; Prasicek, G.; Salcher, B.; Hölbling, D.; Pfalzner-Gibbon, C.; Mandl, L.; et al. Influence of rheology on landslide-dammed lake impoundment and sediment trapping: Back-analysis of the Hintersee landslide dam. Geomorphology 2022, 414, 108363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Fan, X.; Yang, W.; Huang, W.; Borthwick, A. Hydro-sediment-morphodynamic processes of the baige landslide-induced barrier Lake, Jinsha River, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 126134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Zhao, W.Y.; Luo, Z.G. The effects of Attabad landslide secondary geohazard on the Karakoram Highway. J. Catastrophology 2019, 34, 81–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.T.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.W. Analyses on formation conditions and triggering mechanism of Attabad landslide. China Saf. Sci. J. 2020, 30, 148–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gardezi, H.; Bilal, M.; Cheng, Q.; Xing, A.; Zhuang, Y.; Masood, T. A comparative analysis of Attabad landslide on January 4, 2010, using two numerical models. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Yao, L.K.; Huang, Y.D.; Ali, S. Railway Alignment design in high risk area of landslide and collapse damming with the chain of quake lake disasters. Railw. Stn. Des. 2019, 63, 17–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Wei, Y.X.; Liu, J.F.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, G.Z. Mountain disasters and countermeasures of traffic engineering along China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. High Speed Railw. Technol. 2018, S02, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.D.; Dang, T.M. Estimation of suspended sediment concentration in downstream of the Ba river basin using remote sensing images. Inzynieria Miner. Pol. Miner. Eng. Soc. 2021, 1, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, P.M.; Wang, C.-K.; Huang, A.-T. The spatial-temporal distribution of Goci-derived suspended sediment in Taiwan coastal water induced by typhoon Soudelor. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Mantravadi, V.S. Study on distribution characteristics of suspended sediment in yellow river estuary based on remote sensing. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Peng, J.; Jiang, L.; Feng, J. Temporal and spatial distribution of suspended sediment concentration in lakes based on satellite remote sensing and internet of things. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 87849–87856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ni, Y.; Pang, Z.; Li, X.; Ju, H.; He, G.; Lv, J.; Yang, K.; Fu, J.; Qin, X. An effective water body extraction method with new water index for sentinel-2 imagery. Water 2021, 13, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.D. Multi-Spectral Water Index (MUWI): A native 10-m multi-spectral water index for accurate water mapping on sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Seo, I.W.; Lyu, S. Investigating mixing patterns of suspended sediment in a river confluence using high-resolution hyperspectral imagery. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wang, M.M.; Zhou, T.; Chen, W.F. Progress in remote sensing monitoring of lake area. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 115–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Xu, S.-D.; Lin, Q. Quantitative application study on remote sensing of suspended sediment. China Ocean Eng. 2012, 26, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.M. Mult-temporal analyses of remote sensing on distribution of suspended sediment in Xiamen Estuary. Port Water Eng. 2008, 422, 51–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, Y.M.; Huang, Y.G. An analysis of distribution of suspended sediment in Estuary by using remote sensing technology. Port Waterw. Eng. 2008, 421, 19–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, M.; Ma, R.; Ding, J. Application of MODIS data in monitoring suspended sediment of Taihu Lake, China. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kong, J.L.; Sun, X.M.; Du, D.; Chen, P. Retrieval of sea surface suspended sediment concentration of Bohai gulf offshore area based on semi-analysis model. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2014, 30, 33–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Han, Y.C.; Chen, J.X.; Zhang, Y.J. Observation of suspended sediment in sea area around Dajin Island based on multi-source remote sensing data. J. Zhejiang Univ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 54, 985–995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.K. Identifying flood with high bedload content using MODIS data. J. Catastrophology 2005, 20, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Liu, D.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Hassan, J. Glacier surging controls glacier lake formation and outburst floods: The example of the Khurdopin Glacier, Karakoram. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2022, 208, 103710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Hagemann, S. Estimating the characteristics of runoff inflow into Lake Gojal in ungauged, highly glacierized upper Hunza River Basin, Pakistan. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 24, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazai, N.A.; Cui, P.; Carling, P.A.; Wang, H.; Hassan, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Jin, W. Increasing glacial lake outburst flood hazard in response to surge glaciers in the Karakoram. Earth-Science Rev. 2021, 212, 103432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Luo, Z.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Yang, H. Multiscale water body extraction in urban environments from satellite images. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4301–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaras, E.; Falchi, U.; Parente, C.; Vallario, A. Accuracy evaluation for coastline extraction from Pléiades imagery based on NDWI and IHS pan-sharpening application. Appl. Geomat. 2022, 15, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Latif, A. Extraction of urban water bodies from high-resolution remote-sensing imagery using deep learning. Water 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Liu, C.; Zhou, R.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q. Classification for high resolution remote sensing imagery using a fully convolutional network. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.C.; Zhou, T.G.; Li, C.F. Urban water extraction based on multi-source remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the Eplww3s 2011: 2011 International Conference on Ecological Protection of Lakes-Wetlands-Watershed and Application of 3s Technology, Nanchang, China, 25–26 June 2011; Volume 3, pp. 312–315. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, L.; Deng, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. Water 2018, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Luo, J.; Sheng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ming, D. An Adaptive Water Extraction Method from Remote Sensing Image Based on NDWI. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2011, 40, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated water extraction index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, K.; Liang, Z.L. Change monitoring of key lakes in Jiangsu province in 2009–2019 based on remote sensing. J. Geomat. 2022, 47, 172–176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özelkan, E. Water Body Detection Analysis Using NDWI Indices Derived from Landsat-8 OLI. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 29, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawak, S.; Luis, A. A Rapid Extraction of Water Body Features from Antarctic Coastal Oasis Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Remote Sensing Data. Aquat. Procedia 2015, 4, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, O.S.; Gulgen, F.; Sanli, F.B.; Ates, A.M. The performance analysis of different water indices and algorithms using sentinel-2 and landsat-8 images in determining water surface: Demirkopru dam case study. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 7883–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Avdan, U. Water extraction technique in mountainous areas from satellite images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.X. Construction and validation of GF-2 image water body index in complex environment. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2022, 34, 50–58. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chukwuka, A.V.; Egware, T.U.; Okali, K.D.; Fadahunsi, A.A.; Oluwakotanmi, P.G.; Emasoga, P.; Ibor, O.R.; Oni, A.A.; Adeogun, A.O. The Influence of Lake Morphology, Landscape Structure, and Urbanization Factors on Bird Community Composition in Wetlands of Four Tropical Lakes. Wetlands 2022, 42, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Du, C.; Liu, F.Q.; Li, R. Analysis of suspended sediment concentration in Songhua River based on remote sensing technology. J. Eng. Heilongjiang Univ. 2022, 13, 18–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X. Retrieve of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Suspended Sediment in Bohai Bay Based on GF-1 Remote Sensing Satellite. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2020, 15, 134–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
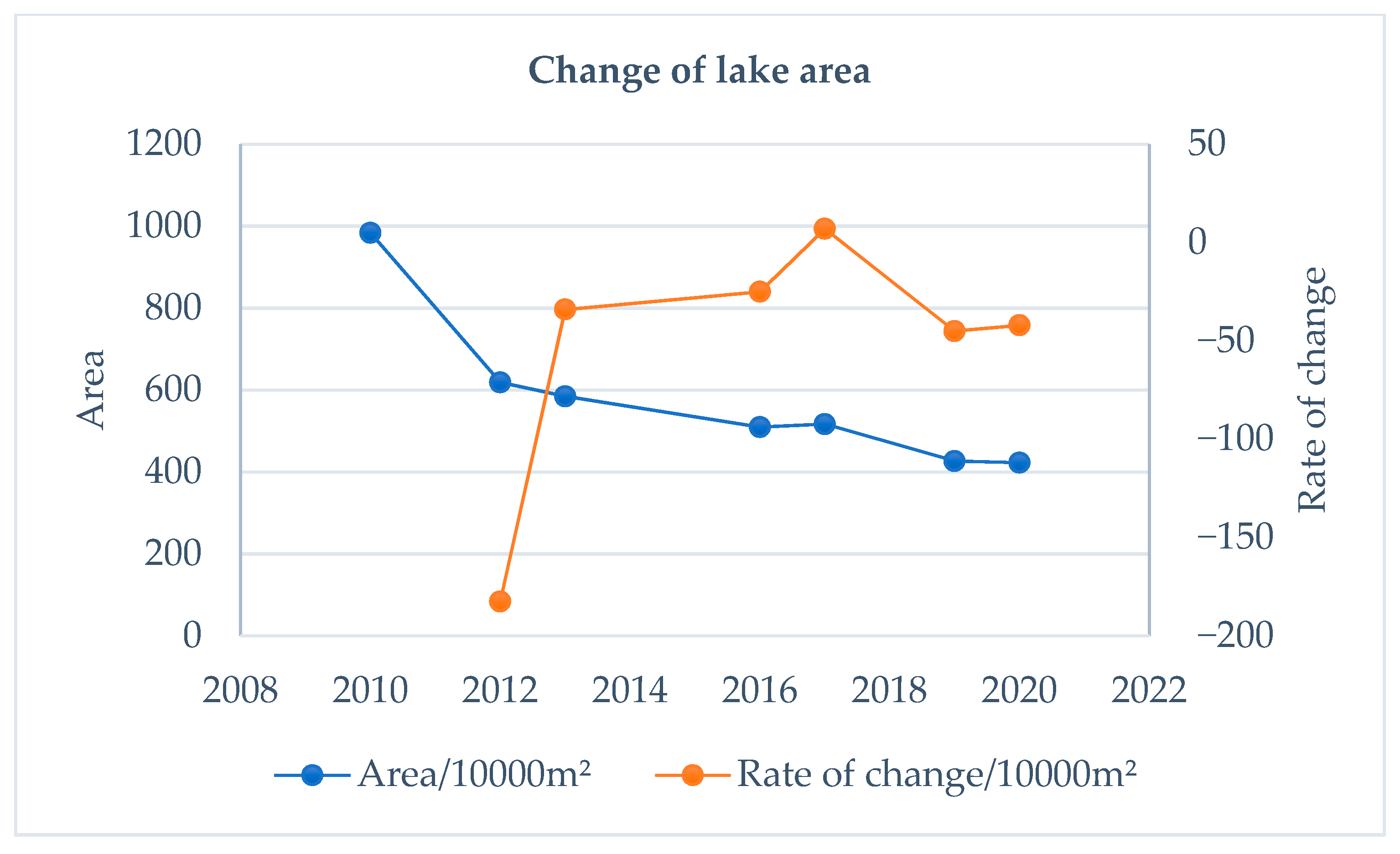

| Time | Types of Data | Spatial Resolution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NOV2010 | QuickBird | 0.6 m, 4-band bundling |
| 2 | NOV2012 | QuickBird | 0.6 m, 4-band bundling |
| 3 | AUG2013 | Pleiades | 0.5 m, 4-band bundling |
| 4 | JUN2016 | WorldView2 | 0.5 m, 4-band bundling |
| 5 | JUL2017 | Pleiades | 0.5 m, 4-band bundling |
| 6 | SEP2019 | Pleiades | 0.5 m, 4-band bundling |
| 7 | JUL2020 | WorldView2 | 0.5 m, 4-band bundling |
| Data | GF-2 | WorldView2 | GF-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NDWI | CWI | CWI | CWI |
| Overall accuracy | 99.33 | 99.97 | 99.3 | 100 |
| Kappa coefficient | 45.31 | 94.86 | 94.62 | 100 |
| Model | Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | single-band | near-infrared band | low |
| green band | high | ||
| red band | high | ||
| 2 | band-ratio | green band/red band | low |
| 3 | multi-band | B1/(B2 + B3) | high |
| Year | 2010 | 2012 | 2013 | 2016 | 2017 | 2019 | 2020 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall accuracy/% | 86.02 | 87.32 | 90.13 | 91.13 | 91.27 | 89.2 | 90.12 | 89.31 |
| Kappa coefficient/% | 81.29 | 82.66 | 85.76 | 86.12 | 86.88 | 83.57 | 84.19 | 84.35 |
| Year | 2010 | 2012 | 2013 | 2016 | 2017 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area/104 m2 | 984 | 619 | 585 | 510 | 517 | 427 | 423 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Qi, Y.; Ye, W.; Cao, G.; Wang, Y. Changes in the Hydrological Characteristics of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake on the Karakoram Highway. Water 2024, 16, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050714
Li Y, Yang H, Qi Y, Ye W, Cao G, Wang Y. Changes in the Hydrological Characteristics of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake on the Karakoram Highway. Water. 2024; 16(5):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050714
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yousan, Hongkui Yang, Youhui Qi, Wenqian Ye, Guangchao Cao, and Yanhe Wang. 2024. "Changes in the Hydrological Characteristics of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake on the Karakoram Highway" Water 16, no. 5: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050714
APA StyleLi, Y., Yang, H., Qi, Y., Ye, W., Cao, G., & Wang, Y. (2024). Changes in the Hydrological Characteristics of the Attabad Landslide-Dammed Lake on the Karakoram Highway. Water, 16(5), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050714






